Abstract
Soil respiration (Rs) is a significant contributor to the global carbon cycle, with its two main sources—microbial (heterotrophic, Rh) and plant root (autotrophic, Ra) respiration—being sensitive to various environmental factors. This study investigates the impact of ecosystem disturbances (Ds), including fire, biogenic (insects and pathogens), and harvesting, on soil respiration in Russia’s forest ecosystems. We introduced response factors to account for the effects of these disturbances on Rh over three distinct stages of ecosystem recovery. Our analysis, based on data from case studies, remote sensing data, and the national forest inventory, revealed that Ds increase Rh by an average of 2.1 ± 3.2% during the restoration period. Biogenic disturbances showed the highest impacts, with average increases of 16.5 ± 3.2%, while the contributions of clearcuts and wildfires were, on average, less pronounced—2.0 ± 3.1% and 0.8 ± 3.3%, respectively. These disturbances modify forest soil dynamics by affecting soil temperature, moisture, and nutrient availability, influencing carbon fluxes over varying timescales. This research underscores the role of ecosystem disturbances in altering soil carbon dynamics and highlights the need for improved data and monitoring of forest disturbances to reduce uncertainty in soil carbon flux estimates.
1. Introduction
In the global carbon budget, soil respiration (Rs) is one of the largest carbon fluxes from terrestrial ecosystems to the atmosphere [1]. It depends on several factors such as soil temperature, moisture, plant litter [2], fine root biomass [3], nutrients’ availability [4], and features of plant communities, among others. Rs is driven by microbial respiration (the heterotrophic flux, Rh) and by plant root respiration (the autotrophic flux, Ra). These two components have different sensitivities to environmental change, which can lead to an increase, a decrease, or no net change in total CO2 flux from the soil, depending on the influencing factors [5,6].
Disturbances (Ds) in ecosystems can impact Rs and its main components [7,8], depending on the type, extent, frequency, and severity of Ds, as well as the ecosystem’s specific characteristics, such as land use/land cover, vegetation properties, and the ecosystem’s buffering capacity and adaptive thresholds.
According to some estimates, Ds are responsible for 20%–50% of all Rh in boreal and temperate forests [9]. In some cases, tree cover loss can increase carbon release from soil due to increased soil temperature [10,11,12]. However, in the long term, tree loss may reduce Rs due to the removal of above-ground vegetation and the cessation of root respiration until the forest canopy recovers [13,14]. In addition, the loss of vegetation can reduce not only autotrophic respiration but also heterotrophic respiration by decreasing the supply of root exudates, an important carbon source for microbial activity [15].
In northern Palearctic forest ecosystems, the most common Ds are fires, pest attacks, and harvesting (among others, e.g., the impact of wind [16], which was not considered here due to the lack of Rs measurements). Ds affect approximately 200 × 103 km2 of forest in Russia annually, with about 30 × 103 km2 resulting in stand replacement [17]. Fire impacts initially manifest as combustion of the surface organic layer and disturbing/replacing of forest stands, which are important drivers of carbon flux from the soil. In boreal regions, fire leads to biomass losses of 15%–35% above ground and 37%–70% below ground [18]. Recent satellite-based estimates showed that the average area of vegetation fires in Russia from 2000 to 2019 was between 110 and 130 × 103 km2 per year if short-term and low-temperature fires were not included [19,20,21]. Specifically, the average forest fire’s area between 2002 and 2017 was estimated at 50 to 70 × 103 km2 year−1 during 2001–2019, with 53% of the burned area in stocked forests, 22% in natural grassland and shrubs, and 24% in agricultural land [22]. The area of stand-replacing fires was estimated at around 20–25 × 103 km2 year−1 based on remote sensing data [23,24]. While direct fire emissions can be reliably estimated, there is variability in these estimates [17,25]. Post-fire ecosystem development and carbon flux dynamics may play a more significant role in determining the total efflux and the duration of carbon release than just combustion losses [3]. However, studies on post-fire carbon effluxes remain limited.
The role of forest fires in Russia is dual. In the central and southern parts of the forest zone, wildfires have dramatic negative impacts on the ecology, economy, well-being, and health of the local population. Fires in remote, sparsely populated, high-latitude regions are an inherent feature of forest development, supporting regeneration and regulating productivity. These processes are particularly important in permafrost areas, which cover approximately 70% of Russia’s forested regions. After intensive ground fires on permafrost, forest regeneration shows a productivity increase of 20%–40%, especially during early development stages [26], which, in turn, leads to increased Rh.
Forest pests and pathogens affect the carbon cycle of forest ecosystems in several harmful ways. First, trees killed by aggressive insects or pathogens contribute large amounts of dead organic matter, which decomposes over time, serving as a primary source for soil organic matter and Rh [27]. Second, defoliation, growth reductions, and tree mortality reduce the gross primary production of affected stands [28], reducing the input of fresh organic matter into the soil both directly after the Ds and for several subsequent years. Third, stand-replacing biogenic Ds, particularly in combination with following fires very often become starting points of new succession [29].
Some experimental studies comparing attacked and unattacked stands showed no significant increase in respired carbon at pest-affected plots [27,30,31]. However, other studies indicated a decrease in Rs flux. For example, Nuckolls et al. [32] reported a 20% decrease in soil CO2 efflux in the first year following a biotic disturbance, while Hancock et al. [33] found a 40% reduction in growing season Rs in stands infested by beech bark disease.
The decomposition of fine roots after tree die-off initially leads to an increase in Rh [34] followed by a decline due to loss of fine root inputs as respiratory substrate [35,36,37]. Additionally, growth reductions over multiple years also reduce carbon transfer to above- and belowground dead organic matter pools, which may further decrease Rh. Another factor may be changes in the soil microclimate following infestation, as tree mortality reduces transpiration and increases soil moisture [31,38].
The reported results from studies on the impacts of harvesting on soil respiration are diverse, which is attributable to a range of factors such as the harvesting method [39], tree species’ composition [40], stand age [41], and climatic conditions [39]. Studies found that harvesting may increase Rs [42,43,44,45,46], have no impact [47], or decrease Rs [48].
Most Rs measurements in the literature come from undisturbed forests and are used to assess the effects of ecological conditions on Rs. To achieve a realistic Rs assessment at a large spatial scale, it is essential to account for the impact of Ds. The primary aim of this study was to summarize the existing knowledge and quantify, with a certain level of confidence, the impact of Ds on the Rh in forest ecosystems in Russia. The specific objectives were to compile and synthesize empirical data, to derive and parameterize disturbance response functions, and to upscale the results to the national level.
2. Materials and Methods
Our methodology comprised three steps: (1) a literature review to compile a database of Rs measurements and identify theoretical response curves for Rs relative changes following disturbance; (2) parameterization to fit the response equations using collected measurements; and (3) upscaling to apply these response equations to the national forest inventory to estimate, at the country scale, the impact of Ds on Rs.
We conducted a systematic literature search to select Rs measurements from both disturbed and undisturbed (control) forest stands. We started with established databases on Rs [1,49,50] (we checked the original source research papers) and complemented these by searching Google Scholar, Google LLC, Mountain View, CA, USA; accessed on 1 June 2024; and the Web of Science, Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA; accessed on 1 June 2024. Only data from studies that measured Rs in both control and disturbed forest ecosystems, for the period more than one year after disturbance, were used in the analysis. The main selection criteria were measurements spanning the entire vegetation period or a full calendar year. Due to the scarcity of such data across a wide range of ecosystems, we also included data from studies with single Rs measurements, if these measurements were taken simultaneously in recovering and undisturbed plots. Studies that measured Rs without removing the ground vegetation were excluded. The collected database is presented in the Supplementary Materials.
