Abstract
This study presents the long-term (over the last 8000 years) natural variability of a portion of the Picea mariana-moss bioclimatic domain belonging to Québec’s Clay Belt. The landscapes are dominated by mesic-subhydric clay and early successional forests composed of Populus tremuloides, Pinus banksiana and Picea mariana. The natural variability (fires and vegetation) of one of these landscapes was reconstructed by means of pollen and macroscopic charcoal analysis of sedimentary archives from two peatlands in order to assess when and how such landscapes were formed. Following an initial afforestation period dominated by Picea (8000–6800 cal. Years BP), small and low-severity fires favored the development and maintenance of landscapes dominated by Picea and Abies balsamea during a long period (6800–1000 BP). Over the last 1000 years, fires have become more severe and covered a larger area. These fires initiated a recurrence dynamic of early successional stands maintained until today. A decline of Abies balsamea has occurred over the last centuries, while the pollen representation of Pinus banksiana has recently reached its highest abundance. We hypothesize that the fire regime of the last millennium could characterize Québec’s Clay Belt belonging to the western Picea mariana-moss and Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera domains.
1. Introduction
Boreal forest landscapes develop under the combined influence of climate, natural (fires, insect outbreaks) and anthropogenic (logging, fires of human origin) disturbances, as well as physical environment [1,2]. This combination of factors generated the contemporary landscape diversity defined, at different spatial scales, through hierarchies of ecological classification [3,4]. These classifications consider the physical features, such as the abundance of lakes, the area covered by peatlands or sandy soils and the relief. All these physical features have a strong influence on the long-term history of fire and vegetation [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Knowing the long-term natural variability of landscapes, it will become easier to define forest strategies in regard to ecosystem management and climatic changes [16,17,18,19,20].
In each boreal landscape, the species are distributed along a toposequence of surficial deposits, slope and drainage conditions, from bedrock and well-drained soils (till, clay or sand) to poorly drained organic soils. In northeastern North America, jack pine (Pinus banksiana Lambert) and black spruce (Picea mariana (Miller) Britton, Sterns & Poggenburgh) are well adapted to sites characterized by bedrock or sandy soil [21,22]. Thick, moderately well-drained soils support a vegetation more demanding with respect to the nutrient regime, such as trembling aspen (Populus tremuloides Michaux), white birch (Betula papyrifera Marshall) and balsam fir (Abies balsamea (Linnaeus) Miller), whereas poorly-drained soils are mainly colonized by P. mariana and Larix laricina (Du Roi) K. Koch. Under the influence of natural disturbances, mainly fires, the vegetation of each portion of the toposequence changes with time. For example, after fires on well-drained rich soils, the light-demanding early successional species (P. tremuloides, B. papyrifera) give way to late successional ones (P. mariana, A. balsamea), thereby defining a successional forest dynamic [23]. However, in other parts of the landscape, as on low altitude and undulated or flat relief where P. mariana and P. banksiana are dominant, fires can occur so frequently spaced in time that cohorts of early successional species succeed one another, creating a recurrence dynamic of stands dominated by these species [24,25]. Under such circumstances, stands dominated by early successional species can be considered in equilibrium with climate and disturbance regimes. These examples show that, in the context of the eastern Canadian boreal forest, P. mariana can be considered as both an early and a late successional species.
In an integrative study of paleoecological data covering the major biomes of Québec (Canada) initiated in order to demonstrate the specificity of each biome, Blarquez et al. [26] suggest that in the boreal coniferous forest dominated by Picea mariana, biomass burning was higher during the mid-Holocene period (~6000 to 4000 cal. Years BP) than during the late Holocene (over ~4000 years). Some sites show a brief increase of fire frequency around 1000 cal. Years BP, possibly related to the Medieval climatic optimum [10,27,28]. The majority of the study lakes considered by Blarquez et al. [26] are located in the western part of the Picea mariana domains (moss and lichen). If fires were less frequent during the late Holocene, they were, however, larger in extent [27]. The widespread general decline of fire frequency during the late Holocene in the P. mariana domains would be explained by climatic factors, i.e., an increase in annual precipitation, as well as a decrease of temperature (mainly during July), a shorter growing season and lower summer insolation [10,26,27,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. Blarquez et al. [26] also suggest that fire frequency increased throughout the Holocene in the boreal mixedwood. Numerous sites studied in this biome are, however, located in eastern Québec, where hydroclimatic conditions differ greatly from those prevailing in the western part of the province. Indeed, annual precipitation is more than 200 mm higher in eastern Québec [36]. Moreover, the mixedwood includes three bioclimatic domains according to Québec classification; these are, from north to south, Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera, Abies balsamea-Betula alleghaniensis and Acer saccharum-Betula alleghaniensis [4]. Specific fire reconstruction studies in the Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera domain show a gradual increase of fire events during the late Holocene, and some of these studies were undertaken in the Clay Belt of Québec [37,38] and Ontario [12] (Figure 1).
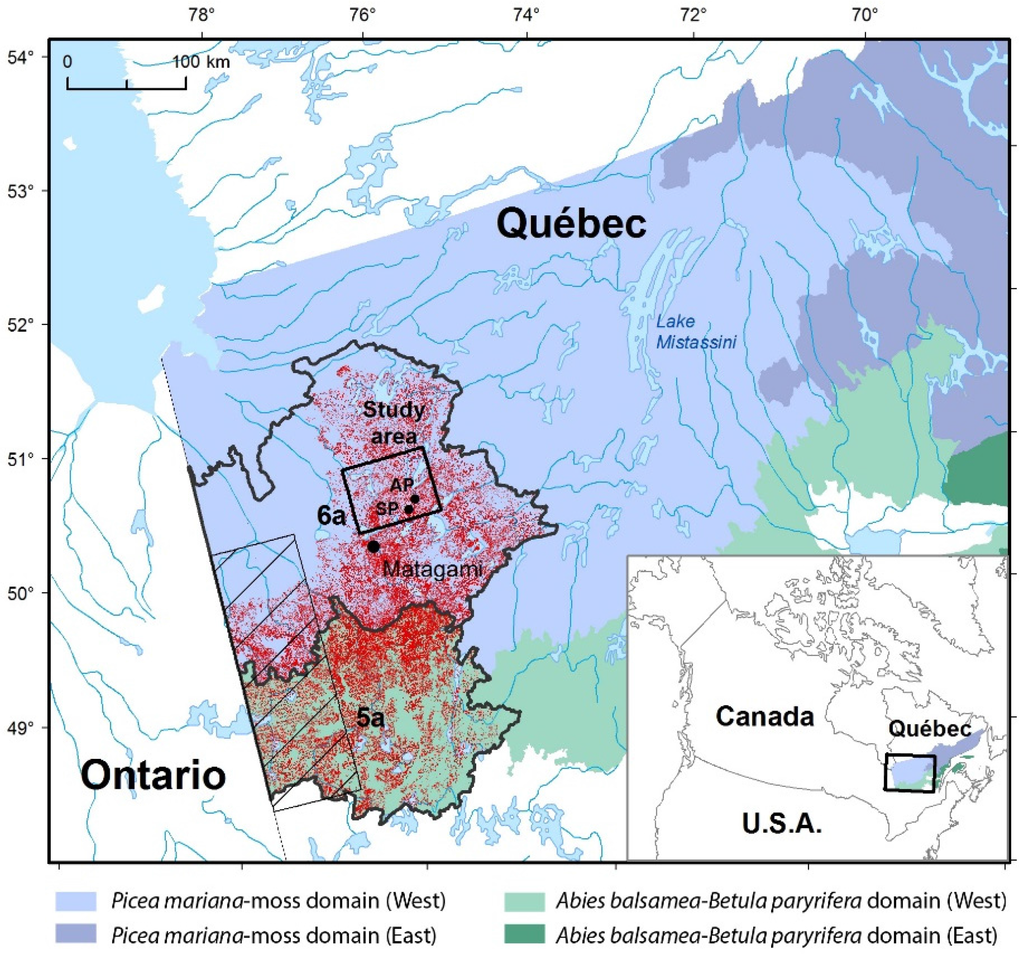
Figure 1.
Location of the study area (4000 km2) in Québec’s Picea mariana-moss bioclimatic domain, Canada [4]. The study area is located in ecological region 6a (Plaine du lac Matagami). The two peatlands studied are codified as: AP: Aspen peatland and SP: Shadow peatland. Ecological region 5a (Plaine du lac Abitibi) is part of the western Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera bioclimatic domain. The sector with oblique lines located close to the border with Ontario corresponds to the fire origin map created by Bergeron et al. [7]. The red dots indicate the clay deposit distribution (QMFFP forest maps) corresponding to Québec’s Clay Belt.
