Recombinant Goose Circoviruses Circulating in Domesticated and Wild Geese in Poland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. Screening and GoCV Genome Recovery
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
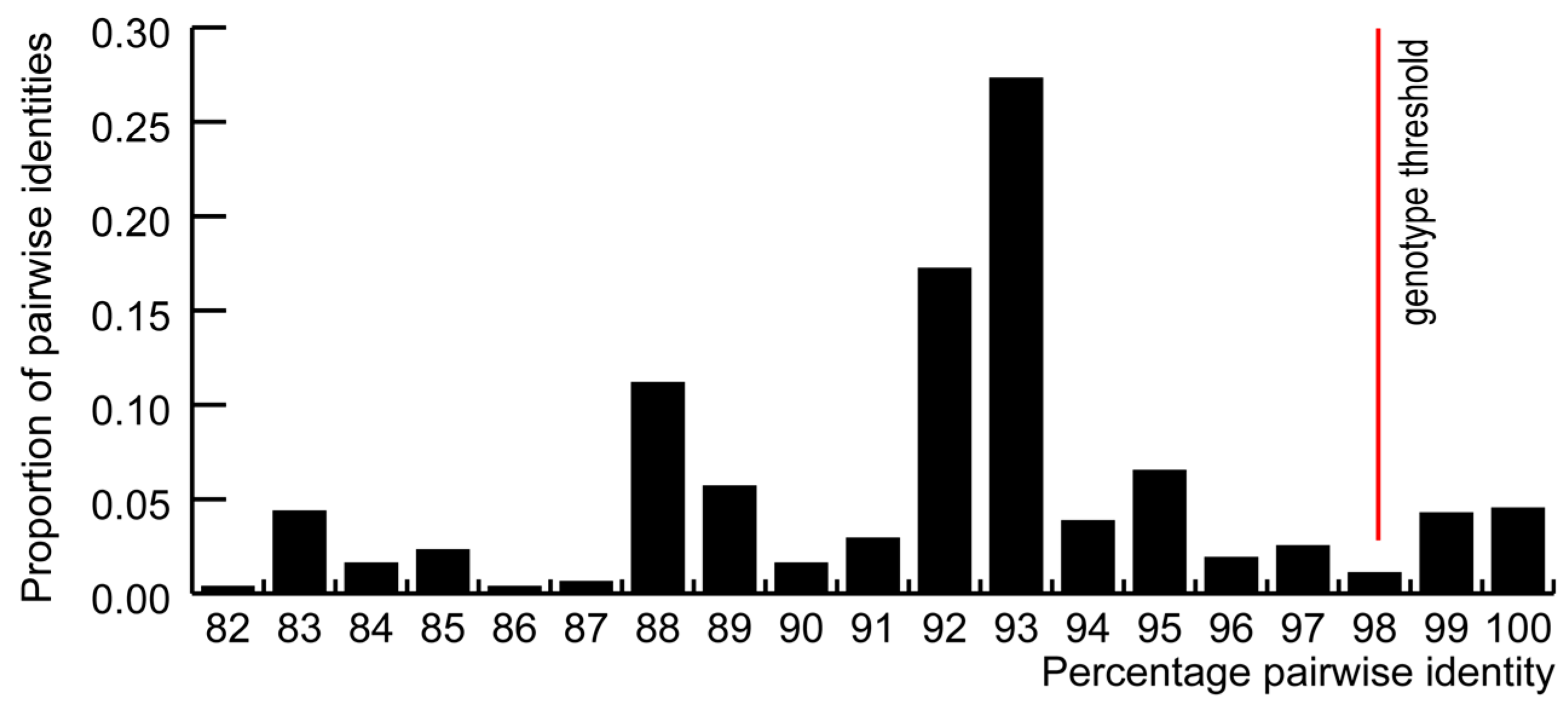
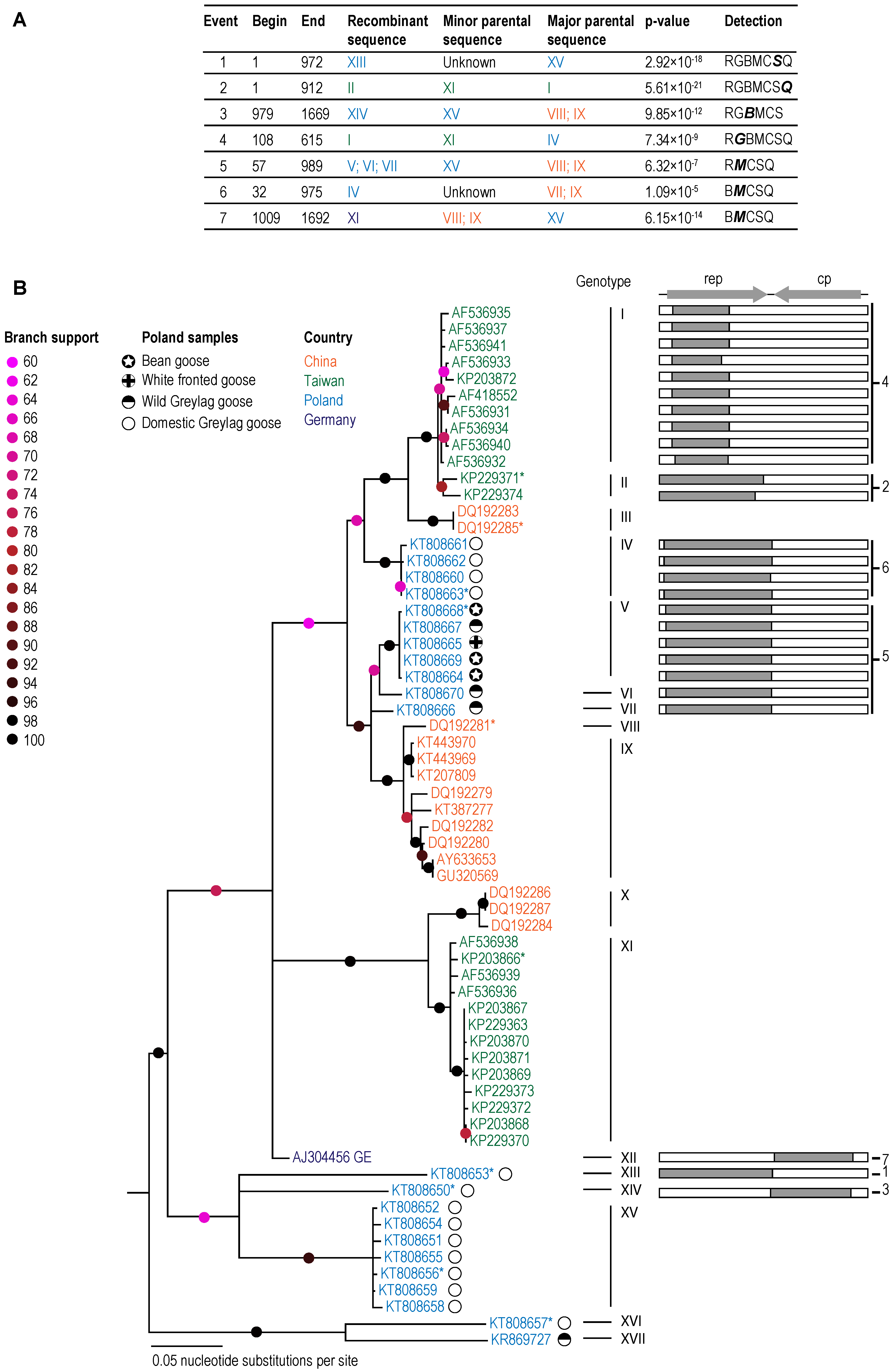
3.1. GoCV in Domestic and Wild Geese in Poland
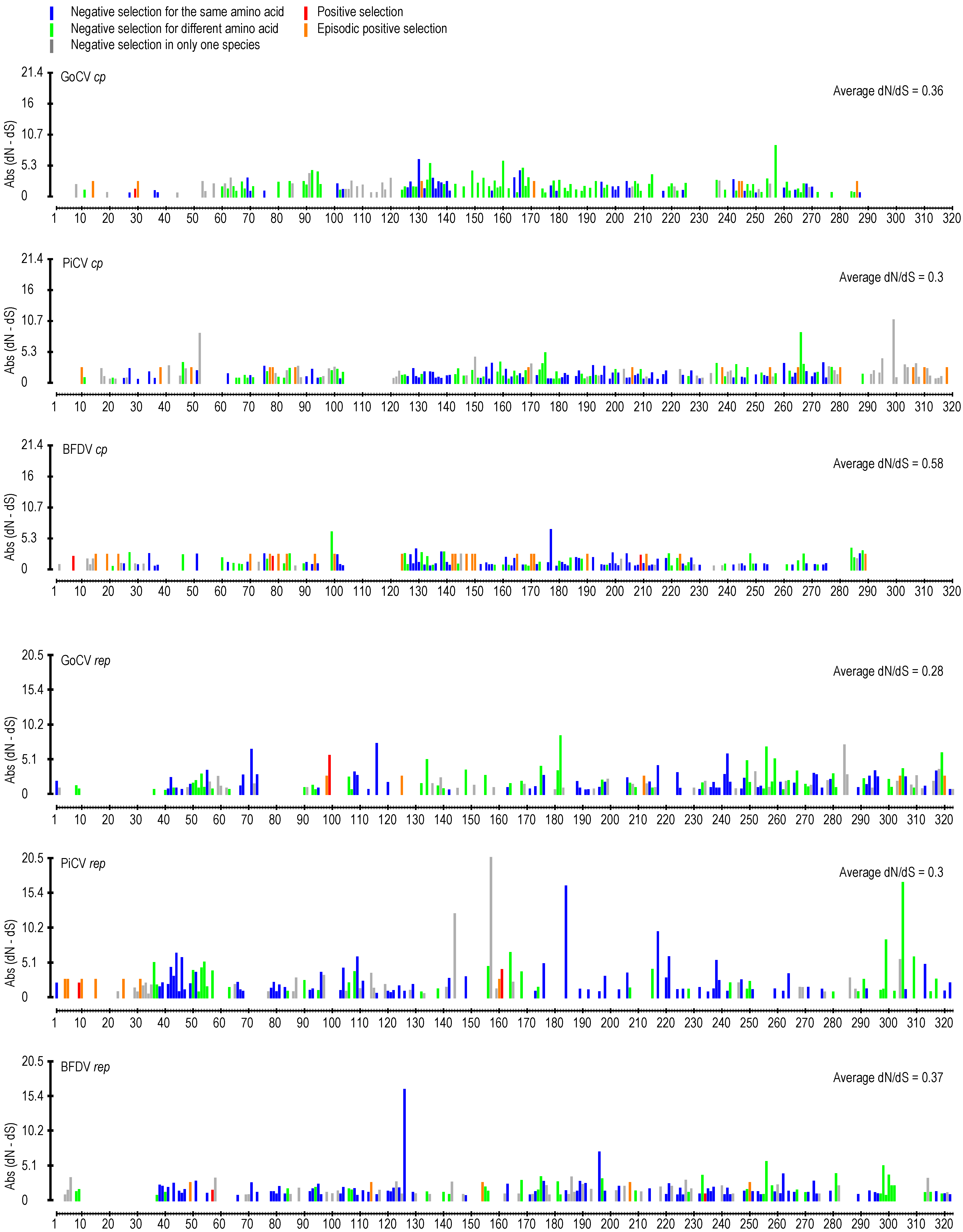
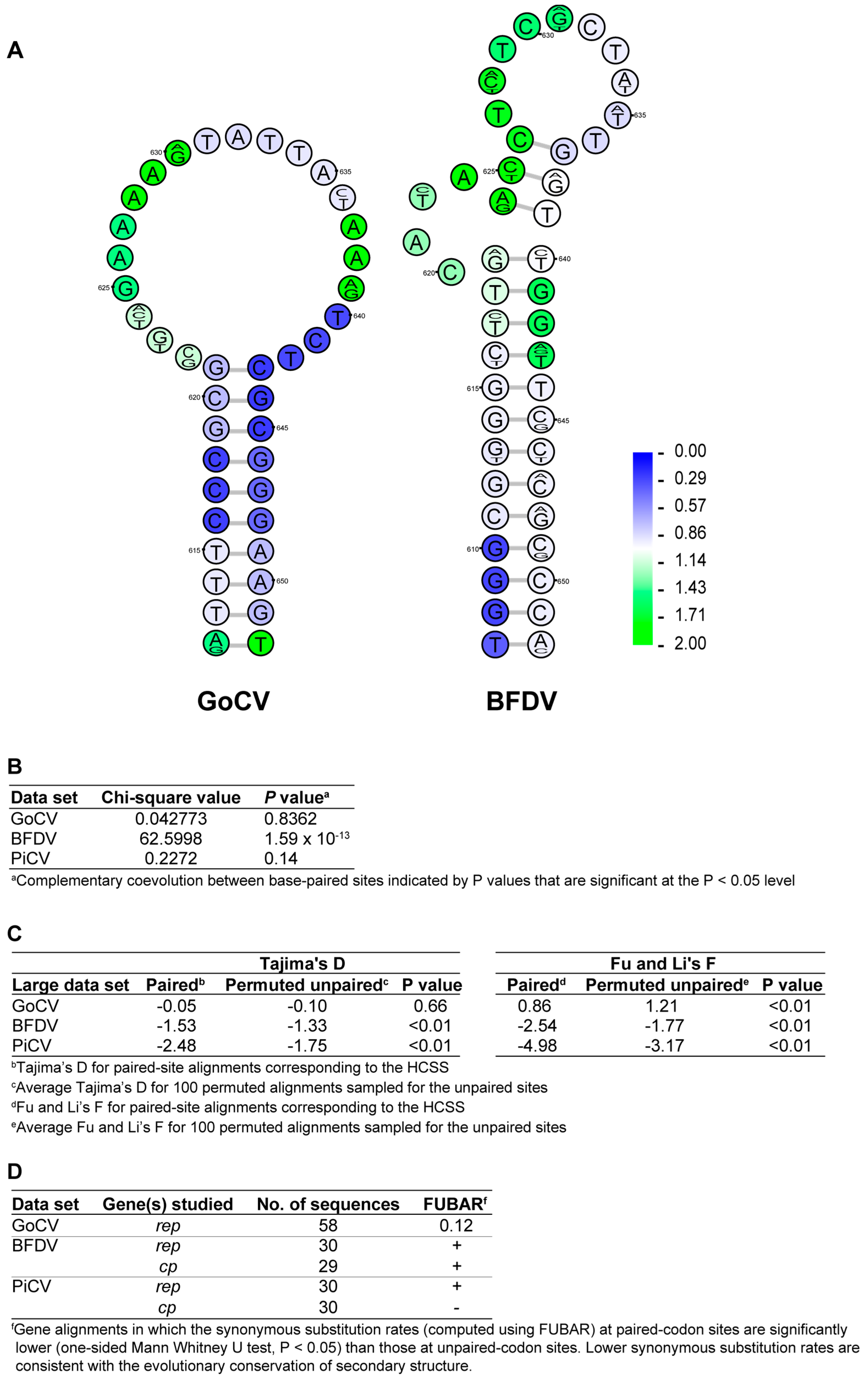
3.2. DNA Secondary Structure Analysis of GoCV Genomes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosario, K.; Breitbart, M.; Harrach, B.; Segales, J.; Delwart, E.; Biagini, P.; Varsani, A. Revisiting the taxonomy of the family circoviridae: Establishment of the genus cyclovirus and removal of the genus gyrovirus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbart, M.; Delwart, E.; Rosario, K.; Segales, J.; Varsani, A.; Ictv Report, C. Ictv virus taxonomy profile: Circoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1997–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadie, J.; Nguyen, F.; Groizeleau, C.; Amenna, N.; Fernandez, B.; Guereaud, C.; Guigand, L.; Robart, P.; Lefebvre, B.; Wyers, M. Pigeon circovirus infection: Pathological observations and suggested pathogenesis. Avian Pathol. 2001, 30, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coletti, M.; Franciosini, M.P.; Asdrubali, G.; Passamonti, F. Atrophy of the primary lymphoid organs of meat pigeons in italy associated with circoviruslike particles in the bursa of fabricius. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Tian, J.; Tan, X.; Yu, H.T.; Ding, S.Q.; Sun, H.X.; Yu, X.P. Pathological observations of an experimental infection of geese with goose circovirus. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D. Circoviruses: Immunosuppressive threats to avian species: A review. Avian Pathol. 2000, 29, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenzel, T.; Pestka, D.; Choszcz, D. The prevalence and genetic characterization of chlamydia psittaci from domestic and feral pigeons in poland and the correlation between infection rate and incidence of pigeon circovirus. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 3009–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soike, D.; Kohler, B.; Albrecht, K. A circovirus-like infection in geese related to a runting syndrome. