Abiotic Nitrite Incorporation into Organic Matter in Volcanic and Non-Volcanic Soil Within Rainforest Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2. Dissolved Organic Nitrogen
2.3. Dissolved Organic Nitrogen Sterilization
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Microcosm Experiment
2.6. Labelled Nitrogen Concentration
2.7. Data Analysis
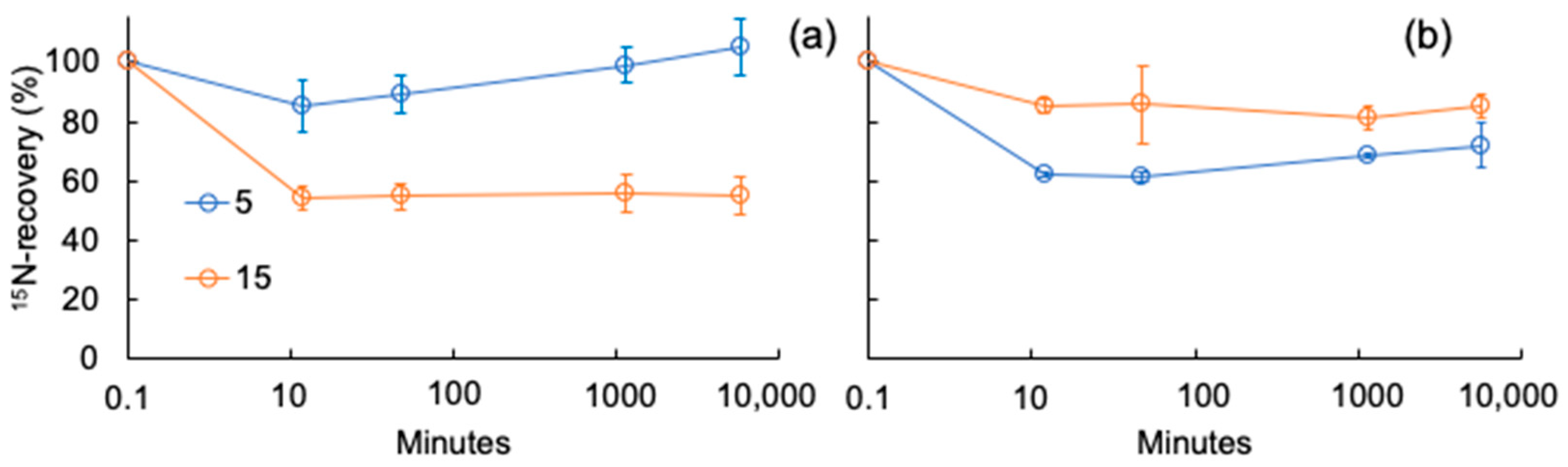
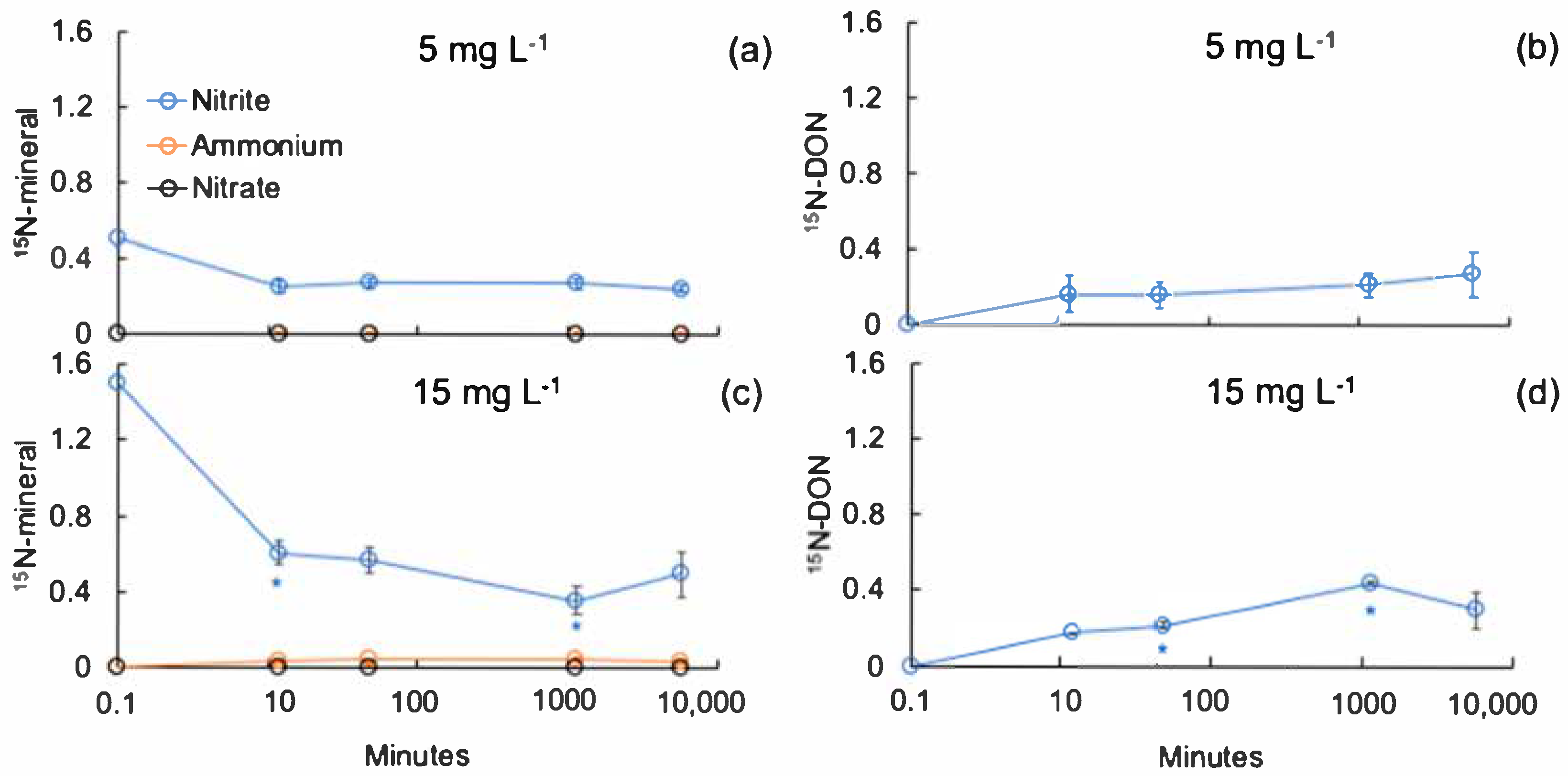
3. Results
3.1. Soil Solution Characterization
3.2. Nitrite Transformation to Organic Nitrogen Forms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huygens, D.; Rütting, T.; Boeckx, P.; Van Cleemput, O.; Godoy, R.; Müller, C. Soil nitrogen conservation mechanisms in a pristine south chilean Nothofagus ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2448–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huygens, D.; Boeckx, P.; Templer, P.H.; Paulino, L.; Van Cleemput, O.; Oyarzún, C.E.; Müller, C.; Godoy, R. Mechanisms for retention of bioavailable nitrogen in volcanic rainforest soil. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.; United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources: International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS), Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Berntson, G.M.; Aber, J.D. The importance of fast nitrate immobilization in N-saturated temperate forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus, F.; Stock, S.; Eschenbach, W.; Dyckmans, J.; Merino, C.; Nájera, F.; Köster, M.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Dippold, M.A. Ferrous wheel hypothesis: Abiotic nitrate incorporation into dissolved organic matter. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 245, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.; Rancourt, D.G.; Chadwick, O.A.; Chorover, J. Iron solid-phase differentiation along a redox gradient in basaltic soils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedin, L.O.; Armesto, J.J.; Johnson, A.H. Patterns of nutrient loss from unpolluted, old-growth temperate forests: Evaluation of biogeochemical theory. Ecology 1995, 76, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakis, S.S.; Hedin, L.O. Fluxes and fates of nitrogen in soil of an unpolluted old-growth temperate forest, southern Chile. Ecology 2001, 82, 2245–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakis, S.S.; Hedin, L.O. Nitrogen loss from unpolluted South American forests mainly via dissolved organic compounds. Nature 2002, 415, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhai, J.; Zeng, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhu, L.; Fu, T.; Zhang, Q. Rapid aqueous-phase dark reaction of phenols with nitrosonium ions: Novel mechanism for atmospheric nitrosation and nitration at low pH. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Führ, F.; Bremner, J.M. Beeinflussende faktoren in der fixierung des nitrit-stockstoffs durch die organische masse des bodens. Atompraxis 1964, 10, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Führ, F.; Bremner, J.M. Untersuchungen zur fixierung des nitrit-stickstoffs durch die organische masse des bodens. Landw. Forsch. 1964, 11, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Boudot, J.; Chome, T. Internal nitrogen cycling in two humic-rich acidic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, B.P.; Fierer, N.; Schimel, J.P. Abiotic nitrate incorporation, anaerobic microsites, and the ferrous wheel. Biogeochemistry 2008, 91, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzhugh, R.D.; Lovett, G.M.; Venterea, R.T. Biotic and abiotic immobilization of ammonium, nitrite, and nitrate in soils developed under different tree species in the Catskill Mountains, New York, USA. Glob. Change Biol. 2003, 9, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricks, B.; Kaye, J.; Seidel, R. Abiotic nitrate retention in agroecosystems and a forest soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizewski, F.R.; Kaye, J.P.; Martínez, C.E. Nitrate transformation and immobilization in particulate organic matter incubations: Influence of redox, iron and (a)biotic conditions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Chen, D.; Phillips, O.L.; Gundersen, P.; Zhou, X.; Gurmesa, G.A.; Li, S.; Zhu, W.; Hobbie, E.A.; Wang, X.; et al. Dynamics and multi-annual fate of atmospherically deposited nitrogen in montane tropical forests. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2076–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gan, C.; Cai, D.; Ma, J.; Cai, G.; Liu, S. Influence of parent material and land use on abiotic N2O production following NH2OH and NO2− addition. Geoderma Reg. 2025, 41, e00944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Chorover, J.; Dail, D.B. A mechanism of abiotic immobilization of nitrate in forest ecosystems: The ferrous wheel hypothesis. Glob. Change Biol. 2003, 9, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Dail, D.B.; Chorover, J. Iron interference in the quantification of nitrate in soil extracts and its effect on hypothesized abiotic immobilization of nitrate. Biogeochemistry 2008, 90, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzio, W.; Sadzawka, A.; Besoain, E.; Lara, P. Influence of volcanic materials on red clay soil genesis. R.C. Suelo Nutr. Veg. 2003, 3, 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, L.; Vivallos, W.; Alfaro, G.; Cisternas, M.E. Geoquímica de los esquistos paleozoicos de Bahía Mansa, Osorno, Chile. In Actas del V Congreso Geológico Chileno; Repositorio Sernageomin: Santiago, Chile, 1988; Volume 2, pp. E75–E96. Available online: https://repositorio.sernageomin.cl/items/b60dd54c-ae73-4764-a2c3-3183333779e5 (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Sanyal, P.; Acharya, B.C.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Sarkar, A.; Agrawal, S.; Bera, M.K. Origin of graphite, and temperature of metamorphism in Precambrian Eastern Ghats Mobile Belt, Orissa, India: A carbon isotope approach. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 36, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohne, T.; Rinklebe, J.; Diaz-Bone, R.A.; Du Laing, G. Controlled variation of redox conditions in a floodplain soil: Impact on metal mobilization and biomethylation of arsenic and antimony. Geoderma 2011, 160, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschenbach, W.; Lewicka-Szczebak, D.; Stange, C.F.; Dyckmans, J.; Well, R. Measuring 15N abundance and concentration of aqueous nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium by membrane inlet quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6076–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, R.; Oliver, M.A. Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists, 1st ed.; John Wiley & SonsWiley: Chichester, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Bremner, J.M. Factors affecting chemical transformations of nitrite in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollhagen, A.C.; Goodale, C.L.; Martínez, C.E. Contrasting fates of nitrate between organic and iron oxide-rich horizons of an acidic forest soil under oxic and suboxic conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 157, 108237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analysis | Units | Volcanic | Non-Volcanic |
|---|---|---|---|
| DON 1 | mg L−1 | 26.20 ± 4.93 | 5.29 ± 0.01 |
| DOC 2 | mg L−1 | 35.62 ± 0.25 | 23.78 ± 0.36 |
| EC 3 | dS m−1 | 1.90 ± 0.06 | 2.00 ± 0.08 |
| pHw 4 | unitless | 4.30 ± 0.04 | 3.80 ± 0.05 |
| N-NH4+ | mg L−1 | 2.00 ± 0.77 | 2.53 ± 1.01 |
| N-NO3− | mg L−1 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.04 |
| N-NO2− | mg L−1 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matus, F.; Dyckmans, J.; Stock, S.C.; Merino, C.; Dippold, M.A.; Kuzyakov, Y. Abiotic Nitrite Incorporation into Organic Matter in Volcanic and Non-Volcanic Soil Within Rainforest Ecosystems. Forests 2025, 16, 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060930
Matus F, Dyckmans J, Stock SC, Merino C, Dippold MA, Kuzyakov Y. Abiotic Nitrite Incorporation into Organic Matter in Volcanic and Non-Volcanic Soil Within Rainforest Ecosystems. Forests. 2025; 16(6):930. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060930
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatus, Francisco, Jens Dyckmans, Svenja C. Stock, Carolina Merino, Michaela A. Dippold, and Yakov Kuzyakov. 2025. "Abiotic Nitrite Incorporation into Organic Matter in Volcanic and Non-Volcanic Soil Within Rainforest Ecosystems" Forests 16, no. 6: 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060930
APA StyleMatus, F., Dyckmans, J., Stock, S. C., Merino, C., Dippold, M. A., & Kuzyakov, Y. (2025). Abiotic Nitrite Incorporation into Organic Matter in Volcanic and Non-Volcanic Soil Within Rainforest Ecosystems. Forests, 16(6), 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060930








