Abstract
Soil organic carbon (SOC) pool plays an extremely important role in regulating the global carbon (C) cycle and climate change. Atmospheric nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) deposition caused by human activities has significant impacts on soil C sequestration potential of terrestrial ecosystem. To investigate the effects of N and P deposition on soil C sequestration and C-N coupling relationship in broad-leaved evergreen forests, a 6-year field nutrient regulation experiment was implemented in subtropical Castanopsis sclerophylla forests with four different N and P additions: N addition (100 kg N·hm−2·year−1), N + P (100 kg N·hm−2·year−1 + 50 kg P·hm−2·year−1), P addition (50 kg P·hm−2·year−1), and CK (0 kg N·hm−2·year−1). The changes in the C and N contents and stable isotope distributions (δ13C and δ15N) of different soil organic fractions were examined. The results showed that the SOC and total nitrogen (STN) (p > 0.05) increased with N addition, while SOC significantly decreased with P addition (p < 0.05), and N + P treatment has low effect on SOC, STN (p > 0.05). By density grouping, it was found that N addition significantly increased light fraction C and N (LFOC, LFN), significantly decreased the light fraction C to N ratio (LFOC/N) (p < 0.05), and increased heavy fraction C and N (HFOC, HFN) accumulation and light fraction to total organic C ratio (LFOC/SOC, p > 0.05). Contrary to N addition, P addition was detrimental to the accumulation of LFOC, LFN and reduced LFOC/SOC. It was found that different reactive oxidized carbon (ROC) increased under N addition but ROC/SOC did not change, while N + P and P treatments increased ROC/SOC, resulting in a decrease in SOC chemical stability. Stable isotope analysis showed that N addition promoted the accumulation of new soil organic matter, whereas P addition enhanced the transformation and utilization of C and N from pre-existing organic matter. Additionally, N addition indirectly increased LFOC by significantly decreasing pH; significantly contributed to LFOC and ROC by increasing STN accumulation promoted by NO3−-N and NH4+-N; and decreased light fraction δ13C by significantly increasing dissolved organic C (p < 0.05). P addition had directly significant negative effect on LFOC and SOC (p < 0.05). In conclusion, six-year N deposition enhances soil C and N sequestration while the P enrichment reduces the content of soil C, N fractions and stability in Castanopsis sclerophylla forests. The results provide a scientific basis for predicting the soil C sink function of evergreen broad-leaved forest ecosystem under the background of future climate change.
1. Introduction
Forests represent an important global terrestrial carbon (C) sink, yet we still lack a clear understanding of those mechanisms that control C storage in forest ecosystems [1,2]. Due to changes in atmospheric chemistry (e.g., rising atmospheric CO2 concentration), nitrogen (N) deposition, phosphorus (P) deposition, climate change, or anthropogenic interference, the ecosystem C cycle process is in a dynamically non-equilibrium state, causing terrestrial ecosystems behave as C sources or sinks [3,4]. Therefore, accurate estimation of the size of the forest C sink and temporal trends are key to achieving a thorough understanding of the global terrestrial C cycle and the mechanisms underpinning C accumulation with shifts in N and P deposition [5,6]. Among various limiting factors, N and P are two key nutrients that regulate plant growth and ecosystem productivity [5,6,7]. In recent centuries, human-induced atmospheric deposition has significantly increased N and P inputs to terrestrial ecosystems [8,9]. Studies have shown that the N deposition rate in China has increased from 11.1 kg ha−1∙year−1 to 15.3 kg ha−1∙year−1 over the last 30 years and higher in the subtropics than in the temperate regions [9]. Meanwhile, global ecosystem P inputs have increased from 0.3 Tg·yr−1 before the industrial era to 14–16 Tg·year–1 between 2005 and 2010, and this upward trend continues [8].
Forest ecosystems account for 60% of total terrestrial ecosystem C, with about 70% of C stored in soil [10,11]. Small changes in forest soil C pools could lead to significant changes in atmospheric CO2 concentrations and thus influence global climate change in the future [10,12]. Due to the strong coupling of C, N, and P, increased atmospheric N and P deposition alters belowground C accumulation and cycling [7]. Currently, forest SOC and its response to global change have received extensive attention from scholars at both national and international levels [5,6]. N and P inputs affect SOC sequestration not only by changing the total C pool size but also by altering its chemical composition [7]. These changes stem from shifts in plant and microbial communities [13,14,15,16]. SOC comprises various active components with different stability and turnover rates [17]. It has been classified into labile C fractions (including microbial biomass C, dissolved organic C, light fraction organic C, and reactive oxidized C, etc.) and nonlabile C fractions (including heavy fraction organic C and difficult-to-biodegrade organic C, etc.) [17]. Light fraction organic C (LFOC) is organic C with a density of less than 2 g·cm−3, accounting for 15% to 32% of the total SOC, between plant residues and humus, mostly gathered in the soil surface layer [18]. Heavy fraction organic C (HFOC) has a particle density of more than 2 g·cm−3, is mainly composed of humic substances firmly bound to clay minerals, exists in the form of organic-inorganic complexes, has a very slow decomposition rate, and plays a very important role in soil C sequestration [18]. Readily oxidizable carbon (ROC) that can be oxidized by K2MnO4 includes aromatic and humic substances [19]. The labile C fraction serves as a sensitive indicator of soil quality and responds quickly to environmental changes, while the nonlabile fractions reflect SOC stability due to their resistance to microbial decomposition [11,18,20]. Therefore, assessing the size and composition of SOC pools under global climate change is essential for predicting SOC dynamics with precision.
N and P inputs can alter the fractional composition of SOC by altering the quantity and quality of plant litter, chemical reaction effects and microbial utilization preferences for organic matter [4,7,21]. Combined with the existing N deposition studies, it was found that the trends of SOC and its fractions under N-enriched conditions were often inconsistent among different sites, depending on ecosystem types and environmental factors [13,14,15,16]. In alpine tundra zone, N addition accelerates the decomposition of soil organic matter (SOM) and enhances HFOC stability [22]. In southern Chinese tropical forests, N inputs promoted labile C decomposition but had no effect on nonlabile C and SOC [23]. Nevertheless, a meta-analysis of 36 studies revealed that SOC separated by density fractionation increased by 21.3% in the light fraction following N treatment [13]. Currently, a substantial body of research has been conducted on the response of soil C to N deposition in a variety of geographical regions; however, there is still a paucity of studies examining the effects of N deposition on the content of organic C fractions and the stability of C pools in broadleaf evergreen forest areas [11,24,25]. Moreover, considering the strong coupling mechanism between forest soil N and C, C and N interactions ultimately determine the forest soil C cycle and C balance status. In order to deeply understand the mechanism of soil C sequestration, it is especially important to investigate the changing rules of organic C and N components and their interactions [5,6,7]. Additionally, studies on the effects of P addition and N and P co-addition on SOC fractions are very limited compared to N addition, and the mechanisms of their effects are still unclear [26].
