Phenology and Synchrony of Scymnus coniferarum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) with Multiple Adelgid Species in the Puget Sound, WA, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
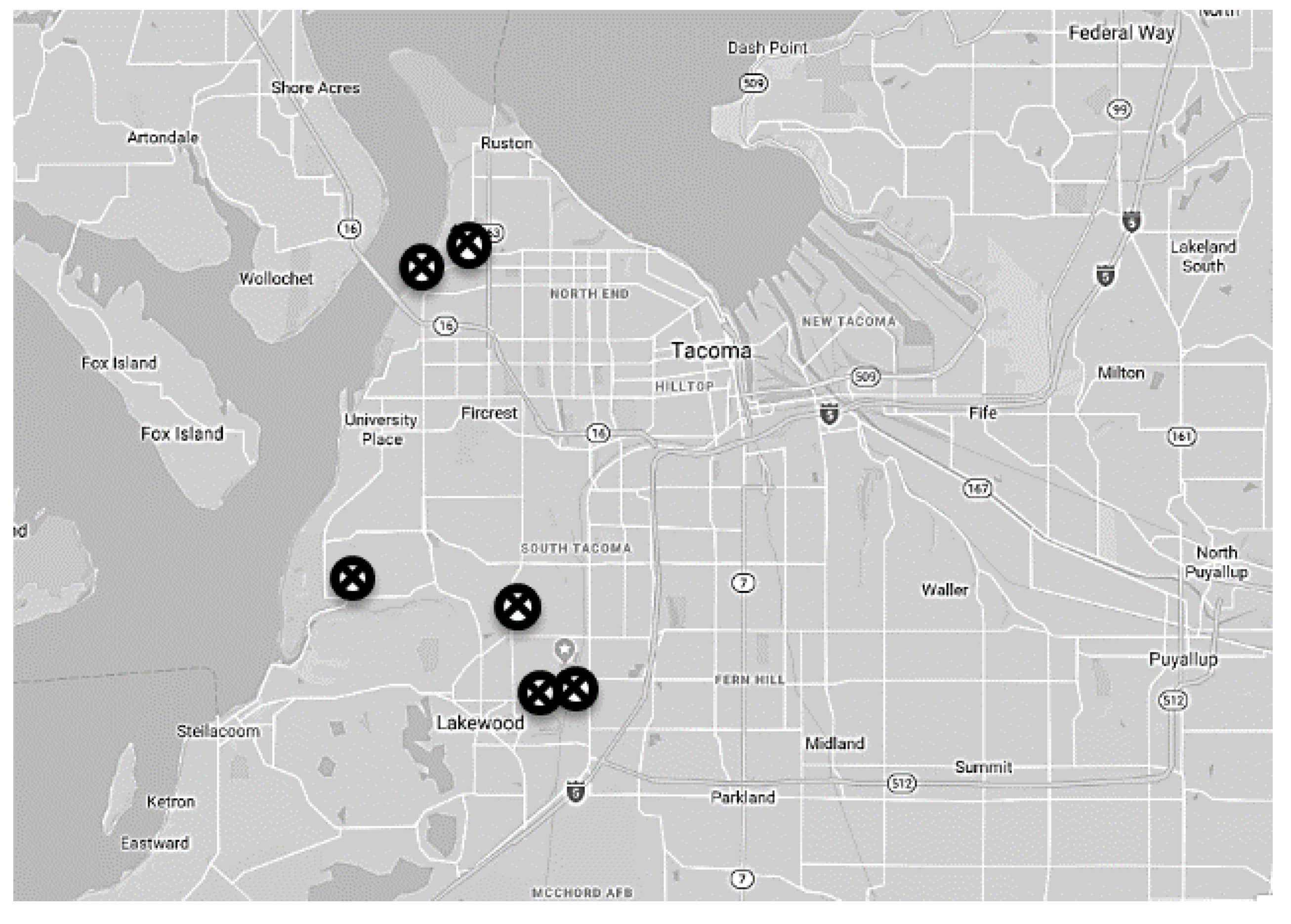
2.1. Location and Timing of Experiments
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Adelgid Species Identification
2.5. DNA Barcode Sequencing and Morphological Examination of S. coniferarum
3. Results
3.1. Adelgid Species Identification
