Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Nutrient Resorption in Populus euphratica Oliv Across Various Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
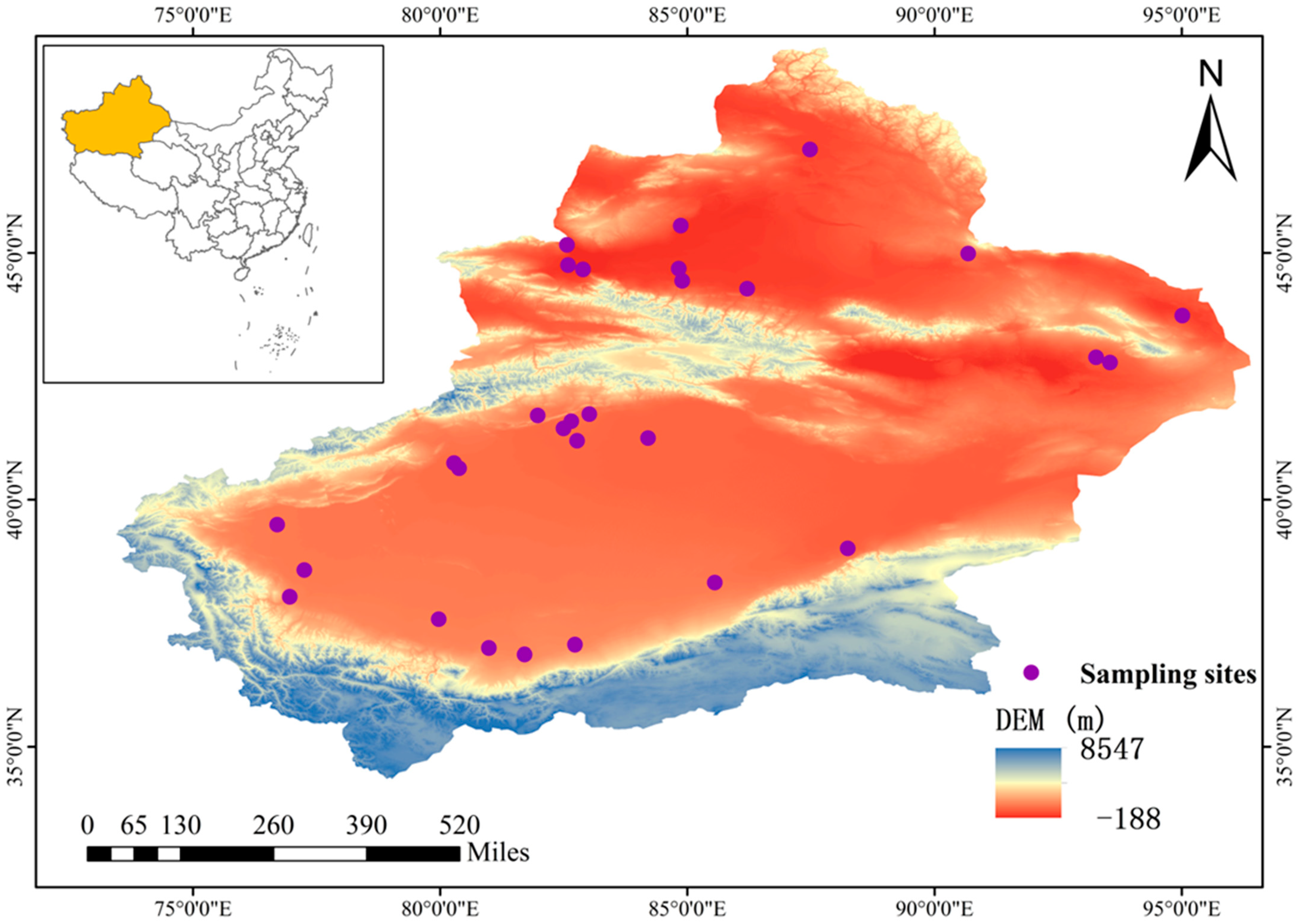
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analyzing
2.2.1. Sample Acquisition
2.2.2. Experimental Analysis
2.3. Identifying the Controlling Factors of Nutrient Resorption
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nutrient Status of Populus euphratica Leaves
3.2. Correlation Between Leaf Nutrient and Nutrient Resorption
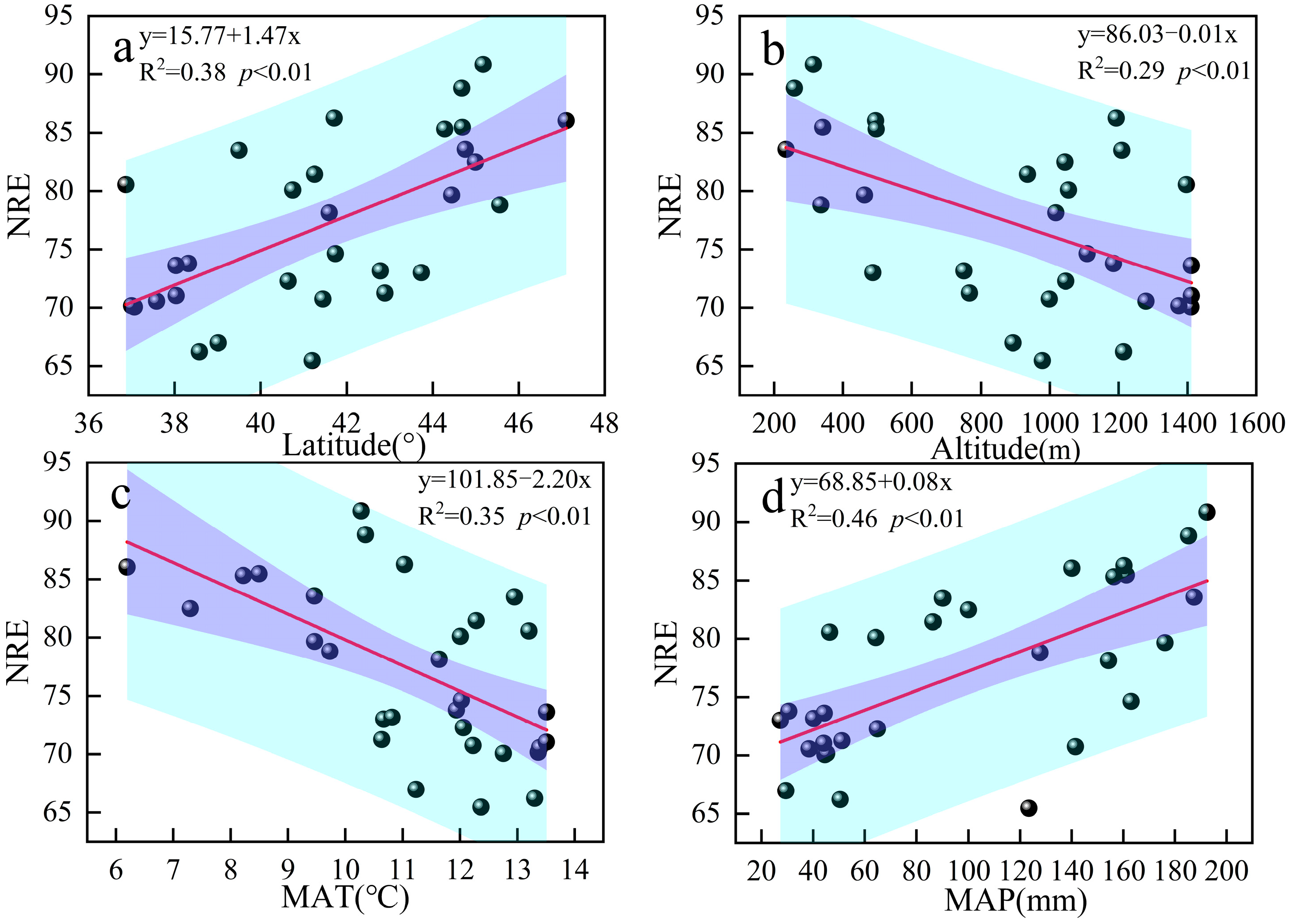
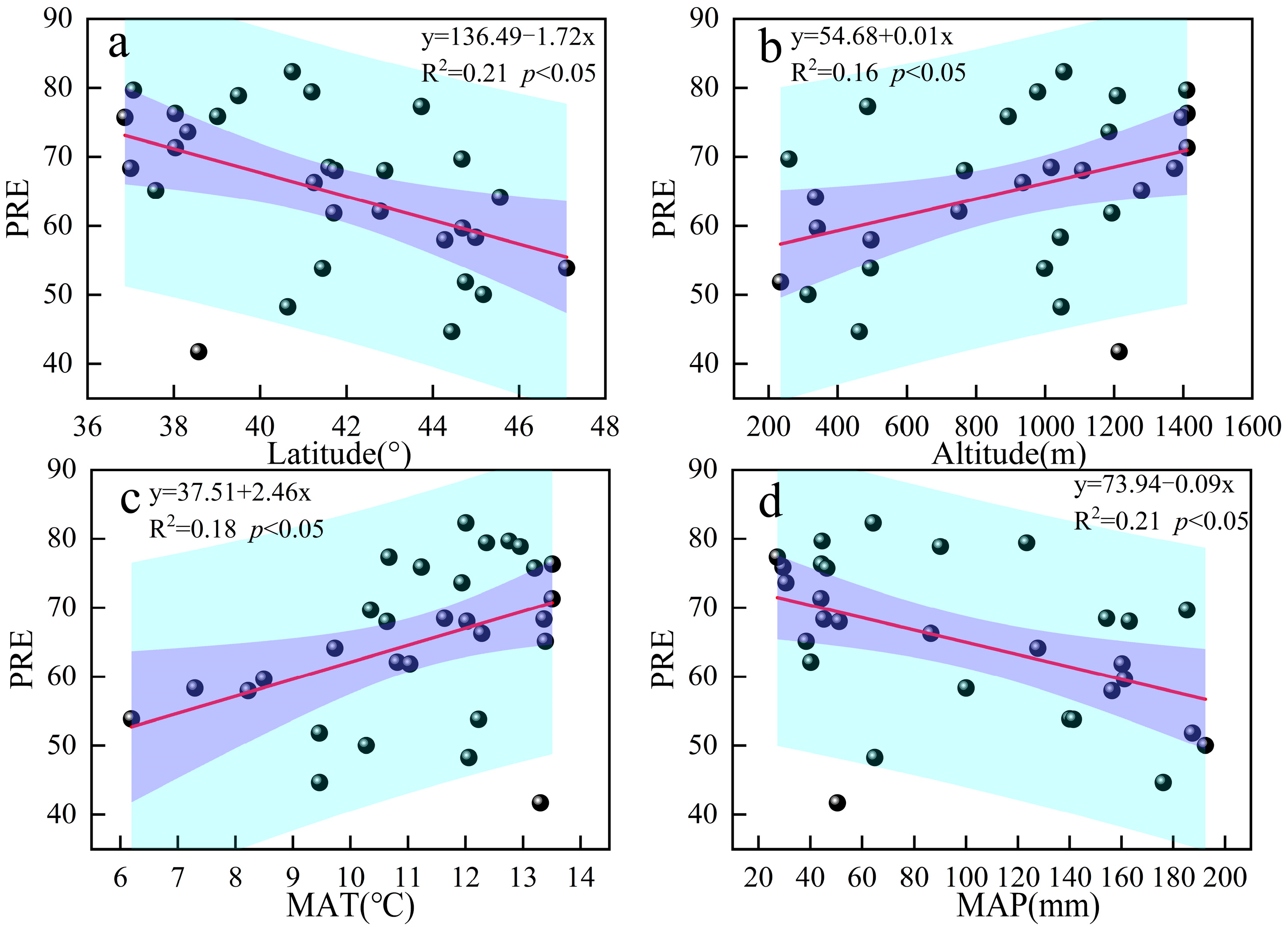
3.3. Relationship Between Nutrient Resorption and Environmental Factors
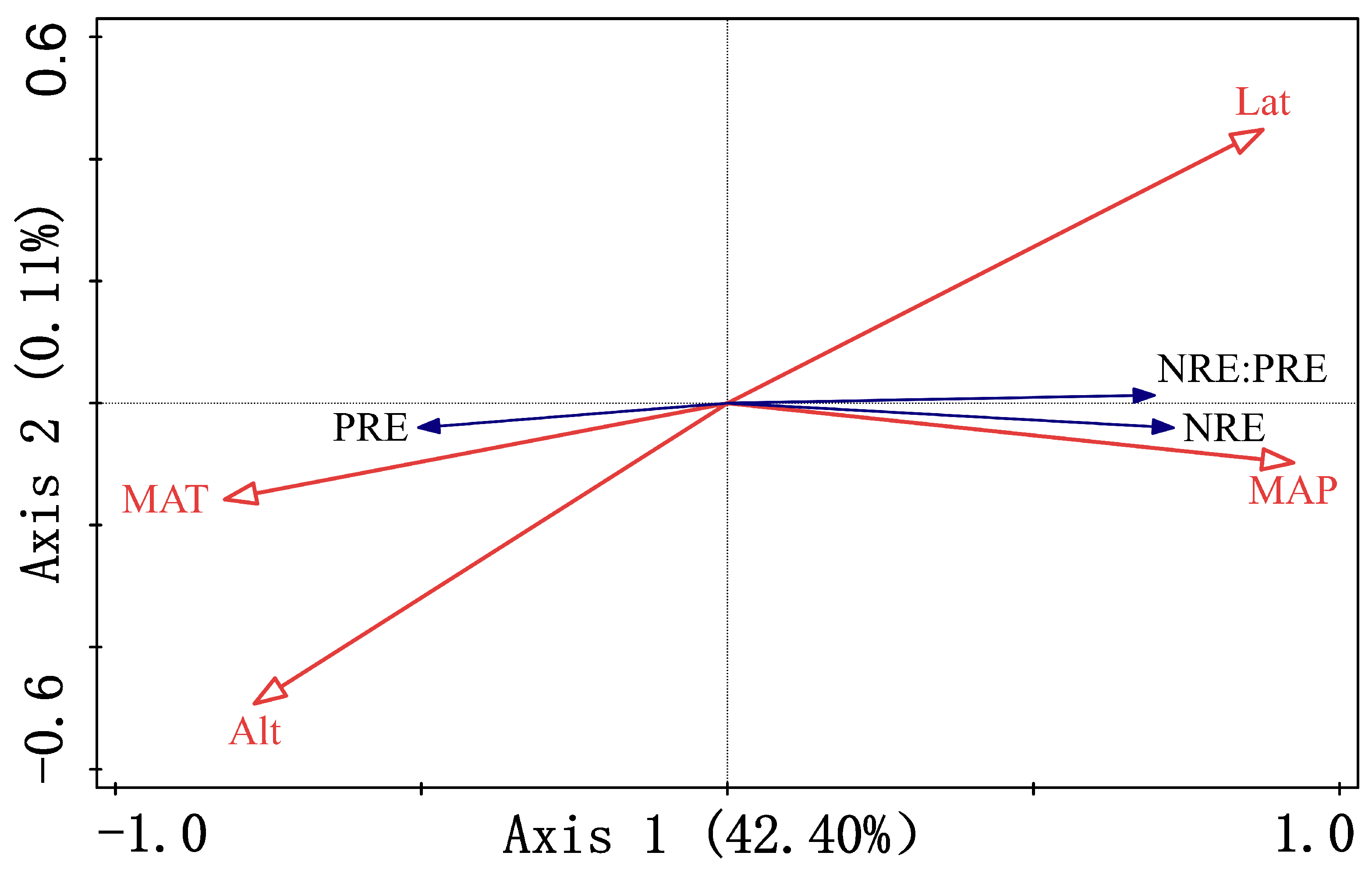
3.4. Key Environmental Drivers of Nutrient Resorption
4. Discussion
4.1. Connection Between Nutrient Resorption and Leaf Nutrients
4.2. Nutrient Resorption in Response to Environmental Factors
4.3. Identifying Main Drivers of Nutrient Resorption in Populus euphratica
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ngr | Nitrogen concentration in green leaves |
| Pgr | Phosphorus concentration in green leaves |
| Nsen | Nitrogen concentration in senescent leaves |
| Psen | Phosphorus concentration in senescent leaves |
| N:Pgr | Denotes the ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus concentration in green leaves |
| N:Psen | Denotes the ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus concentration in senescent leaves |
| NRE | Nitrogen resorption efficiency |
| PRE | Phosphorus resorption efficiency |
| NRE:PRE | Denotes the ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus resorption efficiency |
| MAT | Mean annual temperature |
| MAP | Mean annual precipitation |
| Lat | Latitude |
| Alt | Altitude |
Appendix A
| Sampling Site | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Altitude (m) | MAT (°C) | MAP (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 82.59 | 44.76 | 235 | 9.46 | 187.43 |
| 2 | 82.89 | 44.67 | 259 | 10.35 | 185.31 |
| 3 | 82.73 | 37.07 | 1410 | 12.75 | 44.57 |
| 4 | 88.25 | 39.01 | 893 | 11.23 | 29.39 |
| 5 | 76.71 | 39.50 | 1209 | 12.95 | 90.10 |
| 6 | 80.28 | 40.74 | 1054 | 12.01 | 64.27 |
