Role of Stand Density in Shaping Interactions and Growth Strategies of Dioecious Tree Species: A Case Study of Fraxinus mandshurica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sites
2.2. Spatial Structure Measurement
2.3. Growth Traits Measurement
2.4. Phenotype and Nutrients of Nutritive Organ
2.5. Physicochemical Properties of Rhizosphere Soil
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
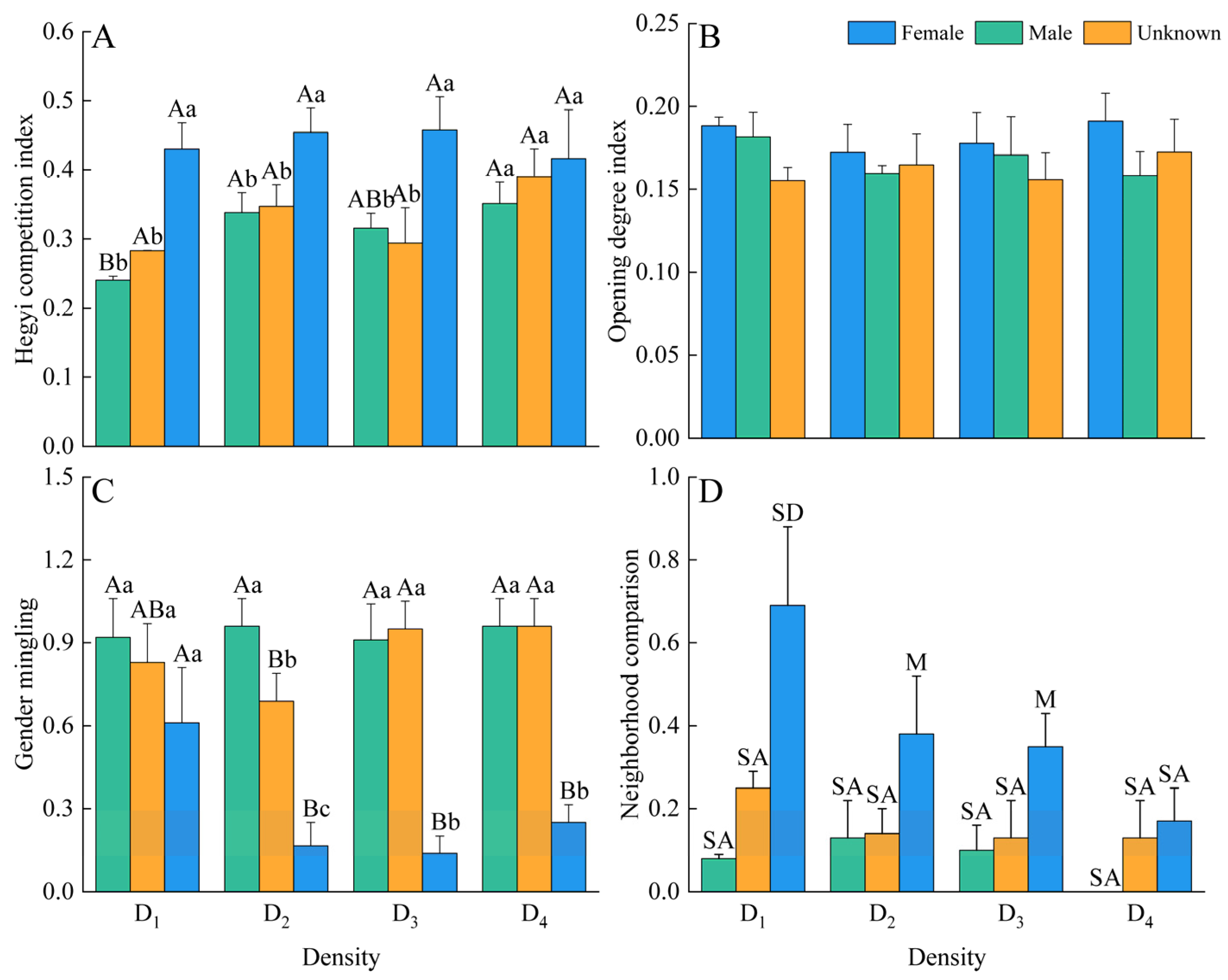
3.1. Spatial Structure
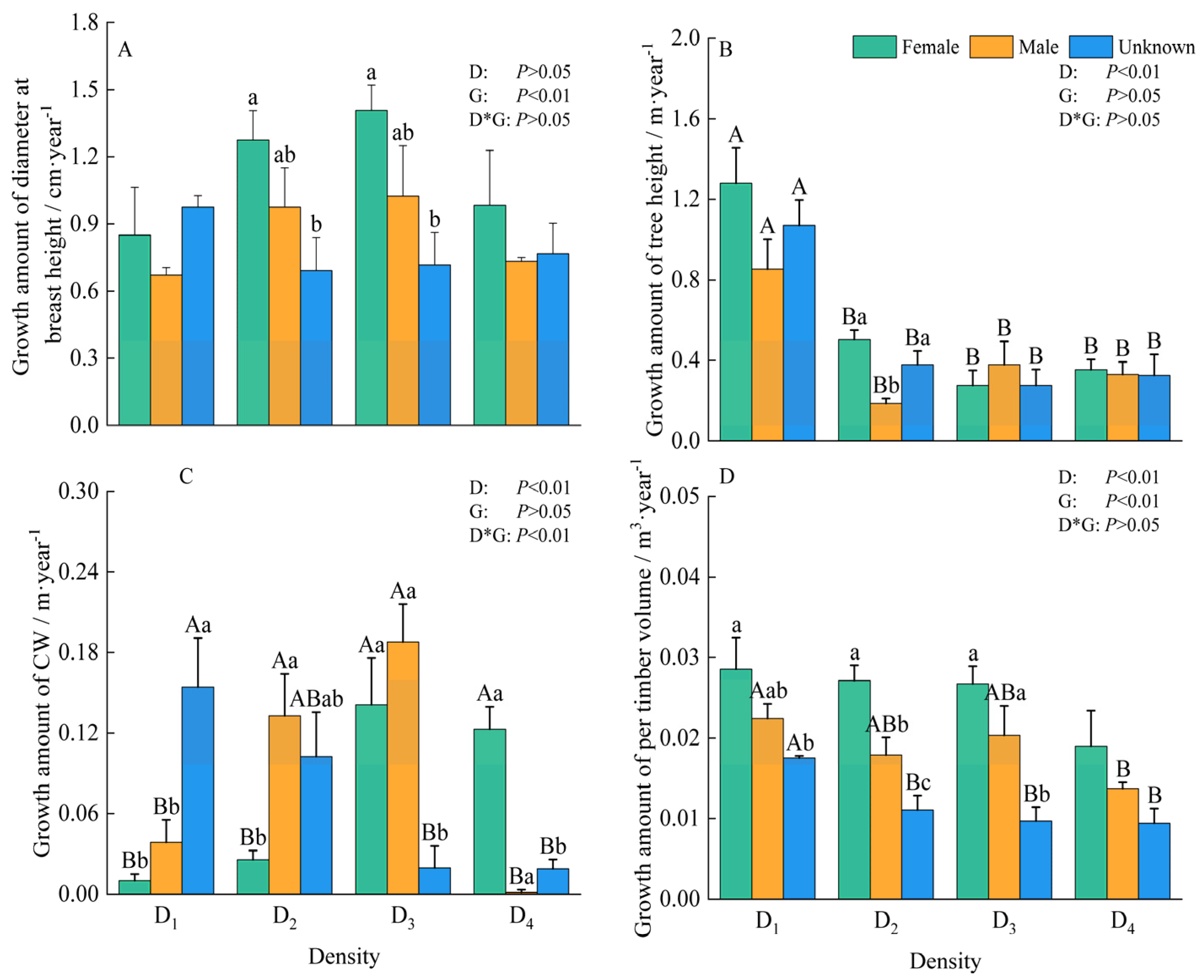
3.2. Growth Traits
3.3. Nutritional Organ Morphology
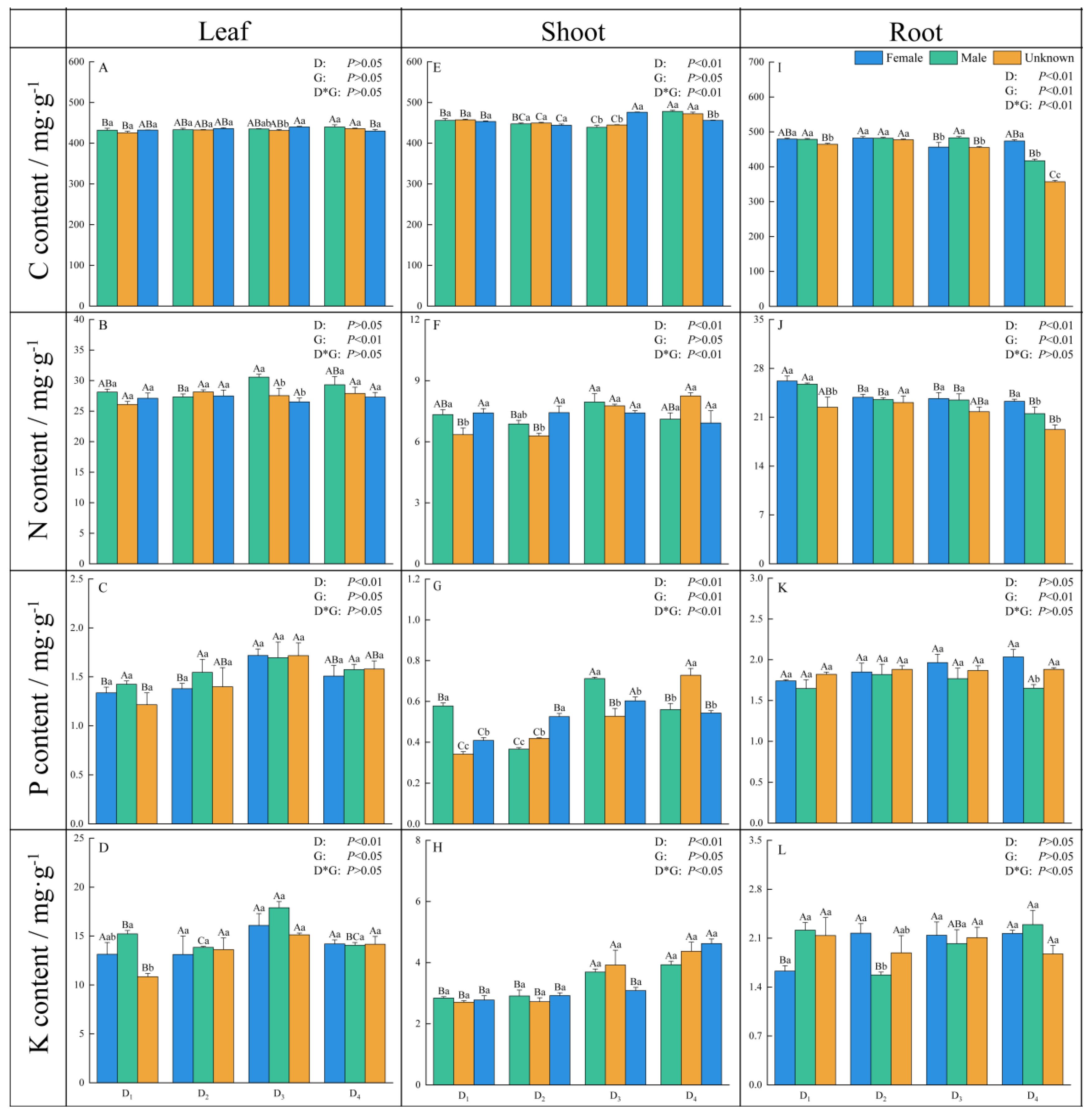
3.4. Nutrition in Vegetative Organs
3.5. Rhizosphere Soil Physicochemical Properties
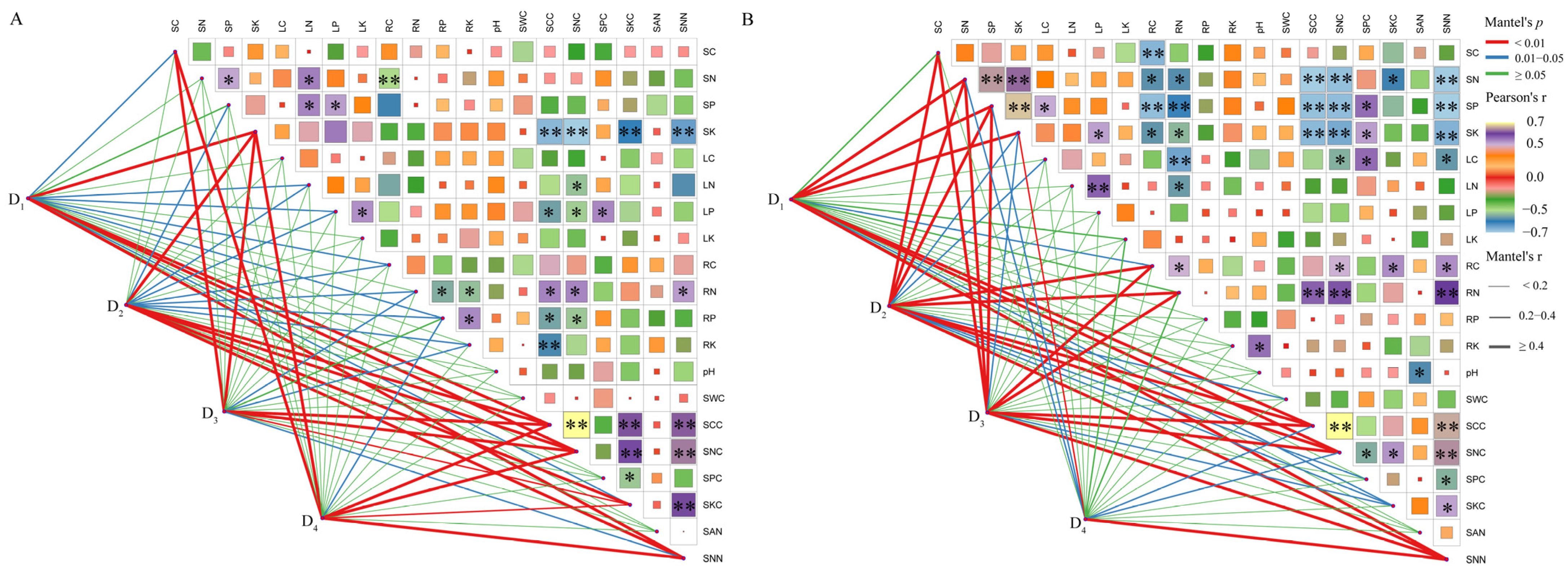
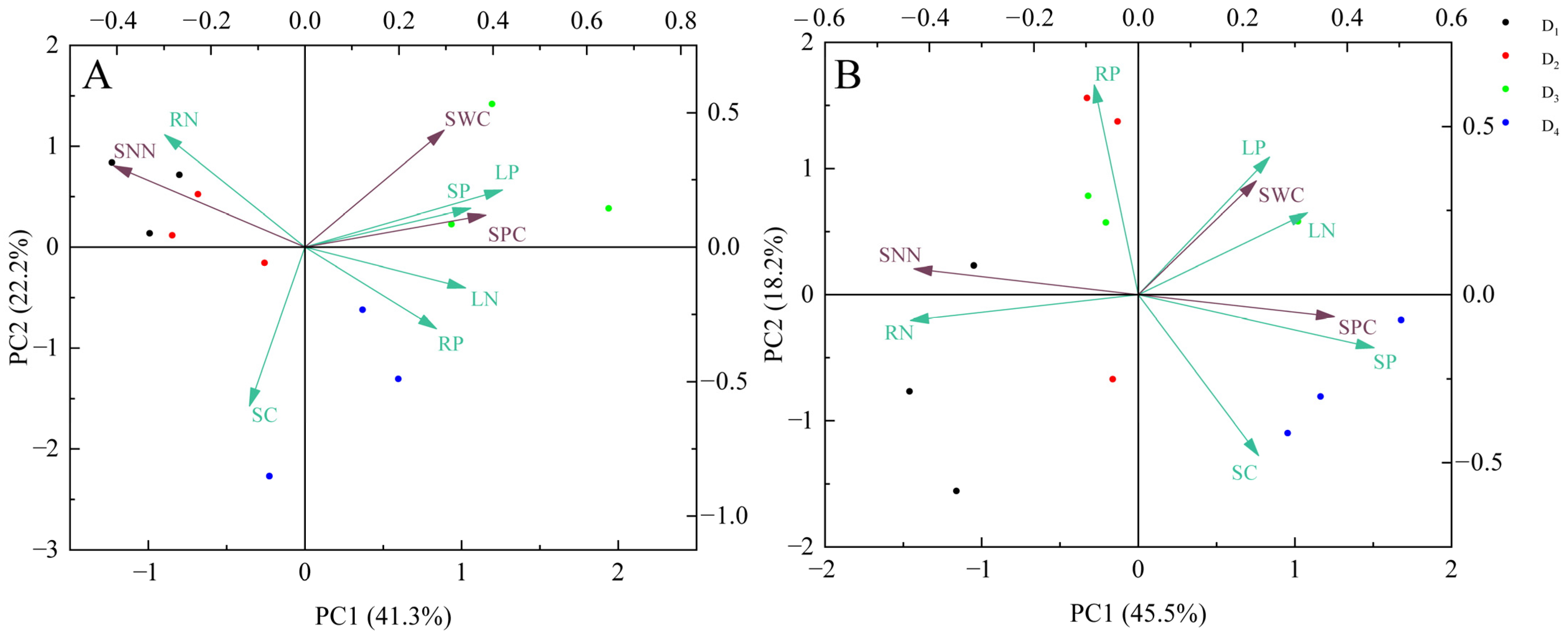
3.6. Comprehensive Analysis of Growth Traits and Soil Physicochemical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. The Response of Spatial Structure in Male and Female Plants to Density
4.2. Response of Morphological Development of Male and Female Plants to Density
4.3. The Response of Nutrients in Reproductive Organs of Male and Female Plants and the Physicochemical Properties of Rhizosphere Soil to Density
4.4. The Interactive Mechanisms Between the Developmental Strategies of Male and Female Plants and Density
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DBH | Diameter at breast height |
| TH | Tree height |
| CW | Crown width |
| TV | Tree volume of timber |
| SC | Carbon content of shoots |
| SN | Nitrogen content of shoots |
| SP | Phosphorus content of shoots |
| SK | Potassium content of shoots |
| LC | Carbon content of leaves |
| LN | Nitrogen content of leaves |
| LP | Phosphorus content of leaves |
| LK | Potassium content of leaves |
| RC | Carbon content of absorptive roots |
| RN | Nitrogen content of absorptive roots |
| RP | Phosphorus content of absorptive roots |
| RK | Potassium content of absorptive roots |
| pH | Soil pH |
| SWC | Soil water content |
| SCC | Soil carbon content |
| SNC | Soil nitrogen content |
| SPC | Soil phosphorus content |
| SKC | Soil potassium content |
| SAN | Soil ammonium nitrogen content |
| SNN | Soil nitrate nitrogen content |
References
