Comparative Study of Water Absorption and Dimensional Stability Between Bamboo Nodes and Internodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
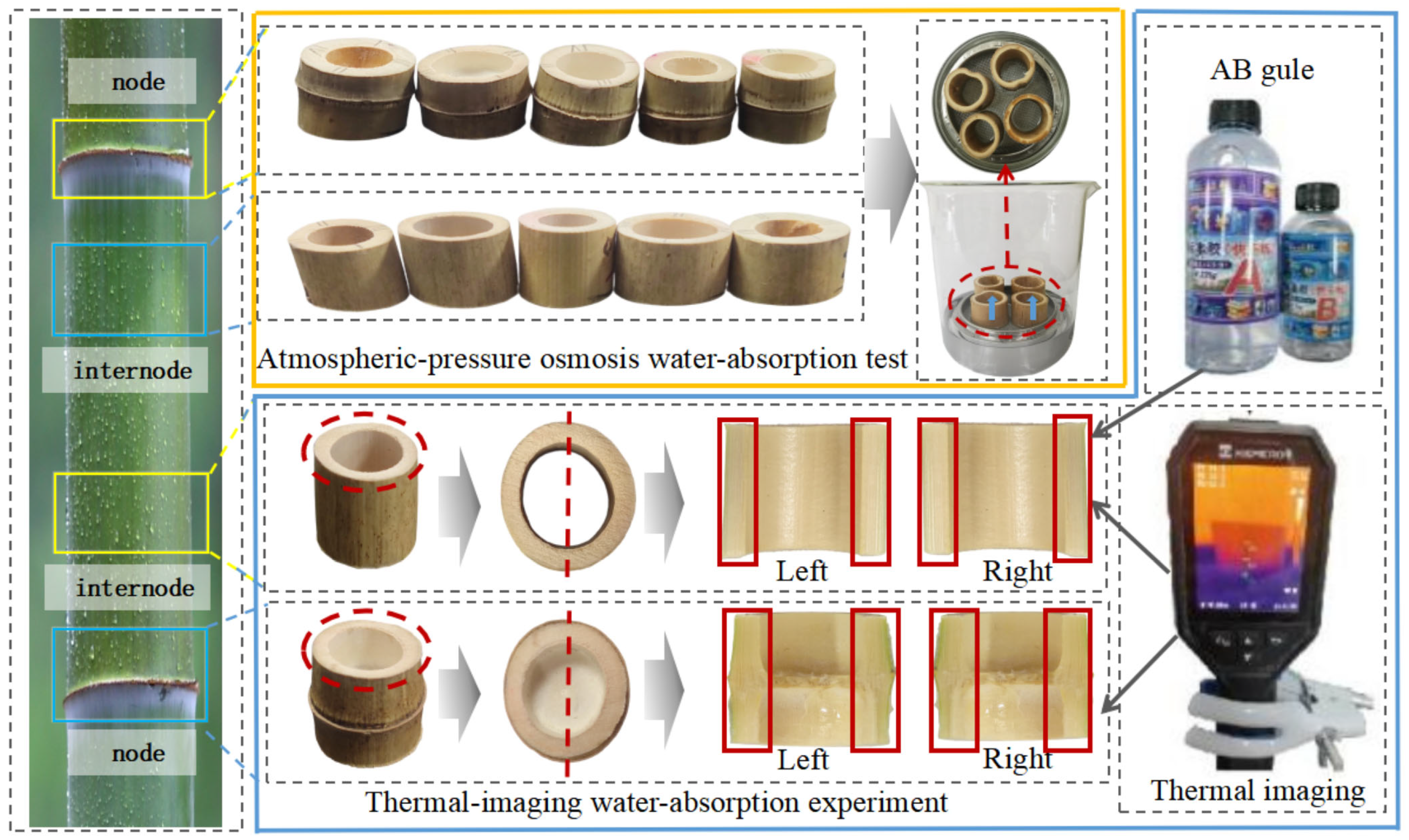
2.1. Water Permeability Test
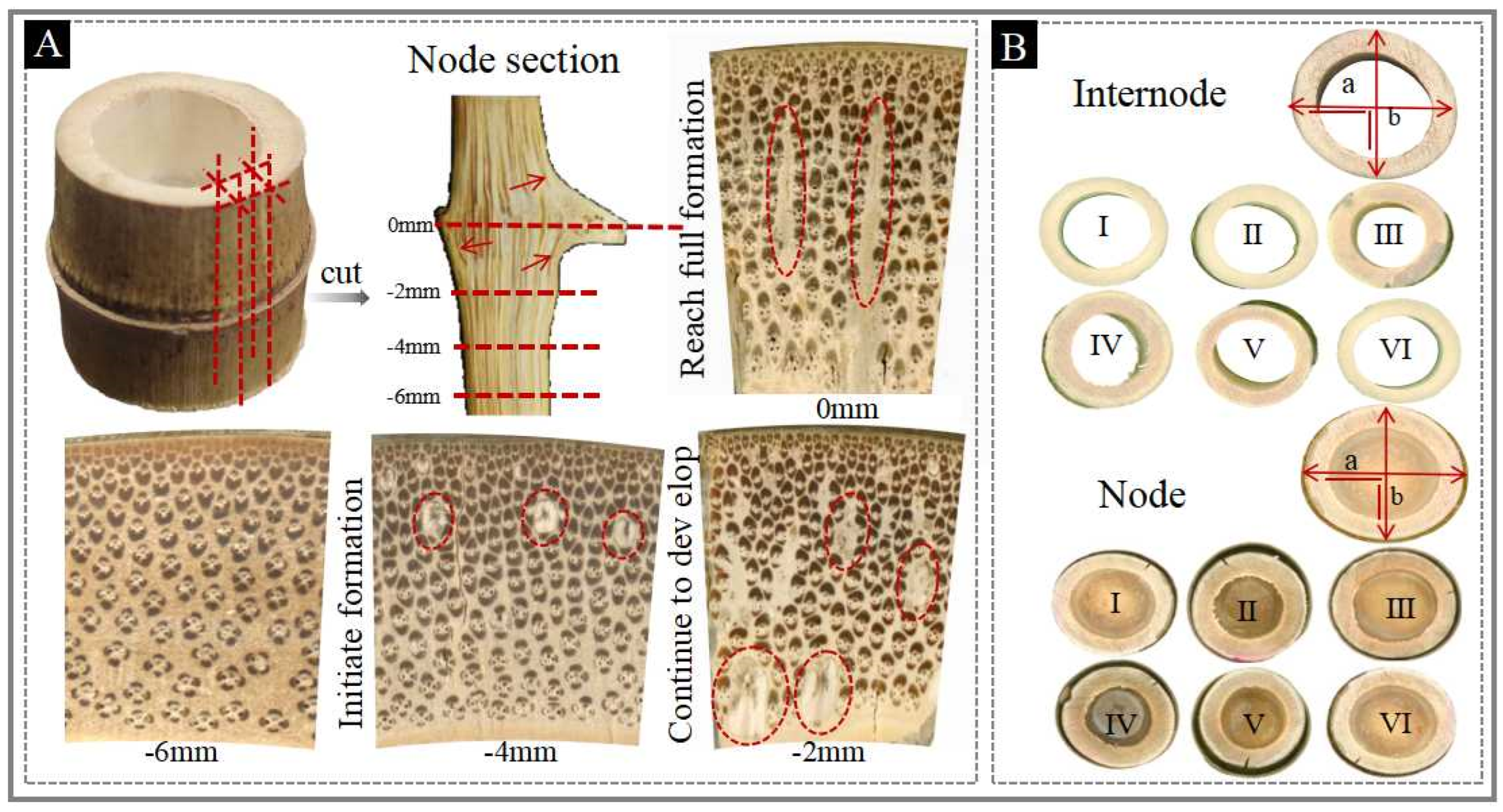
2.2. Dimensional Stability Test
2.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Test
2.4. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry
2.5. Chemical Composition Test
3. Results and Discussion
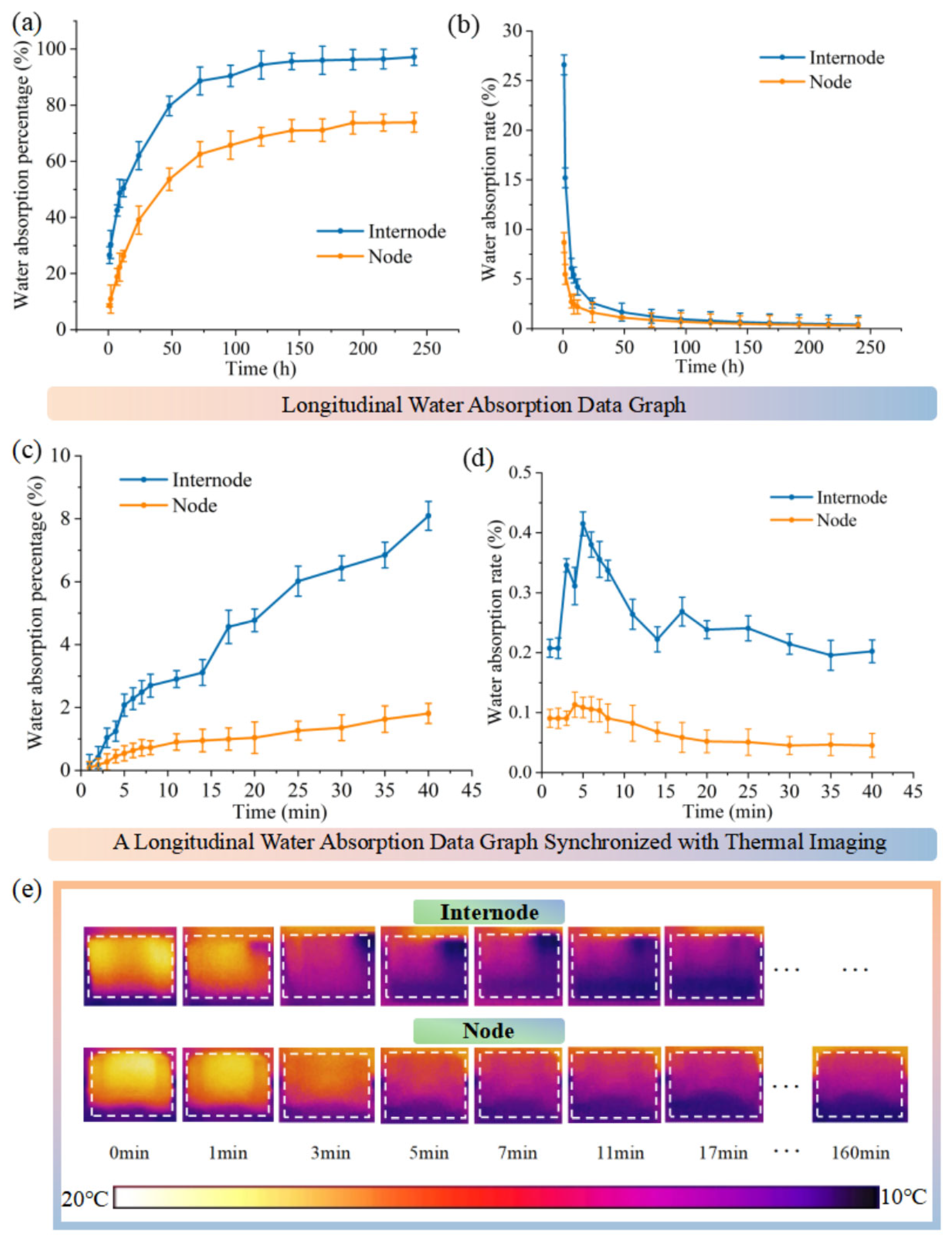
3.1. Water Absorption Behavior
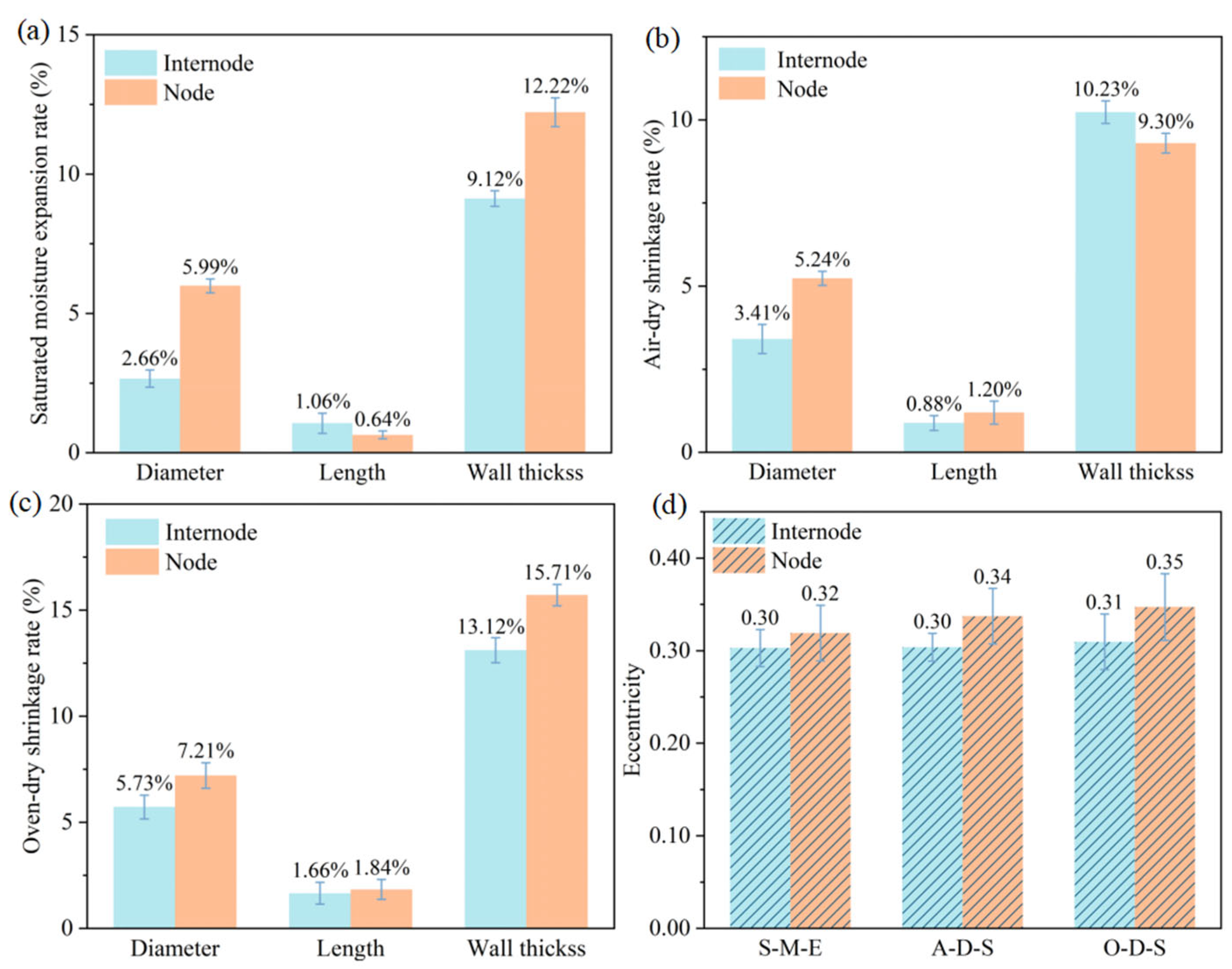
3.2. Dimensional Stability
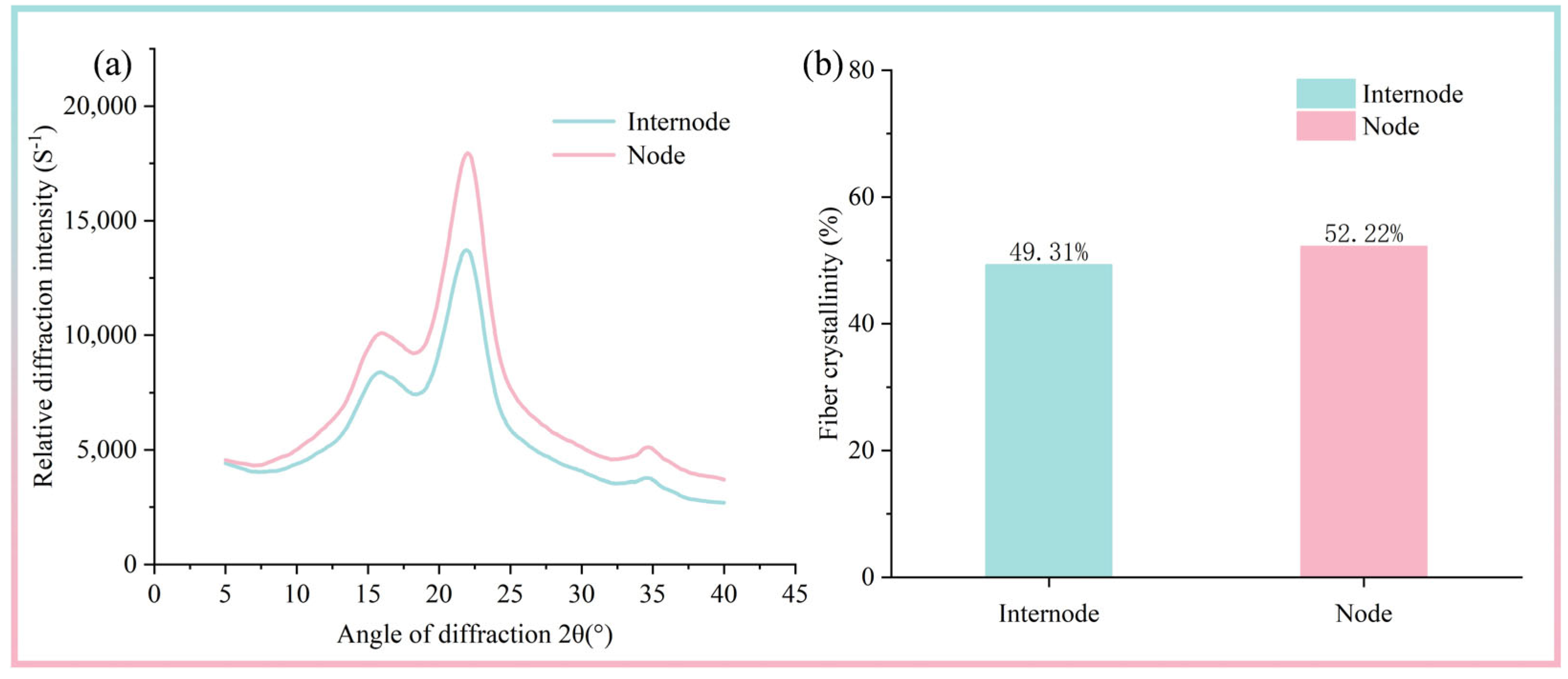
3.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
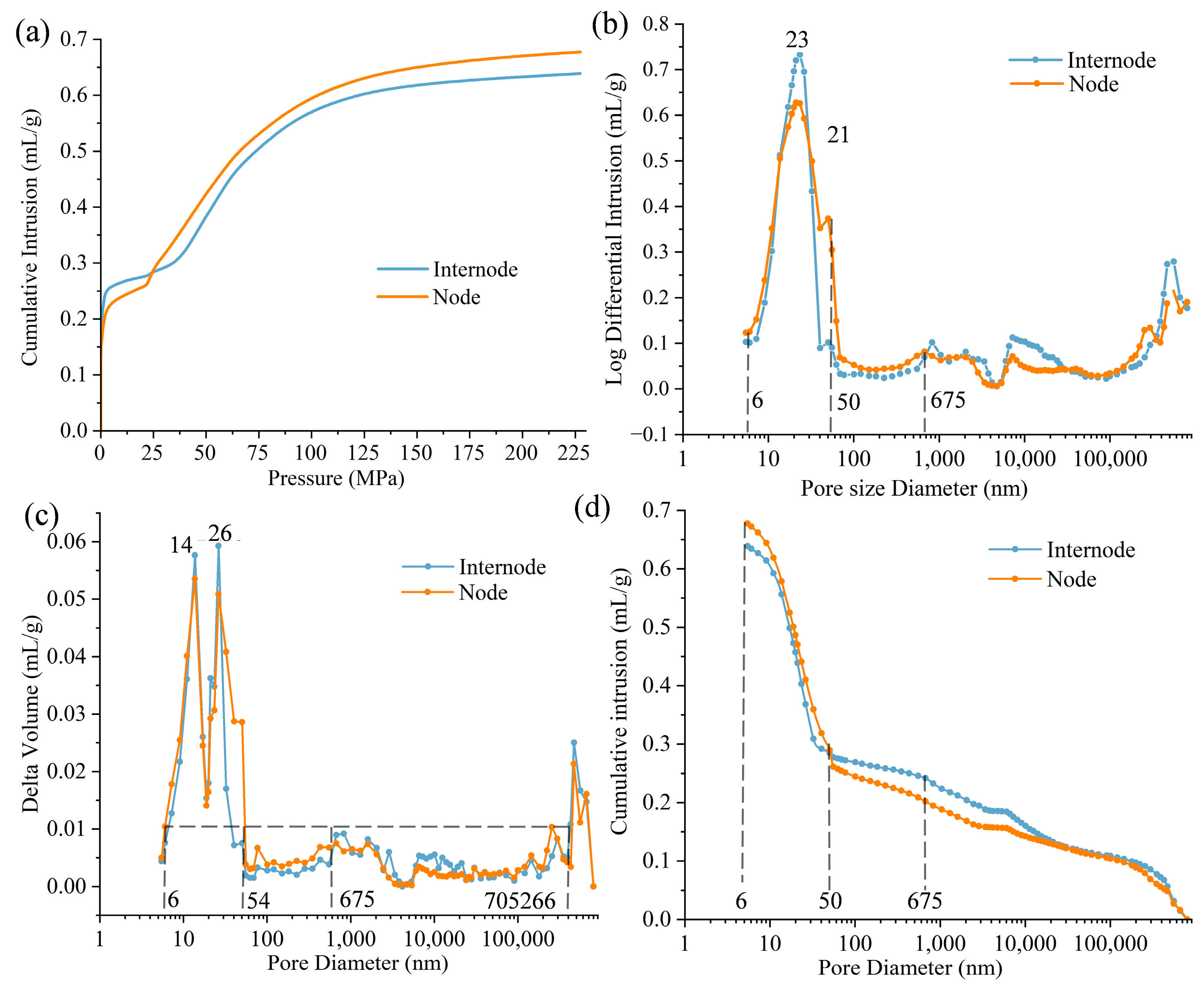
3.4. Pore Structure Analysis
3.5. Analysis of Chemical Composition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaur, P.J.; Yadav, P.; Gupta, M.; Khandegar, V.; Jain, A. Bamboo as a Source for Value Added Products: Paving Way to Global Circular Economy. BioResources 2022, 17, 5437–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, Z.; Liu, H.; Ma, X.; Lian, J.; Wang, X. Flattened Bamboo for Replacing Plastic Products—An Eco-Friendly Material to Manufacture Clothes Hangers. BioResources 2025, 20, 5467–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, P.; Parveen, A.; Modak, A.; Adhikari, A.; Chakrabortty, S. Microplastic Pollution: A Global Environmental Crisis Impacting Marine Life, Human Health, and Potential Innovative Sustainable Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macleo, M.; Arp, H.P.H.; Tekman, M.B.; Jahnke, A. The Global Threat from Plastic Pollution. Science 2021, 373, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zeng, C. Research and Application Progress of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. World Bamboo Ratt. 2024, 22, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Song, J.; Anderson, D.P.; Chang, P.R.; Hua, Y. Bamboo Fiber and Its Reinforced Composites: Structure and Properties. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1449–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.D.; Jamiru, T.; Sadiku, R.E.; Kupolati, W.K.; Agwuncha, S.C.; Ekundayo, G. The Use of Polypropylene in Bamboo Fibre Composites and Their Mechanical Properties—A Review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, Z.; Yan, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, R. Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Pretreatment and Lignin Regeneration for the Development of a Bamboo Leaf-Based Bioplastic. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1484585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Topicalities in the Research and Application of Bamboo and Wood. Forests 2024, 15, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielis, J. Book Review: Bamboo–The Plant and Its Uses. J. Am. Bamboo Soc. 2015, 28, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Pande, S.K.; Pandey, S. Bamboo for the 21st Century. Int. For. Rev. 2008, 10, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amada, S.; Untao, S. Fracture Characteristics of Bamboo and Application to Composite Materials. Compos. Part A 2001, 32, 451–459. [Google Scholar]
- Harison, A. Bamboo as an Alternative to Steel for Green Construction towards Low-Cost Housing. J. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2017, 6, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Rahman, M.R.; Hamdan, S.; Sanaullah, K. Recent Developments in Bamboo Fiber-Based Composites: A Review. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 2655–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Fu, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J. Influence of Temperature and Humidity Variations on the Strain Response of Raw Bamboo. J. For. Eng. 2019, 4, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Amada, S.; Untao, S. Fracture Properties of Bamboo. Compos. Part B Eng. 2001, 32, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.; Kinane, B.; Sweeney, C.; O’Reilly, P.; McDonnell, P. The Biomechanics of Bamboo: Investigating the Role of the Nodes. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhou, Q.; Fu, F.; Li, W. Effect of Bamboo Nodes on the Mechanical Properties of P. edulis (Phyllostachys edulis) Bamboo. Forests 2021, 12, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, F.; Feng, P. A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Effects of Bamboo Nodes on the Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Culms. Eng. Struct. 2023, 297, 116975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Feng, X.; Xia, Z.; Deng, S.; Wang, X. Gradient Variation and Correlation Analysis of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Materials 2024, 17, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P. Hygrothermal Performance of Moso Bamboo-Based Building Material. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bath, Bath, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Lourenco, A.; Wei, X.; Gominho, J.; Wang, G.; Cheng, H. Structural and Chemical Analysis of Three Regions of Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Materials 2024, 17, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, L. Research Progress on Drying of Raw Bamboo. World For. Res. 2024, 37, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Honghai, L.; Yuqi, S.; Yu, X. Impact of Supercritical CO2 Dewatering on Hygroscopic Properties, Dimensional Stability, Chemical Composition, and Microstructure of Moso Bamboo: A Comparison with Conventional Kiln Drying. Dry. Technol. 