Stable C isotope (δ13C) composition provides insights into the degree of soil organic matter decomposition, minor processes of transformation and migration in SOC composition. Stable N isotope (δ15N) reflects soil N cycling dynamics across temporal and spatial scales [27]. Soil microorganisms preferentially use δ12C and δ14N compounds during decomposition, leading to the relative enrichment of δ13C and δ15N in SOM [28]. Typically, SOM derived from fresh plant residues is large, low-density and depleted in δ13C, whereas SOM from older plant material tends to be higher in density and enriched in δ13C [27,28]. Currently, systematic studies on SOM stable isotope dynamics in broad-leaved evergreen forests remain limited. To improve understanding of soil C cycling and storage, it is imperative to investigate the relationship between soil C and N isotope abundance alongside N deposition in ecosystems.
Castanopsis sclerophylla is a dominant species in subtropical evergreen broad-leaved secondary forests across China, particularly in the south of the Yangtze River. It demonstrates strong soil adaptability and serves as a pioneer broad-leaved forest species for barren mountain afforestation, playing a key role in subtropical forest restoration. This study built upon field-based nutrient addition trials, to investigate the dynamics of soil organic matter fractions and their regulatory mechanisms in evergreen broad-leaved forests dominated by Castanopsis sclerophylla. Based on the differential nutrient demands of subtropical broad-leaved forest ecosystems for N and P, we hypothesize that: (1) N addition will exert stronger promoting effects on soil C and N fractions than P addition, while combined N and P addition will show significantly greater enhancement effects compared to single nutrient additions; (2) The increase in labile C fractions will be more pronounced than that in recalcitrant C fractions across N and P addition treatments; (3) N addition will lead to a greater increase in N fractions relative to C fractions, thereby reducing the soil C:N ratio, whereas the opposite pattern will occur under P addition. Furthermore, we propose that N and P addition treatments will alter soil physicochemical properties, consequently modifying both the content and stability of soil C and N fractions. The results will help to accurately predict the feedback effect of SOC dynamics of evergreen broad-leaved forest on future atmospheric N and P deposition, and provide a scientific basis for soil C sequestration and emission reduction of evergreen broad-leaved forest ecosystem under the background of global change.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Descriptions
This study was conducted in Jitan Township, Shitai County, Anhui Province (30°01′47″ N, 117°21′23″ E), at an elevation of 100~150 m. The area has a humid subtropical climate, with an average annual temperature of 16 °C. Historical temperature extremes range from a maximum of 38.8 °C to a minimum of −8.9 °C. Over the past decade, average annual precipitation reached 1521 mm, with most rainfall occurring between April and September. The region supports diverse vegetation, including subtropical deciduous evergreen forests and planted forests of Phyllostachys heterocycla, Cunninghamia lanceolata, and Pinus massoniana. The soil is classified as acidic yellow-brown soil. The experiment site was dominated by a 46-year-old Castanopsis sclerophylla stand, accounting for 80–90% of the canopy cover, with a density of 800–1189 trees·hm−1 (diameter at breast height (DBH) ≥ 5 cm), and a maximum DBH of 30.6 cm. Companion species included Liquidambar formosana and Pinus massoniana, etc., while the understory shrubs were Loropetalum chinensis, Camellia cuspidata, Elaeagnus pungens, and Lindera aggregata.
2.2. Experimental Design and Treatments
The N and P addition experiment was started in 2011. It included three treatments and one control, namely N addition (100 kg N·hm−2·year−1), N + P (100 kg N·hm−2·year−1 + 50 kg P·hm−2·year−1), P addition (50 kg P·hm−2·year−1), and CK (0 kg N·hm−2·year−1), with three replicates per treatment. Twelve standard plots of 15 m × 15 m were set up in a randomized block design with 8~10 m isolation zones between the plots in a stand of Castanopsis sclerophylla with basically similar stand conditions. Nutrients were added four times per year—in January, April, July, and October—using backpack sprayers. Ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) was used as the N source, and calcium superphosphate [Ca(H2PO4)2] was used as the P source. Prior to application, NH4NO3 and Ca(H2PO4)2 were dissolved in 20 L of water and sprayed evenly across the understory of each plot. To maintain consistency and control for water effects, the control plots received the same volume of water without added nutrients.
2.2.1. Soil Sampling
In July 2018, soil samples were collected from the 0–10 cm soil layer using the five-point method using a volumetric ring. Fresh soil samples were promptly transported to the laboratory for processing. Samples that can not be processed immediately were sealed and stored in a freezer or snap-frozen for preservation. After collection, soil samples were cleaned of stones and coarse roots. One portion was used to measure water content, NH4+-N, NO3−-N, dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen (DOC, DON), and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen (MBC, MBN), which were kept at low temperatures and passed through a 5 mm soil sieve before analysis. The remaining soil was air-dried in a ventilated room. Depending on analytical requirements, it was sieved through 2 mm and 100 mesh sieves, thoroughly mixed, and stored in light-proof bags for later use.
2.2.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Carbon Fraction Measurements
Soil moisture content was measured by 105 °C drying method. Soil pH was determined after mixing air-dried, 100-mesh sieved soil with distilled water at a 1:2.5 (soil: water) mass ratio, shaking, and allowing the mixture to stand for 30 min before measurement with the PHB-3 pH meter (Sanxin, Shanghai, China). Ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) were extracted using 1.0 mol·L−1 KCl and quantified with the FIAstar 5000 Analyzer (Copenhagen, FOSS, Denmark). Soil phosphorus (TP) was digested by wet digestion and determined by the FIAstar 5000 Analyzer (Copenhagen, FOSS, Sweden). Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen (SOC and STN) were determined using an EA3000 C/N analyzer (Vector, Milano, Italy) from soil passed through a 100-mesh sieve. DOC and DON were extracted using 0.5 mol·L−1 K2SO4 and analyzed with the Multi 3100 C/N analyzer (Analytik Jena AG, Jena, Germany). MBC and MBN were fumigated using chloroform, and C and N contents were determined using the Multi 3100 C/N analyzer (Analytik Jena AG, Jena, Germany), with a correction factor of 0.45 used for soil microbial biomass C and N [29].
Determination of low, medium, and high activity readily oxidizable organic carbon (LROC, MROC and HROC) [30]: Air-dried soil sample containing 30 mg of C was placed into 100 mL bottles and 25 mL of KMnO4 solution at concentrations of 333, 167, and 33.3 mmol L−1 were added, respectively. The bottle was sealed and placed on a shaker for 1 h. After shaking, the sample was centrifuged for 5 min, and then the supernatant was diluted with deionized water at a ratio of 1:250 liquid to water. The dilutions were colorimetrically measured on a spectrophotometer at 565 nm with a standard solution that must contain 1 mg of carbon, and the ROC of the soil sample can be measured based on the amount of KMnO4 solution consumed, with each consumption of 1 mmol·L−1 KMnO4 solution corresponding to the oxidation of 9 mg of C.