- McEwan, A.; Marchi, E.; Spinelli, R.; Brink, M. Past, present and future of industrial plantation forestry and implication on future timber harvesting technology. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, T.H.; Shakoor, A.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Zhang, X.; Gilani, M.M.; Kumar, U.; Chen, X.; Yan, W. Perspectives of plantation forests in the sustainable forest development of China. iForest 2021, 14, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, F.; Gilani, H.; Sannaei, A.; Hussain, K.; Ali, A. Stand structure determines aboveground biomass across temperate forest types and species mixture along a local-scale elevational gradient. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 486, 118984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouvé, R.; Bontempes, J.D.; Seynave, I.; Collet, C.; Lebourgeois, F. Stand density, tree social status and water stress influence allocation in height and diameter growth of Quercus petraea (Liebl.). Tree Physiol. 2015, 35, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gebauer, R.; Volarík, D.; Urban, J.; Borja, I.; Nagy, N.E.; Eldhuset, T.D.; Krokene, P. Altered light conditions following thinning affect xylem structure and potential hydraulic conductivity of Norway spruce shoots. Eur. J. For. Res. 2014, 133, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A. Forest stand structure and functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Ecol. Inform. 2019, 98, 665–677. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.L.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.L.; Luo, M.L.; Chu, C.J.; Fang, S.Q. Sexual competition and kin recognition co-shape the traits of neighboring dioecious Diospyros morrisiana seedlings. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 162. [Google Scholar]
- Vizcaíno-Palomar, N.; Gómez-Aparicio, L.; Pavón-García, J.; Bartolomé-Esteban, C.; Álvarez-Jiménez, J.; Zavala, M.A. Main biotic drivers of tree growth in a developing Juniperus thurifera stand in central Spain. Eur. J. For. Res. 2014, 133, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munné-Bosch, B. Sex ratios in dioecious plants in the framework of global change. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 109, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Xiang, W.H.; Wang, X.P.; Xiao, W.F.; Chen, L.; Li, S.G.; Sun, H.; Deng, X.W.; Forrester, D.I.; Zeng, L.X.; et al. Effects of stand age, richness and density on productivity in subtropical forests in China. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar]
