Passive Long-Term Acoustic Sampling Reveals Multiscale Temporal Ecological Pattern and Anthropogenic Disturbance of Campus Forests in a High Density City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
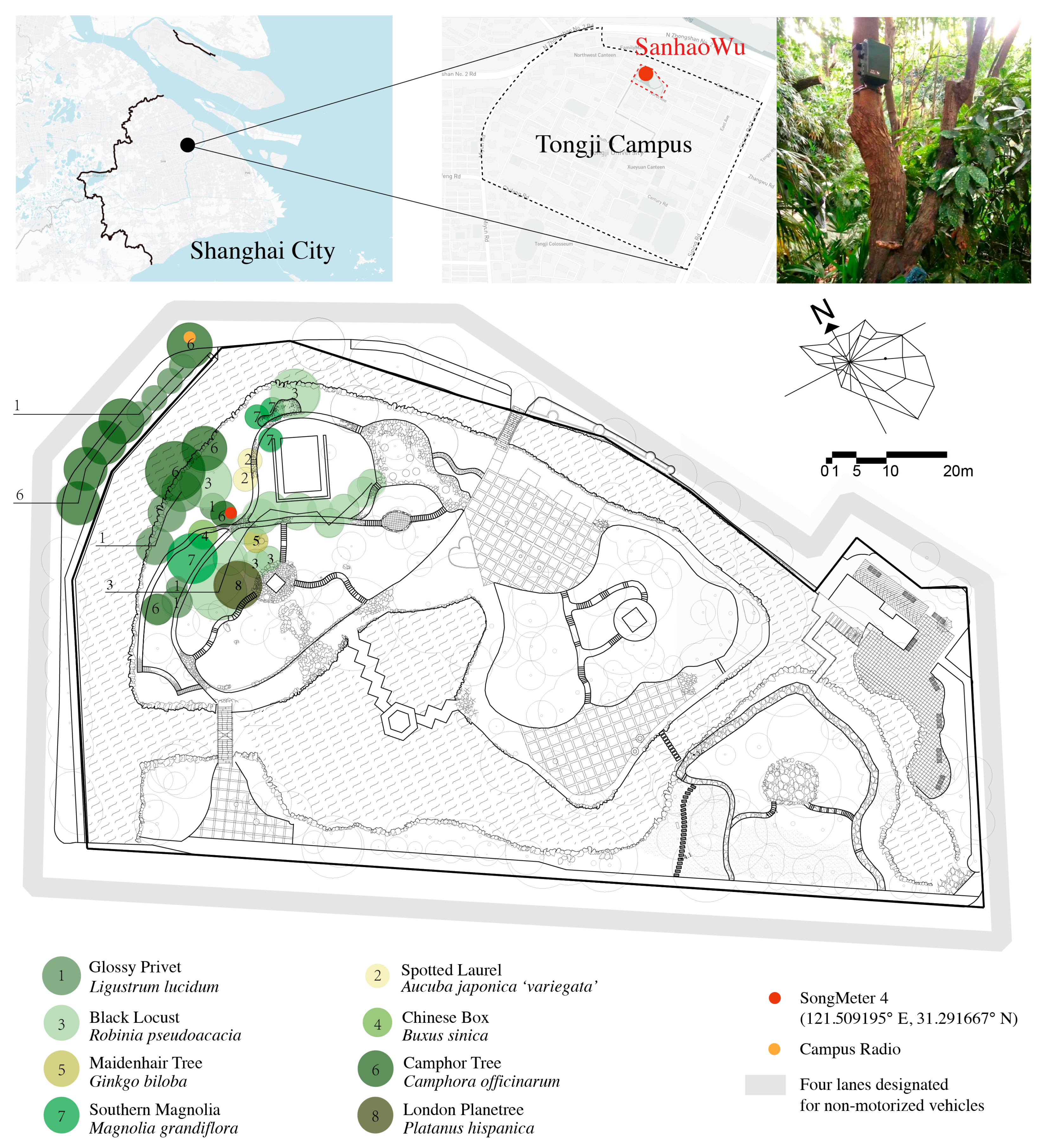
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Acoustic Indices Computation
2.4. Data Visualization
2.5. Statistical Analysis
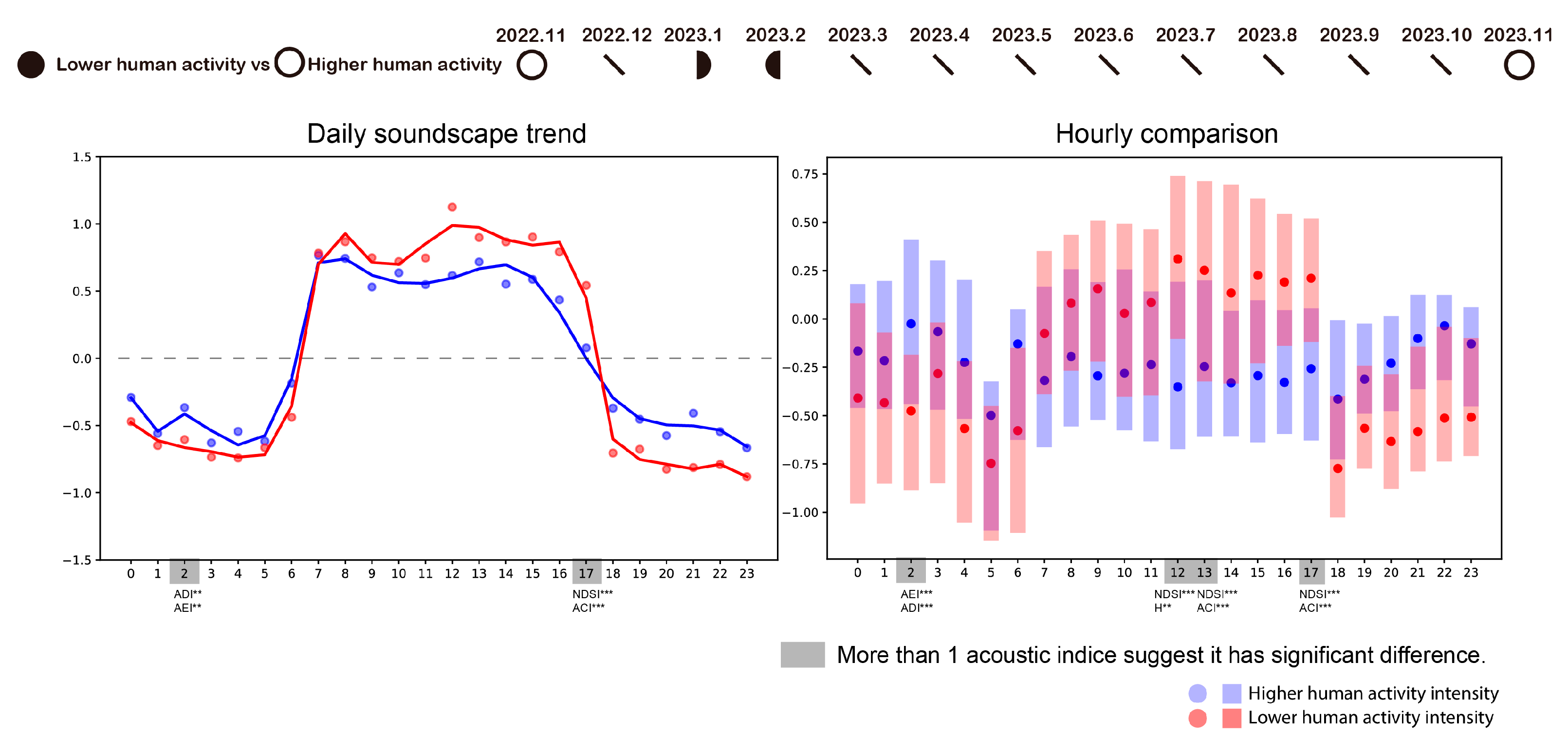
3. Results
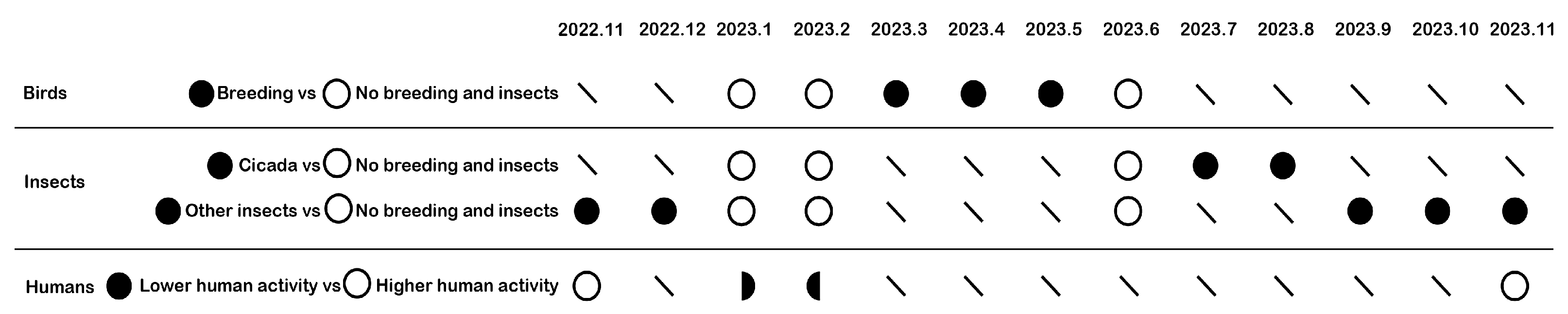
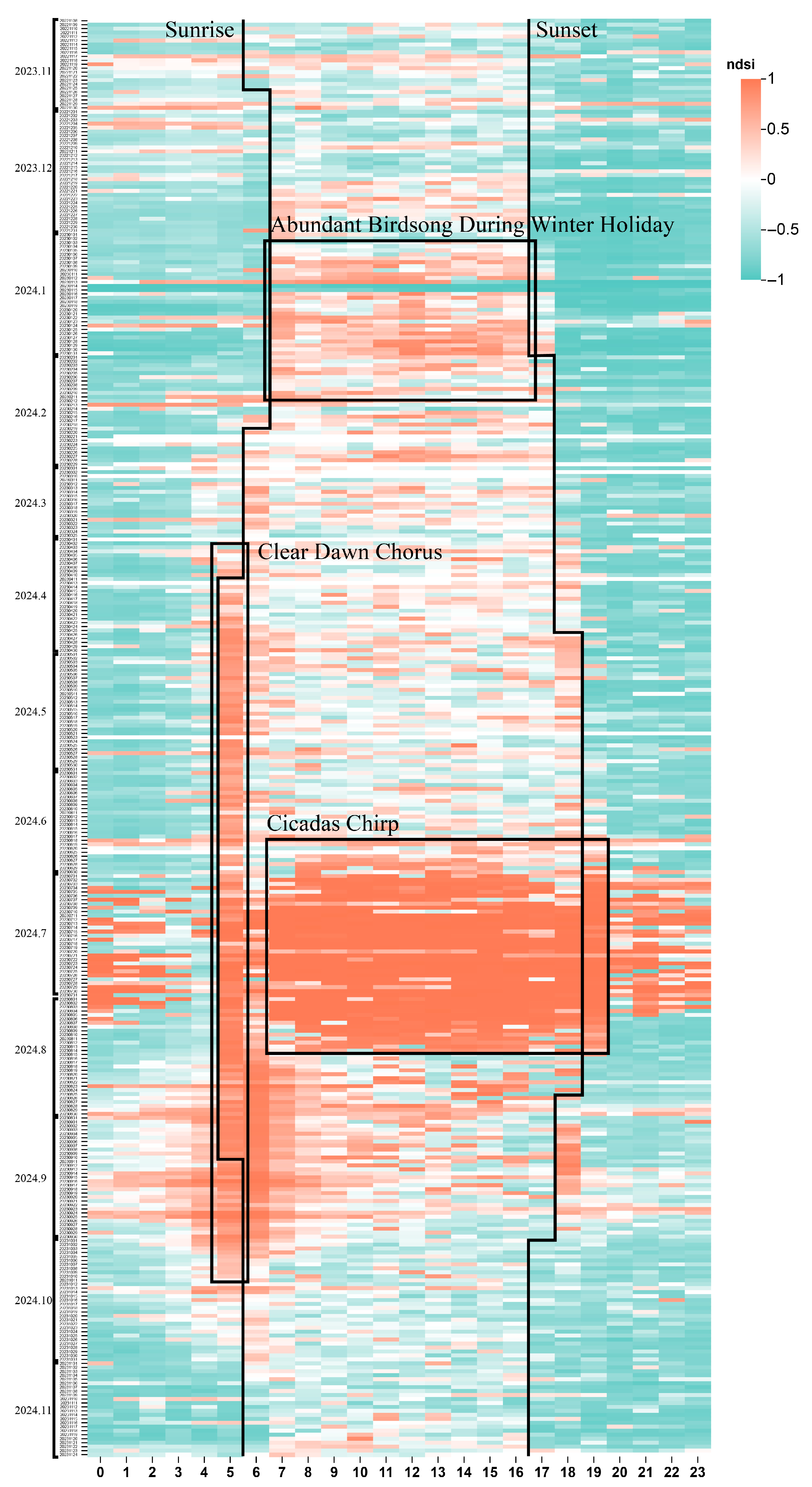
3.1. Ecological Vital Patterns Across Different Time Scales
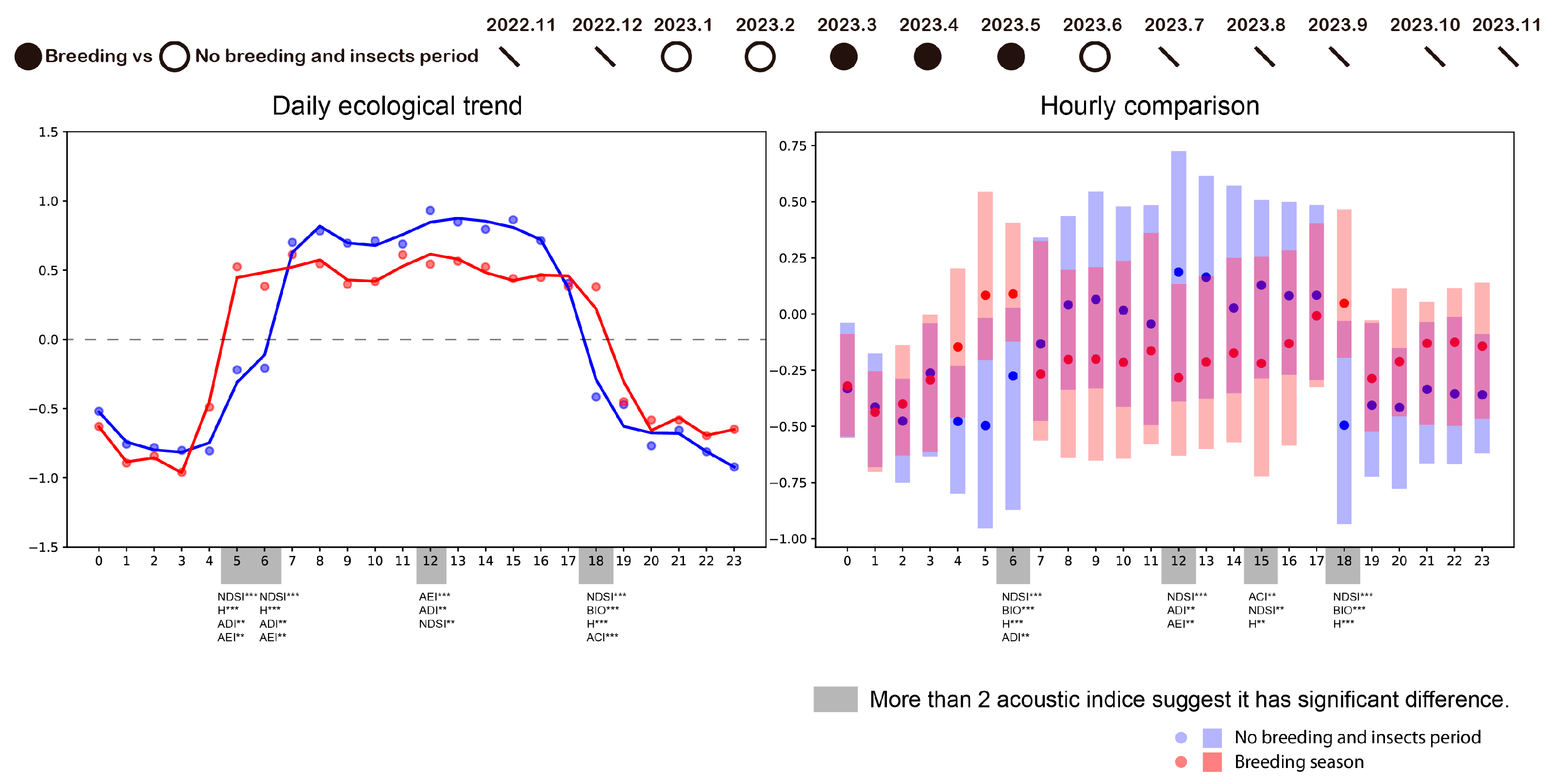
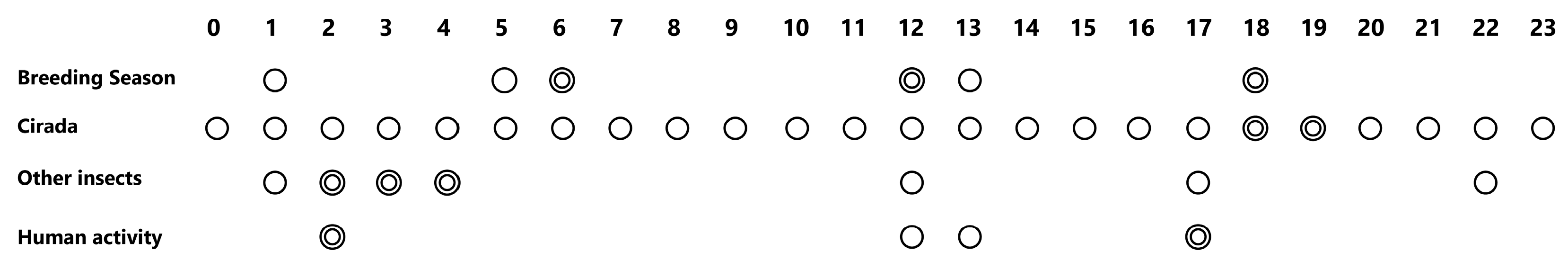
3.2. How Bird Breeding Seasons Influence Daily Ecological Pattern
3.3. How Insects Influence Daily Ecological Pattern
3.4. How Human Activity Intensity Influences Daily Ecological Pattern
4. Discussion
4.1. The Relationship Between Phenology and Ecological Patterns
4.2. Big Data Visualization and Statistical Analysis Help Ecological Pattern Understanding and Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, M.J.N.; Kim, M.J. A systematic review of smart city research from an urban context perspective. Cities 2024, 150, 105027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; Gardner, R.H. Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice: Pattern and Process; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4939-2793-7. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, D.M. A conceptual framework for studying species composition in fragments, islands and other patchy ecosystems. J. Biogeogr. 2002, 29, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Dubey, V.; Choudhury, S.; Das, A.; Jeengar, D.; Sujatha, B.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, N.; Semwal, A.; Kumar, V. Insects as bioindicator: A hidden gem for environmental monitoring. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1146052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhta, E.; Sulkava, P. The impact of nature-based tourism on bird communities: A case study in Pallas-Yllästunturi National Park. Environ. Manag. 