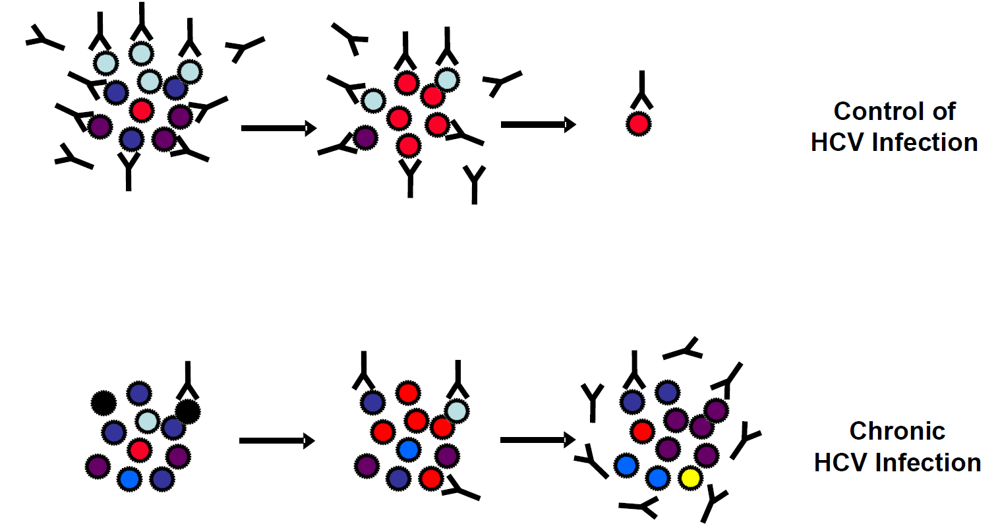
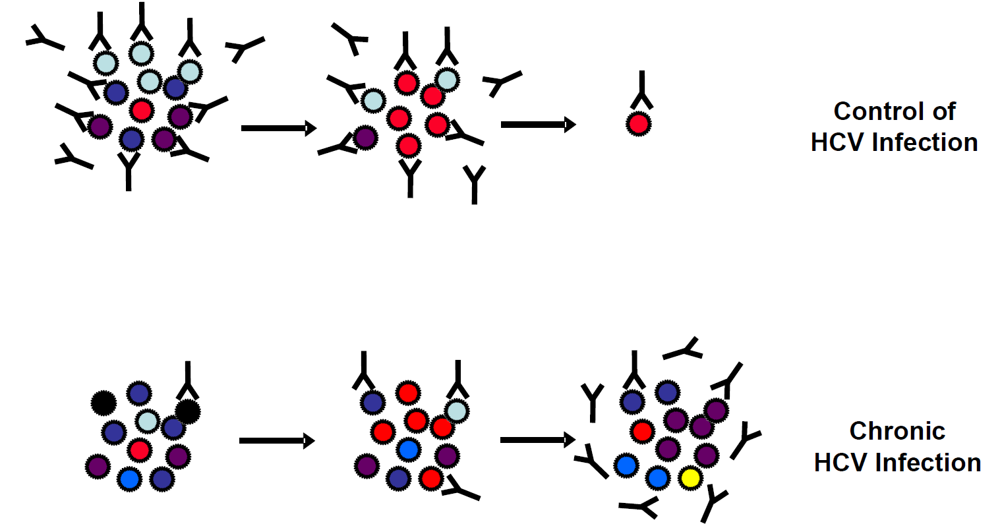
Abstract
The precise role of adaptive immune responses in the clinical outcome of HCV infection is still only partially defined. Recent studies suggest that viral-host cell interactions during the acute phase of infection are essential for viral clearance or progression into chronic HCV infection. This review focuses on different aspects of the adaptive immune responses as determinants of the different outcomes of HCV infection, clearance or persistent infection, and outlines current concepts of HCV evasion strategies. Unravelling these important mechanisms of virus-host interaction will contribute to the development of novel strategies to prevent and control HCV infection.
1. Introduction
Hepatitis C virus (HCV), a member of the Flaviridae family, infects 3% of the population resulting in chronic infection in the majority of cases. HCV chronic hepatitis frequently results in progressive fibrosis, cirrhosis with an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma [1]. These latter complications have become leading indications for liver transplantation in developed countries. There is no vaccine and the standard of care treatment, a combination of pegylated interferon and ribavirin, is limited by resistance in a large fraction of patients, toxicity and high costs. After exposure to HCV, 60 to 80% of infected persons develop persistent viremia despite the generation of HCV-specific antibodies and HCV-specific cellular immune responses [2,3]. Persistent viremia - detected by polymerase chain reaction - remains positive after more than 6 months. Studies of host responses in the course of HCV infection have been hampered by the fact that acute HCV infection is asymptomatic in most individuals and thus frequently not recognized. Moreover, the chimpanzee is the only immunocompetent animal susceptible to HCV infection and there are major differences between HCV infection in chimpanzees and in humans. Studies of the host’s immune responses in humans thus rely on patient cohorts. Through the availability of serial samples from acute and chronic HCV infected patients, insights into the humoral and cellular immune responses in the course of HCV infection could be gained in the past years.
The present review focuses on different aspects of the adaptive immune responses as determinants of the different outcomes of HCV infection, clearance or persistent infection, and outlines current concepts of HCV evasion strategies.
2. The humoral responses to HCV infection
Neutralizing antibodies are generally an important mechanism for control of initial viremia and protection from re-infection in viral infections. However, the role of the humoral immune response in the clearance of HCV infection has been questioned for a long time. While anti-HCV antibodies can easily be detected in the course of HCV infection by commercially available antibody assays approximately 50 to 60 days after HCV infection [4], these tests only attest a humoral immune response to HCV proteins but they do not evaluate the neutralizing ability of these antibodies. The ability of antibodies to neutralize HCV can solely be evaluated using relevant model systems.
Determining the relative role of antibodies in the course of HCV infection has long been hampered by the absence of a convenient model system for evaluating the neutralizing activity of anti-HCV antibodies. HCV infects only humans and chimpanzees and for a long time the chimpanzee represented the only validated animal model for the study of HCV (reviewed in [5]). Over the past years, the development of sensitive and robust in vitro neutralization assays based on human hepatoma cell lines and HCV pseudotyped particles[6-8], HCV-like particles [9-11] and recombinant cell culture-derived HCV (HCVcc) [12-19] then allowed to conveniently study the role of neutralizing antibodies in acute and chronic HCV infection. Moreover, the recent development of an in vivo model based on immunodeficient mice repopulated with human livers, the uPA-SCID mice [20], enabled investigators for the first time to determine the role of antibodies in HCV infection in a small animal model [21,22].
Early studies investigating immune responses in chimpanzees and humans suggested that HCV clearance could occur in the absence of neutralizing antibodies or that antibody responses alone are not sufficient to eradicate HCV in the majority of cases [23-27]. Moreover, individuals who cleared HCV are not protected against re-infection, although chimpanzees and individuals who have cleared HCV seem to be less likely to develop chronic infection after re-exposure [28-30]. Since the development of novel model systems for the study of HCV infection and neutralization in vitro, the availability of sequential serum samples from homogenous patient cohorts, well-defined viral inoculum and viral surrogate ligands used for neutralization assays, isolate-specific neutralizing antibodies have been detected in acutely HCV infected individuals who subsequently cleared viral infection. In contrast, the humoral immune responses seem to be delayed in patients developing chronic HCV infection, thereby allowing the virus to escape the host’s immune surveillance.
2.2. Viral escape from neutralizing antibodies
As HCV has evolved several mechanisms to escape from the host immune responses (reviewed in [45]), neutralizing antibodies and HCV co-exist during chronic infection in patients who did not mount efficient immune responses able to clear the virus during acute infection (Figure 1). Viral escape from antibody-mediated neutralization has been shown to occur on several levels and in line to reports of other viruses, a combination of different mechanisms may also apply to HCV. These include (1) the high variability of the HCV genome and limited induction of cross-neutralization antibodies, (2) induction of antibodies interfering with neutralizing antibodies, (3) the association of HCV with serum factors such as low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and very low density lipoproteins (VLDL), (4) the interplay of HCV glycoproteins with high-density liporoteins (HDL), (5) the shielding of neutralizing epitopes by glycosylation of defined amino acids of envelope glycoproteins, and (6) direct cell-to-cell transfer of the virus. As these mechanisms have been reviewed elsewhere [45], this review will focus on recent studies demonstrating both in vitro and in vivo viral adaptations leading to escape from neutralizing antibodies.