The aim of this study is to explain the long-term natural variability of the vegetation and fire in a Québec Clay Belt landscape dominated by early successional species (Populus tremuloides, Pinus banksiana and Picea mariana) (Figure 1). These stands are abundant throughout the Clay Belt. Considering the type of landscape (vegetation, surficial deposit) and the increase of fires during the last millennium in some areas dominated by clay, we hypothesize that the mesic-subhydric clay of our studied landscape was also affected by increased fire activity during the late Holocene, which promoted the maintenance until now of early successional species through a recurrent forest dynamic. To test this hypothesis, we first analyzed the contemporary vegetation of a 4000 km2 study area with the objective of understanding the current forest dynamics. We then reconstructed the long-term vegetation and fire history through pollen and macroscopic charcoal analyses of two selected peatlands in order to obtain insight into the forest dynamics at the margin of the peatlands.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area covers 4000 km2 within the Picea mariana-moss bioclimatic domain, more specifically within the ‘Plaine du lac Matagami’ ecological region [4] (Figure 1). Annual mean temperature at the Matagami weather station [36] is between −1 and −2 °C. July is the warmest month of the year (mean: 16.8 °C) and January the coldest (mean: −20 °C). Total annual precipitation varies between 800 and 1000 mm, of which 25%–30% falls as snow. This region is characterized by a flat to gently undulated relief, low to mid altitudes (200–400 m) and the presence of some large lakes. An important portion of the ecological region belongs to the Clay Belt, a vast half-moon shaped area stretching from eastern Ontario to western Québec. The Clay Belt is characterized by thick clayey glaciolacustrine deposits left by postglacial lakes Barlow (southern area) and Ojibway (northern area), which reached their maximum water level 8000 years ago when the retreating Laurentide ice sheet was further north [39]. Soon after and for a short period, a readvancing ice sheet surged southward into glacial Lake Ojibway, incorporating glacial material into glaciolacustrine sediments and forming the compact Cochrane Till. This till, the low altitude and the flat relief all played an important role in the development of large peatlands in the northeastern part of the ecological region.
A reconstruction of the contemporary fire history (1700–2000 AD) in a 15,000 km2 area located along the Québec-Ontario border and belonging mainly to the Clay Belt showed that fires burned large areas especially during the 1820 and 1910 periods [7,32,40] (Figure 1). Since then, only a few fires have occurred, most of them in the Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera domain, and mainly of anthropogenic origin. The post-fire forest dynamics are characterized by two main successional pathways. The first is mostly observed in the northwestern part dominated by Cochrane Till. In this sector, numerous Picea mariana forests have been paludified and this process of peat accumulation, controlled by flat relief, lower altitude and fire activities, is still active at the edge of the peatlands [41]. The second successional pathway is typical of mesic and subhydric clay, mostly undulated relief and higher altitude (Clay Belt). Populus tremuloides, Pinus banksiana and P. mariana early successional forests evolve towards P. mariana-Abies balsamea late successional forests if the time elapsed after fire is long enough [22]. Due to the vast area covered by fires of the 1910 period [7,40], this late successional forest is currently rare.
2.2. Contemporary Forest Landscapes
During the first phase of this study, the current forest composition and dynamics of the 4000 km2 study area, belonging to the Clay Belt, were defined by using forest maps produced by the Québec Ministry of Forests, Fauna and Parks (QMFFP). These maps (scale 1:20,000) were produced by photointerpretation of aerial photographs taken in the 2005–2010 period. In total, 38,887 forest stands were delineated and defined on the basis of their vegetation composition and structure (density, age) as well as physical characteristics (surficial deposit, drainage, slope and altitude). The age of forest stands identified on maps was studied with the aim of establishing links with Bergeron et al. [7,40]. However, these links were difficult to make because many stands on the QMFFP maps were identified as pertaining to the 70-year-old age-class, suggesting fires in the 1950 period. This age was estimated by photointerpretation mainly on the basis of tree height and density, and without information on the contemporary fire history. Moreover, older forests were classified into the 120-year maximum age class. In order to acquire knowledge on the fire contemporary history of the studied area, we created a fire origin map. Fieldwork (2013 and 2014) was conducted at 140 sites. For each site, we collected fire scars or, in their absence, a cross section of the collar from one to five trees per site. In total, 313 trees were sampled from the dominant individuals. In the laboratory, samples were dried and sanded, and the number of rings was counted using a binocular magnifier. Years of stand origin show a dominance of trees belonging to the ca. 1820 and ca. 1910 periods. As expected, our results are comparable to those of Bergeron et al. [7,40] and not to those of QMFFP forest maps. We also identified the 1970 period, which was characterized by some small fire events. Based on this information, the majority of forest stands referred to on the QMFFP maps as being 90 years old and, erroneously, 70 years old were assigned to the 1910 period of origin, whereas the majority of the 120 year-old stands were considered as having an origin close to 1820.
The 38,887 stands were subjected to a redundancy analysis (RDA). The RDA was conducted simultaneously on matrices characterizing forest composition (Y matrix, 38,887 records, five species: Picea mariana, Abies balsamea, Pinus banksiana, Populus tremuloides, Betula papyrifera) and site characteristics (X matrix, 38,887 records, five variables: altitude, slope, surficial deposit, drainage, period of origin). The RDA characterized each forest stand according to five ordination axes. All axes were submitted to K-means partitioning in order to group forest stands with comparable vegetation and site characteristics. Each group of stands composes a landscape [2,42].
2.3. Study Sites and Sampling
During the second phase of this study, two ombrotrophic peatlands located in a landscape belonging to the Clay Belt and dominated by early successional stands (Populus tremuloides, Pinus banksiana, Picea mariana) were selected for the reconstruction of the Holocene fire and vegetation history. The two peatlands are situated 10.5 km apart (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Aspen peatland (hereafter “Aspen”, 50°00.46′ N; 77°00.14′ W) covers an area of 30 ha and lies at an altitude of 283 m. Shadow peatland (hereafter “Shadow”, 49°56.57′ N; 77°06.43′ W) covers an area of 15 ha at an altitude of 280 m. Both are dominated by Ericaceae on a carpet of Sphagnum moss. Shrubby P. mariana (height 14 m) form a low density stratum (20%–40%). In Aspen, the coring site for organic sediments lies 100 m from both sides of the forest, whereas in Shadow the coring site is located 25 m from the forest border. These two locations were selected to obtain a long temporal sequence (Aspen) and a shorter one but with a stronger signal of the local forest dynamics (Shadow). Sampling was conducted by excavating a trench with a shovel, and then cutting peat monoliths (30 cm × 30 cm × 30 cm) from top to bottom. The absence of water from the trench during excavation made it possible to collect a complete section of peat right down to the underlying marine clay. Monoliths were stored in the laboratory at 4 °C until analysis.
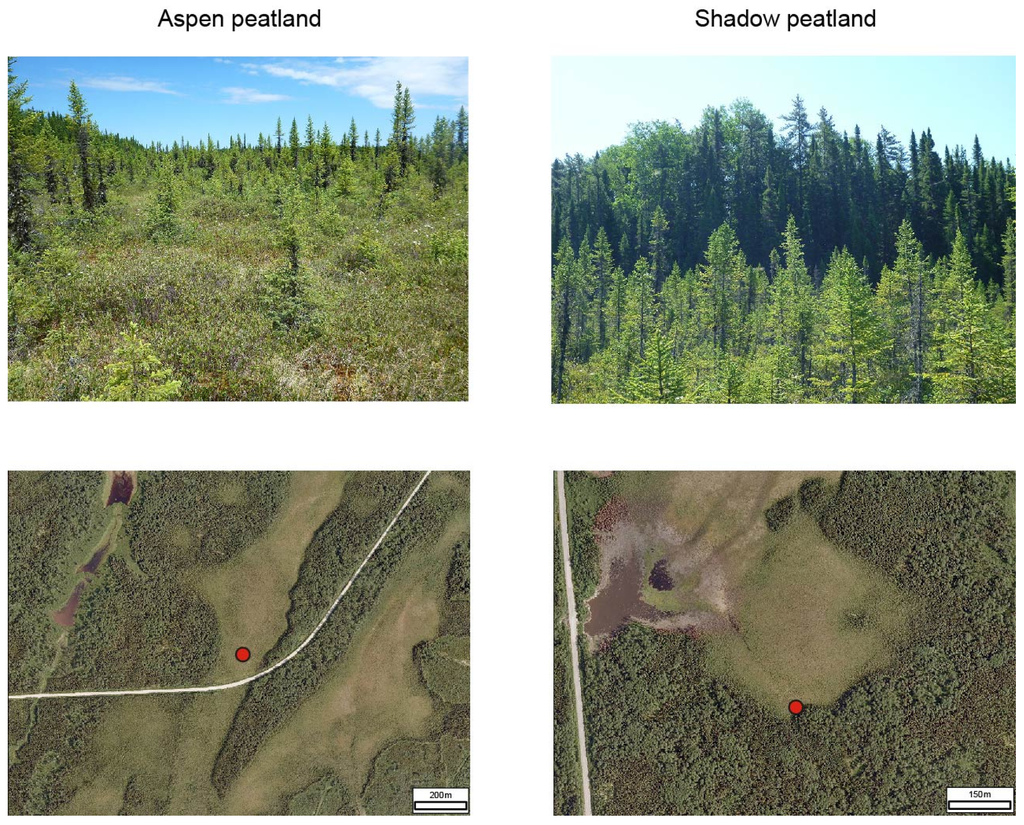

Figure 2.
Study sites (Aspen and Shadow peatlands) where paleoecological reconstructions were conducted. Upper portion: overview of the peatlands and their forest environment. Lower portion: aerial photographs and location of sedimentary cores (red dots).