Determination of LFOC(N) and HFOC(N) [31]: Air-dried soil passed through a 2 mm sieve was dispersed in a 1.8 g·cm−3 solution of NaI solution, shaken for 1 h and centrifuged for 5 min. The supernatant was siphoned off, filtered, and the process repeated five times. The light fraction was washed with 100 mL of 0.01 mol·L−1 CaCl2 solution and 200 mL of distilled water, then dried and weighed. The remaining fraction was washed with 100 mL 0.01 mol·L−1 CaCl2 solution, then rinsed with 200 mL of distilled water, then dried and weighed to obtain the heavy fraction. The content of organic C and N in the light and heavy fractions was determined using an EA3000 C/N analyzer (Vector, Milano, Italy).
Determination of stable isotopes in the light and heavy fraction: Soil samples were air dried to constant weight and sieved through a 0.154 mm mesh. The abundance of stable C and N isotopes (δ13C and δ15N, ‰) was determined using an isotope mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific Delta V Advantage, Waltham, MA, USA). Isotopic abundances were calculated as follows:
where R is 13C/12C or 15N/14N, Rsp is the R-value of the soil sample, Rsd is the R-value of the reference material, C isotopes are standardized by PBD (Pee Dee Belemnite), and N isotopes are standardized by N2 in the standard atmosphere.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
One-way ANOVA and Duncan’s method were used to analyze the significance of differences between treatments. Pearson correlation analysis was used to assess the correlation between SOC fractions and environmental factors. Random forest modeling was used to explore the key factors affecting soil C fractions. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was established using the R 4.2.3 ‘lavaan’ package, which was be further to analyze the pathways driven by N and P addition to SOC. The SEM were developed by incorporating existing knowledge regarding the potential influences of explanatory variables on soil organic carbon and nitrogen dynamics, and model performance was assessed through both the χ2 goodness-of-fit test and the root mean square error of approximation [32]. Data were analyzed using R 4.2.3, and charts were plotted using Excel 2003, Visio 2021, R 4.2.3, and Origin 2014.
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Under N and P Addition
As shown in Figure 1, different physicochemical indicators changed under N and P addition. Under N addition, only MBN, SOC/STN, and pH showed decreased compared to CK, with a significant decline in pH, while soil moisture content and NO3−-N increased significantly (p < 0.05). Under N + P treatment, the measured indicators NH4+-N, pH, SOC, and SOC/STN showed a decrease, with pH decreasing at a significant level, while soil moisture content, NO3−-N, DOC, MBN, and TP significantly increased (p < 0.05). P treatment decreased NH4+-N, MBC, STN, pH, SOC, and SOC/STN, with NH4+-N and SOC decreasing at significant levels, while significantly increasing soil moisture content, DON, and TP (Figure 1, p < 0.05).
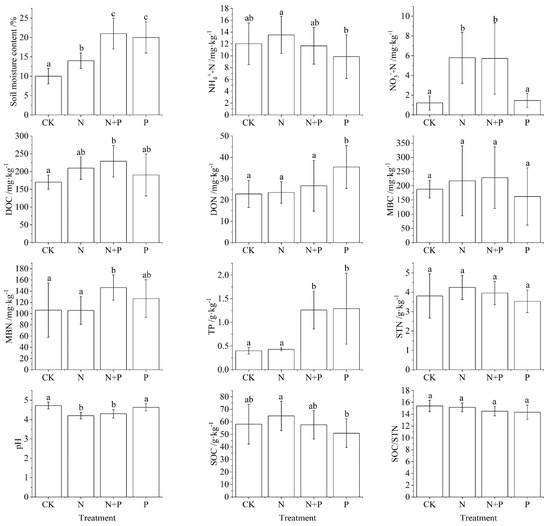
Figure 1.
Changes in soil physicochemical properties under N and P addition in a Castanopsis sclerophylla forest in the Anhui Province of China. Treatments are control (CK), nitrogen addition (N), phosphorus addition (P), and co-addition of nitrogen and phosphorus (N + P). Dissolved organic carbon: DOC; dissolved organic nitrogen: DON; microbial biomass carbon: MBC; microbial biomass nitrogen: MBN; soil organic carbon: SOC; soil total nitrogen: STN; total phosphorus: TP; Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05). Error bars are standard errors (n = 9).
3.2. Effect of N and P Addition on Different Active ROC
As shown in Table 1, N addition only had a significant effect on ROC, while N + P only had a significant effect on HROC (p < 0.05). The different active ROC increased under N addition, but did not reach significant levels (p > 0.05, Figure 2). Under N + P treatment, ROC increased attributed to the increased MROC and LROC. ROC did not change significantly with P addition, whereas HROC decreased, and MROC and LROC showed an increased trend (p > 0.05, Figure 2).

Table 1.
Soil C fraction analysis of variance under N and P addition in a Castanopsis sclerophylla forest in the Anhui Province of China.
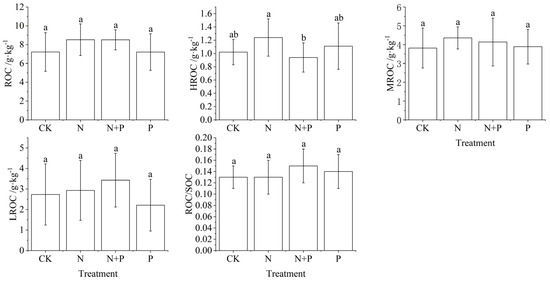
Figure 2.
Changes of different active ROC under N and P addition in a Castanopsis sclerophylla forest in the Anhui Province of China. Treatments are control (CK), nitrogen addition (N), phosphorus addition (P), and co-addition of nitrogen and phosphorus (N + P). Reactive oxidized carbon: ROC; high activity readily oxidizable organic carbon: HROC; medium activity readily oxidizable organic carbon: MROC; low activity readily oxidizable organic carbon: LROC; reactive oxidized carbon/soil organic carbon: ROC/SOC; different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05). Error bars are standard errors (n = 9).
3.3. Effects of N and P Addition on Light and Heavy Fractions C and N
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed that N addition significantly effected LFOC, LFON and LFOC/N (Table 1). P addition only significantly influenced LFOC and HFOC/N (p < 0.05). N + P had no significant effect on LFOC, LFN, HFOC, and HFN (Table 1, p > 0.05). N addition significantly increased LFOC and LFN and significantly decreased LFOC/N (p < 0.05), while increasing HFOC and HFN and decreasing HFOC/N (p > 0.05, Figure 3). LFOC and LFN did not change significantly under N + P treatment (p > 0.05, Figure 3). Under P addition, LFOC and LFN showed a decrease, while HFOC and HFN showed an increase (p > 0.05), and HFOC/N decreased to a significant level (p < 0.05, Figure 3).