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, N.W.; Smyth, J.A.; Weston, J.H.; Borghmans, B.J.; Palya, V.; Glavits, R.; Ivanics, E.; Dan, A.; Todd, D. Diagnosis of goose circovirus infection in hungarian geese samples using polymerase chain reaction and dot blot hybridization tests. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Chang, P.C.; Lee, M.S.; Shien, J.H.; Ou, S.J.; Shieh, H.K. Nucleotide sequences of goose circovirus isolated in taiwan. Avian Pathol. 2003, 32, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavits, R.; Ferenczi, E.; Ivanics, E.; Bakonyi, T.; Mato, T.; Zarka, P.; Palya, V. Co-occurrence of west nile fever and circovirus infection in a goose flock in hungary. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozdrun, W.; Wozniakowski, G.; Samorek-Salamonowicz, E.; Czekaj, H. Viral infections in goose flocks in poland. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 15, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, X.; He, S.; Liu, X. Genome analysis and epidemiological investigation of goose circovirus detected in eastern china. Virus Genes 2007, 35, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenzel, T.; Farkas, K.; Varsani, A. Genome sequence of a diverse goose circovirus recovered from greylag goose. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00767-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fungwitaya, P.; Bunlertcharoensuk, A.; Uttamaburana, W.; Sariya, L.; Chaichoune, K.; Ratanakorn, P.; Boonyarittichaikij, R. Prevalence of psittacine beak and feather disease and avian polyomavirus disease infection in captive psittacines in the central part of thailand by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. J. Appl. Anim. Sci. Vol. 2009, 2, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Julian, L.; Piasecki, T.; Chrzastek, K.; Walters, M.; Muhire, B.; Harkins, G.W.; Martin, D.P.; Varsani, A. Extensive recombination detected among beak and feather disease virus isolates from breeding facilities in poland. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piasecki, T.; Wieliczko, A. Detection of beak and feather disease virus and avian polyomavirus DNA in psittacine birds in poland. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2010, 54, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel, T.; Koncicki, A. The epidemiology, molecular characterization and clinical pathology of circovirus infections in pigeons–current knowledge. Vet. Q. 2017, 37, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pass, D.A.; Perry, R.A. The pathology of psittacine beak and feather disease. Aust. Vet. J. 1984, 61, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halami, M.; Nieper, H.; Müller, H.; Johne, R. Detection of a novel circovirus in mute swans (cygnus olor) by using nested broad-spectrum pcr. Virus Res. 2008, 132, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenzel, T.; Piasecki, T.; Chrzastek, K.; Julian, L.; Muhire, B.M.; Golden, M.; Martin, D.P.; Varsani, A. Pigeon circoviruses display patterns of recombination, genomic secondary structure and selection similar to those of beak and feather disease viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhire, B.M.; Varsani, A.; Martin, D.P. Sdt: A virus classification tool based on pairwise sequence alignment and identity calculation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Muscle: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. Rdp4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evolut. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of phyml 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. Jmodeltest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stover, B.C.; Muller, K.F. Treegraph 2: Combining and visualizing evidence from different phylogenetic analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, B.; Moola, S.; Mabona, A.; Weighill, T.; Sheward, D.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Scheffler, K. Fubar: A fast, unconstrained bayesian approximation for inferring selection. Mol. Biol. Evolut. 2013, 30, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semegni, J.Y.; Wamalwa, M.; Gaujoux, R.; Harkins, G.W.; Gray, A.; Martin, D.P. Nasp: A parallel program for identifying evolutionarily conserved nucleic acid secondary structures from nucleotide sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2443–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhire, B.M.; Golden, M.; Murrell, B.; Lefeuvre, P.; Lett, J.M.; Gray, A.; Poon, A.Y.; Ngandu, N.K.; Semegni, Y.; Tanov, E.P.; et al. Evidence of pervasive biologically functional secondary structures within the genomes of eukaryotic single-stranded DNA viruses. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1972–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, N.R.; Zuker, M. Unafold: Software for nucleic acid folding and hybridization. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 453, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golden, M.; Martin, D. Dooss: A tool for visual analysis of data overlaid on secondary structures. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkins, G.W.; Martin, D.P.; Christoffels, A.; Varsani, A. Towards inferring the global movement of beak and feather disease virus. Virology 2014, 450–451, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample ID | Sampling Date | Species | Common Name | Age | Health Status | Broad Spectrum Primer Positive | GoCV Positive | GenBank Accession # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 21 November 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | Yes | Yes | KT808664 |
| G2 | 3 December 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | No | No | N/A |
| G3 | 3 December 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| G4 | 3 December 2014 | Anser albifrons | White fronted goose | Y | H | Yes | Yes | KT808665 |
| G5 | 20 November 2014 | Anser anser | Wild Greylag goose | A | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| G6 | 20 November 2014 | Anser anser | Wild Greylag goose | Y | H | Yes | Yes | KT808666 |
| G7 | 20 November 2014 | Anser anser | Wild Greylag goose | A | H | No | No | N/A |
| G8 | 20 November 2014 | Anser anser | Wild Greylag goose | A | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| G9 | 20 November 2014 | Anser anser | Wild Greylag goose | A | H | Yes | Yes | KT808667 |
| G10 | 20 November 2014 | Anser albifrons | White fronted goose | A | H | No | No | N/A |
| G11 | 21 November 2014 | Anser albifrons | White fronted goose | Y | H | No | No | N/A |
| G12 | 21 November 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| G13 | 21 November 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | No | No | N/A |
| G14 | 21 November 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | No | No | N/A |