2.4. Characterization of the Contemporary Forest Surrounding the Peatlands
To characterize the forest surrounding each peatland, three parallel transects (50 m × 4 m; 200 m2) 10 m apart were delineated. Live tree stems (˃2 cm in diameter at breast height) were identified and counted. The stems representing forest regeneration (˂2 cm in diameter) were identified and numbered in plots (1 m2) distributed every 5 m along each transect (10 plots per transect). A cross section of the collar was cut from five of the largest stems in order to determine their age. Finally, a moss sample was collected from the soil surface in the forest surrounding Aspen, as well as from a stand dominated by Picea mariana and Abies balsamea located 10 km north of Aspen, to obtain a picture of the pollen representation of current vegetation. In the laboratory, the stem counts of individuals exceeding 2 cm per species and per diameter class were transformed into relative basal area per species. Regenerating tree stems were analyzed to define the frequency of species per sampling site (stocking of regeneration). The basal samples were sanded and growth rings counted to determine the stand year of origin.
2.5. Stratigraphy and Chronology
Prior to specific analyses, sediments were cleaned and cut into continuous 1-cm thick slices. The general composition of the organic matrix (Sphagnum, herbaceous, brown mosses, wood remains) was determined qualitatively from analysis of subsamples [43,44]. A total of 20 samples were subjected to radiocarbon dating by accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS). They were first prepared in the radiochronology laboratory of Université Laval’s Centre for Northern Studies, then dated at Kerk Laboratory, University of California (Irvine). Dated samples consist of charcoal fragments, with the exception of one sample from the base of the Aspen sedimentary core (seeds). CALIB 7.0.4 software and the IntCal13 database [45,46] were used to determine the probability distributions in calibrated years for each of the 14C datings (±2σ). The median of the probability distribution was selected as the calibrated date. Dated charcoal fragments with overlapping calendar age distributions were considered as originating from the same fire [25]. Net vertical peat accumulation rates (mm·year−1) were calculated between calibrated dates. The models were developed using CLAM 2.2 software [47], applying a linear interpolation between each level dated (1000 iterations). All results are expressed as calibrated years BP.
2.6. Macrocharcoal Analysis
The fire history of forests surrounding the two peatlands was reconstructed by charcoal analysis following a modified version of the procedure used by Hörnberg et al. [48]. Subsamples (2 cm3) were taken at 2 cm intervals and soaked in a potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution (5%) for 24 h, then sieved through a 0.425 mm mesh screen. The remaining particles were bleached in a sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) solution (10%) to distinguish charcoal from dark organic matter. Charcoal particles were counted in a petri dish using a stereomicroscope (20× magnification). They were picked from the petri dish, placed in weighing boats and oven-dried overnight (±50 °C). The mass of charcoal (anthracomass) was determined for each sample using an electronic balance, and data are expressed as anthracomass (mg·2 cm−3) [49,50].
2.7. Reconstruction of Vegetation History
To reconstruct vegetation history, 1 cm3 subsamples (3 cm3 in the upper portion of the cores corresponding to the acrotelm of the peatlands) were collected for pollen analyses. Analyses were conducted at 2 cm intervals for sections with high charcoal content (as determined by prior charcoal analysis) and at 4 cm intervals for sections with low charcoal content. Subsamples, as well as two samples of surface moss, were processed using chemical treatments with KOH (10%), HCl (10%) and an acetolysis solution [51]. Lycopodium tablets with a known concentration were added to each subsample prior to preparation, in order to calculate pollen concentration (grains cm−3). Pollen counts were made at 400× magnification. At least 300 grains of terrestrial vascular plant pollen (excluding Ericaceae and Cyperaceae) were counted for each level, using an optical microscope (400× magnification). Results are expressed in percentages. The curves of only the most abundant pollen taxa are presented in the diagrams. The diagrams were subdivided into pollen assemblage zones (PAZ) using the stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis CONISS program of Tilia software [52]. Percentages were first transformed by a square root, in order to increase the importance of rare or poorly represented taxa (e.g., Populus) and to reduce the importance of those strongly represented (e.g., Betula).
To synthesize changes in vegetation through time, principal component analysis (PCA) was used on the combined Aspen and Shadow pollen datasets. Because the variables are dimensionally homogeneous, a dispersion (variance/covariance) matrix was used [42,53]. The number of pollen types was reduced by selecting taxa with a value greater than or equal to 1% in at least one sample, and creating a collective category among the pollen types (herbs). Cyperaceae and Ericaceae pollen were excluded. This selection resulted in 11 pollen types. For PCA, the relative frequencies (in percent) of the pollen types were square-root transformed. This transformation was performed in order to optimize the signal-to-noise ratio and stabilize the variances. PCA calculations were performed using R software version 3.2.2 (http://cran.r-project.org/).
3. Results
3.1. Contemporary Forest Landscapes of the Study Area
In order to understand the distribution and the dynamic of the vegetation and to select the most appropriate landscape for the paleoecological reconstruction, the study area (4000 km2) was divided into eight landscapes (Figure 3; Table S1). Each shows specific characteristics in regard to forest composition, altitude, surficial deposit, slope, drainage and fire period of origin. The landscapes are mainly distributed along an eastward altitudinal gradient (225–250 to 300–375 m) corresponding to an increase of relatively well-drained forests on clay. Along the gradient, the proportion of slopes higher than 4% increases continuously, whereas the area covered by open peatlands decreases. Landscape P4b (553 km2) was selected because it contains the highest proportion of stands dominated or sub-dominated by early successional species (mainly Populus tremuloides). Stands composed mainly of Picea mariana and growing on mineral soils are abundant. Clay covers a large part of it, and drainage is mainly mesic or subhydric. Altitude varies from 275 to 300 m. The majority of forest stands originated from fires of the 1910 period. Late successional Picea mariana-moss and Abies balsamea stands originating mainly from fires of the 1820 period are very rare (less than 2%), and landscape P3 contains the highest proportion of this last community (close to 10%; Table S1).
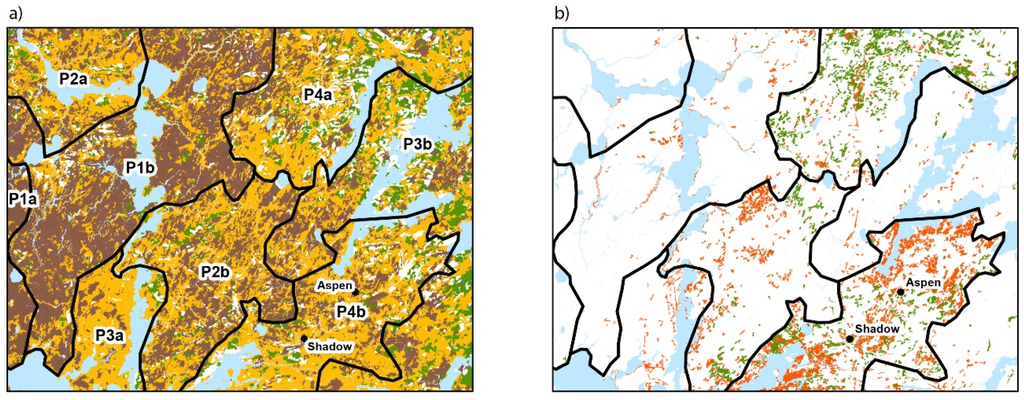
Figure 3.
Delineation of the boundaries of the landscapes (P1–P4) in the study area. (a) Distribution of the surface deposits: organic deposits (brown), clay (orange) and till (green); (b) Distribution of the forest stands dominated by Populus tremuloides (orange) and Pinus banksiana (green). Aspen and Shadow peatlands are located in landscape P4b. The information on surficial deposits and forest cover was compiled from QMFFP forest maps. The description of the landscapes is presented in Table S1.
3.2. Contemporary Forest Surrounding the Two Peatlands Studied
The contemporary forests surrounding the Aspen and Shadow peatlands developed following a fire that occurred in 1917. The forest bordering Aspen is deciduous, dominated by Populus tremuloides and subdominated by Picea mariana, whereas Pinus banksiana is sparse (Figure 4). The number of P. tremuloides stems greater than 10 cm in diameter is close to 700 ha−1 whereas the basal area approaches 30 m2·ha−1. Regeneration essentially consists of P. mariana (stocking of 70%). The shrubs Alnus alnobetula subsp. crispa (Aiton) Raus and Alnus incana subsp. rugosa (Du Roi) R.T. Clausen) are abundant (90%). The pollen assemblage of the surface moss sample is mainly dominated by Picea (43%), P. banksiana (36%), Alnus (10%) and Betula (5%) (Table 1). Although P. tremuloides is dominant in the forest, it is entirely absent from the pollen assemblage. The forest surrounding Shadow is mixed. The number of stems belonging to the 10 cm diameter class or greater is on the order of 300 ha−1 for P. mariana, 200 for P. tremuloides and 100 for P. banksiana. The basal area of each of these three species is 10 m2·ha−1. Undergrowth vegetation is dominated by Alnus (stocking of 80%). Forest regeneration is sparse, with a few P. tremuloides (10%) and P. mariana (5%); the P. mariana regeneration is far less abundant than at Aspen. The pollen assemblage of the moss sample collected in the Picea mariana-Abies balsamea stand situated about 10 km north of Aspen (landscape P3b; Figure 3) primarily consists of Picea (49%), P. banksiana (23%), Alnus (12%), Betula (10%) and Abies balsamea (2%) (Table 1). In this landscape, P. mariana-A. balsamea stands cover close to 5% of the surface area (Table S1).