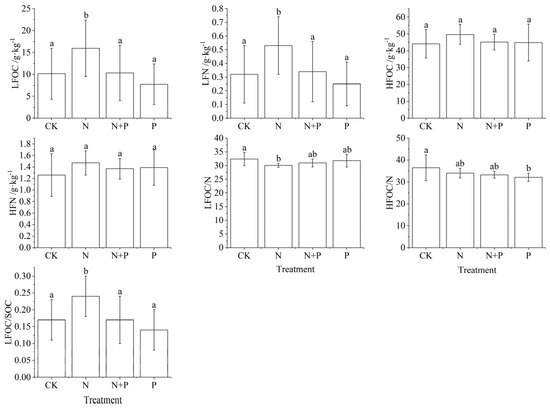
Figure 3.
Changes in light and heavy fractions under N and P addition in a Castanopsis sclerophylla forest in the Anhui Province of China. Treatments are control (CK), nitrogen addition (N), phosphorus addition (P), and co-addition of nitrogen and phosphorus (N + P). Light fraction carbon: LFOC; light fraction nitrogen: LFN; heavy fraction carbon: HFOC; heavy fraction nitrogen: HFN; light fraction carbon/nitrogen: LFOC/N; heavy fraction carbon/nitrogen: HFOC/N; light fraction carbon/soil organic carbon: LFOC/SOC; different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05). Error bars are standard errors (n = 9).
3.4. Effects of N and P Addition on C and N Stable Isotopes of Soil Density Fractions
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed that N and P addition significantly affected the δ13C and δ15N abundances in both light and heavy fractions, except for light fraction δ15N under P addition (Table 1, p < 0.05). N addition only significantly increased light fraction δ15N abundance compared to CK (p < 0.05). Under N + P, δ13C decreased in both fractions, with a significant reduction in the heavy fraction (p < 0.05, Figure 4). δ15N increased significantly in both fractions under N + P treatment (p < 0.05). P addition significantly reduced δ13C abundance in both the light and heavy fractions (p < 0.05, Figure 4).
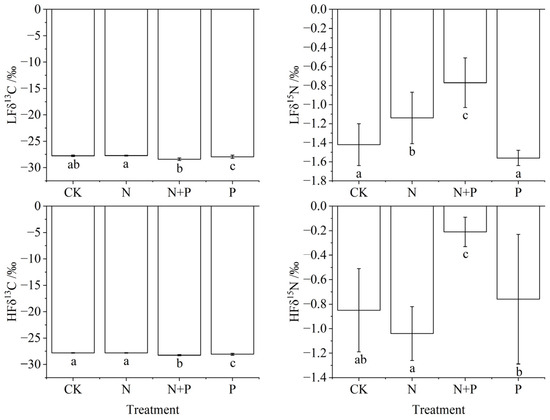
Figure 4.
Changes in stable isotope of light and heavy fractions under N and P addition in a Castanopsis sclerophylla forest in the Anhui Province of China. Treatments are control (CK), nitrogen addition (N), phosphorus addition (P), and co-addition of nitrogen and phosphorus (N + P). Light fraction δ13C: LFδ13C; light fraction δ15N: LFδ15N; heavy fraction δ13C: HFδ13C; heavy fraction δ15N: HFδ15N; different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05). Error bars are standard errors (n = 9).
3.5. Correlation Between Environmental Factors and Soil C Fractions
Random forests analysis identified significant effects of STN, pH on LFOC, STN on HFOC, STN and NH4+-N on ROC, while P treatments, TP, and soil moisture content significantly influenced δ13C abundance in heavy fractions (p < 0.05, Figure 5). Correlation analysis revealed that soil moisture reduced HFOC/N and both light and heavy fraction δ13C abundance; NH4+-N significantly increased LFOC, HFOC, ROC, and SOC, while it negatively affected LFOC/N; NO3−-N significantly promoted DOC and LFOC; TP significantly reduced HFOC/N and HFδ13C abundance; soil pH negatively affected DOC, LFOC, but positively influenced LFOC/N (p < 0.05, Figure 6). Structural equation modeling (SEM) indicated that N addition indirectly increased LFOC by significantly reducing pH (p < 0.05). Increased NO3−-N enhanced TN accumulation, which significantly contributed to light and heavy fraction C and ROC (p < 0.05, Figure 7). P addition had a direct significant negative effect on both LFOC and SOC (p < 0.05, Figure 7).
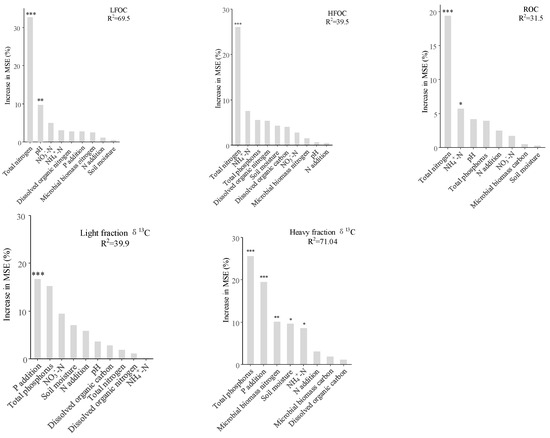
Figure 5.
Random forest model screening factors affecting organic C fraction in a Castanopsis sclerophylla forest in the Anhui Province of China. Nitrogen addition: N addition; phosphorus addition: P addition; light fraction carbon: LFOC; heavy fraction carbon: HFOC; reactive oxidized carbon: ROC; * denotes p < 0.05, ** denotes p < 0.01, and *** denotes p < 0.001.
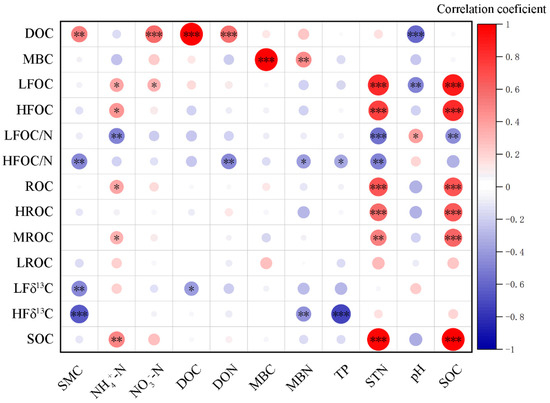
Figure 6.
