Contrasting Effects of Moso Bamboo Expansion into Broad-Leaved and Coniferous Forests on Soil Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Experimental Design
2.2. Soil Sampling and Measurement
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Moso Bamboo Expansion on Soil Physico-Chemical Properties
3.2. Impacts of Moso Bamboo Encroachment on Soil Microbial Assemblages
3.3. Relationship Between Soil Microbial Communities and Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of PF Expansion into MF on Soil Microbial Community Structure
4.2. Effect of PF Encroachment into CF on Soil Microbial Community Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Q.-F.; Liang, C.-F.; Chen, J.-H.; Li, Y.-C.; Qin, H.; Fuhrmann, J.J. Rapid Bamboo Invasion (Expansion) and Its Effects on Biodiversity and Soil Processes. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayston, S.J.; Campbell, C.D.; Bardgett, R.D.; Mawdsley, J.L.; Clegg, C.D.; Ritz, K.; Griffiths, B.S.; Rodwell, J.S.; Edwards, S.J.; Davies, W.J.; et al. Assessing Shifts in Microbial Community Structure across a Range of Grasslands of Differing Management Intensity Using CLPP, PLFA and Community DNA Techniques. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 25, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merilä, P.; Malmivaara-Lämsä, M.; Spetz, P.; Stark, S.; Vierikko, K.; Derome, J.; Fritze, H. Soil Organic Matter Quality as a Link between Microbial Community Structure and Vegetation Composition along a Successional Gradient in a Boreal Forest. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Fu, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, R. Effects of Understory Removal and Litter Addition on Leaf and Twig Decomposition in a Subtropical Chinese Fir Plantation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 5004–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Liu, Y.; Bai, J.; Li, A.; Deng, W.; Bai, T.; Liu, X.; Lai, M.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Impact of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Expansion into Japanese Cedar Plantations on Soil Fungal and Bacterial Community Compositions. Forests 2022, 13, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, R.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.; Wan, S. Understory Removal Accelerates Nucleic Phosphorus Release but Retards Residual Phosphorus Release in Decomposing Litter of Phyllostachys edulis in Subtropical China. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; van Straalen, N.M. The Unseen Majority: Soil Microbes as Drivers of Plant Diversity and Productivity in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wen, Z.; Yang, Y.-Z. Effects of Plant Functional Traits on Ecosystem Services: A Review. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 45, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, W.K.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Amatangelo, K.; Dorrepaal, E.; Eviner, V.T.; Godoy, O.; Hobbie, S.E.; Hoorens, B.; Kurokawa, H.; Pérez-Harguindeguy, N.; et al. Plant Species Traits Are the Predominant Control on Litter Decomposition Rates within Biomes Worldwide. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Huang, Z. Functional Trait Variation and Community-Weighted Means of Tree Traits Can Alter Soil Microbial Biomass and Community Composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 170, 108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; van der Sande, M.T.; Amissah, L.; Dabo, J.; Mohammed Abdul, S.; Poorter, L. Herbaceous Species and Dry Forest Species Have More Acquisitive Leaf Traits than Woody Species and Wet Forest Species. Funct. Ecol. 2024, 38, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Fang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Duan, C.; Chen, Q.; Song, X.; Tian, X. Enlarging Interface Reverses the Dominance of Fungi over Bacteria in Litter Decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 198, 109543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-M.; Wu, F.-Z.; Ji, Y.; Xia, J.; Wei, S.-Y.; Yuan, C.-X.; Peng, Y.; Ni, X.-Y.; Yue, K. Global Patterns and Influencing Factors of Initial Concentrations of Phenols in Plant Litter. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2023, 47, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negesse, Z.; Pan, K.; Guadie, A.; Justine, M.F.; Azene, B.; Pandey, B.; Wu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L. Plant Invasions Alter Soil Biota and Microbial Activities: A Global Meta-Analysis. Plant Soil 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, K.; Collantes, M.B.; Yahdjian, L.; Escartin, C.; Anchorena, J.A. Increased Litter Decomposition Rates of Exotic Invasive Species Hieracium pilosella (Asteraceae) in Southern Patagonia, Argentina. Plant Ecol. 2019, 220, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, B.; Siemann, E.; Lu, X. Plant Invasion Affects Litter Decomposition Differently in Native and Invasive Plant Conditioned Soils. Plant Soil 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Tang, S.-L.; Pai, C.-W.; Whitman, W.B.; Coleman, D.C.; Chiu, C.-Y. Changes in the Soil Bacterial Communities in a Cedar Plantation Invaded by Moso Bamboo. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Meng, M.; Biswas, S.R.; Ye, L.; Zhang, J. Effects of Land Use Change on the Composition of Soil Microbial Communities in a Managed Subtropical Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 373, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Siemann, E.; Cui, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L. Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Invasion Effects on Litter, Soil and Microbial PLFA Characteristics Depend on Sites and Invaded Forests. Plant Soil 2019, 438, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, L.; Liang, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, B. Coupling Bacterial Community Assembly to Microbial Metabolism across Soil Profiles. mSystems 2020, 5, e00298-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Cui, H.; Hu, X.; Qi, L. Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Expansion Enhances Soil pH and Alters Soil Nutrients and Microbial Communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Tian, D.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; He, N.; Niu, S. Microbes Drive Global Soil Nitrogen Mineralization and Availability. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, H.; Liang, C.; Shao, S.; Fuhrmann, J.J.; Chen, J.; Xu, Q. Moso Bamboo Invasion Has Contrasting Effects on Soil Bacterial and Fungal Abundances, Co-Occurrence Networks and Their Associations with Enzyme Activities in Three Broadleaved Forests across Subtropical China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 498, 119549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larpkern, P.; Moe, S.R.; Totland, Ø. Bamboo Dominance Reduces Tree Regeneration in a Disturbed Tropical Forest. Oecologia 2011, 165, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Niu, J.; Fang, H.; Feng, Y.; Bai, T.; Zhang, M.; Deng, W.; Siemann, E.; Zhang, L. Moso Bamboo Expansion Reduced Soil N2O Emissions While Accelerated Fine Root Litter Decomposition: Contrasting Non-Additive Effects. Plant Soil 2024, 501, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Ouyang, M.; Yang, Q.; Lu, H.; Yang, G.; Chen, F.; Shi, J.-M. Degradation of Litter Quality and Decline of Soil Nitrogen Mineralization after Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys pubscens) Expansion to Neighboring Broadleaved Forest in Subtropical China. Plant Soil 2016, 404, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Compson, Z.G.; Gui, X.; Yang, Q.; Song, Q.; Huang, D.; Ren, Z.; Luan, F. Weak Responses of Soil Microorganisms to Leaf Litter Inputs after Native Phyllostachys edulis Invasion into Adjacent Native Forests. Plant Soil 2024, 494, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Hu, W.; Dai, Y.; Ai, L.; Wu, M.; Hu, J.; Zuo, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, H.; Ma, J. Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houzeau) Invasion Affects Soil Microbial Communities in Adjacent Planted Forests in the Lijiang River Basin, China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1111498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.-H.; Chiu, C.-Y. Changes in Soil Microbial Community Structure and Activity in a Cedar Plantation Invaded by Moso Bamboo. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 91, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.-F.; Jiang, P.-K.; Wu, J.-S.; Zhou, G.-M.; Shen, R.-F.; Fuhrmann, J.J. Bamboo Invasion of Native Broadleaf Forest Modified Soil Microbial Communities and Diversity. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; He, H.; Liang, C.; Chen, J.; Qin, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Jia, W.; Zheng, X.; et al. Moso Bamboo Expansion into a Broadleaved Forest Alters the Dominant Soil Organic Carbon Source. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 74, e13366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Pan, Y.; Yang, P.; Hu, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.; Yan, X. A Comparison of Microbial Composition under Three Tree Ecosystems Using the Stochastic Process and Network Complexity Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1018077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossio, D.A.; Scow, K.M. Impacts of Carbon and Flooding on Soil Microbial Communities: Phospholipid Fatty Acid Profiles and Substrate Utilization Patterns. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 35, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frostegård, A.; Bååth, E. The Use of Phospholipid Fatty Acid Analysis to Estimate Bacterial and Fungal Biomass in Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1996, 22, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Zhong, B.; Chen, W.; Mo, J.; Wang, F.; Lu, X. Consistent Effects of Nitrogen Addition on Soil Microbial Communities across Three Successional Stages in Tropical Forest Ecosystems. CATENA 2023, 227, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Shao, S.; Qin, H.; Xu, Q.; Liang, C.; Chen, J. Moso Bamboo Invasion Changes the Assembly Process and Interactive Relationship of Soil Microbial Communities in a Subtropical Broadleaf Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 536, 120901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sasaki, A.; Toda, M.; Nakatsubo, T. Changes in Soil Microbial Community and Activity in Warm Temperate Forests Invaded by Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). J. For. Res. 2016, 21, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, B.; Li, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wan, S. Contrasting Effect of Thinning and Understory Removal on Soil Microbial Communities in a Subtropical Moso Bamboo Plantation. Forests 2022, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, N.; Shi, W.; Hou, L.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Huang, L.; Gu, H.; Yang, Q.; Deng, G.; Yang, G. Superior Growth, N Uptake and NH4+ Tolerance in the Giant Bamboo Phyllostachys edulis over the Broad-Leaved Tree Castanopsis fargesii at Elevated NH4+ May Underlie Community Succession and Favor the Expansion of Bamboo. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 1606–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.L.; Qi, Y.C.; Peng, Q.; Dong, Y.S.; Guo, S.F.; Yan, Z.Q.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, Z.L. Effects of Exogenous Carbon Input on Key Processes of Terrestrial Ecosystem Carbon Cycling and the Microbiological Driving Mechanisms. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.S.; Zou, N. Research Progress on the Impact of Phyllostachys pubescens Expansion on Forest Ecosystems and Its Management. J. Jianghan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 49, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ying, Q.; Liu, J. Effects of Lime Application and Understory Removal on Soil Microbial Communities in Subtropical Eucalyptus L’Hér. Plantations. Forests 2019, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, V.L.; Smith, J.L.; Bolton, H. Fungal-to-Bacterial Ratios in Soils Investigated for Enhanced C Sequestration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