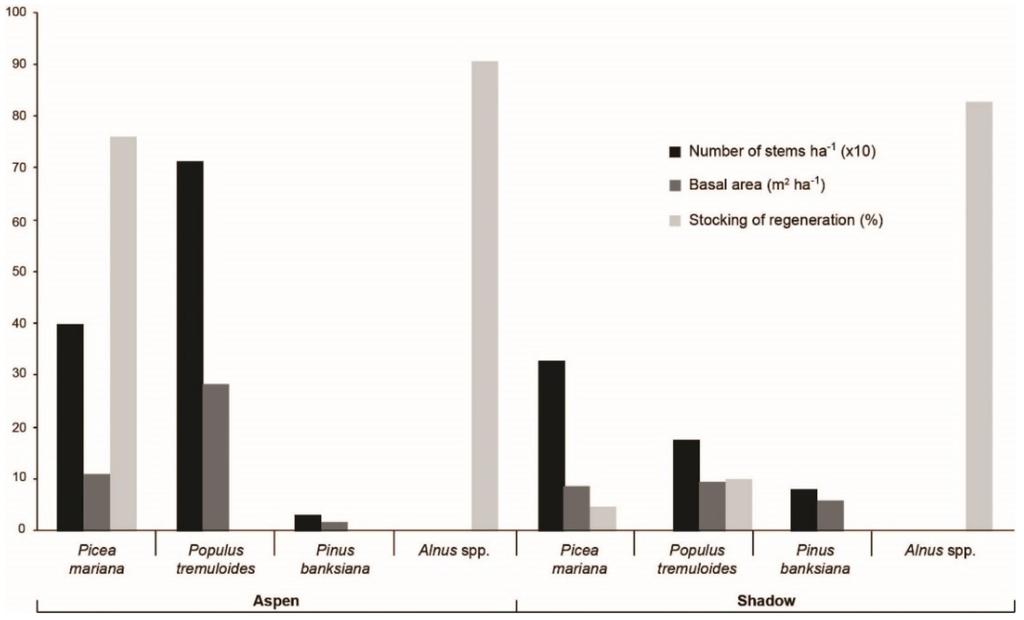
Figure 4.
Characteristics of the contemporary forests surrounding Aspen and Shadow peatlands.

Table 1.
Pollen representation (selected species) of current vegetation of two stands in the study area. The first stand is located in the forest close to Aspen peatland. The second is located in landscape P3b (Figure 3).
3.3. Stratigraphy and Chronology of Sedimentary Cores
At Aspen, the peat lies on clay and is 134 cm thick at the sampling point (Figure 5). At the base, a peat composed of brown mosses (134–110 cm) is overlain by peat that is a mixture of Sphagnum and herbaceous remains (110–40 cm) and poorly decomposed Sphagnum (40–0 cm). A date of 7990 BP was obtained for the onset of peat accumulation (Table 2, Figure 5). After a first period (7990–5370 BP) during which the sedimentary accumulation rate averaged 0.18 mm·year−1, the rate remained low until very recently (5370–290 BP; 0.03–0.14 mm·year−1). At Shadow, the peat is 96 cm thick at the sampling point. The matrix consists essentially of Sphagnum with numerous wood remains. A charcoal fragment from the point of contact with clay was dated to 4110 BP. The numerous pieces of wood found at the organo-mineral contact during excavation of the trench suggest that the late initiation of peat inception at the sampling point is linked to a process of paludification of an ancient forest originally present locally. The sedimentary accumulation rate was variable over time (0.07 to 0.37 mm·year−1). The very high rate of accumulation in the upper portion of samples from both peatlands is the result of less compaction and decomposition of the peat compared to that at lower levels. No charred layer resulting from a fire in situ that could have caused a hiatus in sediment accumulation was observed.
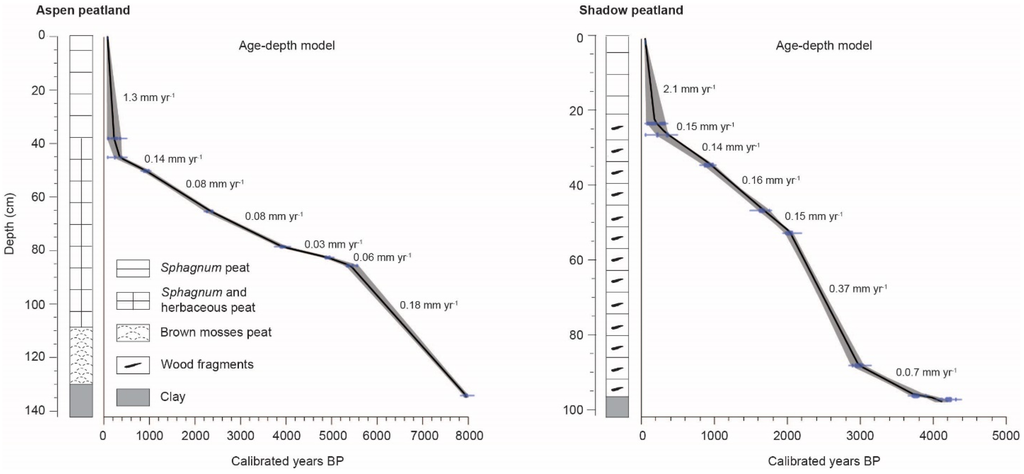
Figure 5.
Stratigraphy and age-depth model of the sedimentary cores collected at the Aspen and Shadow peatlands.

Table 2.
Radiocarbon ages from Aspen and Shadow peatlands, calibrated with an IntCal13 calibration curve [46] using Calib software version 7.0.4 [45] or Clam [47].
3.4. Reconstruction of the Fire History
Based on data from the anthracomasses and radiocarbon dates of the two sedimentary cores, at least eight fires were identified at Aspen and Shadow. For both peatlands, some successive layers are characterized by high charcoal concentrations. At Aspen (Figure 6), four of the eight dated fires occurred before 2000 BP (5370, 4910, 3880 and 2330 BP), and four in the last 1000 years (880–840, 290, 180 and 50 BP). Some charcoals were found at a depth of about 60 and 92 cm, but were too small and too few to make dating possible. At Shadow (Figure 7), three of the eight fires occurred before 2900 BP (4110, 3680 and 2900 BP), and the five others were dated from 1960, 1670, 1550–1580, 835, 300 and 100 BP. Only the last millennium registered relatively synchronous fires between the two sites, specifically those dating from 880–840 (Aspen) and 835 BP (Shadow), 290 BP (Aspen) and 300 BP (Shadow), as well as 50 BP (Aspen) and 100 BP (Shadow). The most recent 14C dates are related to dendrochronological data: the date of 180 BP (Aspen) is associated to fires of the 1820 period, and those of 100 and 50 BP to fires of the 1920 period.
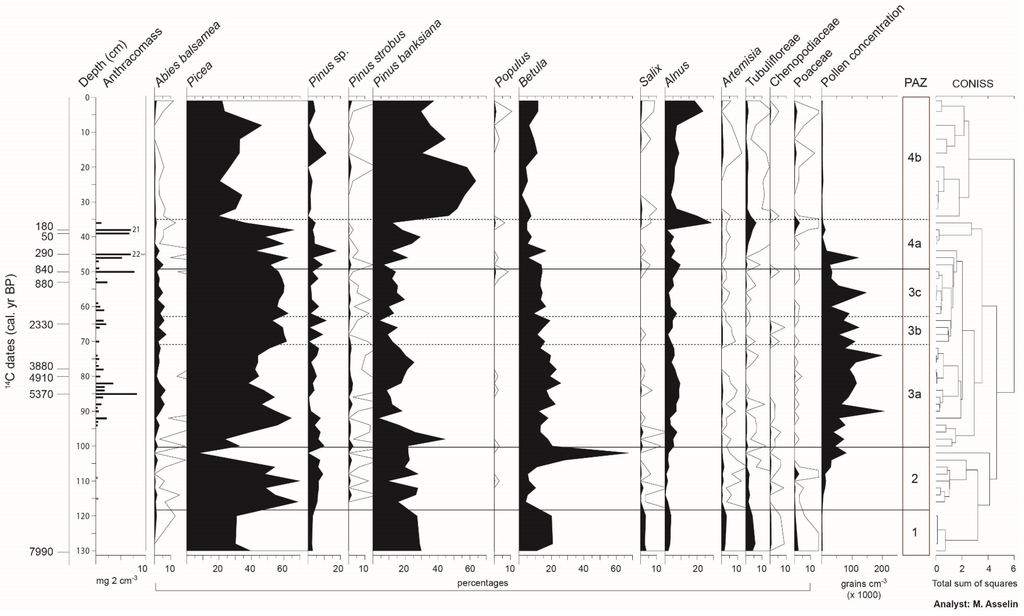
Figure 6.
Pollen diagram (percentages; selected taxa) and charcoal content (mg·2 cm−3) of the sedimentary core collected at Aspen peatland. Open curves show a 10× exaggeration.
