Effects of Different Vegetation Types on Soil Quality in Golden Huacha (Camellia petelotii) National Nature Reserve
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
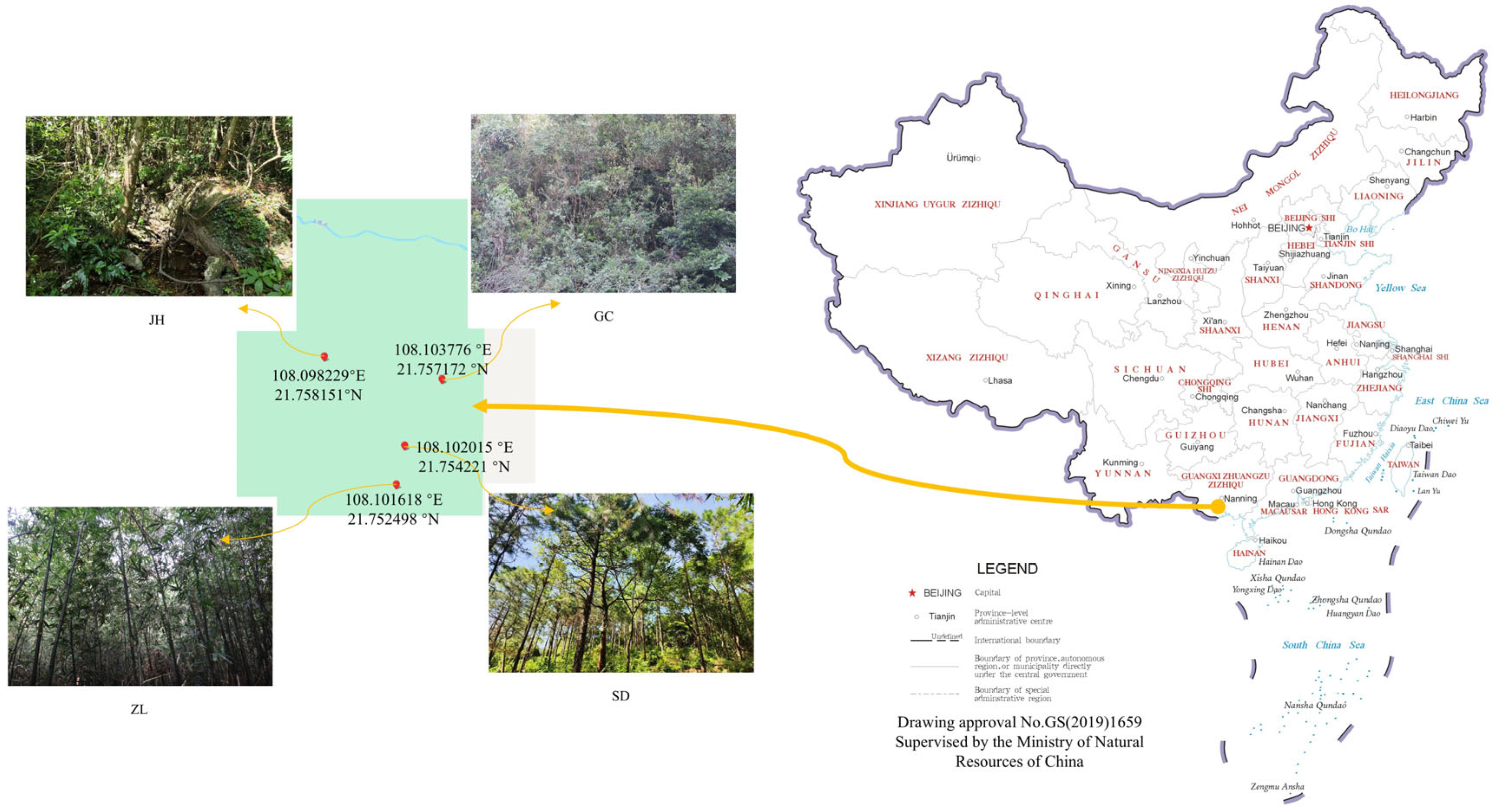
2.1. Site Information
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Chemical Properties and Enzyme Activity Determination
2.4. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Sequence and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
3.2. Soil Enzyme Activity
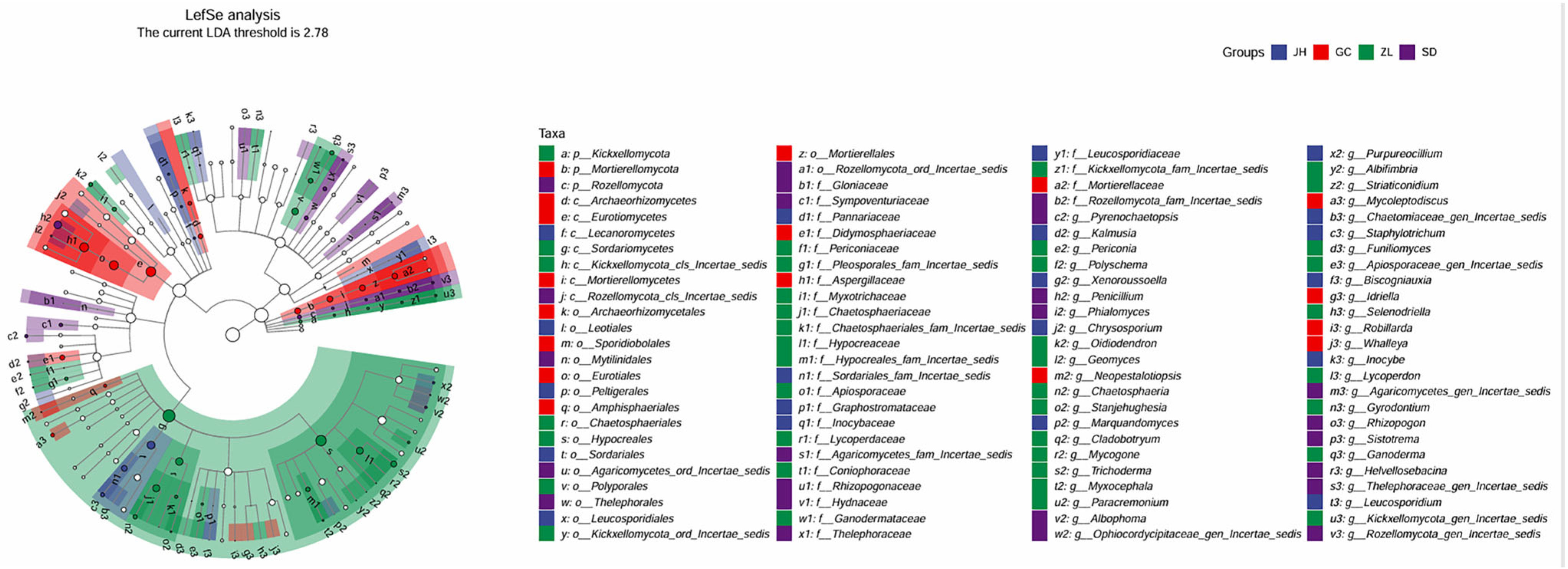
3.3. Soil Microorganism
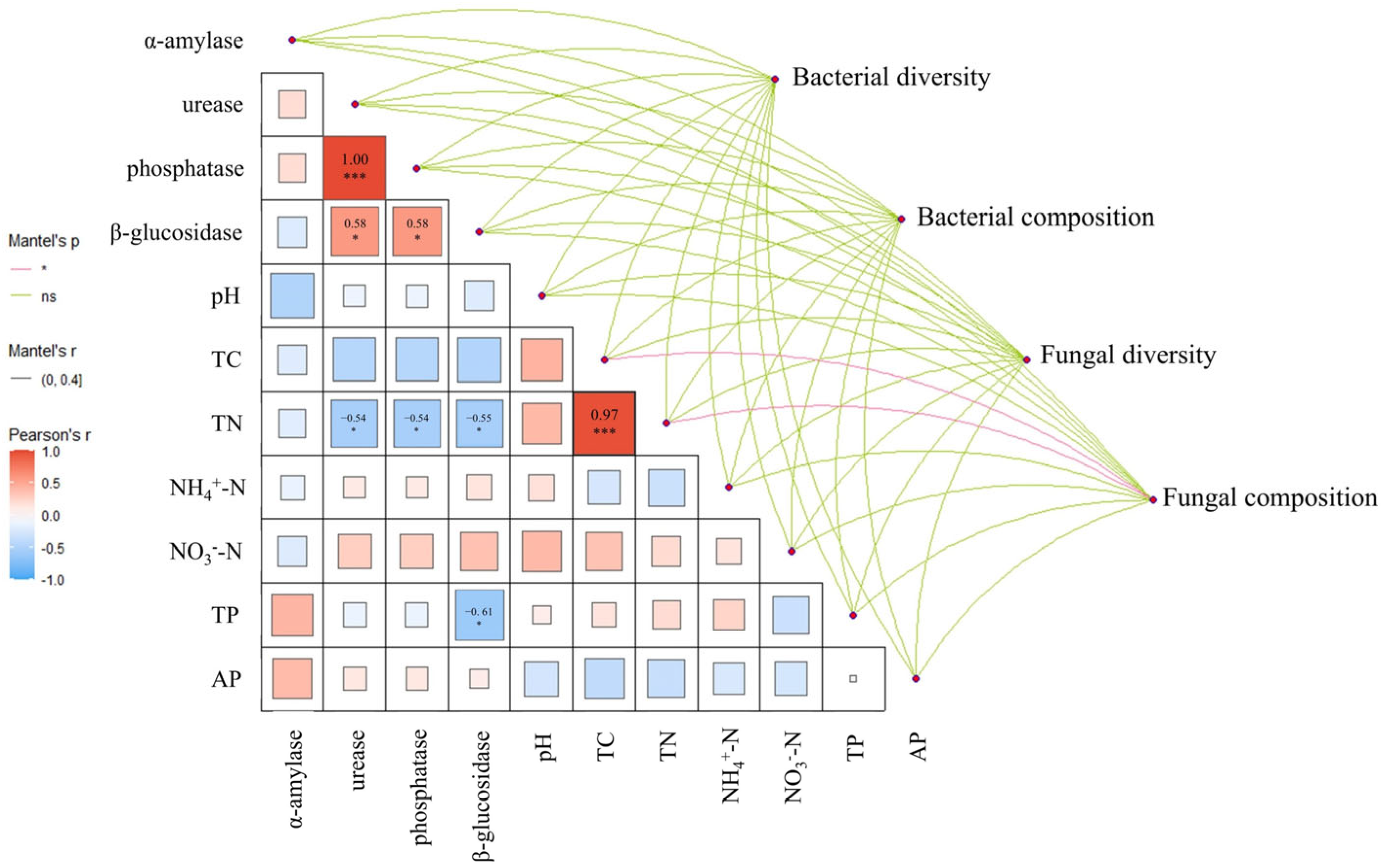
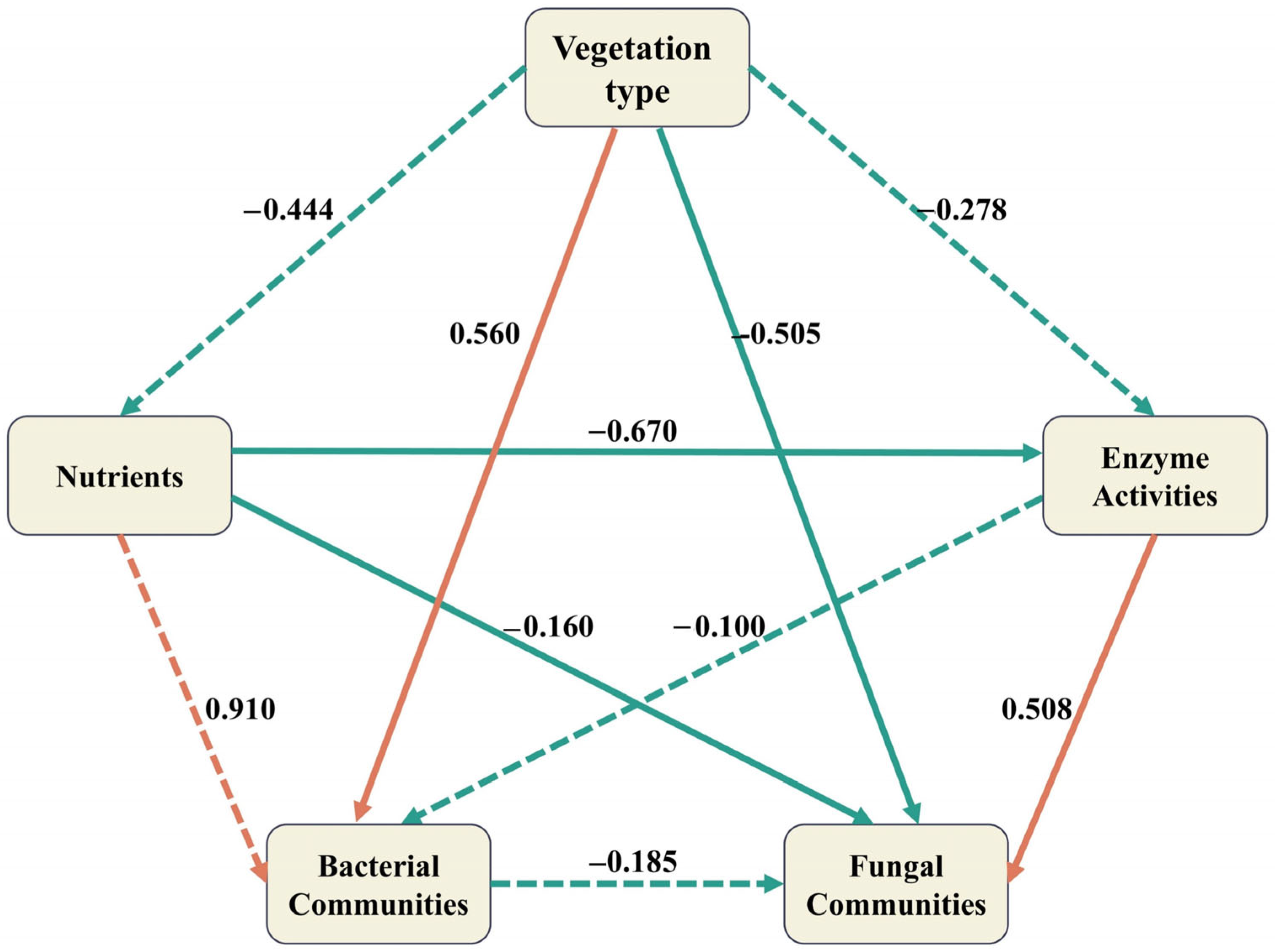
3.4. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in Soil Chemical Properties
4.2. Differences in Soil Enzyme Activities
4.3. Differences in Soil Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paquette, A.; Messier, C. The Role of Plantations in Managing the World’s Forests in the Anthropocene. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, S.; Zhou, W.; Qi, L.; Zhou, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Shao, G.; Yu, D. Opportunities and Challenges for the Protection and Ecological Functions Promotion of Natural Forests in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 410, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R.; Honnay, O. Forest Restoration, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning. BMC Ecol. 2011, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, H.R.P.; Bach, E.M.; Bartz, M.L.C.; Bennett, J.M.; Beugnon, R.; Briones, M.J.I.; Brown, G.G.; Ferlian, O.; Gongalsky, K.B.; Guerra, C.A.; et al. Global Data on Earthworm Abundance, Biomass, Diversity and Corresponding Environmental Properties. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, C.; Han, X.; Jiang, S. Soil Nutrient and Microbiological Property Recoveries via Native Shrub and Semi-Shrub Plantations on Moving Sand Dunes in Northeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Shi, J.; Ren, W. Organic Amendment Effects on Cropland Soil Organic Carbon and Its Implications: A Global Synthesis. CATENA 2023, 231, 107343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Reeve, J.R.; Norton, J.M. Soil Enzyme Activities and Abundance of Microbial Functional Genes Involved in Nitrogen Transformations in an Organic Farming System. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Sun, H.; Yang, J.; Qin, J.; Shen, D.; Chen, Y. Variations in Soil Enzyme Activities and Microbial Communities along an Altitudinal Gradient on the Eastern Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Forests 2021, 12, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; van der Putten, W.H. Belowground Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning. Nature 2014, 515, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrinho, A.; Mendes, L.W.; de Araujo Pereira, A.P.; Araujo, A.S.F.; Vaishnav, A.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Singh, B.K. Soil Microbial Diversity Plays an Important Role in Resisting and Restoring Degraded Ecosystems. Plant Soil 2024, 500, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, S.; Briones, M.J.I.; Gan, H.; Behan-Pelletier, V.M.; Friman, V.-P.; de Groot, G.A.; Hannula, S.E.; Lindo, Z.; Philippot, L.; Tiunov, A.V.; et al. A Methodological Framework to Embrace Soil Biodiversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 107536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, D.P.; Araujo, A.S.F.; de Araujo Pereira, A.P.; Mendes, L.W.; da França, R.F.; da Silva, T.d.G.E.; de Oliveira, J.B.; Araujo, J.S.; Duda, G.P.; Menezes, R.S.C.; et al. Forest-to-Pasture Conversion Modifies the Soil Bacterial Community in Brazilian Dry Forest Caatinga. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 151943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Li, X.; Bardgett, R.D.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Revillini, D.; Sonne, C.; Xia, C.; Ruan, H.; Liu, Y.; Cao, F.; et al. Deforestation Impacts Soil Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services Worldwide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2318475121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.C.; Smith, K.L. Soil Microbial Diversity and the Sustainability of Agricultural Soils. Plant Soil 1995, 170, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The Interplay between Microbial Communities and Soil Properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, T.M.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; Calderón, F.; Jackson, L.E. Soil Enzyme Activities, Microbial Communities, and Carbon and Nitrogen Availability in Organic Agroecosystems across an Intensively-Managed Agricultural Landscape. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Ascher, J.