Geopolitical Conflict and Resource Trade Flows: A Study on the Impact of the Russia–Ukraine Conflict on China’s Timber Imports from Russia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Hypothesis
2.2. Methods
2.3. Variable Definitions
2.3.1. Dependent Variable
2.3.2. Independent Variable
2.3.3. Control Variables
2.4. Data Resources
3. Results
3.1. Estimation Result of the Basic Model
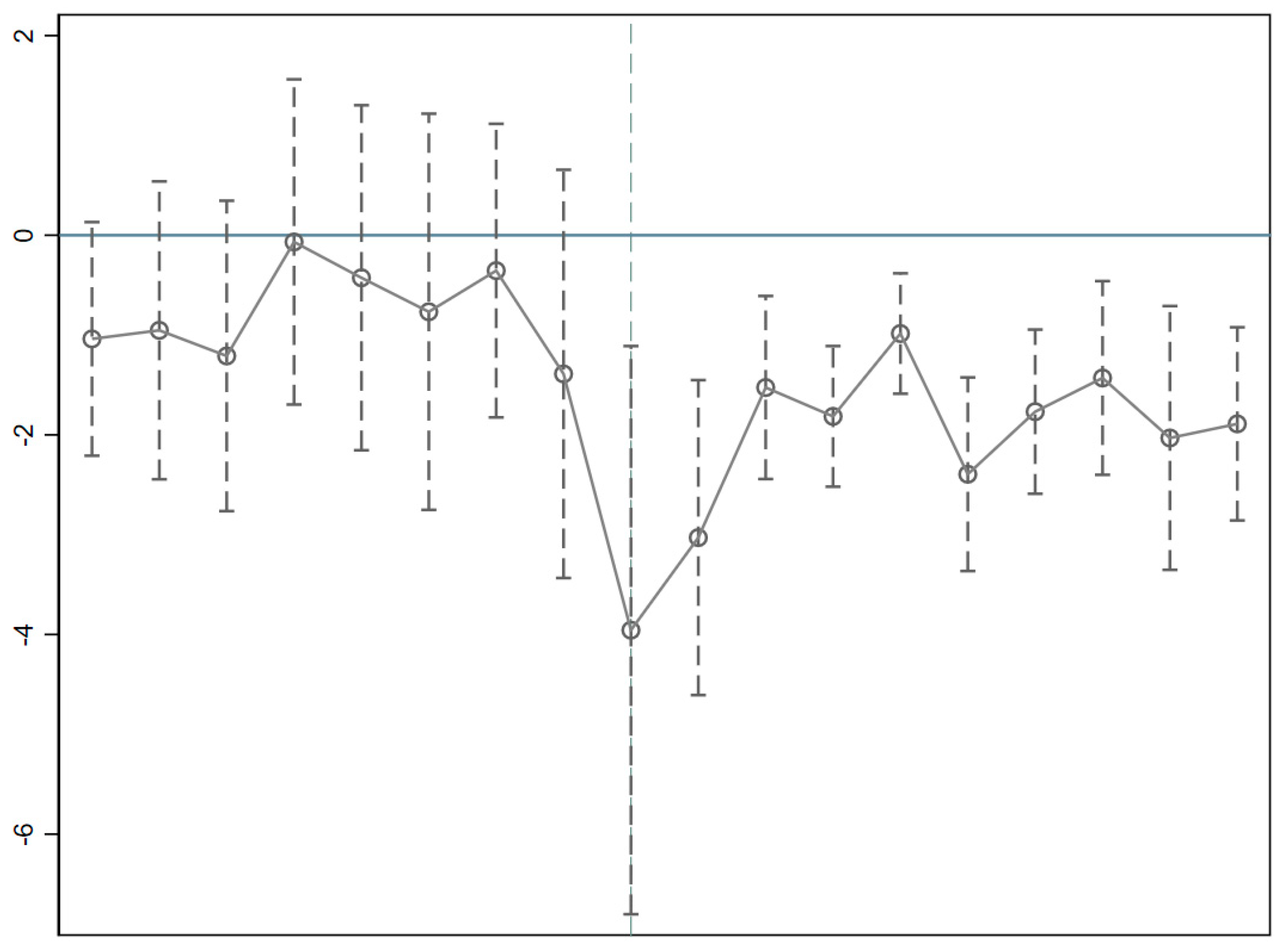
3.2. Parallel Trend Test
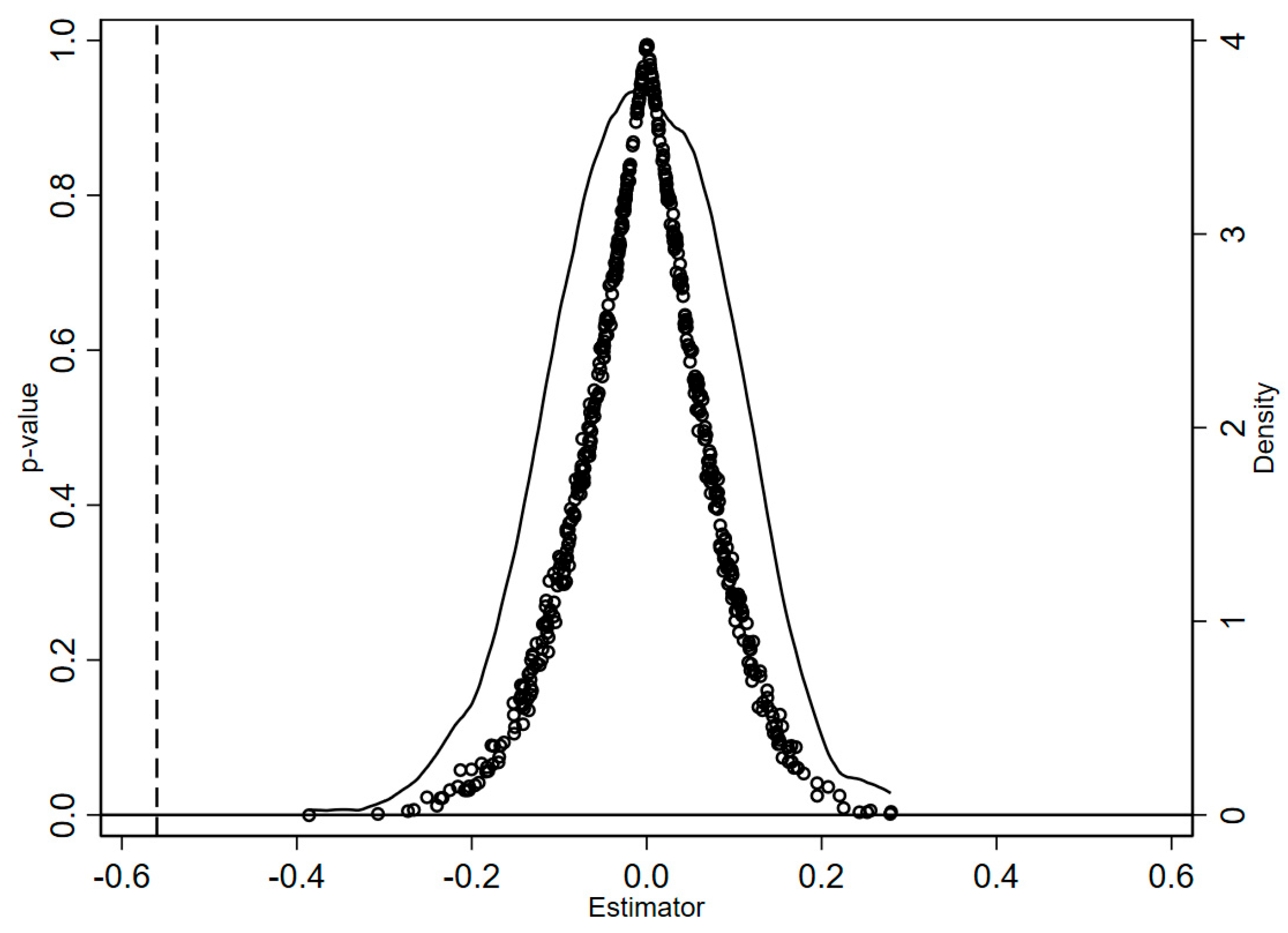
3.3. Placebo Test
3.4. Robustness Checks
3.4.1. Alternative Measures of the Dependent Variable
3.4.2. Sample and Data Processing
3.5. Mechanism Test
3.5.1. Intensification of Timber Price Volatility
3.5.2. Weakening of Timber Supply Capacity
3.6. Heterogeneity Analysis
3.6.1. Degree of Forestry Industrialization
3.6.2. Provincial Timber Supply Capacity
3.7. Further Analysis
4. Conclusions and Implications
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Policy Recommendations
4.3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lin, W. Effects of Regional Financial Development on the Resilience of Wood-Processing Enterprises. Forests 2025, 16, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Hou, F.; Yang, Y.; Han, Z.; Liu, C. An Assessment of the International Competitiveness of China’s Forest Products Industry. For. Policy Econ. 2020, 119, 102256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Q. Changes of China’s Forestry and Forest Products Industry over the Past 40 Years and Challenges Lying Ahead. For. Policy Econ. 2021, 123, 102352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-Y.; Gaston, C. A Trade Flow Analysis of the Global Softwood Log Market: Implications of Russian Log Export Tax Reduction and New Zealand Log Production Restriction. Forestry 2016, 89, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Liu, B.; Gao, M. Mechanism and Prediction of China-Russia Timber Trade from the Perspective of Sustainable Development. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2020, 15, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbu, M.C.; Tudor, E.M. State of the Art of the Chinese Forestry, Wood Industry and Its Markets. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 17, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, I.; Simola, H. How Important Are Russia’s External Economic Links? Asian Econ. Pap. 2022, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoltceva, N.; Tian, G.; Chang, S. The Competitiveness of the Wood Forest Product Trade and Its Sustainable Development: The Case of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. Forests 2025, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilkov, A.; Tian, G. Blockchain as a Solution to the Problem of Illegal Timber Trade between Russia and China: SWOT Analysis. Int. For. Rev. 2019, 21, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, C.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L. A System Dynamics Approach to Resilience Analysis in the Sino-Russian Timber Supply Chain. Forests 2025, 16, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, X. Imperfect Competition in China’s Import Market of Roundwood and Lumber Products. J. Agric. Appl. Econ. 2018, 50, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Yang, Y. The Impact of Changes in Russian Log Export Tariffs on China’s Log Imports. Int. Wood Prod. J. 2024, 15, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, G. Study on Quality Measurement and Influencing Factors of Russian Wood Forest Products Imported from China under the Background of High-Quality Development. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Feng, J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, M.; Kang, W.; Meng, X. Input–Output Analysis of Wood Industry Agglomeration and Industrial Chain Linkages in Heilongjiang Province. Forests 2025, 16, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Su, H.; Qian, W. The Impact of Supply and Demand Shocks on Chinese Wood Market. Forests 2025, 16, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhu, C. China’s Wood-Based Forest Product Imports and Exports: Trends and Implications. Int. For. Rev. 2023, 25, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, L.; Koren, M.; Szeidl, A. Imported Inputs and Productivity. Am. Econ. Rev. 2015, 105, 3660–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschman, A.O. National Power and the Structure of Foreign Trade; Univ. of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1980; pp. 25–60. Available online: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=BezqxPq50dwC (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Cui, L.; Yue, S.; Nghiem, X.-H.; Duan, M. Exploring the Risk and Economic Vulnerability of Global Energy Supply Chain Interruption in the Context of Russo-Ukrainian War. Resour. Policy 2023, 81, 103373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeev, R.V.; Pyzhev, A.I. The Timber Industry in Russia under Sanctions: Losses and Opportunities. Vopr. Ekon. 2023, 4, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peksen, D.; Peterson, T.M. Sanctions and Alternate Markets: How Trade and Alliances Affect the Onset of Economic Coercion. Polit. Res. Q. 2016, 69, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simola, H. Trade Sanctions and Russian Production. BOFIT Policy Brief No. 4/2022. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10419/256796 (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Gordeev, R.V.; Pyzhev, A.I. Impact of Trade Restrictions on the Russian Forest Industry: Evidence from Siberian Timber Producers. Forests 2023, 14, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susilawati, D.; Kanowski, P. Cleaner Production in the Indonesian Pulp and Paper Sector: Improving Sustainability and Legality Compliance in the Value Chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durugbo, C.M.; Al-Balushi, Z. Supply Chain Management in Times of Crisis: A Systematic Review. Manag. Rev. Q. 2022, 73, 1179–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M.; Managi, S. The Spillover Effects of Rising Energy Prices Following 2022 Russian Invasion of Ukraine. Econ. Anal. Policy 2023, 77, 680–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznikov, S.N.; Pavlyukova, A.V.; Tishchenko, I.A. Peculiarities of the Post-Sanctions Reversal of Export Flows in Russia’s Forest and Pulp-and-Paper Industries. Econ. Consult. 2025, 1, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrov, V.; Grieveson, R.; Holzner, M.; Kochnev, A.; Landesmann, M.; Podkaminer, L.; Pöschl, J. The Russian Economy amidst the War and Sanctions. Russia Monitor No. 1. 2024. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10419/303471 (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, B.; Diao, G.; Tao, C.; Wang, C. Does China’s Natural Forest Logging Ban Affect the Stability of the Timber Import Trade Network? For. Policy Econ. 2023, 152, 102974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z. Sustainability of Forest Development in China from the Perspective of the Illegal Logging Trade. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S. Wood Trade Responses to Ecological Rehabilitation Program: Evidence from China’s New Logging Ban in Natural Forests. For. Policy Econ. 2021, 122, 102339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshk, O.M.G.; Pollins, B.M.; Reuveny, R. Trade Still Follows the Flag: The Primacy of Politics in a Simultaneous Model of Interdependence and Armed Conflict. J. Polit. 2004, 66, 1155–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Estrada, M.A.; Koutronas, E. The Impact of the Russian Aggression against Ukraine on the Russia-EU Trade. J. Policy Model. 2022, 44, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apeti, A.E.; N’doua, B.D. The Impact of Timber Regulations on Timber and Timber Product Trade. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 213, 107943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, P.; Lamica, A.; Parajuli, R. Projected Effects of the Russian Invasion of Ukraine on Global Forest Products Markets. For. Policy Econ. 2024, 168, 103301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvich, E.; Prilepskiy, I. The Impact of Financial Sanctions on the Russian Economy. Russ. J. Econ. 2015, 1, 359–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L. The Russia-Ukraine War, Energy Poverty, and Social Conflict: An Analysis Based on Global Liquified Natural Gas Maritime Shipping. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 166, 103263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Hong, Y. Can Geopolitical Risks Excite Germany Economic Policy Uncertainty: Rethinking in the Context of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 51, 103420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenfeld, J.; Tian, S.; Sokolowski, F.; Wyrebkowski, M.; Kasprowicz, M. Business Retreats and Sanctions Are Crippling the Russian Economy. SSRN Working Paper, 19 July 2022. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4167193 (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Mbah, R.E.; Wasum, D.F. Russian-Ukraine War: A Review of the Economic Impact of Russian-Ukraine Crisis on the USA, UK, Canada, and Europe. Adv. Soc. Sci. Res. J. 2022, 9, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudaykulova, M.; Yuanqiong, H.; Khudaykulov, A. Economic Consequences and Implications of the Ukraine-Russia War. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Bus. Adm. 2022, 8, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, P. Reported Social Unrest Index: March 2022 Update. IMF Work. Pap. 2022, 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thaqeb, S.A.; Algharabali, B.G. Economic Policy Uncertainty: A Literature Review. J. Econ. Asymmetries 2019, 20, e00133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.M.; Chin, M.W.C.; Ee, Y.S.; Fung, C.Y.; Giang, C.S.; Heng, K.S.; Kong, M.L.F.; Lim, A.S.S.; Lim, B.C.Y.; Lim, R.T.H.; et al. What Is at Stake in a War? A Prospective Evaluation of the Ukraine and Russia Conflict for Business and Society. Glob. Bus. Organ. Excell. 2022, 41, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, R.K.; Ghosh, I. Time-Varying Relationship between Geopolitical Uncertainty and Agricultural Investment. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 52, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, O.K.; Eshraghi, A. Corporate Decisions in Times of War: Evidence from the Russia Ukraine Conflict. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 48, 102920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Sharma, L.S.; Aier, B. Russia-ukraine conflict: Insights on implications of war for businesses. J. Int. Bus. Econ. 2022, 23, 94–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlin, T. War-Induced (Im)Mobilities and Immobilizing Effects in the Context of the Russo-Ukrainian War. Mobilities 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenenko, O.; Sliusarenko, M.; Onofriichuk, A.; Onofriichuk, V.; Remez, A. Impact of the Russian–Ukrainian War on the National Economy of Russia. J. Interdiscip. Econ. 2023, 36, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Bašić, F.; Bogunović, I.; Barcelo, D. Russian-Ukrainian War Impacts the Total Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, T. War in Ukraine, and Extensive Forest Damage in Central Europe: Supplementary Challenges for Forests and Timber or the Beginning of a New Era? For. Policy Econ. 2022, 140, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Q. Polluting Thy Neighbor: Unintended Consequences of China’s Pollution Reduction Mandates. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2016, 76, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Gao, Y.; Shan, L. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Trade Scale of China’s Import of Russian Woody Forest Products. For. Econ. 2022, 44, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Si, W. The Impact of Export Tax Rebate Policy on Agricultural Trade Exports under the Background of Sino-US Trade Friction—Based on the Analysis of Triple Difference and Synthetic Control Method. Int. Bus. 2024, 5, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.L.; Hsu, J. Digitalization and Country Distance in International Trade: An Empirical Analysis of European Countries. Telecommun. Policy 2025, 49, 102877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Y.; Shen, C.H.-h.; Wu, Z.X. Firm-Level Political Risk and Debt Choice. J. Corp. Financ. 2023, 78, 102332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.D.; Bennett, A.E.; Smith, M.D.; Liverpool-Tasie, L.S.O.; Katengeza, S.P.; Infante, D.M.; Tschirley, D.L. Price Volatility in Fish Food Systems: Spatial Arbitrage as an Adaptive Strategy for Small-Scale Fish Traders. Ecol. Soc. 2024, 29, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, U.; Hasnaoui, A.; Khan, M.; Zahoor, N.; Nawaz, F. Analyzing Fossil Fuel Commodities’ Return Spillovers during the Russia and Ukraine Crisis in the Energy Market. Energy Econ. 2024, 135, 107651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.; Zhang, M.M. Evolutionary Game on International Energy Trade under the Russia Ukraine Conflict. Energy Econ. 2023, 125, 106827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.; Trollman, H.; Trollman, F.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Parra-López, C.; Duong, L.; Martindale, W.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Hdaifeh, A.; et al. The Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Its Implications for the Global Food Supply Chains. Foods 2022, 11, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawtani, D.; Gupta, G.; Khatri, N.; Rao, P.K.; Hussain, C.M. Environmental Damages Due to War in Ukraine: A Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Du, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Trade Embodied CO2 Transfers from Transportation Sector: A Nested Multi-Scale Input-Output Perspective. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 119, 103727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, S. The Russia–Ukraine War and Global Trade Reallocations. Econ. Lett. 2023, 226, 111075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, L.; Luo, B. International Trade Sanctions Imposed Due to the Russia-Ukraine War May Cause Unequal Distribution of Environmental and Health Impacts. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajayya, A.; Kumar, G.A.; Rose, R.L. How the Russia–Ukraine Conflict Caused Trade Diversion? In Harnessing AI, Machine Learning, and IoT for Intelligent Business; Hamdan, A., Braendle, U., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 1, pp. 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, T.; Truszkowski, J.; Norman, M.; Boner, M.; Buliga, B.; Chater, C.; Jennings, H.; Saunders, J.; Sibley, R.; Antonelli, A.; et al. A Framework for Tracing Timber Following the Ukraine Invasion. Nat. Plants 2024, 10, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-C.; Lee, J.-Y.; Liu, W.-Y. Risk Analysis of Regions with Suspicious Illegal Logging and Their Trade Flows. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Meaning | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnQtyict | Timber Import Volume (m3) | 4903 | 8.799 | 2.150 | 0.000 | 13.270 |
| did | Difference-in-Differences Variable | 4903 | 0.052 | 0.223 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| lnratect | Exchange Rate (per 100 RMB) | 4903 | 5.505 | 1.848 | 1.553 | 6.690 |
| lndistct | Trade Distance Cost | 4903 | 13.210 | 0.536 | 11.83 | 14.020 |
| lnpopct | Population of the Exporting Country (Thousands of People) | 4903 | 11.120 | 1.264 | 8.535 | 12.740 |
| lngdpct | GDP of the Exporting Country (Million USD) | 4903 | 14.890 | 1.355 | 12.260 | 17.190 |
| lnexportct | Trade Export Value of the Exporting Country (Million USD) | 4903 | 10.750 | 1.230 | 7.973 | 12.100 |
| lntradeit | Provincial Import and Export Trade Volume (Ten Thousand USD) | 4903 | 15.990 | 1.361 | 12.550 | 18.460 |
| lnfpevit | Provincial Forest Product Export Value (RMB) | 4903 | 20.690 | 1.541 | 16.690 | 22.960 |
| lnQtyict | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) |
| did | −0.383 ** | −0.710 *** | −0.663 *** | −0.390 * | −0.531 *** | −0.545 *** | −0.559 *** | −0.560 *** |
| (0.171) | (0.205) | (0.215) | (0.202) | (0.206) | (0.207) | (0.207) | (0.207) | |
| lndistct | −1.853 *** | −1.848 *** | −2.139 *** | −2.387 *** | −2.390 *** | −2.436 *** | −2.459 *** | |
| (0.612) | (0.623) | (0.538) | (0.522) | (0.521) | (0.524) | (0.524) | ||
| lnpopct | 3.328 | 13.540 *** | 14.950 *** | 14.470 *** | 14.610 *** | 14.730 *** | ||
| (3.379) | (3.491) | (3.497) | (3.516) | (3.517) | (3.521) | |||
| lngdpct | −2.861 *** | −1.865 *** | −1.888 *** | −1.900 *** | −1.906 *** | |||
| (0.476) | (0.552) | (0.582) | (0.580) | (0.580) | ||||
| lnratect | −1.919 *** | −1.827 *** | −1.844 *** | −1.854 *** | ||||
| (0.547) | (0.554) | (0.553) | (0.554) | |||||
| lnexportct | −0.012 | 0.034 | 0.032 | |||||
| (0.294) | (0.294) | (0.295) | ||||||
| lntradeit | 0.831 *** | 0.995 *** | ||||||
| (0.231) | (0.254) | |||||||