3.2. Predator/Host Density Relationships and Seasonal Patterns
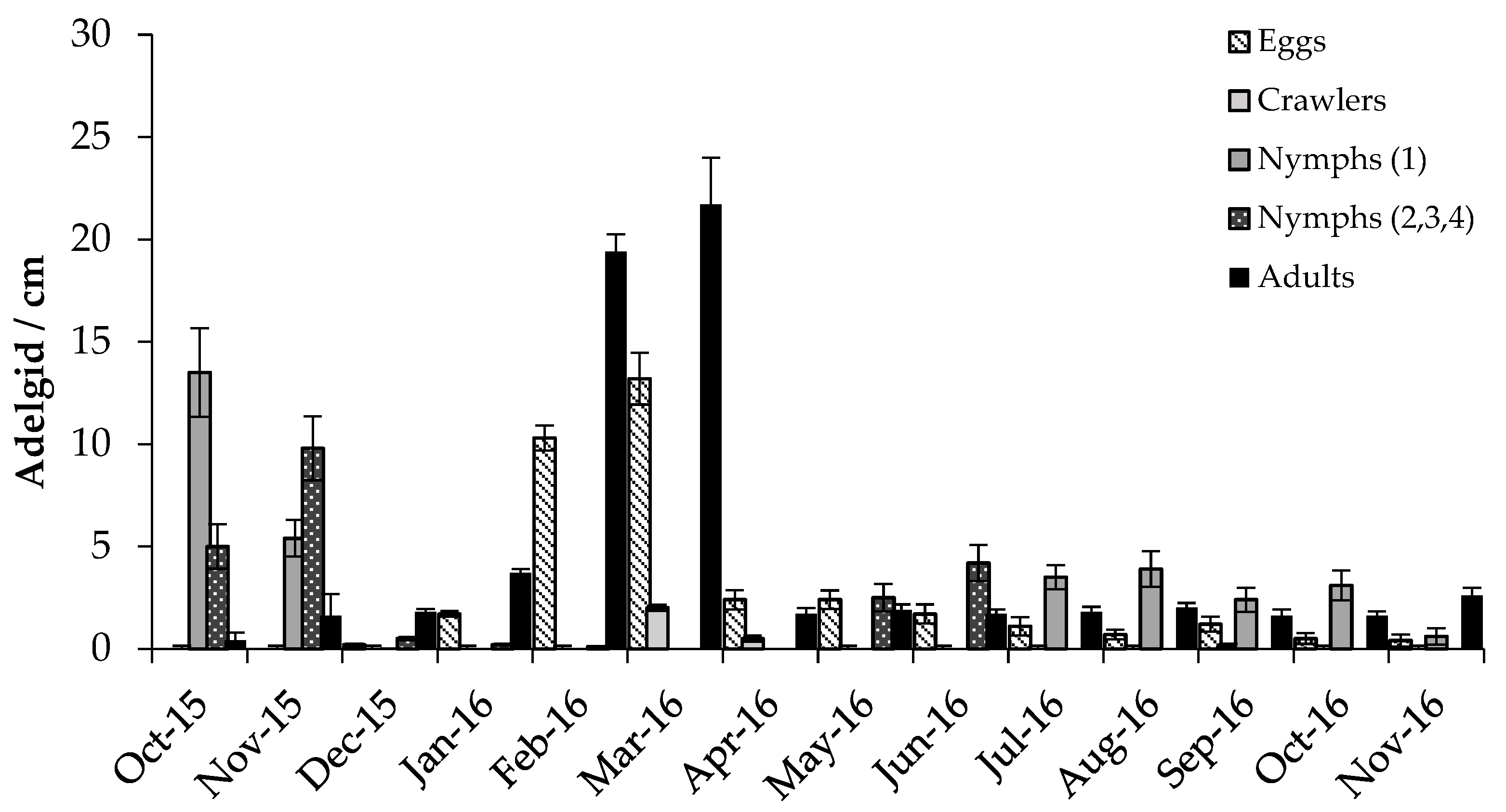
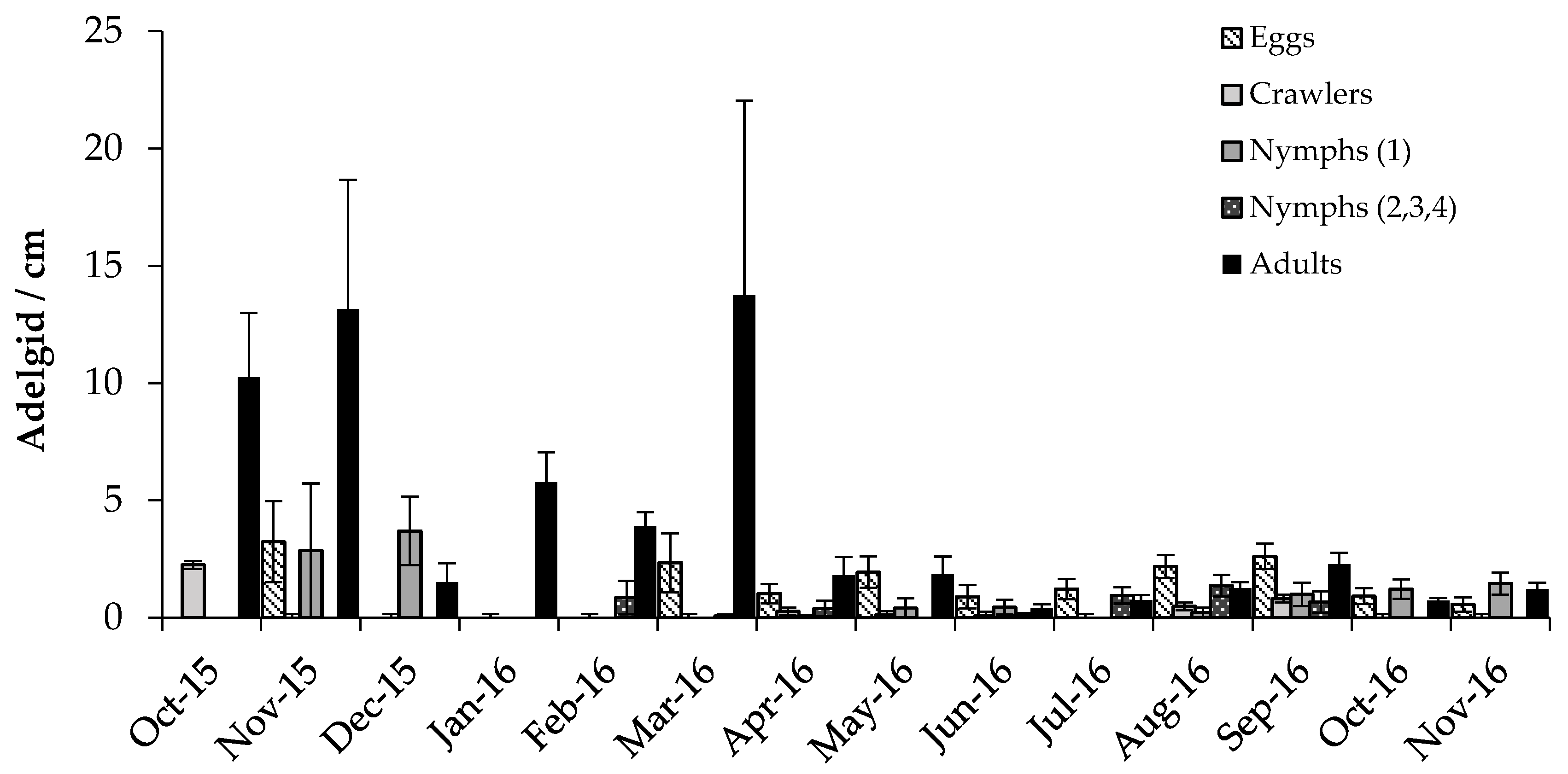
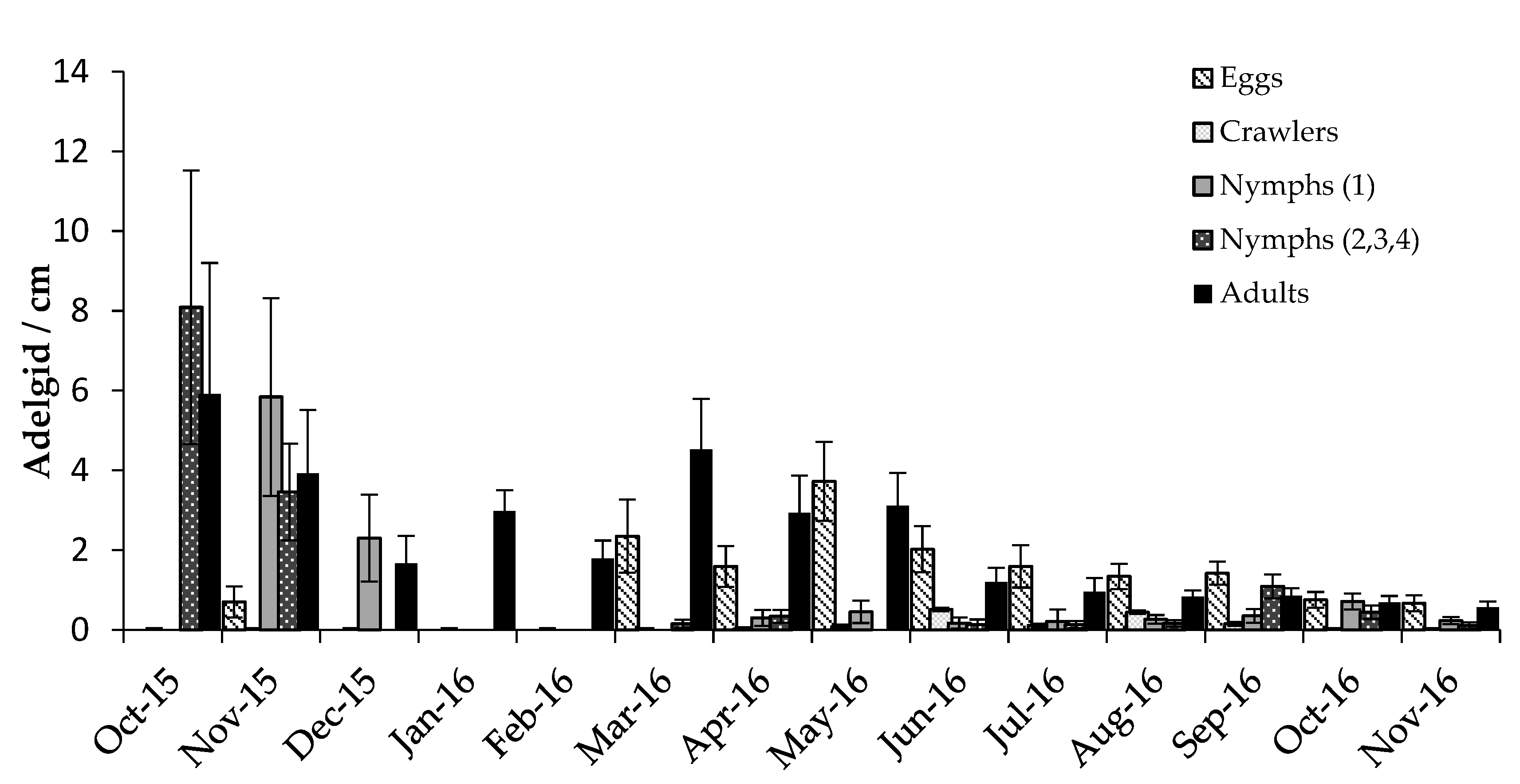
3.2.1. Adelgids
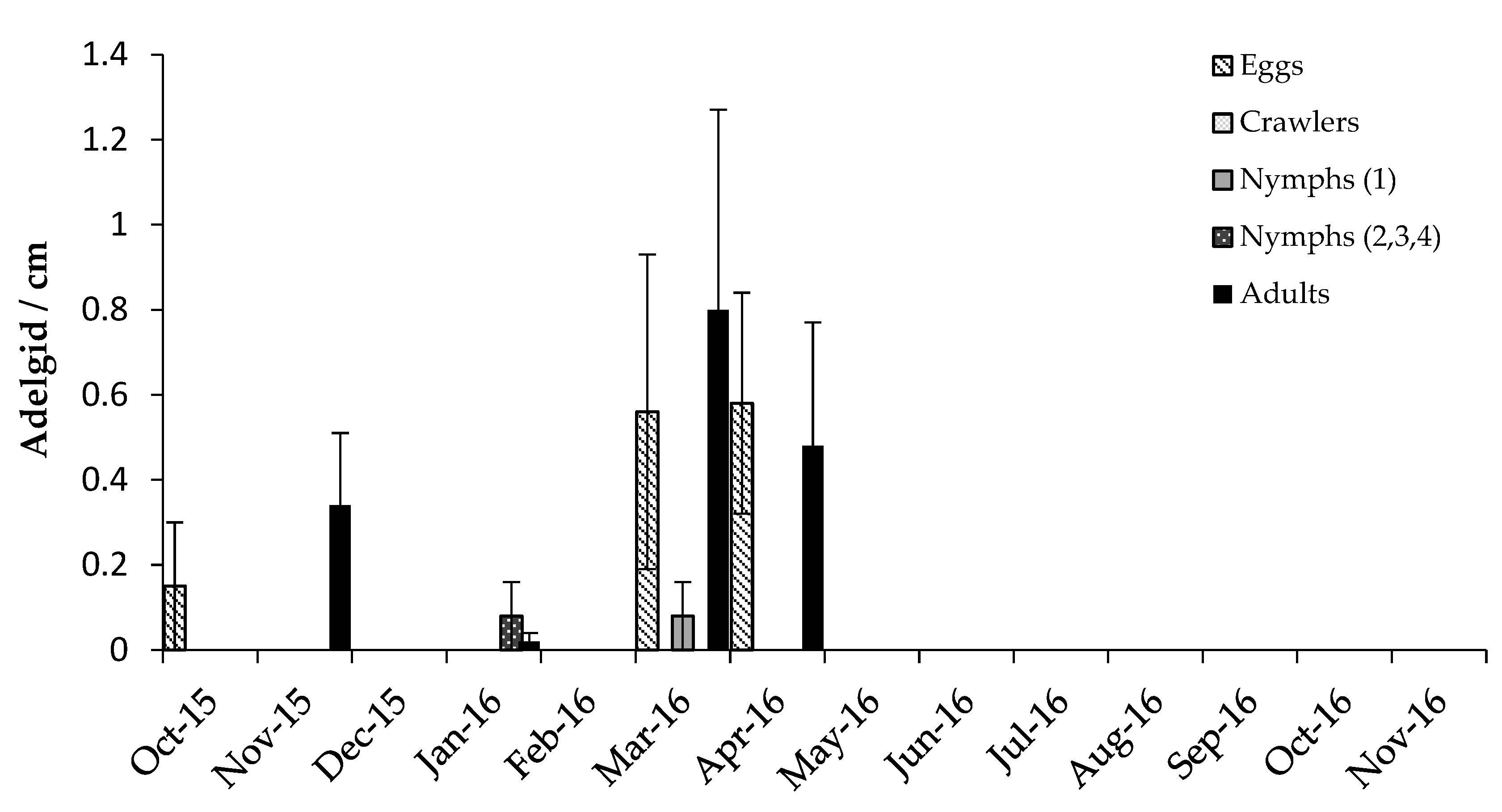
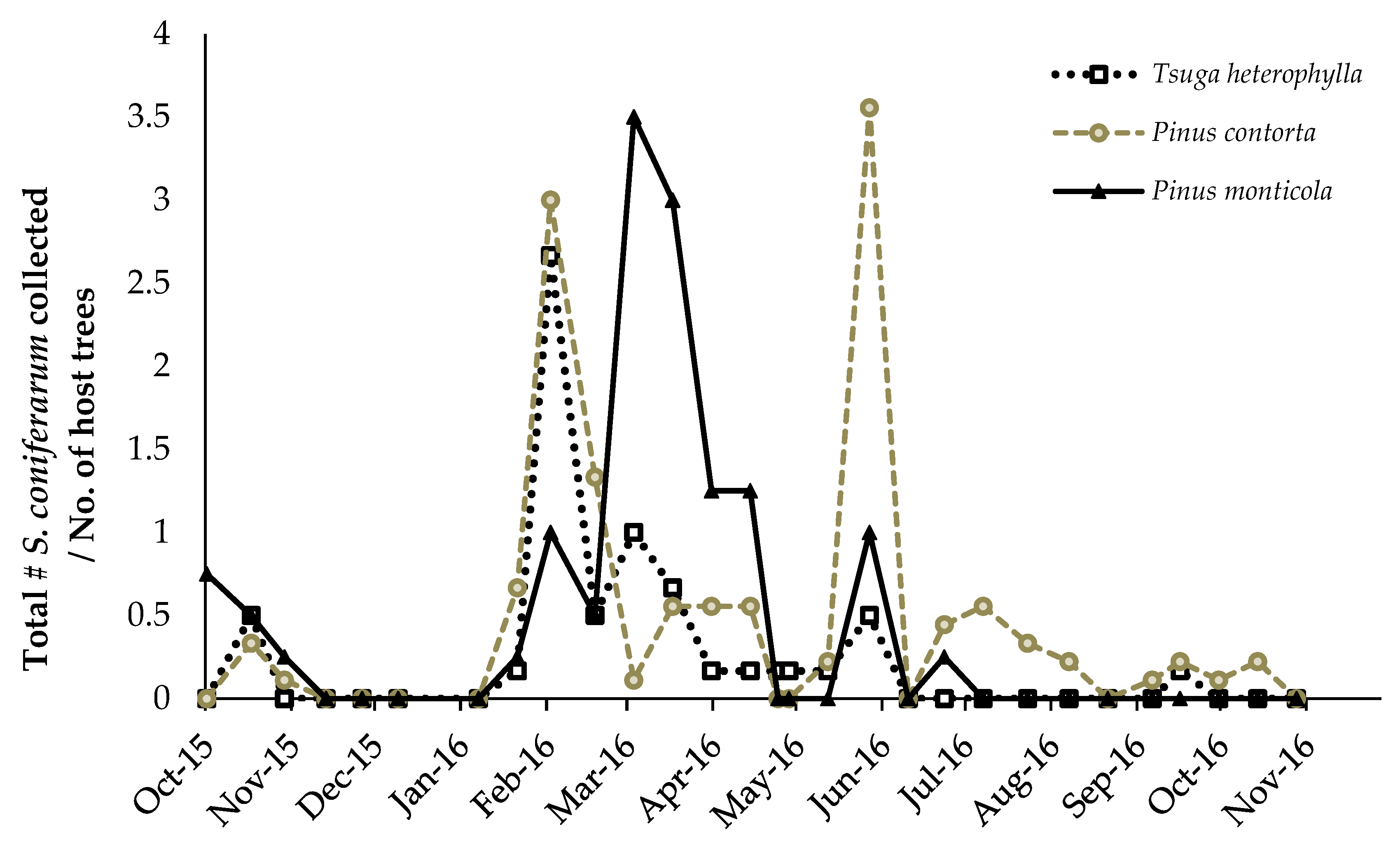
3.2.2. Scymnus coniferarum
3.3. DNA Barcode Sequencing and Morphological Examination of S. coniferarum
4. Discussion
4.1. Background
4.2. Predator/Host Density Relationships and Seasonal Patterns
4.3. DNA Barcode Sequencing and Morphological Examination of S. coniferarum