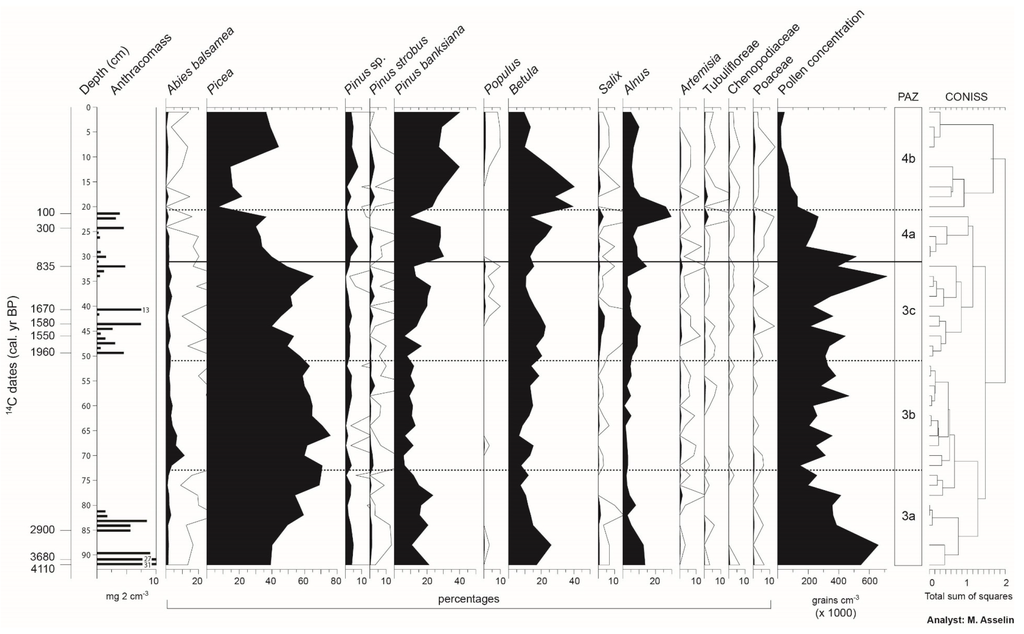
Figure 7.
Pollen diagram (percentages; selected taxa) and charcoal content (mg·2 cm−3) of the sedimentary core collected at Shadow peatland. Open curves show a 10× exaggeration.
3.5. Vegetation History
Four pollen assemblage zones (PAZs 1 to 4) can be defined in the pollen diagrams of the two sites (Figure 6 and Figure 7). The sedimentary core collected at Aspen covers a longer period (8000 years) than that from Shadow (4100 years); this is why PAZs 1 and 2 (the oldest zones) are observable only in the diagram of the former. In PAZ 1 (ca. 8000 to ca. 7600 BP), at the base of the Aspen diagram, the pollen assemblages are relatively rich in herbaceous taxa (Artemisia, Tubuliflorae, Chenopodiaceae, Poaceae) and shrubs (Salix, Alnus). Arboreal taxa are primarily represented by Picea (probably Picea mariana), Pinus banksiana and Betula. The Betula pollen in this zone could be a mixture of Betula papyrifera and the shrubby species Betula glandulosa Michaux. The low pollen concentrations suggest that this first stage in plant colonization after the retreat of postglacial Lake Ojibway was characterized by open forests (afforestation period). PAZ 2 (ca. 7600 to ca. 6800 BP) shows a gradual increase of pollen concentrations and a decline in the representation of herbaceous taxa, interpreted as a signal of a densification of the forest cover. Pollen assemblages are essentially dominated by Picea (40%–50%) and P. banksiana (20%–30%). Maximum values are recorded for Betula (50%–60%) at the summit of the zone.
PAZ 3 (ca. 6800 to ca. 780–735 BP) of both diagrams covers a long period during which Abies balsamea is well represented (maximum: 10%), as is Picea (45%–65%). This zone is divided into three subzones. Subzone 3a extends over more than 3000 years (ca. 6800 to ca. 3100 BP at Aspen; >ca. 2600 BP at Shadow). It shows relatively high percentages of Pinus banksiana, Betula and Alnus. In subzone 3b (ca. 3100–2200 BP at Aspen; ca. 2600–2000 BP at Shadow), a drop in the pollen representation of P. banksiana and Alnus can be noted. Finally, subzone 3c (ca. 2200–2000 to ca. 780–735 BP) is characterized by a slight increase of P. banksiana (Aspen) and P. banksiana and Alnus (Shadow).
On both sites, PAZ 4 corresponds to the last ca. 800 years, and can be divided into two subzones: 4a (ca. 780–745 to ca. 160–115 BP) and 4b (<ca. 160–115 BP). Pollen concentrations are very low because Sphagnum peat in the top section is less decomposed and less compact, which dilutes the pollen in the peat. The pollen representation of Abies balsamea declines from the base to the summit of subzone 4a, then drops in subzone 4b, particularly in the diagram of Aspen. In both diagrams, the beginning of subzone 4b is marked by a notable increase of Pinus banksiana (>40% at Aspen; >30% at Shadow), and the species reaches its maximum percentage in this subzone.
The major trend of the PAZs for both sites was compared objectively by applying principal component analysis (PCA) to the combined Aspen and Shadow pollen datasets. The first axis of PCA accounts for 42.0% of the variance within data and represents the major vegetation gradient (Figure 8a). High (positive) PCA axis 1 scores are driven by Pinus banksiana, Alnus and Betula, three early successional species in these landscapes, whereas low (negative) PCA axis 1 scores are driven by Picea and Abies balsamea (Figure 8b), two late successional species. The trend in PCA axis 1 scores for the Shadow site is similar to that for the Aspen site. The four PAZ are also highlighted by axis 1. At Shadow and Aspen, there is a pronounced change at about 100–150 BP (PAZ 4b/4a). The change is more gradual at Shadow but more abrupt at Aspen. From ca. 2500 BP to today, a linear trend can be observed in PCA axis 1 scores. This trend is best evidenced at Shadow, which is situated closer to the forest. There is a gradual transition from negative to positive scores, showing that P. banksiana was increasing to the detriment of A. balsamea and Picea.
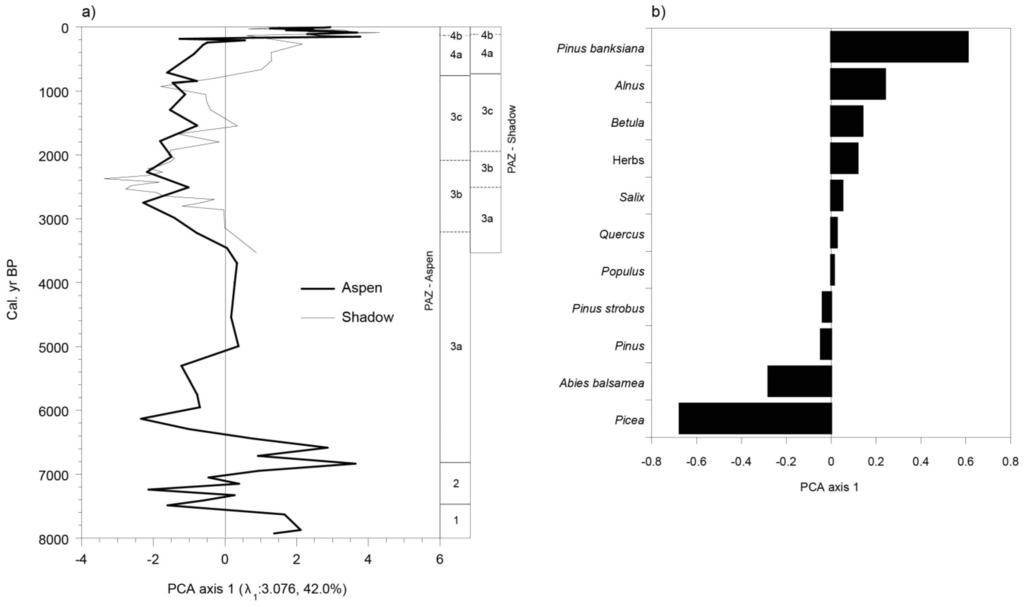
Figure 8.
Principal component analysis (PCA) results for the combined pollen assemblages of Aspen and Shadow sites. (a) Stratigraphic plot of PCA axis 1 sample scores for the Aspen and Shadow sites over time. Horizontal lines separate pollen assemblage zones (PAZs). The first eigenvalue and percentage of variance are given; (b) PCA axis 1 variable loadings.
4. Discussion
This study presents the long-term natural variability (fire and vegetation) of a portion of the Picea mariana-moss bioclimatic domain belonging to Québec’s Clay Belt. This variability has been described through paleoecological analysis of sediment cores from two bogs 10.5 km apart, located in a forested landscape dominated by early successional species (Populus tremuloides, Pinus banksiana, Picea mariana). The sediment core from Aspen (100 m from the forest) provides a continuous history (vegetation and fire events) of 8000 years, whereas that from Shadow (25 m from the forest) covers a period of 4000 years. The results increase our knowledge about the Holocene history (fire and vegetation) of western Québec boreal forests, mainly based on paleoecological studies of lake sediments. The results from the two peatlands support our initial hypothesis specifying that increased fire activity during the late Holocene on mesic-subhydric clay promoted the development and maintenance of early successional species through a fire recurrence dynamic. Four main periods were recognized in the long-term vegetation and fire history of the forests surrounding our study sites. For each, we compare our results with those of lakes studied in western Québec Picea mariana-moss and Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera domains (Figure S1; Table S2). These lakes are located in low-altitude landscapes dominated by peatlands (Pessière, Geais, Profond, Raynald, Loutre, Garot), in mid-altitude landscapes with undulated clay (Cèdres, Schön, Francis, Pas de Fond) and relatively high-altitude landscapes with undulated till (Twin, Richard, Aurélie, Nans). The latter are located to the east of our study area, near Lake Mistassini.