| G15 | 21 November 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | Yes | Yes | KT808668 |
| G16 | 21 November 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | Yes | Yes | KT808669 |
| G17 | 21 November 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | No | No | N/A |
| G18 | 22 November 2014 | Anser anser | Wild Greylag goose | A | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| G19 | 22 November 2014 | Anser anser | Wild Greylag goose | A | H | Yes | Yes | KT808670 |
| G20 | 22 November 2014 | Anser anser | Wild Greylag goose | A | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| G21 | 23 November 2014 | Anser albifrons | White fronted goose | A | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| G22 | 23 November 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | No | No | N/A |
| G23 | 23 November 2014 | Anser fabalis | Bean goose | A | H | No | No | N/A |
| G24 | 23 November 2014 | Anas platyrhynchos | Mallard duck | A | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| DG1 | 6 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808650 |
| DG2 | 6 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| DG3 | 6 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808651 |
| DG4 | 6 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808652 |
| DG5 | 6 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808653 |
| DG6 | 6 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808654 |
| DG7 | 6 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808655 |
| DG8 | 6 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808656 |
| DG9 | 5 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| DG10 | 5 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| DG11 | 5 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808657 |
| DG12 | 5 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | No | N/A |
| DG13 | 5 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808658 |
| DG14 | 5 December 2014 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | A * | H | Yes | Yes | KT808659 |
| DG15 | 5 June 2015 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | Y ** | S *** | Yes | Yes | KT808660 |
| DG16 | 5 June 2015 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | Y ** | S *** | Yes | Yes | KT808661 |