Correlation analysis between soil C fraction and environmental factors in a Castanopsis sclerophylla forest in the Anhui Province of China. Dissolved organic carbon: DOC; microbial biomass carbon: MBC; light fraction carbon: LFOC; heavy fraction carbon: HFOC; light fraction carbon/nitrogen: LFOC/N; heavy fraction carbon/nitrogen: HFOC/N; reactive oxidized carbon: ROC; high activity readily oxidizable organic carbon: HROC; medium activity readily oxidizable organic carbon: MROC; low activity readily oxidizable organic carbon: LROC; light fraction δ13C: LFδ13C; heavy fraction δ13C: HFδ13C; soil organic carbon: SOC; soil moisture content: SMC; dissolved organic nitrogen: DON; microbial biomass nitrogen: MBN; total phosphorus: TP; soil total nitrogen: STN; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001.
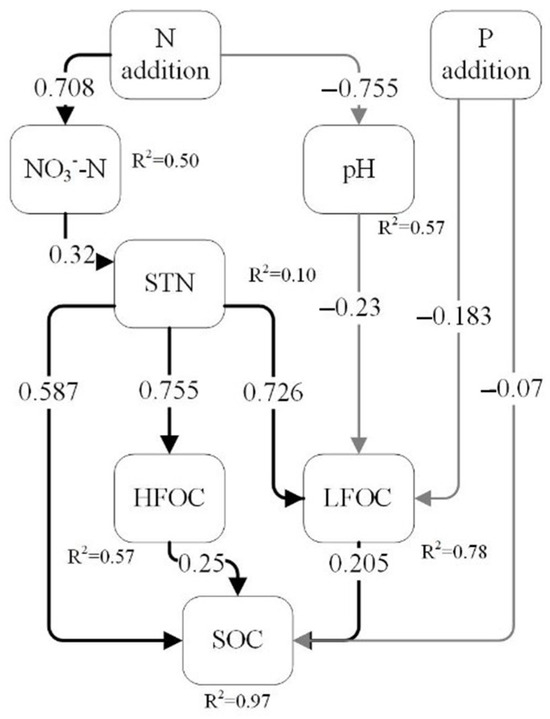
Figure 7.
Structural equation model of soil C fraction in a Castanopsis sclerophylla forest in the Anhui Province of China. χ2 = 26.91, p = 0.612, df = 16, CFI = 1, RMSEA = 0, SRMR = 0.08. Nitrogen addition: N addition; phosphorus addition: P addition; heavy fraction carbon: HFOC; soil total nitrogen: STN; light fraction carbon: LFOC; soil organic carbon: SOC. The arrows indicate the hypothesized direction of causality, the numbers on the arrows are standardized path coefficients, the black arrows indicate positive effects, the grey arrows indicate negative effects, and the R2 behind the variable represents the degree to which the model explains the different variables.
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of SOC and Its Fractions to N and P Addition
Exogenous N and P influenced soil C sequestration by altering soil chemistry, microbial activity, and SOM decomposition, etc. [33,34]. In this study, N addition, P addition, and N + P treatments had distinct effects on SOC. N addition tended to increase SOC accumulation, although not significantly (p > 0.05) [11,33]. Previous research suggests that ecosystem N enrichment can increase soil C inputs by promoting plant organic matter production and may reduce SOM decomposition through several mechanisms [11,35,36]. For example, exogenous N inputs can reduce microbial ‘N mining’ of SOM by slowing down the degree of microbial N limitation, or indirectly reduce microbial utilization of organic matter by inhibiting soil microbial activity and ‘priming effect’ through the promotion of soil acidification [35]. In addition, exogenous N inputs can also increase the chemical stability of SOM through chemical reactions, such as direct condensation with SOM or forming compounds resistant to microbial degradation [4,37,38]. Unlike N enrichment, P addition significantly reduced SOC and STN in this study (p < 0.05). Some studies have shown that ecosystem P enrichment has been shown to promote the desorption of organic compounds from soil minerals, making them more available for microbial decomposition [39,40]. In other studies of P-limited forests, P addition can enhance microbial access to SOC for decomposition by alleviating soil P limitation [41,42]. In addition, increased P availability can also enhance microbial N use, leading to the breakdown of organic N compounds and reducing SOC levels [35]. Notably, co-addition of N and P did not significantly affect SOC in this study (p > 0.05). In summary, N enrichment tends to promote SOC accumulation, P enrichment reduces SOC, and combined N and P enrichment has minimal impact on soil C stocks in this region.
Beyond changes in SOC, the proportion of its component allocation more accurately reflects the impact of N addition on the soil C pool [9,11]. In this study, N addition significantly increased LFOC and LFN (p < 0.05), while promoting HFOC and HFN accumulation (p > 0.05), and significantly decreasing LFOC/N (p < 0.05). These findings align with previous studies [4,13]. N deposition can increase soil particulate organic C and mineral-bound organic C content through increased plant C inputs [4,43]. Simultaneously, the decrease in the C to N ratio of the light fraction may be due to the replenishment of the light fraction components by fresh organic matter and the addition is less decomposed [20]. In terms of the density grouping of SOC fractions, even though N addition promoted both light and heavy fractions of organic C, it reduced the proportion of stable C fractions in SOC [26]. This differential effect may stem from the distinct origins of these fractions. The light fraction mainly consists of partially decomposed plant residues and animal and microbial remains, which are more directly derived from organic matter inputs. In contrast, adsorption-bound organic C in heavy fractions is mainly derived from metabolites produced by microbial decomposition processes [44]. In addition, the significant decrease in soil pH associated with soil N enrichment may promote the release of mineral organic C, therefore, it had a negative effect on the accumulation of heavy fraction C. In tropical forests, soil particulate organic C content significantly increased, while mineral bound organic C content significantly decreased after adding N [45].
In the Castanopsis sclerophylla forests, P addition promoted the decomposition of light fractions. Similarly, in P-limited tropical forests, the alleviation of microbial P-limitation under P addition resulted in an increase in microbial growth activity, thereby enhancing SOM decomposition [41,42]. While previous studies have shown that inorganic P enrichment facilitates the desorption of mineral-adsorbed organic matter, making it more available for microbial decomposition and reducing mineral-bound organic C, our results show a different trend. In this study, P addition increased HFOC and its proportion in SOC. This may be due to enhanced decomposition products of the light fraction, which promoted the accumulation of mineral-bound organic C [34,39,40]. Additionally, the C and N fractions of the light fraction did not change significantly under the N + P treatment, which may be due to the fact that N addition promoted SOM input, while P addition promoted the decomposition of SOM by microorganisms [41,42].
Unlike previous studies, the ROC efficiency generally declined with excessive addition of N (>60 kg N·hm−2·year−1), N addition promoted the transformation of reactive organic C into more stable and inert forms, after 7 years of N application (100 kg N·hm−2·year−1) in this region, exogenous N inputs increased the accumulation of both labile and nonlabile organic C in the soil, so that the stability of the soil C pool did not change [22,46]. Under N + P and P treatments, no significant changes were observed for the different ROC fractions (p > 0.05), whereas in terms of chemical stability, the stability of soil C pools showed a decrease.