Using the state-of-the-art HCV cell culture model, Zhong et al. investigated adaptation of HCV in vitro [46]. The authors demonstrated that HCV can establish persistent infection in vitro, which lead to the selection of viral and cellular variants that favour the survival of both the virus and the host [46]. The virus acquired increased specific infectivity whereas the host cell became resistant to HCV infection. This resistance may be due to down-regulation of HCV entry factor expression or a defect in HCV replication or a combination of these mechanisms [46]. While substantial progress in understanding the HCV life cycle has been made, the interplay between host cell entry factors, HCV envelope glycoproteins and neutralizing antibodies is only about to be investigated. Recent evidence suggests that neutralizing antibodies isolated from chronic HCV patients interfere with entry steps that are closely linked to the interaction of HCV with SR-BI and CD81 [15,47]. Evasion from antibody-mediated neutralization through decreased receptor binding has been reported for viruses such as HIV-1 [48]. This mechanism seems also to apply to HCV. The cell culture-adapted mutation G451R initially described by Zhong et al. [46] has been shown to be less dependent on SR-BI and CD81 on the entry level [16]. Moreover, this mutant demonstrated an increased binding to CD81 and CD81 mimics while being more sensitive to neutralizing antibodies [16].
In chronic HCV infected patients, HCV coexists with anti-HCV antibodies. It is thus most interesting to understand how HCV evolves in the presence of neutralizing antibodies. A recent study addressed this important question by investigating in vitro HCV escape mutants through multiple rounds of selection by the well-described anti-E2 monoclonal antibody AP33 [49]. The authors described an in vitro escape mutation HCV N415Y that lowered viral fitness probably by affecting viral entry but without affecting binding to CD81 [49] suggesting that mutations modulating interaction with host cell factors other than CD81 may contribute to escape of HCV from neutralizing antibodies. Taken together, these studies show that in cell culture, mutations within the HCV envelope glycoproteins arise that modulate viral entry and neutralization by anti-HCV antibodies.
As described above, resolution of infection appears to require rapid, vigourous and multi-specific antiviral host immune responses [43,45,50,51]. Patients who subsequently develop chronic infection have been shown to develop a delayed and inefficient neutralizing antibody response [43] allowing HCV infection to persist for lifetime despite the presence of neutralizing antibodies. It is believed that the adaptive immune system exerts constant pressure on the virus thereby leading to the emergence of HCV escape mutants. However, little is known about the role of neutralizing antibodies in driving HCV sequence evolution in the course of infection. A recent study addressed this important question and provided insights into the time-course of induction of neutralizing antibodies and viral escape from neutralizing responses in a cohort of young intravenous drug users [44]. Studying autologous humoral immune responses in individual subjects, the authors demonstrate that during acute HCV infection, earlier HCV variants were neutralized by autologous plasma samples prior to neutralization of later HCV variants, similar to what has been shown in a chronic HCV patient [52], suggesting that neutralizing antibodies are responsible for envelope sequence changes over time [44]. In line with previous results obtained in a cohort of patients from a single-source HCV outbreak [43], this study demonstrated an association of high-titer neutralizing antibodies and spontaneous viral clearance whereas persistent HCV infection was associated with low-titer or absent neutralizing antibodies during the acute phase [44]. These data suggest that humoral immune response pressure drives HCV envelope glycoprotein sequence evolution resulting either in effective clearance of circulating viral variants and resolution of infection or emergence of viral escape variants and progression into chronic infection. Analysis of sequence substitutions that occurred in HCV envelope glycoproteins during acute infection were monitored throughout E1E2 but most of them were located in the HVR1 region [44]. Mapping of amino acid substitutions involved in escape from neutralizing antibodies showed that significant loss of sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies could be attributed to 3 HVR1 mutations (K384T, K408R and S405P) [44]. A similar time-course study had previously been conducted in the well-characterized chronic HCV patient H [52]. Consistent with the results obtained during the acute phase study described above [44], von Hahn et al. demonstrated that throughout the course of this chronic HCV infection, the patient’s antibodies lagged behind the rapidly evolving viral variants, i.e. they were able to neutralize HCV strains that had been circulating several months or years before but not the present or future viral variants of the patient [47,52]. This raised the question of the mechanisms underlying escape of such quasispecies from neutralizing antibodies. By investigating the interaction of these neutralizing antibody-escape variants and HCV host cell factors, Keck et al. described a single viral variant from this patient that was characterized by reduced infectivity, diminished CD81 binding and resistance to a panel of anti-E2 antibodies (domain B antibodies and AP33). Thus by escaping from neutralizing antibodies, HCV seems to loose in infectivity due to lower binding to CD81. It is worth noting that several mutations within E2 but outside the anti-E2 epitopes as well as the CD81 binding regions may account for escape from these neutralizing antibodies as site-directed mutations were able to restore sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies and CD81 dependency [47]. The most important mutations responsible for reduced infectivity and binding to CD81 were S501N and V506A, suggesting that mutation of theses amino acids affect the conformation of E2 necessary for interaction with CD81 [47]. However, these mutations did not account for escape from humoral responses. Interestingly, an additional mutation at residue 444 is necessary in order to lead to complete escape from neutralizing antibodies – this additional mutation at position 444 seems to negatively modulate antibody-mediated neutralization in concert with the mutations at residues 501 and 506 [47].
Recently, Zhang et al. described an additional escape mechanism whereby the presence of non neutralizing antibodies interferes with the function of neutralizing antibodies, resulting in the reduction or blockage of their effect [53,54]. Two epitopes within a short segment of E2 were mapped: epitope I, at amino acids 412-419, and epitope II, at amino acids 434-446. Epitope I has been recognized as an important neutralization site, while epitope II interfered with antibody to epitope I inhibiting neutralization of the virus [53]. Epitope I- and epitope II- specific antibodies were detected in plasma from chronically HCV-infected patients. Kinetic studies in patient H revealed that antibody to epitope II appeared within 51 days of infection, while antibody to epitope I was not detectable until day 643. Interestingly, by absorbing out antibody to epitope II, neutralizing activity of plasma was enhanced and broadened to include additional genotypes of HCV [54].
3. T cell responses to HCV infection
The majority of primary infections are asymptomatic and often unrecognized. Thus, studies of T cell immune responses during acute HCV infection have only been possible in experimentally infected chimpanzees or individuals with occupational needle stick exposure or IVDU involved in epidemiological follow-up for which the time of contamination is documented. A large body of evidence suggests that a strong, multispecific and long-lasting T-cell immune response appears to be important for control of viral infection (reviewed in [27,55]).
Three types of T cell-mediated responses can be raised against HCV [27,55]. First, an efficient primary immune response during the acute phase, leading to a resolved HCV infection and maintenance of an efficient CD4 and CD8 memory. This immune response is sustained and targets multiple viral proteins, especially during the acute phase of the response. Second an efficient but transient primary immune response, leading to partial control of the infection, but ultimately CD4 memory cells are absent while CD8 memory cells are present at a variable level, leading to chronic infection. Third, a lack of efficient primary immune response, leading to chronic infection. Memory CD4 and CD8 memory cells are less frequent, functionally impaired and target less viral proteins than in patients with resolved infection.
This review will focus on cellular and viral factors that may influence the efficiency and maintenance of primary T cell mediated immune responses including incomplete differentiation of effector and memory T cell populations, immune exhaustion resulting from persistent high viral loads mediated by programmed death-1 (PD-1) protein signalling, suppression by regulatory T (Treg) cells and immune escape mutations.