2014, 53, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramola, G.C.; Rawat, N.; Singh, R.; Sajwan, A.S.; Sahu, L.; Rawat, P. Insects as Ecological Indicators: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2024, 14, 260–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, J.E.G.; Fernie, K.J. Avian wildlife as sentinels of ecosystem health. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 36, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, N.; Traversini, V.; Lorini, C.; De Sio, S.; Galea, R.P.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Arcangeli, G. Urban Noise and Psychological Distress: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, J.L.; House, L.O.; Valli, C.; Jaeger, S.R.; Moore, M.; Morrow, J.L.; Traill, W.B. Effect of information about benefits of biotechnology on consumer acceptance of genetically modified food: Evidence from experimental auctions in the United States, England, and France. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2004, 31, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.; Crumpler, C.; Notley, H. Evidence for Environmental Noise Effects on Health for the United Kingdom Policy Context: A Systematic Review of the Effects of Environmental Noise on Mental Health, Wellbeing, Quality of Life, Cancer, Dementia, Birth, Reproductive Outcomes, and Cognition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C.; Dent, M.L.; Gannon, W.L.; McCauley, R.D.; Römer, H.; Southall, B.L.; Stansbury, A.L.; Stoeger, A.S.; Thomas, J.A. The Effects of Noise on Animals. In Exploring Animal Behavior Through Sound: Volume 1: Methods; Erbe, C., Thomas, J.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 459–506. ISBN 978-3-030-97540-1. [Google Scholar]