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havill, N.P.; Shiyake, S.; Lamb, A.G.; Foottit, R.G.; Yu, G.; Paradis, A.; Elkinton, J.; Montgomery, M.E.; Sano, M.; Caccone, A. Ancient and modern colonization of North America by hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae), an invasive insect from East Asia. J. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 2065–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orwig, D.A.; Foster, D.R.; Mausel, D.L. Landscape patterns of hemlock decline in New England due to the introduced hemlock woolly adelgid. J. Biogeogr. 2002, 29, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, A.E.; Reynolds, B.C.; Coots, C.I.; Havill, N.P.; Brownie, C.; Tait, A.R.; Hanula, J.L.; Joseph, S.V.; Galloway, A.B. Establishment, hybridization and impact of Laricobius predators on insecticide-treated hemlocks: Exploring integrated management of the hemlock woolly adelgid. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 335, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.S. Density-dependent feedback and population cycles in Adelges tsugae (Homoptera: Adelgidae) on Tsuga canadensis. Environ. Entomol. 1991, 20, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R. Key cues and factors for improving HWA predator recovery efforts. In Fifth Symposium on Hemlock Woolly Adelgid in the Eastern United States, 1st ed.; FHTET, 2010-07; Onken, B., Reardon, R., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Asheville, NC, USA, 2010; pp. 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mausel, D.L.; Salom, S.M.; Kok, L.T.; Davis, G.A. Establishment of the hemlock woolly adelgid predator, Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae), in the eastern United States. Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federal Register. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2013/03/06/2013-05141/availability-of-an-environmental-assessment-and-finding-of-no-significant-impact-for-a-biological (accessed on 24 July 2018).