- Rosati, A.; Paoletti, A.; Al Hairi, R.; Morelli, A.; Famiani, F. Resource investments in reproductive growth proportionately limit investments in whole-tree vegetative growth in young olive trees with varying crop loads. Tree Physiol. 2018, 38, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabska, M.; Pers-Kamczyc, E.; Zytkowiak, R.; Adamczyk, D.; Iszkulo, G. Sexual dimorphism in the chemical composition of male and female in the dioecious tree, Juniperus communis L., growing under different nutritional conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Gadow, K.V.; Cheng, Y.X.; Zhao, X.H. Reproduction and vegetative growth in the dioecious shrub Acer barbinerve in temperate forests of Northeast China. Plant Reprod. 2015, 28, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.X.; He, X.H.; Xu, X.; Yang, D.M. Scaling relationships among twig components are affected by sex in the dioecious tree Populus cathayana. Trees 2015, 29, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banuelos, M.J.; Obeso, J.R. Resource allocation in the dioecious shrub Rhamnus alpinus: The hidden costs of reproduction. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2004, 6, 397–413. [Google Scholar]
- Teitel, Z.; Pickup, M.; Field, D.L.; Barrett, S.C.H. The dynamics of resource allocation and costs of reproduction in a sexually dimorphic, wind-pollinated dioecious plant. Plant Biol. 2016, 18, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dong, T.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, H.X. Populus deltoides females are more selective in nitrogen assimilation than males under different nitrogen forms supply. Trees 2015, 29, 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Dong, T.; Duan, B. Sex-specific carbon and nitrogen partitioning under N deposition in Populus cathayana. Trees 2014, 28, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.G.; Zhao, Z.H.; Bai, C.; Liu, W.Z. A novel approach for assessing the neighborhood competition in two different aged forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 422, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Hui, G.Y.; Liu, W.Z.; Hu, Y.B.; Zhang, G.Q. A novel method for calculating stand structural based on the relationship of adjacent trees. Forests 2022, 13, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, A.; Härdtle, W.; Bruelheide, H.; Kunz, M.; Li, Y.; Oheimb, G.V. Neighbourhood interactions drive overyielding in mixed-species tree communities. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, A.; Wang, Y.H.; Webb, A.A.; Yu, P.T.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.B. Modelling the response of larch growth to age, density, and elevation and the implications for multifunctional management in northwest China. J. For. Res. 2023, 34, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Hui, G.Y.; Hu, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.H.; Guan, X.L.; Gadow, K.V.; Zhang, G.G. Designing near-natural planting patterns for plantation forests in China. For. Ecosyst. 2019, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.R.; Zhang, P.; Shen, H.L. Competition intensity affects growing season nutrient dynamics in Korean pine trees and their microhabitat soil in mixed forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 539, 121018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.N.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhao, X.H. Effect of sex ratio, habitat factors and neighborhood competition on stem growth in the dioecious tree Fraxinus mandshurica. Ecol. Res. 2014, 29, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerhoulas, L.P.; Kolb, T.E.; Koch, G.W. Tree size, stand density, and the source of water used across seasons by ponderosa pine in northern Arizona. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 289, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.R.; Dash, J.P.; Lee, J.R.; Russell, B.M.; Dungey, H.S. Quantifying the influence of seedlot and stand density on growth, wood properties and the economics of growing radiata pine. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2018, 91, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.W.; Yang, L.X.A. Long-term effect of Larix monocultures on soil physicochemical properties and microbes in northeast China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 96, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wei, X.; Wei, Q.Y. Responses of early distribution and developmental traits of male and female trees to stand density in Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr. plantation. Forests 2022, 13, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmond, S.C.; Garner, M.; Flannery, S.; Whittemore, A.T.; Hipp, A.L. Leaf