Impact of Forest Management on Wood Production under Climate Change in the Bonis Catchment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
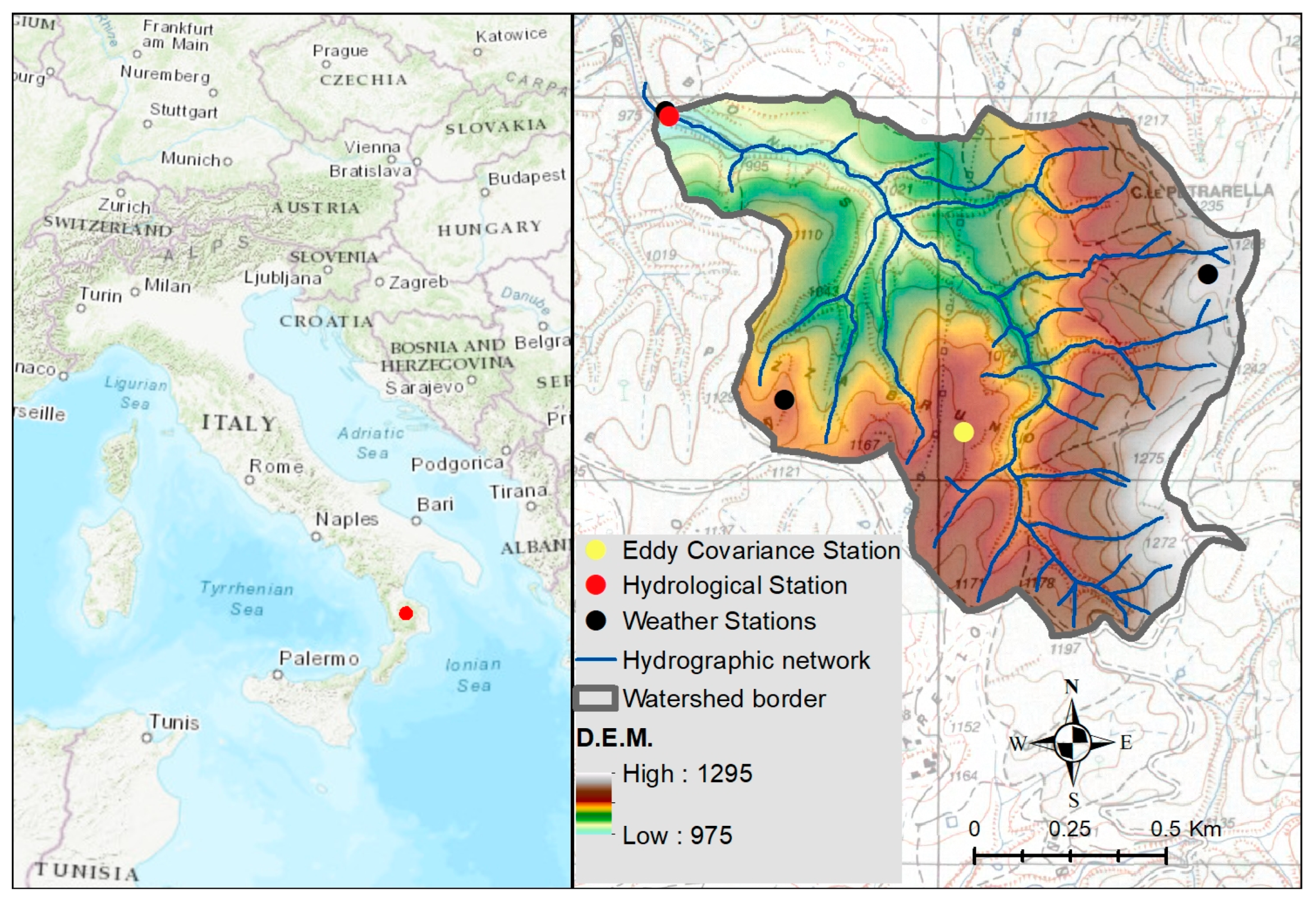
2.1. Study Site
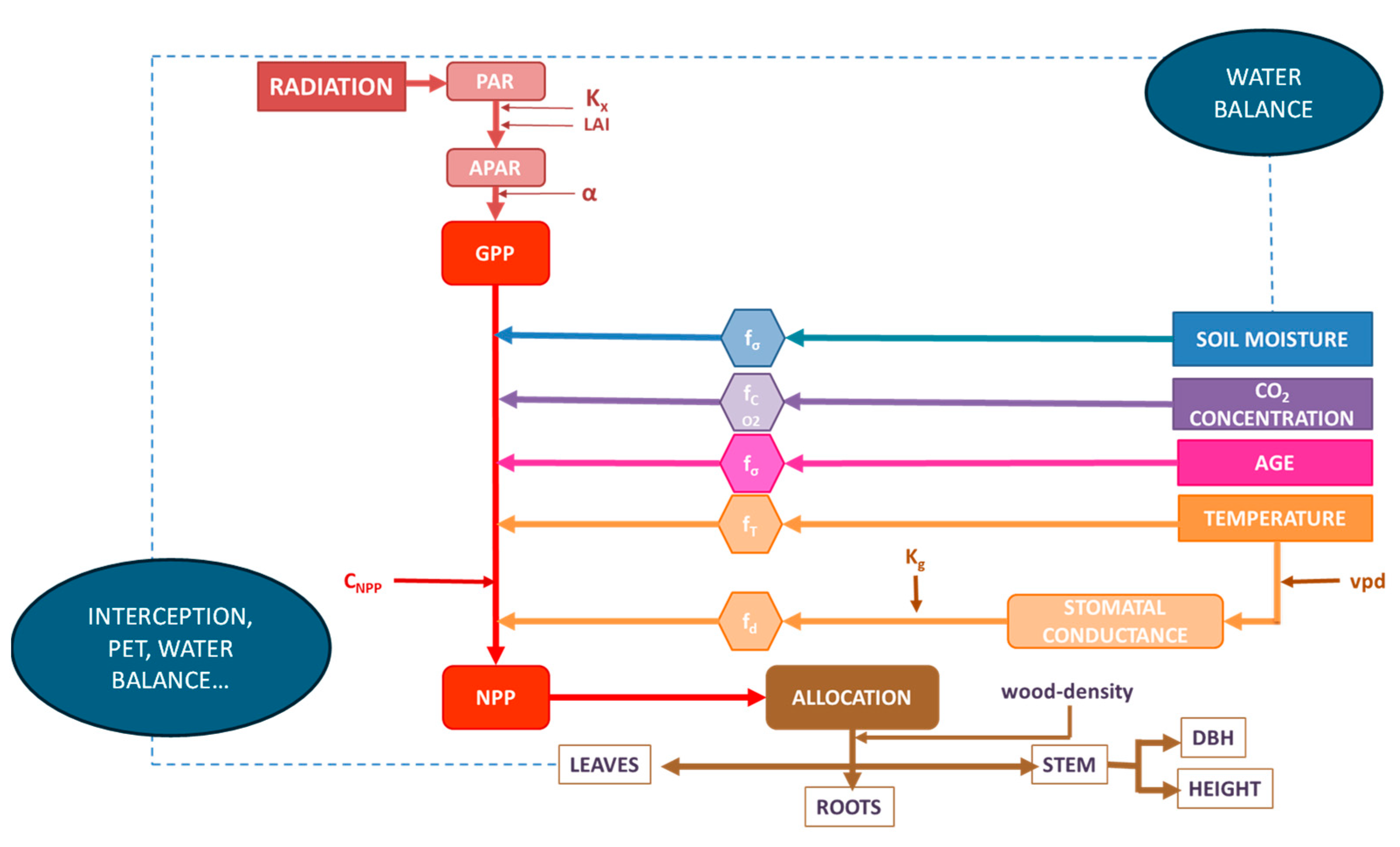
2.2. Model Description
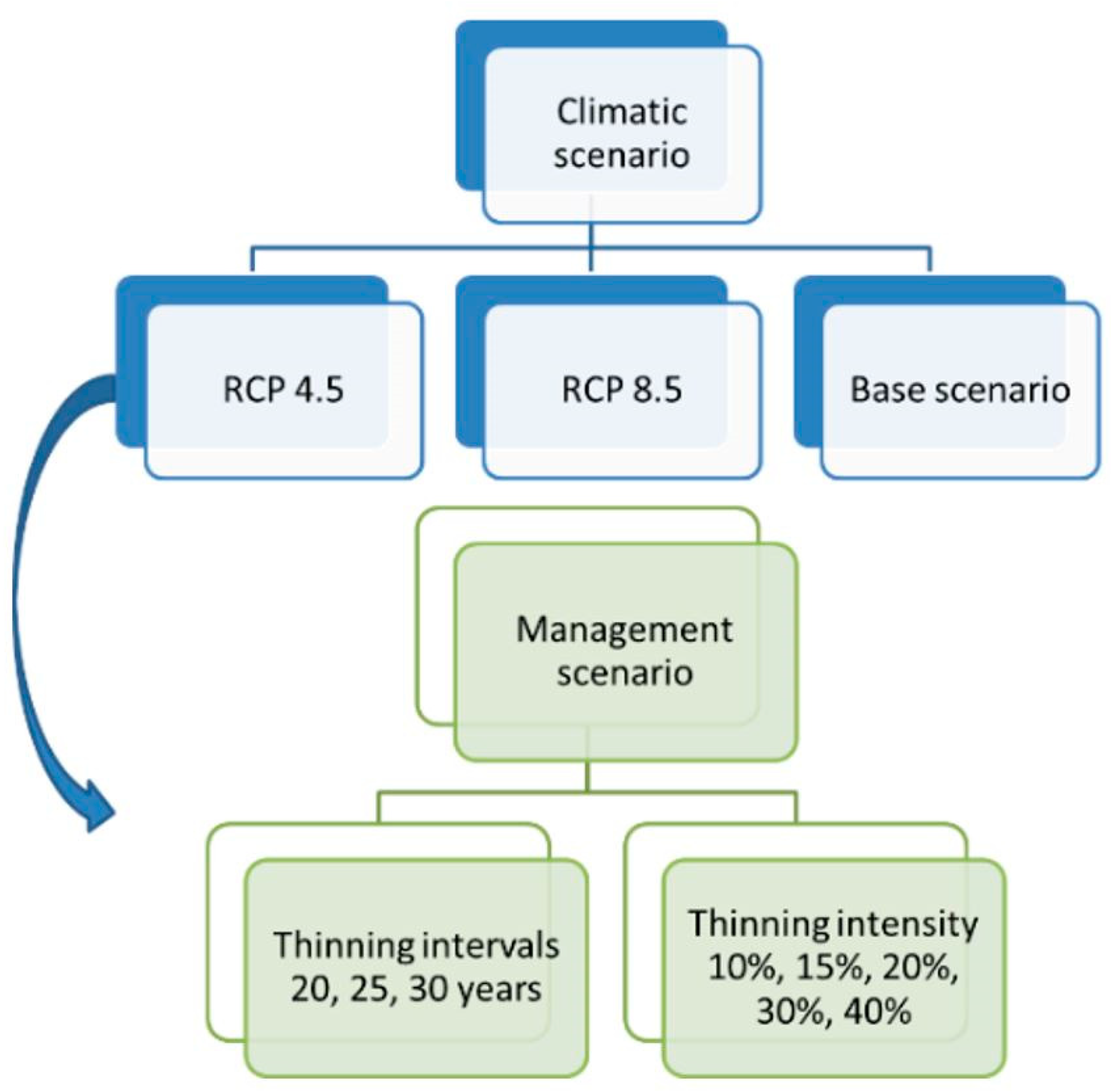
2.3. Management Scenarios
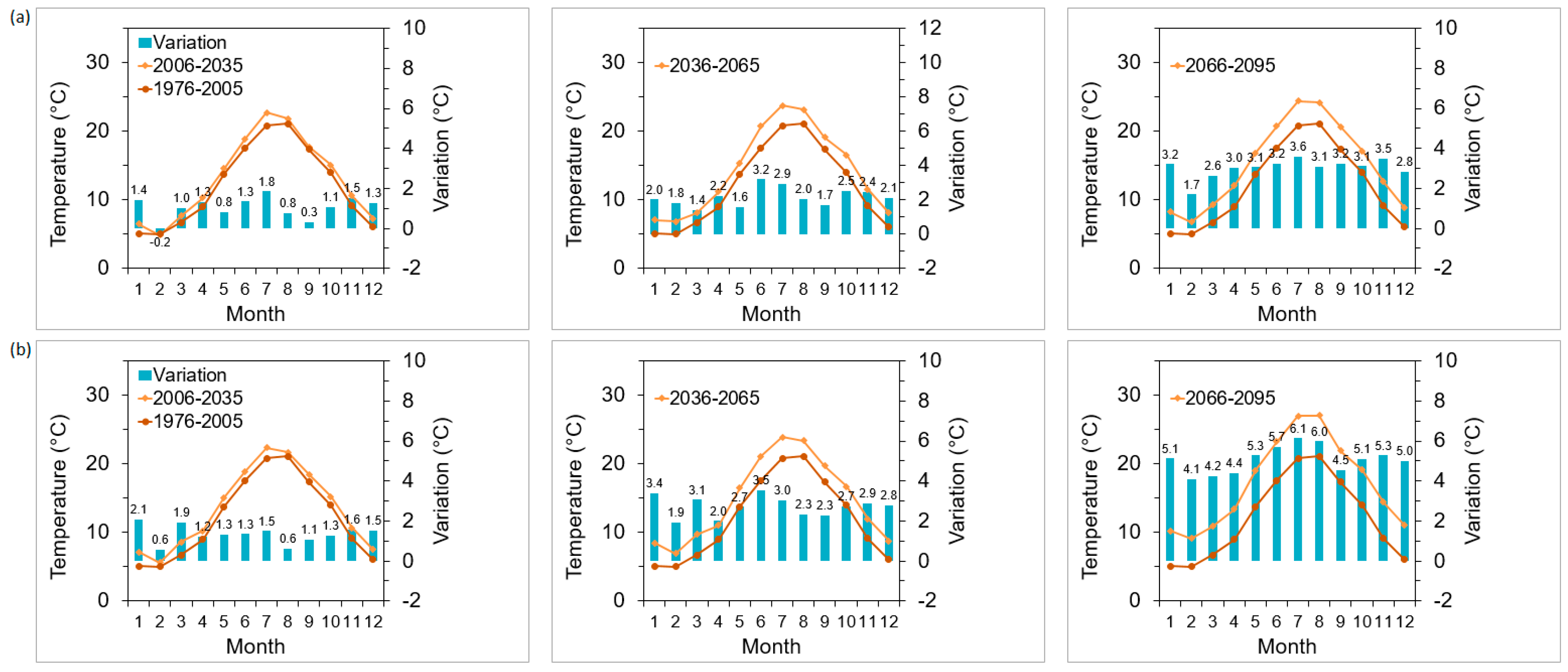
2.4. Climate Scenarios
3. Results and Discussion
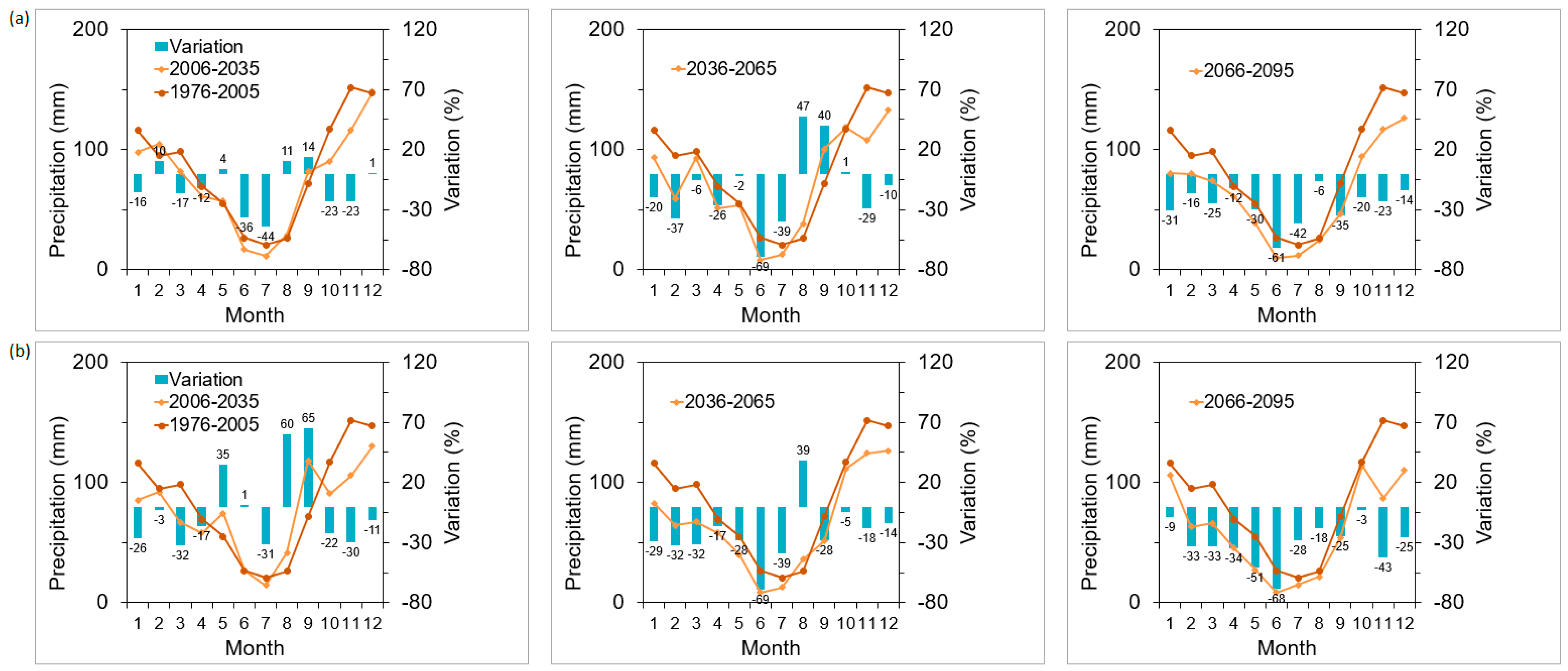
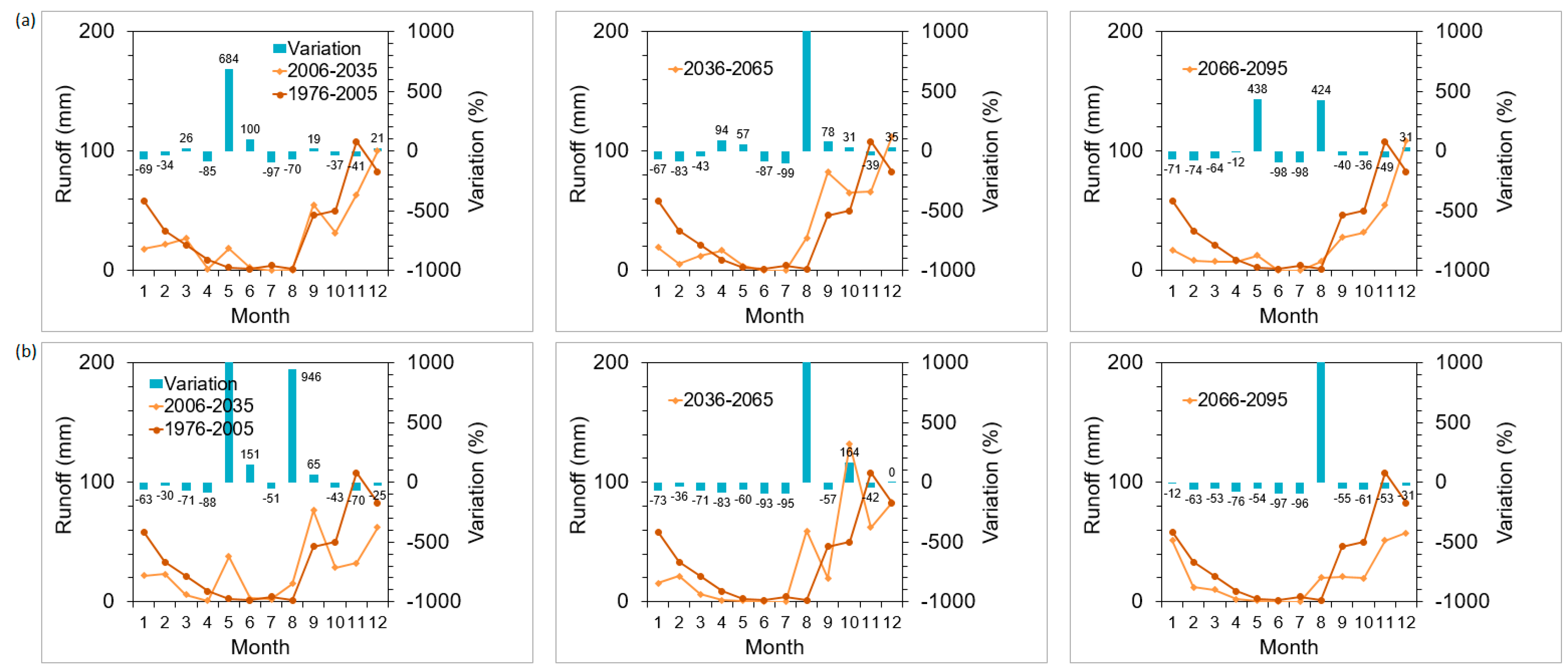
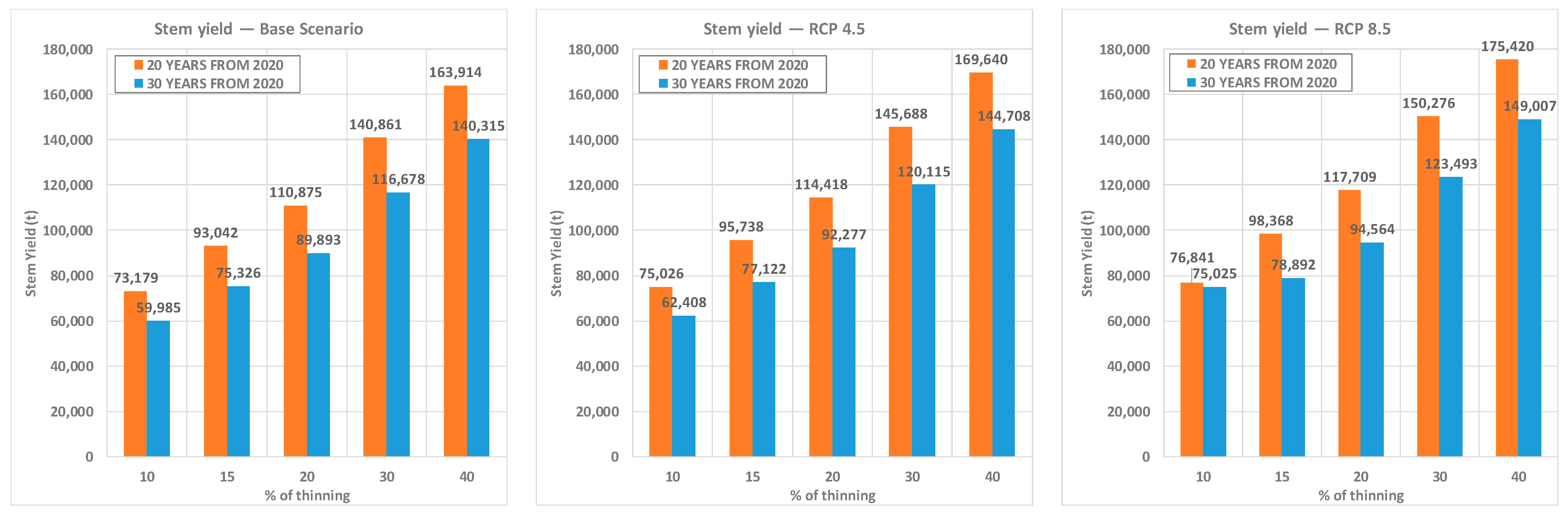
3.1. No-Management Option with Climate Scenario Simulations
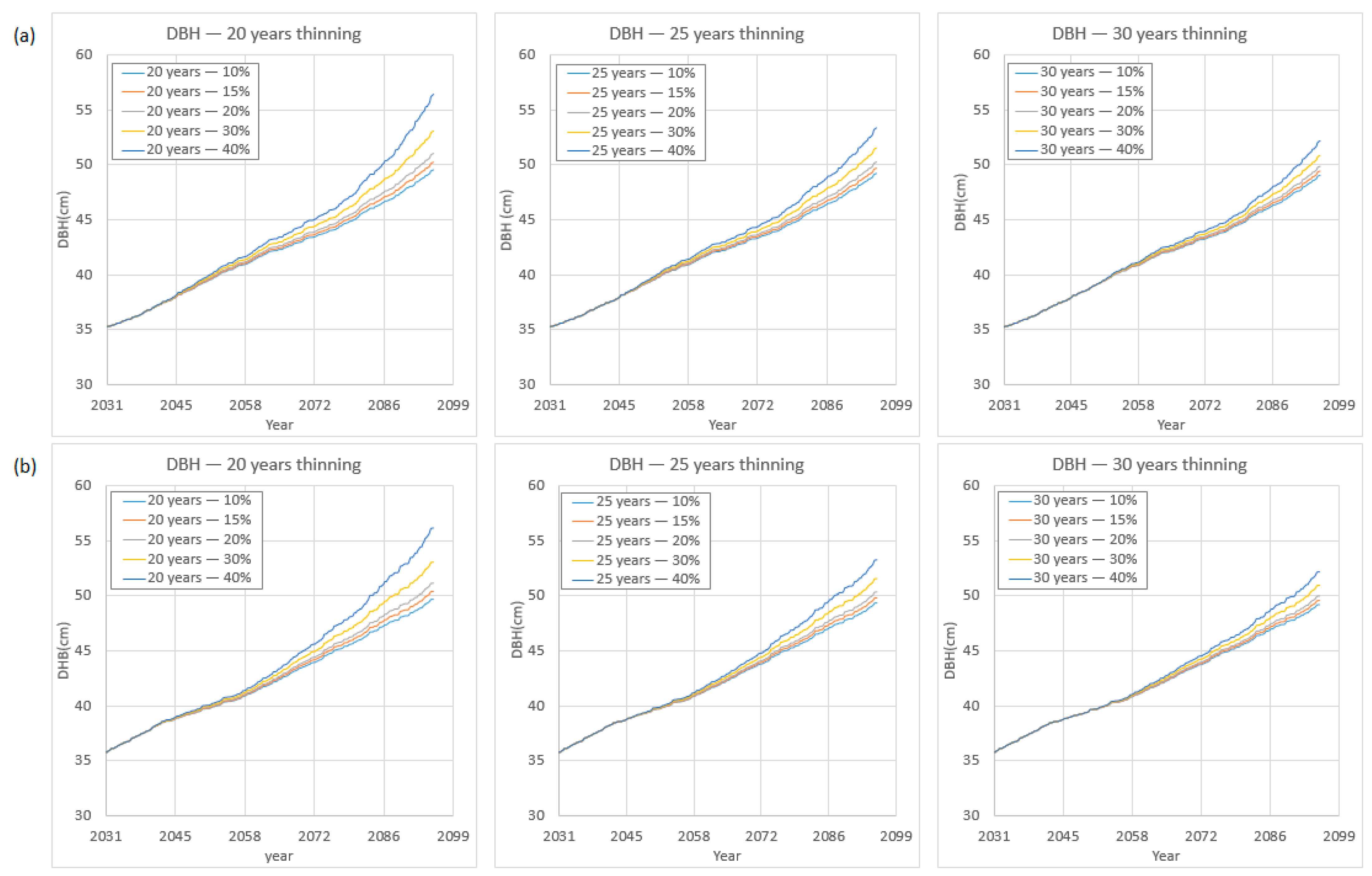
