Development of a Surrogate Neutralization Assay for Norovirus Vaccine Evaluation at the Cellular Level
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Recombinant Norovirus Virus-Like Particles
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Plasmid Construction
2.4. Lentivirus Production and Transduction
2.5. RNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.6. Attachment Assay
2.7. Animal Immunization
2.8. Histo-Blood Group Antigen Blocking Assay
2.9. Attachment Inhibition Assay
2.10. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.11. Cellular Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
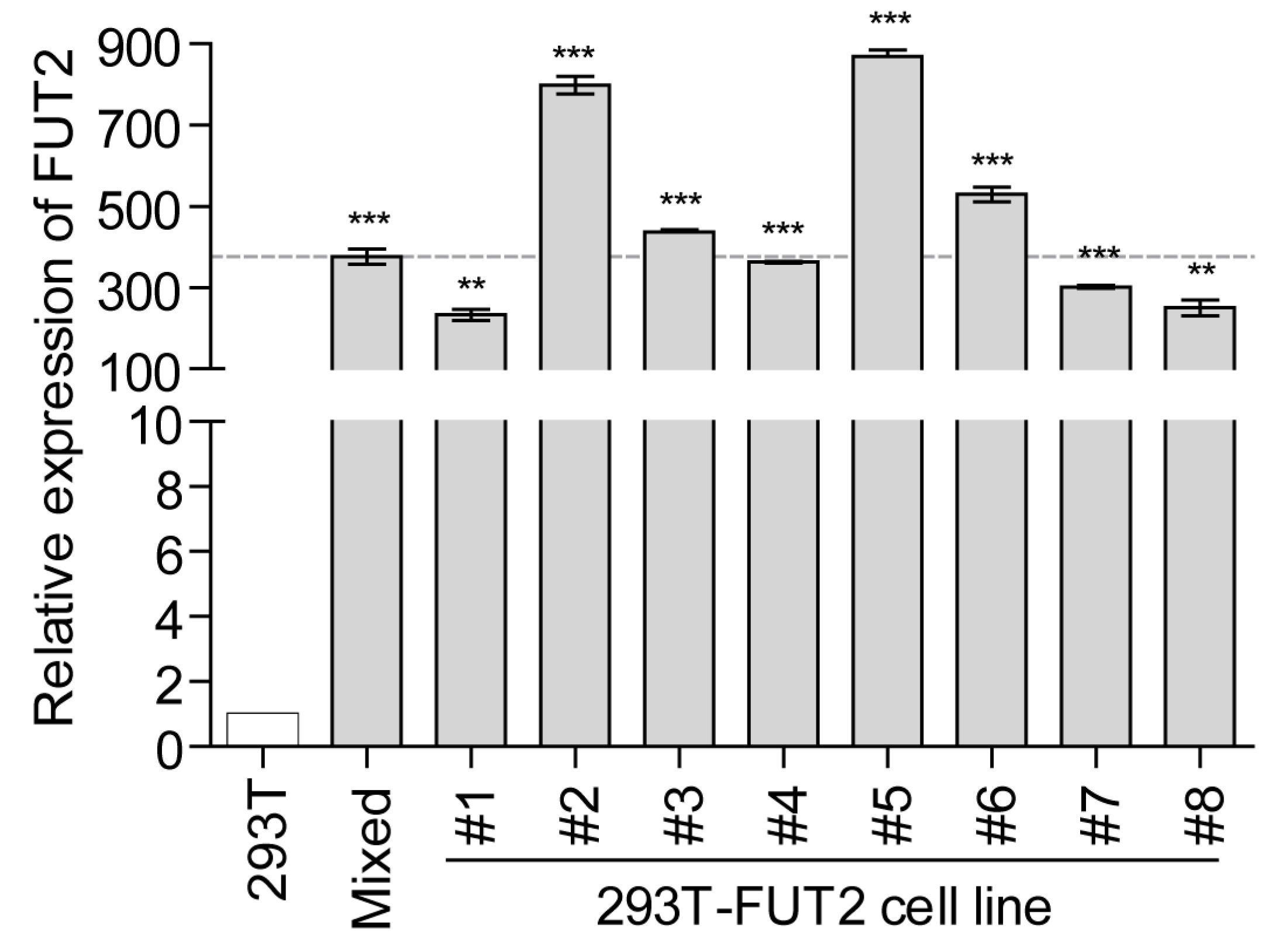
3.1. Establishment of Stable FUT2-Overexpressing 293T Cell Lines
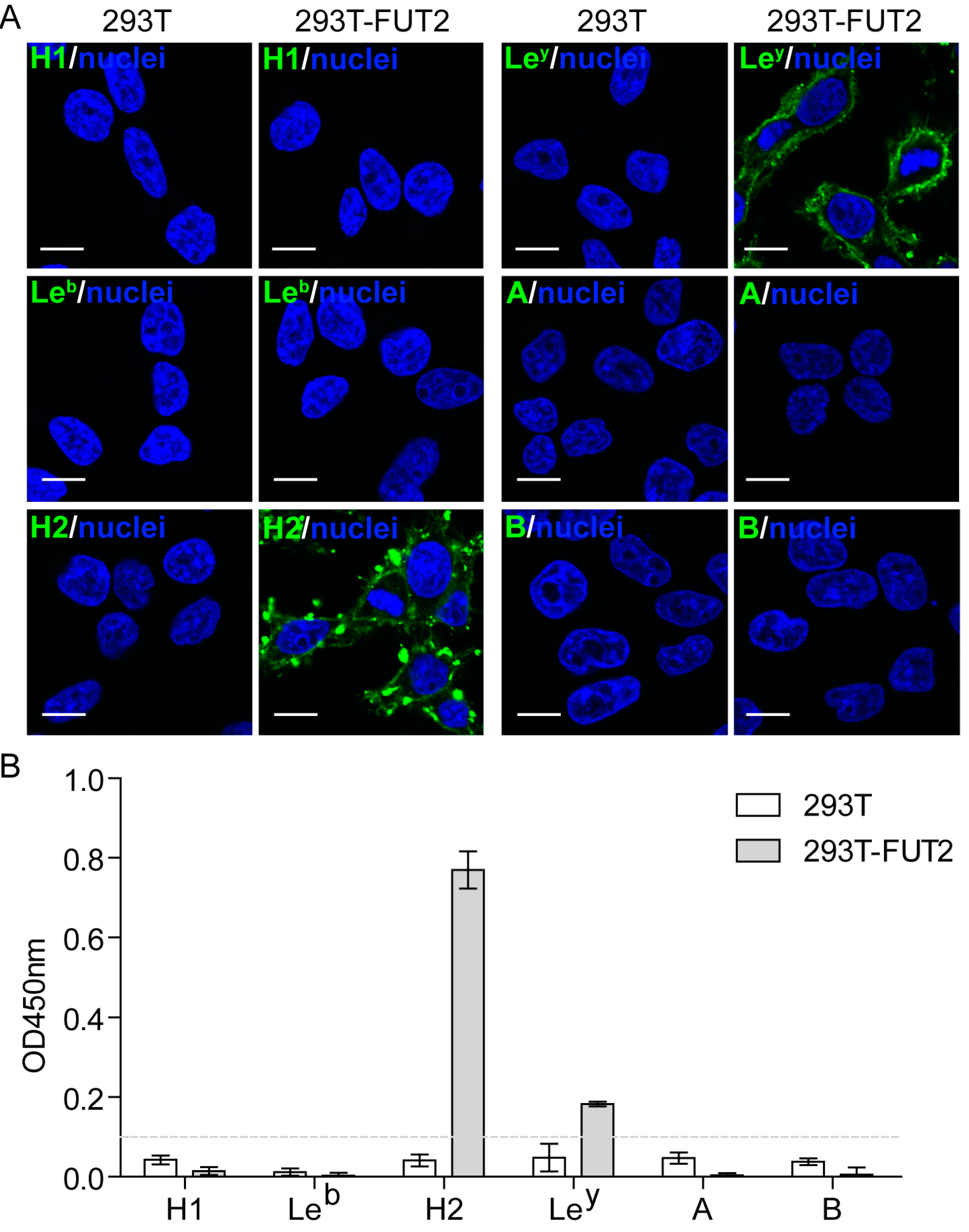
3.2. Expression of HBGAs in 293T-FUT2 Cells
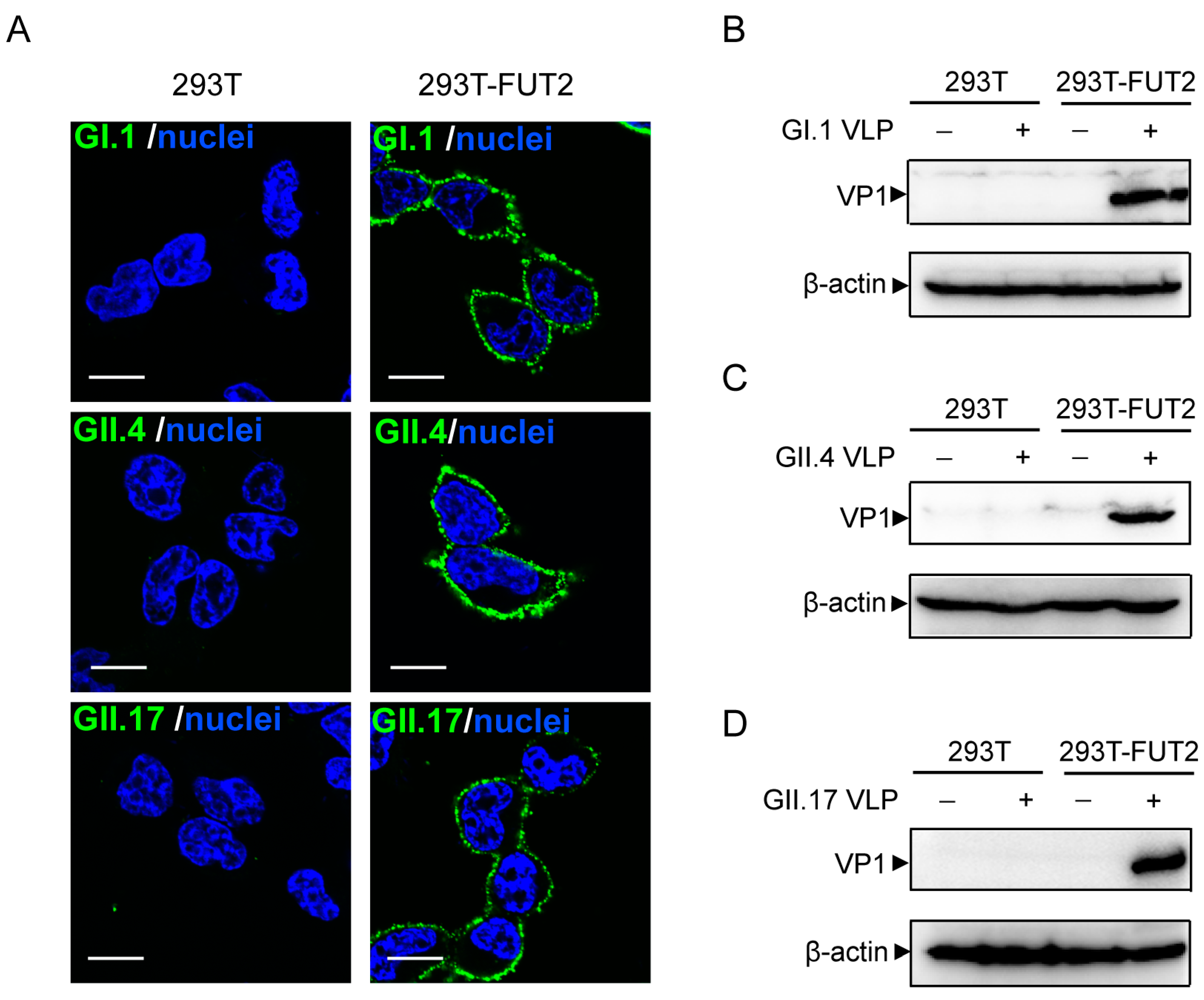
3.3. Attachment of Norovirus Virus-Like Particles to 293T-FUT2 Cells
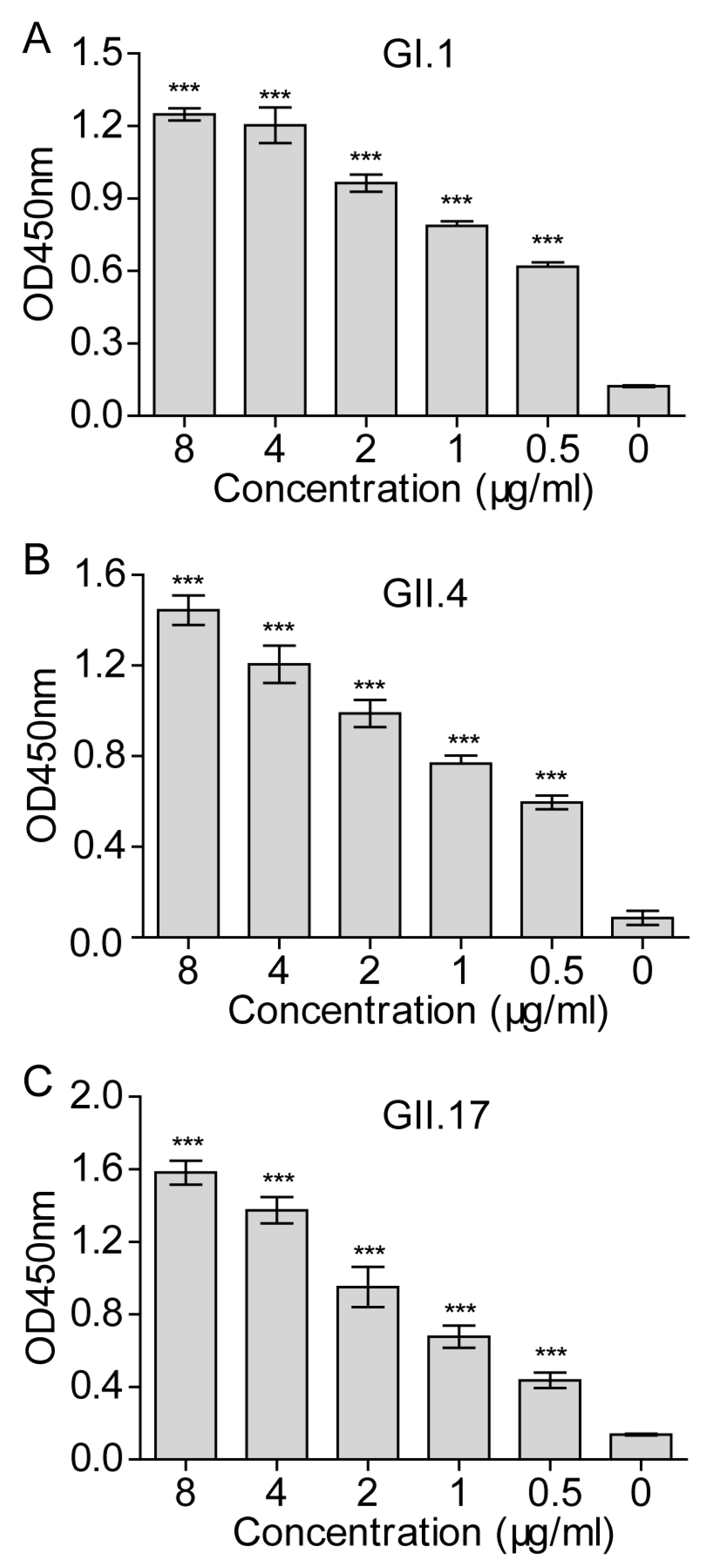
3.4. Establishment of a Cellular ELISA Assay to Detect Norovirus Virus-Like Particles Attachment
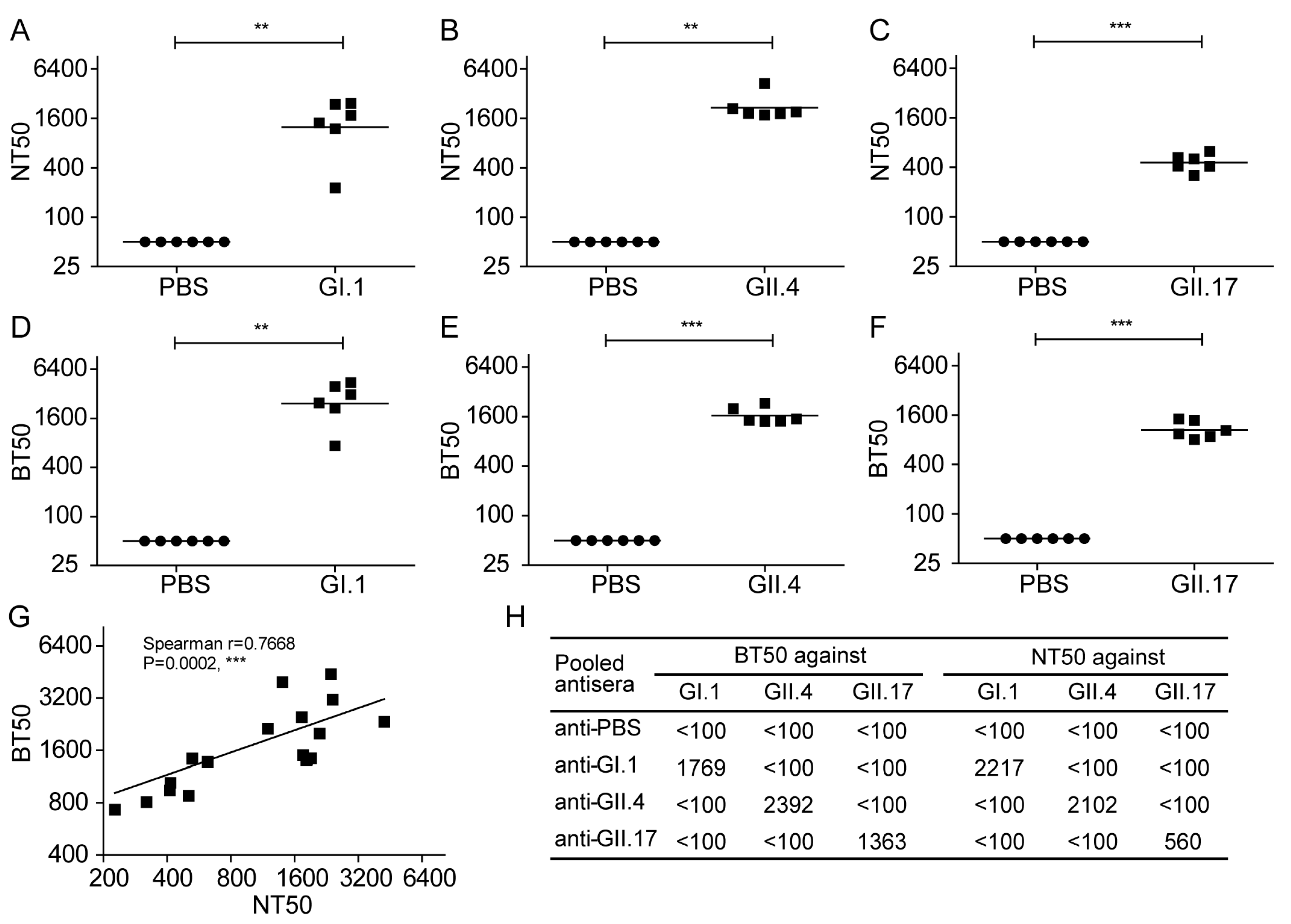
3.5. Inhibition of the NoV VLP Attachment to 293T-FUT2 Cells by NoV VLP-Specific Antisera
3.6. Evaluation of Norovirus Vaccine In Vitro at the Cellular Level
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karst, S.M.; Wobus, C.E.; Goodfellow, I.G.; Green, K.Y.; Virgin, H.W. Advances in norovirus biology. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, S.M.; Lopman, B.A.; Ozawa, S.; Hall, A.J.; Lee, B.Y. Global economic burden of norovirus gastroenteritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroneman, A.; Vega, E.; Vennema, H.; Vinje, J.; White, P.A.; Hansman, G.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Katayama, K.; Koopmans, M. Proposal for a unified norovirus nomenclature and genotyping. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, E.; Barclay, L.; Gregoricus, N.; Shirley, S.H.; Lee, D.; Vinje, J. Genotypic and epidemiologic trends of norovirus outbreaks in the United States, 2009 to 2013. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.K.; Watanabe, M.; Zhu, S.; Graves, C.L.; Keyes, L.R.; Grau, K.R.