| DG17 | 5 June 2015 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | Y ** | S *** | Yes | Yes | KT808662 |
| DG18 | 5 June 2015 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | Y ** | S *** | Yes | Yes | KT808663 |
| DG19 | 5 June 2015 | Anser anser | Domestic goose | Y ** | S *** | Yes | No | N/A |
| Accession | Description | Country | Host | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF418552 | Goose circovirus isolate TW | Taiwan | Anser anser | I |
| AF536931 | Goose circovirus isolate TW1/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | I |
| AF536932 | Goose circovirus isolate TW2/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | I |
| AF536933 | Goose circovirus isolate TW3/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | I |
| AF536934 | Goose circovirus isolate TW4/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | I |
| AF536935 | Goose circovirus isolate TW5/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | I |
| AF536936 | Goose circovirus isolate TW6/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | XI |
| AF536937 | Goose circovirus isolate TW7/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | I |
| AF536938 | Goose circovirus isolate TW8/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | XI |
| AF536939 | Goose circovirus isolate TW9/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | XI |
| AF536940 | Goose circovirus isolate TW10/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | I |
| AF536941 | Goose circovirus isolate TW11/2001 | Taiwan | Anser anser | I |
| AJ304456 | Goose circovirus isolate DE | Germany | Anser sp. | XII |
| AY633653 | Goose circovirus isolate yk1 | China | Anser anser | IX |
| DQ192279 | Goose circovirus isolate yk2 | China: Zhejiang | Anser anser | IX |
| DQ192280 | Goose circovirus isolate yk3 | China: Zhejiang | Anser anser | IX |
| DQ192281 | Goose circovirus isolate yk4 | China | Anser anser | VIII |
| DQ192282 | Goose circovirus isolate xs1 | China | Anser anser | IX |
| DQ192283 | Goose circovirus isolate xs2 | China | Anser anser | III |
| DQ192284 | Goose circovirus isolate xs3 | China | Anser anser | X |
| DQ192285 | Goose circovirus isolate xs4 | China | Anser anser | III |
| DQ192286 | Goose circovirus isolate xs5 | China | Anser anser | X |
