Dynamics of Coarse Woody Debris Characteristics in the Qinling Mountain Forests in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
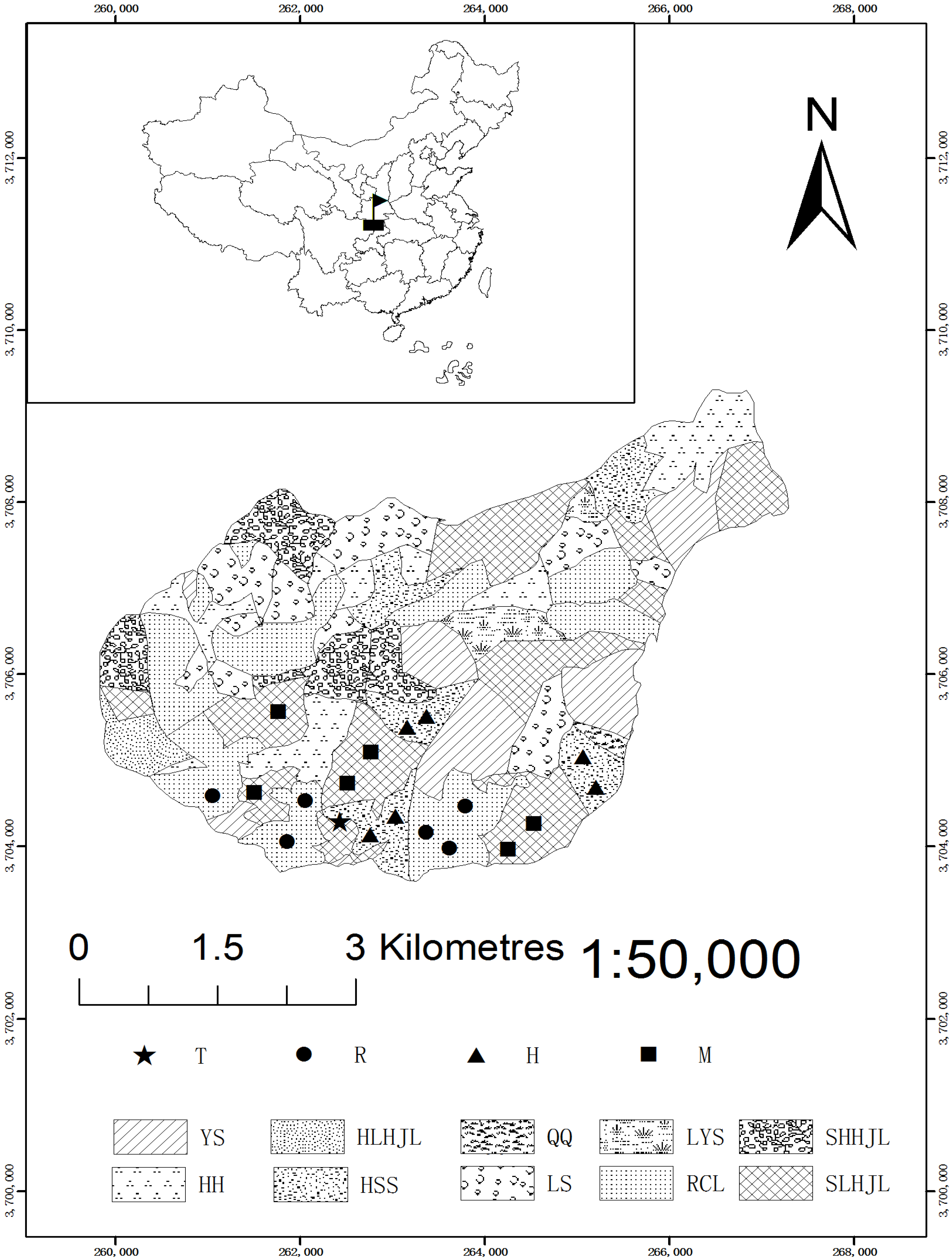
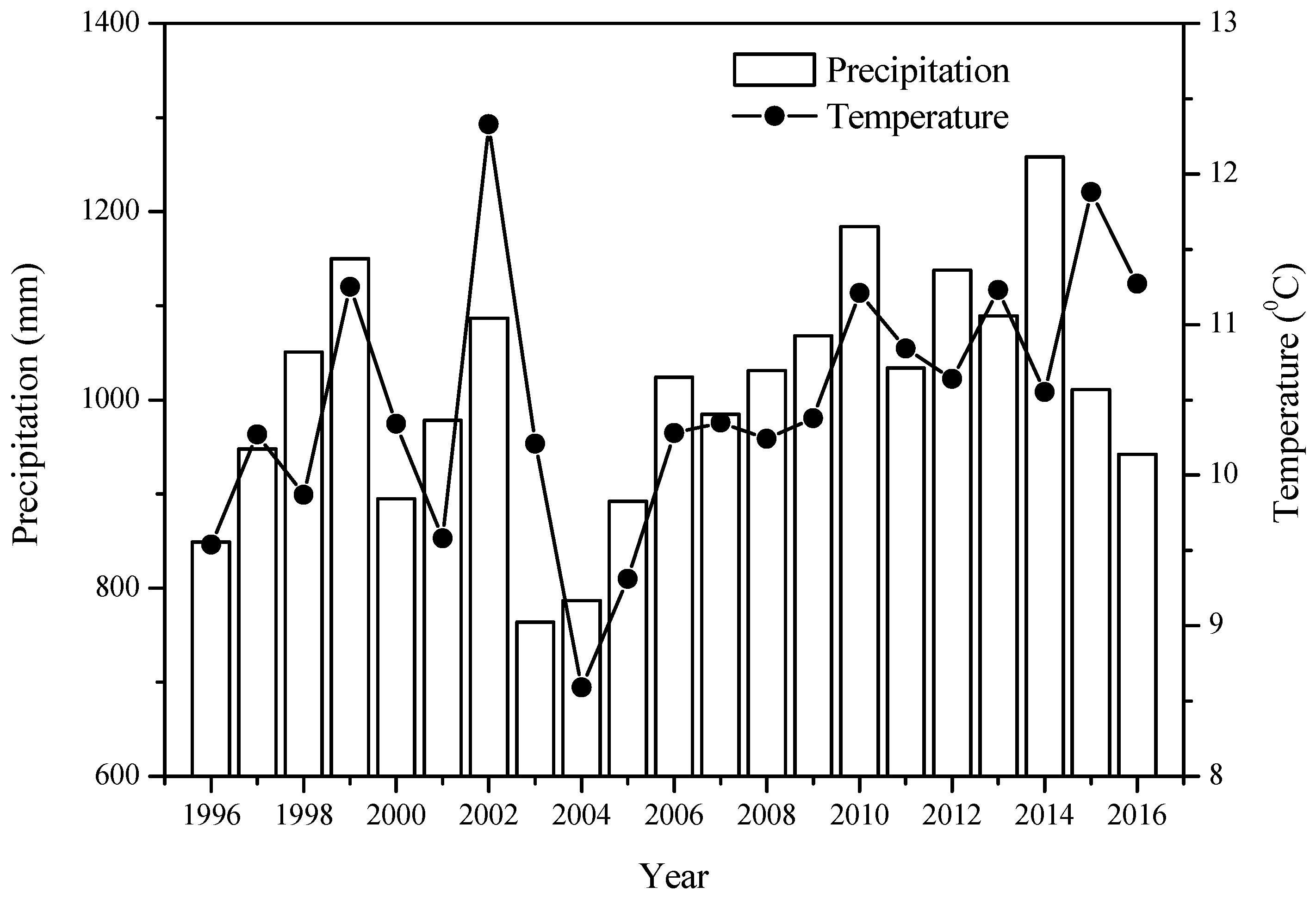
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Sampling
2.3. Calculation of Forest Biomass
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Dynamics of the Forest Biomass
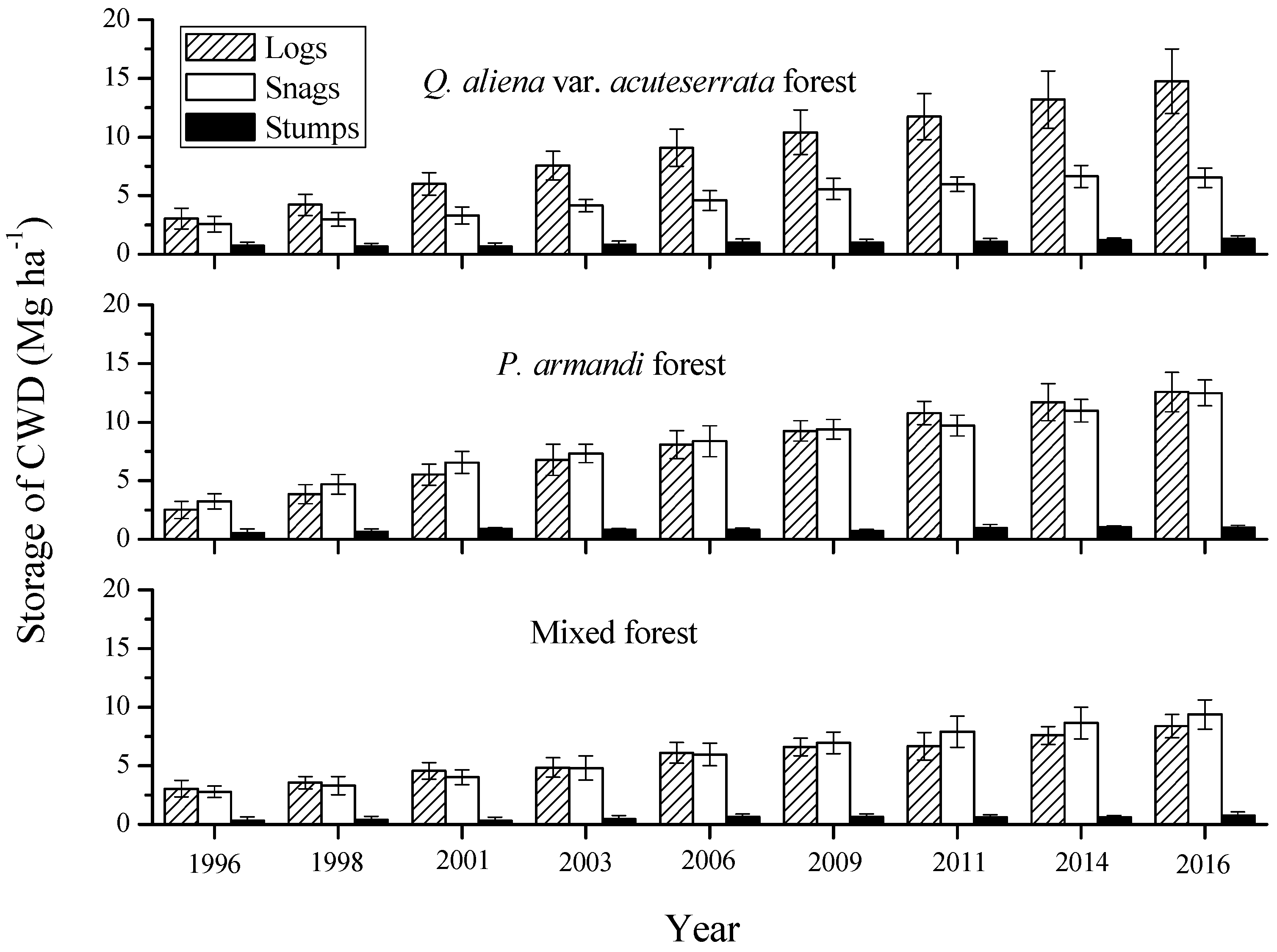
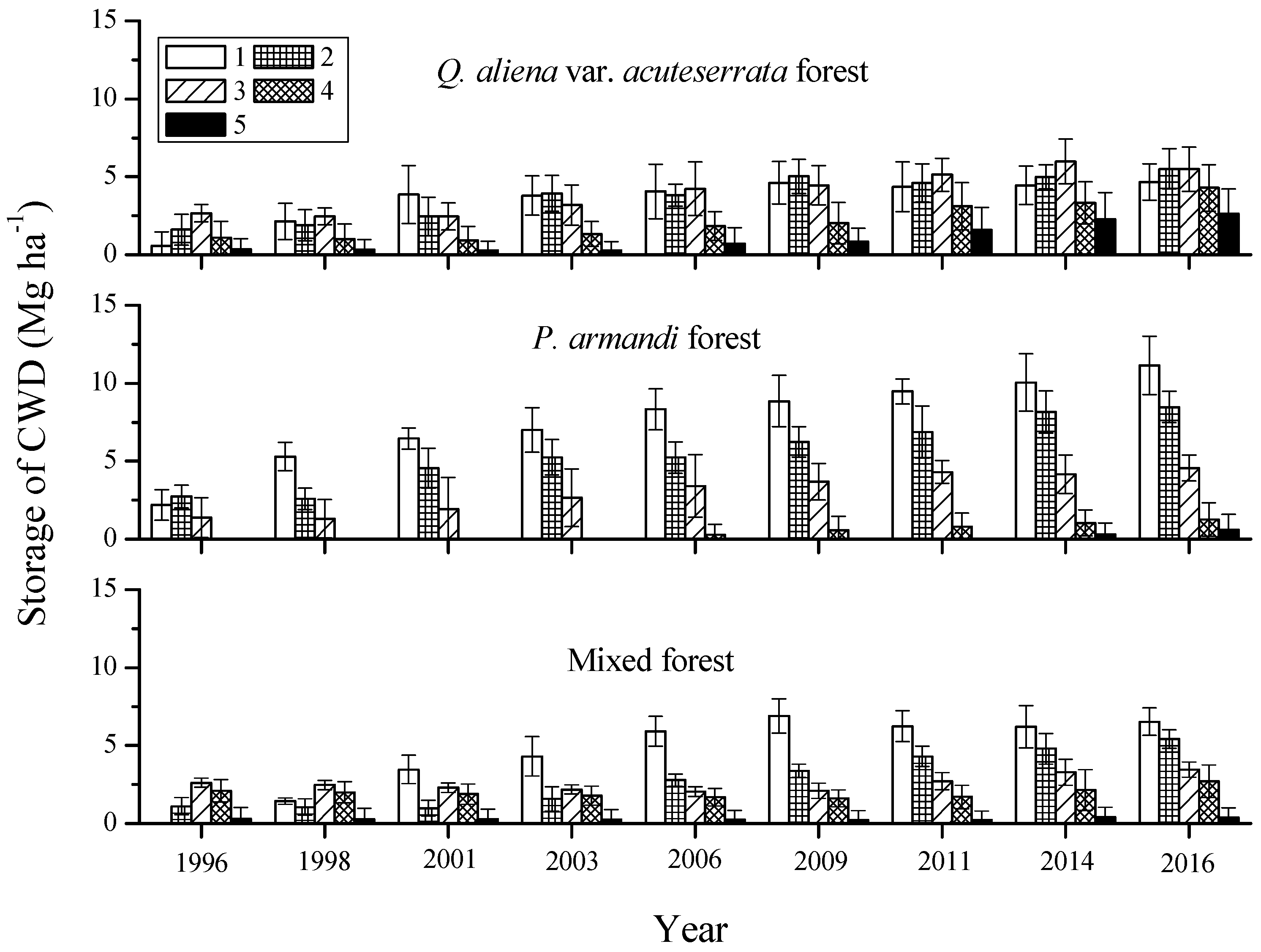
3.2. Mass Characteristics of Coarse Woody Debris (CWD)
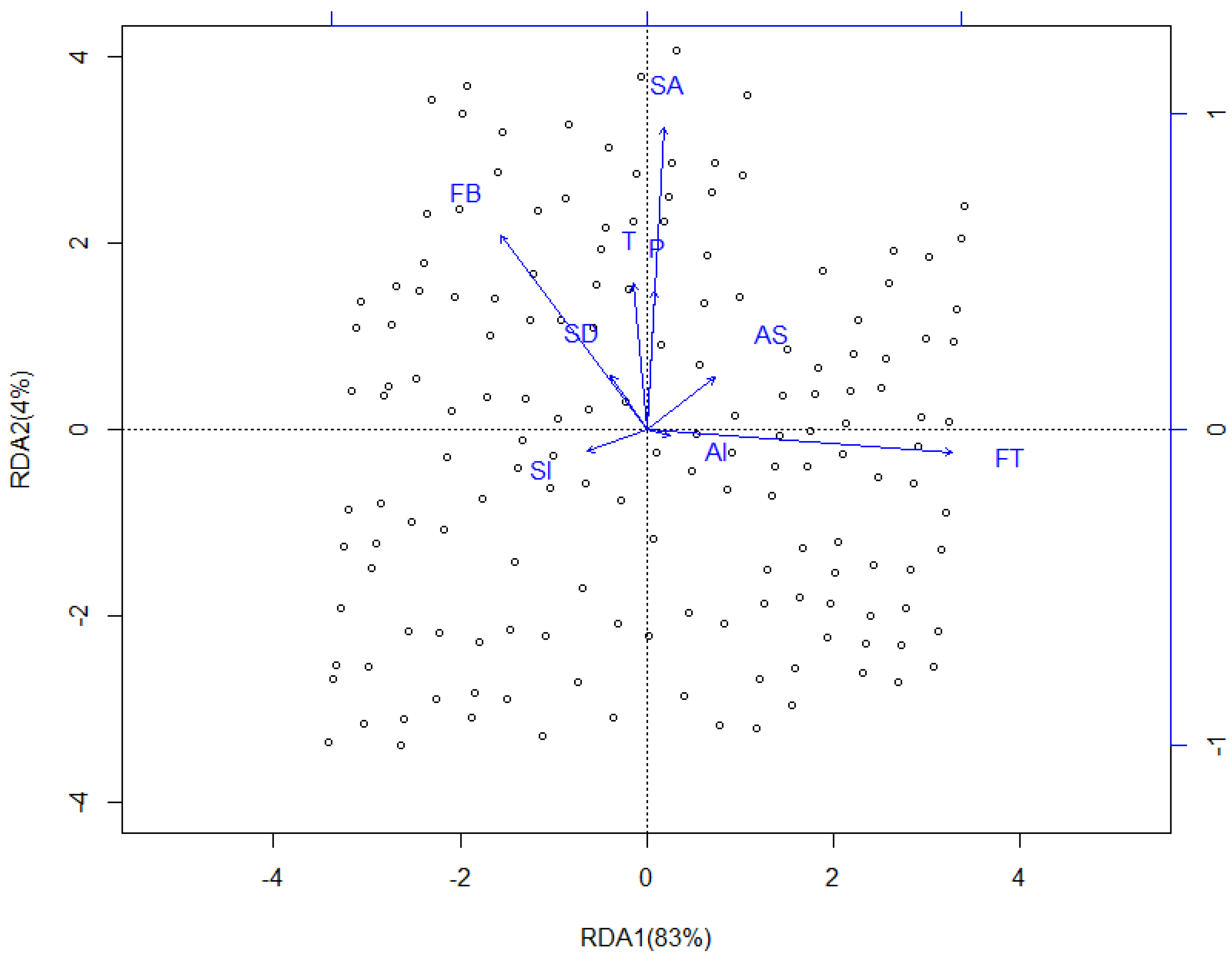
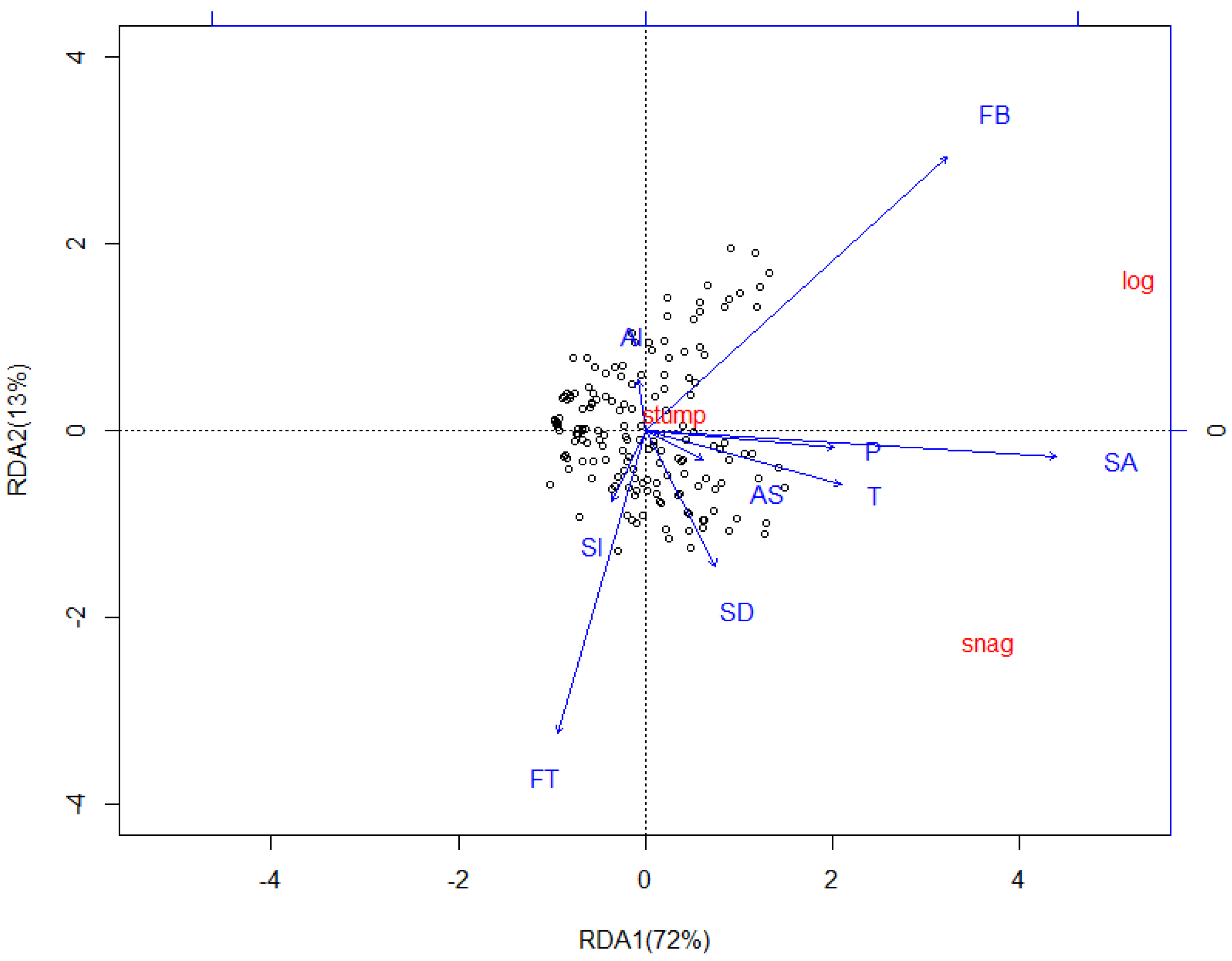
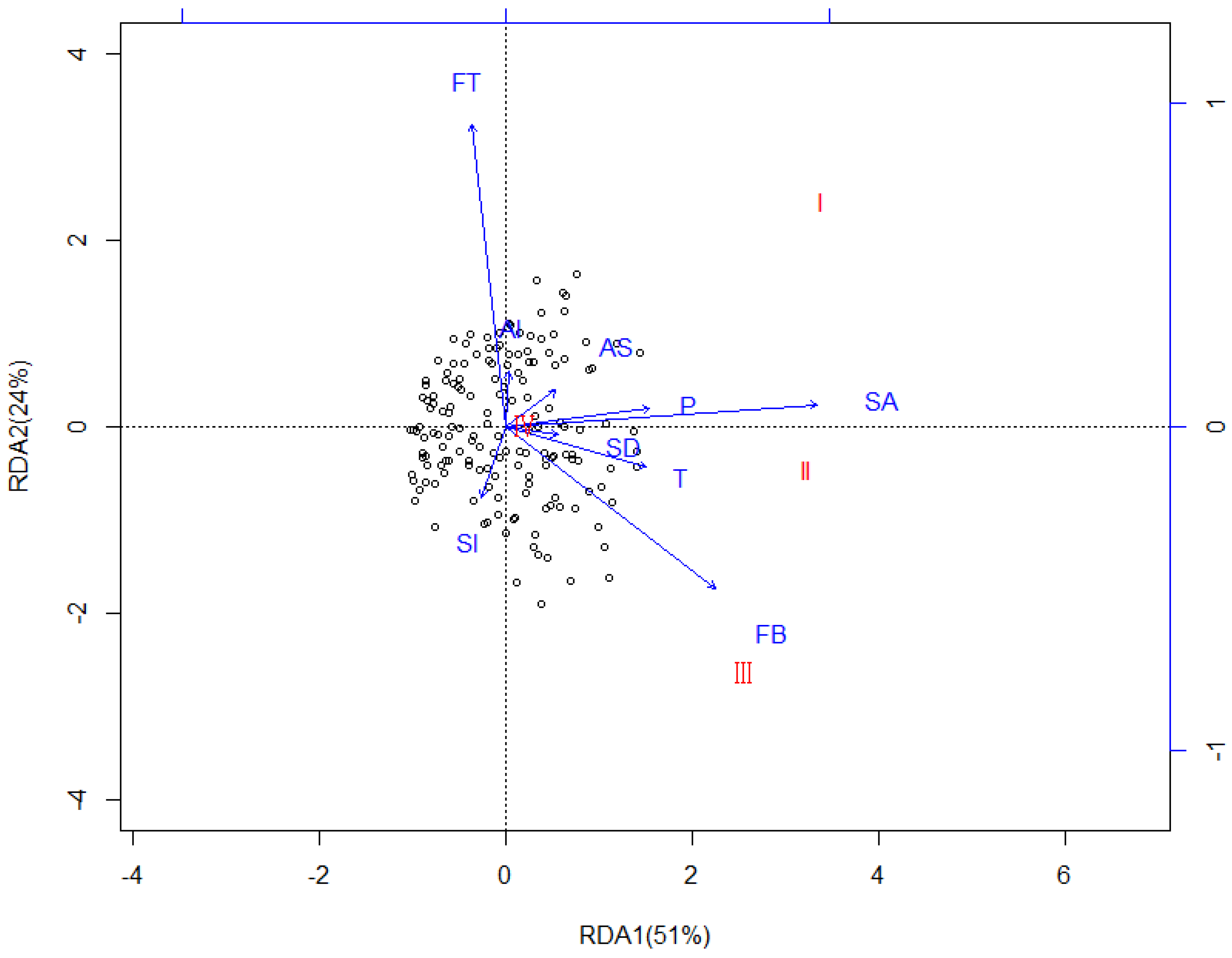
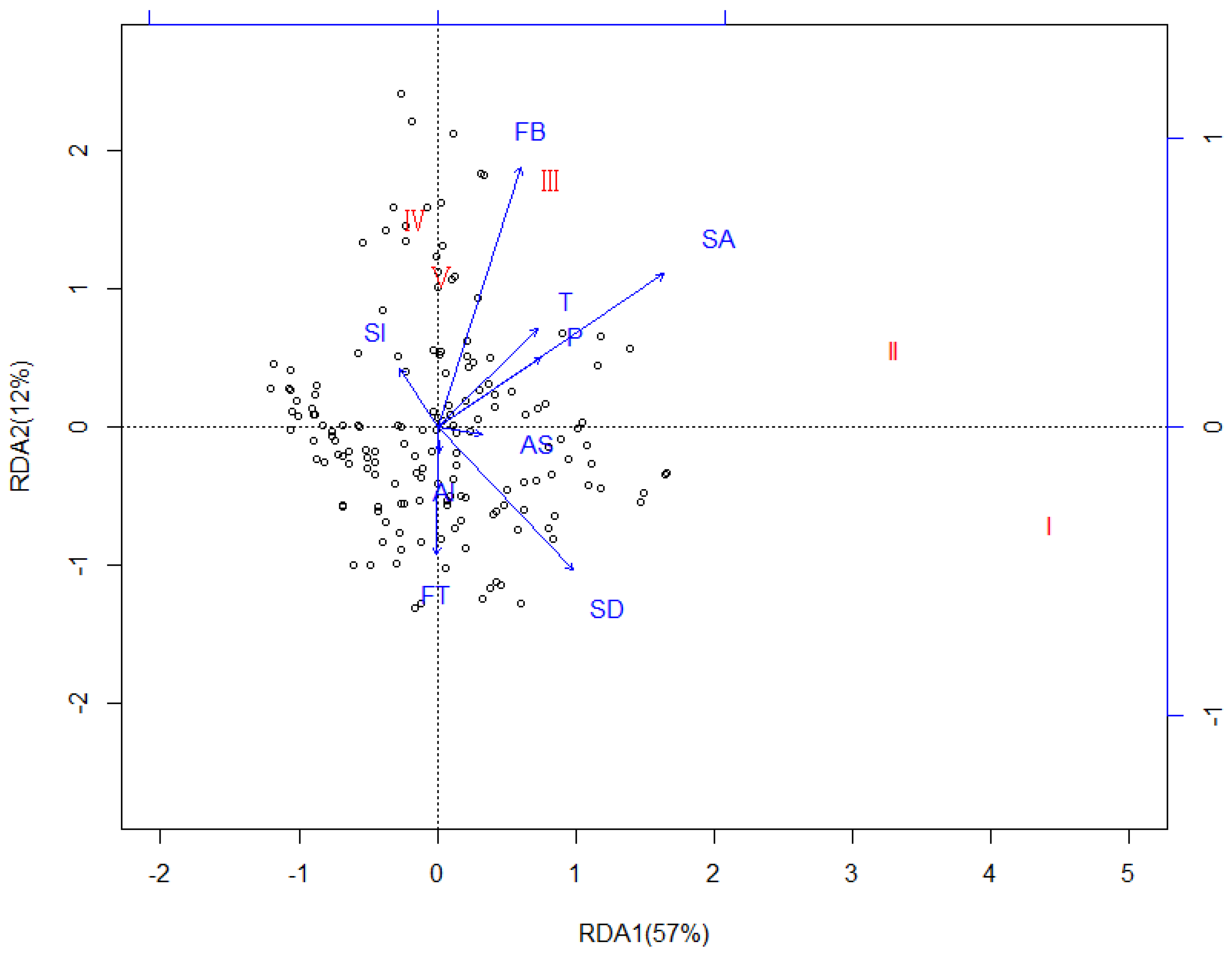
3.3. Redundancy Analysis (RDA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montes, F.; Canellas, I. Modelling coarse woody debris dynamics in even-aged Scots pine forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 221, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janisch, J.; Harmon, M. Successional changes in live and dead wood carbon stores: Implications for net ecosystem productivity. Tree Physiol. 2002, 22, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, J.K.; Waide, R.B. Nitrogen immobilization by decomposing woody debris and the recovery of tropical wet forest from hurricane damage. Oikos 1995, 72, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Kimmins, J.P.; Peel, K.; Steen, O. Mass and nutrients in woody debris in harvested and wildfire-killed lodgepole pine forests in the central interior of British Columbia. Can. J. For. Res. 2011, 27, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, M.A.; Fahey, T.J. Mass and nutrient content of decaying boles in an Engelmann spruce-subalpine fir forest, Rocky Mountain National Park, Colorado. Can. J. For. Res. 1990, 20, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Z.B. History, current situation and tendency of CWD ecological research. Chin. J. Ecol. 1991, 10, 45–50, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gough, C.M.; Vogel, C.S.; Kazanski, C.; Nagel, L.; Flower, C.E.; Curtis, P.S. Coarse woody debris and the carbon balance of a north temperate forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 244, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, C.W.; Liknes, G.C. Relationships between forest fine and coarse woody debris carbon stocks across latitudinal gradients in the United States as an indicator of climate change effects. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, M.E.; Franklin, J.F. Tree seedlings on logs in Picae-Tsuga forests of Oregon and Washington. Ecology 1989, 70, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, L.S. Use of coarse woody debris by the plant community of a Hawaiian montane cloud forest. Biotropica 2000, 32, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Nally, R.; Parkinson, A.; Horrocks, G.; Conole, L.; Tzaros, C. Relationships between terrestrial vertebrate diversity, abundance and availability of coarse woody debris on south-eastern Australian floodplains. Biol. Conserv. 2001, 99, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, S.K.; Jull, M.J.; Rogers, B.J. Abundance and attributes of wildlife trees and coarse woody debris at three silvicultural systems study areas in the Interior Cedar-Hemlock Zone, British Columbia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 233, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, M.E.; Franklin, J.F.; Swanson, F.J.; Sollins, P.; Gregory, S.; Lattin, J.; Anderson, N.; Cline, S.; Aumen, N.; Sedell, J. Ecology of coarse woody debris in temperate ecosystems. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1986, 15, 133–302. [Google Scholar]
- Magnússon, R.Í.; Tietema, A.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Hefting, M.M.; Kalbitz, K. Tamm review: Sequestration of carbon from coarse woody debris in forest soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 377, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovkin, V.; Bodegom, P.M.V.; Kleinen, T.; Wirth, C. Plant-driven variation in decomposition rates improves projections of global litter stock distribution. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, M.E.; Ferrell, W.K.; Franklin, J.F. Effects on carbon storage of conversion of old-growth forests to young forests. Science 1990, 247, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, J.; Weishampel, P.; Smith, M.L.; Kolka, R.; Birdsey, R.A.; Ollinger, S.V.; Ryan, M.G. Detrital carbon pools in temperate forests: Magnitude and potential for landscape-scale assessment. Can. J. For. Res. 2009, 39, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.B.; Woodall, C.W.; Fraver, S.; D’Amato, A.W.; Domke, G.M.; Skog, K.E. Residence times and decay rates of downed woody debris biomass/carbon in eastern US forests. Ecosystems 2014, 17, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Hou, L.; Wei, X.; Shang, Z.C.