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.B.; Iovine, N.M.; Wobus, C.E.; Vinje, J.; et al. Enteric bacteria promote human and mouse norovirus infection of B cells. Science 2014, 346, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettayebi, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Murakami, K.; Broughman, J.R.; Karandikar, U.; Tenge, V.R.; Neill, F.H.; Blutt, S.E.; Zeng, X.L.; Qu, L.; et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science 2016, 353, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, P.R.; Lindesmith, L.; Yount, B.; Moe, C.L.; Baric, R.S. Binding of Norwalk virus-like particles to ABH histo-blood group antigens is blocked by antisera from infected human volunteers or experimentally vaccinated mice. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12335–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoBue, A.D.; Lindesmith, L.; Yount, B.; Harrington, P.R.; Thompson, J.M.; Johnston, R.E.; Moe, C.L.; Baric, R.S. Multivalent norovirus vaccines induce strong mucosal and systemic blocking antibodies against multiple strains. Vaccine 2006, 24, 5220–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czako, R.; Atmar, R.L.; Opekun, A.R.; Gilger, M.A.; Graham, D.Y.; Estes, M.K. Serum hemagglutination inhibition activity correlates with protection from gastroenteritis in persons infected with Norwalk virus. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravn, V.; Dabelsteen, E. Tissue distribution of histo-blood group antigens. Apmis 2000, 108, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marionneau, S.; Ruvoen, N.; Le Moullac-Vaidye, B.; Clement, M.; Cailleau-Thomas, A.; Ruiz-Palacois, G.; Huang, P.W.; Jiang, X.; Le Pendu, J. Norwalk virus binds to histo-blood group antigens present on gastroduodenal epithelial cells of secretor individuals. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutson, A.M.; Atmar, R.L.; Graham, D.Y.; Estes, M.K. Norwalk virus infection and disease is associated with ABO histo-blood group type. