Integrating UAV-RGB Spectral Indices by Deep Learning Model Enables High-Precision Olive Tree Segmentation Under Small Sample
Abstract
1. Introduction
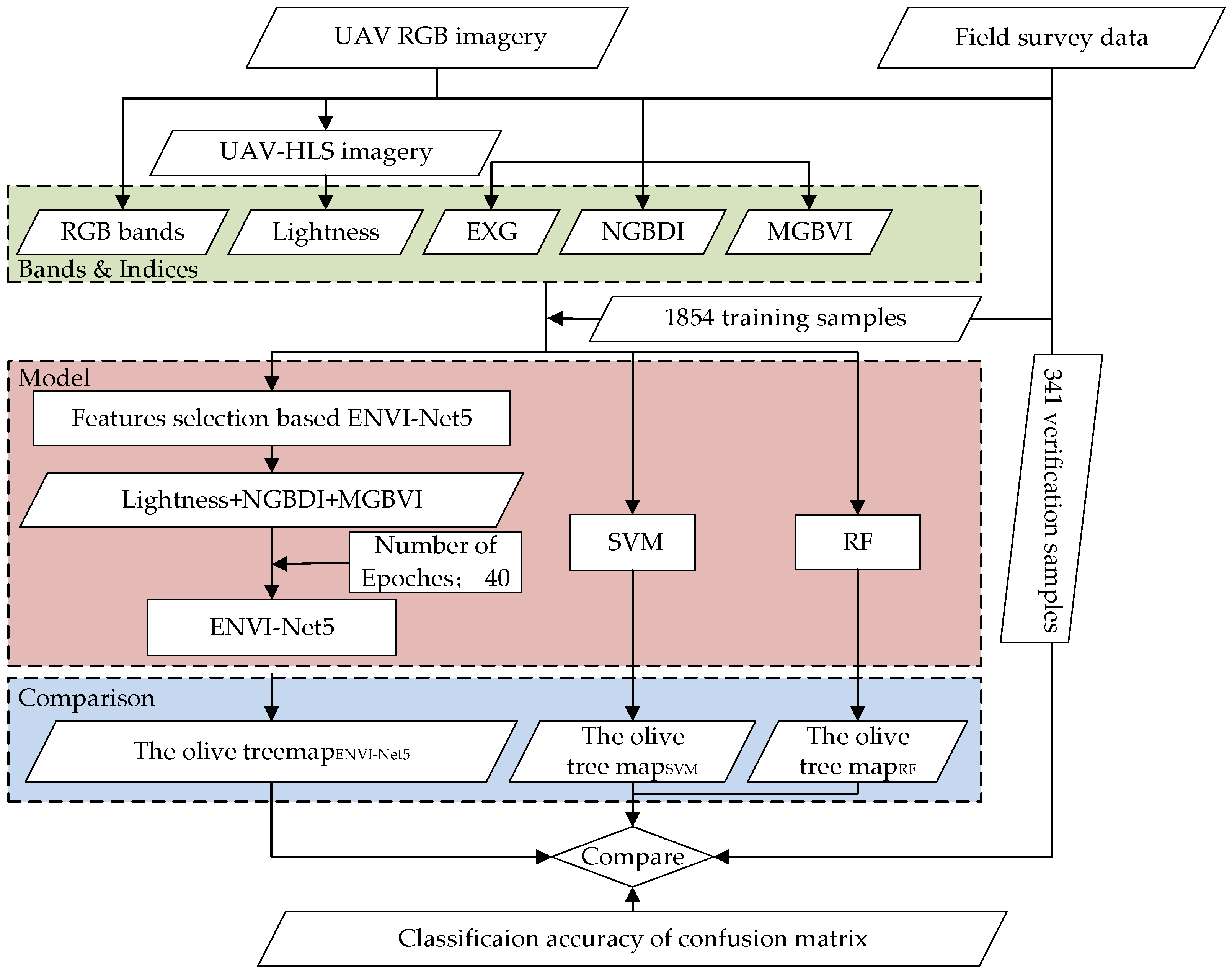
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Survey Region
2.2. RGB-UAV Data and Samples
2.2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2.2. Sample Selection
2.2.3. UAV-RGB Index Combination
2.3. Model and Parameter Settings
2.3.1. ENVI-Net5 Model
2.3.2. SVM Model
2.3.3. RF Model
2.3.4. Parameter Settings
2.4. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Extraction Accuracy of Olive Trees Under Different Iteration Numbers in the ENVI-Net5 Model
3.2. Comparison of Deep Learning Results Across Different Classification Schemes
3.3. Results of Olive Information Extraction Based on SVM and RF Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Low-Cost UAV-RGB Remote Sensing Technology for Fine-Scale Monitoring of Plantation Forests
4.2. The Combination of Lightness, NGBDI, and MGBVI Based on UAV-RGB Can Distinguish Subtle Differences Between Olive Trees and Other Vegetation
4.3. ENVI-Net5 Based on Optimal Band Feature Combinations for High-Accuracy Classification of Plantations Under Small-Sample Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michalopoulos, G.; Kasapi, K.A.; Koubouris, G.; Psarras, G.; Arampatzis, G.; Hatzigiannakis, E.; Kavvadias, V.; Xiloyannis, C.; Montanaro, G.; Malliaraki, S.; et al. Adaptation of Mediterranean Olive Groves to Climate Change through Sustainable Cultivation Practices. Climate 2020, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiljeg, A.; Panđa, L.; Domazetović, F.; Marić, I.; Gašparović, M.; Borisov, M.; Milošević, R. Comparative Assessment of Pixel and Object-Based Approaches for Mapping of Olive Tree Crowns Based on UAV Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.A.; Amato, M.; Celano, G.; Koubouris, G.C. Organic olive orchards on sloping land: More than a specialty niche production system? J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 89, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wei, J.; Lin, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, H.; Yang, K. Extraction of Olive Crown Based on UAV Visible Images and the U2-Net Deep Learning Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Lai, R. Extraction of Broad-Leaved Tree Crown Based on UAV Visible Images and OBIA-RF Model: A Case Study for Chinese Olive Trees. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.T.; Ostrovsky, M. From space to species: Ecological applications for remote sensing. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neigh, C.S.R.; Masek, J.G.; Nickeson, J.E. High-Resolution Satellite Data Open for Government Research. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2013, 94, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroditi, T.; Thomas, A.; Xanthoula, P.; Anastasia, L.; Javid, K.; Dimitris, K.; Georgios, K.; Dimitrios, M. Application of Multilayer Perceptron with Automatic Relevance Determination on Weed Mapping Using UAV Multispectral Imagery. Sensors 2017, 17, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetai, B.; Račič, M.; Lisec, A. Deep Learning for Detection of Visible Land Boundaries from UAV Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Li, Y.; Cen, H.; Zhu, J.; Yin, W.; Wu, W.; Zhu, H.; Sun, D.; Zhou, W.; He, Y. Combining UAV-Based Vegetation Indices and Image Classification to Estimate Flower Number in Oilseed Rape. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, B. Research on Vegetation Information Extraction from Visible UAV Remote Sensing Images. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fifth International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Xi’an, China, 18–20 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H. A Comparison Between UAV-RGB and ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 Images for the Assessment of Aboveground Biomass in a Temperate Forest. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Näsi, R.; Honkavaara, E.; Lyytikäinen-Saarenmaa, P.; Blomqvist, M.; Litkey, P.; Hakala, T.; Viljanen, N.; Kantola, T.; Tanhuanpää, T.; Holopainen, M. Using UAV-Based Photogrammetry and Hyperspectral Imaging for Mapping Bark Beetle Damage at Tree-Level. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15467–15493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cini, E.; Marzialetti, F.; Paterni, M.; Berton, A.; Acosta, A.T.R.; Ciccarelli, D. Integrating UAV imagery and machine learning via Geographic Object Based Image Analysis (GEOBIA) for enhanced monitoring of Yucca gloriosa in Mediterranean coastal dunes. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 258, 107377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Feng, H.; Li, C.; Yang, G.; Fu, Y.; Li, Z.; Pei, H. Estimation of Leaf Nitrogen Concentration of Winter Wheat Using UAV-Based RGB Imagery. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture (CCTA), Jilin, China, 12–15 August 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Schirrmann, M.; Giebel, A.; Gleiniger, F.; Pflanz, M.; Lentschke, J.; Dammer, K.H. Monitoring Agronomic Parameters of Winter Wheat Crops with Low-Cost UAV Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Nie, Z.; Li, G.; Zhu, W. Multi-Altitude Corn Tassel Detection and Counting Based on UAV RGB Imagery and Deep Learning. Drones 2024, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adão, T.; Hruška, J.; Pádua, L.; Bessa, J.; Peres, E.; Morais, R.; Sousa, J.J. Hyperspectral Imaging: A Review on UAV-Based Sensors, Data Processing and Applications for Agriculture and Forestry. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, M.H. Fusion-Based Approaches and Machine Learning Algorithms for Forest Monitoring: A Systematic Review. Wild 2025, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafemann, L.G. Forest Species Recognition Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Zang, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, M.; Cao, P.; Tang, S.; Wang, X. Rapid Forest Change Detection Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and Artificial Intelligence. Forests 2024, 15, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Hao, Z.; Post, C.J.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Lin, L. Individual Tree Crown Detection and Classification of Live and Dead Trees Using a Mask Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network (Mask R-CNN). Forests 2024, 15, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryono, T.; Andrian, R.; Safe’I, R.; Nopriyanto, Z. Utilisation of convolutional neural network on deep learning in predicting digital image to tree damage type. Int. J. Internet Manuf. Serv. 2024, 10, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, P.; Vieira, G.; Canário, J.; Vincent, W.F.; Pina, P.; Mora, C. A trained Mask R-CNN model over PlanetScope imagery for very-high resolution surface water mapping in boreal forest-tundra. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 304, 114047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, F.; Yan, H.; Liu, Y. Study on Remote Sensing Image Classification of Oasis Area Based on ENVI Deep Learning. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 2231–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-K. Building segmentation in agricultural land using high resolution satellite imagery based on deep learning approach. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 43, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Du, W.; Zhang, H.; Ge, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S. Classification of Different Winter Wheat Cultivars on Hyperspectral UAV Imagery. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; He, Z.; Ding, H. Research on the Sparse Plastic Shed Extraction from High Resolution Images Using ENVINet 5 Deep Learning Method. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2021, 36, 908–915. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Kovacs, J.M. The application of small unmanned aerial systems for precision agriculture: A review. Precis. Agric. 