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, S.X. Decay and nutrient dynamics of coarse woody debris in the Qinling Mountains, China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.F.S.G.; Castilho, C.V.D.; Cavalcante, C.D.O.; Pimentel, T.P.; Fearnside, P.M.; Barbosa, R.I. Production and stock of coarse woody debris across a hydro-edaphic gradient of oligotrophic forests in the northern Brazilian Amazon. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 364, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefidi, K.; Darabad, F.E.; Azaryan, M. Effect of topography on tree species composition and volume of coarse woody debris in an Oriental beech (Fagus orientalis Lipsky) old growth forests, northern Iran. iForest 2016, 9, e1–e8. [Google Scholar]
- Palviainen, M.; Finér, L.; Laiho, R.; Shorohova, E.; Kapitsa, E.; Vanha-Majamaa, I. Carbon and nitrogen release from decomposing Scots pine, Norway spruce and silver birch stumps. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 390–398. [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Using, S.; Bartsch, N. Decay dynamic of coarse and fine woody debris of a beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forest in Central Germany. Eur. J. For. Res. 2009, 128, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Yagihashi, T.; Niiyama, K.; Kassim, A.R.; Ripin, A. Coarse woody debris stocks and inputs in a primary hill dipterocarp forest, Peninsular Malaysia. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2016, 28, 382–391. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.F.; Li, Y.L.; Zhou, G.Y.; Wenigmann, K.O.; Zhang, D.Q.; Wenigmann, M.; Liu, S.Z.; Zhang, Q.M. Dynamics of coarse woody debris and decomposition rates in an old-growth forest in lower tropical China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siitonen, J.; Martikainen, P.; Punttila, P.; Rauh, J. Coarse woody debris and stand characteristics in mature managed and old-growth boreal mesic forests in southern Finland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 128, 211–225. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, E.R.; Wang, X.H.; Huang, J.J.; Zeng, F.R.; Gong, L. Long-lasting legacy of forest succession and forest management: Characteristics of coarse woody debris in an evergreen broad-leaved forest of Eastern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 252, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, J.M.; Lawrence, D. Woody debris stocks and fluxes during succession in a dry tropical forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 232, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Moseley, K.R.; Castleberry, S.B.; Ford, W.M. Coarse woody debris and pine litter manipulation effects on movement and microhabitat use of Ambystoma talpoideum in a Pinus taeda stand. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 191, 387–396. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona, M.R.; Armesto, J.J.; Aravena, J.C.; Perez, C.A. Coarse woody debris biomass in successional and primary temperate forests in Chiloe Island, Chile. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 164, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymañski, C.; Fontana, G.; Sanguinetti, J. Natural and anthropogenic influences on coarse woody debris stocks in Nothofagus—Araucaria, forests of northern Patagonia, Argentina. Austral Ecol. 2017, 42, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.X.; Cheng, Y.P. Woody plant flora of the Huoditang forest region. J. Northwest For. Coll. 1996, 11, 1–10, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Harmon, M.E.; Sexton, J. Guidelines for Measurements of Woody Debris in Forest Ecosystems; US LTER Network Office, University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ringvall, A.; Ståhl, G. Field aspects of line intersect sampling for assessing coarse woody debris. For. Ecol. Manag. 1999, 119, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.G.; Peng, H. Standing crops and productivity of the major forest-types at the Huoditang forest region of the Qinling Mountains. J. Northwest For. Coll. 1996, 11, 92–102, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wenger, K.F. Forestry Handbook; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, T.R.; Honorio Coronado, E.N.; Phillips, O.L.; Martin, J.; van der Heijden, G.M.; Garcia, M.; Silva Espejo, J. Low stocks of coarse woody debris in a southwest Amazonian forest. Oecologia 2007, 152, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.Y.; Liu, G.H.; Xu, S.L. Biomass and net production of forest vegetation