4.2. Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Response of Soil Light and Heavy Fractions to N and P Addition
In this region, N addition significantly increased light fraction δ15N abundance (p < 0.05), slightly increased light fraction δ13C abundance and decreased heavy fraction δ15N (p > 0.05) [47]. This result aligns with Liu et al. (2017), who reported that soil δ15N increased significantly with the N addition [47]. Soil δ15N are regulated by N input fluxes and N output fluxes [48]. Compared to soil and plant δ15N values, atmospheric N deposition is usually a source of isotope depletion [48]. Therefore, if N export rate remains constant, an increase in the N input rate will decrease the δ15N value of the soil. However, the continuous input of exogenous N with low δ15N values into the soil, combined with microbial preferences for δ14N compounds by microbial decomposition of organic matter, nitrification, and denitrification can result in the loss of δ14N-rich forms (e.g., N2, NO3−-N, and DON) [49]. These losses, along with the uptake of N by the plants, have contributed to the continuous accumulation of δ15N-rich compounds in soil [49,50]. With N addition, soil δ13C abundance reflects a balance between inputs of low δ13C organic matter from plants and increased 13C enrichment from soil C decomposition [51]. The increased δ13C abundance under N addition in this region may be due to increased input of fresh SOM or plant residues promoting microbial decomposition while it also reduced microbial decomposition of pre-existing δ13C-rich organic matter [28,36]. In addition, the lower δ15N values of the heavy fraction may be attributed to the fact that the heavy fraction organic matter was partially derived from microbial low δ15N abundance decomposition products [49,50].
Considering P addition depletes SOC and SON, and drives the decomposition of light and heavy fractions, the decrease in the abundance of δ13C and δ15N of light fractions in this region under P addition may be due to the decomposition of the original δ13C- and δ15N-rich light fraction organic matter. Related studies have shown that exogenous phosphorus promotes soil N uptake by trees, which may result in a decrease in STN [27]. Microorganisms often lose in competition with plants for nutrients but exhibit greater flexibility in nutrient acquisition [27]. When N becomes limited, soil microbial sources of N are expected to shift from inorganic N (NO3−-N) to organic N, thereby enhancing utilization of soil organic N pools to avoid direct competition with plants [27]. This shift may result in increased microbial utilization of pre-existing organic matter in the soil [27]. Additionally, the possible reason for P addition inducing a small increase in HFOC, HFON, heavy fraction δ15N abundance, and the decrease in HFOC/N, may mainly originate from the input of light fraction δ15N-rich decomposition products [27,28].
The content of C and N fractions in the light and heavy fractions did not change significantly under the N + P treatment (p > 0.05); however, δ13C decreased in both fractions, with a significant reduction in the heavy fraction (p < 0.05), and δ15N increased significantly in both fractions (p < 0.05), suggesting that the C composition of the light and heavy fractions changed by N + P. In this study, MBC and MBN increased under N + P, indicating that microbial growth activity was promoted. The N and P enrichment may have facilitated the limitation of elemental C requirements for microbial growth in the soil system [27]. The increase in DOC and slight decrease in SOC suggest that N and P inputs not only promote the consumption of newly imported organic matter, but also the loss of pre-existing δ13C-rich organic matter by decomposition, resulting in a decrease in light and heavy fraction δ13C [49,50,51]. Similar to N addition, N and P addition inputs enhanced the accumulation of light and heavy fractions δ15N. Considering the microbial preference for δ14N utilization, enrichment of δ15N-rich organic matter appears to reduce microbial exploitation of pre-existing organic matter. Therefore, N addition may increase soil C pool stability through fractionation of stable isotopes [47].
4.3. Factors Affecting Changes in SOC Fractions Under N and P Addition
Randomized forests analysis showed that the increase in STN due to N addition which had a significant effect on soil C fractions (LFOC, HFOC, and ROC), while N addition induced significant decrease in pH significantly affected LFOC [52,53]. Significant accumulation of TP promoted by P addition and significant increase in soil moisture under N and P addition had significant effects on light and heavy fraction δ13C abundance (p < 0.05) [54]. Correlation analysis revealed that NH4+-N significantly promoted the accumulation of LFOC, HFOC, ROC, DOC, SOC, while significantly reduced LFOC/N. NO3−-N significantly increased LFOC (p < 0.05). These findings suggest that N-induced enrichment of soil available N contributes to the enhancement of soil C sinks in this region [54]. In addition to directly increasing plant litter production, it has been shown that N enrichment can promote the rate of microbial decomposition of litter by increasing soil moisture and available N, thus promoting SOC inputs [54].
We also found that a significant increase in DOC under N addition, which corresponded with a decline in light fraction δ13C (p < 0.05). Previous studies offer differing explanations for this pattern. One interpretation suggests that increased soil moisture under N and P addition promotes the decomposition of older C in both light and heavy fractions, resulting in leaching of δ13C-rich DOC from the soil [54]. Alternatively, increased soil moisture may increase low δ13C DOC inputs from plant root secretions and decomposition of surface organic matter, and reduce microbial consumption of soil C fractions [55]. In this study, the significant increase in soil moisture under N and P addition likely contributed to reduce both light and heavy fraction δ13C abundance by enhancing DOC (p < 0.05). Combining the differences in the effects of N and P additions on SOC, the significant increase in soil moisture mediated by N additions may improve soil DOC inputs, while increased DOC reduces the consumption of LFOC by soil microorganisms and decreases the loss of light fraction δ12C. P additions tend to promote the decomposition of light fraction, increasing the export of δ13C-rich DOC [55].
In this study, decreasing soil pH promoted the accumulation of DOC and LFOC while reducing LFOC/N (p < 0.05). However, lower pH did not suppress microbial biomass, possibly because the broadleaf forest soils in this region are naturally weakly acidic and local microbial communities have adapted to such conditions [20]. Despite this adaptation, ongoing acidification may still inhibit microbial decomposition of SOM [26,52,53]. SEM further confirmed that N addition indirectly increased LFOC by significantly lowering pH (p < 0.05) [20,35]. Previous studies indicate that soil acidification can reduce the source of mineral-bound C by decreasing microbial metabolites [52,53]. Meanwhile, a decrease in soil acidity results in the loss of exchangeable metal ions (e.g., calcium, magnesium, etc.), which are critical for stabilizing mineral-bound carbon [4,52,53]. However, in this study, we did not observe a decline in heavy fraction C associated with lower pH. In addition, SEM indicated that N addition significantly increased LFOC and HFOC by promoting NO3−-N and TN accumulation. Nonetheless, SEM did not confirm a direct effect of available N on C fractions. Wang et al. (2021) proposed that increased available N may indirectly promote C accumulation through enhanced organic matter input, decreased microbial N mining from SOM, and reduced plant uptake of organic N [27,43]. In contrast, P addition had a significant direct negative effect (p < 0.05) on both LFOC and SOC, which further proved that P enrichment may impair soil C sequestration in Castanopsis sclerophylla forests in this region [42].
