Assessing Anthropogenic Impacts on the Carbon Sink Dynamics in Tropical Lowland Rainforest Using Multiple Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study of Jianfengling, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Imagery
2.2.2. Plot and Terrain Data
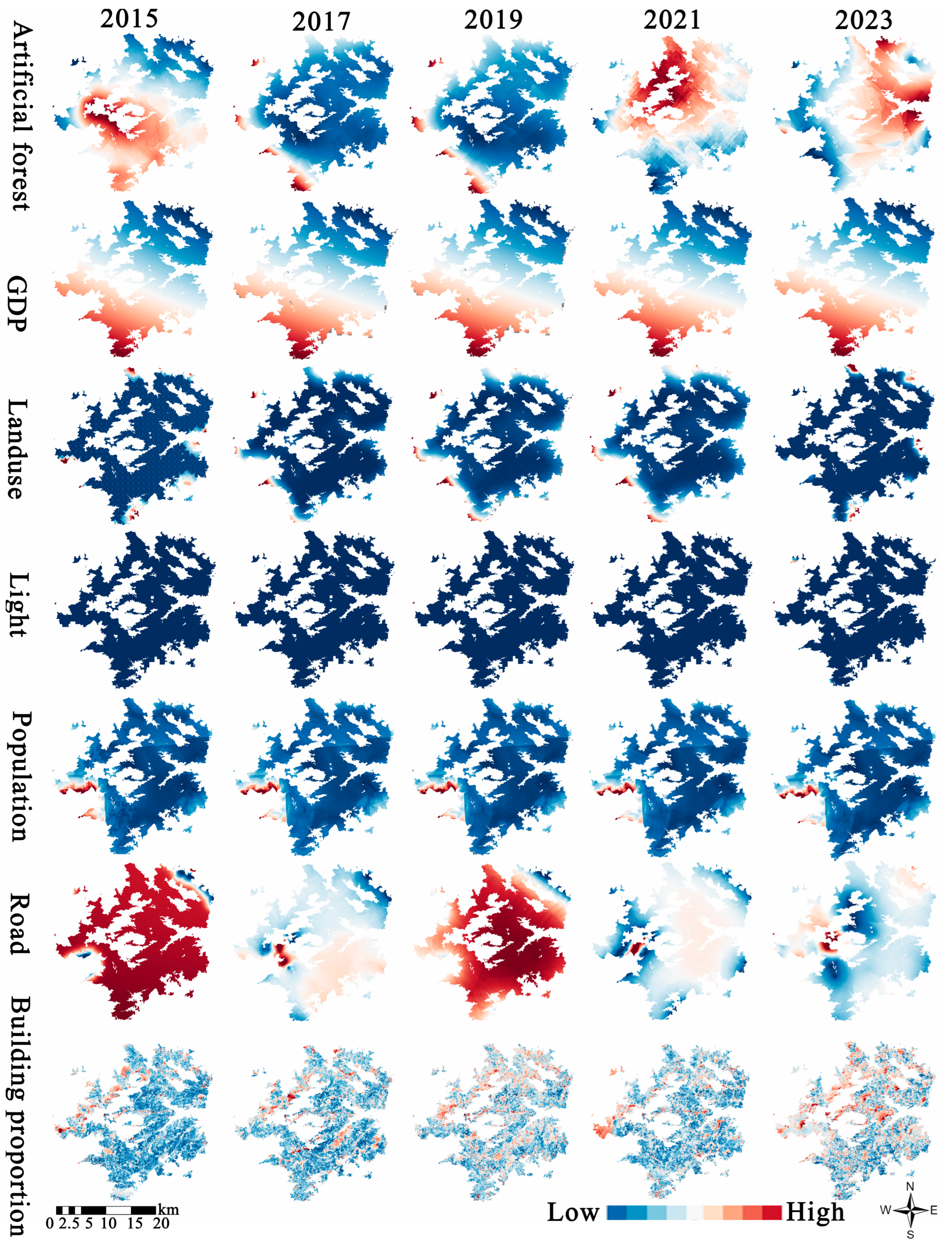
2.2.3. Anthropogenic Disturbance Data
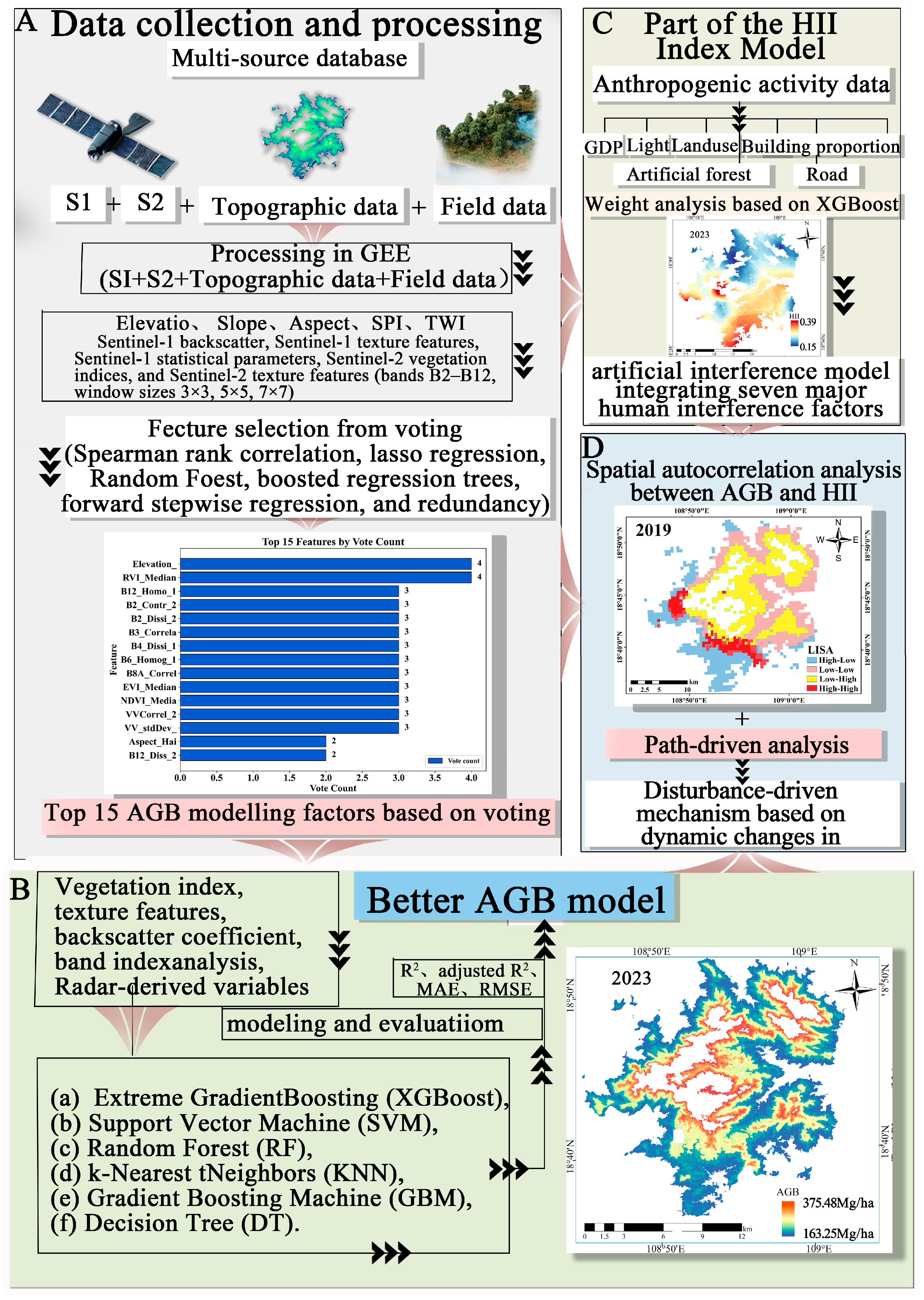
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. AGB Estimation Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data
2.3.2. The Establishment of the HII Model
2.3.3. Mann–Kendall of AGB and HII
2.3.4. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis Between AGB and HII
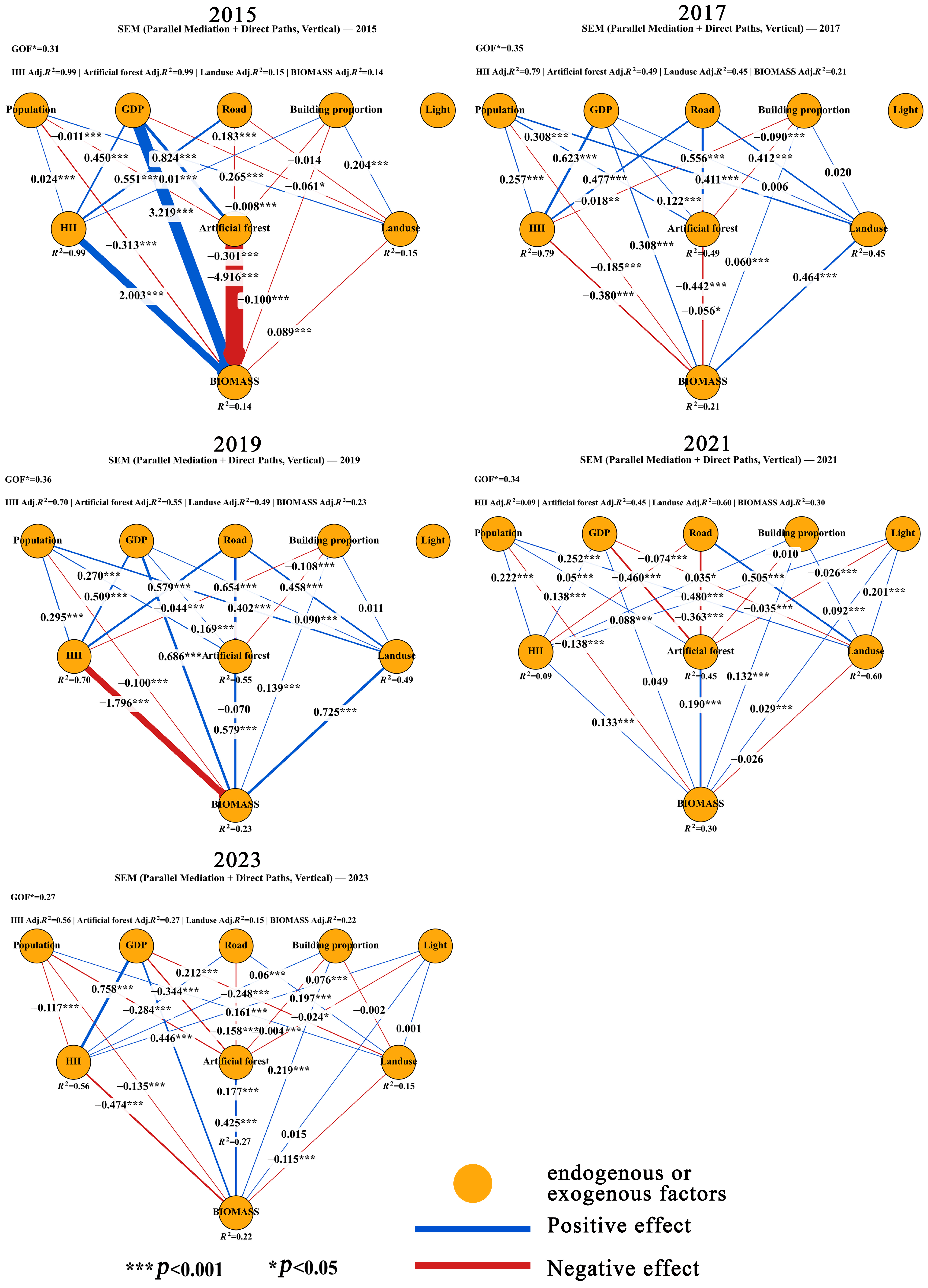
2.3.5. Construction of the Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) of Anthropogenic Factors
3. Results
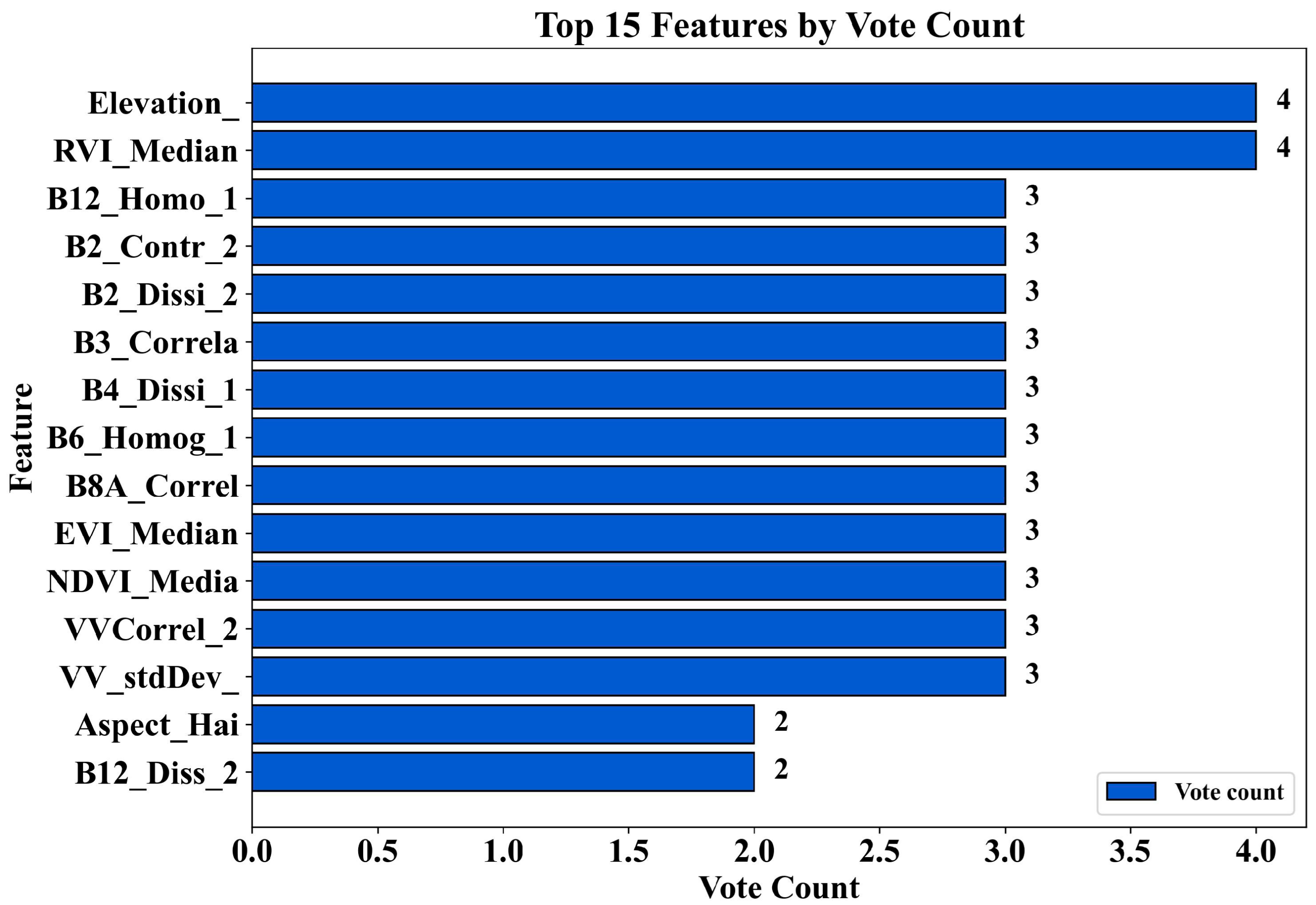
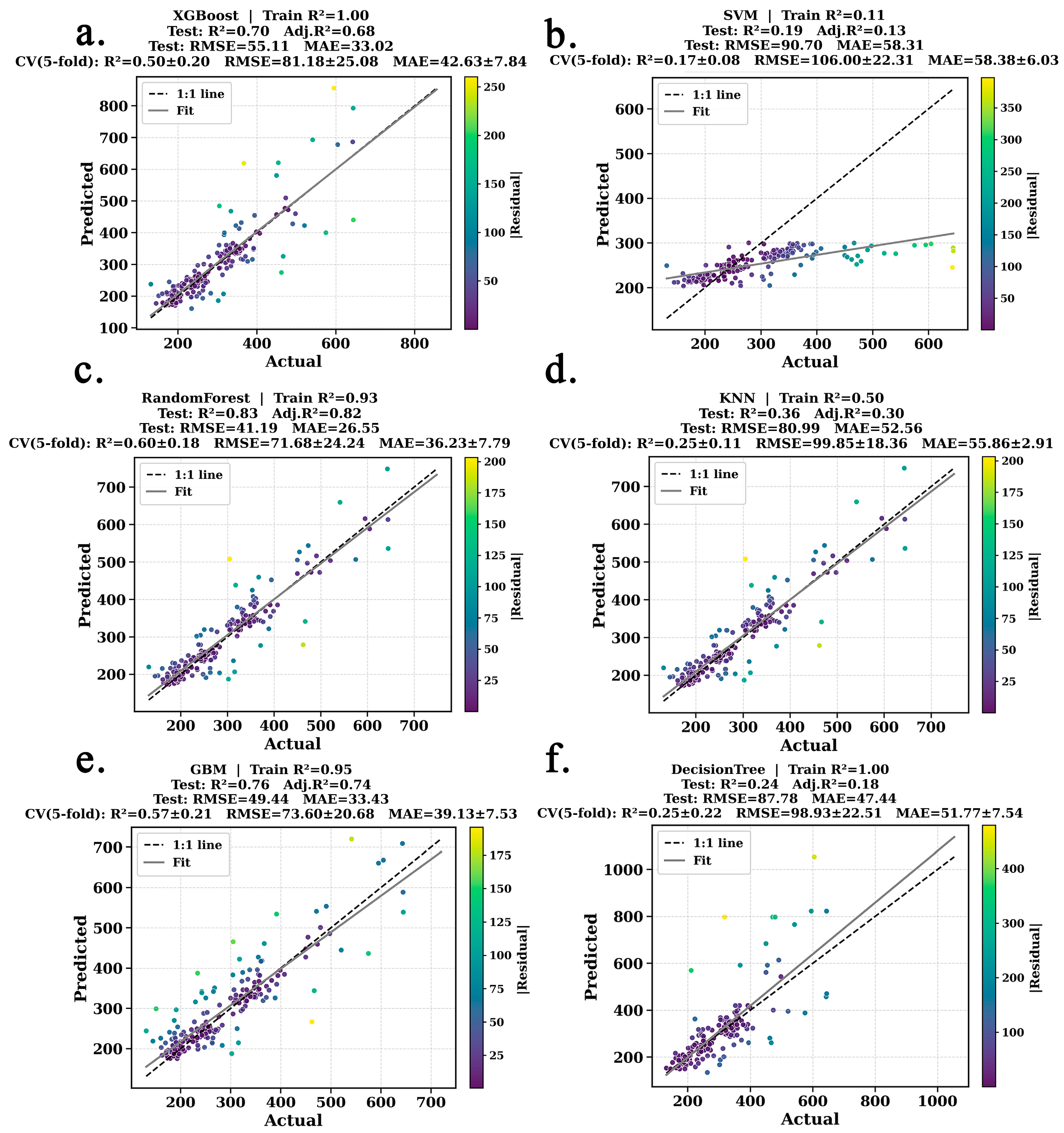
3.1. AGB Model Based on Vote-Based Variable Screening
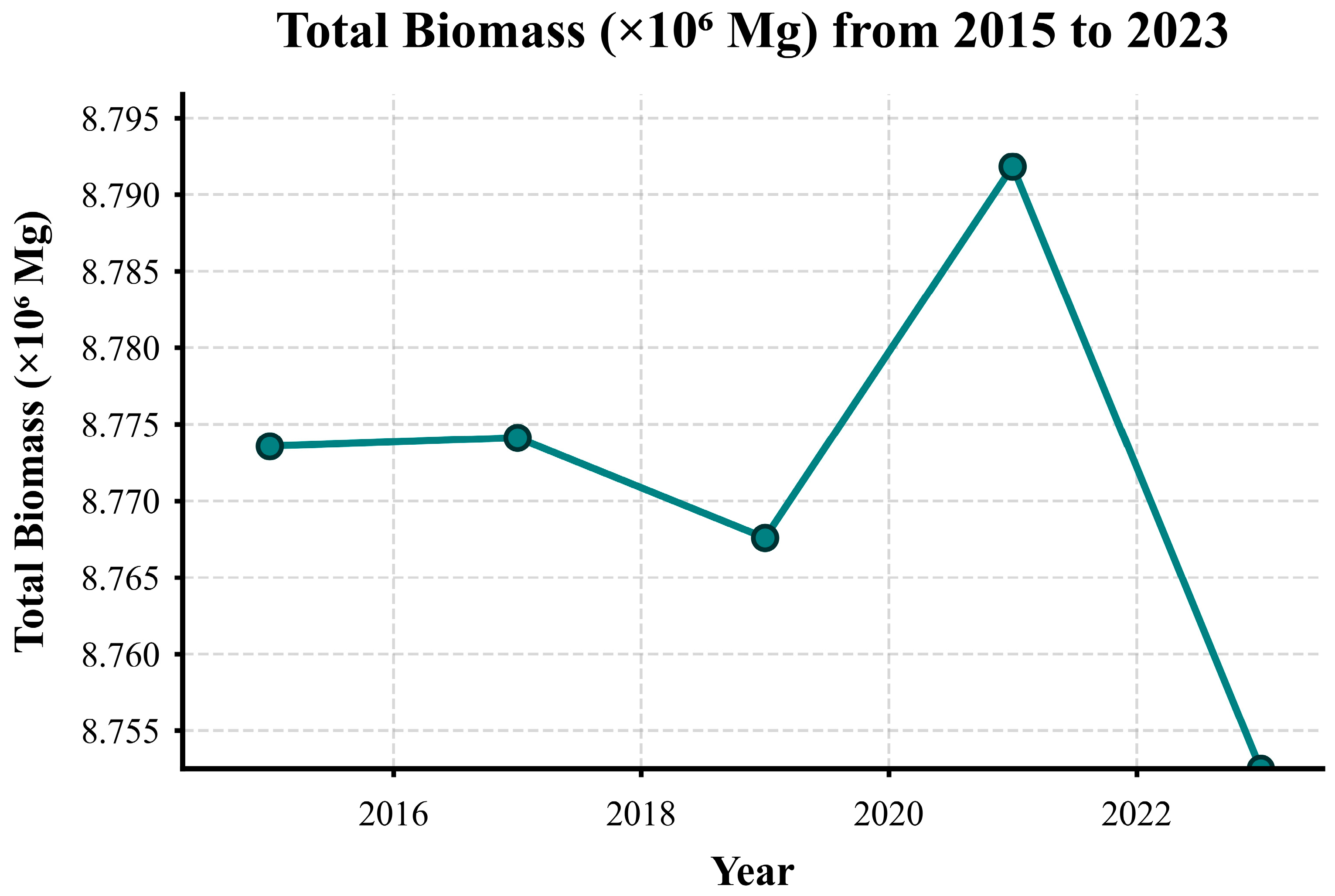
3.2. Spatiotemporal Estimation and Dynamic Analysis of AGB
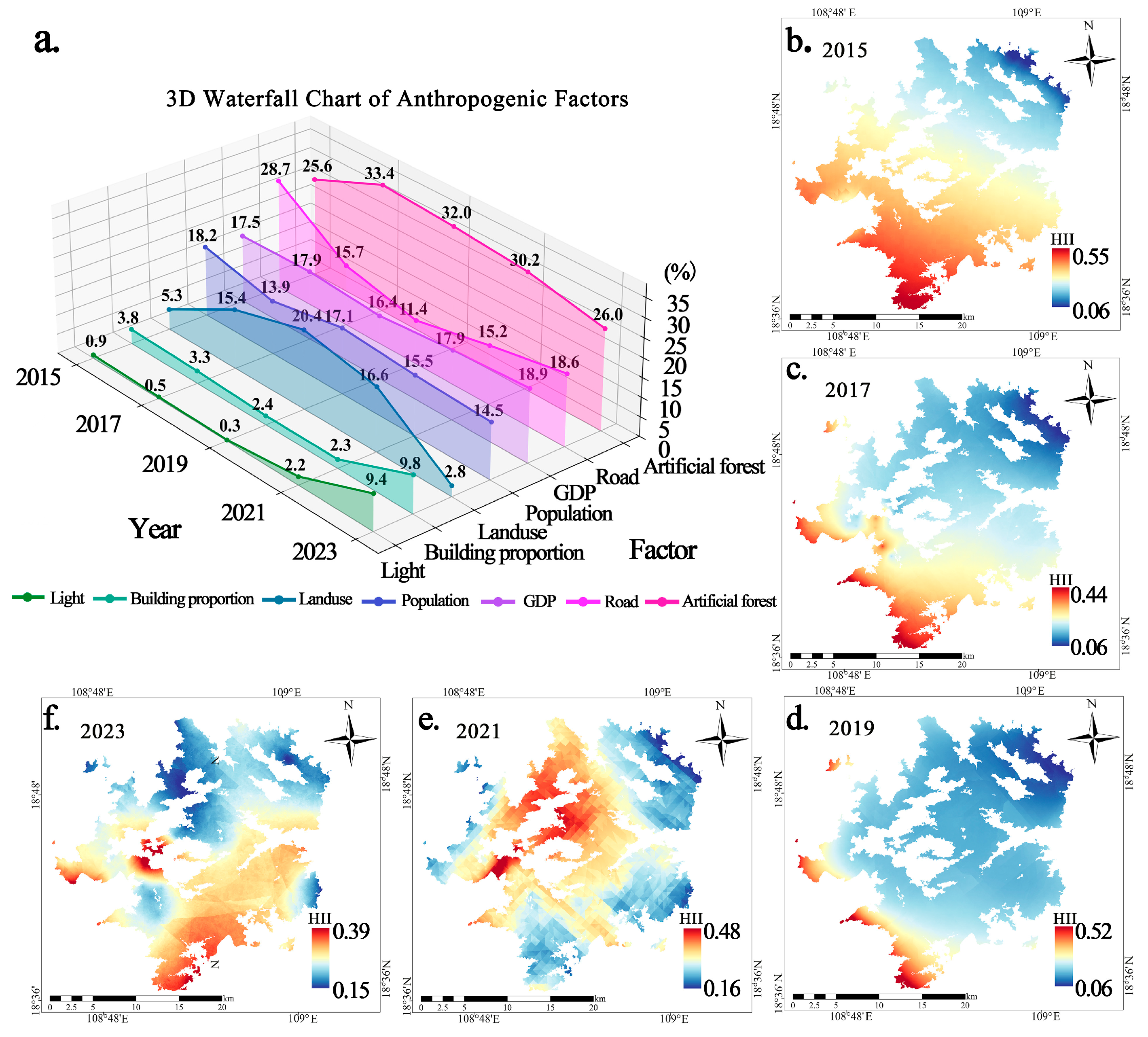
3.3. The Construction of HII and the Recognition of Temporal Patterns
3.4. Analysis of the Changing Trends Between AGB and HII
3.5. Breakpoints and Segmented Responses in the ΔHII–ΔAGB Relationship
3.6. Construction of PLS-SEM of Anthropogenic Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Disturbance Responses and Edge Effects in AGB Spatial Patterns
4.2. Policy Interventions and Time-Lag Effects
4.3. Contributions, Limitations, and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonan, G.B. Forests and Climate Change: Forcings, Feedbacks, and the Climate Benefits of Forests. Science 2008, 320, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G. A Large and Persistent Carbon Sink in the World’s Forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, C.; Li, B.; Jiang, S. Changes in Species-Level Biomass and Its Relationship with Climate and Forest Disturbances in the Great Xing’an Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 4442–4454. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Tan, X.; Ren, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z. Historical Changes and Multi-Scenario Prediction of Land Use and Terrestrial Ecosystem Carbon Storage in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, V.H.; Joyce, L.A.; McNulty, S.; Neilson, R.P.; Ayres, M.P.; Flannigan, M.D.; Hanson, P.J.; Irland, L.C.; Lugo, A.E.; Peterson, C.J.; et al. Climate Change and Forest Disturbances. BioScience 2001, 51, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Gao, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y. Effects of Climate Change and Land Use/Cover Changes on Carbon Sequestration in Forest Ecosystems in the Coastal Area of China. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6, 1271239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; Ciais, P.; Peylin, P.; Huang, Y.; Sitch, S.; Wang, T. The Carbon Balance of Terrestrial Ecosystems in China. Nature 2009, 458, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Sang, W. Biomass Allocation, Morphology and Photosynthesis of Invasive and Noninvasive Exotic Species Grown at Four Irradiance Levels. Acta Oecologica 2007, 31, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; Lawrence, K.T.; Hackler, J.L.; Brown, S. The Spatial Distribution of Forest Biomass in the Brazilian Amazon: A Comparison of Estimates. Glob. Change Biol. 2001, 7, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahvanainen, T.; Forss, E. Individual Tree Models for the Crown Biomass Distribution of Scots Pine, Norway Spruce and Birch in Finland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, G.; Xu, H. A Review on Forest Biomass Models. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2020, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chang, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiao, L.; Feng, Y.; Wu, W.; Wu, H. Spatial Pattern of Forest Biomass and Its Influencing Factors in the Great Xing’an Mountains, Heilongjiang Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, A.; Bernier, P.Y.; Guindon, L.; Villemaire, P.; Guo, X.J.; Stinson, G.; Bergeron, T.; Magnussen, S.; Hall, R.J. Mapping Attributes of Canada’s Forests at Moderate Resolution through KNN and MODIS Imagery. Can. J. For. Res. 2014, 44, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardina, C.P.; Ryan, M.G.; Binkley, D.; Fownes, J.H. Primary Production and Carbon Allocation in Relation to Nutrient Supply in a Tropical Experimental Forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2003, 9, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, S.L.; Lawrence, R.L.; Squires, J.R. Predicting Relative Species Composition within Mixed Conifer Forest Pixels Using Zero-Inflated Models and Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, H.S.; Liang, Y.; Hawbaker, T.J.; Henne, P.D.; Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, Z.; Huang, C. Integrating Forest Inventory Data and MODIS Data to Map Species-Level Biomass in Chinese Boreal Forests. Can. J. For. Res. 2018, 48, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.; Gao, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, F.; Zhou, R. Research on Forest Biomass and Stock Volume Model Based on Stand Height and Canopy Density. For. Resour. Manag. 2021, 2, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zheng, G.; Shen, G.; Moskal, L.M. Characterizing Spatiotemporal Variations of Forest Canopy Gaps Using Aerial Laser Scanning Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatantran, A.; Dubayah, R.; Roberts, D.; Hofton, M.; Blair, J.B. Mapping Biomass and Stress in the Sierra Nevada Using Lidar and Hyperspectral Data Fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2917–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Souyris, J.C.; Angelliaume, S.; Garestier, F. The Compact Polarimetry Alternative for Spaceborne SAR at Low Frequency. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3208–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Li, Z.; Pang, Y.; Tian, X. Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry Based Mean Tree Height Extraction Technique. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2007, 43, 66–70+145. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, L.; Chen, E.; Li, Z.; Qi, F.; Lei, Z. A Review on Forest Height and Above-Ground Biomass Estimation Based on Synthetic Aperture Radar. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 31, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Ou, G.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Lin, R.; Xu, C. Multi-Source Remote Sensing Estimation of Forest Biomass Based on Machine Learning Algorithm. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2024, 39, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Lv, G.; Xu, J.; Cui, G. Integrating Multi-Source Remote Sensing to Assess Forest Aboveground Biomass in the Khingan Mountains of North-Eastern China Using Machine-Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Yan, M.; van der Tol, C.; Li, Z.; Su, Z.; Chen, E.