| lnfpevit | −0.154 | |||||||
| (0.094) | ||||||||
| _cons | 8.819 *** | 33.310 *** | −3.760 | −70.940 * | −87.550 ** | −82.220 ** | −96.640 ** | −96.990 ** |
| (0.024) | (8.095) | (39.680) | (37.730) | (37.780) | (38.020) | (38.160) | (38.220) | |
| Obs | 4903 | 4903 | 4903 | 4903 | 4903 | 4903 | 4903 | 4903 |
| R2 | 0.520 | 0.522 | 0.522 | 0.527 | 0.528 | 0.529 | 0.530 | 0.531 |
| Date FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Country FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Province FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | lnpqtyict | lnvalueict | lnpvalveict | lnQtyict |
| did | −0.389 ** | −0.653 *** | −0.464 ** | −0.606 *** |
| (0.172) | (0.197) | (0.204) | (0.207) | |
| _cons | −79.417 ** | −89.940 *** | −81.542 ** | −96.687 ** |
| (34.618) | (34.454) | (33.376) | (38.290) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 4903 | 4903 | 4903 | 4872 |
| R2 | 0.457 | 0.515 | 0.444 | 0.526 |
| Date FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Country FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Province FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Variables | lnrangeict | lnsupplyct |
| did | 0.184 ** | −2.539 *** |
| (0.085) | (0.224) | |
| _cons | −11.294 | 31.191 |
| (17.357) | (25.186) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 4725 | 409 |
| R2 | 0.275 | 0.876 |
| Date FE | Yes | Yes |
| Country FE | Yes | Yes |
| Province FE | Yes |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degree of Industrialization | Timber Supply Capacity of the Province | |||
| Variables | High | Low | High | Low |
| did | −0.733 ** | −0.338 | −0.849 | −0.436 ** |
| (0.358) | (0.260) | (0.438) | (0.199) | |
| _cons | −95.957 * | −85.394 | −216.149 ** | −59.734 |
| (50.126) | (56.380) | (70.013) | (41.472) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 2020 | 2883 | 1204 | 3699 |
| R2 | 0.612 | 0.518 | 0.661 | 0.520 |
| Date FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Country FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Province FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Variables | lnPLit | lnPVit |
| did | 0.085 *** | 0.206 *** |
| (0.021) | (0.033) | |
| _cons | 0.400 | 1.201 * |
| (0.416) | (0.657) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 1374 | 1340 |
| R2 | 0.614 | 0.531 |
| Province FE | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dou, P.; Shi, Z.; Hou, F. Geopolitical Conflict and Resource Trade Flows: A Study on the Impact of the Russia–Ukraine Conflict on China’s Timber Imports from Russia. Forests 2025, 16, 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111643
Dou P, Shi Z, Hou F. Geopolitical Conflict and Resource Trade Flows: A Study on the Impact of the Russia–Ukraine Conflict on China’s Timber Imports from Russia. Forests. 2025; 16(11):1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111643
Chicago/Turabian StyleDou, Panpan, Zhenghuang Shi, and Fangmiao Hou. 2025. "Geopolitical Conflict and Resource Trade Flows: A Study on the Impact of the Russia–Ukraine Conflict on China’s Timber Imports from Russia" Forests 16, no. 11: 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111643
APA StyleDou, P., Shi, Z., & Hou, F. (2025). Geopolitical Conflict and Resource Trade Flows: A Study on the Impact of the Russia–Ukraine Conflict on China’s Timber Imports from Russia. Forests, 16(11), 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111643