2025, 43, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, F.; Fei, B. Effect of Moisture Content, Heating Time and Temperature on the Bending Mechanical Properties of Phyllostachys iridescens. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2024, 82, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Fang, C.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Chen, Q.; Liu, R.; Luo, J.; Fei, B. Research Progress on Water in Bamboo Cell Walls. J. Bamboo Res. 2020, 39, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, Q.; Fei, B. Different Characteristics in the Hygroscopicity of the Graded Hierarchical Bamboo Structure. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 176, 114333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, W.; Shao, C. Bioinspired Fluorine-Free Superhydrophobic Wood: Binary Micro-/Nanostructure Engineering for Chemically Stable and Mechanically Robust Green Materials. Prog. Org. Coat. 2025, 209, 109582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chang, W.-S.; Ansell, M.P. Thermal and hygroscopic expansion characteristics of bamboo. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.–Struct. Build. 2018, 171, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesche, H. Mercury Porosimetry: A General (Practical) Overview. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2006, 23, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martina, E.; Conrad, C.M. An Empirical Method for Estimating the Degree of Crystallinity of Native Cellulose Using the X-ray Diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, E.W. The Dynamics of Capillary Flow. Phys. Rev. 1921, 17, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.C. Pore-Size Distribution in Porous Materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1949, 41, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wu, S.; Wei, P.; Xu, W. Handicraft Process, Aesthetic Characteristics, and Design Applications of Molten Metal Inlaid in Wood for Home Furnishings. BioResources 2025, 20, 6426–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Shi, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Lian, J.; Wang, X. Study on Hot-Press Drying Process for the Flatten-Bamboo Slice. Dry. Technol. 2025, 43, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, S.; Shang, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Ma, Q.; Tian, G. 3D Visualization of Bamboo Node’s Vascular Bundle. Forests 2021, 12, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wei, L.; Miao, Q.; Luo, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, L.; Huang, L. Study on the Physicochemical Properties of Different Parts of Green Bamboo. J. China Pulp Pap. 2016, 31, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shang, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z. Three-Dimensional Visualization of the Vascular Bundle in a Branched Bamboo Node. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1256772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Unraveling the inhibition of bamboo node on dry shrinkage: Insights from the specific vascular structure of bamboo node. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 211, 118193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, H.; Jia, S.; Xie, J. Effect of Bamboo Nodes on Crack Generation of Round Bamboo and Bamboo-Based Composites During Drying. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2023, 81, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Q.; Hao, X.; Xu, K.; Li, X.; Li, X. Hygroexpansion Behaviors of Bamboo in Response to Moisture Absorption and Desorption. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokye, R.; Kalong, R.M.; Bakar, E.S.; Ratnasingam, J.; Jawaid, M.; Awang, K. Variations in Moisture Content Affect the Shrinkage of Gigantochloa scortechinii and Bambusa vulgaris at Different Heights of the Bamboo Culm. BioResources 2014, 9, 7484–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y. Bamboo Node Effect on the Tensile Properties of Side Press-Laminated Bamboo Lumber. Wood Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Bao, Y.; Li, N.; Hou, J. A Multiscale Investigation of Cross-Sectional Shrinkage in Bamboo Culms Using Natural-Speckle Digital Image Correlation During Drying. Forests 2025, 16, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Deng, S.; Xu, R.; Chen, Q.; Xu, P. Effect of Bamboo Nodes on the Mechanical Properties. Forests 2024, 15, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, K.; Nakai, T.; Shirai, T.; Yamamoto, H. Changes in the Cellulose Crystallinity of Moso Bamboo Cell Walls During the Growth Process by X-ray Diffraction Techniques. J. Wood Sci. 2015, 61, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusov, A.N.; Prusova, S.M.; Radugin, M.V.; Zakharov, A.G. Interrelation Between the Crystallinity of Polysaccharides and Water Absorption. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 88, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, H.; Yu, S. Mechanically Robust Bamboo Node and Its Hierarchically Fibrous Structural Design. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, E.-L.; Yang, S.; Cao, C.; Liu, X.; Peng, G.; Shang, L.; Tian, G.; Ma, Q.; Ma, J. Visualizing Complex Anatomical Structure in Bamboo Nodes Based on X-ray Microtomography. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Zhang, B.; Fu, W.; Zhou, J. Hygrothermal Strain Response of Raw Bamboo. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2019, 55, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Deng, S.; Qin, S.; Wang, X. Effect of Boric Acid-Borax Combined Thermal Modification on the Properties of Rubberwood. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2025, 43, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tze, M.P.; Niemz, P. Porosity and Pore Size Distribution of Different Wood Types as Determined by Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2010, 69, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUPAC. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquerol, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.; Llewellyn, P.; Maurin, G. Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Song, K.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Yin, Y. Comparison of Changes in Micropores and Mesopores in the Wood Cell Walls of Sapwood and Heartwood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Huang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Fei, B. Effect of Hygrothermal Treatment on the Porous Structure and Nanomechanics of Moso Bamboo. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | Mean Difference | df | Std. Error Difference | t | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water-absorption rate | 0.23662 | 166 | 0.03891 | 6.082 | 0 |
| Water-absorption velocity | 0.06335 | 166 | 0.01135 | 5.583 | 0 |
| Samples | Total Intrusion Volume (mL/g) | Total Surface Area (m2/g) | Median Pore Diameter (nm) | Mean Pore Diameter (nm) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internode | 0.6388 ± 0.03 | 85.97 ± 0.26 | 30.92 ± 0.11 | 29.72 ± 0.12 | 46.6736 ± 0.06 |
| Node | 0.6774 ± 0.02 | 95.08 ± 0.37 | 35.92 ± 0.16 | 28.50 ± 0.09 | 46.9996 ± 0.07 |
| Samples | Cellulose | Hemi- Cellulose | Acid-Insoluble Lignin | Acid-Soluble Lignin | Lignin | The Three Major Substances |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internode | 39.4 ± 0.33% | 20.1 ± 0.29% | 25.0 ± 0.37% | 1.4 ± 0.11% | 26.4 ± 0.19% | 85.9 ± 0.27% |
| Node | 37.3 ± 0.21% | 23.5 ± 0.31% | 25.4 ± 0.41% | 2.4 ± 0.09% | 27.8 ± 0.23% | 88.6 ± 0.31% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, N.; Li, Z.; Yan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H. Comparative Study of Water Absorption and Dimensional Stability Between Bamboo Nodes and Internodes. Forests 2025, 16, 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111685
Su N, Li Z, Yan Q, Chen Y, Xu H. Comparative Study of Water Absorption and Dimensional Stability Between Bamboo Nodes and Internodes. Forests. 2025; 16(11):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111685
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Na, Zonglin Li, Qingqing Yan, Yiwen Chen, and Haocheng Xu. 2025. "Comparative Study of Water Absorption and Dimensional Stability Between Bamboo Nodes and Internodes" Forests 16, no. 11: 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111685
APA StyleSu, N., Li, Z., Yan, Q., Chen, Y., & Xu, H. (2025). Comparative Study of Water Absorption and Dimensional Stability Between Bamboo Nodes and Internodes. Forests, 16(11), 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111685