in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1996, 16, 497–508, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.; Lei, R.D. Carbon dioxide sequestration of main shrub species in a natural secondary Pinus tabulaeformis forest at the Huoditang forest zone in the Qinling Moutains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 6077–6084, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.D.; Wang, X.R.; Zhang, J.L.; Zheng, L.Y.; Cui, H.X. Characteristics of shrub layer biomass and carbon density in different forest types and different regions in Hubei province. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2014, 29, 46–51, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Harmon, M.E. Dynamic study of coarse woody debris in temperate forest ecosystem. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1992, 3, 99–104, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Muller, R.N.; Liu, Y. Coarse woody debris in an old-growth deciduous forest on the Cumberland plateau, southeastern Kentucky. Can. J. For. Res. 1991, 21, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, M.; Brown, S.; Lugo, A.E.; Torres-Lezama, A.; Bello Quintero, N. The quantity and turnover of dead wood in permanent forest plots in six life zones of Venezuela. Biotropica 1998, 30, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.G.; Niklasson, M.; Hedin, J.; Aronsson, G.; Gutowski, J.M.; Linder, P.; Ljungberg, H.; Mikusiński, G.; Ranius, T. Densities of large living and dead trees in old-growth temperate and boreal forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 161, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakala, T.; Kuuluvainen, T.; Gauthier, S.; De Grandpré, L. Standing dead trees and their decay-class dynamics in the northeastern boreal old-growth forests of Quebec. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedlar, J.H.; Pearce, J.L.; Venier, L.A.; McKenney, D.W. Coarse woody debris in relation to disturbance and forest type in boreal Canada. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 158, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakala, T.; Kuuluvainen, T.; Grandpré, L.D.; Gauthier, S. Trees dying standing in the northeastern boreal old-growth forests of Quebec: Spatial patterns, rates, and temporal variation. Can. J. For. Res. 2006, 37, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wei, X.; Shang, Z.C.; Cheng, F.; Hu, Z.Y.; Zheng, X.F.; Zhang, S.X. Impacts of CWD on understory biodiversity in forest ecosystems in the Qinling Mountains, China. Pak. J. Bot. 2015, 47, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, M.; Palace, M.; Asner, G.P.; Pereira, R.; Silva, J.N.M. Coarse woody debris in undisturbed and logged forests in the eastern Brazilian Amazon. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, R.; Berretti, R.; Lingua, E.; Piussi, P. Coarse woody debris, forest structure and regeneration in the Valbona Forest Reserve, Paneveggio, Italian Alps. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 235, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Dang, G.D. Coarse woody debris in an Abies fargesii forest in the Qinling Mountains. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 1998, 22, 434–440, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Wang, D.X.; Zhang, S.Z.; Liu, W.Z.; Shen, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.N. Reserves of litter and woody debris of two main forests in the Xiaolong Mountains, Gansu, China. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2011, 17, 46–50, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, P.; Qiu, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.X. Characteristics in coarse woody debris mediated by forest developmental stage and latest disturbances in a natural secondary forest of Pinus tabulaeformis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, M.E.; Chen, H. Coarse woody debris dynamics in two old growth ecosystems. Bioscience 1991, 41, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Xing, X.R.; Huang, D.M.; Liu, C.D.; He, J.Y. Storage and dynamics of coarse woody debris in Castanopsis eyrei forest of Wuyi Mountain, with some considerations for its ecological effects. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 1996, 20, 132–143, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.L.; Yang, W.; Yang, Z.Z.; Chen, X.P.; Yang, C.P.; Li, Q.; Li, F.; Chen, C.M. Electroantennographic and behavioral responses of Dendroctonus armandi (Coleoptera: Ipidae) to host plant volatiles. Chin. J. Ecol. 2011, 30, 724–729, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, V. The Ecological Role of Coarse Woody Debris: An Overview of the Ecological Importance of CWD in BC Forests; Ministry of Forests, Research Program: Victoria, BC, Canada, 1997.