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Landi, L.; Pietramellara, G.; Renella, G. Microbial Diversity and Soil Functions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil Enzymes in a Changing Environment: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, R.P. Soil Enzyme Activities as Indicators of Soil Quality; Doran, J.W., Coleman, D.C., Bezdicek, D.F., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; pp. 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The Diversity and Biogeography of Soil Bacterial Communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Teng, C.; Pang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Qiu, J.; Lei, J.; Su, X.; Zhu, W.; Ding, C. Intercropping Changed the Soil Microbial Community Composition but No Significant Effect on Alpha Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1370996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ding, C.; Teng, C.; Zhang, W.; Su, X.; Zhu, W. Impacts of Litter Microbial Community on Litter Decomposition in the Absence of Soil Microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0023924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Wang, R.; Cong, X.; Pang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zhu, W.; Ding, C. Factors Influencing the Change of Phyllosphere Microbial Community of Three Populus Spp. in the Same Habitat. Forests 2024, 15, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, W.; Huo, Y.; Cong, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Su, X.; Zhang, W.; Ding, C. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Communities Vary between Poplar Species in the Same Habitat. Rhizosphere 2024, 29, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. The Measurement of Diversity in Different Types of Biological Collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric Estimation of the Number of Classes in a Population. Scand. J. Statist. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Van Zwieten, L.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Wang, H. Soil Parent Material Controls Organic Matter Stocks and Retention Patterns in Subtropical China. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, T.; Sha, G.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ren, K.; Yang, C. Soil Enzyme Activities of Typical Plant Communities after Vegetation Restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meng, Z.; Ren, X.; Han, Y. Variations in the Physicochemical Properties of Soil, Enzyme Activities, and the Characteristics of Bacterial Communities within Algal Biocrusts and Subsoils across Different Plant Communities. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 58, e03455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondeau, A.; Smith, P.C.; Zaehle, S.; Schaphoff, S.; Lucht, W.; Cramer, W.; Gerten, D.; Lotze-Campen, H.; Müller, C.; Reichstein, M.; et al. Modelling the Role of Agriculture for the 20th Century Global Terrestrial Carbon Balance. Glob. Change Biol. 2007, 13, 679–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Curtis, P.S. Effects of Forest Management on Soil C and N Storage: Meta Analysis. For. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 140, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lin, T.-C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xiong, D.; Chen, S.; Wu, F.; Yang, Y. Forest Conversion Effects on Soil Organic Carbon Are Regulated by Soil Aggregate Stability and Not by Recalcitrance: Evidence from a Reforestation Experiment. CATENA 2022, 219, 106613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Gutknecht, J.; Nadrowski, K.; Geißler, C.; Kühn, P.; Scholten, T.; Both, S.; Erfmeier, A.; Böhnke, M.; Bruelheide, H.; et al. Relationships Between Soil Microorganisms, Plant Communities, and Soil Characteristics in Chinese Subtropical Forests. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.U.; Vitousek, P.M. Effects of Plant Composition and Diversity on Nutrient Cycling. Ecol. Monogr. 1998, 68, 121–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, G.; Yin, Y.; Gao, R.; Lin, C. Effects of Forest Conversion on Soil Labile Organic Carbon Fractions and Aggregate Stability in Subtropical China. Plant Soil 2009, 323, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, H.; Xu, Z.; Tan, B.; You, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Guo, L.; et al. Litter Chemical Traits Strongly Drove the Carbon Fractions Loss during Decomposition across an Alpine Treeline Ecotone. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, L.M.; do Rosário Zucchi, M.; de Jesus, T.B.; da Silva Júnior, J.B.; Hadlich, G.M. δ13C, δ15N and TOC/TN as Indicators of the Origin of Organic Matter in Sediment Samples from the Estuary of a Tropical River. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Classen, A.T.; Wang, W.-W.; Zhao, X.