| 7 | 80.39 | 40.64 | 1046 | 12.06 | 64.88 |
| 8 | 80.99 | 37.00 | 1375 | 13.36 | 45.25 |
| 9 | 85.56 | 38.32 | 1185 | 11.94 | 30.59 |
| 10 | 93.27 | 42.89 | 766 | 10.63 | 51.12 |
| 11 | 95.02 | 43.73 | 487 | 10.67 | 27.25 |
| 12 | 87.48 | 47.10 | 495 | 6.20 | 140.06 |
| 13 | 84.21 | 41.25 | 935 | 12.28 | 86.38 |
| 14 | 93.55 | 42.78 | 750 | 10.81 | 40.16 |
| 15 | 90.68 | 44.99 | 1044 | 7.30 | 99.96 |
| 16 | 82.57 | 45.17 | 314 | 10.28 | 192.41 |
| 17 | 76.96 | 38.03 | 1411 | 13.51 | 44.32 |
| 18 | 84.83 | 44.69 | 341 | 8.50 | 161.18 |
| 19 | 86.21 | 44.28 | 497 | 8.22 | 156.30 |
| 20 | 79.97 | 37.58 | 1297 | 13.39 | 38.38 |
| 21 | 77.25 | 38.58 | 1214 | 13.30 | 50.45 |
| 22 | 84.87 | 45.56 | 336 | 9.73 | 127.70 |
| 23 | 84.90 | 44.44 | 463 | 9.46 | 176.13 |
| 24 | 82.77 | 41.20 | 978 | 12.37 | 123.37 |
| 25 | 81.71 | 36.87 | 1397 | 13.20 | 46.38 |
| 26 | 82.65 | 41.59 | 1017 | 11.64 | 154.27 |
| 27 | 81.98 | 41.71 | 1193 | 11.03 | 160.26 |
| 28 | 82.50 | 41.45 | 998 | 12.23 | 141.46 |
| 29 | 76.96 | 38.03 | 1411 | 13.51 | 44.09 |
| 30 | 83.02 | 41.74 | 1108 | 12.02 | 163.01 |
References
- Killingbeck, K.T. Nutrients in Senesced Leaves: Keys to the Search for Potential Resorption and Resorption Proficiency. Ecology 1996, 77, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, I.; Grau, O.; Sardans, J.; Margalef, O.; Peguero, G.; Asensio, D.; Llusia, J.; Ogaya, R.; Gargallo-Garriga, A.; Van Langenhove, L.; et al. High foliar K and P resorption efficiencies in old-growth tropical forests growing on nutrient-poor soils. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 8969–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, S.C.; Townsend, A.R.; Davidson, E.A.; Cleveland, C.C. Stoichiometric patterns in foliar nutrient resorption across multiple scales. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Liu, S.; Fan, L.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y. Nutrient stoichiometric and resorption characteristics of the petals of four common urban greening Rosaceae tree species. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1201759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenovsky, R.E.; Pietrasiak, N.; Short, T.H. Global temporal patterns in plant nutrient resorption plasticity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2019, 28, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Reed, S.C.; Lu, X.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Coexistence of multiple leaf nutrient resorption strategies in a single ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 144951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.-S.; Shi, F.-X.; Mao, R. Biomass allocation between leaf and stem regulates community-level plant nutrient resorption efficiency response to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in a temperate wetland of Northeast China. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 14, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, G. Effects of climate, soil, and leaf traits on nutrient resorption efficiency and proficiency of different plant functional types across arid and semiarid regions of Northwest China. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Han, X. Global scaling the leaf nitrogen and phosphorus resorption of woody species: Revisiting some commonly held views. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, D.; Lu, X.; Fang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chu, C.; Li, M.; Chen, H. Widespread controls of leaf nutrient resorption by nutrient limitation and stoichiometry. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-L.; Zhang, X.-H.; Shi, F.-X.; Mao, R. Effect of shrub encroachment on leaf nutrient resorption in temperate wetlands in the Sanjiang Plain of Northeast China. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.; Hui, D. Responses of Nutrient Resorption to Human Disturbances in Phoebe bournei Forests. Forests 2022, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Chen, X.-P.; Li, J.-L.; Hu, D.-D.; Wang, M.-T.; Zhong, Q.-L.; Cheng, D.-L. Nitrogen and phosphorus contents and resorption efficiency of thirty broadleaved woody plants in Yangjifeng, Jiangxi, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Luo, Y.; Yan, Z.; Chen, J.; Eziz, A.; Li, K.; Han, W. Resorptions of 10 mineral elements in leaves of desert shrubs and their contrasting responses to aridity. J. Plant Ecol. 2019, 12, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.Z.; Terrer, C.; Pellegrini, A.F.A.; Ahlström, A.; Van Lissa, C.J.; Zhao, X.; Xia, N.; Wu, X.H.; Jackson, R.B. Global patterns of terrestrial nitrogen and phosphorus limitation. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, W.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, Q.; Peng, C.; Koerner, S.E.; Guo, L. Growing season temperature and precipitation affect nutrient resorption in herbaceous species through a foliar stoichiometric control strategy. Plant Soil. 2023, 493, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, M.; Ran, J.; Huang, H.; Niklas, K.J. Global Data Analysis Shows That Soil Nutrient Levels Dominate Foliar Nutrient Resorption Efficiency in Herbaceous Species. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Jiao, P.; Peng, C.; Li, Y.; Song, S. Adaptation Strategies of Populus euphratica to Arid Environments Based on Leaf Trait Network Analysis in the Mainstream of the Tarim River. Forests 2024, 15, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ye, M.; Munire, M. Structural parameter acquisition of Populus euphratica by WorldView-2 remote sensing image. Arid Zone Res. 2021, 38, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Jiao, P.; Zhai, J.; Liu, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J.; Gai, Z.; et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals spatiotemporal regulation and function of heteromorphic leaves in Populus. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhai, J.; Song, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Sex differences in morphological and stoichiometric characteristics of Populus euphratica Oliv. branches and leaves. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.F.; Zhai, J.T.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, Z.J. Relationship of changes in the stem and leaf morphology, nutrient and endogenous hormone contents and flower bud number of Populus euphratica Oliv. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 3873–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Li, Y.; Fu, A. Climate change may accelerate the decline of desert riparian forest in the lower Tarim River, Northwestern China: Evidence from tree-rings of Populus euphratica. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 105997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Hao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Populus euphratica counteracts drought stress through the dew coupling and root hydraulic redistribution processes. Ann. Bot. 2023, 131, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y. Variation in leaf carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics of Populus euphratica along a vertical riverbank gradient and associated environmental explanation in a desert riparian area in China. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2023, 29, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Han, Z.J.; Su, M.X.; Zhang, M. Transcriptomic Profile Analysis of Populus talassica × Populus euphratica Response and Tolerance Under Salt Stress Conditions. Genes 2022, 13, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.L.; Qiu, C.; Sun, J.H.; Xu, J.D.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, J.T.; Zhang, S.H.; Wu, Z.H.; Li, Z.J. Identification of AP2/ERF gene family of Salicaceae and their response to salt stress, abscisic acid, and gibberellic acid in Populus euphratica seeds. Biol. Plant. 2023, 67, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, K.; Mohammat, A.; Han, W. Nitrogen and phosphorus resorption of desert plants with various degree of propensity to salt in response to drought and saline stress. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagedeng; Xia, G.; Lin, T.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Analysis of nutrient resorption efficiency and homeostasis of four tree species in Kanas natural forest, Xinjiang, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 1046444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergutz, L.; Manzoni, S.; Porporato, A.; Novais, R.F.; Jackson, R.B. Global resorption efficiencies and concentrations of carbon and nutrients in leaves of terrestrial plants. Ecol. Monogr. 