Automatic Registration of Terrestrial and UAV LiDAR Forest Point Clouds Through Canopy Shape Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The DSM captures the height variation and spatial distribution of forest canopies, which exhibit consistency and distinguishability across platforms. Unlike methods requiring detailed identification of tree positions, DSM-based representation involves less data, greatly reducing storage and computational demands and enabling faster initial matching.
- (2)
- Traditional methods require precise tree location extraction, a complex and time-consuming process susceptible to noise, occlusion, and forest structural variability. The proposed method simplifies the process by aligning based on global morphology and local geometric features, enhancing automation.
- (3)
- Under the guidance of macro-scale DSM structures, the Fast Point Feature Histogram descriptors further enrich local geometric representations, enabling the registration process to balance global consistency and local alignment accuracy. This improves robustness and adaptability across diverse forest structures.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
3. Methods
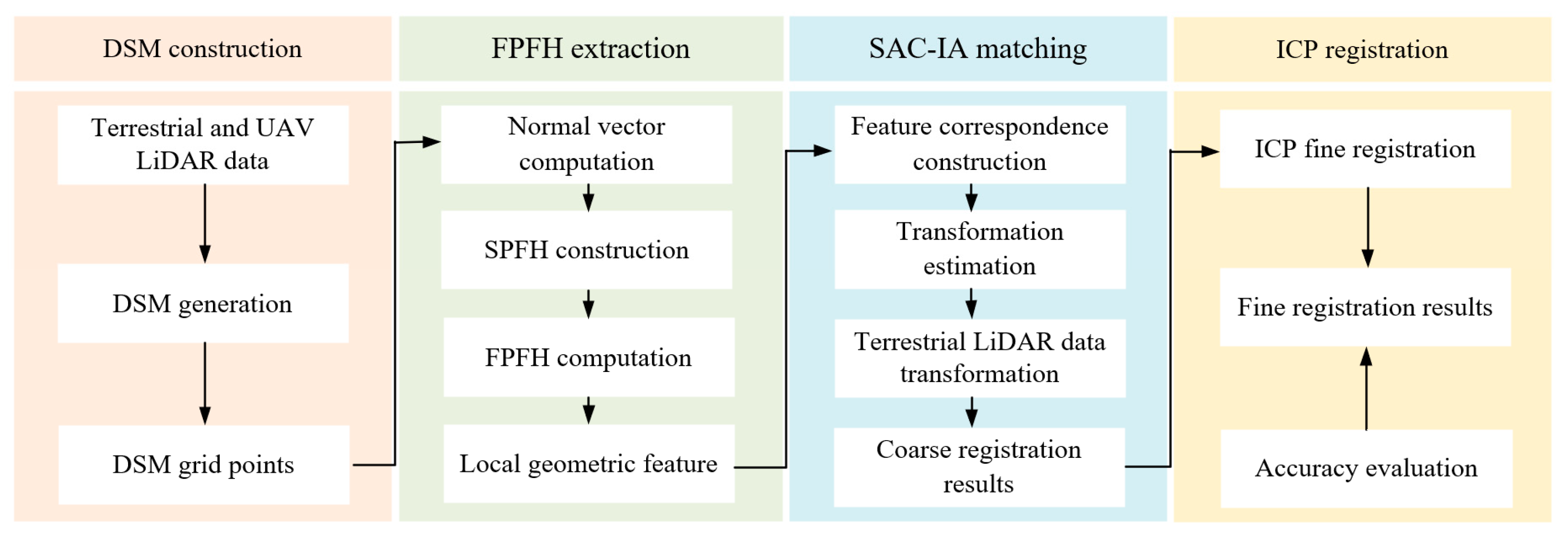
3.1. Overview
3.2. DSM Construction
3.3. FPFH Extraction
3.4. SAC-IA Matching
3.5. Fine Registration Using ICP
3.6. Evaluation Criteria
4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Registration Performance
5.2. Comparison with Existing Studies
5.3. Potential for Extension and Limitations of the Proposed Method
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, K.S.; Treitz, P.M.; Wulder, M.A.; St-Onge, B.A.; Flood, M. LiDAR remote sensing of forest structure. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2003, 27, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimble, D.A.; Evans, D.L.; Carlson, G.C.; Parker, R.C.; Grado, S.C.; Gerard, P.D. Characterizing vertical forest structure using small-footprint airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, A.T.; Crookston, N.L.; Evans, J.S.; Hall, D.E.; Falkowski, M.J. Nearest neighbor imputation of species-level, plot-scale forest structure attributes from LiDAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2232–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Yang, X.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Jupp, D.; Strahler, A. Measuring forest structure and biomass in New England forest stands using Echidna ground-based lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Nelson, R.F.; Næsset, E.; Ørka, H.O.; Coops, N.C.; Gobakken, T. Lidar sampling for large-area forest characterization: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froidevaux, J.S.P.; Zellweger, F.; Bollmann, K.; Jones, G.; Obrist, M.K. From field surveys to LiDAR: Shining a light on how bats respond to forest structure. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, C.J.; Rowell, E.M.; Seielstad, C.A. A data-driven framework to identify and compare forest structure classes using LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, H.L.; Nelson, C.R.; Larson, A.J.; Safford, H.D. Using LiDAR to develop high-resolution reference models of forest structure and spatial pattern. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 434, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuville, R.; Bates, J.S.; Jonard, F. Estimating forest structure from UAV-mounted LiDAR point cloud using machine learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrill, K.R.; Lefsky, M.A.; Bradford, J.B.; Ryan, M.G. Forest structure estimation and pattern exploration from discrete-return LiDAR in subalpine forests of the central Rockies. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 2081–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanera, J.A.; García-Abril, A.; Pascual, C.; Tejera, R.; Martín-Fernández, S.; Tokola, T.; Valbuena, R. Fusion of airborne LiDAR and multispectral sensors reveals synergic capabilities in forest structure characterization. GISci. Remote Sens. 2016, 53, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Liu, K.; Shen, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, H. Estimation of forest structural parameters using UAV-LiDAR data and a process-based model in ginkgo planted forests. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4175–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijerín-Triviño, J.; Moreno-Fernández, D.; Zavala, M.A.; Astigarraga, J.; García, M. Identifying forest structural types along an aridity gradient in peninsular Spain: Integrating low-density LiDAR, forest inventory, and aridity index. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, M.; McRoberts, R.E.; Chirici, G.; Marchetti, M. Estimating and mapping forest structural diversity using airborne laser scanning data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Coops, N.C.; Tompalski, P.; Nielsen, S.E.; Bater, C.W.; Stadt, J.J. Regional mapping of vegetation structure for biodiversity monitoring using airborne LiDAR data. Ecol. Inform. 2017, 38, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, X.; Ruan, H. Comparison of UAV LiDAR and digital aerial photogrammetry point clouds for estimating forest structural attributes in subtropical planted forests. Forests 2019, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Su, Y.; Hu, T.; Wang, R.; Ma, Q.; Yang, Q.; Guo, Q. A novel framework to automatically fuse multi-platform LiDAR data in forest environments based on tree locations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2165–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Deng, Y.; Shao, D.; Liu, Y. Target-free ULS–TLS point-cloud registration for alpine forest lands. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 190, 106460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Kan, H.; Tan, R.; Yang, B.; Guan, Q.; Zhu, N.; Dong, Z. Multisource forest point cloud registration with semantic-guided keypoints and robust RANSAC mechanisms. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 115, 103105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, P.; Liu, Q.