The effects of Ds on Rs and Rh are influenced by numerous factors, and existing knowledge gaps make accurate assessments challenging. The incomplete quantification of key ecosystem processes affected by Ds, combined with often biased spatial and temporal data on the extent and the severity of Ds, makes it difficult to accurately assess their impact on soil effluxes at large scales [9]. This challenge is particularly relevant for the vast and heterogeneous territory of Russia. In this study, we used approximations to estimate the severity of Ds’ impacts on soil carbon efflux, helping to understand how data gaps impact the uncertainty of practical applications in soil respiration assessments.
We developed a model of Rh response to major forest Ds and response factors for assessing Rh during the period of restoration (PoR). The PoR was divided into three specific stages. Stage I, the immediate post-disturbance response, usually lasts from 1 to 5 years, depending on the type of Ds, and continues until the direct consequences of the Ds are realized (e.g., post-fire tree mortality). Stage II, the initial restoration, ends when the net primary production of a young, restored generation of trees returns to pre-disturbance levels. This stage is usually defined by indices of biological productivity, which are estimated via satellite observations, and lasts until 10–20 years after the Ds. Stage III lasts until soil effluxes return to pre-disturbance levels, usually 30–60 years after Ds. This stage involves the decomposition of an extra amount of coarse woody debris (CWD) produced by the Ds. The end of Stage III marks the completion of the restoration period. The durations of these stages were determined based on the literature review and an analysis of the Rs database (see Supplementary Materials).
Our analysis indicated that the restoration period in coniferous and hardwood deciduous forests lasts approximately 60 years, while for softwood deciduous forests dominated by pioneer species, such as birch and aspen, it requires about 30 years. These periods cover the young and middle-aged forest age groups.
Note that the described succession dynamics during the PoR phase after stand-replacing disturbances are typical for the boreal zone, particularly in the middle and southern subzones, which make up approximately 85% of Russian forests. In ecotone regions, succession dynamics have specific characteristics. To the north, in the forest–tundra ecotone, the PoR phase significantly lengthens, and some forest areas affected by fire undergo a prolonged period of ‘green desertification’ [51]. To the south, in the forest–steppe and steppe regions, forest management activities influence the restoration process by supporting natural regeneration and planting new forests.
For this study, it was assumed that (1) typically Rs measurements were not conducted in stands with recent signs of Ds (except for certain Ds-specific studies, such as fire chronosequences); (2) the efflux from on- and above-ground coarse woody debris (CWD) decomposition is not included in soil respiration but estimated separately; and (3) in the case of combined Ds (e.g., fires in stands previously affected by insect defoliators), the estimates were attributed to the most pronounced destructive agent (fire in this case).
The assessment approach incorporated several simplifications. First, it was assumed that there are no long-period temporal trends in disturbance regimes, allowing constant response factors to be used during the PoR. This assumption is valid for fire and biogenic Ds between 1990 and 2020. Second, the current age structure of Russian forests formed by Ds (60 years for coniferous and 30 years for deciduous tree species) was used. Third, all calculations were provided for stand-replacing Ds to minimize inconsistencies in the empirical data for weak and moderate Ds, which to some extents are reflected by forest stands’ inventory. This includes crown and steady soil (peat) fires, which frequently occur on permafrost that covers approximately two-thirds of Russian forests. The PoR was estimated to be 60 years, divided into three stand age groups used in the Russian forest inventory. Initial data on Russian forests and Ds were derived from IIASA databases [52], official forest statistics from the Federal Forest Agency of the Russian Federation, and scientific publications [53].
Due to limitations in available observations, we adopted a hybrid approach that combined ecosystem dynamics theory with empirical data. The form of the Rh response to disturbances were based on Odum’s [54] classic ecosystem theory and the framework of Harmon et al. [9]. We then parametrized the Rh response curve by applying regression analysis to the available measurements [55].
To assess the impact of Ds on the Rh estimates for Russia, we applied the response factors to the modeling system developed to assess Rh [50]. The calculation was based on matrices describing recognized temporal dynamics of Rh, taking into account the specifics of Russian forest management and regional Ds’ regimes.
3. Results
Ds such as fire, biogenic agents, and harvesting exhibited distinct Rh dynamics during the PoR (Figure 1). The parameterization of equation 1 (Table 1) was based on the soil respiration database (see Supplementary Materials). Because soil Rh responses to disturbances are highly variable and often contradictory, we limited our empirical dataset to stand-replacing Ds.
where D(t) is the deviation of heterotrophic respiration from the pre-disturbance level (in %); a, b, c, and d are the model parameters; and t is the time since disturbance, in years.
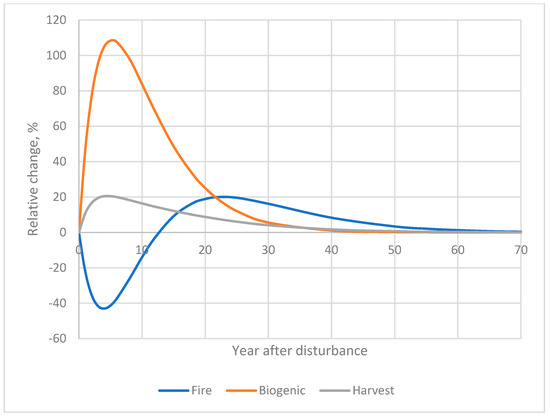
Figure 1.
Relative change in heterotrophic soil respiration after disturbances (% to undisturbed Rh): A—post-fire; B—after biogenic agents; C—post-harvest dynamics.

Table 1.
Model parameters (Equation (1)).
To assess the effect of Ds on forest soil Rh at the national scale, we considered the following components: (1) the age structure of the Russian forest, based on national forest inventory data; (2) the proportion of the forest area affected by different types of Ds (fire, harvest, biogenic), derived from inventory and remote sensing sources; (3) the average response factors for Rh during the stages of the PoR, linked to stand age and based on model (1). Table 2 presents data on the state of Russian forests in 2020 and the results of applying the above models to estimate forest soil Rh.

Table 2.
Assessment of the impact of disturbances (Ds) on heterotrophic soil respiration (Rh) in Russian forests.
According to official statistical data, three types of Ds—fires, biogenic factors, and harvest—affect approximately 200 × 103 km2 of land in Russia annually, with about 30 × 103 km2 resulting in stand replacement [17]. Overall, the data of Table 2 are higher at about 20% because they additionally accounted for mortality in affected forests during the next 5 years after the year of disturbance. Using data on forest area distribution by age groups and ratios between the major disturbance types, along with response factors, we estimated the impact of each type of D on the Rh from soils across Russia.
Fire. The annual area affected by stand-replacing fire was assessed at 22 × 103 km2, accounting for 65% of the total area impacted by stand-replacing Ds of major forest-forming species, based on remote sensing estimates [56,57]. Results indicated that stand-replacing fires increased Rh by 0.8% during the PoR, contributing an additional 0.24% to the total annual Rh across all forest areas (Table 2).
Biogenic factors. On average, biogenic agents cause stand-replacing tree mortality across 2 × 103 km2 per year under “normal” conditions. Considering periodic pandemic outbreaks and drought waves, which occur two to three times per decade in different regions, the impacted area was estimated to increase by one-third, reaching 3 × 103 km2. The response factor for Rh during the PoR was estimated at 16.5% (Table 2), resulting in an additional annual correction of +0.46% for the entire forest area of Russia.
Timber harvesting. Assuming an annual harvested area of 104 km2, this D resulted in an average increase in Rh of 2.0% during the PoR (Table 2). The harvested area represents approximately 29% of the total annually disturbed area, leading to an additional +0.27% to Rh from harvesting activities across Russia.
4. Discussion
Soil respiration is a key component of the ecosystem carbon budget, with even small variations potentially shifting a forest from a carbon sink to a carbon source. While the effects of forest disturbances on soil respiration are recognized, documented observations remain limited, particularly at large spatial scales. Given the increasing frequency and intensity of disturbances associated with climate change, their role in shaping soil respiration dynamics is becoming more critical.