- Soga, M.; Gaston, K.J. The Ecology of Human–Nature Interactions. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20191882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Jahn, O.; Jung, K.; Mitesser, O.; Ammer, C.; Böhm, S.; Ehbrecht, M.; Farina, A.; Renner, S.C.; Pieretti, N.; et al. Temporal dynamics of acoustic diversity in managed forests. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 12, 1392882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehne, L.M.; Padgham, B.L.; Olden, J.D. The Soundscapes of Lakes across an Urbanization Gradient. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, W.; Gage, S.H.; Kasten, E.P. Analysis and interpretation of variability in soundscapes along an urban–rural gradient. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 103, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, Z.; Yin, L.; Jiang, S.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, Y. Research on spatiotemporal variation characteristics of soundscapes in a newly established suburban forest park. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 78, 127766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burivalova, Z.; Maeda, T.M.; Purnomo; Rayadin, Y.; Boucher, T.; Choksi, P.; Roe, P.; Truskinger, A.; Game, E.T. Loss of temporal structure of tropical soundscapes with intensifying land use in Borneo. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, E.; Gibb, R.; Glover-Kapfer, P.; Jones, K. Passive acoustic monitoring in ecology and conservation. WWF Conserv. Technol. Ser. 2017, 1, 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.R.P.J.; O’Connell, D.P.; Deichmann, J.L.; Desjonquères, C.; Gasc, A.; Phillips, J.N.; Sethi, S.S.; Wood, C.M.; Burivalova, Z. Passive acoustic monitoring provides a fresh perspective on fundamental ecological questions. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, N.; Duarte, M.H.L.; Sousa-Lima, R.S.; Rodrigues, M.; Young, R.J.; Farina, A. Determining Temporal Sampling Schemes for Passive Acoustic Studies in Different Tropical Ecosystems. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2015, 8, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S.; Axel, A.C.; Tucker, D.; Gage, S.H. Connecting soundscape to landscape: Which acoustic index best describes landscape configuration? Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Wang, C.; Sun, Z.; van den Bosch, C.K.; Zhao, D.; Sun, B.; Xu, X.; Bian, Q.; Bai, Z.; Wei, K.; et al. Soundscape mapping for spatial-temporal estimate on bird activities in urban forests. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 57, 126822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sheppard, S.; Sun, Z.; Hao, Z.; Jin, J.; Bai, Z.; Bian, Q.; Wang, C. Soundscapes of urban parks: An innovative approach for ecosystem monitoring and adaptive management. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 71, 127555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamosa Izaguirre, M.; Barrantes-Madrigal, J.; Segura Sequeira, D.; Spínola-Parallada, M.; Ramírez-Alán, O. It is not just about birds: What do acoustic indices reveal about a Costa Rican tropical rainforest? Neotrop. Biodivers. 2021, 7, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradfer-Lawrence, T.; Bunnefeld, N.; Gardner, N.; Willis, S.G.; Dent, D.H. Rapid assessment of avian species richness and abundance using acoustic indices. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradfer--Lawrence, T.; Gardner, N.; Bunnefeld, L.; Bunnefeld, N.; Willis, S.G.; Dent, D.H. Guidelines for the use of acoustic indices in environmental research. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Camargo, U.; Roslin, T.; Ovaskainen, O. Spatio-temporal scaling of biodiversity in acoustic tropical bird communities. Ecography 2019, 42, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe and Sound: A Standard for Bioacoustic Data|WILDLABS. Available online: https://wildlabs.net/discussion/safe-and-sound-standard-bioacoustic-data (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Bradfer-Lawrence, T.; Desjonquères, C.; Eldridge, A.; Johnston, A.; Metcalf, O. Using acoustic indices in ecology: Guidance on study design, analyses and interpretation. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2023, 14, 2192–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer, I.; Lima, H.; Sugai, L.S.M.; Llusia, D. Acoustic indices as proxies for biodiversity: A meta-analysis. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 2209–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, B.T.; Hornberg, J.; Haselhoff, T.; Sutcliffe, R.; Ahmed, S.; Moebus, S.; Gruehn, D. A widened array of metrics (WAM) approach to characterize the urban acoustic environment; a case comparison of urban mixed-use and forest. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 185, 108387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, I.B.; Fewster, R.; Truskinger, A.; Towsey, M.; Roe, P.; Vasques Filho, D.; Lee, W.; Gaskett, A. Assessing the potential of acoustic indices for protected area monitoring in the Serra do Cipó National Park, Brazil. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towsey, M.; Znidersic, E.; Broken-Brow, J.; Indraswari, K.; Watson, D.M.; Phillips, Y.; Truskinger, A.; Roe, P. Long-duration, false-colour spectrograms for detecting species in large audio data-sets. J. Ecoacoustics 2018, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, Z.; Bellisario, K.; Zeng, R.; Li, N.; Zhou, W.; Pijanowski, B.C. How well do acoustic indices measure biodiversity? Computational experiments to determine effect of sound unit shape, vocalization intensity, and frequency of vocalization occurrence on performance of acoustic indices. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueur, J. Sound Analysis and Synthesis with R.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-77645-3. [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrass, A.J.; Rennert, P.; Williams, C.; Titheridge, H.; Jones, K.E. Biases of acoustic indices measuring biodiversity in urban areas. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.; Hedes, R.; Sandstrom, A.; Ruete, A.; Hiron, M.; Hedblom, M.; Eggers, S.; Mikusiński, G. Hybrid bioacoustic and ecoacoustic analyses provide new links between bird assemblages and habitat quality in a winter boreal forest. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2021, 11, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueur, J.; Aubin, T.; Simonis, C. Seewave: A free modular tool for sound analysis and synthesis. Bioacoustics 2008, 18, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammides, C.; Goodale, E.; Dayananda, S.K.; Kang, L.; Chen, J. Do acoustic indices correlate with bird diversity? Insights from two biodiverse regions in Yunnan Province, south China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Rivera, L.J.; Pijanowski, B.C. soundecology: Soundscape Ecology. R Package Version 1.3.2. 2016. Available online: https://github.com/ljvillanueva/soundecology (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Scarpelli, M.D.A.; Roe, P.; Tucker, D.; Fuller, S. Soundscape phenology: The effect of environmental and climatic factors on birds and insects in a subtropical woodland. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorb, K.; Jankowiak, Ł.; Zbyryt, A. Light-emitting greenhouses affect daily vocalization behavior in birds. J. Ornithol. 2023, 164, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillemann, F.; Cole, E.F.; Keen, S.C.; Sheldon, B.C.; Farine, D.R. Diurnal variation in the production of vocal information about food supports a model of social adjustment in wild songbirds. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.K.; Robillard, T.; ter Hofstede, H. The circadian calling activity of a lebinthine cricket with high-frequency calls is unaffected by cicada choruses in the day. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stölting, H.; Moore, T.E.; Lakes-Harlan, R. Substrate vibrations during acoustic signalling in the cicada Okanagana rimosa. J. Insect Sci. 2002, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, B.L. The Niche Hypothesis: A virtual symphony of animal sounds, the origins of musical expression and the health of habitats. Soundscape Newsl. 1993, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. The interference of cicada sounds on bird singing behavior. Master’s Thesis, Department of Forest Environment and Resources, National Taiwan University, Taiwan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, E.G.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Roe, P.; Sousa-Lima, R.S. The Caatinga Orchestra: Acoustic indices track temporal changes in a seasonally dry tropical forest. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, S.; Towsey, M.; Allen-Ankins, S.; Roe, P.; Schwarzkopf, L. Using a Novel Visualization Tool for Rapid Survey of Long-Duration Acoustic Recordings for Ecological Studies of Frog Chorusing. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 9, 761147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, Y.F.; Towsey, M.; Roe, P. Revealing the ecological content of long-duration audio-recordings of the environment through clustering and visualisation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Su, H.; Sullivan, W.C.; Lin, G.; Pryor, M.; Jiang, B. Impacts of sights and sounds on anxiety relief in the high-density city. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2024, 241, 104927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Xu, W.; Ji, W.; Kim, G.; Pryor, M.; Sullivan, W.C. Impacts of nature and built acoustic-visual environments on human’s multidimensional mood states: A cross-continent experiment. J. Environ. Psychol. 2021, 77, 101659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Acoustic Indices | Abbreviation | Computing Method | Information | Relationship with Biophony Richness | Calculation Package in R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acoustic Complexity Indices | ACI | Normalized summation | The complexity of STDFT matrix | Positive [36,37] | seewave [38] |