2012, 13, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shang, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Q. Investigating the impact of classification features and classifiers on crop mapping performance in heterogeneous agricultural landscapes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Guyot, G. Potentials and limits of vegetation indices for LAI and APAR assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Su, B. Significant Remote Sensing Vegetation Indices: A Review of Developments and Applications. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 1353691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendig, J.; Yu, K.; Aasen, H.; Bolten, A.; Bennertz, S.; Broscheit, J.; Gnyp, M.L.; Bareth, G. Combining UAV-based plant height from crop surface models, visible, and near infrared vegetation indices for biomass monitoring in barley. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 39, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y. Extraction of vegetation information from visible unmanned aerial vehicle images. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Yang, C.; Li, E.; Cai, X.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y. Object-Based Wetland Vegetation Classification Using Multi-Feature Selection of Unoccupied Aerial Vehicle RGB Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yang, H.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chai, X. Wheat biomass, yield, and straw-grain ratio estimation from multi-temporal UAV-based RGB and multispectral images. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 234, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.R.; Wang, C.; Morris, J.T. RGB Indices and Canopy Height Modelling for Mapping Tidal Marsh Biomass from a Small Unmanned Aerial System. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Eitel, J.U.; Engels, M.; Zhu, J.; Ma, Y.; Liao, F.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Yao, X.; Cheng, T.; et al. Improving Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) remote sensing of rice plant potassium accumulation by fusing spectral and textural information. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahnejad, A.; Panagiotidis, D. Tree Species Classification and Health Status Assessment for a Mixed Broadleaf-Conifer Forest with UAS Multispectral Imaging. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaar, F.; Yılmaz, A.; Topcu, A.E.; Alzoubi, Y.I. Remote Sensing Image Segmentation for Aircraft Recognition Using U-Net as Deep Learning Architecture. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, M.; Mohanty, S.; Dey, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Pattnaik, P.K. Convolutional Neural Network Segmentation for Satellite Imagery Data to Identify Landforms Using U-Net Architecture. In Networks and Systems, Proceeding of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Pattern Recognition (CIPR), Baripada, India, 15–16 March 2024; Das, A.K., Nayak, J., Naik, B., Himabindu, M., Vimal, S., Pelusi, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Dahiya, N.; Sood, V.; Singh, S.; Sharma, A. ENVINet5 deep learning change detection framework for the estimation of agriculture variations during 2012–2023 with Landsat series data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balha, A.; Mallick, J.; Pandey, S.; Gupta, S.; Singh, C.K. A comparative analysis of different pixel and object-based classification algorithms using multi-source high spatial resolution satellite data for LULC mapping. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 14, 2231–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wei, L.; Yu, H.; Kou, W. UAV Imagery-Based Classification Model for Atypical Traditional Village Landscapes and Their Spatial Distribution Pattern. Drones 2024, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, G.; Messina, G.; De Luca, G.; Fiozzo, V.; Praticò, S. Monitoring the vegetation vigor in heterogeneous citrus and olive orchards. A multiscale object-based approach to extract trees’ crowns from UAV multispectral imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Kou, W.; Lai, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Lu, N. Improved estimation of aboveground biomass in rubber plantations by fusing spectral and textural information from UAV-based RGB imagery. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.T.; Lin, C.H.; Jhu, C.L.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, M.J.; Liu, W.M. Semantic Segmentation of Lotus Leaves in UAV Aerial Images via U-Net and DeepLab-based Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Computer Symposium (ICS), Tainan, Taiwan, 17–19 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huangfu, W.; Qiu, H.; Cui, P.; Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Ullah, M.; Kamp, U. Automated extraction of mining-induced ground fissures using deep learning and object-based image classification. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 2189–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yue, Y.; Liu, S.; Brandt, M.; Chen, Z.; Tong, X.; Wang, K.; Chang, J.; Fensholt, R. Beyond tree cover: Characterizing southern China’s forests using deep learning. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 9, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, J.; Niu, J. Extracting Spatial Distribution Information of Alfalfa Artificial Grassland Based on Deep Learning Method. Chin. J. Grassl. 2023, 45, 22–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]




| VI. | Name | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGBVI | Modified green-blue vegetation index | [27] | |
| EXG | Excess Green Vegetation Index | [18] | |
| NGBDI | Normalized green-blue difference index | [18] |
| Scheme | Combinations | Image Layers |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | RGB | 3 |
| S2 | RGB + EXG | 4 |
| S3 | RGB + NGBDI | 4 |
| S4 | RGB + MGBVI | 4 |
| S5 | RGB + Lightness | 4 |
| S6 | Lightness + EXG + NGBDI | 3 |
| S7 | Lightness + MGBVI + NGBDI | 3 |
| Accuracy Evaluation Indexes | Number of Epoches | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | |
| OA | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.78 | 0.88 |
| Kappa | 0.61 | 0.82 | 0.46 | 0.74 |
| PA | 0.25 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.77 |
| UA | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.76 | 0.88 |
| Accuracy Evaluation Indexes | Scheme | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | |
| OA | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.98 |
| Kappa | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.96 |
| PA | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 0.95 |
| UA | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.92 |
| Accuracy Evaluation Indexes | S7 | RF | SVM |
|---|---|---|---|
| OA | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.90 |
| Kappe | 0.96 | 0.81 | 0.79 |
| PA | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.93 |
| UA | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhou, Y.; Kou, W.; Fauzi, S.S.M. Integrating UAV-RGB Spectral Indices by Deep Learning Model Enables High-Precision Olive Tree Segmentation Under Small Sample. Forests 2025, 16, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060924
Zhang Y, Wei L, Zhou Y, Kou W, Fauzi SSM. Integrating UAV-RGB Spectral Indices by Deep Learning Model Enables High-Precision Olive Tree Segmentation Under Small Sample. Forests. 2025; 16(6):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060924
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuqi, Lili Wei, Yuling Zhou, Weili Kou, and Shukor Sanim Mohd Fauzi. 2025. "Integrating UAV-RGB Spectral Indices by Deep Learning Model Enables High-Precision Olive Tree Segmentation Under Small Sample" Forests 16, no. 6: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060924
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wei, L., Zhou, Y., Kou, W., & Fauzi, S. S. M. (2025). Integrating UAV-RGB Spectral Indices by Deep Learning Model Enables High-Precision Olive Tree Segmentation Under Small Sample. Forests, 16(6), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060924