This study advances previous research by providing a large-scale assessment of how different disturbances modify soil respiration estimates at a national scale. Unlike many existing studies that focused on localized site-specific effects, we combined empirical observations with expert-based assessments to develop a more comprehensive framework for evaluating disturbance-driven changes in soil respiration. Our approach allows for a broader and more scalable estimation of soil respiration responses to disturbances, even in cases where direct field measurements are scarce.
By integrating observational data and expert judgment, this study refined existing models and enhanced their applicability to large-scale carbon cycle assessments. Furthermore, the findings contribute to improving the representation of disturbance-induced carbon fluxes in ecosystem models, ultimately enhancing the accuracy of carbon budget projections in the context of a changing climate.
We examined the effects of three key disturbance agents: fire, biogenic disturbances, and harvesting. However, we acknowledge that other disturbances exist and that combined effects are frequently observed in nature. For example, fire often follows insect outbreaks, where the increased fuel load can intensify fire severity. Despite the ecological significance of such interactions, the combined effects of multiple disturbances on soil respiration remain poorly documented in the literature and were, therefore, not considered in this study.
4.1. Fire
Fire severity is a critical factor in assessing its impacts on forest ecosystems and its influence on Rs and Rh, particularly during initial development stages [3,15,58,59,60]. This variability likely explains the wide range of estimates in the literature regarding Rh dynamics following a fire. A classic ecosystem theory on secondary succession suggests an increase in Rh following a fire, with a reduction in Rs [9,61]. Most studies supported this, reporting either a reduction or no significant change in Rs after a fire [3,62,63,64,65,66,67,68].
Soils become sterile at a temperature around 200 °C [69], whereas severe fires can raise surface temperatures to 600–800 °C. Managed prescribed burns, commonly used to reduce fuel loads and wildfire intensity, generally do not alter soil respiration and its components [70,71]. The effect of fire on both Rs and Rh is strongly dependent on the season of the fire event [71]. Low- to moderate-intensity superficial ground fires in spring, which are not stand-replacing, also do not significantly affect soil processes, although even such fires can temporarily increase pH and nutrient availability, potentially leading to restoration or altering the dominant vegetation [72]. Rs and Rh may increase over time after these types of fires [73,74].
Severe fires, including crown, peat (soil), and steady ground fires, commonly occur in summer and early autumn during dry periods. These fires destroy pre-burn forest ecosystems and cause major changes in ecosystem functions and restoration pathways. Stand-replacing fires account for 20%–40% of the total burned area in Russia [17]. These fires significantly affect ecosystem properties and processes, such as species composition, biometric characteristics of stands, stock and structures of organic matter, temperature regime and moisture, and other physical and chemical properties of upper soil layers. The forest environment is due to a change in the microclimate conditions, as well as major components of the production process such as NPP and Rh [75,76]. Over time, such fires change the course of forest-forming processes, succession patterns, and the dynamics of future generations of forests [26,77]. Post-fire (pyrogenic) successions of different development stages cover about 30%–40% of boreal coniferous forest areas [78]. While the classical view suggests a consistent increase in post-fire soil effluxes, emerging research proposes multiple periods of carbon sinks during recovery [9].
Depending on the burning intensity, both increases and decreases in Rs were observed during the immediate reaction (Stage I: 1–3 years, and in some cases up to 5–7 years). On the one hand, enhanced microbial activity, up to twice the usual rate, often follows due to increased nutrient and substrate availability in the soil and enhanced soil temperatures [79]. In the permafrost regions near Yakutsk, severe fires in larch forests substantially increased the depth of the active soil layer from about 0.5–0.7 m to 1.5–2 m, which resulted in double Rh but an overall decline in Rs, due to reduced autotrophic respiration [66]. Post-fire ecosystems generally have warmer soils [80,81], which can affect Rs rate (e.g., [82,83]). Warmer conditions increase the sensitivity of soil carbon flux due to moisture fluctuations. The release of available C and N upon heating promotes microbial recovery, even under a low water potential condition [84]. In boreal high-latitude ecosystems, soil warming usually increases the depth of the active soil layer, enhancing the decomposition of carbon previously immobilized in permafrost [85] and promoting a faster recovery of the next tree generation, which is often more productive than the previous one during the restoration period [26].
On the other hand, stand-replacing fires often reduce soil microbial activity or even result in microbial mortality due to intense heating, leading to significant reductions in soil effluxes during Stage I of the PoR. These effects, combined with the death of fine roots and the green forest floor (i.e., mosses, lichens), can lead to reductions in Rs of up to twofold [63,86]. Most studies reported a reduction in the CO2 flux after fire compared to pre-fire levels [8,39,86,87,88,89]. For example, Amiro et al. [90] reported a 25% reduction in Rs during the 15-year period following a fire. A recent global meta-analysis of 1327 individual observations from 170 studies found that wildfires reduced Rs, Rh, and Ra by 20.4, 25.0, and 33.5%, respectively [71].
The recovery time for Rs in boreal forests varies, typically averaging between 3 and 10 years [73] but may extend to around 20 years at sites affected by high-intensity fires [91]. Chronosequence studies following stand-replacing fires generally showed lower Rs in younger post-fire stands compared to undisturbed forests, but very old sites often exhibit lower respiration rates than middle-aged stands [3,81,92]. Reporting that Rs in severely burned forests was significantly lower than in intact forests means that the Rh flux after a fire can increase by up to, and exceed, the pre-burn level. Generally, a fire results in a reduction in Rs [39,58,66,87,88,89,93,94,95]. According to a meta-analysis by [71], Rh is more sensitive to fire-induced disturbance than Rs, with recovery times for Rh from 3 to 24 years, depending on biome type and fire severity.
The restoration stage (Stage II) after a fire lasts between 7–8 and 13–20 years, depending on the quality of the growth conditions. Recovering NPP after stand-replacing fires in boreal forests, based on satellite-derived indices of bioproductivity, requires over 13 years for the restoration of forests in Central Siberia. Restoration of evergreen needle-leaved forests occurs faster than for deciduous needle-leaved forests [96]. The average lengths of restoration of NPP for all of Russia’s forests was shorter—around 10 years [21], but this was basically caused by the dominance of ground fires. Estimates from boreal regions in North America are similar—between 7 and 14 years [63,97,98]. Rh after severe fires initially declines during the first 1–3 years (Stage I), gradually grows further, remains, on average, lower than the pre-burn values up to 10–12 years after the fire, and exceeds the pre-burn level up to the end of the PoR.
4.2. Biogenic Disturbances
Russia’s forest inventory estimates that the national total area of dead stands due to biogenic disturbances (i.e., insects and pathogens) remained relatively stable at approximately 20 × 103 km2 during 2001–2018 (i.e., less than 0.3% forested area), with a stable annual loss of approximately 2 × 103 km2. According to scientific publications, there were nine major outbreaks of the Siberian moth (Dendrolimus sibiricus Chetverikov), which is the most dangerous defoliator of taiga forests, between 1978 and 2017 in southern Central Siberia [99]. Russian experts estimate that the damage caused by biogenic disturbance is nearly equivalent to wildfire damage [100]. The Russian pathological monitoring system reported that areas affected by biogenic agents were around 55 × 103 km2 year−1 during the aforementioned period. In these territories, tree mortality exceeds the natural level by more than twofold. Outbreaks of insects and pathogens largely do not occur in high-latitude boreal forests due to low temperatures limiting the development of biogenic agents. Official estimates of tree cover losses due to biogenic factors and unfavorable weather conditions during the last decade were reported between 1.6 and 2 × 103 km2 year−1, with around 45% attributed to insect outbreaks, 25% to pathogens, 20% to unfavorable weather conditions, and 10% to other factors [101].