- Sturtevant, B.R.; Bissonette, J.A.; Long, J.N.; Roberts, D.W. Coarse woody debris as a function of age, stand structure, and disturbance in boreal Newfoundland. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, T.; Franklin, J.; Thomas, T. Coarse woody debris in Douglas-fir forests of western Oregon and Washington. Ecology 1988, 69, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.Q.; Higuchi, N.; Schimel, J.P.; Ferreira, L.V.; Melack, J.M. Decomposition and carbon cycling of dead trees in tropical forests of the central Amazon. Oecologia 2000, 122, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brischke, C.; Rapp, A.O. Influence of wood moisture content and wood temperature on fungal decay in the field: Observations in different micro-climates. Wood Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.J.; He, X.J.; Hong, W.; Qin, D.H.; Liu, J.S.; Cai, C.T. Quantitative characteristics of coarse woody debris in natural Rhododendron simiarum forests in Tianbaoyan National Nature Reserve. J. Fujian Coll. For. 2008, 28, 293–298, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]

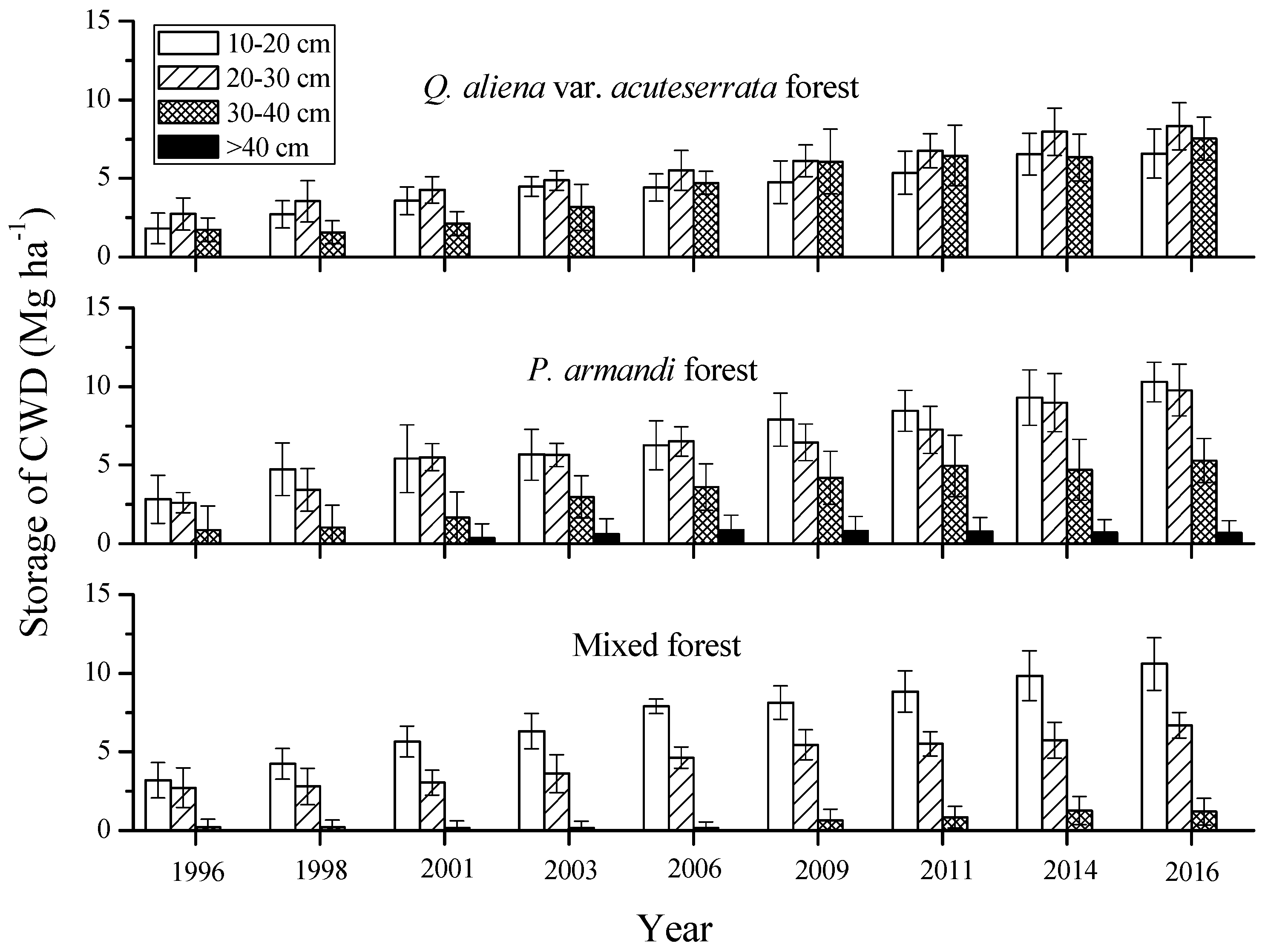
| Sample Plots | Litter Horizons | Soil Type | Latitude and Longitude | Altitude (m) | Aspect | Slope | Stand Density (Trees·ha−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oi | Oe | Oa | |||||||
| Q. aliena var. acuteserrata 1# | 51% | 23% | 26% | mountain brown earth | 33°20′55″ N 108°23′54″ E | 1597 | 318° | 32° | 1183 |
| Q. aliena var. acuteserrata 2# | 54% | 21% | 25% | dark brown earth | 33°19′20″ N 108°25′48″ E | 1641 | 14° | 28° | 1482 |
| Q. aliena var. acuteserrata 3# | 52% | 25% | 23% | mountain brown earth | 33°20′49″ N 108°25′58″ E | 1620 | 277° | 26° | 1232 |
| Q. aliena var. acuteserrata 4# | 56% | 21% | 23% | mountain brown earth | 33°19′10″ N 108°28′48″ E | 1640 | 260° | 23° | 1024 |
| Q. aliena var. acuteserrata 5# | 53% | 20% | 27% | dark brown earth | 33°20′08″ N 108°28′12″ E | 1671 | 240° | 30° | 1086 |
| Q. aliena var. acuteserrata 6# | 52% | 25% | 23% | mountain brown earth | 33°20′42″ N 108°29′21″ E | 1534 | 218° | 18° | 1584 |
| P. armandi 1# | 58% | 31% | 11% | mountain brown earth | 33°19′26″ N 108°27′10″ E | 1410 | 288° | 34° | 1628 |
| P. armandi 2# | 61% | 28% | 11% | mountain brown earth | 33°19′30″ N 108°27′54″ E | 1460 | 198° | 32° | 1486 |
| P. armandi 3# | 61% | 25% | 14% | mountain brown earth | 33°22′54″ N 108°28′02″ E | 1483 | 245° | 27° | 1712 |
| P. armandi 4# | 57% | 28% | 15% | mountain brown earth | 33°23′10″ N 108°28′10″ E | 1532 | 194° | 22° | 1426 |
| P. armandi 5# | 62% | 24% | 14% | mountain brown earth | 33°21′10″ N 108°32′39″ E | 1540 | 243° | 29° | 1267 |
| P. armandi 6# | 60% | 23% | 17% | dark brown earth | 33°22′01″ N 108°32′19″ E | 1983 | 245° | 15° | 1834 |
| Mixed forest 1# | 54% | 18% | 28% | dark brown earth | 33°22′24″ N 108°27′10″ E | 1580 | 257° | 22° | 1354 |
| Mixed forest 2# | 48% | 26% | 26% | mountain brown earth | 33°19′01″ N 108°30′24″ E | 1481 | 204° | 24° | 1288 |
| Mixed forest 3# | 50% | 24% | 26% | mountain brown earth | 33°20′10″ N 108°30′42″ E | 1424 | 255° | 32° | 1078 |
| Mixed forest 4# | 52% | 23% | 25% | mountain brown earth | 33°21′05″ N 108°24′48″ E | 1582 | 73° | 26° | 1041 |
| Mixed forest 5# | 46% | 22% | 32% | dark brown earth | 33°21′20″ N 108°26′50″ E | 1798 | 182° | 31° | 1121 |
| Mixed forest 6# | 48% | 24% | 28% | dark brown earth | 33°23′18″ N 108°25′40″ E | 1627 | 202° | 21° | 1311 |
| Type | Characteristics | Decay Class | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | ||
| Snags | Leaves | Present | Absent | Absent | Absent | As logs |
| Bark | Tight | Loose | Partly present | Absent | ||
| Crown, branch, and twig | All present | Only branches present | Only large branch stub present | Absent | ||
| Bole | Recently dead | Standing, firm | Standing, decayed | Heavily decayed, soft, and block structure | ||
| Indirect measure | Cambium still fresh, died less than 1 year | Cambium decayed, knife blade penetrates a few millimeters | Knife blade penetrates less than 2 cm | Knife blade penetrates 2–5 cm | Knife blade penetrates all the way | |
| Logs | Structure integrity | Sound | Sapwood slightly rotting, heartwood sound | Sapwood missing, heartwood mostly sound | Heartwood decayed | Soft |
| Leaves | Present | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | |
| Branches | All twig present | Larger twig present | Larger branches present | Branch stubs present | Absent | |
| Bark | Present | Present | Often present | Often absent | Absent | |
| Bole shape | Round | Round | Round | Round to oval | Oval to flat | |
| Wood consistency | Solid | Solid | Semisolid | Partly soft | Fragmented to powdery | |
| Color of wood | Original color | Original color | Original color to faded | Original color to faded | Heavily faded | |
| Position of log on ground | Elevated on support point | Elevated on support point | Near or on ground | All of log on ground | All of log on ground | |
| Invaded by roots | No | No | Sapwood area | Throughout | Throughout | |
| Indirect measure | Cambium still fresh, died less than 1 year | Cambium decayed, knife blade penetrates a few millimeters | Knife blade penetrates less than 2 cm | Knife blade penetrates 2–5 cm | Knife blade penetrates all the way | |