shape and size variation in bur oaks: An empirical study and simulation of sampling strategies. Am. J. Bot. 2021, 108, 1540–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.Q.; Goebel, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Gu, J.C. Spatial–temporal variations of absorptive fine roots in the organic and soil layers of a Larix gmelinii forest. Trees 2021, 35, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Gao, G.Q.; Ma, Y.Y.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, S.Y.; Gu, J.C. Shift of root nitrogen-acquisition strategy with tree age is mediated by root functional traits along the collaboration gradient of the root economics space. Tree Physiol. 2023, 43, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.F.; Lu, J.Y.; Yin, L.M.; Wang, P.; Chen, W.X. Coupled of carbon and nitrogen mineralization in rhizosphere soils along a temperate forest altitudinal gradient. Plant Soil 2022, 500, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares AA, V.; Leite, H.G.; Souza, A.L.; Silva, S.R.; Lourenco, H.M.; Forrester, D.I. Increasing stand structural heterogeneity reduces productivity in Brazilian Eucalyptus monoclonal stands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 373, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Berube-Deschenes, A.; Franceschini, T.; Schneider, R. Quantifying competition in white spruce (Picea glauca) plantations. Ann. For. Sci. 2017, 74, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Dong, T.F.; Duan, B.L.; Korpelainen, H.; Niinemets, Ü.; Li, C.Y. Sexual competition and N supply interactively affect the dimorphism and competiveness of opposite sexes in Populus cathayana. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Bi, J.W.; Liu, X.C.; Kang, J.Y.; Korpelainen, H.; Niinemets, U.; Li, C.Y. Microstructural and physiological responses to cadmium stress under different nitrogen levels in Populus cathayana females and males. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Myers-Smith, I.H.; Hik, D.S. Uniform female-biased sex ratios in alpine willows. Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Duan, B.L.; Chen, J.; Korpelainen, H.; Niinements, Ü.; Li, C.Y. Males exhibit competitive advantages over females of Populus deltoides under salinity stress. Tree Physiol. 