Forest pests and pathogens affect the Rh flux in forest ecosystems, providing inputs of large amounts of dead organic matter—the main source for Rh [27]—while reducing the gross primary production of stands [28], which decreases the input of fresh organic matter into the soil. However, the decrease in NPP in the early stages of post-disturbance development is partially offset by the rapid development of grasses on the forest floor. The significant biomass productivity of grasses and herbaceous perennials may increase Ra from the rhizosphere, in addition to increased Rh driven by higher organic matter inputs and elevated soil temperatures [102]. The complete defoliation of dark coniferous forests in Central Siberia can deliver up to 10 t ha−1 of zoogenic fall (i.e., excrement and dead larvae) [103,104]. Many studies and models predicted an increase in Rh following a disturbance by pests [102,105,106] associated with an increase in decaying organic input [107]. For example, carbon efflux from soils of Central Siberian forests that were completely defoliated by the Siberian moths was 1.5 times higher than in undisturbed forests during the third year after the invasion [103]. However, other studies showed variable impacts of biogenic agents on soil and forest floor carbon, ranging from decreased carbon stocks and soil CO2 efflux [108] to no change in these variables [109]. These discrepancies can be explained by differences in pre-existing understory vegetation, tree mortality rates, and the size of canopy gaps formed after disturbance [102].
Damage to or death of deciduous trees results in significant leaf litter deposition on the soil surface in the year of insect or pathogen outbreaks. The carbon from this labile material is mainly released into the atmosphere during the first two years, and a substantial part (up to 20%–25%) is washed away by runoff [103]. Coniferous needles, on the other hand, remain on dead trees for 1–3 years, delaying their decomposition [109]. Dead tree stems can persist standing for an extended period [109,110,111]. The decomposition rate of standing deadwood can be extremely low, with carbon release through decomposition over decades to centuries [111,112,113]. In intensively managed forests, the occurrence of fire at locations previously infested by insects is not reported [114,115]. However, about half of Russian forests are unmanaged, and areas affected by insect mortality (so called shelkoprjadniki) are often subjected to severe fire.
Climate changes, such as reduced minimum winter temperature, increased summer temperatures, and altering summer precipitation, can lead to an expansion of climatically suitable habitats for insects [116,117]. Consequently, both native and invasive alien insect species are affecting forests. The last two decades have demonstrated some impressive examples. Outbreaks of the Siberian silk moth in 2000–2001 enveloped the area above 105 km2 in Central Siberia—an area where historically large outbreaks of this pest had not been observed [118]. The four-eyed fir bark beetle Polygraphus proximus Blandf, not known in Siberia 20 years ago, now poses a significant threat to millions of hectares of fir forests in southern Central Siberia [119].
Despite numerous publications on the topic, the impact of insects on the carbon dynamics in ecosystems and their response to global climate change remain poorly documented [120]. The possibility to include the consequences of biotic disturbances in the calculations of soil heterotrophic carbon flux is particularly limited by our understanding of disturbance severity, which can have many linear and nonlinear effects [107]. Another source of uncertainty is the lack of knowledge about the long-term impacts on carbon cycling from insect and pathogen outbreaks.
This study focused on the impacts of insects and pathogen outbreaks located in the southern part of the forest zone of Russia. These most important groups contribute about half of the total impact of all biogenic Ds affecting heterotrophic respiration in forest ecosystems. During the initial 4–6 years, Rh is elevated up to twice the pre-disturbance level. In the following 5–15 years, Rh declines, approaching pre-disturbance levels, and then gradually decreases until the end of the PoR. Note that a substantial portion of dead stands originating from insect and pathogen outbreaks are later affected by severe fires.
4.3. Harvest
Wood harvesting in Russia has fluctuated since the 1990s, with a notable decline from about 350 M m3 year−1 in the early 1990s to 150 M m3 year−1 by the end of the 1990s. It gradually increased to 219 M m3 year−1—in 2019, followed by a decrease to 188 M m3 year−1 in 2023. The corresponding logged area ranged between 18 and 9 × 103 km2 year−1. These figures include industrial harvests from mature stands and about 10%–15% from other clearcuts (mostly for sanitary reasons).
Clearcutting is the primary logging method in Russia, often causing substantial soil disturbance. Typically, the proportion of undisturbed patches, skidding trails, and loading sites is estimated at 59%–71%, 18%–29%, and 6%–15% of the total logging area in boreal forests [121], and in many cases, the destruction of the soil surface can reach 40%–60% [122]. The transformation of logged areas leads to a mix of organic layers, CWD, and mineral soil horizons, prompting some soil scientists to classify soils in clearcut areas as a specific type called “detritus turbozems” [123]. Introducing Scandinavian harvest technologies can reduce soil disturbance by up to 20%, but the extent of this technology’s adoption in Russia is unclear. Following a harvest, large amounts of logging residues, including broken trees (which could reach up to 40%–50% of pre-disturbed growing stock volume), remain on site [124]. In taiga forests, low-quality coniferous trees and deciduous trees are often left after a harvest. Under the current system of forest management in Russia, more than 80% of harvested areas are left for natural reforestation, with 60%–70% dominated by early successional species like birch and aspen.
Reported effects of harvesting on Rs vary due to factors like the harvesting method [39], tree species’ composition [40], stand age [41], and climatic conditions [39]. Studies show that harvesting might increase Rs [42,43,44,45,46], have no effect [47], or decrease Rs [48]. The results of a global meta-analysis [125] indicated that harvesting and thinning did not significantly change Rs. The authors attributed this to a compensation effect: a reduction in root Ra due to tree cover loss was offset by an increase in Rh, resulting from canopy opening and the associated rise in soil temperature.
Studies reporting both Ra and Rh rates showed an increase in heterotrophic CO2 flux of about 20% [125]. However, most studies on harvest technologies used in Russia reported a reduction in Rs (up to 40% of pre-harvest levels) due to soil destruction and tree root mortality [47,126], though Rh was reported to increase compared to intact forests [127]. The decomposition of dead roots and logging residuals are responsible for rising Rs and particularly Rh at a later stage of restoration [42,128]. It was also reported that forest root production generally increases up to a stand age of 70–100 years [129,130], leading to increased Ra. Increased belowground production could also stimulate Rh by providing greater amounts of fresh root litter and exudates [131]. Tree stand productivity and leaf area also increase from young to middle-aged boreal forests, followed by a decline in older forests [131,132], influencing above-ground litter input and the long-term dynamics of Rh.
Overall, harvest impacts on soil fluxes in Russia’s boreal forests can be categorized as occurring in distinct stages, similar to other Ds. The initial response stage lasts 3–7 years after harvest, during which a substantial part of the broken trees and undergrowth die. A dense green forest floor develops, particularly in more southern regions, gradually offsetting the decline in total and autotrophic respiration. The restoration stage of the new tree generation usually ends in 5–15 years. In the southern regions with intensive forest management, forests were planted on logged areas, but recent active reforestation did not exceed 2 × 103 km2 year−1. On average, about 10%–20% of logged areas are not successfully restored during this period.
The restoration process may last up to 30 years, depending on the bioclimatic zone with typical restoration successions (with or without a change in species). By the end of the PoR, the dominant species and ecosystem structure resemble the pre-disturbance state. Decreases in Rs of different intensities are typical for the first two stages, with a gradual increase in the third stage, often exceeding pre-disturbed levels due to the decomposition of harvested residues, the destroyed soil surface, and after the downing of snags (10–50 years after the harvest, depending on the bioclimatic zones). Mean annual Rs was reported to be about 12% higher in 40–50-year-old clearcut stands compared to undisturbed stands, with Rs decreasing again as stand age increased [131].
4.4. Caveats and Limitations
Despite our efforts to assemble the most comprehensive, harmonized dataset and to ground our modeling in both theory and observation, several important limitations remain, including:
- The temporal and spatial coverage of Rs measurement, including short measurement windows (many studies reported Rs only over part of the growing season) and geographic gaps (remote and infrastructure-poor regions were underrepresented).