5. Conclusions
This study revealed distinct effects of N and P additions on soil C and N fractions in Castanopsis sclerophylla forests. N addition promoted the accumulation of SOC, STN, LFOC, LFN, HFOC and HFN, accompanied by a decrease in the LFOC/N and an increase in the LFOC/SOC. Contrary to N addition, P addition reduced SOC and STN, LFOC and LFN accumulation, while increasing HFOC and HFN and decreasing the LFOC/SOC ratio. SOC, STN, LFOC and LFN showed no significant changes under N + P treatment (p > 0.05). Potassium permanganate oxidation analysis indicated that N addition did not reduce SOC stability, whereas N + P and P addition treatments decreased the stability of the soil C pool. Stable isotope data further revealed contrasting mechanisms of soil C and N accumulation under different nutrient inputs. N addition increased δ13C- and δ15N-enriched organic matter in the light fraction while reducing δ15N in the heavy fraction. In contrast, P addition enhanced the decomposition of δ13C- and δ15N-rich light fraction organic matter. The LFOC and LFN did not change significantly under the N + P treatment, whereas the decrease in δ13C and the increase of δ15N indicated changes in the organic matter composition of the light and heavy fractions. Additionally, N addition significantly lowered soil pH, which promoted LFOC accumulation. NO3−-N and NH4+-N enrichment increased STN content (p > 0.05) and significantly promoted ROC and LFOC under N addition. In contrast, P addition had a direct and significant negative effect on LFOC and SOC (p < 0.05). This study provides a theoretical basis for predicting the future changes of C sink function and ecosystem C sequestration potential of evergreen broad-leaved forest, and provide scientific support for formulating reasonable nutrient management policies and coping strategies with climate change in southern China.
Author Contributions
X.X. and Y.D. designed the research; Material preparation, data collection, and analyses were performed by Y.D. and L.C.; The first draft of the manuscript was written by Y.D., X.X. and Y.D. modified the manuscript and improved the English language and grammatical editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31770672 and 31370626), the National Basic Research Program of China (2010CB950602), General Project of Basic Sciences in Higher Education Institutions in Jiangsu Province (23KJB2220009) and Special Funding for Suzhou Polytechnic Institute of Agriculture Innovative Research Team (CXTD202406).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Forestry Bureau of Shitai County, Anhui for their assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tang, X.L.; Zhao, X.; Bai, Y.F.; Tang, Z.Y.; Wang, W.T.; Zhao, Y.C.; Wan, H.W.; Xie, Z.Q.; Shi, X.Z.; Wu, B.F.; et al. Carbon pools in China’s terrestrial ecosystems: New estimates based on an intensive field survey. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.X.; Deng, Z.Q.; Yu, Y.C.; Xu, X.N.; Bi, L.L.; Tao, X. Differential responses of soil respiration and its components to nitrogen application in urban forests. Forests 2022, 13, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.F.; Williams, C.A. The terrestrial carbon sink. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2018, 43, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, C.C.; Deng, J.; Zhang, B.W.; Chen, F.S.; Chen, W.; Fang, X.M.; Li, J.J.; Zu, K.L.; Bu, W.S. Response of tree growth to nutrient addition is size dependent in a subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Shi, Y.; Sun, W.J.; Chang, J.F.; Zhu, J.X.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.P.; Zhang, H.T.; Yu, L.F.; et al. Terrestrial carbon sinks in China and around the world and their contribution to carbon neutrality. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 861–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.R.; Wen, Z.Y.; Yin, R.Y.; Deng, P.F.; Gao, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, X.N. Soil organic carbon turnover response to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in eastern China: Evidence from stable carbon isotopes. Forests 2023, 14, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Martinez, V.; Collins, S.L.; McLaren, J.R. Long-term fertilization increases soil but not plant or microbial N in a Chihuahuan Desert grassland. Biogeosciences 2024, 21, 2655–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuelas, J.; Poulter, B.; Sardans, J.; Ciais, P.; van der Velde, M.; Bopp, L.; Boucher, O.; Godderis, Y.; Hinsinger, P.; Llusia, J.; et al. Human-induced nitrogen-phosphorus imbalances alter natural and managed ecosystems across the globe. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jia, Y.L.; Yu, G.R.; He, N.P.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Y.F. Anthropogenic reactive nitrogen deposition and associated nutrient limitation effect on gross primary productivity in inland water of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Ren, C.J.; Wang, C.K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Luo, Y.Q.; Luo, Z.K.; Du, Z.G.; Zhu, B.; Yang, Y.H.; Jiao, S.; et al. Global turnover of soil mineral-associated and particulate organic carbon. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, C.E.; Hobbie, S.E.; Bach, E.M.; Hofmockel, K.S.; Kazanski, C.E. Nitrogen addition changes grassland soil organic matter decomposition. Biogeochemistry 2015, 125, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Feng, W.; Niu, S.; Plante, A.F.; Luo, Y.; Wang, K. Different responses of soil organic carbon fractions to nitrogen additions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.B.; Wang, G.A.; Huang, C.H.; Gao, R.T.; Xi, B.D.; Zhu, B.A. Physico-chemical protection, rather than biochemical composition, governs the responses of soil organic carbon decomposition to nitrogen addition in a temperate agroecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.J.; Zhu, W.X.; Zhou, Y.B.; Yin, Y. Soil organic carbon chemical functional groups under different revegetation types are coupled with changes in the microbial community composition and the functional genes. Forests 2019, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.L.; Li, Z.J.; Wakelin, S.A.; Yu, W.T.; Liang, Y.C. Mineral fertilizer alters cellulolytic community structure and suppresses soil cellobiohydrolase activity in a long-term fertilization experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 55, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Elliott, E.T. Methods for physical separation and characterization of soil organic matter fractions. Geoderma 1993, 56, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.T. Physical fractionation of soil and structural and functional complexity in organic matter turnover. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 52, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Luetzow, M.; Koegel-Knabner, I.; Ekschmitt, K.; Flessa, H.; Guggenberger, G.; Matzner, E.; Marschner, B. SOM fractionation methods: Relevance to functional pools and to stabilization mechanisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2183–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Niu, S.L.; Li, L.H.; Zhang, L.X.; Yu, G.R. Soil carbon fractions in grasslands respond differently to various levels of nitrogen enrichments. Plant Soil 2014, 384, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Lu, X.K.; Aoyagi, R.; Mo, J.M. Reconsidering the phosphorus limitation of soil microbial activity in tropical forests. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.C.; Townsend, A.R.; Gleixner, G.; Lehman, S.J.; Turnbull, J.; Bowman, W.D. Variable effects of nitrogen additions on the stability and turnover of soil carbon. Nature 2002, 419, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Gilliam, F.S.; Gundersen, P.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Mo, J.M. Interactive effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on soil microbial communities in a tropical forest. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiroff, W.A.; Zak, D.R.; Upchurch, R.A.; Salley, S.O.; Grandy, A.S. Anthropogenic N deposition alters soil organic matter biochemistry and microbial communities on decaying fine roots. Global Change Biol. 2019, 25, 4369–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.P.; Liu, W.F.; Zhang, W.X.; Shao, Y.H.; Duan, H.L.; Chen, B.D.; Wei, X.H.; Fan, H.B. Long-term nitrogen addition changes soil microbial community and litter decomposition rate in a subtropical forest. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.G.; Zhang, Q.F.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, B. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil organic carbon: Review and prospects. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 46, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Penuelas, J.; Li, T.; Liu, H.Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.G.; Sardans, J.; Jiang, Y. Natural abundance of 13C and 15N provides evidence for plant-soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a N-fertilized meadow. Ecology 2021, 102, e03348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Geng, S.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Setala, H.; Gu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.X.; Han, S.J. Addition of nitrogen enhances stability of soil organic matter in a temperate forest. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Joergensen, R.G.; Pommerening, B.; Chaussod, R.; Brookes, P.C. Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction—An automated procedure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.B.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agr. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, H.H.; Campbell, C.A.; Brandt, S.A.; Lafond, G.P.; Townleysmith, L. Light-fraction organic matter in soils from long-term crop rotations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J. Structural Equation Modeling and Natural Systems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.H.; Xu, X.; Ju, C.H.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Wilsey, B.J.; Luo, Y.Q.; Fan, W. Long-term, amplified responses of soil organic carbon to nitrogen addition worldwide. Global Change Biol. 2021, 27, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhao, Y.; He, S.; Wu, Z.D.; Yue, M.; Hong, M. Metagenomics reveals the response of desert steppe microbial communities and carbon-nitrogen cycling functional genes to nitrogen deposition. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1369196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Qiao, C.L.; Yang, S.; Bai, W.M.; Liu, L.L. Microbial carbon use efficiency and priming effect regulate soil carbon storage under nitrogen deposition by slowing soil organic matter decomposition. Geoderma 2018, 332, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Clark, J.S.; Kovach, K.R.; Townsend, P.A.; Swenson, J.J. Remotely sensed crown nutrient concentrations modulate forest reproduction across the contiguous United States. Ecology 2024, 105, e4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FOG, K. The effect of added nitrogen on the rate of decomposition of organic matter. Biol. Rev. 1988, 63, 433–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, I.A.; Dieleman, W.; Luyssaert, S.; Subke, J.A.; Reichstein, M.; Ceulemans, R.; Ciais, P.; Dolman, A.J.; Grace, J.; Matteucci, G.; et al. Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Schleuss, P.M. Addition of inorganic phosphorus to soil leads to desorption of organic compounds and thus to increased soil respiration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 130, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Diakova, K.; Aburto, F.; Doetterl, S.; Borovec, J. Sorption and desorption of organic matter in soils as affected by phosphate. Geoderma 2022, 405, 115377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.R.; Kim, M.; Hatt, J.K.; Phillips, J.R.; Yao, Q.M.; Song, Y.; Hazen, T.C.; Mayes, M.A.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Phosphate addition increases tropical forest soil respiration primarily by deconstraining microbial population growth. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 130, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.F.; Porter, W.; Phillips, J.R.; Aidar, M.P.M.; Lebreux, S.J.; Schadt, C.W.; Mayes, M.A. Phosphorus rather than nitrogen enhances CO2 emissions in tropical forest soils: Evidence from a laboratory incubation study. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 71, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chlus, A.; Geygan, R.; Ye, Z.; Zheng, T.; Singh, A.; Couture, J.J.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Kruger, E.L.; Townsend, P.A. Foliar functional traits from imaging spectroscopy across biomes in eastern North America. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 494–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandy, A.S.; Neff, J.C. Molecular C dynamics downstream: The biochemical decomposition sequence and its impact on soil organic matter structure and function. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.G.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, C.Y.; Zhu, B. Nitrogen addition has contrasting effects on particulate and mineral-associated soil organic carbon in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.N.; Liu, W.C.; Zhu, Y.F.; Li, J.X.; Wen, Y.H.; Liu, F.H.; Ren, C.J.; Han, X.H. Effects of Short-term Nitrogen Addition on Soil Organic Carbon Components in Robinia pseudoacacia L. Plantation. Huanjing Kexue 2023, 44, 2767–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Peng, B.; Xia, Z.W.; Jiang, P.; Bai, E. Effect of nitrogen addition on the variations in the natural abundance of nitrogen isotopes of plant and soil components. Plant Soil 2017, 412, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, R.; Austin, A.T.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Yoo, K.; Matzek, V.; Kendall, C.; Uebersax, A.; Brenner, D.; Baisden, W.T. Global patterns of the isotopic composition of soil and plant nitrogen. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookshire, E.N.J.; Hedin, L.O.; Newbold, J.D.; Sigman, D.M.; Jackson, J.K. Sustained losses of bioavailable nitrogen from montane tropical forests. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.B.; Liu, D.W.; Wu, H.H.; Lu, X.T.; Fang, Y.T.; Cheng, W.X.; Luo, W.T.; Jiang, P.; Shi, J.S.; et al. Aridity threshold in controlling ecosystem nitrogen cycling in arid and semi-arid grasslands. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Liu, H.Y.; Yin, J.F.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Xu, Z.W.; Jiang, Y. Response of soil carbon to nitrogen and water addition differs between labile and recalcitrant fractions: Evidence from multi-year data and different soil depths in a semi-arid steppe. Catena 2019, 172, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilling, A.; Keiluweit, M.; Gutknecht, J.L.M.; Grandy, A.S. Priming mechanisms providing plants and microbes access to mineral-associated organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 158, 108265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Bougoure, J.J.; Nico, P.S.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Weber, P.K.; Kleber, M. Mineral protection of soil carbon counteracted by root exudates. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.Q.; Wang, S.L.; Zhang, C.M.; Tang, H.; Li, X.Q.; Wu, Z.J.; Luo, J. Soil microbial activity and nutrients of evergreen broad-leaf forests in mid-subtropical region of China. J. Forestry Res. 2015, 26, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Lu, Q.; Li, L.; Han, X.; Wan, S. Non-additive effects of water and nitrogen addition on ecosystem carbon exchange in a temperate steppe. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).