3.2. Mechanisms of T cell failure
In contrast to acute resolving HCV infection, persisting acute HCV infection is associated with a weak and only monospecific CD4+ T cell responses [77]. Regarding the role of CD8+ T cells, recent studies in humans demonstrated that even strong CD8+ T cell responses in the acute phase of infection may not be adequate to prevent progression to chronicity [64,67,78]. Urbani et al. showed that at clinical onset, CD8 responses are similarly weak and narrowly focused in both self-limited and chronically evolving infections [67]. At this stage, CD4 responses are deeply impaired in patients with a chronic outcome as they are weak and of narrow specificity, unlike the strong, broad and T helper 1-oriented CD4 responses associated with resolving infections.
An important issue is to determine what signals allow to sustain memory cells. In murine models of viral infections, an acute viral infection is generally associated with a high expansion of effector cells that differentiate from naïve cells [79]. This expansion phase is followed by a contraction phase leading to the elimination of ~90% of effector cells, while the remaining effector cells differentiate into long-lived protective memory cells. In human, the differentiation pathways of effector and memory cells may not be similar, and effector cells may be replenished from memory cells. Therefore, it is of crucial importance to identify the mechanisms that allow some patients to maintain HCV-specific memory, while some other are inefficient in controlling the infection. Some key factors may be IL-7 and IL-15, that have been demonstrated to be involved in the induction and homeostasis of CD8 memory cells [80]. IL-7Rα expression is decreased upon T-cell activation: during acute viral infections, the expression of IL-7Rα by viral antigen-specific T cells is transiently decreased [69,81,82] and recovers at late time points after infection when an efficient memory response is obtained [69,83] while IL-7Rα expression remains at a low level in the setting of inefficient memory responses in chronically infected subjects [81]. IL-7Rαhigh expression may therefore allow identifying cells that will give rise to memory cells, at least in the setting of infections that lead to an inflammatory response [69], but not when antigen is presented in a non inflammatory context [84]. Indeed, IL-7Rα expression follows an IL-7-independent program of expression [85] that may be controlled by the level of inflammation [84,85] or the strength of TCR signalling or viral load at time of antigen presentation [82]. IL-15 is also involved in survival of memory cells, especially when IL-7 signalling is present in limiting conditions [69,80]. Indeed, IL-15 is critical for memory cell survival in normal animals, where IL-7 may be limiting due to competition with naïve cells, which use IL-7, but not IL-15, signalling for homeostatic proliferation [86-90]. The CD4-mediated production of another cytokine of the same family, IL-21, has been shown recently to be of crucial importance in avoiding deletion and maintaining memory responses of CD8 T cells in the murine model of LCMV infection [91-93]. Whether IL-21 is also critically involved in maintaining memory HCV-specific memory in humans remains to be determined.
In the context of HCV infection, expression of IL-7Rα by total CD4 and CD8 T cells as well as by HCV-specific cells has been reported to be reduced in the blood of patients with chronic infection as compared with patients with resolved infection [94], although such decreased IL-7Rα expression by HCV-specific memory cells remains controversial [95,96]. IL-7Rα expression is even more decreased in liver CD8+ lymphocytes than in blood lymphocytes from chronic patients [95]. Interestingly, patients with acute infection who subsequently resolved the infection had higher baseline values of IL-7Rα expression (i.e. at time of acute infection) than patients with acute infection who subsequently evolved toward chronic infection [94]. However, this picture may be even more complex, as two profiles of IL-7Rα expression have been observed in chronic HCV patients: most patients have exhausted HCV-specific CD8+ T cells, with low IL-7Rα expression, low proliferative and IFN-γ secretion potential, but some patients have HCV-specific T cells that express high levels of IL-7Rα expression and maintain an efficient proliferative and IFN-γ secretion potential, similar to HCV-specific T cells from patients who resolved their infection [96].
In the chronic phase, virus specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses are also detectable. However HCV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells isolated from chronically infected patients usually display functional and maturation defects including reduced cytotoxic potential, reduced secretion of Th1-type cytokines and a reduced proliferative capacity in response to ex vivo antigenic stimulation [57,97,98]. CD8+ T cell exhaustion such as observed during chronic HCV infection is described in different murine models of persistent infection with highly replicative viruses and may result from deficient CD4+ T cell help (reviewed in [99]). Ulsenheimer et al. have described functionally altered HCV specific CD4+ T cells in acute and chronic hepatitis C [100]. CD8+T cell exhaustion and persistent infection are more likely to develop when CD4+ T cells help is lacking or lost (Figure 2). Helper CD4+ T cells activate or license dendritic cells to optimally prime CD8+ T cells, recognition of antigen on the same antigen-presenting cell by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells is likely to be a key feature of antigen-specific T cell help. Thus the failure of CD4+HCV specific T cells may limit CD8+ T cells opportunities of priming by fully activated HCV antigen- loaded DC [27].
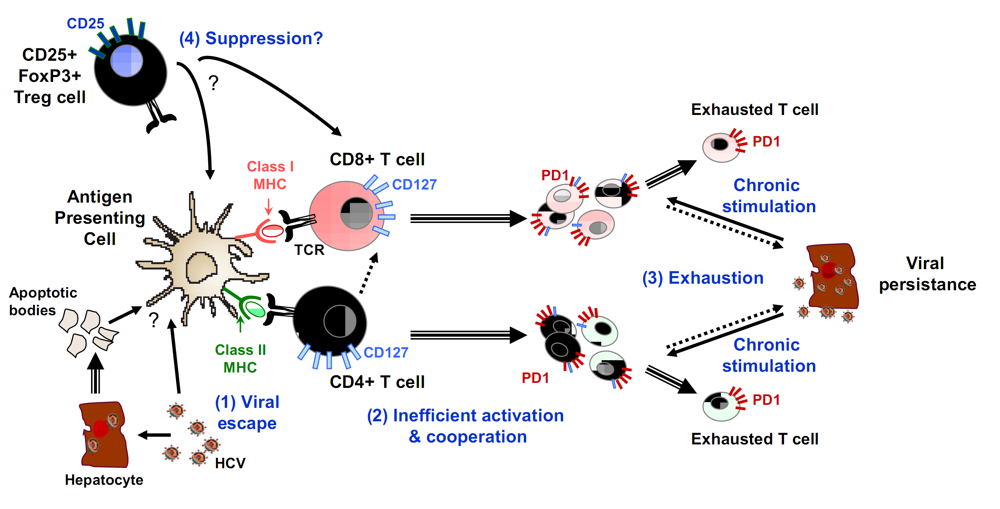
Figure 2.
Examples of mechanisms resulting in impairment of T cell responses leading to chronic HCV infection. Chronic HCV infection is associated with impaired CD8+ T cell responses including reduced cytotoxic potential, reduced secretion of Th1 type cytokines and reduced proliferative capacity in response to ex vivo antigenic stimulation. Four possible mechanisms of T cell response failure are shown here: (1) viral escape with mutations in HLA restricted epitopes impairing antigen recognition, (2) loss of functional CD4+ T cell responses, (3) overexpression of PD1 in CD8+ T cells; when PD1 binds to its ligand PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1), which is preferentially expressed by virus-infected cells, an inhibitory signal is transmitted to CD8+ T cells, resulting in blocking of the T cell receptor-mediated activation signal, (4) induction of regulatory T cells. Arrows with single line indicate functional interactions while arrows with double lines indicate cell differentiation.
Figure 2.
Examples of mechanisms resulting in impairment of T cell responses leading to chronic HCV infection. Chronic HCV infection is associated with impaired CD8+ T cell responses including reduced cytotoxic potential, reduced secretion of Th1 type cytokines and reduced proliferative capacity in response to ex vivo antigenic stimulation. Four possible mechanisms of T cell response failure are shown here: (1) viral escape with mutations in HLA restricted epitopes impairing antigen recognition, (2) loss of functional CD4+ T cell responses, (3) overexpression of PD1 in CD8+ T cells; when PD1 binds to its ligand PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1), which is preferentially expressed by virus-infected cells, an inhibitory signal is transmitted to CD8+ T cells, resulting in blocking of the T cell receptor-mediated activation signal, (4) induction of regulatory T cells. Arrows with single line indicate functional interactions while arrows with double lines indicate cell differentiation.