| Acoustic Diversity Indices | ADI | Shannon-Wiener indices | Shannon entropy on the spectral content | Positive [39] | soundecology [40] |
| Bioacoustics Indices | BIO | Summation of integrals | Relative avian abundance | Positive [36,37] | soundecology [40] |
| Normalized Difference Soundscape Indices | NDSI | Summation of integrals | The ratio of human-generated to biological acoustic components | Positive [36] | seewave [38] |
| Acoustic Entropy Indices | H | Shannon-Wiener indices | Shannon evenness of the amplitude envelope and frequency spectrum | Positive [34] | seewave [38] |
| Acoustic Evenness Indices | AEI | Gini indices | Gini coefficient on the spectral content | Negative [34,39] | soundecology [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Sun, X.; Xie, H. Passive Long-Term Acoustic Sampling Reveals Multiscale Temporal Ecological Pattern and Anthropogenic Disturbance of Campus Forests in a High Density City. Forests 2025, 16, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081289
Xu X, Sun X, Xie H. Passive Long-Term Acoustic Sampling Reveals Multiscale Temporal Ecological Pattern and Anthropogenic Disturbance of Campus Forests in a High Density City. Forests. 2025; 16(8):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081289
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaoqing, Xueyao Sun, and Hanbin Xie. 2025. "Passive Long-Term Acoustic Sampling Reveals Multiscale Temporal Ecological Pattern and Anthropogenic Disturbance of Campus Forests in a High Density City" Forests 16, no. 8: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081289
APA StyleXu, X., Sun, X., & Xie, H. (2025). Passive Long-Term Acoustic Sampling Reveals Multiscale Temporal Ecological Pattern and Anthropogenic Disturbance of Campus Forests in a High Density City. Forests, 16(8), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081289