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 1335–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marionneau, S.; Cailleau-Thomas, A.; Rocher, J.; le Moullac-Vaidye, B.; Ruvoen, N.; Clement, M.; le Pendu, J. ABH and Lewis histo-blood group antigens, a model for the meaning of oligosaccharide diversity in the face of a changing world. Biochimie 2001, 83, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.D.; Ernst, L.K.; Nair, R.P.; Lowe, J.B. Molecular cloning, sequence, and expression of a human GDP-l-fucose:β-d-galactoside 2-α-l-fucosyltransferase cDNA that can form the H blood group antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6674–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.; Moe, C.; Marionneau, S.; Ruvoen, N.; Jiang, X.; Lindblad, L.; Stewart, P.; le Pendu, J.; Baric, R. Human susceptibility and resistance to Norwalk virus infection. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, M.M.; Rydell, G.E.; Grahn, A.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.; Akerlind, B.; Hutson, A.M.; Estes, M.K.; Larson, G.; Svensson, L. Antibody prevalence and titer to norovirus (genogroup II) correlate with secretor (FUT2) but not with ABO phenotype or Lewis (FUT3) genotype. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindberg, E.; Akerlind, B.; Johnsen, C.; Knudsen, J.D.; Heltberg, O.; Larson, G.; Bottiger, B.; Svensson, L. Host genetic resistance to symptomatic Norovirus (GGII.4) infections in Denmark. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2720–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutson, A.M.; Airaud, F.; LePendu, J.; Estes, M.K.; Atmar, R.L. Norwalk virus infection associates with secretor status genotyped from sera. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 77, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bureau, V.; Marionneau, S.; Cailleau-Thomas, A.; Le Moullac-Vaidye, B.; Liehr, T.; le Pendu, J. Comparison of the three rat GDP-l-fucose:β-d-galactoside 2-α-l-fucosyltransferases FTA, FTB and FTC. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 1006–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.M.; Carvalho, A.S.; Guillon, P.; Seixas, S.; Azevedo, M.; Almeida, R.; Ruvoen-Clouet, N.; Reis, C.A.; le Pendu, J.; Rocha, J.; et al. Infection-associated FUT2 (Fucosyltransferase 2) genetic variation and impact on functionality assessed by in vivo studies. Glycoconj. J. 2010, 27, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marionneau, S.; Airaud, F.; Bovin, N.V.; Le Pendu, J.; Ruvoen-Clouet, N. Influence of the combined ABO, FUT2, and FUT3 polymorphism on susceptibility to Norwalk virus attachment. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofling, J.C.; Hauzenberger, E.; Holgersson, J. Absorption of anti-blood group A antibodies on P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1/immunoglobulin chimeras carrying blood group A determinants: Core saccharide chain specificity of the Se and H gene encoded α1,2 fucosyltransferases in different host cells. Glycobiology 2002, 12, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guix, S.; Asanaka, M.; Katayama, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Neill, F.H.; Atmar, R.L.; Estes, M.K. Norwalk virus RNA is infectious in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12238–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Ku, Z.; Cai, Y.; Sun, B.; Leng, Q.; Huang, Z. Detection, characterization and quantitation of coxsackievirus A16 using polyclonal antibodies against recombinant capsid subunit proteins. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 173, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ku, Z.; Dai, W.; Chen, T.; Ye, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jin, X.; Huang, Z. A bivalent virus-like particle based vaccine induces a balanced antibody response against both enterovirus 71 and norovirus in mice. Vaccine 2015, 33, 5779–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Ku, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.; Cong, Y.; Huang, Z. Chimeric virus-like particle vaccines displaying conserved enterovirus 71 epitopes elicit protective neutralizing antibodies in mice through divergent mechanisms. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Debbink, K.; Swanstrom, J.; Vinje, J.; Costantini, V.; Baric, R.S.; Donaldson, E.F. Monoclonal antibody-based antigenic mapping of norovirus GII.4-2002. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Beltramello, M.; Donaldson, E.F.; Corti, D.; Swanstrom, J.; Debbink, K.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Baric, R.S. Immunogenetic mechanisms driving norovirus GII.4 antigenic variation. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, Z.; Ye, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Z. Single neutralizing monoclonal antibodies targeting the VP1 GH loop of enterovirus 71 inhibit both virus attachment and internalization during viral entry. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12084–12095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Kurihara, C.; Oka, T.; Shimoike, T.; Fujii, Y.; Takai-Todaka, R.; Park, Y.; Wakita, T.; Matsuda, T.; Hokari, R.; et al. Norovirus binding to intestinal epithelial cells is independent of histo-blood group antigens. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, Z.; Ye, X.; Huang, X.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Su, Z.; Huang, Z. Neutralizing antibodies induced by recombinant virus-like particles of enterovirus 71 genotype C4 inhibit infection at pre- and post-attachment steps. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus and its histo-blood group antigen receptors: An answer to a historical puzzle. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus-host interaction: Implications for disease control and prevention. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2007, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Farkas, T.; Zhong, W.; Tan, M.; Thornton, S.; Morrow, A.L.; Jiang, X. Norovirus and histo-blood group antigens: Demonstration of a wide spectrum of strain specificities and classification of two major binding groups among multiple binding patterns. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6714–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutson, A.M.; Atmar, R.L.; Marcus, D.M.; Estes, M.K. Norwalk virus-like particle hemagglutination by binding to H histo-blood group antigens. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Huang, Q.; Long, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, T.; Tan, M.; Zhang, Q.L.