MRV-YOLO: A Multi-Channel Remote Sensing Object Detection Method for Identifying Reclaimed Vegetation in Hilly and Mountainous Mining Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Introduction to YOLOv8
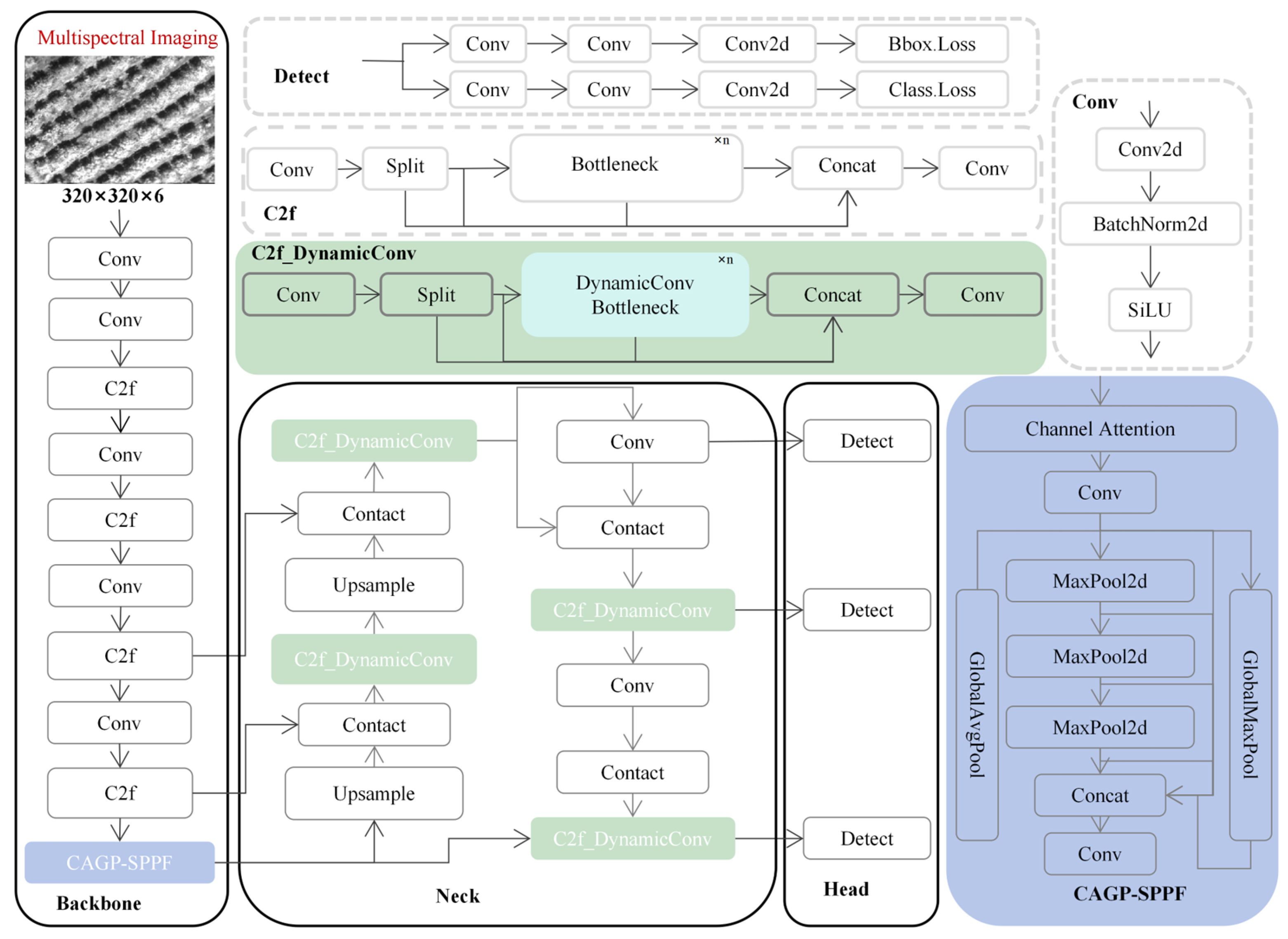
2.2. Introduction to MRV-YOLO
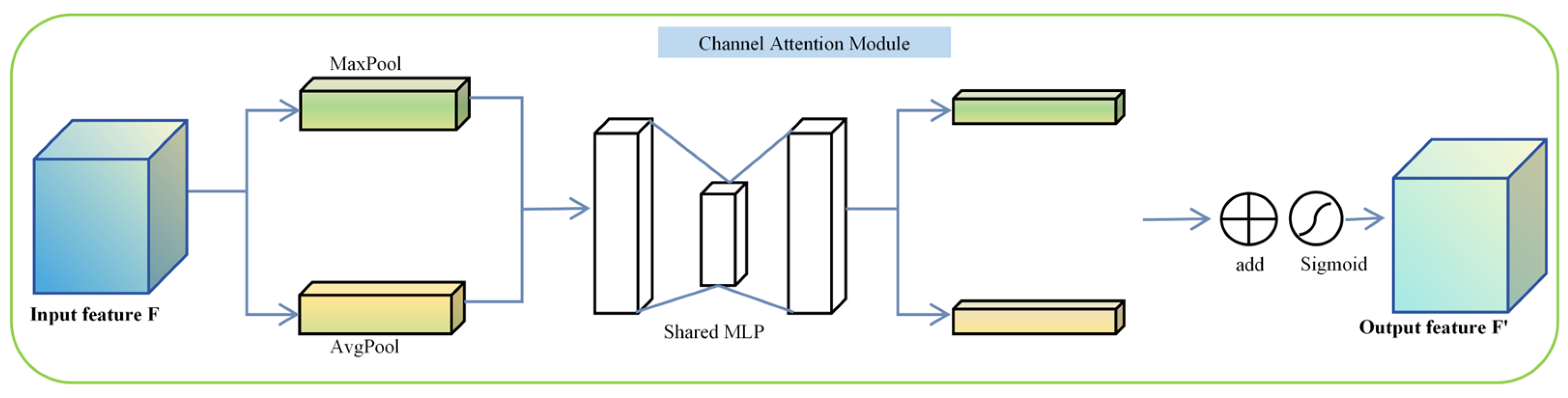
2.2.1. CAGP-SPPF for Channel Attention and Global Pooling SPPF Module
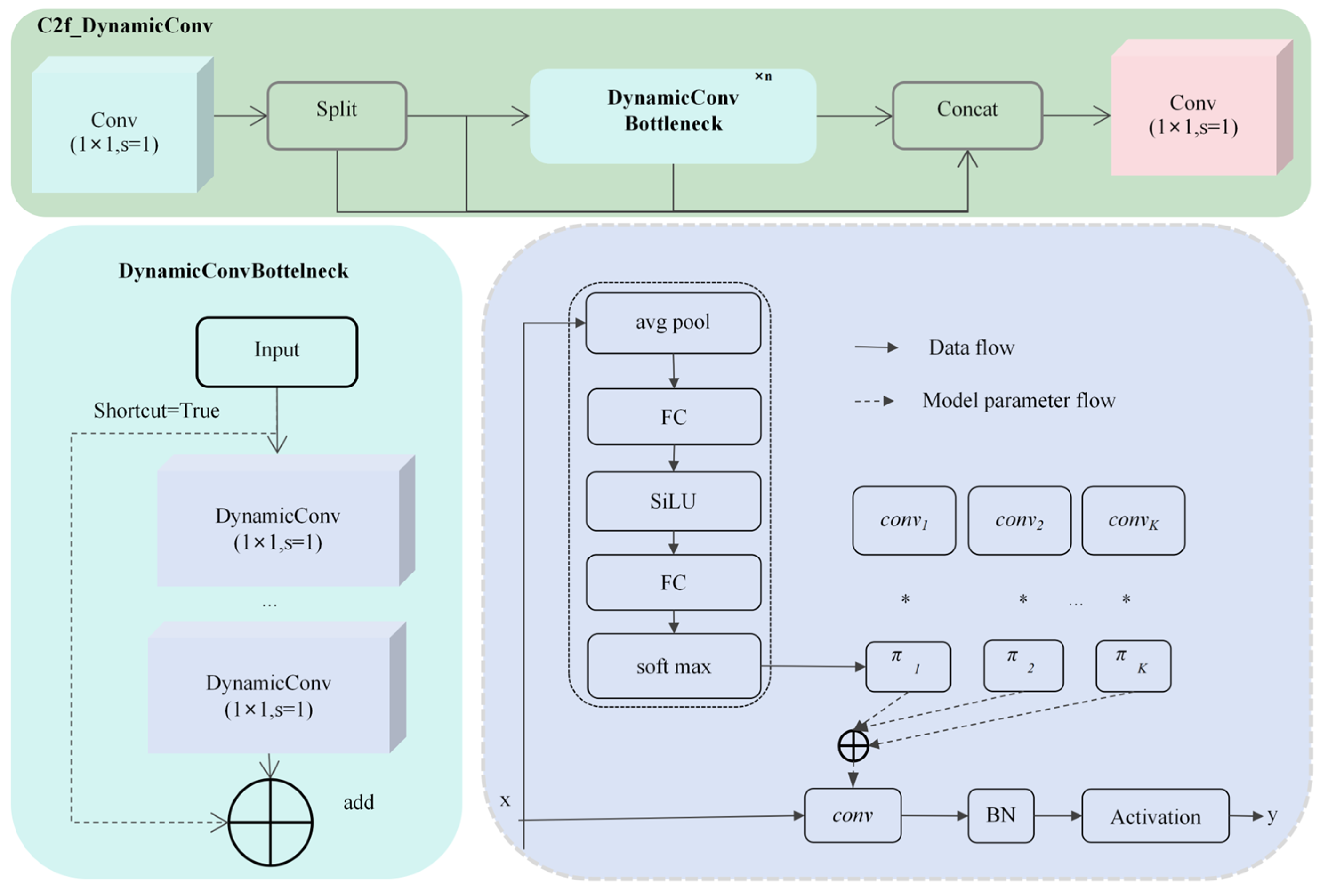
2.2.2. DynamicConv for Convolution Replacement in C2f Botternet
3. Experiments and Setups
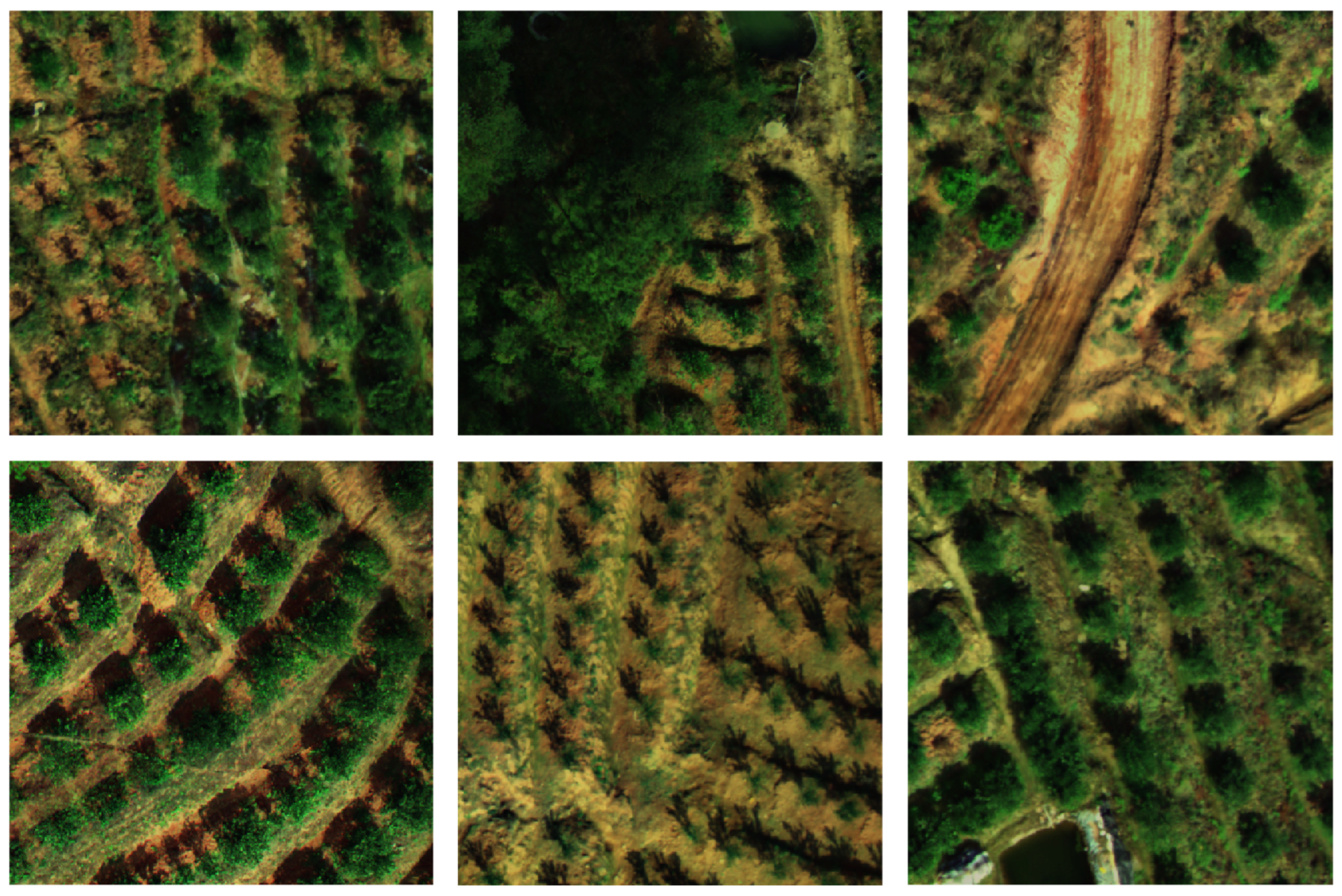
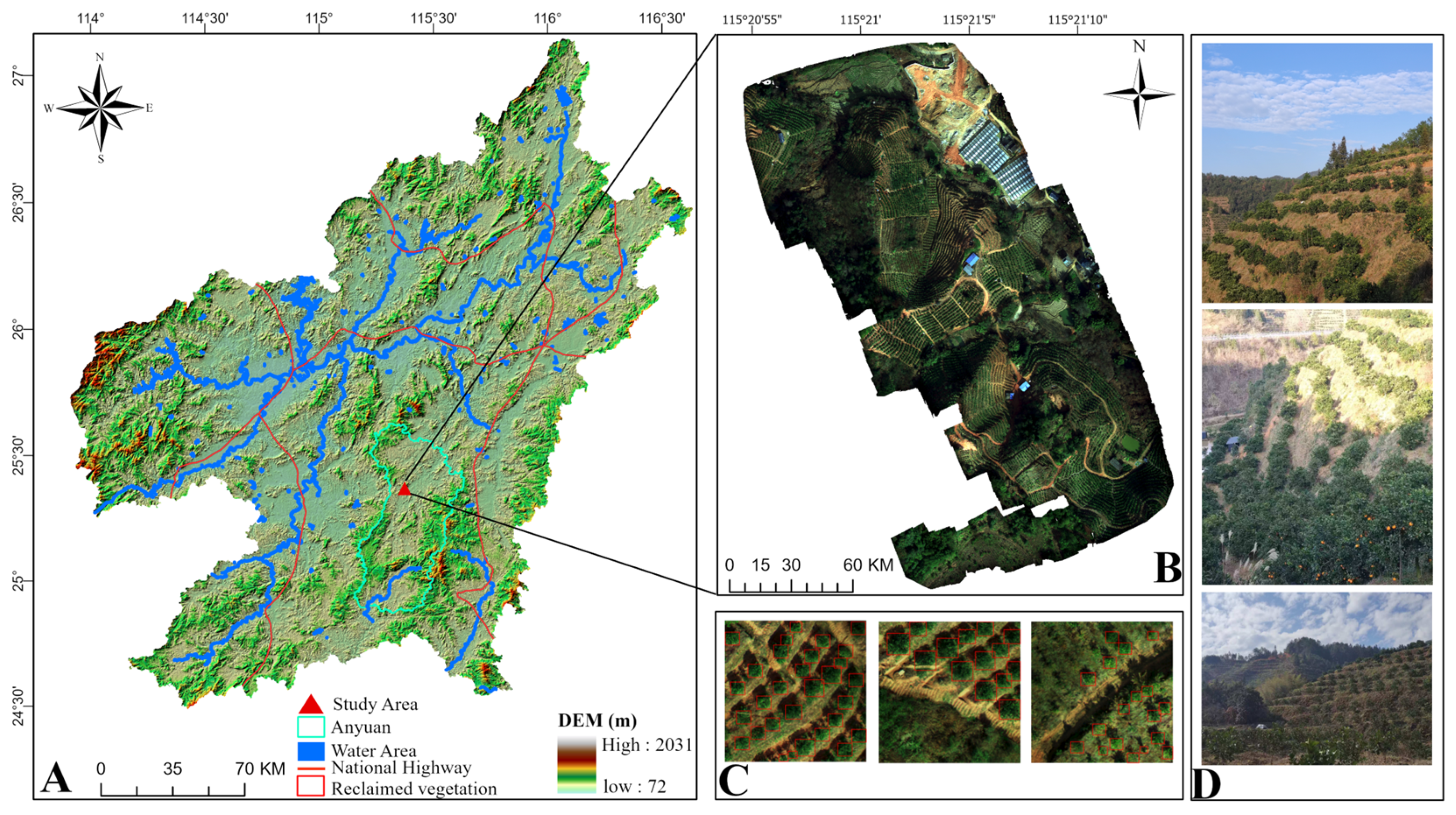
3.1. Study Area and Dataset
3.1.1. Study Area Overview
3.1.2. Data Processing and Dataset Descriptions
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
3.3. Experimental Environment Settings
4. Results Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Structural Analysis of Experiments Comparing Different Target Detection Models
4.2. Analysis of Ablation Experiments
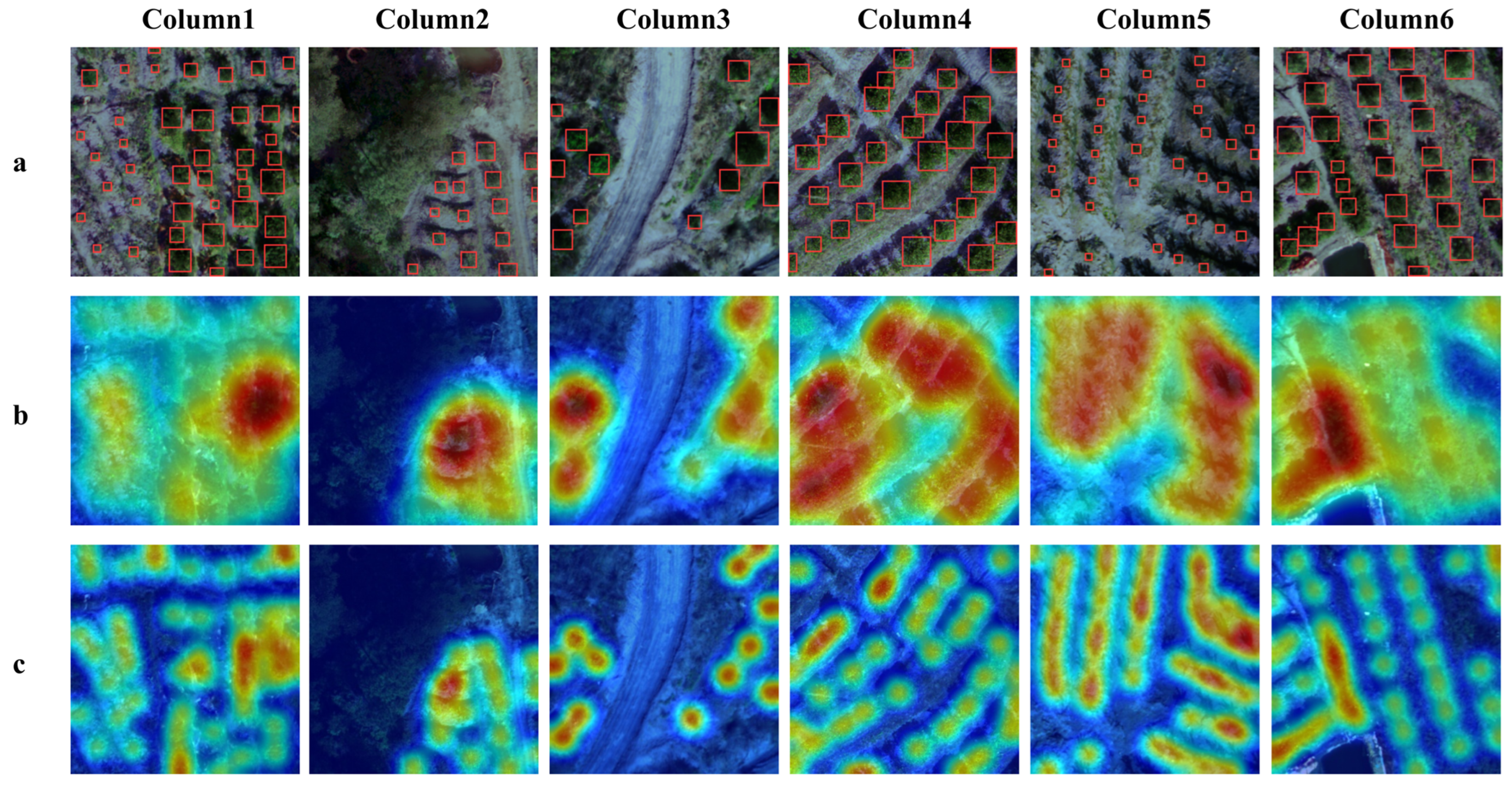
4.3. Model Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, J.; Xu, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zheng, C. Evaluation of resource and environmental carrying capacity in rare earth mining areas in China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Tao, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y. Advancing ecological restoration: A novel 3D interpolation method for assessing ammonia-nitrogen pollution in rare earth mining areas. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2025, 276, 127192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, F.; Li, Q. Remote sensing monitoring of land damage and restoration in rare earth mining areas in 6 counties in southern Jiangxi based on multisource sequential images. J. Environ. Manage 2020, 267, 110653. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Chen, Y.; Wan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z.; Sun, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Y. Cross-sensitivity analysis of land use transition and ecological service values in rare earth mining areas in southern China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Mapping annual land disturbance and reclamation in rare-earth mining disturbance region using temporal trajectory segmentation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 69112–69128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Meng, L.; Chen, X. Analysis of vegetation dynamics from 2001 to 2020 in China‘s Ganzhou rare earth mining area using time series remote sensing and SHAP-enhanced machine learning. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 84, 102887. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Li, H.; Xu, F. Analysis and discrimination of hyperspectral characteristics of typical vegetation leaves in a rare earth reclamation mining area. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 174, 106465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Fan, X. Spectral Variations of Reclamation Vegetation in Rare Earth Mining Areas Using Continuous–Discrete Wavelets and Their Impact on Chlorophyll Estimation. Forests 2024, 15, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X. Detailed Land Use Classification in a Rare Earth Mining Area Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data for Sustainable Agricultural Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 33582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Xu, S.; Cai, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Yao, C.; Ge, G. Integrated strategies enhance soil fertility restoration effectiveness in ion-adsorption rare earth mining areas: A meta-analysis. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 58, e03465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Zhuang, X.; Schaefer, G.; Feng, J.; Guan, L.; Fang, H. Deep-Learning-Based Multispectral Satellite Image Segmentation for Water Body Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7422–7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parelius, E.J. A Review of Deep-Learning Methods for Change Detection in Multispectral Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramich, J.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Fischer, A. Improved red-edge chlorophyll-a detection for Sentinel 2. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Park, J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; Kweon, I.S. Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, J.E.; Oughton, E.J. Surveying You Only Look Once (YOLO) Multispectral Object Detection Advancements, Applications, and Challenges. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 7366–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi, K.; Watanabe, K.; Ha, Q.; Tejero-De-Pablos, A.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. Multispectral Object Detection for Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the on Thematic Workshops of ACM Multimedia 17th Mountain View, California, CA, USA, 23–27 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shammari, D.; Whelan, B.M.; Wang, C.; Bramley, R.G.V.; Bisho, T.F.A. Assessment of red-edge based vegetation indices for crop yield prediction at the field scale across large regions in Australia. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Li, J.; Cai, X.; Dong, X.