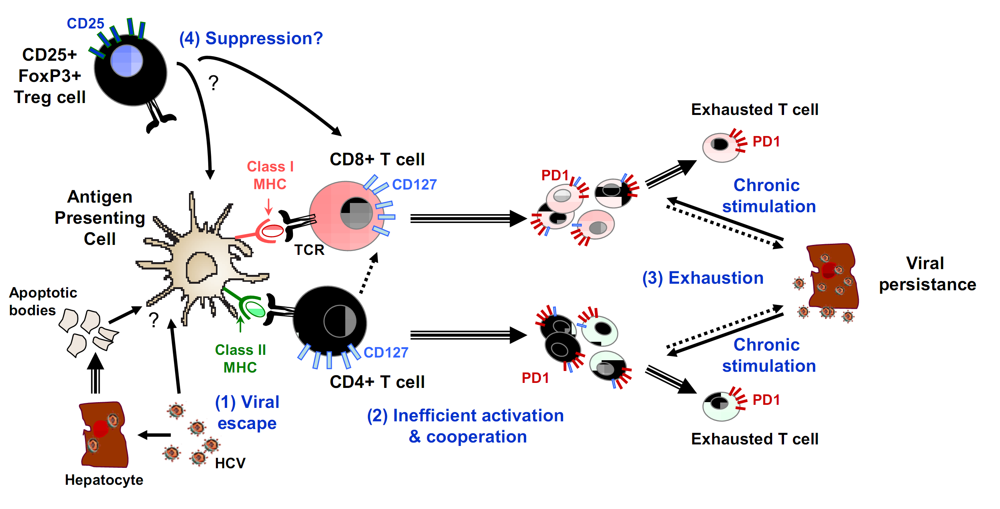
Another mechanism that may be involved in secondary T cell failure of HCV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in chronic HCV infection is signalling through programmed death 1 receptor (PD-1) (Figure 2). Down regulation of virus –specific T-cell responses via signalling through PD-1 on T cells has been linked with virus-specific T-cell deficiency during chronic viral infections in a murine model and in humans [101,102]. Several recent studies have demonstrated high expression levels of PD-1 in HCV-specific CD8+ T cells in patients with persistent HCV infection [55,95,103,104]. HCV-specific T cells that demonstrated increased expression of PD-1 on their surface exhibited impaired IFN-γ production, cytotoxic activity and proliferative potential in response to ex vivo HCV antigen stimulation [55,95,103]. Such impaired functional properties could be reversed by in vitro blockade of PD-1 interaction with its ligand PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1), demonstrating a causal relationship between PD-1 expression and exhaustion [95,103].
Different T-cell subsets with suppressive functions have been described (Figure 2). Among these, CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells have been involved in the control of auto-immunity and immune responses, through various mechanisms including the inhibition of APC maturation and T-cell activation (reviewed in [105]). An increased frequency of Treg cells has been observed in patients with chronic HCV infection compared to individuals who spontaneously resolved HCV infection [106-109]. However, a recent study in chimpanzees showed no difference in the frequency of Treg cells and the extent of suppression irrespective of the outcome of the infection [110]. Evidence against a role for Treg in promoting the development of chronic infection was recently reported in a prospective study of 27 acutely infected subjects. This study showed that there was no significant difference in the proportion of CD4+CD25high T cells in the peripheral blood at baseline between the 15 subjects who developed chronic infection and the 12 subjects that subsequently cleared the infection [65]. The frequency for both groups was higher than in healthy controls and did not vary over time. Further studies are thus required to define the potential role of Treg in the outcome of primary HCV infection.
Viral escape from CD8+T cells is another important mechanism of T cell response failure in patients developing persistent infection [111-115] (Figure 2). Studies in humans and chimpanzees have shown that mutations in HLA class I restricted epitopes targeted by CD8+ T cells, occur early in HCV infection and are associated with persistence [116,117]. The role of HLA alleles in determining the outcome of HCV infection has been recently studied in an Irish cohort of women accidentally infected with HCV [118]. The HLA class I alleles A3, B27 and Cw*01 were associated with viral clearance whereas B8 was associated with viral persistence indicating that the host genetic background is an important variable that can influence infection outcome [118]. Interestingly stable cytotoxic T cell escape mutations have been linked to maintenance of viral fitness [119]. According to these authors, these observations elucidate potential mechanism by which viral persistence is established. Whereas consequences of stable integration of escape mutations into viral genomes are not clear, it is possible that epitopes presented by the most prevalent MHC class I molecules in human population will eventually be lost or become less dominant [120].
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
In the last few years, considerable progress has been made in studying humoral and cellular responses in the course of HCV infection. While the role of neutralizing antibodies in outcome of HCV infection has long been questioned, the development of novel and convenient model systems for HCV infection showed an association between strong and early neutralizing responses and viral clearance. A self-limited course of acute hepatitis C is associated with a vigorous CD4+ and CD8+ T cell response targeting multiple HCV regions and with intrahepatic production of IFN-γ [23,24,51,56,57]. Clearance of HCV is thus probably mediated by a coordinated action of cellular and neutralizing immune responses. Only rare studies analyzed in parallel both humoral and cellular immune responses in the course of HCV infection [52]. Von Hahn et al. demonstrated that during chronic HCV infection in patient H, HCV is subjected to selection pressure from humoral and cellular immune responses resulting in the continuous generation of escape variants [52]. These data underscore that neutralizing antibody responses and cellular antiviral immunity are frequently impaired due to both viral and host factors leading to viral escape from the host’s immune surveillance and development of chronic infection.
Novel insights into the mechanisms underlying successful immune responses against HCV in individuals spontaneously clearing infection and elucidation of escape mechanisms from adaptive immune responses in chronic HCV patients will be essential for an improved understanding of HCV pathogenesis. Unravelling these important mechanisms of virus-host interactions will contribute to the development of novel strategies to prevent and control HCV infection.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Heidi Barth, Inserm U748, Strasbourg for helpful discussions. The authors’ work is supported by Inserm, France, the European Union (ERC-2008-AdG-233130-HEPCENT), the Chair of Excellence Program of the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-05-CEXC-008), France, the Agence Nationale de la Recherche sur le SIDA et les Hépatites Virales (ANRS-06221 and 2008/354), France, the CONECTUS programme of the University of Strasbourg, France, the Ligue contre le Cancer, France, and the Else-Kröner-Fresenius Stiftung (P17/07//A83/06), Bad Homburg, Germany.