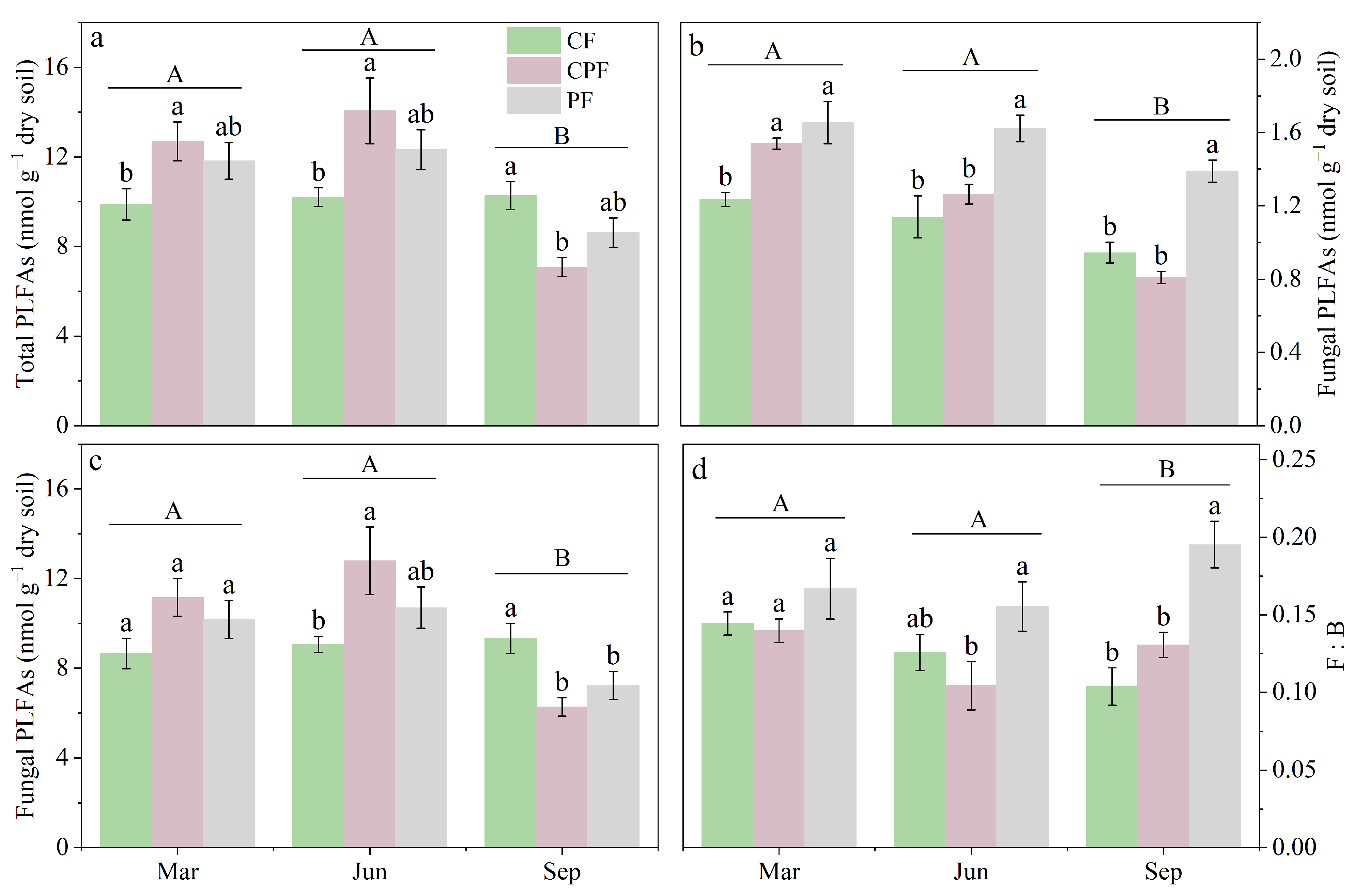
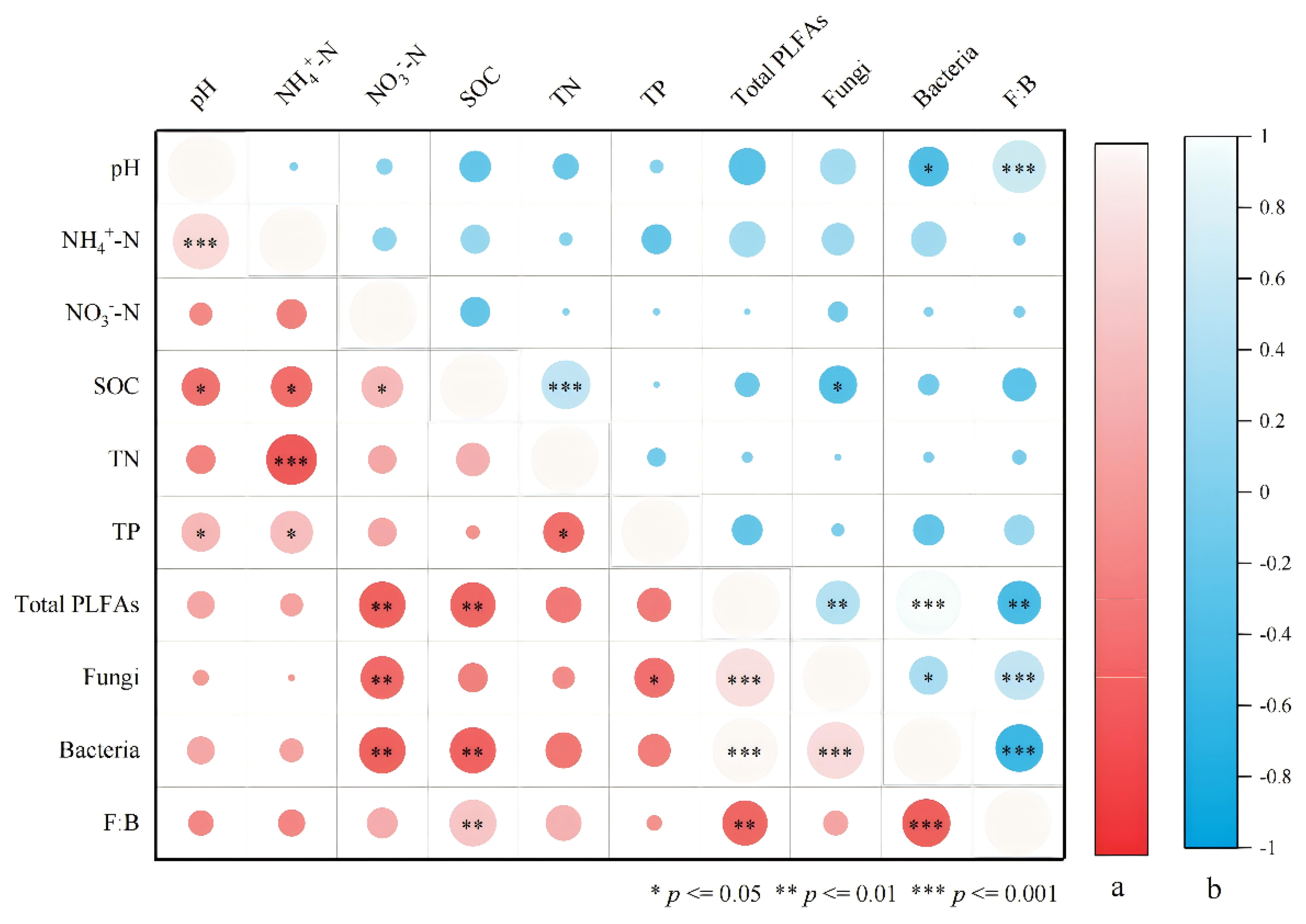
| pH | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | SOC (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF | 4.76 ± 0.03 b | 9.02 ± 0.04 b | 17.50 ± 0.97 a | 67.11 ± 3.01 a | 3.55 ± 0.07 a | 0.57 ± 0.01 b |
| MPF | 5.05 ± 0.03 a | 18.28 ± 1.32 a | 14.61 ± 0.65 b | 61.41 ± 1.59 a | 3.54 ± 0.08 a | 0.61 ± 0.02 ab |
| PF | 4.99 ± 0.02 a | 20.45 ± 2.17 a | 14.24 ± 0.49 b | 47.76 ± 1.70 b | 3.08 ± 0.13 b | 0.66 ± 0.02 a |
| pH | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | SOC (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 4.79 ± 0.04 b | 15.68 ± 2.79 a | 13.22 ± 0.57 a | 79.50 ± 3.26 a | 3.99 ± 0.28 a | 0.64 ± 0.01 a |
| CPF | 4.76 ± 0.04 b | 11.21 ± 2.17 a | 14.13 ± 1.05 a | 52.60 ± 2.22 b | 2.92 ± 0.17 b | 0.68 ± 0.02 a |
| PF | 5.14 ± 0.04 a | 16.74 ± 2.71 a | 14.77 ± 0.67 a | 50.74 ± 1.93 b | 3.33 ± 0.19 b | 0.65 ± 0.01 a |
| Variables | Total PLFAs | Fungal PLFAs | Bacterial PLFAs | F:B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| Time | 17.537 | <0.01 | 18.473 | <0.01 | 15.973 | <0.01 | 1.278 | 0.295 |
| Forest type | 7.448 | <0.01 | 1.523 | 0.236 | 7.785 | <0.01 | 5.059 | <0.05 |
| Time × forest type | 0.463 | 0.762 | 1.301 | 0.295 | 0.401 | 0.806 | 1.191 | 0.337 |
| Variables | Total PLFAs | Fungal PLFAs | Bacterial PLFAs | F:B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| Time | 15.65 | <0.01 | 28.96 | <0.01 | 12.434 | <0.01 | 2.15 | 0.136 |
| Forest type | 1.574 | 0.226 | 33.622 | <0.01 | 1.277 | 0.295 | 13.114 | <0.01 |
| Time × forest type | 5.446 | <0.01 | 3.478 | <0.05 | 4.89 | <0.05 | 2.305 | 0.084 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, R.; Long, W.; Kong, F.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Li, R.; Wan, S. Contrasting Effects of Moso Bamboo Expansion into Broad-Leaved and Coniferous Forests on Soil Microbial Communities. Forests 2025, 16, 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071188
Lin R, Long W, Kong F, Zhu J, Wang M, Liu J, Li R, Wan S. Contrasting Effects of Moso Bamboo Expansion into Broad-Leaved and Coniferous Forests on Soil Microbial Communities. Forests. 2025; 16(7):1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071188
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Rong, Wenjie Long, Fanqian Kong, Juanjuan Zhu, Miaomiao Wang, Juan Liu, Rui Li, and Songze Wan. 2025. "Contrasting Effects of Moso Bamboo Expansion into Broad-Leaved and Coniferous Forests on Soil Microbial Communities" Forests 16, no. 7: 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071188
APA StyleLin, R., Long, W., Kong, F., Zhu, J., Wang, M., Liu, J., Li, R., & Wan, S. (2025). Contrasting Effects of Moso Bamboo Expansion into Broad-Leaved and Coniferous Forests on Soil Microbial Communities. Forests, 16(7), 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071188