- Disturbance severity and characterization. Severity gradients and the compound of multiple disturbances were not fully captured.
- Methodological variability among studies, including different instruments, techniques, and the lack of direct partitioning between Ra and Rh.
- Modeling assumptions. We assumed that post-disturbance response curves and their parameters remained constant over multi-decadal restoration periods, neglecting potential shifts under changing climate or soil conditions, as well as neglecting trends in disturbance regimes.
- Uncertainty quantification. Formal error propagation through our multi-step workflow was hindered by missing variance and covariance information in the underlying studies; we therefore relied on standard error estimates at each stage and expert judgment to gauge overall uncertainty.
By acknowledging these caveats, we framed our national-scale estimates of disturbance-driven changes in heterotrophic soil respiration as provisional and highlighted priority areas for future field campaigns, standardized measurements, and model refinement.
5. Conclusions
Our findings indicate that major disturbances lead to elevated Rh in disturbed areas throughout the Period of Restoration, with an annual average increase of +2.1 ± 3.2%, including +0.8 ± 3.3% in burnt areas, +16.5 ± 3.2% of areas affected by insects and pathogens, and +2.0 ± 3.1% in harvested areas. Assuming the current age structure of Russian forests and the length of the PoR of 60 years, the overall increase in Rh due to disturbances for all the forest land of Russia is estimated to be approximately +1.0 ± 1.5%.
The uncertainties associated with these results are difficult to quantify using formal methods. We estimate uncertainties by calculating the standard error of the model result compared to available measurements. Expert estimates suggest that uncertainties resulting from simplifications in accounting, limitation in available data, multiplicity of potential impacts, and inconsistency or contradictions in empirical estimates imply an overall potential error within the range of 30%–40%.
Heterotrophic soil respiration is not only a key indicator of the destructive component of production processes in forest ecosystems but also an important measure of their overall stability. The results of this study show that, during the recovery period following stand-replacing disturbances in Russian forests, there is a weak and statistically insignificant positive trend in heterotrophic respiration. These findings support the conclusion about the current resilience of the world’s forests [133], even in the face of elevated disturbance levels—such as those experienced in Russia over the last decade.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f16060925/s1: Figure S1. Reported changes in heterotrophic soil respiration after fire events. Figure S2. Reported changes in heterotrophic soil respiration after harvest events. Figure S3. Whittaker biome diagram showing field measurements of Rs. Table S1. Reference data on heterotrophic soil respiration response to disturbances.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.; methodology, A.S. and D.S.; validation, L.M.; formal analysis, D.S.; investigation, L.M.; data curation, L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S. and L.M.; writing—review and editing, L.M. and D.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research (L.M., A.S.) was carried out as part of the most important innovative project of national importance “Development of a system for the ground-based and remote monitoring of carbon pools and greenhouse gas fluxes in the territory of the Russian Federation, ensuring the creation of recording data systems on the fluxes of climate-active substances and the carbon budget in forests and other terrestrial ecological systems” by the Ministry of science and higher education of the Russian Federation (Registration number: 123030300031-6).
Data Availability Statement
Soil respiration database is available here [55] and in the Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bond-Lamberty, B.; Ballantyne, A.; Berryman, E.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Jian, J.; Morris, K.A.; Rey, A.; Vargas, R. Twenty Years of Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities in Measuring and Understanding Soil Respiration. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2024, 129, e2023JG007637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, R.D.; Castro, M.S.; Melillo, J.M.; Steudler, P.A.; Aber, J.D. Fluxes of Greenhouse Gases between Soils and the Atmosphere in a Temperate Forest Following a Simulated Hurricane Blowdown. Biogeochemistry 1993, 21, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Amiro, B.D.; Quideau, S.A. Effects of Forest Floor Organic Layer and Root Biomass on Soil Respiration Following Boreal Forest Fire. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadelhoffer, K.J. The Potential Effects of Nitrogen Deposition on Fine-Root Production in Forest Ecosystems. New Phytol. 2000, 147, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Zhang, X.; Piao, S.; Janssens, I.A.; Fu, G.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Dai, E.; Yu, C.; et al. Warming Homogenizes Apparent Temperature Sensitivity of Ecosystem Respiration. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, W.; Gundersen, P.; Fang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, H. Nitrogen Addition Reduces Soil Respiration in a Mature Tropical Forest in Southern China. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Úbeda, X.; Rein, G.; Cerdà, A. (Eds.) Fire Effects on Soil Properties; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2019; ISBN 978-1-4863-0813-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Kumara, C.; Pumpanen, J.; Heinonsalo, J.; Metslaid, M.; Orumaa, A.; Jõgiste, K.; Berninger, F.; Köster, K. Long-Term Effects of Forest Fires on Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Extracellular Enzyme Activities in a Hemiboreal Forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 135291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, M.E.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Tang, J.; Vargas, R. Heterotrophic Respiration in Disturbed Forests: A Review with Examples from North America. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116, G00K04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.I.; Little, W.S.; Houghton, R.A.; Scott, N.A.; White, J.D. The Net Carbon Flux Due to Deforestation and Forest Re-Growth in the Brazilian Amazon: Analysis Using a Process-Based Model. Glob. Change Biol. 2004, 10, 908–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Andrews, J.A. Soil Respiration and the Global Carbon Cycle. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.R.; Vitousek, P.M.; Holland, E.A. Tropical Soils Could Dominate the Short-Term Carbon Cycle Feedbacks to Increased Global Temperatures. Clim. Change 1992, 22, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M. Introduction to Soil Microbiology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, R.D.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Canary, J.D.; Kaye, J.P. Roots Exert a Strong Influence on the Temperature Sensitivity of Soil Respiration. Nature 1998, 396, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Doerr, S.H.; Ekroos, J.; Ibáñez, T.S.; Islam, M.R.; Santín, C.; Soares, M.; Kljun, N. No Recovery of Soil Respiration Four Years after Fire and Post-Fire Management in a Nordic Boreal Forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2025, 364, 110454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, R.; Schelhaas, M.-J.; Rammer, W.; Verkerk, P.J. Increasing Forest Disturbances in Europe and Their Impact on Carbon Storage. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvidenko, A.; Schepaschenko, D. Climate Change and Wildfires in Russia. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2013, 6, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, E.I.; Kharuk, V.I.; Ranson, K.J. Wildfires Dynamics in Siberian Larch Forests. Forests 2016, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VEGA-Science BEГA-Science—A Unique Tool for Satellite Data Scientific Analysis. Available online: http://sci-vega.ru/ (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Bondur, V.G.; Voronova, O.S.; Cherepanova, E.V.; Tsydylina, M.N.; Zima, A.L. The Spatiotemporal analysis of multiannual wildfires and emissions of greenhouse gases and aerosols in Russia based on satellite data. Investig. Earth Space 2020, 4, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondur, V.G.; Tsidilina, M.N.; Cherepanova, E.V. Satellite Monitoring of Wildfire Impacts on the Conditions of Various Types of Vegetation Cover in the Federal Districts of the Russian Federation. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2019, 55, 1238–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartalev, S.A.; Styzenko, F.V.; Egorov, V.A.; Loupian, E.A. Satellite-based assessment of Russian forest fire mortality. For. Sci. 2015, 2, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Krylov, A.; McCarty, J.L.; Potapov, P.; Loboda, T.; Tyukavina, A.; Turubanova, S.; Hansen, M.C. Remote Sensing Estimates of Stand-Replacement Fires in Russia, 2002–2011. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasischke, E.S.; Penner, J.E. Improving Global Estimates of Atmospheric Emissions from Biomass Burning. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2004, 109, D14S01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorohova, E.; Kuuluvainen, T.; Kangur, A.; Jogiste, K. Natural Stand Structures, Disturbance Regimes and Successional Dynamics in the Eurasian Boreal Forests: A Review with Special Reference to Russian Studies. Ann. Des Sci. For. 2009, 66, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedykh, V.N. Forest Forming Process; Nauka Publishing: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.J.P.; Trahan, N.A.; Wilkes, P.; Quaife, T.; Stephens, B.B.; Elder, K.; Desai, A.R.; Negron, J.; Monson, R.K. Persistent Reduced Ecosystem Respiration after Insect Disturbance in High Elevation Forests. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, W.J.; Addy, N.D. Phytophagous Insects as Regulators of Forest Primary Production. Science 1975, 190, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruel, J.-C.; Wermelinger, B.; Gauthier, S.; Burton, P.J.; Waldron, K.; Shorohova, E. Selected Examples of Interactions Between Natural Disturbances. In Boreal Forests in the Face of Climate Change: Sustainable Management; Girona, M.M., Morin, H., Gauthier, S., Bergeron, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 123–141. ISBN 978-3-031-15988-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lovett, G.M.; Arthur, M.A.; Weathers, K.C.; Griffin, J.M. Long-Term Changes in Forest Carbon and Nitrogen Cycling Caused by an Introduced Pest/Pathogen Complex. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morehouse, K.; Johns, T.; Kaye, J.; Kaye, M. Carbon and Nitrogen Cycling Immediately Following Bark Beetle Outbreaks in Southwestern Ponderosa Pine Forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 2698–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuckolls, A.E.; Wurzburger, N.; Ford, C.R.; Hendrick, R.L.; Vose, J.M.; Kloeppel, B.D. Hemlock Declines Rapidly with Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Infestation: Impacts on the Carbon Cycle of Southern Appalachian Forests. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.E.; Arthur, M.A.; Weathers, K.C.; Lovett, G.M. Carbon Cycling along a Gradient of Beech Bark Disease Impact in the Catskill Mountains, New York. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Pegoraro, E.; Tedeschi, V.; De Parri, I.; Jarvis, P.G.; Valentini, R. Annual Variation in Soil Respiration and its Components in a Coppice Oak Forest in Central Italy. Glob. Change Biol. 2002, 8, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhupinderpal-Shingh; Nordgren, A.; Löfvenius, M.O.; Högberg, M.N.; Mellander, P.-E.; Högberg, P. Tree Root and Soil Heterotrophic Respiration as Revealed by Girdling of Boreal Scots Pine Forest: Extending Observations beyond the First Year. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.G.; Law, B.E. Interpreting, Measuring, and Modeling Soil Respiration. Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štursová, M.; Šnajdr, J.; Cajthaml, T.; Bárta, J.; Šantrůčková, H.; Baldrian, P. When the Forest Dies: The Response of Forest Soil Fungi to a Bark Beetle-Induced Tree Dieback. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1920–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clow, D.W.; Rhoades, C.; Briggs, J.; Caldwell, M.; Lewis, W.M. Responses of Soil and Water Chemistry to Mountain Pine Beetle Induced Tree Mortality in Grand County, Colorado, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, S174–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, X. Soil Respiration and the Environment, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-12-088782-8. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, B.; Laskowski, R. (Eds.) Litter Decomposition: A Guide to Carbon and Nutrient Turnover, 1st ed.; Advances in Ecological Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-08-092011-5. [Google Scholar]
- Concilio, A.; Ma, S.; Ryu, S.-R.; North, M.; Chen, J. Soil Respiration Response to Experimental Disturbances over 3 Years. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 228, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, D.E.; Cronan, C.S. Comparative Soil CO2 Evolution, Litter Decay, and Root Dynamics in Clearcut and Uncut Spruce-Fir Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 1998, 103, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londo, A.J.; Messina, M.G.; Schoenholtz, S.H. Forest Harvesting Effects on Soil Temperature, Moisture, and Respiration in a Bottomland Hardwood Forest. J. Soil Sci. 1999, 63, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Geng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Niklaus, P.A.; Schmid, B.; He, J.-S. Effect of Clear-Cutting Silviculture on Soil Respiration in a Subtropical Forest of China. J. Plant Ecol. 2013, 6, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darenova, E.; Cater, M.; Pavelka, M. Different Harvest Intensity and Soil CO2 Efflux in Sessile Oak Coppice Forests. iForest 2016, 9, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, V.; Pellicone, G.; Bernardini, V.; Cinti, B.D.; Froio, R.; Marziliano, P.A.; Matteucci, G.; Ricca, N.; Turco, R.; Veltri, A. Short-Time Effect of Harvesting Methods on Soil Respiration Dynamics in a Beech Forest in Southern Mediterranean Italy. iForest 2017, 10, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striegl, R.G.; Wickland, K.P. Effects of a Clear-Cut Harvest on Soil Respiration in a Jack Pine—Lichen Woodland. Can. J. For. Res. 1998, 28, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parro, K.; Köster, K.; Jõgiste, K.; Seglinš, K.; Sims, A.; Stanturf, J.A.; Metslaid, M. Impact of Post-Fire Management on Soil Respiration, Carbon and Nitrogen Content in a Managed Hemiboreal Forest. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond-Lamberty, B.P.; Thomson, A.M. A Global Database of Soil Respiration Data, Version 4.0.; ORNL DAAC: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhortova, L.V.; Schepaschenko, D.; Moltchanova, E.; Shvidenko, A.; Khabarov, N.; See, L. Respiration of Russian Soils: Climatic Drivers and Response to Climate Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremov, D.F.; Shvidenko, A.Z. Long-Term Ecological Consequences of Catastrophic Forest Fires in Forests of Far East and Their Contribution to Global Processes. In Forest Fire Management at Ecoregional Level; World Bank, Publ. “Alex”: Moscow, Russia, 2004; pp. 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shvidenko, A.; Schepaschenko, D.; McCallum, I.; Nilsson, S. Russian Forests and Forestry. Available online: http://www.iiasa.ac.at/models-tools-data/russian-forests-and-forestry-database (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Schepaschenko, D.; Moltchanova, E.; Fedorov, S.; Karminov, V.; Ontikov, P.; Santoro, M.; See, L.; Kositsyn, V.; Shvidenko, A.; Romanovskaya, A.; et al. Russian Forest Sequesters Substantially More Carbon than Previously Reported. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, E.P. The Strategy of Ecosystem Development. Science 1969, 164, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhortova, L.V.; Schepaschenko, D.; Shvidenko, A. Soil Respiration Database. Available online: https://pure.iiasa.ac.at/17556 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Bartalev, S.A.; Stytsenko, F.V. An Assessment of the Forest Stands Destruction by Fire Based on the Remote Sensing Data on a Seasonal Distribution of Burnt Areas. For. Sci. 2021, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyukavina, A.; Potapov, P.; Hansen, M.C.; Pickens, A.H.; Stehman, S.V.; Turubanova, S.; Parker, D.; Zalles, V.; Lima, A.; Kommareddy, I.; et al. Global Trends of Forest Loss Due to Fire From 2001 to 2019. Front. Remote Sens. 2022, 3, 825190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, S.R.; Rogers, B.M.; Treseder, K.K.; Randerson, J.T. Fire Severity Influences the Response of Soil Microbes to a Boreal Forest Fire. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wan, S. Impacts of Fire on Soil Respiration and Its Components: A Global Meta-Analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 336, 109496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Yedinak, K.M.; Sulman, B.N.; Berry, T.D.; Kruger, K.; Whitman, T. Effects of Fire and Fire-Induced Changes in Soil Properties on Post-Burn Soil Respiration. Fire Ecol. 2024, 20, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, F.S., III; Matson, P.A.; Vitousek, P. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4419-9504-9. [Google Scholar]