2016, 36, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.Y.; Song, M.Y.; Pang, J.Y. Effects of NH4+ and NO3–on sexual dimorphism responses to manganese stress in a dioecious tree species. Trees 2018, 32, 473–488. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, V.F.; Bispo, R.L.B.; Loiola, P.D. A case of gender equality: Absence of sex-related costs in a dioecious tropical forest tree species. Plant Ecol. 2021, 222, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zhao, X.H.; Gao, L.S.; Gadow, K. Gender, neighboring competition and habitat effects on the stem growth in dioecious Fraxinus mandshurica trees in a northern temperate forest. Ann. For. Sci. 2009, 66, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Korpelainen, H.; Li, C.Y. Sexual differences and sex ratios of dioecious plants under stressful environments. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 14, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, M.; Takao, M.; Makita, A. Sex-different response in growth traits to resource heterogeneity explains male-biased sex ratio. Acta Oecologica-Int. J. Ecol. 2016, 75, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korgiopoulou, C.; Bresta, P.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Karabourniotis, G. Sex-specific structural and functional leaf traits and sun-shade acclimation in the dioecious tree Pistacia vera (Anacardiaceae). Funct. Plant Biol. 2019, 4, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.C.; Chen, B.J.W.; Korpelainen, H.; Niinemets, U.; Li, C.Y. Belowground ecological interactions in dioecious plants: Why do opposites attract but similar ones repel? Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iszkuto, G.; Boratyński, A. Initial period of sexual maturity determines the greater growth rate of male over female in the dioecious tree Juniperus communis subsp. communis. Acta Oecologica 2011, 37, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Barreda, S.; Sangüesa-Barreda, G.; García-González, M.D.; Camarero, J.J. Sex and tree rings: Females neither grow less nor are less water-use efficient than males in four dioecious tree species. Dendrochronologia 2022, 73, 125944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.M.; Preusser, S.; Backes, B.; Werner, W. Leaf traits of Central-European beech (Fagus sylvatica) and oaks (Quercus petraea/robur): Effects of severe drought and long-term dynamics. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 559, 121823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.L.; Wang, J.J.; Wu, H.F.; Valverde-Barrantes, O.J.; Wang, R.; Zeng, H.; Kardol, P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Feng, Y.L. Nonlinearity of root trait relationships and the root economics spectrum. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, A.; Wong, M.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Batterman, S.A.; Staver, A.C. Nitrogen and phosphorus availability alters tree-grass competition intensity in savannas. J. Ecol. 2024, 112, 1026–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.L.; Lin, X.Z.; Li, W.; Guo, C.J.; Han, J.A.; Yu, L. Nutrient resorption responses of female and male Populus cathayana to drought and shade stress. Physiol. Plant. 2023, 175, e13980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.S.; Song, A.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Peng, L.; Cheng, N.N.; Cao, B.H. Comparison of C, N and P Stoichiometry in Different Organs of Fraxinus velutina. Forests 2023, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuggiola, A.; Bugmann, H.; Zingg, A.; Dobbertin, M.; Rigling, A. Reduction of stand density increases drought resistance in xeric Scots pine forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 15, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.X.; Zhu, Y.J.; Sun, F.Y.; Korpelainen, H.; Niinemets, Ü.; Li, C.Y. Male, female, and mixed-sex poplar plantations support divergent soil microbial communities. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, N.; Liu, T.; Tang, M. Gender effects of dioecious plant Populus cathayana on fungal community and mycorrhizal distribution at different arid zones in Qinghai, China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Tigabu, M.; Xu, Q.L.; Ma, X.Q.; Li, M. Rhizosphere soil nutrients and bacterial community diversity of four broad-leaved trees planted under Chinese fir stands with different stocking density levels. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6, 1135692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Density | Gender | SAN (mg·g−1) | SNN (mg·g−1) | SCC (mg·g−1) | SNC (mg·g−1) | SPC (mg·g−1) | SKC (mg·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Female | 3.20 ± 0.58 Ba | 52.33 ± 3.49 Aa | 80.14 ± 1.06 Aa | 6.80 ± 0.27 Aa | 0.71 ± 0.05 Bb | 4.80 ± 0.27 Aa |