4.1. The Afforestation Phase (ca. 8000 to ca. 6800 BP)
At Aspen, only a few isolated charcoal pieces were found in the sediments that represent the period between the beginning of vegetation colonization following the draining of the waters of proglacial Lake Ojibway (ca. 8000 BP) and the densification of the forest cover (forest phase) around 6800 BP. The rarity of charcoal during this first period corresponding to afforestation (PAZs 1 and 2) can be linked to the low initial density of the forest, which may have been too sparse to support recurrent fire activity. At Aspen, the presence of brown mosses and seeds of Menyanthes trifoliata Linnaeus indicates minerotrophic and water-saturated soil at the time and supports the hypothesis that the very humid local conditions present initially could have prevented fires from propagating toward the center of the peatland. The reconstructions of fire history from lake sediments in western Québec Picea mariana-moss domain also suggest a low fire frequency during the afforestation phase [10].
4.2. A Landscape Dominated by Late and Early Successional Forest Stands (ca. 6800 to ca. 2500 BP)
The beginning of the forest phase at Aspen (ca. 6800 BP; PAZ 3a) is marked by an increase in the pollen representation of Abies balsamea, a late successional species that is generally under-represented in pollen assemblages [54]. Until 2500 BP, at least four fires occurred in the surrounding forests (5370, 4910, 3880 and 2330 BP). The presence of smaller quantities of charcoal fragments at other levels of the core indicates that it may be possible that other fires occurred during this period. In the forests bordering Shadow, fires occurred at dates different from those at Aspen (4110, 3680, 2900 BP). Since the two sites are only 10.5 km apart, this asynchronism suggests that the fires covered small areas and were not severe. We hypothesize that this type of fire regime promoted the development of Picea mariana-Abies balsamea stands. Early successional species (Betula papyrifera, Pinus banksiana, Alnus spp.) were also well represented in the pollen diagrams, suggesting that the landscapes were composed of stands belonging to late and early successional stages. Our results concerning the fires differ from those based on lake sediments which show a relatively high fire frequency (expressed by a number of fires per millenium). However, there is a wide variation in the maximum frequency of fires and the period during which this rate was maintained [10,15,27,31,34].
4.3. Landscapes Dominated by Picea mariana and Abies balsamea (ca. 2500 to ca. 2100 BP)
Anthracomass values for the period corresponding to ca. 2500 to ca. 2100 BP (PAZ 3b) are low at Aspen, whereas no charcoal particles were found at Shadow. The pollen representation of Abies balsamea is still relatively high, whereas that of Pinus banksiana, Betula and Alnus spp. drops. It is estimated that this period corresponds to a dominance of Picea mariana and A. balsamea forests in the studied landscape, and perhaps in the majority of landscapes belonging to Québec’s Clay Belt. The reconstructions of fire history from lake sediments in the western Picea mariana-moss domain also show a general decrease in fire frequency during this period, but with a certain variability among sites [10,28,31,34].
4.4. Increase of Early Successional Species (ca. 2100 to ca. 800 BP)
Anthracomass values for the period corresponding to ca. 2100 to ca. 800 BP are relatively low at Aspen (PAZ 3c). They are higher at Shadow, however, where three fires occurred in a short lapse of time (1960, 1670 and 1580–1550 BP). The pollen representation of Abies balsamea remains constant, while an increase of Pinus banksiana, Betula and Alnus is observed, especially at Shadow. An increase of P. tremuloides is not evident in the two pollen diagrams because this species is strongly under-represented in pollen assemblages [55]. The variability of fires and vegetation observed between the two peatlands also characterizes lake sites. Fire frequency is relatively high around ca. 1000 BP for some lakes (Profond, Raynald, Richard and Nans; Figure S1) but low for others (Geais, Loutre, Twin, Aurélie). These differences could be associated with the short duration of the Medieval Warm Period, which caused a varied fire pattern in the western portion of Picea mariana-moss domain [28]. Differences in physical features probably do not explain this variability because lakes with high and low fire frequency are located both in peatlands (Profond, Raynald, Geais, Loutre) and till environments (Richard, Nans, Twin, Aurélie).
4.5. More Severe Fires Favored the Development of Landscapes Dominated by Early Successional Species (from 800 BP to the Present-Day)
In the last 1000 years, three of the four dated fires recorded at Aspen and Shadow appear to have affected the two sites simultaneously (840/880–835, 290–300, 50–100 BP). Another fire (180 BP) was only recorded at Aspen. The fact that the forests surrounding the two peatlands were affected by the same fires on three occasions strongly suggests that they once covered wider areas and were more severe than those of the previous periods. In this region, two fire periods that were both severe and extended over a wide area occurred recently, in the 19th (ca. 1820) and 20th (ca. 1910) centuries [7,40]. The fire dating from 180 BP (Aspen) would correspond to ca. 1820, and the fire dating from 50–100 BP to ca. 1910. The link between the recent fires that occurred in the forest bordering the two peatlands and the deposition of charcoal in organic sediments is therefore well-established, suggesting that the same process characterized all of the Holocene period [56], at least in the case of large and severe fires. The fires occurring in our study area (4000 km2) and in the ‘Plaine du lac Matagami’ during the last two centuries are considered natural because this region was sparsely inhabited until recently. The village of Matagami (Figure 1) was founded only in 1963 to open access to the James Bay hydroelectric reservoirs. The fires of the 1910 period are so widely distributed in the western Picea mariana moss domain that any possible role played by Aboriginal peoples living in the area during this fire period would have been minor [2].
The fires of the 19th and 20th centuries may have played an important role in the decrease of A. balsamea as shown on the two pollen diagrams of Aspen and Shadow (Figure 6 and Figure 7). The relative abundance of Abies balsamea until recently is different from the proposed fragmentation of Abies balsamea forests initiated as early as 3500 BP [57]. During the last millennium, the pollen assemblages of Aspen and Shadow are dominated by Pinus banksiana and are at their highest level on the scale of the last 8000 years. An increase of Pinus banksiana in the two last centuries is also recorded elsewhere, notably at Schön Lake located close to the studied peatlands [15]. This recent dominance of early successional species is summarized in Figure 8, where positive scores of the first ordination axis are reported.
Most of the lake sediments studied by previous authors, and located in a peatland environment (Pessière, Geais, Profond, Raynald, Loutre, Figure S1), show a decrease in fire frequency during the last or two last millennia [10,31,34]. However, some lakes indicate an increase in fire frequency during this period in the western Picea mariana-moss domain. This is the case of Schön Lake, located close to the studied peatlands, to the north, in an environment dominated by clay [15,34] (Figure S1). Remy et al. [15] suggest that fire frequency increased since 2000 BP in the western Picea mariana moss (lakes Garot, Schön, Figure S1) and Picea mariana lichen (lakes Loup, Nano, Trèfle, Marie-Ève) domains. Most of these lakes are located in an environment with well-drained surficial deposits; Garot Lake, with an environment dominated by peatlands, is the only exception. Recent methodological advances in fire event reconstruction may lead to new results, and mainly at the extremities of the sediment core [58]. For example, while Ali et al. [10] show a decrease in fire frequency during the last 2000 years BP at Lake Geais, Oris et al. [34] indicate an increase since 1000 years BP for the same lake. An increase of fire frequency has been observed at lakes Francis and Pas de Fond, located in the Clay Belt portion of the western Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera bioclimatic domain [37,38] (Figure S1). Both lakes are associated with a very marked cut ca. 2000 BP, characterized by the transition from a fire frequency higher than 200 years to less than 200 years. Thus, a higher fire incidence in the last millennia could characterize the entire Québec Clay Belt regardless of bioclimatic domain. All these fire activities and climate conditions led to landscapes dominated by early successional species, mainly Pinus banksiana and Populus tremuloides (Figure 9) [59,60].
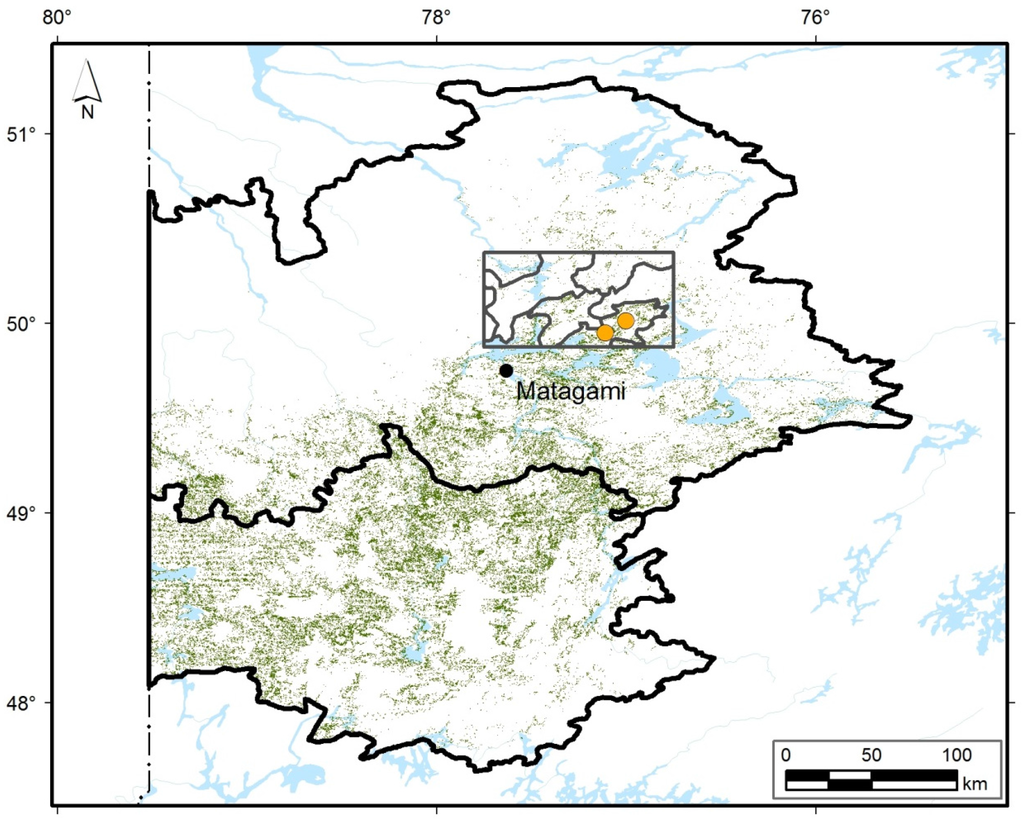
Figure 9.