- Amiro, B.D.; MacPherson, J.I.; Desjardins, R.L.; Chen, J.M.; Liu, J. Post-Fire Carbon Dioxide Fluxes in the Western Canadian Boreal Forest: Evidence from Towers, Aircraft and Remote Sensing. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2003, 115, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.A.; Zepp, R.G.; Tarr, M.A.; Miller, W.L.; Stocks, B.J. Effect of Fire on Soil-Atmosphere Exchange of Methane and Carbon Dioxide in Canadian Boreal Forest Sites. Can. J. For. Res. 1997, 102, 29289–29300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritze, H.; Pennanen, T.; Pietikäinen, J. Recovery of Soil Microbial Biomass and Activity from Prescribed Burning. Can. J. For. Res. 1993, 23, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, C.H. Tundra Fire Effects on Soils and Three Plant Communities along a Hill-Slope Gradient in the Seward Peninsula, Alaska. Arctic 1981, 34, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawamoto, T.; Hatano, R.; Yajima, T.; Takahashi, K.; Isaev, A.P. Soil Respiration in Siberian Taiga Ecosystems with Different Histories of Forest Fire. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2000, 46, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.G. Forest Soil Respiration in Eastern Ontario Jack Pine Ecosystems. Can. J. For. Res. 1985, 15, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.G. Forest Soil Respiration after Cutting and Burning in Immature Aspen Ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 1990, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrasolsas, I.; Khanna, P.K. Changes in Heated and Autoclaved Forest Soils of S.E. Australia. I. Carbon and Nitrogen. Biogeochemistry 1995, 29, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Álvarez, P.A.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Sagra, J.; Moya, D.; Fontúrbel, T.; De las Heras, J. Soil Respiration Changes after Prescribed Fires in Spanish Black Pine (Pinus Nigra Arn. ssp. Salzmannii) Monospecific and Mixed Forest Stands. Forests 2017, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, S.; Gu, Y.; Wu, L.; Hu, H.; He, J. Fire Decreases Soil Respiration and Its Components in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37, 3124–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certini, G. Effects of Fire on Properties of Forest Soils: A Review. Oecologia 2005, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, E.; Köster, K.; Berninger, F.A.; Pumpanen, J.S. Carbon Dioxide, Methane and Nitrous Oxide Fluxes from Podzols of a Fire Chronosequence in the Boreal Forests in Värriö, Finnish Lapland. Geoderma Reg. 2015, 5, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, K.; Berninger, F.; Lindén, A.; Köster, E.; Pumpanen, J. Recovery in Fungal Biomass Is Related to Decrease in Soil Organic Matter Turnover Time in a Boreal Fire Chronosequence. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, E.; Köster, K.; Berninger, F.; Aaltonen, H.; Zhou, X.; Pumpanen, J. Carbon Dioxide, Methane and Nitrous Oxide Fluxes from a Fire Chronosequence in Subarctic Boreal Forests of Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, E.; Köster, K.; Berninger, F.; Prokushkin, A.; Aaltonen, H.; Zhou, X.; Pumpanen, J. Changes in Fluxes of Carbon Dioxide and Methane Caused by Fire in Siberian Boreal Forest with Continuous Permafrost. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyryanova, O.A.; Abaimov, A.P.; Chikhacheva, T.L. The influence of fire on forest formation process in larch forests of Northern Siberia. For. Sci. 2008, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Farber, S.K. Formation of Stands of East Siberia; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Tanaka, N. Effect of Forest Fire on the Fluxes of CO2, CH4 and N2O in Boreal Forest Soils, Interior Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2003, 108, FFR 10-1–FFR 10-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Randerson, J.T.; Lindfors, J.; Chapin, F.S., III. Changes in the Surface Energy Budget after Fire in Boreal Ecosystems of Interior Alaska: An Annual Perspective. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2005, 110, D13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, K.P.; Richter, D.D.; Kasischke, E.S. Succession-Driven Changes in Soil Respiration Following Fire in Black Spruce Stands of Interior Alaska. Biogeochemistry 2006, 80, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Janssens, I.A. Temperature Sensitivity of Soil Carbon Decomposition and Feedbacks to Climate Change. Nature 2006, 440, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Moncrieff, J.B. The Dependence of Soil CO2 Efflux on Temperature. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choromanska, U.; DeLuca, T.H. Microbial Activity and Nitrogen Mineralization in Forest Mineral Soils Following Heating: Evaluation of Post-Fire Effects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, K.P.; Kasischke, E.S.; Richter, D.D. Environmental Controls on Soil CO2 Flux Following Fire in Black Spruce, White Spruce, and Aspen Stands of Interior Alaska. Can. J. For. Res. 2002, 32, 1525–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Ma, K.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Sasa, K. Effects of Post-Fire Conditions on Soil Respiration in Boreal Forests with Special Reference to Northeast China Forests. Front. Biol. China 2009, 4, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, C.; Inclán, R.; Sánchez, D.M.; Clavero, M.A.; Fernández, A.M.; Morante, R.; Cardeña, A.; Blanco, A.; Van Miegroet, H. Effect of Wildfires on Soil Respiration in Three Typical Mediterranean Forest Ecosystems in Madrid, Spain. Plant Soil 2013, 369, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hu, T.; Kim, J.H.; Guo, F.; Song, H.; Lv, X.; Hu, H. The Effect of Fire Disturbance on Short-Term Soil Respiration in Typical Forest of Greater Xing’an Range, China. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Sun, L.; Hu, H.; Weise, D.R.; Guo, F. Soil Respiration of the Dahurian Larch (Larix gmelinii) Forest and the Response to Fire Disturbance in Da Xing’an Mountains, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiro, B.D.; MacPherson, J.I.; Desjardins, R.L. BOREAS Flight Measurements of Forest-Fire Effects on Carbon Dioxide and Energy Fluxes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 96, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, K.; Köster, E.; Orumaa, A.; Parro, K.; Jõgiste, K.; Berninger, F.; Pumpanen, J.; Metslaid, M. How Time since Forest Fire Affects Stand Structure, Soil Physical-Chemical Properties and Soil CO2 Efflux in Hemiboreal Scots Pine Forest Fire Chronosequence? Forests 2016, 7, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Gower, S.T. Soil Surface CO2 Flux in a Boreal Black Spruce Fire Chronosequence. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2003, 108, WFX 5-1–WFX 5-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.D.; Mackenzie, M.D. Spatial Patterns of Soil Respiration Links Above and Belowground Processes along a Boreal Aspen Fire Chronosequence. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, T.; Shen, Z.; Piao, S. Effects of Wildfire on Soil Respiration and its Heterotrophic and Autotrophic Components in a Montane Coniferous Forest. J. Plant Ecol. 2019, 12, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, L.; Cao, J. Contrasting Responses after Fires of the Source Components of Soil Respiration and Ecosystem Respiration. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-González, M.; Gerard, F.; Balzter, H.; Riaño, D. Analysing Forest Recovery after Wildfire Disturbance in Boreal Siberia Using Remotely Sensed Vegetation Indices. Glob. Change Biol. 2009, 15, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, S.J.; Fiske, G.J.; Bunn, A.G. Using Satellite Time-Series Data Sets to Analyze Fire Disturbance and Forest Recovery across Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, T.; O’Neal, K.J.; Csiszar, I. Regionally Adaptable dNBR-Based Algorithm for Burned Area Mapping from MODIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranchikov, Y.N.; Kondakov, Y.P. Outbreaks of Siberian Moth Dendrolimus Superans Sibiricus Tschtvrk in Central Siberia. In Proceedings of the Proc. SOA Interagency Gypsy Moss Forum; USDA Forest Service, NEFES: Radnor, PA, USA, 1997; pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Isaev, A.S. (Ed.) Program of Extraordinary Activities on Biological Struggle with Pests in Forests of Krasnoyarsk Kray; World Bank Project; Federal Forest Service of Russia: Moscow, Russia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- FAFM RF. Overview of Sanitary and Pathological Conditions of Forests of the Russian Federation in 2016; Russian Center of Forest Protection of the Federal Agency of the Russian Federation: Pushkino, Russia, 2017; p. 105. [Google Scholar]