2012, 82, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobe, R.K.; Lepczyk, C.A.; Iyer, M. Resorption efficiency decreases with increasing green leaf nutrients in a global data set. Ecology 2005, 86, 2780–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugnaire, F.I.; Chapin, F.S. Controls over Nutrient Resorption from Leaves of Evergreen Mediterranean Species. Ecology 1993, 74, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Chen, H.Y.H. Global-scale patterns of nutrient resorption associated with latitude, temperature and precipitation. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A.F.M. The vegetation N:P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Tian, D.; Han, W.; Tang, Z.; Fang, J. An assessment on the uncertainty of the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio as a threshold for nutrient limitation in plants. Ann. Bot. 2017, 120, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Tang, L.; Chen, Y.; Fang, J. Relationship Between the Relative Limitation and Resorption Efficiency of Nitrogen vs Phosphorus in Woody Plants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, L.; Achat, D.L.; Jonard, M.; Vidal, D.; Ringeval, B. Soil parent material—A major driver of plant nutrient limitations in terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 3808–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wan, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, G.; Dong, L.; Yang, T.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, J. Effects of rock lithology and soil nutrients on nitrogen and phosphorus mobility in trees in non-karst and karst forests of southwest China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 548, 121392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, B. Ecosystem scale trade-off in nitrogen acquisition pathways. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S. Nutrient resorption of wetland graminoids is related to the type of nutrient limitation. Funct. Ecol. 2005, 19, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Mo, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; He, C.; Wan, X.; Jiang, D. Nutrient resorption patterns of evergreen and deciduous tree species at different altitudes on Mao’er Mountain, Guangxi. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 5776–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sophia, G.; Caldararu, S.; Stocker, B.D.; Zaehle, S. Leaf habit drives leaf nutrient resorption globally alongside nutrient availability and climate. Biogeosciences 2024, 21, 4169–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Q.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Tao, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, X. Characteristics and factors influencing foliar nutrient resorption in plants. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2017, 23, 811–817. [Google Scholar]
- Brant, A.N.; Chen, H.Y.H. Patterns and Mechanisms of Nutrient Resorption in Plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.-S.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Q.-w.; Yang, S.-q.; Li, K.-h.; Han, W.-x. Leaf C:N:P stoichiometry of 67 plant species and its relations with climate factors across the deserts in Xinjiang, China. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2019, 30, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Z.; Jiao, F. Response of Nutrient Resorption of Herbs, Shrubs and Trees to Temperature and Precipitation in China. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, X.; Chen, S.; Pang, S.; Liu, W.; Gao, L.; Yang, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, C.; et al. Distinctive pattern and mechanism of precipitation changes affecting soil microbial assemblages in the Eurasian steppe. iScience 2022, 25, 103893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touche, J.; Calvaruso, C.; De Donato, P.; Turpault, M.P. Drought events influence nutrient canopy exchanges and green leaf partitioning during senescence in a deciduous forest. For. Ecosyst. 2024, 11, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touche, J.; Calvaruso, C.; De Donato, P.; Turpault, M.P. Five successive years of rainfall exclusion induce nutritional stress in a mature beech stand. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 507, 119987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Maximum | Minimum | Average | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green leaves | N (g/kg) | 26.62 | 7.52 | 15.37 | 4.42 |
| P (g/kg) | 1.58 | 0.57 | 0.96 | 0.26 | |
| N:P | 46.77 | 7.48 | 17.40 | 8.08 | |