| DQ192287 | Goose circovirus isolate xs6 | China | Anser anser | X |
| GU320569 | Goose circovirus isolate JX1 | China: Jiangxi | Anser anser | IX |
| KP203866 | Goose circovirus isolate 1020111GB | Taiwan: Yunlin | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP203867 | Goose circovirus isolate 1021024G | Taiwan: Yunlin | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP203868 | Goose circovirus isolate GB20-13 | Taiwan: Kaohsiung | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP203869 | Goose circovirus isolate GB21-9 | Taiwan: Pingtung | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP203870 | Goose circovirus isolate GB25-8 | Taiwan: Pingtung | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP203871 | Goose circovirus isolate GB26-15 | Taiwan: Changhua | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP203872 | Goose circovirus isolate GB27-20 | Taiwan: Yunlin | Anser cygnoides | I |
| KP229363 | Goose circovirus isolate CF13001 | Taiwan: Yunlin | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP229370 | Goose circovirus isolate CD13088 | Taiwan: Chiayi | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP229371 | Goose circovirus isolate CPA13007-1 | Taiwan | Coscoroba coscoroba | II |
| KP229372 | Goose circovirus isolate CJ14010 | Taiwan: Chiayi | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP229373 | Goose circovirus isolate CPA13007-2 | Taiwan | Coscoroba coscoroba | XI |
| KP229374 | Goose circovirus isolate CPA14012 | Taiwan | Coscoroba coscoroba | II |
| KR869727 | Goose circovirus isolate 2GK | Poland | Anser anser | XVII |
| KT207809 | Goose circovirus isolate TD254-2014 | China | Anser anser | IX |
| KT387277 | Goose circovirus isolate Shandong | China | Anser anser | IX |
| KT443969 | Goose circovirus isolate TD227/2013 | China | Anser anser | IX |
| KT443970 | Goose circovirus isolate TD265/2013 | China | Anser anser | IX |
| KT808650 | Goose circovirus isolate DG1 | Poland | Anser anser | XIV |
| KT808651 | Goose circovirus isolate DG3 | Poland | Anser anser | XV |
| KT808652 | Goose circovirus isolate DG4 | Poland | Anser anser | XV |
| KT808653 | Goose circovirus isolate DG5 | Poland | Anser anser | XIII |
| KT808654 | Goose circovirus isolate DG6 | Poland | Anser anser | XV |