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Pan, X.; et al. Modeling Forest Above-Ground Biomass Dynamics Using Multi-Source Data and Incorporated Models: A Case Study over the Qilian Mountains. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 246, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, P.M.; Cárdenas-Domínguez, J.L.; Corral-Rivas, J.J.; Jiménez, E.; López-Sánchez, C.A.; Vega-Nieva, D.J. Modeling of Aboveground Biomass with Landsat 8 OLI and Machine Learning in Temperate Forests. Forests 2020, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Liu, Z. Forest Aboveground Biomass Estimation Using Landsat 8 and Sentinel-1A Data with Machine Learning Algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Villegas, M.H.; Qasim, M.; Csaplovics, E.; González-Martínez, R.; Rodríguez-Buritica, S.; Ramos-Abril, L.N.; Salazar-Villegas, B. Examining the Potential of Sentinel Imagery and Ensemble Algorithms for Estimating Aboveground Biomass in a Tropical Dry Forest. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.; Luiz, L., Jr.; Costa, G.; Feitosa, R.; Bias, E.D.S.; Cereda, A., Jr.; Almeida, C.; La Rosa, L.E.C.; Happ, P.; Chiamulera, L. Leveraging SAR and Optical Remote Sensing for Enhanced Biomass Estimation in the Amazon with Random Forest and XGBoost Models. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, X-3-2024, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zang, R.; Li, X.; Zou, Z.; Han, W. Spatial Pattern of Trees in Tropical Lowland Rain Forest in Bawangling of Hainan Island, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2012, 36, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, D.; Yang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Tian, L. Variations in Species Composition and Community Structure of Natural Forests in Central Hainan’s Mountainous Region. J. Trop. Biol. 2022, 13, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Quan, Z.; Zhang, Y. Value Assessment and Prediction of Regulating Ecosystem Services in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, W.F.; Goosem, M.; Laurance, S.G. Impacts of Roads and Linear Clearings on Tropical Forests. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenteras, D.; Rodríguez, N.; Retana, J.; Morales, M. Understanding Deforestation in Montane and Lowland Forests of the Colombian Andes. Reg. Environ. Change 2011, 11, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yan, C.; Li, R.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Du, G. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Characteristics of Land-Use Change in China during 2010–2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, S.; Jenkins, C.N.; Joppa, L.N.; Gaveau, D.L.A.; Laurance, W.F. Remaining Natural Vegetation in the Global Biodiversity Hotspots. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 177, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, W.F.; Sayer, J.; Cassman, K.G. Agricultural Expansion and Its Impacts on Tropical Nature. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, M.; Li, Y. Numerical Characteristics of Plant Sexual System of the Woody Plants in the 60 ha Plot in the Tropical Rain Forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. Biodivers. Sci. 2019, 27, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Hu, G.; Shen, D. Structural Features of Root-Associated Fungus–Plant Interaction Networks in the Tropical Montane Rainforest of Jianfengling, China. Biodivers. Sci. 2019, 27, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, D.; Liu, X.; Wan, X.; Liu, J. Tropical Forests Classification Based on Weighted Separation Index from Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 Images in Hainan Island. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Yu, H.; Fang, L.; Zheng, X. Synergistic Use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Based on Different Preprocessing for Predicting Forest Aboveground Biomass. Forests 2023, 14, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Automated Cloud, Cloud Shadow, and Snow Detection in Multitemporal Landsat Data: An Algorithm Designed Specifically for Monitoring Land Cover Change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Lee, Z.; Wei, G. Characterization of MODIS-Derived Euphotic Zone Depth: Results for the China Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Moussaoui, E.; Moumni, A.; Lahrouni, A. Assessing the Influence of Different Synthetic Aperture Radar Parameters and Digital Elevation Model Layers Combined with Optical Data on the Identification of Argan Forest in Essaouira Region, Morocco. iForest 2024, 17, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Ren, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z. Optimal Combination of Predictors and Algorithms for Forest Above-Ground Biomass Mapping from Sentinel and SRTM Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Forest Aboveground Biomass Estimation Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Algorithms in Complex Mountain Areas. Sensors 2024, 24, 7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lu, D.; Wang, G.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yu, S. Examining Spectral Reflectance Saturation in Landsat Imagery and Corresponding Solutions to Improve Forest Aboveground Biomass Estimation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamahewage, C.; Owari, T.; Tsuyuki, S.; Matsuura, T. Aboveground Biomass Estimation Using Multimodal Remote Sensing: Evaluating the Fusion of LiDAR, Hyperspectral, and SAR Data. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Digital Elevation Model. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/usgs-eros-archive-digital-elevation-shuttle-radar-topography-mission-srtm-void?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). GDP and Population Data. Available online: https://data.cnki.net/ (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Laurance, W.F.; Clements, G.R.; Sloan, S.; O’Connell, C.S.; Mueller, N.D.; Goosem, M.; Venter, O.; Edwards, D.P.; Phalan, B.; Balmford, A.; et al. A Global Strategy for Road Building. Nature 2014, 513, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Space Agency (ESA)/Copernicus. Sentinel-2 MSI Level-2A Surface Reflectance (2017–2023), Distributed by Google Earth Engine. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/COPERNICUS_S2_SR_HARMONIZED (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Resource and Environmental Science Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Land Use Data. Available online: https://www.resdc.cn/data.aspx?DATAID=264 (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Li, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y. China’s Planted Forest Maps from 1990 to 2020. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 207, 52–67. [Google Scholar]