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Registration of TLS and ULS point cloud data in natural forest based on similar distance search. Forests 2024, 15, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienert, A.; Georgi, L.; Kunz, M.; Maas, H.G.; von Oheimb, G. Comparison and combination of mobile and terrestrial laser scanning for natural forest inventories. Forests 2018, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Chen, D.; Peethambaran, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, S. Point cloud inversion: A novel approach for the localization of trees in forests from TLS data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Valero, J.A.; Martínez-Calvo, A.; Villamayor, M.J.G.; Pérez, M.A.N.; Álvarez-González, J.G.; Montes, F.; Pérez-Cruzado, C. Operationalizing the use of TLS in forest inventories: The R package FORTLS. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 150, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Yu, S.; Liang, X. Branch architecture quantification of large-scale coniferous forest plots using UAV-LiDAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 306, 114121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, H. Classification of forest stratification and evaluation of forest stratification changes over two periods using UAV-LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekry, R.; Yao, W.; Cao, L.; Shen, X. Ground-based/UAV-LiDAR data fusion for quantitative structure modeling and tree parameter retrieval in subtropical planted forest. For. Ecosyst. 2022, 9, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terryn, L.; Calders, K.; Bartholomeus, H.; Bartolo, R.E.; Brede, B.; D’hont, B.; Verbeeck, H. Quantifying tropical forest structure through terrestrial and UAV laser scanning fusion in Australian rainforests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Jing, W. An automated pipeline for extracting forest structural parameters by integrating UAV and ground-based LiDAR point clouds. Forests 2023, 14, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Yang, B.; Liang, X.; Dong, Z.; Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Automated fusion of forest airborne and terrestrial point clouds through canopy density analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 156, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liang, F.; Yang, B.; Xu, Y.; Zang, Y.; Li, J.; Stilla, U. Registration of large-scale terrestrial laser scanner point clouds: A review and benchmark. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Yao, W.; Wan, P.; Luo, L.