- Gordon, R.D. The Scymnini (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) of the United States and Canada: Key to genera and revision of Scymnus, Nephus and Diomus. Bull. Buffalo Soc. Nat. Sci. 1976, 28, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, V.B. The Validity of the Higher Taxonomic Categories of the Tribe Scymnini (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, M.; McDonald, R.; Schwartzberg, L. Scymnus (Pullus) coniferarum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): An adelgid predator native to the western United States. In Proceedings: 20th US Department of Agriculture Interagency Research Forum on Invasive Species, 1st ed.; McManus, K., Gottschalk, K., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Annapolis, MD, USA, 2009; p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, M.; McDonald, R. Host preferences of Scymnus (Pullus) coniferarum: An adelgid predator. In Fifth Symposium on Hemlock Woolly Adelgid in the Eastern United States, 1st ed.; FHTET, 2010-07; Onken, B., Reardon, R., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Asheville, NC, USA, 2010; pp. 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, R.D. The Coccinellidae (Coleoptera) of America North of Mexico. J. N. Y. Entomol. Soc. 1985, 93, 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, M.; Lyon, S. Natural enemies of adelgids in North America: Their prospect for biological control of Adelges tsugae (Homoptera: Adelgidae). In Proceedings of the First Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Review, 1st ed.; FHTET 96-10; Salom, S., Tigner, T., Reardon, R., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 1995; pp. 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, M.; Keena, M. Chapter 5: Scymnus (Neopullus) lady beetles from China. In Implementation and Status of Biological Control of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid, 1st ed.; FHTET, 2011-04; Onken, B., Reardon, R., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2011; pp. 176–199. [Google Scholar]
- Delucchi, V. Pullus impexus (Muls.) (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae), a predator of Adelges piceae (Ratz.) (Hemiptera, Adelgidae), with notes on its parasites. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1954, 45, 243–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Montgomery, M.E. Oviposition, development, and feeding of Scymnus (Neopullus) sinuanodulus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): A predator of Adelges tsugae (Homoptera: Adelgidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2001, 94, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Montgomery, M.E.; Yao, D. Lady beetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) from Chinese hemlocks infested with the hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae Annand (Homoptera: Adelgidae). Coleopts. Bull. 2000, 54, 154–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darr, M.N. Biological Studies and Evaluation of Scymnus coniferarum Crotch, a Predator of Hemlock Woolly Adelgid from Western North America. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Darr, M.N.; McAvoy, T.J.; Brewster, C.C.; Salom, S.M. Field-Cage Evaluation of Survival, Reproduction, and Feeding Behavior of Adult Scymnus coniferarum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), a Predator of Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae). Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Service. Available online: http://planthardiness.ars.usda.gov (accessed on 25 April 2017).
- Statistical Analysis Institute. SAS/Stat User’s Guide; Release v 9.4 Edition; SAS Institute, Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P. The Barcode of Life Data System. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geneious. Available online: http://www.geneious.com (accessed on 15 June 2016).
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcode of Life Data System. Available online: www.barcodinglife.org (accessed on 15 June 2016).
