Study on Historical Vegetation Dynamics in the Artificial Forest Area of Bashang, China: Implications for Modern Ecological Restoration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
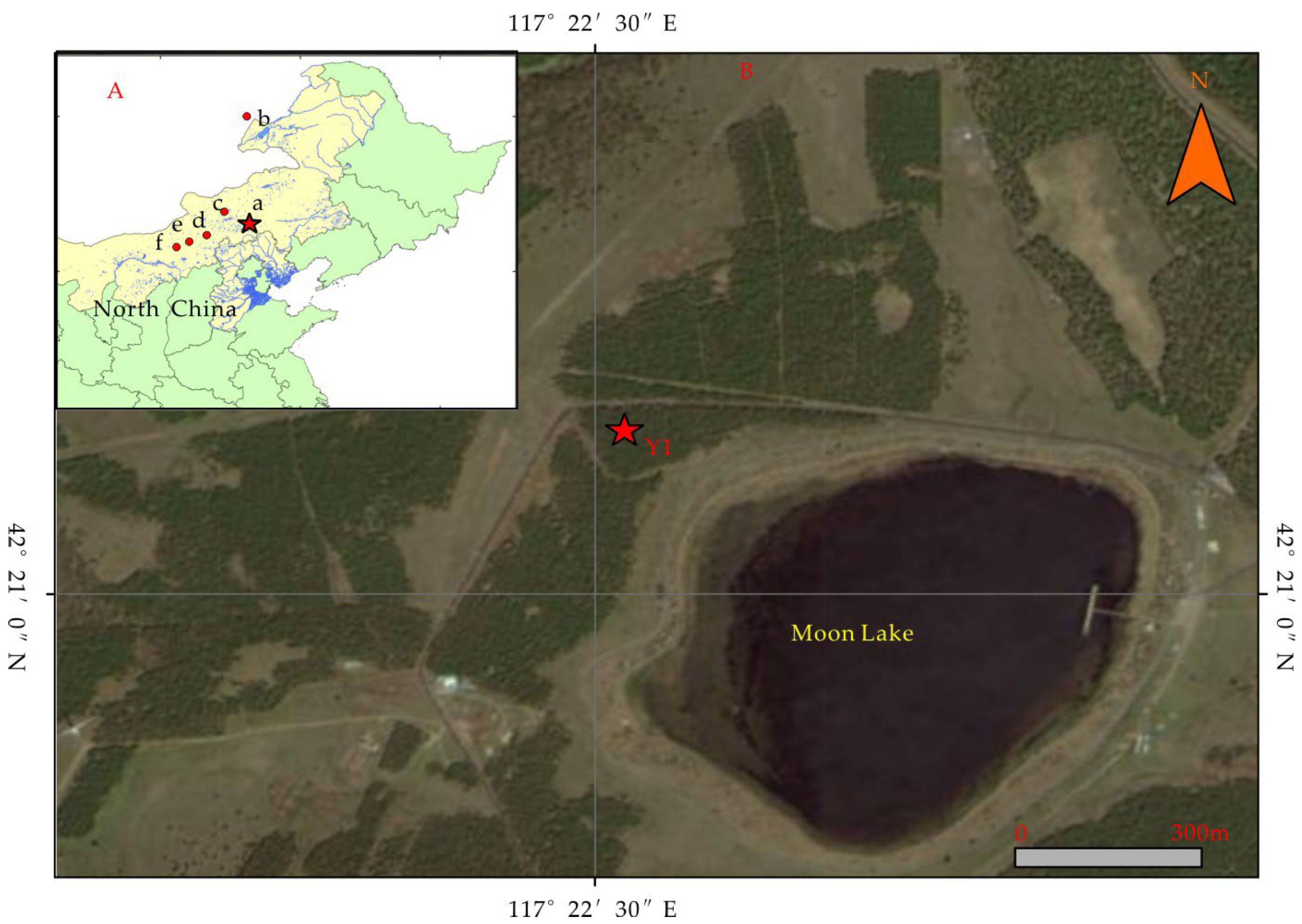
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Materials and Experimental Design
3. Results
3.1. Chronology
3.2. Palynological Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation of the Pollen Data
4.2. Vegetation and Climate Changes in the Study Area
4.3. Comparison with Regional Vegetation and Paleoclimate Records
5. Conclusions
5.1. Vegetation Transformation and Current Ecological Status
5.2. Emerging Environmental Challenges and Restoration Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liu, W.; Li, R.; Shao, H.; Peng, C.; Tian, Y. Shrinkage reasons and countermeasures of Moon Lake area in the eastern part of Bashang Plateau, Chengde City. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2020, 47, 57–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H. Investigation report on the current situation and influencing factors of carbon sink in different forest communities at Bashang area. 2022; (In Chinese, Project Report, Unpublished). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H. Research Report on Ecological Degradation and Suitability Assessment of Typical Vegetation Communities in the Ruyi River Basin. 2023; (In Chinese, Project Report, Unpublished). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. Dynamic Monitoring on Water Level of Angulinao Lake and the Causes of Its Drying up. J. Geoinf. Sci. 2009, 11, 312–318. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xin, Z.; Li, Z.; Keyimu, M. Climate effect on the radial growth of Populus simonii in Northwest of Hebei for last four decades. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 9108–9119, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Nie, H.; Liu, J.; Yuan, G.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A.; Song, B. Ecological and geological interaction model: The coupling of supergene geological processes and ecological characteristics. Geol. Surv. China 2021, 8, 9–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, Q. Remote sensing based temporal and spatial analysis of vegetation cover changes in Bashang area of Hebei Province. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2014, 26, 167–172, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, H. Evolution trend of vegetation coverage and its risk assessment in the Bashang region in Hebei Province. Arid. Zone Res. 2018, 35, 686–694, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Gao, S. Environmental change since 5000cal.a B.P. in the Anguli-Nuur Lake area based on palynological and geochemical records. Quat. Sci. 2017, 37, 130–142, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Cao, X.; Ulrike, H. The vegetation and climate changes since the late glacial period inferred from pollen record of a sediment core in Anguli-Nuur Lake, Hebei Province. Quat. Sci. 2018, 38, 1203–1210, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, A.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Z.; Sun, L. Variation of Paleovegetation and Paleoclimate since the Mid-Holocene in the Yudaokou Area of Weichang County, Hebei Province. South North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 69–72, 93, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Penny, A.M.; Chao, A.; Davies, A.L.; Magurran, A.E. Applying a unified framework to compare taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic diversity in Holocene pollen records. J. Ecol. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Evolution and Mechanism of East Asian Summer Monsoon Since Last Deglacial Recorded by Gonghai Lake. Ph.D. Dissertation, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2015. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Ding, Z. Changes in Plant Diversity On the Chinese Loess Plateau Since the Last Glacial Maximum. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 4096–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwörer, C.; Colombaroli, D.; Kaltenrieder, P.; Rey, F.; Tinner, W.; Austin, A. Early Human Impact (5000–3000 BC) Affects Mountain Forest Dynamics in the Alps. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, S. Chinese Loess Plateau vegetation since the Last Glacial Maximum and its implications for vegetation restoration. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. AR6 Synthesis Report: Climate Change. 2023. (ipcc.ch). Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/syr/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Ivanova, N. Global Overview of the Application of the Braun-Blanquet Approach in Research. Forests 2024, 15, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faegri, K.; Kaland, P.E.; Krzywinski, K. Textbook of Pollen Analysis, 4th ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Chien, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Pollen Flora of China, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1995. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, E.C. Tilia Software, version 1.7.16; Illinois State Museum Research and Collections Center: Springfield, IL, USA, 2011.