| KT808655 | Goose circovirus isolate DG7 | Poland | Anser anser | XV |
| KT808656 | Goose circovirus isolate DG8 | Poland | Anser anser | XV |
| KT808657 | Goose circovirus isolate DG11 | Poland | Anser anser | XVI |
| KT808658 | Goose circovirus isolate DG13 | Poland | Anser anser | XV |
| KT808659 | Goose circovirus isolate DG14 | Poland | Anser anser | XV |
| KT808660 | Goose circovirus isolate DG15 | Poland | Anser anser | IV |
| KT808661 | Goose circovirus isolate DG16 | Poland | Anser anser | IV |
| KT808662 | Goose circovirus isolate DG17 | Poland | Anser anser | IV |
| KT808663 | Goose circovirus isolate DG18 | Poland | Anser anser | IV |
| KT808664 | Goose circovirus isolate G1 | Poland | Anser fabalis | V |
| KT808665 | Goose circovirus isolate G4 | Poland | Anser albifrons | V |
| KT808666 | Goose circovirus isolate G6 | Poland | Anser anser | VII |
| KT808667 | Goose circovirus isolate G9 | Poland | Anser anser | V |
| KT808668 | Goose circovirus isolate G15 | Poland | Anser fabalis | V |
| KT808669 | Goose circovirus isolate G16 | Poland | Anser fabalis | V |
| KT808670 | Goose circovirus isolate G19 | Poland | Anser anser | VI |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stenzel, T.; Dziewulska, D.; Muhire, B.M.; Hartnady, P.; Kraberger, S.; Martin, D.P.; Varsani, A. Recombinant Goose Circoviruses Circulating in Domesticated and Wild Geese in Poland. Viruses 2018, 10, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030107
Stenzel T, Dziewulska D, Muhire BM, Hartnady P, Kraberger S, Martin DP, Varsani A. Recombinant Goose Circoviruses Circulating in Domesticated and Wild Geese in Poland. Viruses. 2018; 10(3):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030107
Chicago/Turabian StyleStenzel, Tomasz, Daria Dziewulska, Brejnev M. Muhire, Penelope Hartnady, Simona Kraberger, Darren P. Martin, and Arvind Varsani. 2018. "Recombinant Goose Circoviruses Circulating in Domesticated and Wild Geese in Poland" Viruses 10, no. 3: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030107
APA StyleStenzel, T., Dziewulska, D., Muhire, B. M., Hartnady, P., Kraberger, S., Martin, D. P., & Varsani, A. (2018). Recombinant Goose Circoviruses Circulating in Domesticated and Wild Geese in Poland. Viruses, 10(3), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030107