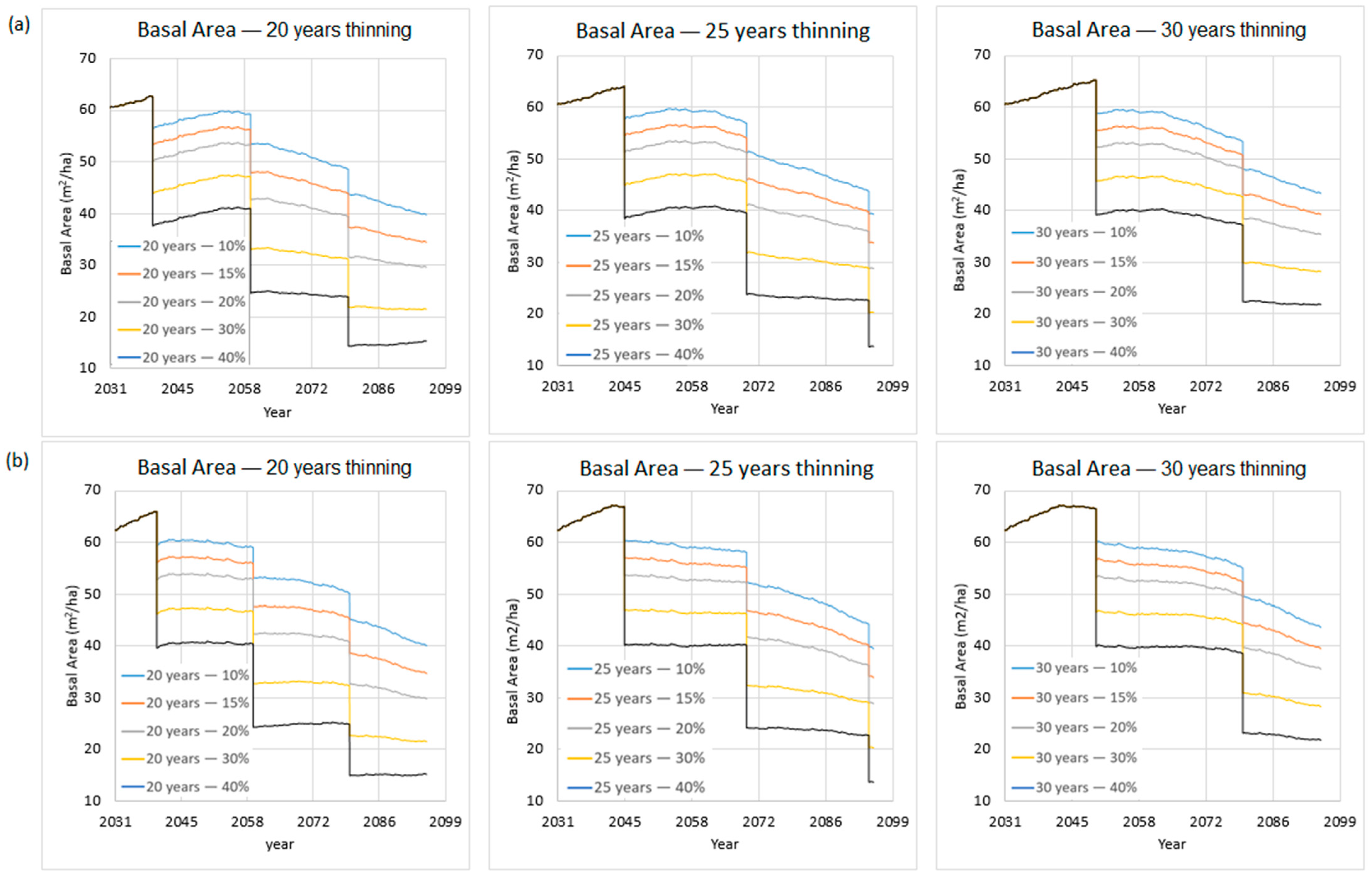
3.2. Management Options and Climate Change Scenario Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bossel, H. TREEDYN3 forest simulation model. Ecol. Model. 1996, 90, 187–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefpour, R.; Temperli, C.; Jacobsen, J.B.; Thorsen, B.J.; Meilby, H.; Lexer, M.J.; Lindner, M.; Bugmann, H.; Borges, J.G.; Palma, J.H.N.; et al. A framework for modeling adaptive forest management and decision making under climate change. Ecol. Soc. 2017, 22. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/26799027 (accessed on 15 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M. Modelling