References and Notes
- Shepard, C.W.; Finelli, L.; Alter, M.J. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, J.T.; Diepolder, H.M.; Zachoval, R.; Gruener, N.H.; Jung, M.C.; Ulsenheimer, A.; Schraut, W.W.; Schirren, C.A.; Waechtler, M.; Backmund, M.; Pape, G.R. Acute hepatitis C: high rate of both spontaneous and treatment-induced viral clearance. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micallef, J.M.; Kaldor, J.M.; Dore, G.J. Spontaneous viral clearance following acute hepatitis C infection: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. J. Viral. Hepat. 2006, 13, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colin, C.; Lanoir, D.; Touzet, S.; Meyaud-Kraemer, L.; Bailly, F.; Trepo, C. Sensitivity and specificity of third-generation hepatitis C virus antibody detection assays: an analysis of the literature. J. Viral. Hepat. 2001, 8, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukh, J. A critical role for the chimpanzee model in the study of hepatitis C. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Bukh, J.; Meunier, J.C.; Granier, C.; Engle, R.E.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Emerson, S.U.; Cosset, F.L.; Purcell, R.H. In vitro assay for neutralizing antibody to hepatitis C virus: evidence for broadly conserved neutralization epitopes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2003, 100, 14199–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.; Zhang, J.; Flint, M.; Logvinoff, C.; Cheng-Mayer, C.; Rice, C.M.; McKeating, J.A. Hepatitis C virus glycoproteins mediate pH-dependent cell entry of pseudotyped retroviral particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2003, 100, 7271–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Dubuisson, J.; Cosset, F.L. Infectious hepatitis C virus pseudo-particles containing functional E1-E2 envelope protein complexes. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, T.F.; Ito, S.; Wong, D.T.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis C virus structural proteins assemble into viruslike particles in insect cells. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 3827–3836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baumert, T.F.; Wellnitz, S.; Aono, S.; Satoi, J.; Herion, D.; Tilman Gerlach, J.; Pape, G.R.; Lau, J.Y.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Blum, H.E.; Liang, T.J. Antibodies against hepatitis C virus-like particles and viral clearance in acute and chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2000, 32, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, D.; Barth, H.; Gissler, B.; Schürmann, P.; Adah, M.I.; Gerlach, J.T.; Pape, G.R.; Depla, E.; Jacobs, D.; Maertens, G.; Patel, A.H.; Inchauspé, G.; Liang, T.J.; Blum, H.E.; Baumert, T.F. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus-like particle binding to target cells by antiviral antibodies in acute and chronic hepatitis C. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9030–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakita, T.; Pietschmann, T.; Kato, T.; Date, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Zhao, Z.; Murthy, K.; Habermann, A.; Krausslich, H.G.; Mizokami, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Liang, T.J. Production of infectious hepatitis C virus in tissue culture from a cloned viral genome. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Gastaminza, P.; Cheng, G.; Kapadia, S.; Kato, T.; Burton, D.R.; Wieland, S.F.; Uprichard, S.L.; Wakita, T.; Chisari, F.V. Robust hepatitis C virus infection in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2005, 102, 9294–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenbach, B.D.; Evans, M.J.; Syder, A.J.; Wolk, B.; Tellinghuisen, T.L.; Liu, C.C.; Maruyama, T.; Hynes, R.O.; Burton, D.R.; McKeating, J.A.; Rice, C.M. Complete replication of hepatitis C virus in cell culture. Science 2005, 309, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberstroh, A.; Schnober, E.K.; Zeisel, M.B.; Carolla, P.; Barth, H.; Blum, H.E.; Cosset, F.L.; Koutsoudakis, G.; Bartenschlager, R.; Union, A.; Depla, E.; Owsianka, A.; Patel, A.H.; Schuster, C.; Stoll-Keller, F.; Doffoel, M.; Dreux, M.; Baumert, T.F. Neutralizing host responses in hepatitis C virus infection target viral entry at postbinding steps and membrane fusion. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, J.; Nielsen, S.; Zhong, J.; Bassendine, M.F.; Drummer, H.E.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A. Identification of a residue in hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein that determines scavenger receptor BI and CD81 receptor dependency and sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12020–12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, J.C.; Russell, R.S.; Goossens, V.; Priem, S.; Walter, H.; Depla, E.; Union, A.; Faulk, K.N.; Bukh, J.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H. Isolation and characterization of broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to the e1 glycoprotein of hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keck, Z.Y.; Li, T.K.; Xia, J.; Gal-Tanamy, M.; Olson, O.; Li, S.H.; Patel, A.H.; Ball, J.K.; Lemon, S.M.; Foung, S.K. Definition of a conserved immunodominant domain on hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein by neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6061–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owsianka, A.M.; Tarr, A.W.; Keck, Z.Y.; Li, T.K.; Witteveldt, J.; Adair, R.; Foung, S.K.; Ball, J.K.; Patel, A.H. Broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuleman, P.; Libbrecht, L.; De Vos, R.; de Hemptinne, B.; Gevaert, K.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Roskams, T.; Leroux-Roels, G. Morphological and biochemical characterization of a human liver in a uPA-SCID mouse chimera. Hepatology 2005, 41, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, M.; Maruyama, T.; Lewis, J.; Giang, E.; Tarr, A.W.; Stamataki, Z.; Gastaminza, P.; Chisari, F.V.; Jones, I.M.; Fox, R.I.; Ball, J.K.; McKeating, J.A.; Kneteman, N.M.; Burton, D.R. Broadly neutralizing antibodies protect against hepatitis C virus quasispecies challenge. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanwolleghem, T.; Bukh, J.; Meuleman, P.; Desombere, I.; Meunier, J.C.; Alter, H.; Purcell, R.H.; Leroux-Roels, G. Polyclonal immunoglobulins from a chronic hepatitis C virus patient protect human liver-chimeric mice from infection with a homologous hepatitis C virus strain. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimme, R.; Bukh, J.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Wieland, S.; Pemberton, J.; Steiger, C.; Govindarajan, S.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Viral and immunological determinants of hepatitis C virus clearance, persistence, and disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2002, 99, 15661–15668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, F.; Wong, D.K.; Dunbar, P.R.; Chapman, R.; Chung, R.T.; Dohrenwend, P.; Robbins, G.; Phillips, R.; Klenerman, P.; Walker, B.D. Analysis of successful immune responses in persons infected with hepatitis C virus. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1499–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, F.; Gruener, N.H.; Urbani, S.; Uggeri, J.; Santantonio, T.; Kammer, A.R.; Cerny, A.; Phillips, R.; Ferrari, C.; Pape, G.R.; Klenerman, P. CD8+ T lymphocyte responses are induced during acute hepatitis C virus infection but are not sustained. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logvinoff, C.; Major, M.E.; Oldach, D.; Heyward, S.; Talal, A.; Balfe, P.; Feinstone, S.M.; Alter, H.; Rice, C.M.; McKeating, J.A. Neutralizing antibody response during acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2004, 101, 10149–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dustin, L.B.; Rice, C.M. Flying under the radar: the immunobiology of hepatitis C. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.H.; Cox, A.; Hoover, D.R.; Wang, X.H.; Mao, Q.; Ray, S.; Strathdee, S.A.; Vlahov, D.; Thomas, D.L. Protection against persistence of hepatitis C. Lancet 2002, 359, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, S.E.; Guerra, B.; Brasky, K.; Miskovsky, E.; Houghton, M.; Klimpel, G.R.; Lanford, R.E. Protective immune response to hepatitis C virus in chimpanzees rechallenged following clearance of primary infection. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, M.E.; Mihalik, K.; Puig, M.; Rehermann, B.; Nascimbeni, M.; Rice, C.M.; Feinstone, S.M. Previously infected and recovered chimpanzees exhibit rapid responses that control hepatitis C virus replication upon rechallenge. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6586–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pileri, P.; Uematsu, Y.; Campagnoli, S.; Galli, G.; Falugi, F.; Petracca, R.; Weiner, A.J.; Houghton, M.; Rosa, D.; Grandi, G.; Abrignani, S. Binding of hepatitis C virus to CD81. Science 1998, 282, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarselli, E.; Ansuini, H.; Cerino, R.; Roccasecca, R.M.; Acali, S.; Filocamo, G.; Traboni, C.; Nicosia, A.; Cortese, R.; Vitelli, A. The human scavenger receptor class B type I is a novel candidate receptor for the hepatitis C virus. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5017–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, D.; Date, T.; Morikawa, K.; Murayama, A.; Miyamoto, M.; Kaga, M.; Barth, H.; Baumert, T.F.; Dubuisson, J.; Wakita, T. Cd81 Expression Is Important For Heterogeneous Hcv Permissiveness Of Huh7 Cell Clones. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5036–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsoudakis, G.; Kaul, A.; Steinmann, E.; Kallis, S.; Lohmann, V.; Pietschmann, T.; Bartenschlager, R. Characterization of the early steps of hepatitis C virus infection by using luciferase reporter viruses. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5308–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, M.B.; Koutsoudakis, G.; Schnober, E.K.; Haberstroh, A.; Blum, H.E.; Cosset, F.-L.; Wakita, T.; Jaeck, D.; Doffoel, M.; Royer, C.; Soulier, E.; Schvoerer, E.; Schuster, C.; Stoll-Keller, F.; Bartenschlager, R.; Pietschmann, T.; Barth, H.; Baumert, T.F. Scavenger receptor BI is a key host factor for Hepatitis C virus infection required for an entry step closely linked to CD81. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.J.; von Hahn, T.; Tscherne, D.M.; Syder, A.J.; Panis, M.; Wolk, B.; Hatziioannou, T.; McKeating, J.A.; Bieniasz, P.D.; Rice, C.M. Claudin-1 is a hepatitis C virus co-receptor required for a late step in entry. Nature 2007, 446, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meertens, L.; Bertaux, C.; Cukierman, L.; Cormier, E.; Lavillette, D.; Cosset, F.L.; Dragic, T. The tight junction proteins claudin-1, -6, and -9 are entry cofactors for hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3555–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploss, A.; Evans, M.J.; Gaysinskaya, V.A.; Panis, M.; You, H.; de Jong, Y.P.; Rice, C.M. Human occludin is a hepatitis C virus entry factor required for infection of mouse cells. Nature 2009, 457, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreux, M.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Fresquet, J.; Guerin, M.; Julia, Z.; Verney, G.; Durantel, D.; Zoulim, F.; Lavillette, D.; Cosset, F.L.; Bartosch, B. Receptor complementation and mutagenesis reveal SR-BI as an essential HCV entry factor and functionally imply its intra- and extra-cellular domains. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helle, F.; Dubuisson, J. Hepatitis C virus entry into host cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Hahn, T.; Rice, C.M. Hepatitis C virus entry. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3689–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavillette, D.; Morice, Y.; Germanidis, G.; Donot, P.; Soulier, A.; Pagkalos, E.; Sakellariou, G.; Intrator, L.; Bartosch, B.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Cosset, F.L. Human serum facilitates hepatitis C virus infection, and neutralizing responses inversely correlate with viral replication kinetics at the acute phase of hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6023–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestka, J.M.; Zeisel, M.B.; Blaser, E.; Schurmann, P.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.L.; Patel, A.H.; Meisel, H.; Baumert, J.; Viazov, S.; Rispeter, K.; Blum, H.E.; Roggendorf, M.; Baumert, T.F. Rapid induction of virus-neutralizing antibodies and viral clearance in a single-source outbreak of hepatitis C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2007, 104, 6025–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, K.A.; Netski, D.M.; Wang, X.H.; Cox, A.L.; Ray, S.C. Selection Pressure From Neutralizing Antibodies Drives Sequence Evolution During Acute Infection With Hepatitis C Virus. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, M.B.; Cosset, F.L.; Baumert, T.F. Host neutralizing responses and pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2008, 48, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Gastaminza, P.; Chung, J.; Stamataki, Z.; Isogawa, M.; Cheng, G.; McKeating, J.A.; Chisari, F.V. Persistent hepatitis C virus infection in vitro: coevolution of virus and host. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11082–11093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keck, Z.Y.; Li, S.H.; Xia, J.; von Hahn, T.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A.; Witteveldt, J.; Patel, A.H.; Alter, H.; Rice, C.M.; Foung, S.K. Mutations in HCV E2 located outside the CD81 binding sites lead to escape from broadly neutralizing antibodies but compromise virus infectivity. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6149–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, P.D.; Doyle, M.L.; Casper, D.J.; Cicala, C.; Leavitt, S.A.; Majeed, S.; Steenbeke, T.D.; Venturi, M.; Chaiken, I.; Fung, M.; Katinger, H.; Parren, P.W.; Robinson, J.; Van Ryk, D.; Wang, L.; Burton, D.R.; Freire, E.; Wyatt, R.; Sodroski, J.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Arthos, J. HIV-1 evades antibody-mediated neutralization through conformational masking of receptor-binding sites. Nature 2002, 420, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal-Tanamy, M.; Keck, Z.Y.; Yi, M.; McKeating, J.A.; Patel, A.H.; Foung, S.K.; Lemon, S.M. In vitro selection of a neutralization-resistant hepatitis C virus escape mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2008, 105, 19450–19455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diepolder, H.M.; Zachoval, R.; Hoffmann, R.M.; Wierenga, E.A.; Santantonio, T.; Jung, M.C.; Eichenlaub, D.; Pape, G.R. Possible mechanism involving T-lymphocyte response to non-structural protein 3 in viral clearance in acute hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet 1995, 346, 1006–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimme, R.; Oldach, D.; Chang, K.M.; Steiger, C.; Ray, S.C.; Chisari, F.V. Determinants of viral clearance and persistence during acute hepatitis C virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Hahn, T.; Yoon, J.C.; Alter, H.; Rice, C.M.; Rehermann, B.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A. Hepatitis C virus continuously escapes from neutralizing antibody and T-cell responses during chronic infection in vivo. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, C.G.; Mihalik, K.; Virata-Theimer, M.L.; Yu, M.Y.; Alter, H.J.; Feinstone, S.M. Hepatitis C virus epitope-specific neutralizing antibodies in Igs prepared from human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2007, 104, 8449–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhong, L.; Struble, E.B.; Watanabe, H.; Kachko, A.; Mihalik, K.; Virata-Theimer, M.L.; Alter, H.J.; Feinstone, S.; Major, M. Depletion of interfering antibodies in chronic hepatitis C patients and vaccinated chimpanzees reveals broad cross-genotype neutralizing activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2009, 106, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.G.; Shoukry, N.H.; Grakoui, A.; Fuller, M.J.; Cawthon, A.G.; Dong, C.; Hasselschwert, D.L.; Brasky, K.M.; Freeman, G.J.; Seth, N.P.; Wucherpfennig, K.W.; Houghton, M.; Walker, C.M. Variable patterns of programmed death-1 expression on fully functional memory T cells after spontaneous resolution of hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5109–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.G.; Walker, C.M. Adaptive immune responses in acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Nature 2005, 436, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; He, X.S.; Nascimbeni, M.; Davis, A.R.; Greenberg, H.B.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Liang, T.J.; Alter, H.; Rehermann, B. Impaired effector function of hepatitis C virus-specific CD8+ T cells in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulze zur Wiesch, J.; Lauer, G.M.; Day, C.L.; Kim, A.Y.; Ouchi, K.; Duncan, J.E.; Wurcel, A.G.; Timm, J.; Jones, A.M.; Mothe, B.; Allen, T.M.; McGovern, B.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Chung, R.T.; Walker, B.D. Broad repertoire of the CD4+ Th cell response in spontaneously controlled hepatitis C virus infection includes dominant and highly promiscuous epitopes. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3603–3613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smyk-Pearson, S.; Tester, I.A.; Lezotte, D.; Sasaki, A.W.; Lewinsohn, D.M.; Rosen, H.R. Differential antigenic hierarchy associated with spontaneous recovery from hepatitis C virus infection: implications for vaccine design. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, J.T.; Diepolder, H.M.; Jung, M.C.; Gruener, N.H.; Schraut, W.W.; Zachoval, R.; Hoffmann, R.; Schirren, C.A.; Santantonio, T.; Pape, G.R. Recurrence of hepatitis C virus after loss of virus-specific CD4(+) T- cell response in acute hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, C.; Valli, A.; Galati, L.; Penna, A.; Scaccaglia, P.; Giuberti, T.; Schianchi, C.; Missale, G.; Marin, M.G.; Fiaccadori, F. T-cell response to structural and nonstructural hepatitis C virus antigens in persistent and self-limited hepatitis C virus infections. Hepatology 1994, 19, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheimer, A.M.; Miner, C.; Lewinsohn, D.M.; Sasaki, A.W.; Kaufman, E.; Rosen, H.R. Novel CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell determinants within the NS3 protein in subjects with spontaneously resolved HCV infection. Hepatology 2003, 37, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberle, J.H.; Formann, E.; Steindl-Munda, P.; Weseslindtner, L.; Gurguta, C.; Perstinger, G.; Grilnberger, E.; Laferl, H.; Dienes, H.P.; Popow-Kraupp, T.; Ferenci, P.; Holzmann, H. Prospective study of viral clearance and CD4(+) T-cell response in acute hepatitis C primary infection and reinfection. J. Clin. Virol. 2006, 36, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, A.L.; Mosbruger, T.; Lauer, G.M.; Pardoll, D.; Thomas, D.L.; Ray, S.C. Comprehensive analyses of CD8+ T cell responses during longitudinal study of acute human hepatitis C. Hepatology 2005, 42, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyk-Pearson, S.; Tester, I.A.; Klarquist, J.; Palmer, B.E.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Golden-Mason, L.; Rosen, H.R. Spontaneous recovery in acute human hepatitis C virus infection: functional T-cell thresholds and relative importance of CD4 help. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folgori, A.; Spada, E.; Pezzanera, M.; Ruggeri, L.; Mele, A.; Garbuglia, A.R.; Perrone, M.P.; Del Porto, P.; Piccolella, E.; Cortese, R.; Nicosia, A.; Vitelli, A. Early impairment of hepatitis C virus specific T cell proliferation during acute infection leads to failure of viral clearance. Gut 2006, 55, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbani, S.; Amadei, B.; Fisicaro, P.; Tola, D.; Orlandini, A.; Sacchelli, L.; Mori, C.; Missale, G.; Ferrari, C. Outcome of acute hepatitis C is related to virus-specific CD4 function and maturation of antiviral memory CD8 responses. Hepatology 2006, 44, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grakoui, A.; Shoukry, N.H.; Woollard, D.J.; Han, J.H.; Hanson, H.L.; Ghrayeb, J.; Murthy, K.K.; Rice, C.M.; Walker, C.M. HCV persistence and immune evasion in the absence of memory T cell help. Science 2003, 302, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaech, S.M.; Tan, J.T.; Wherry, E.J.; Konieczny, B.T.; Surh, C.D.; Ahmed, R. Selective expression of the interleukin 7 receptor identifies effector CD8 T cells that give rise to long-lived memory cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.M.; Thimme, R.; Melpolder, J.J.; Oldach, D.; Pemberton, J.; Moorhead-Loudis, J.; McHutchison, J.G.; Alter, H.J.; Chisari, F.V. Differential CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell responsiveness in hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2001, 33, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, A.J.; Paliard, X.; Selby, M.J.; Medina-Selby, A.; Coit, D.; Nguyen, S.; Kansopon, J.; Arian, C.L.; Ng, P.; Tucker, J.; Lee, C.T.; Polakos, N.K.; Han, J.; Wong, S.; Lu, H.H.; Rosenberg, S.; Brasky, K.M.; Chien, D.; Kuo, G.; Houghton, M. Intrahepatic genetic inoculation of hepatitis C virus RNA confers cross-protective immunity. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7142–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoukry, N.H.; Grakoui, A.; Houghton, M.; Chien, D.Y.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Walker, C.M. Memory CD8+ T cells are required for protection from persistent hepatitis C virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimbeni, M.; Mizukoshi, E.; Bosmann, M.; Major, M.E.; Mihalik, K.; Rice, C.M.; Feinstone, S.M.; Rehermann, B. Kinetics of CD4+ and CD8+ memory T-cell responses during hepatitis C virus rechallenge of previously recovered chimpanzees. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 4781–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanford, R.E.; Guerra, B.; Chavez, D.; Bigger, C.; Brasky, K.M.; Wang, X.H.; Ray, S.C.; Thomas, D.L. Cross-genotype immunity to hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukh, J.; Thimme, R.; Meunier, J.C.; Faulk, K.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Chang, K.M.; Satterfield, W.; Chisari, F.V.; Purcell, R.H. Previously infected chimpanzees are not consistently protected against reinfection or persistent infection after reexposure to the identical hepatitis C virus strain. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8183–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, S.E.; Thomas, D.L.; Brasky, K.M.; Lanford, R.E. Viral persistence, antibody to E1 and E2, and hypervariable region 1 sequence stability in hepatitis C virus-inoculated chimpanzees. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thimme, R.; Lohmann, V.; Weber, F. A target on the move: innate and adaptive immune escape strategies of hepatitis C virus. Antiviral. Res. 2006, 69, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, D.E.; Sugimoto, K.; Newton, K.; Valiga, M.E.; Ikeda, F.; Aytaman, A.; Nunes, F.A.; Lucey, M.R.; Vance, B.A.; Vonderheide, R.H.; Reddy, K.R.; McKeating, J.A.; Chang, K.M. Discordant role of CD4 T-cell response relative to neutralizing antibody and CD8 T-cell responses in acute hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, R.M.; Kim, S.K.; Cornberg, M.; Clute, S.C.; Selin, L.K.; Naumov, Y.N. The privacy of T cell memory to viruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 311, 117–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prlic, M.; Lefrancois, L.; Jameson, S.C. Multiple choices: regulation of memory CD8 T cell generation and homeostasis by interleukin (IL)-7 and IL-15. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, F49–F52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.C.; Williams, M.A.; Bevan, M.J. CD4+ T cells are required for the maintenance, not programming, of memory CD8+ T cells after acute infection. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Leeuwen, E.M.; de Bree, G.J.; Remmerswaal, E.B.; Yong, S.L.; Tesselaar, K.; ten Berge, I.J.; van Lier, R.A. IL-7 receptor alpha chain expression distinguishes functional subsets of virus-specific human CD8+ T cells. Blood 2005, 106, 2091–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boettler, T.; Panther, E.; Bengsch, B.; Nazarova, N.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Blum, H.E.; Thimme, R. Expression of the interleukin-7 receptor alpha chain (CD127) on virus-specific CD8+ T cells identifies functionally and phenotypically defined memory T cells during acute resolving hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 3532–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacombe, M.H.; Hardy, M.P.; Rooney, J.; Labrecque, N. IL-7 receptor expression levels do not identify CD8+ memory T lymphocyte precursors following peptide immunization. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 4400–4407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klonowski, K.D.; Williams, K.J.; Marzo, A.L.; Lefrancois, L. Cutting edge: IL-7-independent regulation of IL-7 receptor alpha expression and memory CD8 T cell development. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4247–4251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldrath, A.W.; Sivakumar, P.V.; Glaccum, M.; Kennedy, M.K.; Bevan, M.J.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D.; Butz, E.A. Cytokine requirements for acute and Basal homeostatic proliferation of naive and memory CD8+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.T.; Ernst, B.; Kieper, W.C.; LeRoy, E.; Sprent, J.; Surh, C.D. Interleukin (IL)-15 and IL-7 jointly regulate homeostatic proliferation of memory phenotype CD8+ cells but are not required for memory phenotype CD4+ cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieper, W.C.; Tan, J.T.; Bondi-Boyd, B.; Gapin, L.; Sprent, J.; Ceredig, R.; Surh, C.D. Overexpression of interleukin (IL)-7 leads to IL-15-independent generation of memory phenotype CD8+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, T.C.; Wherry, E.J.; Boone, D.; Murali-Krishna, K.; Antia, R.; Ma, A.; Ahmed, R. Interleukin 15 is required for proliferative renewal of virus-specific memory CD8 T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schluns, K.S.; Williams, K.; Ma, A.; Zheng, X.X.; Lefrancois, L. Cutting edge: requirement for IL-15 in the generation of primary and memory antigen-specific CD8 T cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 4827–4831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, A.; Kisielow, J.; Schmitz, I.; Freigang, S.; Shamshiev, A.T.; Weber, J.; Marsland, B.J.; Oxenius, A.; Kopf, M. IL-21R on T cells is critical for sustained functionality and control of chronic viral infection. Science 2009, 324, 1576–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.S.; Du, M.; Zajac, A.J. A vital role for interleukin-21 in the control of a chronic viral infection. Science 2009, 324, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsaesser, H.; Sauer, K.; Brooks, D.G. IL-21 is required to control chronic viral infection. Science 2009, 324, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden-Mason, L.; Burton, J.R.; Castelblanco, N.; Klarquist, J.; Benlloch, S.; Wang, C.; Rosen, H.R. Loss of IL-7 receptor alpha-chain (CD127) expression in acute HCV infection associated with viral persistence. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radziewicz, H.; Ibegbu, C.C.; Fernandez, M.L.; Workowski, K.A.; Obideen, K.; Wehbi, M.; Hanson, H.L.; Steinberg, J.P.; Masopust, D.; Wherry, E.J.; Altman, J.D.; Rouse, B.T.; Freeman, G.J.; Ahmed, R.; Grakoui, A. Liver-infiltrating lymphocytes in chronic human hepatitis C virus infection display an exhausted phenotype with high levels of PD-1 and low levels of CD127 expression. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2545–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengsch, B.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Kersting, N.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Panther, E.; von Weizsacker, F.; Blum, H.E.; Pircher, H.; Thimme, R. Analysis of CD127 and KLRG1 expression on hepatitis C virus-specific CD8+ T cells reveals the existence of different memory T-cell subsets in the peripheral blood and liver. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbani, S.; Boni, C.; Missale, G.; Elia, G.; Cavallo, C.; Massari, M.; Raimondo, G.; Ferrari, C. Virus-specific CD8+ lymphocytes share the same effector-memory phenotype but exhibit functional differences in acute hepatitis B and C. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12423–12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spangenberg, H.C.; Viazov, S.; Kersting, N.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; McKinney, D.; Roggendorf, M.; von Weizsacker, F.; Blum, H.E.; Thimme, R. Intrahepatic CD8+ T-cell failure during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2005, 42, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellino, F.; Germain, R.N. Cooperation between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells: when, where, and how. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulsenheimer, A.; Gerlach, J.T.; Gruener, N.H.; Jung, M.C.; Schirren, C.A.; Schraut, W.; Zachoval, R.; Pape, G.R.; Diepolder, H.M. Detection of functionally altered hepatitis C virus-specific CD4 T cells in acute and chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, D.L.; Wherry, E.J.; Masopust, D.; Zhu, B.; Allison, J.P.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Ahmed, R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 2006, 439, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.L.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Kiepiela, P.; Brown, J.A.; Moodley, E.S.; Reddy, S.; Mackey, E.W.; Miller, J.D.; Leslie, A.J.; DePierres, C.; Mncube, Z.; Duraiswamy, J.; Zhu, B.; Eichbaum, Q.; Altfeld, M.; Wherry, E.J.; Coovadia, H.M.; Goulder, P.J.; Klenerman, P.; Ahmed, R.; Freeman, G.J.; Walker, B.D. PD-1 expression on HIV-specific T cells is associated with T-cell exhaustion and disease progression. Nature 2006, 443, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbani, S.; Amadei, B.; Tola, D.; Massari, M.; Schivazappa, S.; Missale, G.; Ferrari, C. PD-1 expression in acute hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is associated with HCV-specific CD8 exhaustion. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11398–11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutebemberwa, A.; Ray, S.C.; Astemborski, J.; Levine, J.; Liu, L.; Dowd, K.A.; Clute, S.; Wang, C.; Korman, A.; Sette, A.; Sidney, J.; Pardoll, D.M.; Cox, A.L. High-programmed death-1 levels on hepatitis C virus-specific T cells during acute infection are associated with viral persistence and require preservation of cognate antigen during chronic infection. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8215–8225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shevach, E.M. Mechanisms of foxp3+ T regulatory cell-mediated suppression. Immunity 2009, 30, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, K.; Ikeda, F.; Stadanlick, J.; Nunes, F.A.; Alter, H.J.; Chang, K.M. Suppression of HCV-specific T cells without differential hierarchy demonstrated ex vivo in persistent HCV infection. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, R.; Tu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Firpi, R.J.; Rosen, H.R.; Liu, C.; Nelson, D.R. An immunomodulatory role for CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T lymphocytes in hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boettler, T.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Panther, E.; Urbani, S.; Ferrari, C.; Blum, H.E.; von Weizsacker, F.; Thimme, R. T cells with a CD4+CD25+ regulatory phenotype suppress in vitro proliferation of virus-specific CD8+ T cells during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7860–7867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushbrook, S.M.; Ward, S.M.; Unitt, E.; Vowler, S.L.; Lucas, M.; Klenerman, P.; Alexander, G.J. Regulatory T cells suppress in vitro proliferation of virus-specific CD8+ T cells during persistent hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7852–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manigold, T.; Shin, E.C.; Mizukoshi, E.; Mihalik, K.; Murthy, K.K.; Rice, C.M.; Piccirillo, C.A.; Rehermann, B. Foxp3+CD4+CD25+ T cells control virus-specific memory T cells in chimpanzees that recovered from hepatitis C. Blood 2006, 107, 4424–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.M.; Rehermann, B.; McHutchison, J.G.; Pasquinelli, C.; Southwood, S.; Sette, A.; Chisari, F.V. Immunological significance of cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope variants in patients chronically infected by the hepatitis C virus. J. Clin. Invest. 1997, 100, 2376–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, A.; Erickson, A.L.; Kansopon, J.; Crawford, K.; Muchmore, E.; Hughes, A.L.; Houghton, M.; Walker, C.M. Persistent hepatitis C virus infection in a chimpanzee is associated with emergence of a cytotoxic T lymphocyte escape variant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1995, 92, 2755–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, A.L.; Kimura, Y.; Igarashi, S.; Eichelberger, J.; Houghton, M.; Sidney, J.; McKinney, D.; Sette, A.; Hughes, A.L.; Walker, C.M. The outcome of hepatitis C virus infection is predicted by escape mutations in epitopes targeted by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 2001, 15, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, A.L.; Mosbruger, T.; Mao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.H.; Yang, H.C.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Pardoll, D.; Thomas, D.L.; Ray, S.C. Cellular immune selection with hepatitis C virus persistence in humans. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tester, I.; Smyk-Pearson, S.; Wang, P.; Wertheimer, A.; Yao, E.; Lewinsohn, D.M.; Tavis, J.E.; Rosen, H.R. Immune evasion versus recovery after acute hepatitis C virus infection from a shared source. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timm, J.; Lauer, G.M.; Kavanagh, D.G.; Sheridan, I.; Kim, A.Y.; Lucas, M.; Pillay, T.; Ouchi, K.; Reyor, L.L.; Schulze zur Wiesch, J.; Gandhi, R.T.; Chung, R.T.; Bhardwaj, N.; Klenerman, P.; Walker, B.D.; Allen, T.M. CD8 epitope escape and reversion in acute HCV infection. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 1593–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.C.; Fanning, L.; Wang, X.H.; Netski, D.M.; Kenny-Walsh, E.; Thomas, D.L. Divergent and convergent evolution after a common-source outbreak of hepatitis C virus. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann-Haefelin, C.; McKiernan, S.; Ward, S.; Viazov, S.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Killinger, T.; Baumert, T.F.; Nazarova, N.; Sheridan, I.; Pybus, O.; von Weizsacker, F.; Roggendorf, M.; Kelleher, D.; Klenerman, P.; Blum, H.E.; Thimme, R. Dominant influence of an HLA-B27 restricted CD8+ T cell response in mediating HCV clearance and evolution. Hepatology 2006, 43, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uebelhoer, L.; Han, J.H.; Callendret, B.; Mateu, G.; Shoukry, N.H.; Hanson, H.L.; Rice, C.M.; Walker, C.M.; Grakoui, A. Stable cytotoxic T cell escape mutation in hepatitis C virus is linked to maintenance of viral fitness. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timm, J.; Li, B.; Daniels, M.G.; Bhattacharya, T.; Reyor, L.L.; Allgaier, R.; Kuntzen, T.; Fischer, W.; Nolan, B.E.; Duncan, J.; Schulze zur Wiesch, J.; Kim, A.Y.; Frahm, N.; Brander, C.; Chung, R.T.; Lauer, G.M.; Korber, B.T.; Allen, T.M. Human leukocyte antigen-associated sequence polymorphisms in hepatitis C virus reveal reproducible immune responses and constraints on viral evolution. Hepatology 2007, 46, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.