Forest stands dominated by Populus tremuloides on clay (green) in ecological region 6a-Plaine du lac Matagami (Picea mariana-moss domain, upper part) and 5a-Plaine du lac Abitibi (Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera domain, lower part). The study area (rectangle), the landscapes delineated in this area (n = 8) and the two studied peatlands (orange points) are illustrated.
Finally, does the last millennium, particularly the last two centuries, correspond to a Holocene period characterized by a decrease in fire occurrence and severity, or does this period constitute the most important period of the entire Holocene in regard to large and severe fires? It may be that, during the recent millennia, landscapes dominated by peatlands show a fire decrease while those composed mainly of clay or other mineral soils an increase. The answer could lie in the type of surficial deposit (peatland vs. clay and other mineral soils) rather than the bioclimatic domain (Picea mariana vs. Abies domains) [8,11].
4.6. Contemporary Forest Dynamics
The forests bordering the two peatlands and the entire landscape studied (P4b, Figure 3) were strongly affected by contemporary fires. We estimate that the fires of the last millennia favoured a recurrence dynamic of Populus tremuloides, Pinus banksiana and Picea mariana stands. Today, forest regeneration is mainly composed of P. mariana accompanied by some P. tremuloides. Based on this type of regeneration, the forests should evolve towards mature P. mariana-P. tremuloides stands [22]. Abies balsamea is presently rare in the landscapes dominated by early successional forests, and this is probably a response to the two close and severe fire periods (1820–1910) that occurred in less than 200 years. If sufficient time elapses before the next fire occurs (approximately 200–250 years) [18], Abies could reach maturity and regenerate abundantly. Late successional forests dominated by Picea mariana and Abies balsamea, such as those that characterized the landscape during the Holocene (ca. 6800 to ca. 800 BP), could thus form once again. However, this possibility remains unlikely in the context of climate change because an increase in frequency and severity of fires is predicted for the western Québec Picea mariana-moss domain [32,33,60].
5. Conclusions
This study carried out in Québec’s Clay Belt (Canada) provides new knowledge about the role of forest fires in landscapes dominated by early successional species (Populus tremuloides, Pinus banksiana, Picea mariana) during the last millennia. More severe and extensive fires stimulated the development and the continuity of these forests through a recurrence dynamic. Such a fire regime differs from that which prevailed for thousands of years during the Holocene, and allowed the growth of the late successional P. mariana and Abies balsamea forests in the western Picea-mariana-moss domain. This information on long-term natural variability provides insights that can guide the development and implementation of sound, ecosystem forest and fire management plans in the context of climate change.
Our study opens the door to the possibility that two types of fire regimes occurred during the Holocene in Québec’s Clay Belt: the first, defined by a decrease in fire frequency during the late Holocene, characterized landscapes dominated by peatlands. The second shows an increase of fires over the last millennium and is related to landscapes mainly formed by mesic-subhydric clays. This second regime could characterize the entire Québec Clay Belt, regardless of bioclimatic domain (Picea mariana-moss and Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera). In order to demonstrate the presence of these two regimes, studies coupling analysis of lake sediments, peatlands and mineral soils should be conducted jointly in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/1999-4907/7/9/205/s1. Figure S1. Delimitation of the study area in western Québec’s Picea mariana-moss bioclimatic domain, Canada, and in ecological region 6a (Plaine du lac Matagami). Ecological region 5a (Plaine du lac Abitibi) is part of the western Abies balsamea-Betula papyrifera bioclimatic domain. The long transect with oblique lines located close to the border with Ontario corresponds to the fire origin map created by Bergeron et al. [7]. The red dots indicate the clay distribution according to QMFFP forest maps. This clay corresponds to the Québec Clay Belt. Codes with a P (peatland) or an L (lakes) correspond to paleoecological studies considered in this study. AP: Aspen peatland, SP: Shadow peatland, LA: Lake Aurélie, LCE: Lake Cèdres, LF: Lake Francis, LGA: Lake Garot, LGE: Lake Geais, LL: Lake Loutre, LN: Lake Nans, LPE: Lake Pessière, LPF: Lake Pas de Fond, LPR: Lake Profond, LRA: Lake Raynald, LRI: Lake Richard, LS: Lake Shön, LT: Lake Twin. Table S1. Description of the eight forest landscapes delineated in the study area (Figure 3). The two peatlands studied are located in landscape P4b. Results are expressed in relative importance of surface area. Table S2. Description of the contemporary vegetation surrounding the lakes studied in the western part of Québec’s boreal forest. The description is based on QMFFP maps and considers a 15 km2 radius around each lake or peatland.
Acknowledgments
This research received financial support through grants from the Fonds de recherche du Québec—Nature et technologies (FRQNT). Scholarships to M. Asselin were provided by Mitacs-Accélération Québec. The authors would like to thank A. Delwaide, M. Bourgon-Desroches, V. Poirier and J. Noël for their technical contributions. A. Ali contributed advice regarding the analysis and interpretation of fire history from lacustrine sediments. He also authorized us to use the pollen and charcoal data of the lakes he studied in western Québec. The English translation of the text was revised by K. Grislis and G. Mercier. We extend our thanks to two anonymous reviewers and the two Academic Editors (S. Gauthier, Y. Bergeron) whose suggestions helped to greatly improve this manuscript.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to all aspects of the work, including designing the experiments, analyzing the data, and writing the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- White, P.S. Pattern, process, and natural disturbance in vegetation. Bot. Rev. 1979, 45, 229–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grondin, P.; Gauthier, S.; Borcard, D.; Bergeron, Y.; Noël, J. A new approach to ecological land classification for the Canadian boreal forest that integrates disturbances. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojar, J.; Klinka, J.; Meidinger, D.V. Biogeoclimatic ecosystem classification in British-Columbia. For. Ecol. Manag. 1987, 22, 119–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucier, J.P.; Grondin, P.; Robitaille, A.; Gosselin, J.; Morneau, C.; Richard, P.J.H.; Brisson, J.; Sirois, L.; Leduc, A.; Morin, H.; et al. Écologie Forestière. In Manuel de Foresterie, 2nd ed.; Éditions MultiMondes: Québec, QC, Canada, 2009; pp. 165–316. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, J.S.; Scotter, G.W. Fire in the boreal forest. Quat. Res. 1973, 3, 444–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackrisson, O. Influence of forest fires on the North Swedish boreal forest. Oikos 1977, 29, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, Y.; Gauthier, S.; Flannigan, M.; Kafka, V. Fire regimes at the transition between mixedwood and coniferous boreal forest in northwestern Québec. Ecology 2004, 85, 1916–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.A.; Hollis, J.L.; Hu, F.S. Climatic and landscape control of the boreal forest fire regime: Holocene records from Alaska. J. Ecol. 2004, 92, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyr, D.; Bergeron, Y.; Gauthier, S.; Larouche, A.C. Are the old growth forests of the Clay Belt part of a fire-regulated mosaic? Can. J. For. Res. 2005, 35, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Carcaillet, C.; Bergeron, Y. Long-term fire frequency variability in the eastern Canadian boreal forest: The influences of climate vs. local factors. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuy, N.; Gauthier, S.; Robitaille, A.; Bergeron, Y. The effects of surficial deposit–drainage combinations on spatial variations of fire cycles in the boreal forest of eastern Canada. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2010, 19, 1083–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genries, A.; Finsinger, W.; Asnong, H.; Bergeron, Y.; Carcaillet, C.; Garneau, M.; Hély, C.; Ali, A.A. Local versus regional processes: Can soil characteristics overcome climate and fire regimes by modifying vegetation trajectories? J. Quat. Sci. 2012, 27, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuosmanen, N.; Fang, K.; Bradshaw, R.H.W.; Clear, J.L.; Seppa, H. Role of forest fires in Holocene stand-scale dynamics in the unmanaged taiga forest of northwestern Russia. Holocene 2014, 24, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senici, D.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Bergeron, Y.; Ali, A.A. The effects of forest fuel connectivity on spatiotemporal dynamics of Holocene fire regimes in the central boreal forest of North America. J. Quat. Sci. 2015, 30, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, C.C.; Lavoie, M.; Girardin, M.; Hély, C.; Bergeron, Y.; Grondin, P.; Oris, F.; Asselin, H.; Ali, A.A. Wildfire size alters long-term vegetation trajectories in boreal forests of eastern North America. J. Biogeogr. In press.