-R.; Mao, B.; Zeng, D.-H. Asymmetric Effects of Litter Removal and Litter Addition on the Structure and Function of Soil Microbial Communities in a Managed Pine Forest. Plant Soil 2017, 414, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M. Response of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities to Long-Term Reclamation of Coastal Saline Soil, Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Tong, Y.; Wen, D.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Barceló, D. Response of Soil Enzyme Activities and Bacterial Communities to the Accumulation of Microplastics in an Acid Cropped Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, F.M.; Dominchin, M.F.; Verdenelli, R.A.; Frasier, I.; Restovich, S.B.; Campilongo Mancilla, E.J.; Mlewski, E.C.; Labuckas, D.; Vargas Gil, S.; Meriles, J.M. Impact of Land Use Changes on Soil Chemical Properties, Enzyme Activities and Microbial Communities in Two Contrasting Localities of the Argentinian Pampas. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 206, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, X.; Ren, Z.; Wang, G. Soil Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity Response to Land Conversion Is Depth-Dependent. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 32, e01923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, J.; Ahmad Bhat, S.; Wei, Y.; Deng, Z.; Li, F. Elimination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Excess Activated Sludge Added for Effective Treatment of Fruit and Vegetable Waste in a Novel Vermireactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Xing, F.; Sun, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, X.; Chen, C.; Li, Z. Responses of Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Microbial Community Properties to Interaction between Nitrogen Addition and Increased Precipitation in a Semi-Arid Grassland Ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ju, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, C.; Kopsch, J.; Fusuo, Z. Nitrogen Deposition in Agroecosystems in the Beijing Area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 113, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an Ecological Classification of Soil Bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-Based Assessment of Soil pH as a Predictor of Soil Bacterial Community Structure at the Continental Scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Maestre, F.T.; Reich, P.B.; Jeffries, T.C.; Gaitan, J.J.; Encinar, D.; Berdugo, M.; Campbell, C.D.; Singh, B.K. Microbial Diversity Drives Multifunctionality in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, E.A.; Vatsa, P.; Sanchez, L.; Gaveau-Vaillant, N.; Jacquard, C.