- National Ecosystem Science Data Center; Zenodo. Artificial Forest Dataset. 2024. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10701417 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, H. Spatial Distribution of Planted Forests in East Asia—Final Products. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Bacher, S.; Buchmann, C.; Carl, G.; Carré, G.; García Marquéz, J.R.; Gruber, B.; Lafourcade, B.; Leitão, P.J.; et al. Collinearity: A Review of Methods to Deal with It and a Simulation Study Evaluating Their Performance. Ecography 2013, 36, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bi, S.; Hao, S.; Cui, Y. Aboveground Biomass Estimation in Forests with Random Forest and Monte Carlo-Based Uncertainty Analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Liang, S. A Proposed Ensemble Feature Selection Method for Estimating Forest Aboveground Biomass from Multiple Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X. Influencing Factors and Models of Stand Biomass for Natural Conifer–Broad-Leaved Mixed Forest in Jilin Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, Q. Monitoring Planted Forest Expansion from 1990–2020 in China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2025. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Jasinski, M.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Yamanokuchi, T.; Wang, C.-G.; Chang, T.-M.; Ren, H.; Kuo, C.-Y.; et al. A Semi-Empirical Scheme for Bathymetric Mapping in Shallow Water by ICESat-2 and Sentinel-2: A Case Study in the South China Sea. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadeer, A.; Shakir, M.; Wang, L.; Talha, S.M. Evaluating Machine Learning Approaches for Aboveground Biomass Prediction in Fragmented High-Elevated Forests Using Multi-Sensor Satellite Data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 36, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Fu, B.; Guo, Q.; Shi, P. Monitoring and Assessment of the Oasis Ecological Resilience Improved by Rational Water Dispatching Using Multiple Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study of the Heihe River Basin, Silk Road. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, V.; Gautam, B.; Karky, B.S.; Maguya, A.; Tegel, K.; Kauranne, T.; Gunia, K.; Hämäläinen, J.; Latva-Käyrä, P.; Nikolaeva, E.; et al. Robustness of Model-Based High-Resolution Prediction of Forest Biomass against Different Field Plot Designs. Carbon Balance Manag. 2015, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Wang, Z.; Sui, L.; Yang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J. Consistency Analysis of Remote Sensing Land Cover Products in the Tropical Rainforest Climate Region: A Case Study of Indonesia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, S.; Liao, Z.; Wang, T.; Gong, W.; Shi, Z. Estimation of Woody Vegetation Biomass in Australia Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data and Stacking Models. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 34975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Xing, J.; Ju, J.; Hou, Q.; Ding, X. Collaborative Consistent Knowledge Distillation Framework for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, W.; Xue, Y. Construction of a Human–Wildlife Spatial Interaction Index in the Three-River Source Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, C.J.; King, D.J.; Mitchell, S.W. Mapping Forest Growth and Decline in a Temperate Mixed Forest Using Temporal Trend Analysis of Landsat Imagery, 1987–2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cheng, F.; Dong, S.; Zhao, H.; Hou, X.; Wu, X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Grassland Aboveground Biomass on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Based on Validatad MODIS NDVI. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, Q. Spatial Correlation Analysis between Human Disturbance Intensity (HDI) and Ecosystem Services Value (ESV) in the Chengdu–Chongqing Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, C.; Lu, J. Understanding the Spatiotemporal Development of Human Settlement in Hurricane-Prone Areas on the US Atlantic and Gulf Coasts Using Nighttime Remote Sensing. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 2141–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, B.; Polasky, S.; Frelich, L.E. Using Structural Equation Models (SEM) to Link Climate Change, Forest Composition, Deer, and Outdoor Recreation. Ecol. Model. 2024, 493, 110731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-C.; Huang, G.-H.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Lin, C.-H. Deep Learning Application for Classification of Ionospheric Height Profiles Measured by Radio Occultation Technique. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, P. Structural Equation Modelling: Adjudging Model Fit. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2007, 42, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheil, D.; Bongers, F. Interpreting Forest Diversity–Productivity Relationships: Volume Values, Disturbance Histories and Alternative Inferences. For. Ecosyst. 2020, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, W.; Zang, R.; Liu, S. Shifting Cultivation and Logging Change Soil Organic Carbon Functional Groups in Tropical Lowland Rainforests on Hainan Island in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 549, 121447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Pechacek, P.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, N.; Zhu, J.; Li, J. Effectiveness of Nature Reserve System for Conserving Tropical Forests: A Statistical Evaluation of Hainan Island, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, C. Securing the Future of Hainan’s Tropical Rainforest: Challenges and Strategies for Conservation. Front. For. Glob. Change 2025, 8, 1576900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, G.; Yue, F.; Zhao, X.; Fu, J. The Landscape Pattern Evolution and Ecological Security Pattern Construction under the Interference of Transportation Network in National Park. Forests 2025, 16, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccini, A.; Walker, W.; Carvalho, L.; Farina, M.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Houghton, R.A. Tropical Forests Are a Net Carbon Source Based on Aboveground Measurements of Gain and Loss. Science 2017, 358, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameray, A.; Bergeron, Y.; Valeria, O.; Montoro Girona, M.; Cavard, X. Forest Carbon Management: A Review of Silvicultural Practices and Management Strategies across Boreal, Temperate and Tropical Forests. Curr. For. Rep. 2021, 7, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dislich, C.; Keyel, A.C.; Salecker, J.; Kisel, Y.; Meyer, K.M.; Auliya, M.; Barnes, A.D.; Corre, M.D.; Darras, K.; Faust, H.; et al. A Review of the Ecosystem Functions in Oil Palm Plantations, Using Forests as a Reference System. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1539–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, T.; Kotowska, M.M.; Hertel, D.; Knohl, A.; Krashevska, V.; Murtilaksono, K.; Scheu, S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Carbon Costs and Benefits of Indonesian Rainforest Conversion to Plantations. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Luo, Y.; Fang, C.; Li, B. Ecosystem Carbon Stock Influenced by Plantation Practice: Implications for Planting Forests as a Measure of Climate Change Mitigation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J.A.G.; Schwarz-von Raumer, H.-G.; Esswein, H.; Müller, M.; Schmidt-Lüttmann, M. Time Series of Landscape Fragmentation Caused by Transportation Infrastructure and Urban Development—A Case Study from Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, N.; Kreft, S.; Kati, V.; Schluck, M.; Jonsson, B.-G.; Mihok, B.; Okarma, H.; Ibisch, P.L. Roadless and Low-Traffic Areas as Conservation Targets in Europe. Environ. Manag. 2011, 48, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Knapp, D.E.; Martin, R.E.; Tupayachi, R.; Anderson, C.B.; Mascaro, J.; Sinca, F.; Chadwick, K.D.; Higgins, M.; Farfan, W.; et al. Targeted Carbon Conservation at National Scales with High-Resolution Monitoring. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5016–E5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.M.; Brudvig, L.A.; Clobert, J.; Davies, K.F.; Gonzalez, A.; Holt, R.D.; Lovejoy, T.E.; Sexton, J.O.; Austin, M.P.; Collins, C.D.; et al. Habitat Fragmentation and Its Lasting Impact on Earth’s Ecosystems. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordway, E.M.; Asner, G.P. Carbon Declines along Tropical Forest Edges Correspond to Heterogeneous Effects on Canopy Structure and Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7863–7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.M.N.J.; Zhai, D.-L.; Dossa, G.G.O.; Shi, J.; Luo, Q.; Xu, J. Roads as Drivers of Above-Ground Biomass Loss at Tropical Forest Edges in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griscom, B.W.; Adams, J.; Ellis, P.W.; Houghton, R.A.; Lomax, G.; Miteva, D.A.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Shoch, D.; Siikamäki, J.V.; Smith, P.; et al. Natural Climate Solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11645–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, C.P.; Cochrane, M.A.; Souza, C.M.; Laurance, W.F. Roads, Deforestation, and the Mitigating Effect of Protected Areas in the Amazon. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 177, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Avila, A.L.; van der Sande, M.T.; Dormann, C.F.; Peña-Claros, M.; Poorter, L.; Mazzei, L.; Ruschel, A.R.; Silva, J.N.M.; de Carvalho, J.O.P.; Bauhus, J.; et al. Disturbance Intensity Is a Stronger Driver of Biomass Recovery than Remaining Tree-Community Attributes in a Managed Amazonian Forest. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razafindratsima, O.H.; Brown, K.A.; Carvalho, F.; Johnson, S.E.; Wright, P.C.; Dunham, A.E. Edge Effects on Components of Diversity and Above-Ground Biomass in a Tropical Rainforest. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Ramler, I.; Sharp, R.; Haddad, N.M.; Gerber, J.S.; West, P.C.; Mandle, L.; Engstrom, P.; Baccini, A.; Sim, S.; et al. Degradation in Carbon Stocks near Tropical Forest Edges. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, R.M.; Orme, C.D.L.; Pearse, W.D.; Zulkifli, N.; Yvon-Durocher, G.; Yusah, K.M.; Yoh, N.; Yeo, D.C.J.; Wong, A.; Williamson, J.; et al. Thresholds for Adding Degraded Tropical Forest to the Conservation Estate. Nature 2024, 631, 8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranglong, A.; Dutta Roy, A.; Das, S.; Deb, S. Estimating Aboveground Biomass and Biodiversity of a Protected Area in Moist Tropical Forest Ecosystem Using Remote Sensing Application. J. Nat. Conserv. 