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Ding, Y.Q.; et al. An outbreak caused by GII.17 norovirus with a wide spectrum of HBGA-associated susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Feng, W.H.; Shi, P.; Ai, J.; Guan, H.X.; Sha, D.; Geng, Q.; Mei, J.; Chen, S.H.; Xiao, Y.; et al. An acute gastroenteritis outbreak caused by GII.17 norovirus in Jiangsu Province, China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 49, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, G.I.; Green, K.Y. Genome of emerging norovirus GII.17, United States, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Ji, L.; Shen, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, D.; Chen, L. Emergence and predominance of norovirus GII.17 in Huzhou, China, 2014–2015. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.C.; Lee, N.; Hung, T.N.; Kwok, K.; Cheung, K.; Tin, E.K.; Lai, R.W.; Nelson, E.A.; Leung, T.F.; Chan, P.K. Rapid emergence and predominance of a broadly recognizing and fast-evolving norovirus GII.17 variant in late 2014. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, K.; Abente, E.J.; Realpe-Quintero, M.; Mitra, T.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Green, K.Y. Evolutionary dynamics of GII.4 noroviruses over a 34-year period. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11890–11901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Suzuki, S.; Aoki, N.; Okajima, T.; Nadano, D.; Uchida, K.; Yamashita, K.; Oka, T.; Katayama, K.; Takeda, N.; et al. Binding of norovirus virus-like particles (VLPs) to human intestinal Caco-2 cells and the suppressive effect of pasteurized bovine colostrum on this VLP binding. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, M.; Robineleon, S.; Appay, M.D.; Kedinger, M.; Triadou, N.; Dussaulx, E.; Lacroix, B.; Simonassmann, P.; Haffen, K.; Fogh, J.; et al. Enterocyte-like differentiation and polarization of the human-colon carcinoma cell-line Caco-2 in culture. Biol. Cell 1983, 47, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- White, L.J.; Ball, J.M.; Hardy, M.E.; Tanaka, T.N.; Kitamoto, N.; Estes, M.K. Attachment and entry of recombinant Norwalk virus capsids to cultured human and animal cell lines. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6589–6597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Vicente, N.; Allen, D.J.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.; Iturriza-Gomara, M.; Buesa, J. Antibodies against lewis antigens inhibit the binding of human norovirus GII.4 virus-like particles to saliva but not to intestinal Caco-2 cells. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, J.; Oshima, M. Expression of the H type 1 blood group antigen during enterocytic differentiation of Caco-2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21209–21216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirato, H.; Ogawa, S.; Ito, H.; Sato, T.; Kameyama, A.; Narimatsu, H.; Zheng, X.F.; Miyamura, T.; Wakita, T.; Ishii, K.; et al. Noroviruses distinguish between type 1 and type 2 histo-blood group antigens for binding. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 10756–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanker, S.; Czako, R.; Sankaran, B.; Atmar, R.L.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V. Structural analysis of determinants of histo-blood group antigen binding specificity in genogroup I noroviruses. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6168–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.T.; Tan, M.; Xia, M.; Hao, N.; Zhang, X.J.C.; Huang, P.W.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.M.; Rao, Z.H. Crystallography of a Lewis-binding norovirus, elucidation of strain-specificity to the polymorphic human histo-blood group antigens. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Tan, M.; Xia, M.; Wei, C.; Huang, P.W.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhong, W.M.; Duan, Z.J.; Jiang, X. Strain-specific interaction of a GII.10 Norovirus with HBGAs. Virology 2015, 476, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, W.; Frank, M.; Kunze, A.; Bally, M.; Parra, F.; Nyholm, P.G.; Hook, F.; Larson, G. Histo-Blood group antigen presentation is critical for binding of norovirus VLP to glycosphingolipids in model membranes. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Tan, M.; Zhong, W.; Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Jiang, X. Human intestinal organoids express histo-blood group antigens, bind norovirus VLPs, and support limited norovirus replication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusi-Kerttula, H.; Tamminen, K.; Malm, M.; Vesikari, T.; Blazevic, V. Comparison of human saliva and synthetic histo-blood group antigens usage as ligands in norovirus-like particle binding and blocking assays. Microbes Infect. 2014, 16, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, J.; Rosen, L. Factors affecting hemagglutination by enteroviruses. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1964, 115, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.K.; Grau, K.R.; Costantini, V.; Kolawole, A.O.; de Graaf, M.; Freiden, P.; Graves, C.L.; Koopmans, M.; Wallet, S.M.; Tibbetts, S.A.; et al. Human norovirus culture in B cells. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, P.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Z. Development of a Surrogate Neutralization Assay for Norovirus Vaccine Evaluation at the Cellular Level. Viruses 2018, 10, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10010027
Wang X, Wang S, Zhang C, Zhou Y, Xiong P, Liu Q, Huang Z. Development of a Surrogate Neutralization Assay for Norovirus Vaccine Evaluation at the Cellular Level. Viruses. 2018; 10(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoli, Shuxia Wang, Chao Zhang, Yu Zhou, Pei Xiong, Qingwei Liu, and Zhong Huang. 2018. "Development of a Surrogate Neutralization Assay for Norovirus Vaccine Evaluation at the Cellular Level" Viruses 10, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10010027
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, S., Zhang, C., Zhou, Y., Xiong, P., Liu, Q., & Huang, Z. (2018). Development of a Surrogate Neutralization Assay for Norovirus Vaccine Evaluation at the Cellular Level. Viruses, 10(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10010027