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; et al. Identification of dominant species of submerged vegetation based on Sentinel-2 red-edge band: A case study of Lake Erhai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Wang, M.; Chu, J.; Sun, J.; Liang, W.; Yu, H. Feature extraction and analysis of reclaimed vegetation in ecological restoration area of abandoned mines based on hyperspectral remote sensing images. J. Arid. Land. 2024, 16, 1409–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.-L.; Qian, W.-X. Infrared small target detection based on isolated hyperedge. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2025, 146, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. DME-YOLO: A real-time high-precision detector of vessel targets in infrared remote sensing images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 16, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, P. Small and dim target detection in infrared imagery: A review, current techniques and future directions. Neurocomputing 2025, 630, 129640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Long, B. MCCANet: A multispectral class-constraint attentional neural network for object detection in mining scenes. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 247, 123233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouret, F.; Morin, D.; Planells, M.; Vincent-Barbaroux, C. Tree Species Classification at the Pixel Level Using Deep Learning and Multispectral Time Series in an Imbalanced Context. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Martín, A.; Mesas-Carrascosa, F.-J.; Gutiérrez, P.A.; Pérez-Porras, F.-J.; Vargas, V.M.; Hervás-Martínez, C. Deep Ordinal Classification in Forest Areas Using Light Detection and Ranging Point Clouds. Sensors 2024, 24, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.; Kamilaris, A.; Karatsiolis, S. A Weakly Supervised Multimodal Deep Learning Approach for Large-Scale Tree Classification: A Case Study in Cyprus. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Huang, Q.; Mei, Y.; Chu, H. MOD-YOLO: Multispectral object detection based on transformer dual-stream YOLO. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2024, 183, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yin, M.; Wang, Z.; Xie, T.; Bei, S. Multispectral Object Detection Based on Multilevel Feature Fusion and Dual Feature Modulation. Electronics 2024, 13, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, J.; Wan, X. TF-YOLO: A Transformer–Fusion-Based YOLO Detector for Multimodal Pedestrian Detection in Autonomous Driving Scenes. World Electr. Vehic. J. 2023, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. IGT: Illumination-guided RGB-T object detection with transformers. Knowl. Based Syst. 2023, 268, 110423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rista, P.R.R.; Saputro, A.H.; Handayani, W. Middle-Level Fusion YOLO on Multispectral Image to Detect Unhealthy Oil Palm Trees. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2866, 012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, D.; Xu, Y.; Yang, G.; Huang, F.; Chen, L. Towards complex scenes: A deep learning-based camouflaged people detection method for snapshot multispectral images. Def. Technol. 2024, 34, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.K.; Liu, H.; Ling, C.X.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y. Object detection of individual mangrove based on improved YOLOv5. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2022, 59, 436–446. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Leonce, A.; Edirisinghe, E.A.; Khafaga, T.; Simkins, G.; Yahya, U.; Shah, M.S. Ghaf Tree Detection from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC), Doha, Qatar, 23–26 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yuan, P. LDS-YOLO: A lightweight small object detection method for dead trees from shelter forest. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2022, 198, 107035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, R.; Shi, W.; Wang, X. Classification of Tree Species in Transmission Line Corridors Based on YOLO v7. Forests 2023, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Liu, K.; Wang, X. Revegetation Detection Method for Rare Earth Mining Areas Using YOLOv8n Network with Integrated Global Features. Nat. Remote Sens. Bull. 2024, 1–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, R.; Sambath, M. YOLOv8: A Novel Object Detection Algorithm with Enhanced Performance and Robustness. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Advances in Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing Systems (ADICS), Chennai, India, 18–19 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Chi, G.; Ju, X.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. YOLO-CWD: A novel model for crop and weed detection based on improved YOLOv8. Crop Prot. 2025, 192, 107169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhan, J.; Zuo, D. EBC-YOLO: A remote sensing target recognition model adapted for complex environments. Earth Sci. Inform. 2025, 18, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z. Dynamic Convolution: Attention Over Convolution Kernels. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Elfwing, S.; Uchibe, E.; Doya, K. Sigmoid-weighted linear units for neural network function approximation in reinforcement learning. Neural Netw. 2017, 107, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. YOLOv11: An Overview of the Key Architectural Enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Band Name | Wavelength |
|---|---|
| Red | 660 nm–20 nm |
| Green | 555 nm–25 nm |
| Blue | 450 nm–35 nm |
| Red Edge1 | 720 nm–10 nm |