2025, 84, 126823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberleitner, F.; Egger, C.; Oberdorfer, S.; Dullinger, S.; Wanek, W.; Hietz, P. Recovery of Aboveground Biomass, Species Richness and Composition in Tropical Secondary Forests in SW Costa Rica. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 479, 118580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorter, L.; Craven, D.; Jakovac, C.C.; van der Sande, M.T.; Amissah, L.; Bongers, F.; Chazdon, R.L.; Farrior, C.E.; Kambach, S.; Meave, J.A.; et al. Multidimensional Tropical Forest Recovery. Science 2021, 374, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Junior, C.H.L.; Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Anderson, L.O.; Fonseca, M.G.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Vancutsem, C.; Achard, F.; Beuchle, R.; Numata, I.; Silva, C.A.; et al. Persistent Collapse of Biomass in Amazonian Forest Edges Following Deforestation Leads to Unaccounted Carbon Losses. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Næsset, E. Remote Sensing in Forestry: Current Challenges, Considerations and Directions. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2024, 97, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolking, S.; Palace, M.W.; Clark, D.B.; Chambers, J.Q.; Shugart, H.H.; Hurtt, G.C. Forest Disturbance and Recovery: A General Review in the Context of Spaceborne Remote Sensing of Impacts on Aboveground Biomass and Canopy Structure. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2009, 114, G00E02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

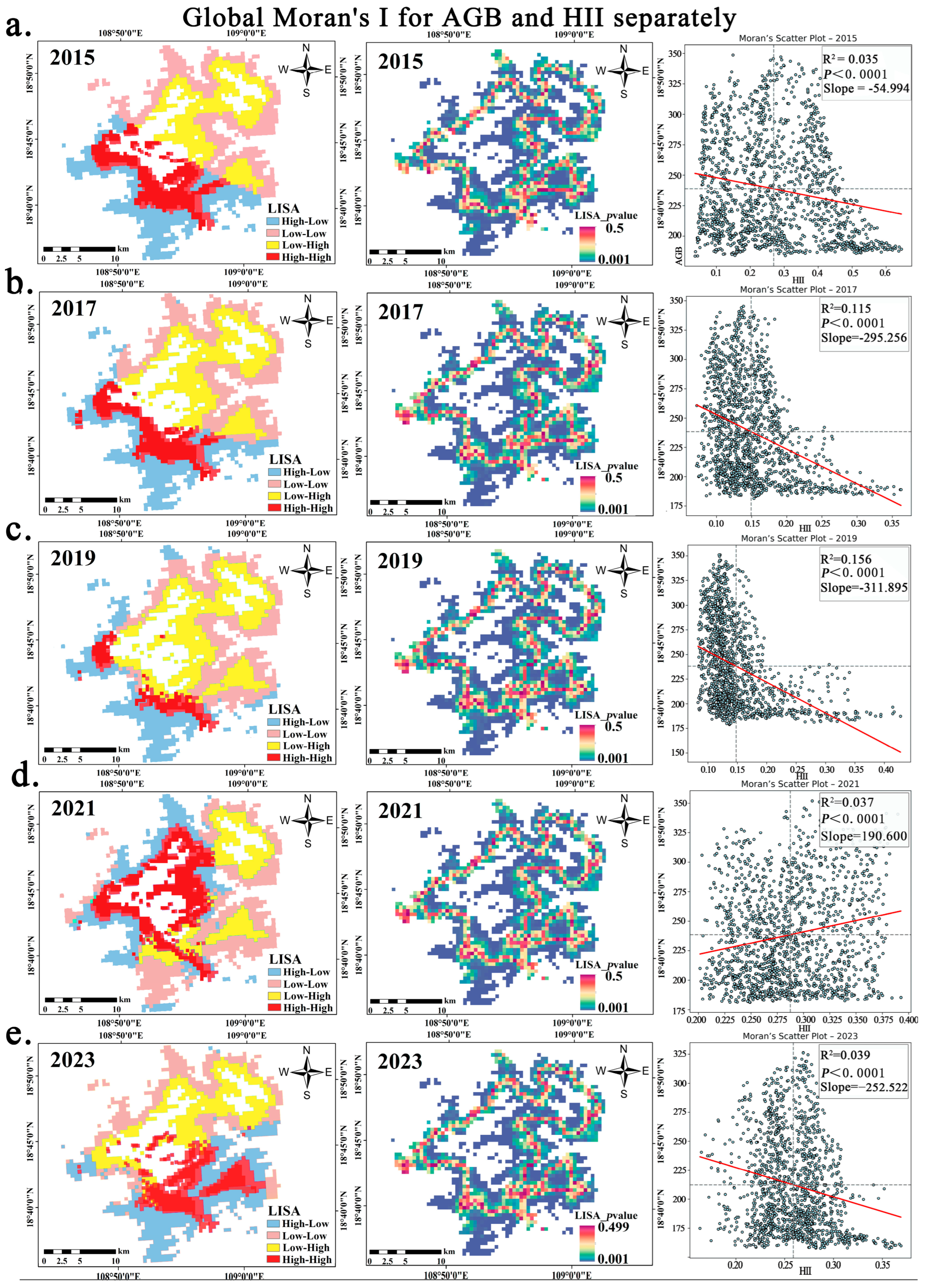

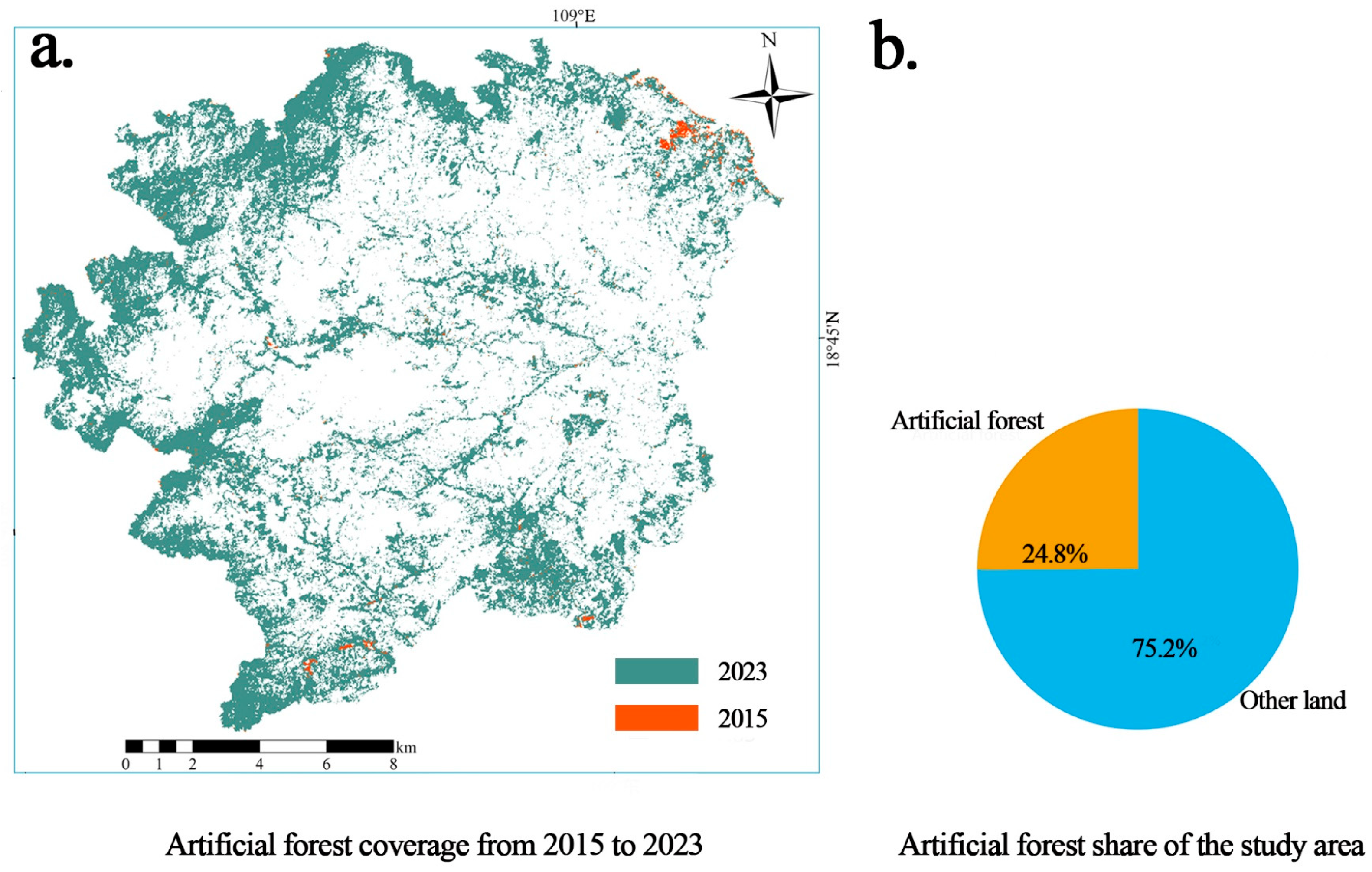
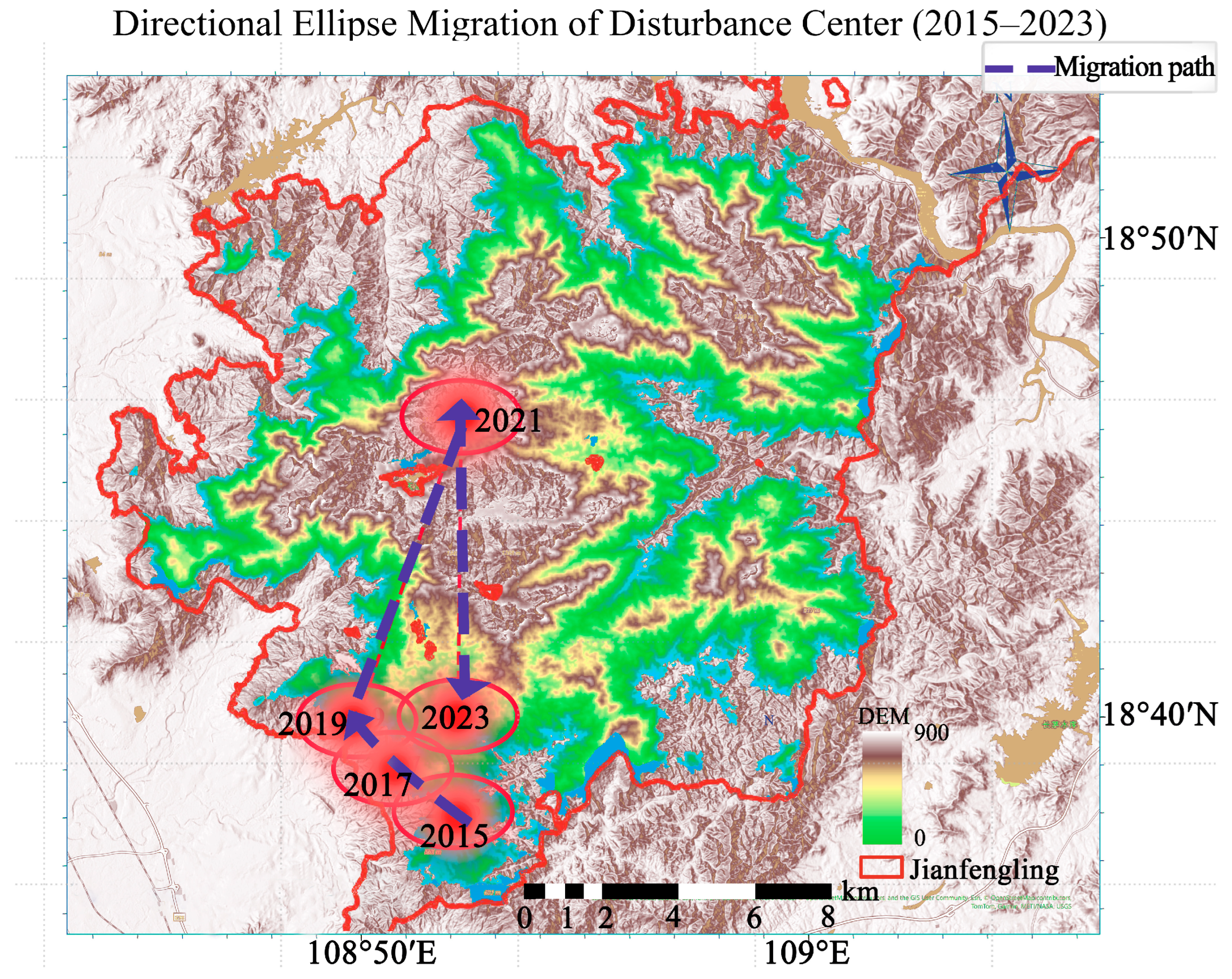
| Year | Bivariate Moran’s I | p Value | Direction | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | −0.1411 | <0.0001 | Negative | TRUE |
| 2017 | −0.2553 | <0.0001 | Negative | TRUE |
| 2019 | −0.2976 | <0.0001 | Negative | TRUE |
| 2021 | 0.1455 | <0.0001 | Positive | TRUE |
| 2023 | −0.1488 | <0.0001 | Negative | TRUE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, S.; Mao, M.; Gong, W.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Jia, J.; et al. Assessing Anthropogenic Impacts on the Carbon Sink Dynamics in Tropical Lowland Rainforest Using Multiple Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study of Jianfengling, China. Forests 2025, 16, 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101611
Mao S, Mao M, Gong W, Chen Y, Ma Y, Chen R, Wang M, Zhang X, Xu J, Jia J, et al. Assessing Anthropogenic Impacts on the Carbon Sink Dynamics in Tropical Lowland Rainforest Using Multiple Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study of Jianfengling, China. Forests. 2025; 16(10):1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101611
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Shijie, Mingjiang Mao, Wenfeng Gong, Yuxin Chen, Yixi Ma, Renhao Chen, Miao Wang, Xiaoxiao Zhang, Jinming Xu, Junting Jia, and et al. 2025. "Assessing Anthropogenic Impacts on the Carbon Sink Dynamics in Tropical Lowland Rainforest Using Multiple Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study of Jianfengling, China" Forests 16, no. 10: 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101611
APA StyleMao, S., Mao, M., Gong, W., Chen, Y., Ma, Y., Chen, R., Wang, M., Zhang, X., Xu, J., Jia, J., & Wu, L. (2025). Assessing Anthropogenic Impacts on the Carbon Sink Dynamics in Tropical Lowland Rainforest Using Multiple Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study of Jianfengling, China. Forests, 16(10), 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101611