- Tomes, J.; Fleischer, P.; Kubov, M.; Fleischer, P. Soil Respiration after Bark Beetle Infestation along a Vertical Transect in Mountain Spruce Forest. Forests 2024, 15, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranchikov, Y.N.; Kondakov, Y.P.; Petrenko, E.S. Catastrophic Outbreaks of Siberian Silk Moth in Forests of Krasnoyarsk Krai. In Safety of Russia. Regional Problems of Safety. Krasnoyarsk Krai; Znanie: Moscow, Russia, 2001; pp. 146–147. [Google Scholar]
- Baranchikov, Y.N.; Perevoznikova, V.D.; Vishnyakova, Z.V. Carbon Emission by Soils in Forests Damaged by the Siberian Moth. Russ. J. Ecol. 2002, 33, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edburg, S.L.; Hicke, J.A.; Lawrence, D.M.; Thornton, P.E. Simulating Coupled Carbon and Nitrogen Dynamics Following Mountain Pine Beetle Outbreaks in the Western United States. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116, G04033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.A.; Dymond, C.C.; Stinson, G.; Rampley, G.J.; Neilson, E.T.; Carroll, A.L.; Ebata, T.; Safranyik, L. Mountain Pine Beetle and Forest Carbon Feedback to Climate Change. Nature 2008, 452, 987–990. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, S.J.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Law, B.E.; Hicke, J.A.; Huang, C.; Houghton, R.A.; McNulty, S.; O’Halloran, T.; Harmon, M.E.; Meddens, A.J.H.; et al. Observations and Assessment of Forest Carbon Dynamics Following Disturbance in North America. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2012, 117, G02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosunen, M.; Lyytikäinen-Saarenmaa, P.; Ojanen, P.; Blomqvist, M.; Starr, M. Response of Soil Surface Respiration to Storm and Ips typographus (L.) Disturbance in Boreal Norway Spruce Stands. Forests 2019, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, J.A.; Allen, C.D.; Desai, A.R.; Dietze, M.C.; Hall, R.J.; Hogg, E.H.; Kashian, D.M.; Moore, D.; Raffa, K.F.; Sturrock, R.N.; et al. Effects of Biotic Disturbances on Forest Carbon Cycling in the United States and Canada. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edburg, S.L.; Hicke, J.A.; Brooks, P.D.; Pendall, E.G.; Ewers, B.E.; Norton, U.; Gochis, D.; Gutmann, E.D.; Meddens, A.J. Cascading Impacts of Bark Beetle-Caused Tree Mortality on Coupled Biogeophysical and Biogeochemical Processes. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhortova, L.V.; Kirdyanov, A.V.; Myglan, V.S.; Guggenberger, G. Wood Transformation in Dead-Standing Trees in the Forest-Tundra of Central Siberia. Biol. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2009, 36, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, M.D. Downed Bole-Wood Decomposition in Lodgepole Pine Forests of Central Oregon. J. Soil Sci. 1994, 58, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, M.E.; Franklin, J.F.; Swanson, F.J.; Sollins, P.; Gregory, S.V.; Lattin, J.D.; Anderson, N.H.; Cline, S.P.; Aumen, N.G.; Sedell, J.R.; et al. Ecology of Coarse Woody Debris in Temperate Ecosystems. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1986, 15, 133–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, J.A.; Meddens, A.J.H.; Kolden, C.A. Recent Tree Mortality in the Western United States from Bark Beetles and Forest Fires. For. Sci. 2016, 62, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulakowski, D.; Jarvis, D. The Influence of Mountain Pine Beetle Outbreaks and Drought on Severe Wildfires in Northwestern Colorado and Southern Wyoming: A Look at the Past Century. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, M.P.; Lombardero, M.J. Assessing the Consequences of Global Change for Forest Disturbance from Herbivores and Pathogens. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 262, 263–286. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.W.; Liebhold, A.M. Climate Change and the Outbreak Ranges of Two North American Bark Beetles. Agric. For. Entomol. 2002, 4, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Shvidenko, A.; Gustafson, E.; McGuire, A.D.; Kharuk, V.I.; Schepaschenko, D.G.; Shugart, H.H.; Tchebakova, N.M.; Vygodskaya, N.N.; Onuchin, A.A.; Hayes, D.J.; et al. Terrestrial Ecosystems and Their Change. In Regional Environmental Changes in Siberia and Their Global Consequences; Groisman, P.Y., Gutman, G., Eds.; Springer Environmental Science and Engineering: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 171–249. ISBN 978-94-007-4569-8. [Google Scholar]
- Knorre, A.A.; Rasnobarskiy, V.G.; Vagnorjus, P.A. The Threat of Disappearing of Fir Stands in Natural Reserve “Stolby” as a Result of Invasion of Four-Eyed Fir Bark Beetle (Polygraphus proximus Blandf.); Scientific Reports of State Natural Reseve “Stolby”: Krasnoyarsk, Russia, 2015; pp. 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Volney, W.J.A.; Fleming, R.A. Climate Change and Impacts of Boreal Forest Insects. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautov, Y.A.; Il’chukov, S.V. Spatial structure of planted trees on the concentrated logging sites in the Komi Republic. For. Sci. 2001, 2, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, V.V. Ecological consequences of mechanized logging in the southern taiga of the Krasnoyarsk region. For. Sci. 2005, 2, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dymov, A.A. The Impact of Clearcutting in Boreal Forests of Russia on Soils: A Review. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2017, 50, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheingauz, A.S. Overview of the Forest Sector in the Russian Far East: Production, Industry, and the Problem of Illegal Logging; Forest Trends: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; ISBN 1-932928-03-0. [Google Scholar]
- Akande, O.J.; Ma, Z.; Huang, C.; He, F.; Chang, S.X. Meta-analysis Shows Forest Soil CO2 Effluxes Are Dependent on the Disturbance Regime and Biome Type. Ecol. Lett. 2023, 26, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Xie, J.; Gao, R.; Qian, W. Effects of Clear-Cutting and Slash Burning on Soil Respiration in Chinese Fir and Evergreen Broadleaved Forests in Mid-Subtropical China. Plant Soil 2010, 333, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, N.T.; Ross-Todd, B.M. Soil Carbon Dynamics in a Mixed Deciduous Forest Following Clear-Cutting with and without Residue Removal. J. Soil Sci. 1983, 47, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumpanen, J.; Westman, C.J.; Ilvesniemi, H. Soil CO2 Efflux from a Podzolic Forest Soil before and after Forest Clear-Cutting and Site Preparation. Boreal Environ. Res. 2004, 9, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Chen, H.Y.H. Fine Root Biomass, Production, Turnover Rates, and Nutrient Contents in Boreal Forest Ecosystems in Relation to Species, Climate, Fertility, and Stand Age: Literature Review and Meta-Analyses. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2010, 29, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Teixeira, K.J.; Herrmann, V.; Morgan, R.B.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Cook-Patton, S.C.; Ferson, A.E.; Muller-Landau, H.C.; Wang, M.M. Carbon Cycling in Mature and Regrowth Forests Globally. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 053009. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, R.L.; Asplund, J.; Nybakken, L.; Biong, R.; Kjønaas, O.J. Harvesting History Affects Soil Respiration and Litterfall but Not Overall Carbon Balance in Boreal Norway Spruce Forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 578, 122485. [Google Scholar]
- Gundale, M.J.; Axelsson, E.P.; Buness, V.; Callebaut, T.; DeLuca, T.H.; Hupperts, S.F.; Ibáñez, T.S.; Metcalfe, D.B.; Nilsson, M.; Peichl, M.; et al. The Biological Controls of Soil Carbon Accumulation Following Wildfire and Harvest in Boreal Forests: A Review. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Houghton, R.A.; Fang, J.; Kauppi, P.E.; Keith, H.; Kurz, W.A.; Ito, A.; Lewis, S.L.; et al. The Enduring World Forest Carbon Sink. Nature 2024, 631, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).