| Stumps | Indirect measure | Cambium still fresh, died less than 1 year | Cambium decayed, knife blade penetrates a few millimeters | Knife blade penetrates less than 2 cm | Knife blade penetrates 2–5 cm | Knife blade penetrates all the way |
| Forest Types | Contents | Regression Equation | Correlation Coefficient | Reliability of 95% of the Estimated Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q. aliena var. acuteserrata | Stem | 0.99763 | 94.24 | |
| Bark | 0.99708 | 95.37 | ||
| Branch | 0.96524 | 84.27 | ||
| Leaf | 0.97832 | 84.45 | ||
| Root | 0.99106 | 89.15 | ||
| Height | 0.78814 | 95.60 | ||
| P. armandi | Stem | 0.99802 | 97.09 | |
| Bark | 0.99698 | 96.73 | ||
| Branch | 0.98656 | 90.60 | ||
| Leaf | 0.98004 | 81.56 | ||
| Root | 0.97927 | 92.13 | ||
| Height | 0.88076 | 98.52 |
| Tree Species | Decay Classes | Diameter Classes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10–20 cm | 20–30 cm | 30–40 cm | >40 cm | ||
| Q. aliena var. acuteserrata | 1 | 0.64 (0.04, n = 3) | 0.66 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.67 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.70 (0.05, n = 2) |
| 2 | 0.55 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.56 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.58 (0.04, n = 3) | 0.60 (0.04, n = 3) | |
| 3 | 0.41 (0.04, n = 2) | 0.42 (0.04, n = 3) | 0.44 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.45 (0.03, n = 2) | |
| 4 | 0.30 (0.02, n = 3) | 0.33 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.35 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.32 (0.03, n = 2) | |
| 5 | 0.20 (0.02, n = 2) | 0.23 (0.02, n = 2) | 0.22 (0.02, n = 2) | 0.20 (0.02, n = 2) | |
| P. armandi | 1 | 0.35 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.36 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.37 (0.03, n = 3) | 0.38 (0.04, n = 2) |
| 2 | 0.30 (0.02, n = 2) | 0.30 (0.03, n = 2) | 0.32 (0.03, n = 2) | 0.32 (0.03, n = 3) | |
| 3 | 0.25 (0.02, n = 3) | 0.26 (0.02, n = 2) | 0.26 (0.02, n = 3) | 0.27 (0.02, n = 2) | |
| 4 | 0.21 (0.02, n = 2) | 0.22 (0.02, n = 3) | 0.23 (0.02, n = 2) | 0.23 (0.02, n = 2) | |
| 5 | 0.17 (0.01, n = 3) | 0.19 (0.02, n = 2) | 0.17 (0.02, n = 2) | 0.17 (0.01, n = 2) | |
| Forest Types | Shifts between Decay Classes | Year | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998 | 2001 | 2003 | 2006 | 2009 | 2011 | 2014 | 2016 | ||
| Q. aliena var. acuteserrata | 0–1 | 1.57 (0.52) | 1.75 (1.34) | 0.42 (0.66) | 0.53 (0.83) | 0.84 (1.15) | 0.19 (0.47) | 0.33 (0.80) | 0.46 (0.70) |
| 1–2 | 0.39 (0.60) | 0.66 (0.84) | 1.53 (1.03) | 0.40 (0.98) | 1.25 (0.92) | 0 | 0.60 (0.75) | 0.66 (0.98) | |
| 2–3 | 0 | 0.23 (0.57) | 0.74 (0.60) | 1.10 (1.08) | 0.51 (0.90) | 0.96 (1.17) | 1.10 (0.91) | 0 | |
| 3–4 | 0 | 0 | 0.45 (0.50) | 0.68 (0.77) | 0.37 (0.57) | 1.11 (0.58) | 0.37 (0.61) | 0.99 (0.60) | |
| 4–5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.43 (0.69) | 0.19 (0.34) | 0.76 (0.84) | 0.73 (0.81) | 0.42 (0.60) | |
| P. armandi | 0–1 | 3.11 (0.20) | 1.22 (0.67) | 0.81 (0.90) | 1.38 (1.05) | 0.66 (0.77) | 0.98 (1.69) | 0.86 (1.10) | 1.12 (0.57) |
| 1–2 | 0 | 1.97 (0.83) | 1.01 (0.80) | 0.21 (0.51) | 1.10 (1.01) | 0.73 (1.19) | 1.34 (0.81) | 0.42 (0.66) | |
| 2–3 | 0 | 0.67 (1.08) | 0.78 (0.87) | 0.80 (0.70) | 0.47 (1.14) | 0.69 (0.80) | 0.17 (0.40) | 0.66 (0.72) | |
| 3–4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.28 (0.68) | 0.30 (0.74) | 0.25 (0.62) | 0.27 (0.50) | 0.26 (0.63) | |
| 4–5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.30 (0.73) | 0.33 (0.82) | |
| Mixed forest | 0–1 | 1.43 (0.21) | 2.04 (0.77) | 0.88 (0.68) | 1.61 (0.74) | 1.03 (0.77) | 0 | 0.30 (0.52) | 0.43 (0.64) |
| 1–2 | 0 | 0 | 0.63 (0.98) | 1.25 (0.66) | 0.65 (0.62) | 0.92 (0.74) | 0.64 (0.64) | 0.81 (0.94) | |
| 2–3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 (0.36) | 0.69 (0.76) | 0.69 (0.64) | 0.43 (0.60) | |
| 3–4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 (0.37) | 0.48 (0.69) | 0.61 (0.96) | |
| 4–5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.19 (0.46) | 0 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Jose, S.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, F.; Hou, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, S. Dynamics of Coarse Woody Debris Characteristics in the Qinling Mountain Forests in China. Forests 2017, 8, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8100403
Yuan J, Jose S, Zheng X, Cheng F, Hou L, Li J, Zhang S. Dynamics of Coarse Woody Debris Characteristics in the Qinling Mountain Forests in China. Forests. 2017; 8(10):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8100403
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Jie, Shibu Jose, Xiaofeng Zheng, Fei Cheng, Lin Hou, Jingxia Li, and Shuoxin Zhang. 2017. "Dynamics of Coarse Woody Debris Characteristics in the Qinling Mountain Forests in China" Forests 8, no. 10: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8100403
APA StyleYuan, J., Jose, S., Zheng, X., Cheng, F., Hou, L., Li, J., & Zhang, S. (2017). Dynamics of Coarse Woody Debris Characteristics in the Qinling Mountain Forests in China. Forests, 8(10), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8100403






