Evidence of Human Parvovirus B19 Infection in the Post-Mortem Brain Tissue of the Elderly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Material and Sampling
2.2. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
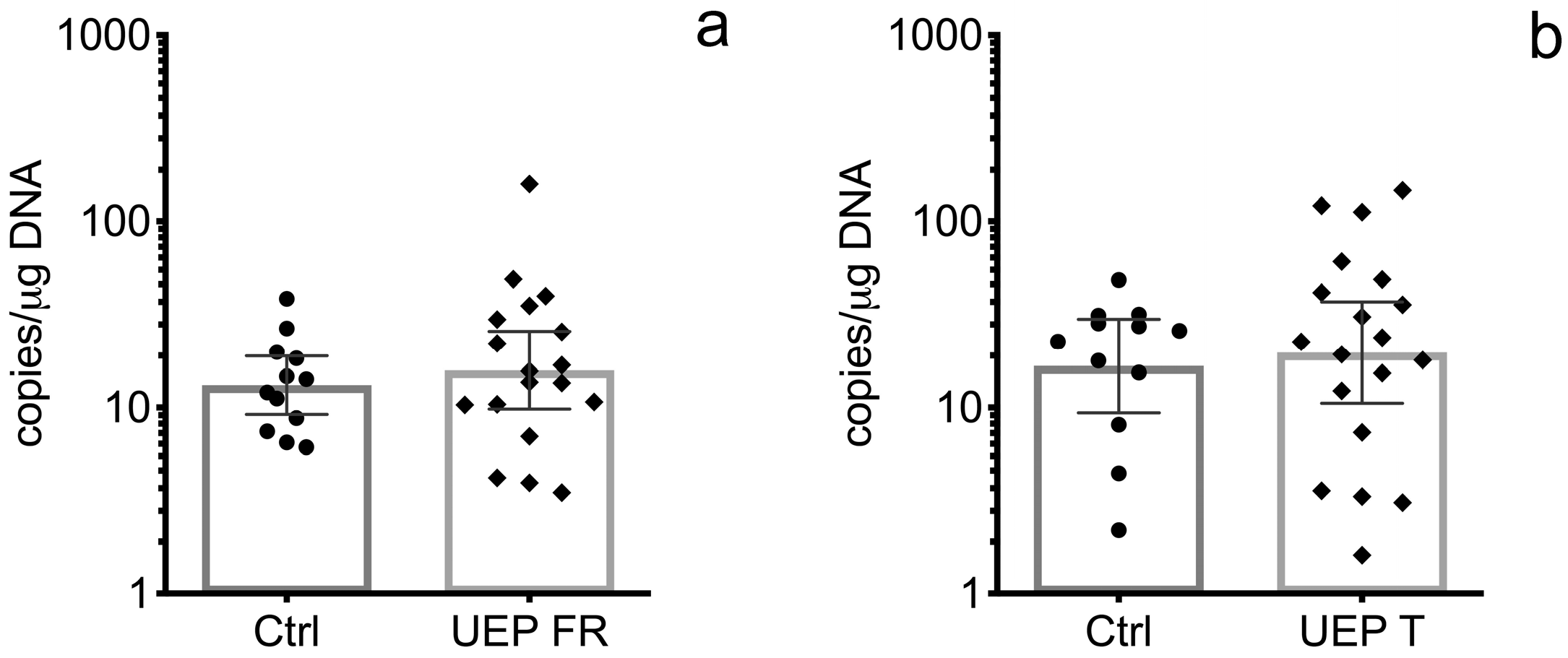
3.1. Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
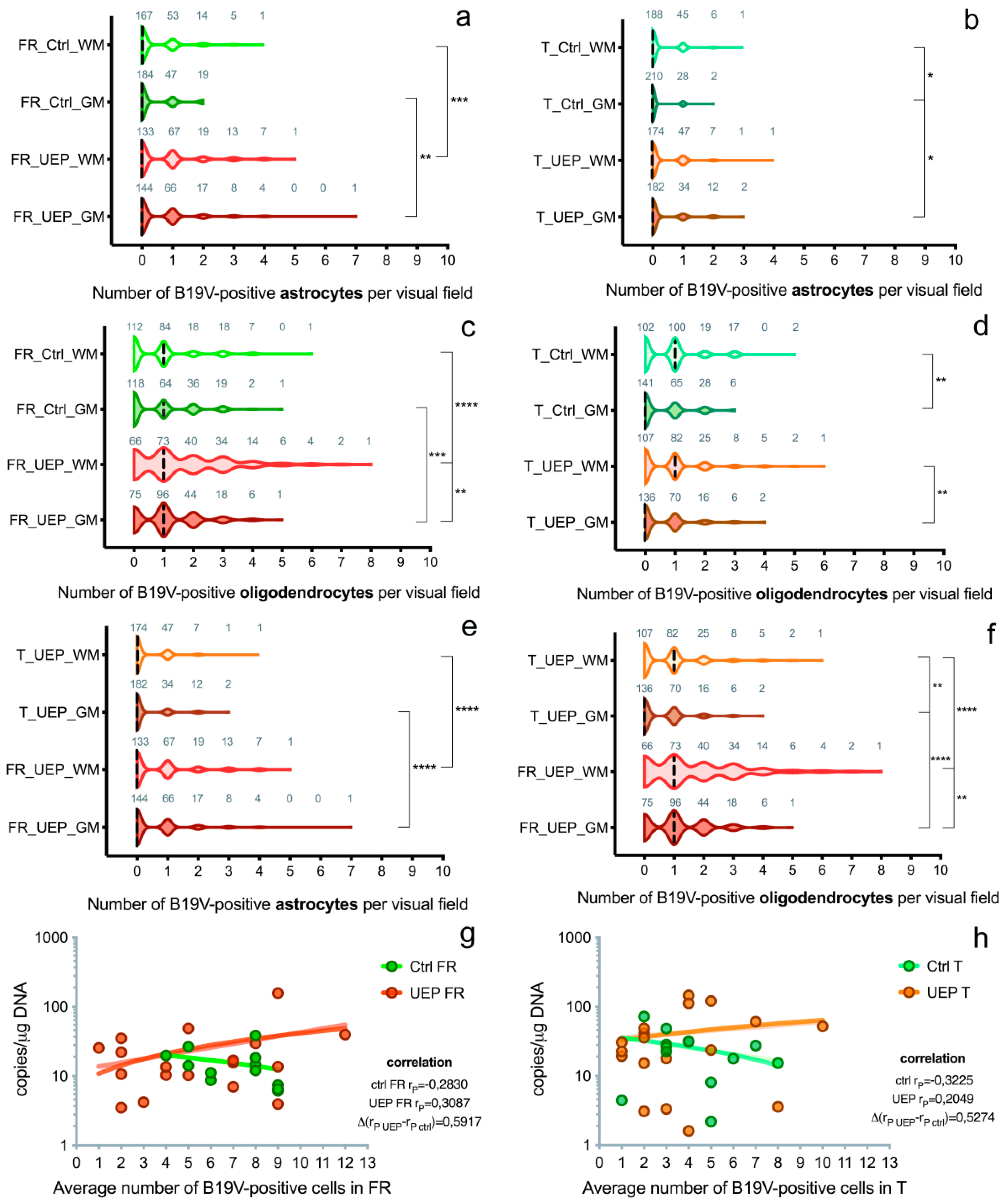
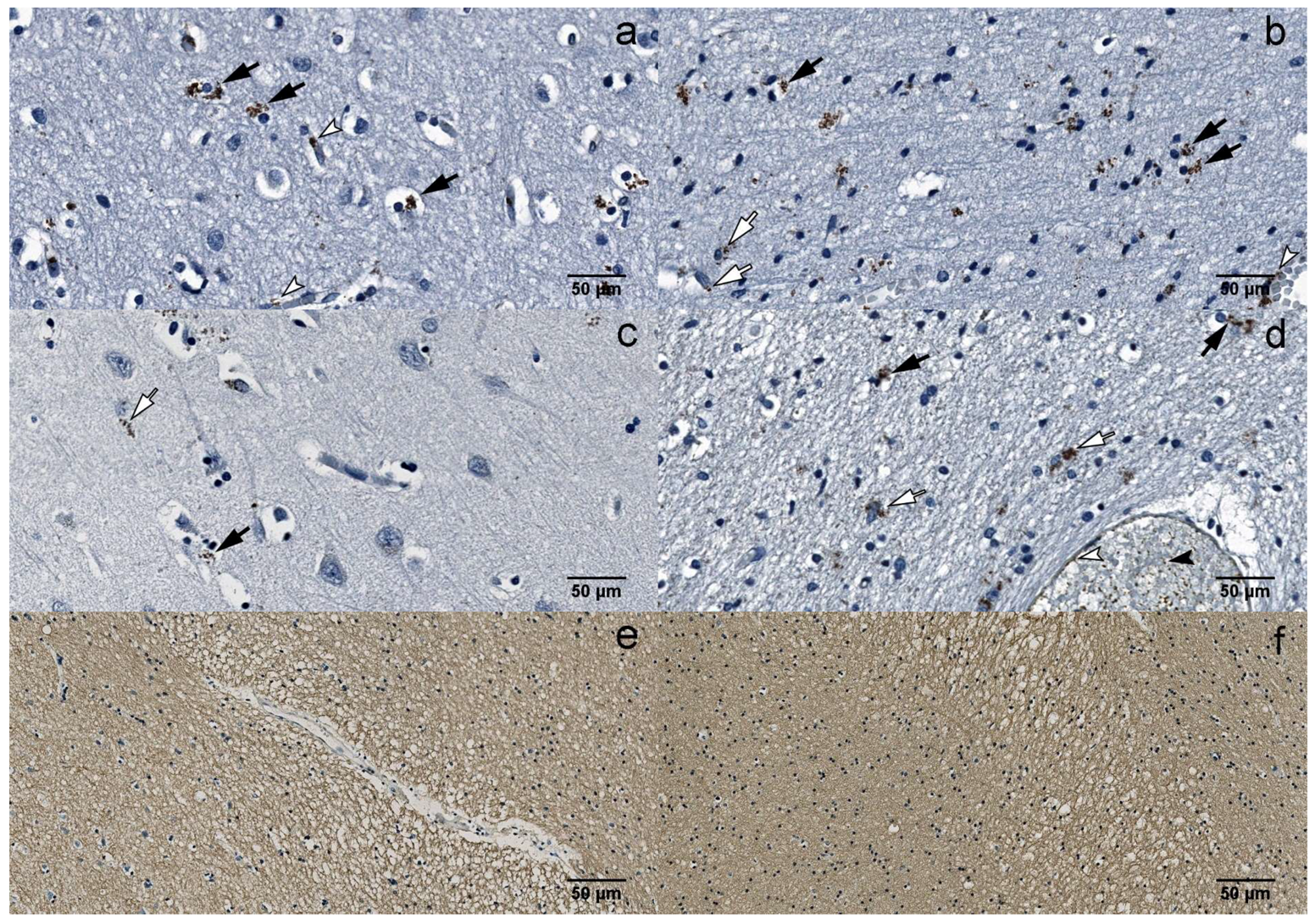
3.2. Immunohistochemistry
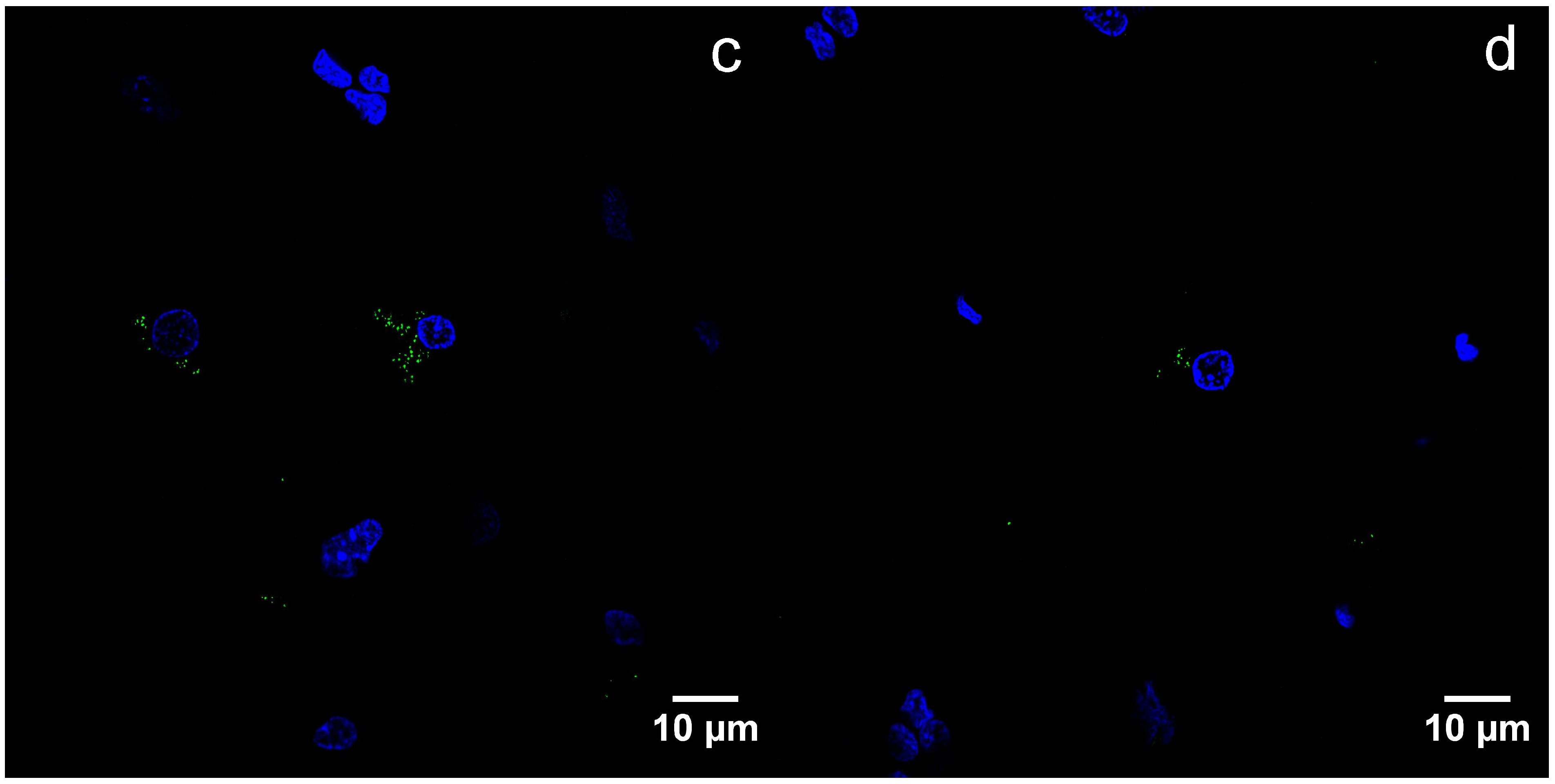
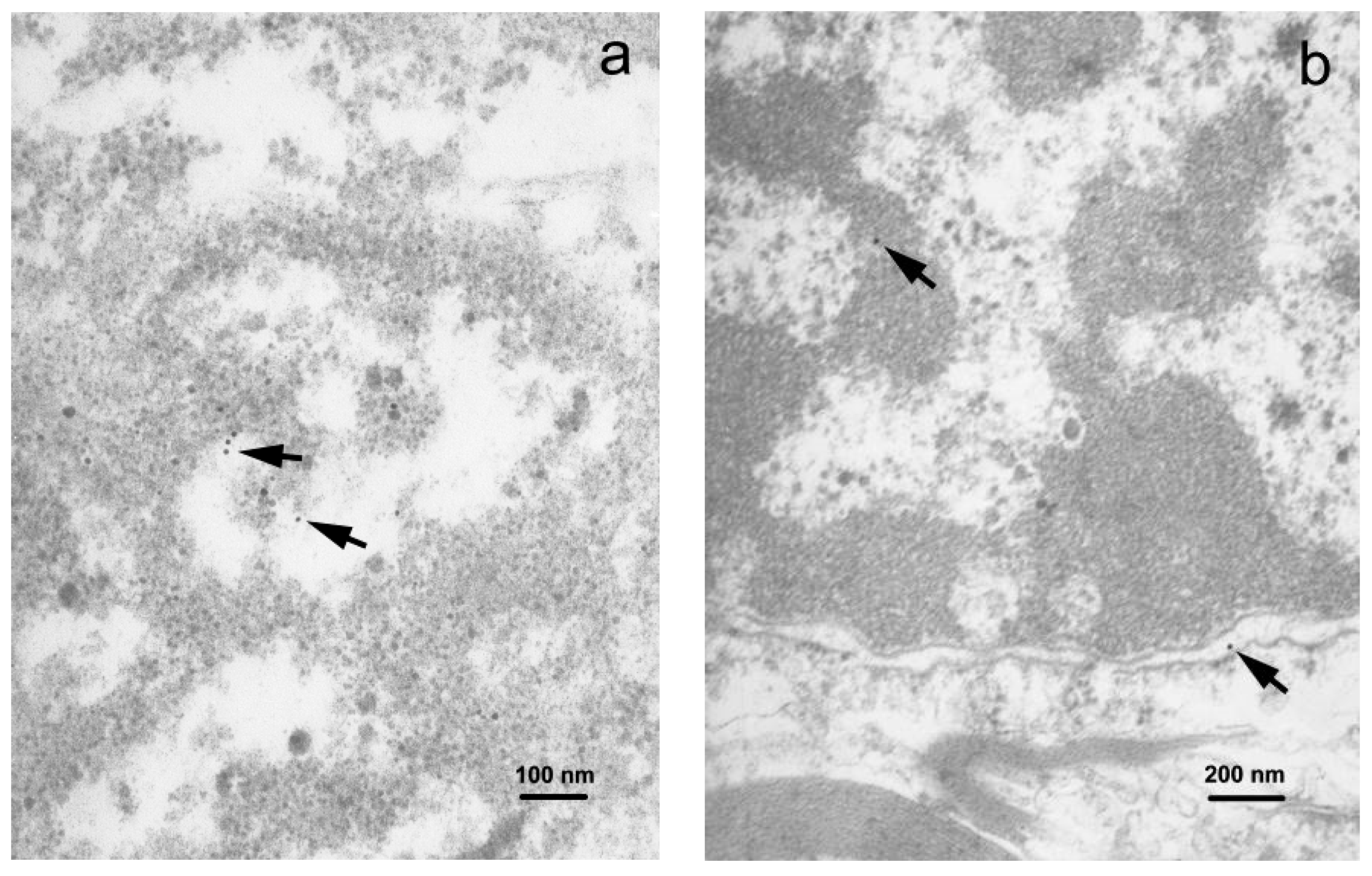
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Immunogold Staining
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Licastro, F.; Carbone, I.; Raschi, E.; Porcellini, E. The 21st Century Epidemic: Infections as Inductors of Neuro-Degeneration Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Immun. Ageing 2014, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, P.A.; McGavern, D.B. Viral Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 11, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barah, F.; Whiteside, S.; Batista, S.; Morris, J. Neurological Aspects of Human Parvovirus B19 Infection: A Systematic Review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2014, 24, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, N.S.; Brown, K.E. Parvovirus B19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokynar, K.; Norja, P.; Hedman, K.; Söderlund-Venermo, M. Tissue Persistence and Prevalence of B19 Virus Types 1-3. Future Virol. 2007, 2, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson-Small, L.A.; Ignatovich, I.V.; Laemmerhirt, M.G.; Hobbs, J.A. Persistent Parvovirus B19 Infection in Non-Erythroid Tissues: Possible Role in the Inflammatory and Disease Process. Virus Res. 2014, 190, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Söderlund-Venermo, M.; Young, N.S. Human Parvoviruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 43–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoto, Y.; Kudoh, T.; Haseyama, K.; Tsutsumi, H. Human Parvovirus B19 and Meningoencephalitis. Lancet 2001, 358, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barah, F.; Vallely, P.J.; Cleator, G.M.; Kerr, J.R. Neurological Manifestations of Human Parvovirus B19 Infection. Rev. Med. Virol. 2003, 13, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douvoyiannis, M.; Litman, N.; Goldman, D.L. Neurologic Manifestations Associated with Parvovirus B19 Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenglet, T.; Haroche, J.; Schnuriger, A.; Maisonobe, T.; Viala, K.; Michel, Y.; Chelbi, F.; Grabli, D.; Seror, P.; Garbarg-Chenon, A.; et al. Mononeuropathy Multiplex Associated with Acute Parvovirus B19 Infection: Characteristics, Treatment and Outcome. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kawashima, H. Acute Encephalitis and Encephalopathy Associated with Human Parvovirus B19 Infection in Children. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2015, 4, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, M.F.; Freund, P.; Draganski, B.; Anderson, E.; Cappelletti, M.; Chowdhury, R.; Diedrichsen, J.; FitzGerald, T.H.B.; Smittenaar, P.; Helms, G.; et al. Widespread Age-Related Differences in the Human Brain Microstructure Revealed by Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazakerley, J.K.; Walker, R. Virus Demyelination. J. Neurovirol. 2003, 9, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servant-Delmasa, A.; Morinetb, F. Update of the Human Parvovirus B19 Biology. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2016, 23, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, A.; Doyle, S. Advances in the Biology, Diagnosis and Host-Pathogen Interactions of Parvovirus B19. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, M.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A. Role of Capsid Proteins in Parvoviruses Infection. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallinella, G. Parvovirus B19 Achievements and Challenges. ISRN Virol. 2013, 2013, e898730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallinella, G. Parvovirus B19: Recent Insights and Implications for Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapy. Microbiol. Medica 2017, 32, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlemann, B.; Margaryan, A.; de Barros Damgaard, P.; Allentoft, M.E.; Vinner, L.; Hansen, A.J.; Weber, A.; Bazaliiskii, V.I.; Molak, M.; Arneborg, J.; et al. Ancient Human Parvovirus B19 in Eurasia Reveals Its Long-Term Association with Humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7557–7562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heegaard, E.D.; Brown, K.E. Human Parvovirus B19. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 485–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dourmashkin, R.R.; McCall, S.A.; Dourmashkin, N.; Hannah, M.J. Virus-like Particles and Enterovirus Antigen Found in the Brainstem Neurons of Parkinson’s Disease. F1000Research 2018, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, J.A. Detection of Adeno-Associated Virus 2 and Parvovirus B19 in the Human Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. J. Neurovirol. 2006, 12, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, J.A.; Waseem, H. How Do Viruses Really Cause Neuropathology?: Is There More to the Story. J. Neuroinfect. Dis. 2016, 7, 1000228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapenko, S.; Roga, S.; Skuja, S.; Rasa, S.; Cistjakovs, M.; Svirskis, S.; Zaserska, Z.; Groma, V.; Murovska, M. Detection Frequency of Human Herpesviruses-6A, -6B, and -7 Genomic Sequences in Central Nervous System DNA Samples from Post-Mortem Individuals with Unspecified Encephalopathy. J. Neurovirol. 2016, 22, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.; Sethares, C. Oligodendrocytes, Their Progenitors and Other Neuroglial Cells in the Aging Primate Cerebral Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowley, M.P.; Cabral, H.; Rosene, D.L.; Peters, A. Age Changes in Myelinated Nerve Fibers of the Cingulate Bundle and Corpus Callosum in the Rhesus Monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 518, 3046–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brorson, K.; Swann, P.G.; Lizzio, E.; Maudru, T.; Peden, K.; Stein, K.E. Use of a Quantitative Product-Enhanced Reverse Transcriptase Assay to Monitor Retrovirus Levels in MAb Cell-Culture and Downstream Processing. Biotechnol. Prog. 2001, 17, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brorson, S.H. A Method for Measurements of the Efficiency of Immunogold Labelling of Epoxy-Embedded Proteins Subjected to Different Retrieval Techniques. Micron 2004, 35, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirenberg, M.J.; Vaughan, R.A.; Uhl, G.R.; Kuhar, M.J.; Pickeli, V.M. The Dopamine Transporter Is Localized to Dendritic and Axonal Plasma Membranes of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons. J. Neurosci. 1996, 76, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.K.; Yin, N.C.; Zaytoun, A.M.; Waseem, H.; Hobbs, J.A. Persistent Adeno-Associated Virus 2 and Parvovirus B19 Sequences in Post-Mortem Human Cerebellum. Cerebellum 2009, 8, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaudien, D.; Polizopoulou, Z.; Koutinas, A.; Schwab, S.; Porombka, D.; Baumgärtner, W.; Herden, C. Leukoencephalopathy Associated with Parvovirus Infection in Cretan Hound Puppies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3169–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, D.B.; Sesack, S.R. Callosal Terminals in the Rat Prefrontal Cortex: Synaptic Targets and Association with GABA-Immunoreactive Structures. Synapse 1998, 29, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uylings, H.B.M.; De Brabander, J.M. Neuronal Changes in Normal Human Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Cogn. 2002, 49, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leisi, R.; Von Nordheim, M.; Ros, C.; Kempf, C. The VP1u Receptor Restricts Parvovirus B19 Uptake to Permissive Erythroid Cells. Viruses 2016, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isumi, H.; Nunoue, T.; Nishida, A.; Takashima, S. Fetal Brain Infection with Human Parvovirus B19. Pediatr. Neurol. 1999, 21, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, Y.; Kato, I.; Saito, T.; Kodera, T.; Ishii, K.K.; Sasaki, T. Human Parvovirus B19 Infection of Monocytic Cell Line U937 and Antibody-Dependent Enhancement. Virology 2006, 345, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, C.; Bassols, A.C.; De la Cabada, F.J.; De la Cabada, J.B.; Rico, E.; Velazquez Ferrari, M.A. Parvovirus B19: Past, Present and Future. Res. Rev. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 5, 86–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, J.R.; Barah, F.; Chiswick, M.L.; McDonnell, G.V.; Smith, J.; Chapman, M.D.; Bingham, J.B.; Kelleher, P.; Sheppard, M.N. Evidence for the Role of Demyelination, HLA-DR Alleles, and Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Parvovirus B19 Meningoencephalitis and Its Sequelae. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SantaCruz, K.S. Neuropathology of JC Virus Infection in Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in Remission. World J. Virol. 2016, 5, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clase, A.C.; Dimcheff, D.E.; Favara, C.; Dorward, D.; McAtee, F.J.; Parrie, L.E.; Ron, D.; Portis, J.L. Oligodendrocytes Are a Major Target of the Toxicity of Spongiogenic Murine Retroviruses. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1026–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahic, M.; Roussarie, J.-P. Axon–Myelin Interactions during a Viral Infection of the Central Nervous System. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, C.S.; Miller, S.E. Modern Uses of Electron Microscopy for Detection of Viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, C.; Bayat, N.; Wolfisberg, R.; Almendral, J.M. Protoparvovirus Cell Entry. Viruses 2017, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäntylä, E.; Kann, M.; Vihinen-Ranta, M. Protoparvovirus Knocking at the Nuclear Door. Viruses 2017, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bär, S.; Daeffler, L.; Rommelaere, J.; Nüesch, J.P.F. Vesicular Egress of Non-Enveloped Lytic Parvoviruses Depends on Gelsolin Functioning. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyi, S.M.; Tan, M.J.A.; Parrish, C.R. Parvovirus Particles and Movement in the Cellular Cytoplasm and Effects of the Cytoskeleton. Virology 2014, 456–457, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Panté, N. Pushing the Envelope: Microinjection of Minute Virus of Mice into Xenopus Oocytes Causes Damage to the Nuclear Envelope. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, A.; Willey, S.J.; Bell, J.E.; Simmonds, P. Comparison of Tissue Distribution, Persistence, and Molecular Epidemiology of Parvovirus B19 and Novel Human Parvoviruses PARV4 and Human Bocavirus. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skuja, S.; Zieda, A.; Ravina, K.; Chapenko, S.; Roga, S.; Teteris, O.; Groma, V.; Murovska, M. Structural and Ultrastructural Alterations in Human Olfactory Pathways and Possible Associations with Herpesvirus 6 Infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, R.C.; Chidlow, G.; French, M.A. Parvovirus B19 Encephalitis Presenting as Immune Restoration Disease after Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauta, W.J. Neural Associations of the Frontal Cortex. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. (Wars) 1972, 32, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skuja, S.; Vilmane, A.; Svirskis, S.; Groma, V.; Murovska, M. Evidence of Human Parvovirus B19 Infection in the Post-Mortem Brain Tissue of the Elderly. Viruses 2018, 10, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10110582
Skuja S, Vilmane A, Svirskis S, Groma V, Murovska M. Evidence of Human Parvovirus B19 Infection in the Post-Mortem Brain Tissue of the Elderly. Viruses. 2018; 10(11):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10110582
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkuja, Sandra, Anda Vilmane, Simons Svirskis, Valerija Groma, and Modra Murovska. 2018. "Evidence of Human Parvovirus B19 Infection in the Post-Mortem Brain Tissue of the Elderly" Viruses 10, no. 11: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10110582
APA StyleSkuja, S., Vilmane, A., Svirskis, S., Groma, V., & Murovska, M. (2018). Evidence of Human Parvovirus B19 Infection in the Post-Mortem Brain Tissue of the Elderly. Viruses, 10(11), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10110582