- Grimm, E.C. CONISS: A FORTRAN 77 program for stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis by the method of incremental sum of squares. Comput. Geosci. 1987, 13, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. _R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing_. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2025. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Reimer, P.J.; Austin, W.E.N.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Butzin, M.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curve (0–55 cal k BP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 725–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, F.; Liang, C.; Li, Q.; Geng, R. Characteristics of the modern pollen assemblages from different vegetation zones in Northeast China: Implications for pollen-based climate reconstruction. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1564–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lu, H.; Chu, G.; Wu, N.; Shen, C.; Wang, C.; Mao, L. 500-year climate cycles stacking of recent centennial warming documented in an East Asian pollen record. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, Z. Surface pollen assemblages of some major forest types in northern china. Quat. Sci. 2005, 25, 585–597, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S. The characteristics of Quaternary sporopollen assemblage and the vegetation succession in Xinjiang. Arid. Land. Geogr. 1991, 2, 1–9, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Spatial patterns of surface pollen in the semi-arid region of central Inner Mongolia and their implications for desertification driving factors. In Proceedings of the 7th First Academic Conference of the Chinese Palynological Society, Guangzhou, China, 23–26 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mosilimany, A.P. Ecological significance of common non-arboreal pollen: Examples from drylands of the Middle East. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 1990, 64, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Du, N.; Weng, C.; Lin, R.; Wei, K. Paleovegetation and paleoenvironment of Manas Lake, Xinjiang, northwestern China during the last 14000 years. Quat. Sci. 1994, 3, 239–248, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Weng, C.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y. Numerical characteristics of pollen assemblages of surface samples from west Kunlun Mountains. Acta Bot. Sin. 1993, 35, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R.; Xiao, J.; Chang, Z.; Zhai, D.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y. Holocene vegetation and climate changes reflected by the pollen record of Hulun Lake, north-eastern Inner Mongolia. Quat. Sci. 2010, 30, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R.; Xiao, J.; Fan, J.; Zhang, S.; Yamagata, H. Pollen evidence for a mid-Holocene East Asian summer monsoon maximum in northern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 176, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Kong, Z. A preliminary investigation on the holocene vegetation changes from pollen analysis in the gaoximage section, hunshandak sandy land. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 2003, 27, 797–804, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Han, R. Climate Change in Otindag Sandy Land During the Holocene. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Jin, H.; Su, Z.; Sun, Z. Climate changes revealed by grain-size cycles of holocene in hunshandake desert. J. Desert Res. 2005, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Li, C.; Jie, D.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, X.; Jiang, G.; Wang, P. Paleoclimate recorded by phytolith in anguli-nuur lake since mid-late holocene. Earth Sci. 2018, 43, 4138–4148. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Zhao, Z. The Climatic and Environmental Evolution Since the Mid-Holocene in Huangqihai, Inner Mongolia. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Xu, Q.; Nakamura, T.; Yang, X.; Liang, W.; Inouchi, Y. Holocene vegetation variation in the Daihai Lake region of north central China: A direct indication of the Asian monsoon climatic history. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2004, 23, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Nakamura, T.; Yang, X.; Inouchi, Y. Pollen evidence of vegetation and climate changes in daihai lake area during the Holocene. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2004, 26, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z. Vegetation and Climate Changes During the Holocene Reflected by Lacustrine Records in Chagan nur Otindag Sandy Land. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Feng, H.; Ma, Y.; Guo, L.; Wan, W. Holocene palaeoenvironment changes recorded by pollen of Baahar Nuur Lake. J. Lanzhou Univ. Nat. Sci. 2009, 45, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, A.; Feng, Z. Holocene climatic reconstructions from the fossil pollen record at Qigai Nuur in the southern Mongolian Plateau. Holocene 2013, 23, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Climate Environment Change of the Record on the Holocene Pollen of the Jijitan Profiles in the Nihewan Basin. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liang, W.; Sun, L. Reconstruction of climatic changes of Yansan mountain area since 5000 a B.P. inferred from Pollen Data. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2004, 24, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Liang, P.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Rioual, P.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ren, X.; et al. Holocene aeolian stratigraphic sequences in the eastern portion of the desert belt (sand seas and sandy lands) in northern China and their palaeoenvironmental implications. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Jia, H.; Peng, C.; Qin, X.; Zhang, H.; He, A.; Wang, L. Palaeoenvironmental changes since the last deglaciation recorded at moon lake on the bashang plateau, northern china: Implications for the future sustainability of regional forests. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl 2024, 649, 112314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
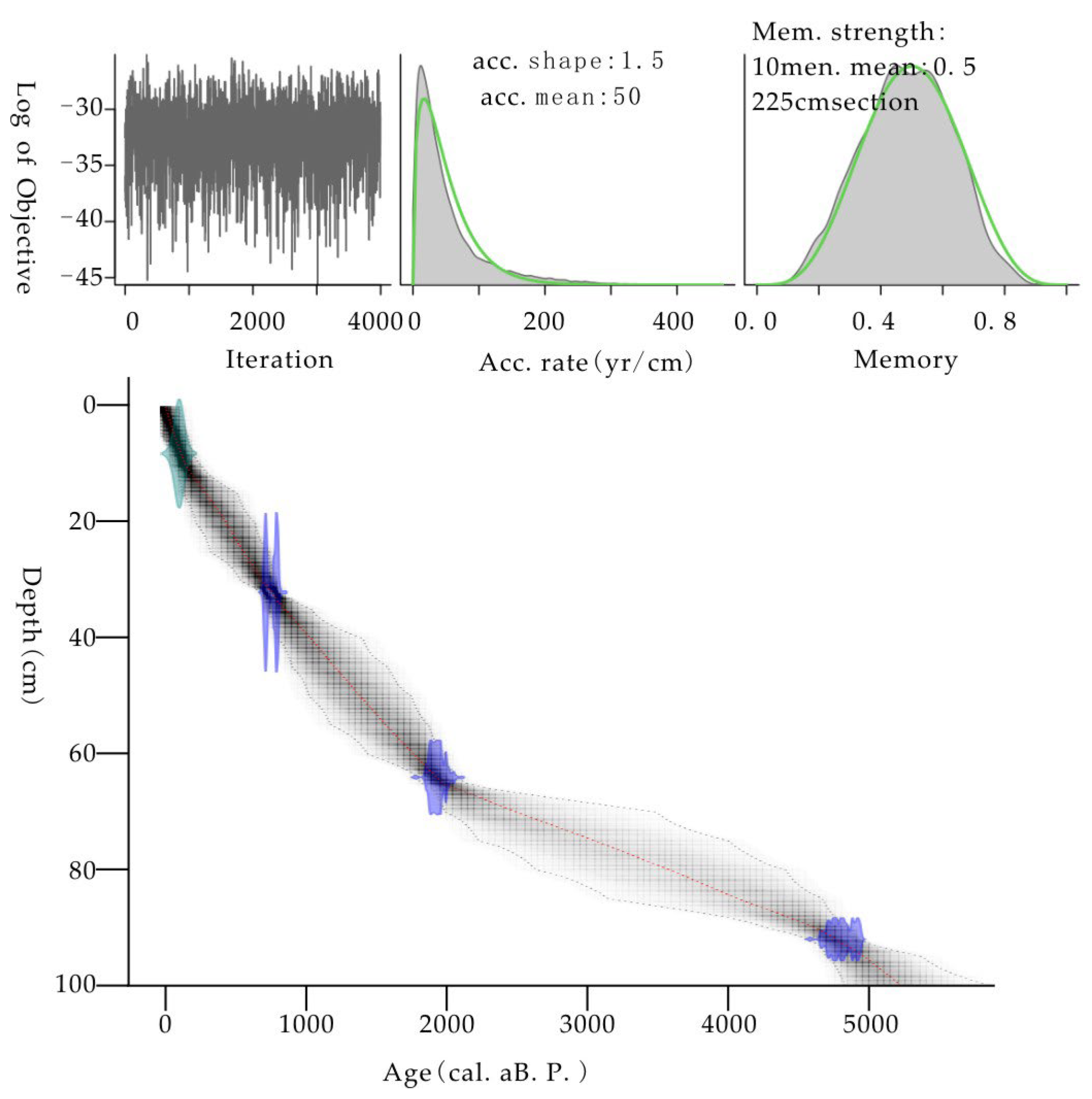


| Lab No. | Depth (cm) | Dated Material | Conventional Radiocarbon Age (a B.P.) | Calibrated Age (cal aB.P.) | δ13C (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-649841 | 8 | Bulk organic | −40+/−30 | −5–−6 (48.7%) −69–−70 (45.9%) −68 (0.8%) | −25.9 |
| Beta-649842 | 32 | Bulk organic | 670+/−30 | 673–628 (53.1%) 594–558 (42.3%) | −25.0 |
| Beta-649843 | 64 | Bulk organic | 1890+/−30 | 1874–1718 (95.4%) | −24.6 |
| Beta-649844 | 92 | Bulk organic | 4140+/−30 | 4824–4571 (93.1%) 4549–4533 (2.3%) | −23.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, H.; Wang, H.; Yin, Z. Study on Historical Vegetation Dynamics in the Artificial Forest Area of Bashang, China: Implications for Modern Ecological Restoration. Forests 2025, 16, 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16091392
Jia H, Wang H, Yin Z. Study on Historical Vegetation Dynamics in the Artificial Forest Area of Bashang, China: Implications for Modern Ecological Restoration. Forests. 2025; 16(9):1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16091392
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Hongjuan, Han Wang, and Zhiqiang Yin. 2025. "Study on Historical Vegetation Dynamics in the Artificial Forest Area of Bashang, China: Implications for Modern Ecological Restoration" Forests 16, no. 9: 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16091392
APA StyleJia, H., Wang, H., & Yin, Z. (2025). Study on Historical Vegetation Dynamics in the Artificial Forest Area of Bashang, China: Implications for Modern Ecological Restoration. Forests, 16(9), 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16091392