| Red Edge1 | 750 nm–15 nm |
| NIR | 840 nm–35 nm |
| Mode | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-DETR(rgb) | 81.5 | 73.2 | 77.1 | 31 | 77 |
| RT-DETR(bands) | 86.2 | 80.6 | 84.8 | 35.8 | 83 |
| YOLOv3(rgb) | 81.3 | 65.9 | 76.7 | 38.7 | 73 |
| YOLOv3(bands) | 84.9 | 73.7 | 81.9 | 42 | 79 |
| YOLOv5(rgb) | 79.5 | 72.2 | 79.7 | 39.3 | 76 |
| YOLOv5(bands) | 84.1 | 81.5 | 86.3 | 42.8 | 83 |
| YOLOv6(rgb) | 81.8 | 71.8 | 80.2 | 41.5 | 77 |
| YOLOv6(bands) | 85.9 | 79 | 85.1 | 44.1 | 82 |
| YOLOv7(rgb) | 83 | 71.4 | 80.4 | 41.9 | 77 |
| YOLOv7(bands) | 87 | 78.4 | 85.2 | 43.6 | 82 |
| YOLOv7-tiny(rgb) | 81 | 65.8 | 75.9 | 34.5 | 73 |
| YOLOv7-tiny(bands) | 80.7 | 78.4 | 82.7 | 38.5 | 80 |
| YOLOv8(rgb) | 84.7 | 73.7 | 82.7 | 43.7 | 79 |
| YOLOv8(bands) | 86.9 | 82.5 | 87 | 44.1 | 85 |
| YOLOv8-AS(rgb) | 83.9 | 77.5 | 84.8 | 50.3 | 81 |
| YOLOv8-AS(bands) | 90.8 | 82.3 | 89.5 | 52.2 | 86 |
| YOLOv10(rgb) | 86.2 | 68.3 | 80 | 40.9 | 76 |
| YOLOv10(bands) | 85.8 | 81.4 | 86.2 | 44.5 | 83 |
| YOLOv11(rgb) | 77.1 | 71.7 | 78.1 | 37.6 | 75 |
| YOLOv11(bands) | 84.9 | 80.7 | 85.4 | 41.1 | 83 |
| our(rgb) | 88.1 | 79.4 | 87.6 | 52.6 | 84 |
| our(bands) | 92.3 | 84.8 | 91.6 | 54.9 | 88 |
| Combination of Different Modules | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPPF + C2f(rgb) | 84.7 | 73.7 | 82.7 | 43.7 | 79 |
| SPPF + C2f(bands) | 86.9 | 82.5 | 87 | 44.1 | 85 |
| CAGP-SPPF + C2f(rgb) | 86.9 | 79.7 | 87.4 | 55.5 | 83 |
| CAGP-SPPF + C2f(bands) | 91 | 84.6 | 90.8 | 59.2 | 88 |
| SPPF + C2f_DynamicConv(rgb) | 87.8 | 77.6 | 86.5 | 55.2 | 82 |
| SPPF + C2f_DynamicConv(bands) | 90 | 84.4 | 90.5 | 58.3 | 87 |
| CAGP-SPPF + C2f_DynamicConv(rgb) | 88.1 | 79.4 | 87.6 | 56.5 | 84 |
| CAGP-SPPF + C2f_DynamicConv(bands) | 92.3 | 84.8 | 91.6 | 54.9 | 88 |