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Trees: An Identification and Information Guide; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1994; p. 987. [Google Scholar]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Dewaard, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Ratnasingham, S.; Dooh, R.T.; Kirk, S.L.; Mackie, P.M.; Hebert, P.D. Critical factors for assembling a high volume of DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. 2005, 360, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWaard, J.; Ivanova, N.; Hajibabaei, M.; Hebert, P. Assembling DNA barcodes: Analytical protocols. In Environmental Genomics, Methods in Molecular Biology, 1st ed.; Martin, C., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 410, pp. 275–293. [Google Scholar]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), version 4; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Darr, M.N.; Salom, S.M.; Brooks, R.K.; Foottit, R.G.; Miller, G.L.; Havill, N.P. First report of Pineus strobi (Hartig, 1839) (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) in western North America. Pan-Pac. Entomol. 2018, 94, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotch, G.R. Revision of Coccinellidae of the United States. Trans. Am. Entomol. Soc. 1874, 4, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, K.S.; Mills, N.J.; Gordh, G.; McMurtry, J.A. Terrestrial arthropod predators of insect and mite pests. In Handbook of Biological Control: Principles and Applications of Biological Control, 1st ed.; Bellows, T.S., Fisher, T.W., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 385–503. [Google Scholar]
- Drooz, A. Insects of Eastern Forests; USDA Forest Service Miscellaneous Publication: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; pp. 84–85.
- Zilahi-Balogh, G.M.; Humble, L.M.; Lamb, A.; Salom, S.M.; Kok, L.T. Seasonal abundance and synchrony between Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae) and its prey, the hemlock woolly adelgid (Homoptera: Adelgidae) in British Columbia. Can. Entomol. 2003, 135, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.R.; Salom, S.M. Biology of hemlock woolly adelgid in the southern Appalachians. In Proceedings of the First Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Review, 1st ed.; Salom, S.M., Tigner, T.C., Reardon, R.C., Eds.; USDA, Forest Service, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 1996; pp. 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- McClure, M.S. Evidence of a polymorphic life cycle in the hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae (Homoptera: Adelgidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1989, 82, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. 2018. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Website Database (10 Year Average 2006–2016 for Tacoma, WA). Available online: http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/ (accessed on 4 September 2018).
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan-Richards, M.; Bulgarella, M.; Sivyer, L.; Dowle, E.J.; Hale, M.; McKean., N.E.; Trewick, S.A. Explaining large mitochondrial sequence differences within a population sample. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Host Tree Species | Adelgid Species | Mean # Adelgids/cm ± SE 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Tsuga heterophylla | Adelges tsugae | 2.39 ± 0.08 A |
| Pinus contorta | Pineus pini | 1.23 ± 0.20 B |
| Pinus monticola | Pineus strobi | 0.82 ± 0.11 B |
| Pseudotsuga menziesii | Adelges cooleyi | 0.04 ± 0.21 C |
| Host Tree Species | n 2 | Mean # S. coniferarum ± SE 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Tsuga heterophylla | 6 | 0.22 ± 0.07 B |
| Pinus contorta | 9 | 0.46 ± 0.25 A |
| Pinus monticola | 4 | 0.44 ± 0.19 A |
| Pseudotsuga menziesii 4 | 4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Species of Host Tree | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Pinus contorta | Pinus monticola | Pseudotsuga menziesii | Tsuga heterophylla | |
| Cluster 1 | 1 (10.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (30.0%) | 6 (60.0%) | 10 |
| Cluster 2 | 29 (40.1%) | 4 (5.6%) | 16 (22.5%) | 22 (31.0%) | 71 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darr, M.N.; Brooks, R.K.; Havill, N.P.; Hoebeke, E.R.; Salom, S.M. Phenology and Synchrony of Scymnus coniferarum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) with Multiple Adelgid Species in the Puget Sound, WA, USA. Forests 2018, 9, 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9090558
Darr MN, Brooks RK, Havill NP, Hoebeke ER, Salom SM. Phenology and Synchrony of Scymnus coniferarum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) with Multiple Adelgid Species in the Puget Sound, WA, USA. Forests. 2018; 9(9):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9090558
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarr, Molly N., Rachel K. Brooks, Nathan P. Havill, E. Richard Hoebeke, and Scott M. Salom. 2018. "Phenology and Synchrony of Scymnus coniferarum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) with Multiple Adelgid Species in the Puget Sound, WA, USA" Forests 9, no. 9: 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9090558
APA StyleDarr, M. N., Brooks, R. K., Havill, N. P., Hoebeke, E. R., & Salom, S. M. (2018). Phenology and Synchrony of Scymnus coniferarum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) with Multiple Adelgid Species in the Puget Sound, WA, USA. Forests, 9(9), 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9090558