- Landres, P.B.; Morgan, P.; Swanson, F.J. Overview of the use of natural variability concepts in managing ecological systems. Ecol. Appl. 1999, 9, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Kuuluvainen, T. Natural variability of forests as a reference for restoring and managing biological diversity in boreal Fennoscandia. Silva Fenn. 2002, 36, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.; Vaillancourt, M.A.; Leduc, A.; de Grandpré, L.; Kneeshaw, D.; Morin, H.; Drapeau, P.; Bergeron, Y. Aménagement Ecosystémique en Forêt Boréale; Presses de l’Université du Québec: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Conedera, M.; Tinner, W.; Neff, C.; Meurer, M.; Dickens, A.F.; Krebs, P. Reconstructing past fire regimes: Methods, applications, and relevance to fire management and conservation. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2009, 28, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyr, D.; Gauthier, S.; Bergeron, Y.; Carcaillet, C. Forest management is driving the eastern North American boreal forest outside its natural range of variability. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogbill, C.V. Dynamics of the boreal forests of the Laurentian Highlands, Canada. Can. J. For. Res. 1985, 15, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, J.; Berger, J.-P. Guide de reconnaissance des types écologiques de la région écologique 6a-Plaine du lac Matagami et 6b-Plaine de la baie de Rupert; ministère des Ressources naturelles et de la Faune, Direction des inventaires forestiers, Division de la classification écologique et productivité des stations: Québec, QC, Canada, 2005.
- Frelich, L.E.; Reich, P.B. Spatial patterns and succession in a Minnesota southern-boreal forest. Ecol. Monogr. 1995, 65, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, A.M. Environmental changes during the past 2000 years in north-central Wisconsin: Analysis of pollen charcoal and seeds from varved lake sediments. Quat. Res. 1978, 10, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frégeau, M.; Payette, S.; Grondin, P. Fire history of the central boreal forest in eastern North America reveals stability since the mid-Holocene. Holocene 2015, 25, 1912–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blarquez, O.; Ali, A.A.; Girardin, M.P.; Grondin, P.; Fréchette, B.; Bergeron, Y.; Hély, C. Regional paleofire regimes affected by non-uniform climate, vegetation and human drivers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.A.; Blarquez, O.; Girardin, M.P.; Hély, C.; Tinquaut, F.; El-Guellab, A.; Valsecchi, V.; Terrier, A.; Bremond, L.; Genries, A.; et al. Control of the multimillenial wildfire size in boreal North America by spring climatic conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20966–20970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Guellab, A.; Asselin, H.; Gauthier, S.; Bergeron, Y.; Ali, A.A. Holocene variations of wildfire occurrence as a guide for sustainable management of the northeastern Canadian boreal forest. For. Ecosyst. 2015, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viereck, L.A. Wildfire in the taiga of Alaska. Quat. Res. 1973, 3, 465–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, A.E.; Gajewski, K. Reconstructing millennial-scale, regional paleoclimates of boreal Canada during the Holocene. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hély, C.; Girardin, M.P.; Ali, A.A.; Carcaillet, C.; Brewer, S.; Bergeron, Y. Eastern boreal North American wildfire risk of the past 7000 years: A model-data comparison. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L14709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardin, M.P.; Ali, A.A.; Carcaillet, C.; Gauthier, S.; Hély, C.; Le Goff, H.; Terrier, A.; Bergeron, Y. Fire in managed forests of eastern Canada: Risks and options. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 294, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardin, M.P.; Ali, A.A.; Carcaillet, C.; Blarquez, O.; Hély, C.; Terrier, A.; Genries, A.; Bergeron, Y. Vegetation limits the impact of a warm climate on boreal wildfires. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oris, F.; Asselin, H.; Finsinger, W.; Hély, C.; Blarquez, O.; Ferland, M.E.; Bergeron, Y.; Ali, A.A. Long-term fire history in northern Québec: Implications for the northern limit of commercial forests. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréchette, B.; Richard, P.J.H.; Grondin, P.; Lavoie, M.; Larouche, A.C. Histoire Postglaciaire de la Végétation et du Climat des Pessières et des Sapinières de l’Ouest du Québec; Direction des Inventaires Forestiers, Gouvernement du Québec: Québec, QC, Canada, 2016.
- Environment Canada. National Climate Data and Information Archive. Canadian Climate Normals 1971–2000. 2013. Available online: http://www.climate.weatheroffice.ec.gc.ca (accessed on 17 September 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Carcaillet, C.; Bergeron, Y.; Richard, P.J.H.; Fréchette, B.; Gauthier, S.; Prairie, Y.T. Change of fire frequency in the eastern Canadian boreal forests during the Holocene: Does vegetation composition or climate trigger the fire regime? J. Ecol. 2001, 89, 930–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcaillet, C.; Richard, P.J.H.; Bergeron, Y.; Fréchette, B.; Ali, A.A. Resilience of the boreal forest in response to Holocene fire-frequency changes assessed by pollen diversity and population dynamics. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2010, 19, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.S.; Hardy, L. L’évolution et l’extension des lacs glaciaires Barlow et Ojibway en territoire québécois. Geogr. Phys. Quat. 1977, 31, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, Y.; Gauthier, S.; Kafka, V.; Lefort, P.; Lesieur, D. Natural fire frequency for the Eastern Canadian boreal forest: Consequences for sustainable forestry. Can. J. For. Res. 2001, 31, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, N.; Bergeron, Y. Successionnel pathways on different surficial deposits in the coniferous boreal forest of the Québec Clay Belt. Can. J. For. Res. 2005, 35, 1984–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bhiry, N.; Robert, É.C. Reconstruction of changes in vegetation and trophic conditions of a palsa in a permafrost peatland, subarctic Québec, Canada. Écoscience 2006, 13, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, M.; Filion, L.; Robert, É.C. Boreal peatland margins as repository sites of long-term natural disturbances of balsam fir/spruce forests. Quat. Res. 2009, 71, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuiver, M.; Reimer, P.J. Extended 14C database and revised CALIB radiocarbon calibration program. Radiocarbon 1993, 35, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, P.J.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Beck, J.W.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Buck, C.E.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. INTCAL 13 and MARINE13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0–50,000 years cal BP. Radiocarbon 2013, 55, 1869–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaauw, M. Methods and code for “classical” age-modelling of radiocarbon sequences. Quat. Geochron. 2010, 5, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörnberg, G.; Ohlson, M.; Zackrisson, O. Stand dynamics, regeneration patterns and long-term continuity in boreal old-growth Picea abies swamp-forests. J. Veg. Sci. 1995, 6, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnan, G.; Lavoie, M.; Payette, S. Impact of fire on long-term vegetation dynamics of ombrotrophic peatlands in northwestern Québec, Canada. Quat. Res. 2012, 77, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasin, I.; Blanck, Y.; Storaunet, O.; Rolstad, J.; Ohlson, M. The charcoal record in peat and mineral soil across a boreal landscape and possible linkages to climate change and recent fire history. Holocene 2013, 23, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faegri, K.; Kaland, P.E.; Krzywinski, K. Textbook of Pollen Analysis, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, E.C. CONISS: A FORTRAN 77 program for stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis by the method of incremental sum of squares. Comput. Geosci. 1987, 13, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, H.J.B. Quantitative Palaeoenvironmental Reconstructions. In Statistical Modelling of Quaternary Science Data; Maddy, D., Brew, J.S., Eds.; Quaternary Research Association: Cambridge, UK, 1995; pp. 161–254. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, P.J.H. Origine et dynamique postglaciaire de la forêt mixte au Québec. Rev. Paleobot. Palynol. 1993, 79, 31–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comtois, P.; Payette, S. Représentation pollinique actuelle et subactuelle des peupleraies boréales au Nouveau-Québec. Geogr. Phys. Quat. 1984, 38, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Brossier, B.; Oris, F.; Finsinger, W.; Asselin, H.; Bergeron, Y.; Ali, A. Using tree-ring to calibrate peak detection in fire reconstruction based on sedimentary charcoal records. Holocene 2014, 24, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Asselin, H.; Larouche, A.C.; Bergeron, Y.; Carcaillet, C.; Richard, P.J.H. Changes in fire regime explain the Holocene rise and fall of Abies balsamea in the coniferous forests of western Québec, Canada. Holocene 2008, 18, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blarquez, O.; Girardin, M.P.; Leys, B.; Ali, A.A.; Aleman, J.C.; Bergeron, Y.; Carcaillet, C. Paleofire reconstruction based on an ensemble-member strategy applied to sedimentary charcoal. Geophysic. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2667–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, H.; Flannigan, M.D.; Bergeron, Y.; Girardin, M.P. Historical fire regime shift related to climate teleconnections in the Waswanipi area, central Quebec, Canada. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2007, 16, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, Y.; Cyr, D.; Girardin, M.; Carcaillet, C. Will climate change drive 21st century burn rates in Canadian boreal forest outside its natural variability: Collating global climate model experiment with sedimentary charcoal data. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2010, 19, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).