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Klenk, H.-P.; Clément, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; van Wezel, G.P. Taxonomy, Physiology, and Natural Products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmuth, B.E.; McDonald, K.A. Production and Characterization of Acidothermus cellulolyticus Endoglucanase in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 77, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Põlme, S.; Kõljalg, U.; Yorou, N.S.; Wijesundera, R.; Ruiz, L.V.; Vasco-Palacios, A.M.; Thu, P.Q.; Suija, A.; et al. Global Diversity and Geography of Soil Fungi. Science 2014, 346, 1256688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häkkinen, L.; Pessi, I.S.; Salonen, A.-R.; Uhlgren, O.; Soinne, H.; Hultman, J.; Heinonsalo, J. Fungal Communities in Boreal Soils Are Influenced by Land Use, Agricultural Soil Management, and Depth. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2025, 101, fiaf002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wei, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, K.; Liu, Y.; Ding, H.; Lei, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Y. Effects of Mixed Decomposition of Pinus Sylvestris Var. Mongolica and Morus Alba Litter on Microbial Diversity. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Hao, M.; Wei, X. Soil Organic C and N Dynamics as Affected by 31 Years Cropping Systems and Fertilization in Highland Agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P.; Kolařík, M.; Štursová, M.; Kopecký, J.; Valášková, V.; Větrovský, T.; Žifčáková, L.; Šnajdr, J.; Rídl, J.; Vlček, Č.; et al. Active and Total Microbial Communities in Forest Soil Are Largely Different and Highly Stratified during Decomposition. ISME J. 2012, 6, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yu, W.-J.; Bau, T.; Matheny, P.B.; Horak, E.; Liu, Y.; Qin, L.-W.; Tang, L.-P.; Ge, Y.-P.; Liu, T.-Z.; et al. Contributions to the Inocybe Umbratica-Paludinella (Agaricales) Group in China: Taxonomy, Species Diversity, and Molecular Phylogeny. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; McCain, C.M.; Meir, P.; Zimmermann, M.; Rapp, J.M.; Silman, M.R.; Knight, R. Microbes Do Not Follow the Elevational Diversity Patterns of Plants and Animals. Ecology 2011, 92, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltedesco, E.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Piepho, H.-P.; Antonielli, L.; Pötsch, E.M.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Gorfer, M. Soil Microbial Community Structure and Function Mainly Respond to Indirect Effects in a Multifactorial Climate Manipulation Experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.J.; Weintraub, M.N.; Hewins, C.R.; Kalisz, S. Relationship between Soil Enzyme Activities, Nutrient Cycling and Soil Fungal Communities in a Northern Hardwood Forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, R.E.; Mcginnis, M.L.; Holub, S.M.; Myrold, D.D. Soil Fungal and Prokaryotic Community Structure Exhibits Differential Short-Term Responses to Timber Harvest in the Pacific Northwest. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Qin, S.; Guan, X.; Jiang, K.; Jiang, M.; Liu, F. Distribution of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Karst River and Its Ecological Risk. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, H.; Cheng, S.; Xu, L.; Lu, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y. Soil Enzyme Activity Regulates the Response of Soil C Fluxes to N Fertilization in a Temperate Cultivated Grassland. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| pH | TC (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | NO3−-N (mg/kg) | TP (g/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZL | 5.17 ± 0.16 A | 28.29 ± 3.52 B | 2.17 ± 0.07 B | 7.06 ± 0.65 A | 14.61 ± 1.04 B | 0.18 ± 0.03 A | 22.73 ± 3.60 A |
| JH | 5.76 ± 0.19 A | 39.76 ± 3.64 AB | 3.13 ± 0.18 B | 6.31 ± 0.36 A | 23.69 ± 4.96 A | 0.05 ± 0.02 B | 18.42 ± 2.97 A |
| SD | 5.45 ± 0.24 A | 26.74 ± 2.51 B | 2.22 ± 0.26 B | 6.94 ± 0.95 A | 10.68 ± 0.69 B | 0.08 ± 0.03 AB | 19.38 ± 3.80 A |
| GC | 5.56 ± 0.39 A | 52.97 ± 6.81 A | 4.69 ± 0.70 A | 5.78 ± 0.67 A | 13.54 ± 1.11 B | 0.17 ± 0.02 A | 19.86 ± 3.10 A |
| F-value | 0.90 | 7.56 | 9.23 | 0.74 | 4.61 | 5.57 | 0.30 |
| p-value | 0.47 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.82 |
| α-Amylase (mg/g) | Urease (mg/g) | Phosphatase (mg/g) | β-Glucosidase (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZL | 18.74 ± 1.8 A | 86.03 ± 4.94 A | 84.14 ± 4.84 A | 228.53 ± 11.46 A |