| Mode | Model Size (MB) | Parameters (MB) | FLOPs (G) | Times Cost (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-DETR | 63 | 31.99 | 103.6 | 12.125 |
| YOLOv3 | 24.4 | 12.13 | 19.3 | 0.268 |
| YOLOv5 | 5.2 | 2.50 | 7.4 | 0.237 |
| YOLOv6 | 8.7 | 4.23 | 11.9 | 0.237 |
| YOLOv7 | 6.5 | 3.03 | 9.7 | 0.366 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 1.58 | 0.72 | 2.4 | 0.160 |
| YOLOv8 | 6.2 | 3.01 | 8.2 | 0.240 |
| YOLOv8-AS | 5.5 | 2.66 | 7.4 | 0.254 |
| YOLOv10 | 5.4 | 2.59 | 7.9 | 0.259 |
| YOLOv11 | 5.7 | 2.73 | 7.1 | 0.223 |
| our | 7.9 | 3.83 | 7.9 | 0.247 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Li, H.; Dai, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, G.; Nie, S.; Zhang, Z. MRV-YOLO: A Multi-Channel Remote Sensing Object Detection Method for Identifying Reclaimed Vegetation in Hilly and Mountainous Mining Areas. Forests 2025, 16, 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101536
Li X, Li H, Dai J, Liu K, Wang G, Nie S, Zhang Z. MRV-YOLO: A Multi-Channel Remote Sensing Object Detection Method for Identifying Reclaimed Vegetation in Hilly and Mountainous Mining Areas. Forests. 2025; 16(10):1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101536
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xingmei, Hengkai Li, Jingjing Dai, Kunming Liu, Guanshi Wang, Shengdong Nie, and Zhiyu Zhang. 2025. "MRV-YOLO: A Multi-Channel Remote Sensing Object Detection Method for Identifying Reclaimed Vegetation in Hilly and Mountainous Mining Areas" Forests 16, no. 10: 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101536
APA StyleLi, X., Li, H., Dai, J., Liu, K., Wang, G., Nie, S., & Zhang, Z. (2025). MRV-YOLO: A Multi-Channel Remote Sensing Object Detection Method for Identifying Reclaimed Vegetation in Hilly and Mountainous Mining Areas. Forests, 16(10), 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101536