| Senescent leaves | N (g/kg) | 7.72 | 1.62 | 4.35 | 1.61 |
| P (g/kg) | 0.99 | 0.18 | 0.42 | 0.18 | |
| N:P | 28.37 | 2.53 | 11.99 | 6.12 | |
| NRE (%) | 90.85 | 65.46 | 77.14 | 7.03 | |
| PRE (%) | 82.31 | 41.74 | 65.10 | 11.00 | |
| NRE:PRE | 1.81 | 0.82 | 1.23 | 0.27 |
| Ordination Axes | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanatory power of quantitative characteristics | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.40 |
| Cumulative explanatory power of quantitative characteristics | 42.4 | 42.51 | 42.54 | 82.92 |
| Correlation between quantitative characteristics and environmental factors | 0.78 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0 |
| Cumulative explanation of the relationship between quantitative characteristics and environmental factors | 99.67 | 99.94 | 100 | 100 |
| Importance Ranking | Environmental Factor | Explanatory Power (%) | Contribution Efficiency (%) | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MAP | 36.2 | 85.1 | 15.9 | 0.002 |
| 2 | MAT | 6.2 | 14.5 | 2.9 | 0.07 |
| 3 | Lat | 0.1 | 0.3 | <0.1 | 0.96 |
| 4 | Alt | <0.1 | 0.1 | <0.1 | 0.986 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Shi, P.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Nutrient Resorption in Populus euphratica Oliv Across Various Environments. Forests 2025, 16, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040629
Zhu J, Shi P, Xu Z, Wang Y. Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Nutrient Resorption in Populus euphratica Oliv Across Various Environments. Forests. 2025; 16(4):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040629
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jiahui, Peijun Shi, Zhonglin Xu, and Yao Wang. 2025. "Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Nutrient Resorption in Populus euphratica Oliv Across Various Environments" Forests 16, no. 4: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040629
APA StyleZhu, J., Shi, P., Xu, Z., & Wang, Y. (2025). Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Nutrient Resorption in Populus euphratica Oliv Across Various Environments. Forests, 16(4), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040629