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W. Efficient co-registration of UAV and ground LiDAR forest point clouds based on canopy shapes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xi, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, C.; Nie, S. Line segment descriptor-based efficient coarse registration for forest TLS–ULS point clouds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5706312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, B.; Yang, L.; Pan, Z.; Dong, L.; Wu, S.; Yu, B. QuadrantSearch: A novel method for registering UAV and backpack LiDAR point clouds in forested areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 63, 5700517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, F.; Chen, Y.C.; Hollaus, M.; Pfeifer, N. A robust and automatic algorithm for TLS–ALS point cloud registration in forest environments based on tree locations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 4015–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shao, J.; Jin, S.; Luo, L.; Ge, J.; Peng, X.; Zhou, G. Automated marker-free registration of multisource forest point clouds using a coarse-to-global adjustment strategy. Forests 2021, 12, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, C.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, Y. A clustering-based automatic registration of UAV and terrestrial LiDAR forest point clouds. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
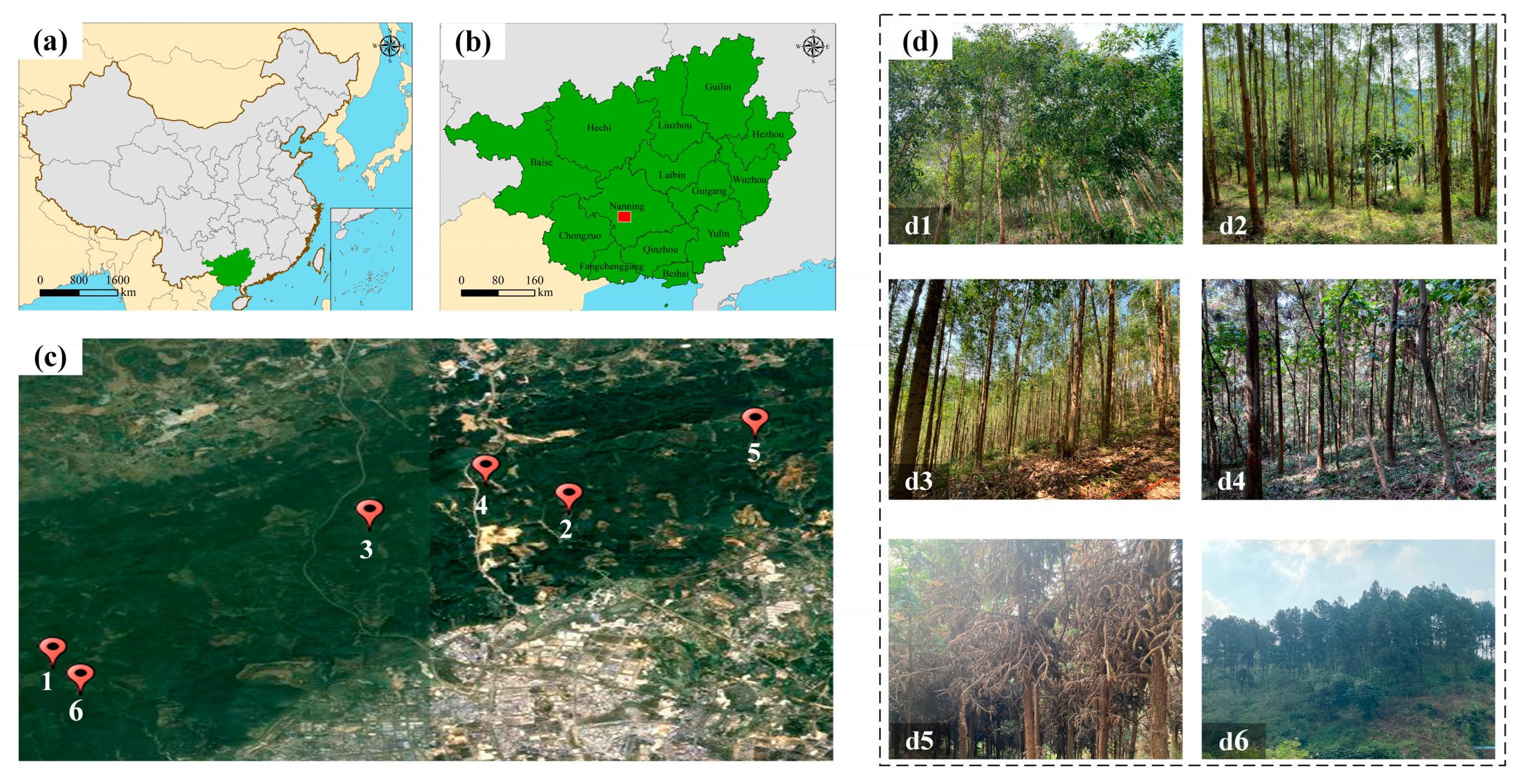


| Plot | Forest Type | Tree Height (m) | Diameters at Breast Height (cm) | Crown Width (m) | Tree Density (Trees/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Broad-leaved | 9.94 | 11.15 | 4.02 | 1167 |
| 2 | 20.12 | 16.43 | 4.71 | 1167 | |
| 3 | 12.39 | 16.14 | 3.10 | 2533 | |
| 4 | Coniferous | 9.05 | 15.63 | 3.14 | 1900 |
| 5 | 12.35 | 9.49 | 3.87 | 2500 | |
| 6 | 13.45 | 21.90 | 5.32 | 667 |
| Manual | Proposed | Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plot 1 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 4.53 |
| Plot 2 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 4.61 |
| Plot 3 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 6.03 |
| Plot 4 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 4.87 |
| Plot 5 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 4.53 |
| Plot 6 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 6.29 |
| Avg. | 0.18 | 0.24 | 5.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Dai, J.; Cai, S. Automatic Registration of Terrestrial and UAV LiDAR Forest Point Clouds Through Canopy Shape Analysis. Forests 2025, 16, 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081347
Yu S, Tang Z, Zhang B, Dai J, Cai S. Automatic Registration of Terrestrial and UAV LiDAR Forest Point Clouds Through Canopy Shape Analysis. Forests. 2025; 16(8):1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081347
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Sisi, Zhanzhong Tang, Beibei Zhang, Jie Dai, and Shangshu Cai. 2025. "Automatic Registration of Terrestrial and UAV LiDAR Forest Point Clouds Through Canopy Shape Analysis" Forests 16, no. 8: 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081347
APA StyleYu, S., Tang, Z., Zhang, B., Dai, J., & Cai, S. (2025). Automatic Registration of Terrestrial and UAV LiDAR Forest Point Clouds Through Canopy Shape Analysis. Forests, 16(8), 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081347