climate effects on diameter growth of red pine trees in boreal Ontario, Canada. Trees For. People 2021, 4, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaheim, A.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Sagadevan, A.A. Integrated modelling approaches to analysis of climate change impacts on forests and forest management. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2011, 16, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WCED. Our Common Future. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 1987.
- Mäkelä, A.; Del Río, M.; Hynynen, J.; Hawkins, M.J.; Reyer, C.; Soares, P.; van Oijen, M.; Tomé, M. Using stand-scale forest models for estimating indicators of sustainable forest management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 285, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, J. Commoditization and the origins of American silviculture. Bull. Sci. Technol. Soc. 2012, 32, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemelä, J.; Young, J.; Alard, D.; Askasibar, M.; Henle, K.; Johnson, R.; Kurttila, M.; Larsson, T.; Matouch, S.; Nowicki, P.; et al. Identifying, managing and monitoring conflicts between forest biodiversity conservation and other human interests in Europe. For. Policy Econ. 2005, 7, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouqueray, T.; Latune, J.; Michel, T.; Frascaria-Lacoste, N. Interdisciplinary modeling and participatory simulation of forest management to foster adaptation to climate change. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 151, 105338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furstenau, C.; Badeck, F.W.; Lasch, P.; Lexer, M.J.; Lindner, M.; Mohr, P.; Suckow, F. Multiple-use forest management in consideration of climate change and the interests of stakeholder groups. Eur. J. For. Res. 2006, 126, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, G.; Cubera, E. Impact of stand density on water status and leaf gas exchange in Quercus ilex. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 254, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.A.; Saha, S.; Bauhus, J. Potential of forest thinning to mitigate drought stress: A meta-analysis. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 380, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M.; Sánchez-Salguero, R.; Rodriguez, C.; Duque Lazo, J.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M.; Palacios-Rodriguez, G.; Camarero, J.J. Is thinning an alternative when trees could die in response to drought? The case of planted Pinus nigra and P. sylvestris stands in southern Spain. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 433, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà-Cabrera, A.; Coll, L.; Martínez-Vilalta, J.; Retana, J. Forest management for adaptation to climate change in the Mediterranean basin: A synthesis of evidence. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 407, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna, T.; Garcia-Chevesich, P.; Neary, D.G.; Scott, D.F.; Benyon, R.G.; Reyna, S.M.; Lábaque, M.; Amani, C.; Pizarro, R.; Iroumé, A.; et al. Forest Management and the Impact on Water Resources: A Review of 13 Countries; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO): Paris, France, 2017; p. 204.
- Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, P. Overview of Ecohydrological Models and Systems at the Watershed Scale. IEEE Syst. J. 2015, 9, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzsch, H.; Grote, R.; Reineking, B.; Rötzer, T.; Seifert, S. Models for forest ecosystem management: A European perspective. Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 1065–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.X.; Li, L.; Zhao, J. A distributed eco-hydrological model and its application. Water Sci. Eng. 2017, 10, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki, M.; Ravazzani, G.; Ceppi, A.; Pellicone, G.; Caloiero, T. Integration of Forest Growth Component in the FEST-WB Distributed Hydrological Model: The Bonis Catchment Case Study. Forests 2021, 12, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresi, F.V.; Maesano, M.; Matteucci, G.; Romagnoli, M.; Sidle, R.C.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G. Root Biomechanical Traits in a Montane Mediterranean Forest Watershed: Variations with Species Diversity and Soil Depth. Forests 2019, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscarelli, R.; Gaudio, R.; Caloiero, T. Climatic trends: An investigation for a Calabrian basin (southern Italy). In The Basis of Civilization–Water Science? Rodda, J.C., Ubertini, L., Eds.; IAHS Publish: Wallingford, UK, 2004; pp. 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrorilli, M.; Rana, G.; Verdiani, G.; Tedeschi, G.; Fumai, A.; Russo, G. Economic Evaluation of Hydrological Ecosystem Services in Mediterranean River Basins Applied to a Case Study in Southern Italy. Water 2018, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabuffetti, D.; Ravazzani, G.; Corbari, C.; Mancini, M. Verification of operational quantitative discharge forecast (QDF) for a regional warning system—The AMPHORE case studies in the upper Po river. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, J.J.; Waring, R.H. A generalized model of forest productivity using simplified concepts of radiation-use efficiency, carbon balance and partitioning. For. Ecol. Manag. 1997, 95, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneta, M.; Silverman, N. A spatially-distributed model to simulate water, energy and vegetation dynamics using information from regional climate models. Earth Interact. 2013, 17, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modelling and assessment, part 1: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veroustraete, F.; Sabbe, H.; Eerens, H. Estimation of carbon mass fluxes over Europe using the C-Fix model and Euroflux data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 376–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoccimarro, E.; Gualdi, S.; Bellucci, A.; Sanna, A.; Giuseppe Fogli, P.; Manzini, E.; Vichi, M.; Oddo, P.; Navarra, A. Effects of tropical cyclones on ocean heat transport in a high-resolution coupled general circulation model. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4368–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buras, A.; Menzel, A. Projecting Tree Species Composition Changes of European Forests for 2061–2090 Under RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 Scenarios. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicone, G. Climate Change Mitigation by Forests: A Case Study on the Role of Management on Carbon Dynamics of a Pine Forest in South Italy. Ph.D. Thesis, Università degli studi della Tuscia–Viterbo, Viterbo, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Collalti, A.; Perugini, L.; Santini, M.; Chiti, T.; Nolè, A.; Matteucci, G.; Valentini, R. A process-based model to simulate growth in forests with complex structure: Evaluation and use of 3D-CMCC Forest Ecosystem Model in a deciduous forest in Central Italy. Ecol. Model. 2014, 272, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornley, J.H.M.; Cannell, M.G.R. Managing forests for wood yield and carbon storage: A theoretical study. Tree Physiol. 2000, 20, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, S.; Montes-Helu, M.; Hart, S.C.; Hungate, B.A.; Koch, G.W.; Moon, J.B.; Finkral, A.J.; Kolb, T.E. Recovery of ponderosa pine ecosystem carbon and water fluxes from thinning and stand-replacing fire. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 3171–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, M.; Tobin, B.; Black, K.; Gioria, M.; Nieuwenhuis, M.; Osborne, B.A. Thinning effects on the net ecosystem carbon exchange of a Sitka spruce forest are temperature-dependent. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 157, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, A.D.; Otsuki, K.; Serengil, Y.; Blanco, J.A.; Yousefpour, R.; Wei, X. A global synthesis on the effects of thinning on hydrological processes: Implications for forest management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 519, 120324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardil, A.; Imbert, J.B.; Camarero, J.J.; Primicia, I.; Castillo, F. Temporal interactions among throughfall, type of canopy and thinning drive radial growth in an Iberian mixed pine-beech forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 252, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, T.D.; Jones, J.A. Summer streamflow deficits from regenerating Douglas-fir forest in the Pacific Northwest USA. Ecohydrology 2017, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, J.; Han, H. Effects of forest thinning on interception and surface runoff in Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation during the growing season. J. Arid Environ. 2020, 181, 104222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Fprn | Parameter to compute allocation factors |
| Sprn | Parameter to compute allocation factors |
| GPP-NPP | GPP/NPP ratio |
| Alpha | Parameter to compute allocation factors |
| wood-density | Wood density |
| Agemax | Maximum age of the plant |
| hdmin: | H/D ratio in carbon partitioning for low |
| phi-theta | Density |
| K | Empirical coefficient of the soil moisture efficiency |
| Albedo | Function for canopy resistance |
| Fpra | H/D ratio in carbon partitioning for low |
| Spra | Density |
| Sla | Plant albedo |
| phi-ea | Parameter to compute allocation factors |
| Canopymax | Parameter to compute allocation factors |
| laimax | Specific leaf area |
| hdmax | Empirical coefficient of the vapor pressure efficiency |
| tcold-leaf | Function for canopy resistance |
| dbhdcmax | Maximum canopy storage capacity |
| dbhdcmin | Maximum leaf area index used |
| denmax | Precipitation interception |
| denmin | H/D ratio in low carbon partitioning |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feki, M.; Ravazzani, G.; Pellicone, G.; Caloiero, T. Impact of Forest Management on Wood Production under Climate Change in the Bonis Catchment. Forests 2024, 15, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030539
Feki M, Ravazzani G, Pellicone G, Caloiero T. Impact of Forest Management on Wood Production under Climate Change in the Bonis Catchment. Forests. 2024; 15(3):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030539
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeki, Mouna, Giovanni Ravazzani, Gaetano Pellicone, and Tommaso Caloiero. 2024. "Impact of Forest Management on Wood Production under Climate Change in the Bonis Catchment" Forests 15, no. 3: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030539
APA StyleFeki, M., Ravazzani, G., Pellicone, G., & Caloiero, T. (2024). Impact of Forest Management on Wood Production under Climate Change in the Bonis Catchment. Forests, 15(3), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030539