| Male | 5.09 ± 0.85 Aa | 52.93 ± 2.23 Aa | 76.19 ± 3.16 Aa | 7.27 ± 0.30 Aa | 0.71 ± 0.09 Bb | 4.17 ± 0.20 Aa | |
| Unknown | 3.38 ± 0.40 Aa | 48.63 ± 3.50 Aa | 61.27 ± 2.84 Ab | 5.68 ± 0.19 Ab | 0.98 ± 0.03 Aa | 4.81 ± 0.05 Aa | |
| D2 | Female | 6.20 ± 0.73 Aa | 46.95 ± 2.49 Aa | 62.97 ± 5.39 Ba | 5.89 ± 0.52 Aa | 0.90 ± 0.05 ABa | 4.37 ± 0.10 ABa |
| Male | 6.73 ± 1.38 Aa | 46.58 ± 2.78 Aa | 61.92 ± 4.78 Ba | 6.03 ± 0.47 Ba | 0.89 ± 0.08 Ba | 4.32 ± 0.09 Aa | |
| Unknown | 3.95 ± 0.51 Aa | 40.97 ± 5.21 Aa | 58.66 ± 2.64 Aa | 5.60 ± 0.25 Aa | 0.79 ± 0.09 Ba | 3.98 ± 0.23 Ba | |
| D3 | Female | 4.13 ± 0.49 Ba | 29.68 ± 3.13 Bb | 37.21 ± 3.33 Cab | 3.10 ± 0.08 Bb | 0.99 ± 0.11 Aa | 3.95 ± 0.10 BCa |
| Male | 4.68 ± 0.44 Aa | 34.19 ± 4.26 Bab | 31.62 ± 2.59 Cb | 3.22 ± 0.18 Cb | 0.92 ± 0.03 ABa | 3.98 ± 0.11 ABa | |
| Unknown | 3.83 ± 0.22 Aa | 45.60 ± 4.72 Aa | 45.27 ± 0.90 Ba | 6.19 ± 0.37 Aa | 0.75 ± 0.06 Ba | 3.70 ± 0.03 Ba | |
| D4 | Female | 3.94 ± 0.65 Ba | 29.03 ± 5.99 Ba | 34.78 ± 2.14 Ca | 2.03 ± 0.07 Cc | 0.84 ± 0.05 ABa | 3.77 ± 0.17 Ca |
| Male | 4.66 ± 0.11 Aa | 27.86 ± 1.52 Ba | 28.83 ± 5.10 Ca | 2.62 ± 0.11 Cb | 1.03 ± 0.08 Aa | 3.66 ± 0.14 Ba | |
| Unknown | 3.35 ± 0.15 Aa | 41.97 ± 3.51 Aa | 34.78 ± 2.14 Ca | 3.20 ± 0.10 Ba | 0.88 ± 0.03 ABa | 3.75 ± 0.24 Ba |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Wei, X.; Wei, Q.; Wu, C. Role of Stand Density in Shaping Interactions and Growth Strategies of Dioecious Tree Species: A Case Study of Fraxinus mandshurica. Forests 2025, 16, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040639
Li W, Wei X, Wei Q, Wu C. Role of Stand Density in Shaping Interactions and Growth Strategies of Dioecious Tree Species: A Case Study of Fraxinus mandshurica. Forests. 2025; 16(4):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040639
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Xing Wei, Qingyu Wei, and Chunze Wu. 2025. "Role of Stand Density in Shaping Interactions and Growth Strategies of Dioecious Tree Species: A Case Study of Fraxinus mandshurica" Forests 16, no. 4: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040639
APA StyleLi, W., Wei, X., Wei, Q., & Wu, C. (2025). Role of Stand Density in Shaping Interactions and Growth Strategies of Dioecious Tree Species: A Case Study of Fraxinus mandshurica. Forests, 16(4), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040639