| JH | 10.54 ± 0.75 B | 86.65 ± 10.07 A | 84.74 ± 9.87 A | 280.31 ± 7.39 A |
| SD | 9.4 ± 0.86 B | 38.65 ± 4.24 B | 37.72 ± 4.16 B | 244.41 ± 9.91 A |
| GC | 13.67 ± 1.69 B | 7.67 ± 0.93 C | 7.4 ± 0.89 C | 176.09 ± 29.43 B |
| F-value | 9.431 | 41.195 | 41.173 | 6.521 |
| p-value | 0.002 | 1.35 × 10−6 | 1.36 × 10−6 | 0.007 |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Permutations | Pseudo-F | p-Value | q-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial community | all | - | 999 | 3.182613 | 0.001 | - |
| JH | GC | 999 | 2.576514 | 0.03 | 0.042 | |
| JH | ZL | 999 | 5.565539 | 0.035 | 0.042 | |
| JH | SD | 999 | 4.430899 | 0.029 | 0.042 | |
| GC | ZL | 999 | 2.563385 | 0.024 | 0.042 | |
| GC | SD | 999 | 1.630788 | 0.083 | 0.083 | |
| ZL | SD | 999 | 3.2443 | 0.023 | 0.042 | |
| Fungal community | all | - | 999 | 2.508656 | 0.001 | - |
| JH | GC | 999 | 1.850886 | 0.020 | 0.034 | |
| JH | ZL | 999 | 3.646726 | 0.029 | 0.034 | |
| JH | SD | 999 | 2.744955 | 0.032 | 0.034 | |
| GC | ZL | 999 | 2.433756 | 0.030 | 0.034 | |
| GC | SD | 999 | 1.653928 | 0.023 | 0.034 | |
| ZL | SD | 999 | 3.05705 | 0.034 | 0.034 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Xu, S.; Gu, W.; Wu, S.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, W.; Liao, N. Effects of Different Vegetation Types on Soil Quality in Golden Huacha (Camellia petelotii) National Nature Reserve. Forests 2025, 16, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050865
Jiang Y, Xu S, Gu W, Wu S, Qiu J, Zhu W, Liao N. Effects of Different Vegetation Types on Soil Quality in Golden Huacha (Camellia petelotii) National Nature Reserve. Forests. 2025; 16(5):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050865
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yong, Sheng Xu, Weiwei Gu, Siqi Wu, Jian Qiu, Wenxu Zhu, and Nanyan Liao. 2025. "Effects of Different Vegetation Types on Soil Quality in Golden Huacha (Camellia petelotii) National Nature Reserve" Forests 16, no. 5: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050865
APA StyleJiang, Y., Xu, S., Gu, W., Wu, S., Qiu, J., Zhu, W., & Liao, N. (2025). Effects of Different Vegetation Types on Soil Quality in Golden Huacha (Camellia petelotii) National Nature Reserve. Forests, 16(5), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050865






