Abstract
Leaf litter quality has been acknowledged as a crucial determinant affecting litter decomposition on broad spatial scales. However, the extent of the contribution of soil fauna to litter decomposability remains largely uncertain. Nor are the effects of leaf size and defensive traits on soil fauna regulating litter decomposability clear when compared to economics traits. Here, we performed a meta-analysis of 81 published articles on litterbag experiments to quantitatively evaluate the response ratio of soil fauna to litter decomposition at the global level. Our results revealed that soil fauna significantly affected litter mass loss across diverse climates, ecosystems, soil types, litter species, and decomposition stages. We observed significantly positive correlations between the response ratio of soil fauna and leaf length, width, and area, whereas the concentrations of cellulose, hemicellulose, total phenols, and condensed tannins were negatively correlated. Regarding economic traits, the response ratio of soil fauna showed no relationship with carbon and nitrogen concentrations but exhibited positive associations with phosphorus concentration and specific leaf area. The mean annual temperature and precipitation, and their interactions were identified as significant moderators of the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition. We evidenced that the contribution of soil fauna to litter decomposability is expected to be crucial under climate change, and that trait trade-off strategies should be considered in modulating litter decomposition by soil fauna.
1. Introduction
Litter, as a multifunctional legacy of plants, plays a pivotal role in driving biogeochemical cycles, while simultaneously providing crucial habitat and food resources for soil organisms [1,2]. The decomposition of litter is a fundamental ecological process that facilitates nutrient cycling and energy transfer, and, ultimately, fosters ecosystem sustainability [3,4]. Abiotic (climatic conditions) and biotic (litter traits, soil fauna, and microbes) factors are crucial drivers of litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems [5,6]. Climatic conditions, primarily temperature and humidity, play pivotal roles: (i) elevated temperatures generally accelerate decomposition by microbial metabolism [7], and (ii) high humidity facilitates microbial activity and enhances litter decomposition. In moist environments, microorganisms can more readily proliferate and decompose organic matter [7,8]. Leaf functional traits also play an essential role in litter decomposition [9], such as stoichiometric traits (e.g., carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentrations), physical traits (e.g., leaf thickness, leaf density, force to tear and punch), and size traits (e.g., leaf length, width, and area). Djukic et al. [10] reported that litter quality and climate accounted for approximately 64–72% of the variability in litter decomposition across 336 global sites, employing standardized substrates for mass loss comparisons. Parton’s [11] model similarly attributes 60–70% of the litter decomposition rate to climatic conditions and litter quality, but the specific contributions of soil fauna to this process remain unclear.
Soil fauna plays an essential role in maintaining the stability of the ecosystem structure and regulating biogeochemical cycles [12]. Owing to the rich species diversity of soil fauna and the intricate relationships among them, identifying the role of a specific species within an ecosystem is often challenging [13]. Therefore, many researchers have used soil biological functional groups as a unit to explore their role in the ecosystem, which can generally be divided into micro-fauna (<0.1 mm; e.g., nematoda, protozoa), meso-fauna (0.1–2 mm; e.g., acari, collembola), and macro-fauna (>2 mm; e.g., myriapoda, coleoptera, oligochaeta) according to body size [14,15,16]. Soil fauna contributes to the litter decomposition process through various mechanisms: earthworms and millipedes facilitate decomposition by ingesting, fragmenting, and mixing the litter with soil, thereby increasing its surface area and accessibility to microorganisms [17,18,19]; insects (larvae and adults) consume leaf litter, mechanically breaking it down and accelerating decomposition, they also introduce microorganisms into the litter through their digestive systems and feces, enhancing decomposition rates [20,21]; Collembola (springtails) and soil mites accelerate litter decomposition by fragmenting organic matter, enhancing nutrient cycling, influencing microbial communities, and modifying soil structure [22,23,24]; and soil nematodes and protozoa can indirectly influence litter decomposition by regulating microbial (bacteria and fungi) populations, which in turn affects decomposition rates [25,26]. Soil fauna can directly affect the physical state of litter and indirectly influence microbial processes and soil structure. The significance of soil fauna in litter decomposition has been widely acknowledged for a long time [5,27,28], but it is uncertain to what extent different soil fauna body sizes or groups have an effect on litter decomposition.
Litter functional traits and soil fauna are recognized as key factors driving litter decomposition [29,30]. The leaf economics spectrum (LES) indicates the trade-off strategies of various functional leaf traits of the “fast–slow” and “acquisitive–conservative” axes [31]. Numerous studies have focused on decomposition and litter economics traits. Most studies have shown the significance of LES and economics traits on litter decomposition: Santiago et al. [32] studied 35 species traits in the tropical rainforest of Panama, and found that the litter decomposition rate was related to the specific leaf area, leaf nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and the leaf decomposition rate was related to the LES that varies from easily decomposable leaves with high nutrient concentrations and high photosynthetic rates to recalcitrant decomposable leaves with low nutrient concentrations and low photosynthetic rates. de la Riva et al. [33] also reported that LES drives the leaf litter decomposition of 20 species in Mediterranean forests. However, the LES explained accounted for only 7–14% of litter decomposition. Therefore, it is necessary to integrate more litter functional traits to explore litter decomposition mechanisms. The size and shape spectrum (SSS) refers to the change axis of traits from small and relatively simple plant organs to larger and more complex-shaped organs, which combined with the LES affect ecological service functions through the afterlife effect of litter [1]. Larger and more complex litter particles (loose layer) provide more habitat for soil fauna to shelter, feed, and reproduce in, whereas smaller litter particles (denser layers) lead to the formation of a small and less hospitable habitat for soil fauna in which it is harder to move and feed [1,34]. Fujii et al. [35] proposed a theory that litter traits (food-traits related to resource economics and stoichiometry, habitat traits related to particle size and shape) provide both food and habitats for soil fauna. Walker et al. [36] conducted a comprehensive analysis of the leaf chemical defense spectrum across 457 tropical and 339 temperate plant species worldwide. These litter traits have an afterlife effect on soil fauna and litter decomposition [37]: (i) traits associated with the LES, including carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and other elements, which can affect the decomposition rate and soil organisms [32]; (ii) traits related to the SSS, including leaf length, leaf width, and leaf area, which moderate the litter layer’s temperature, humidity, and oxygen content, thereby affecting the foraging behavior and nutrient cycling activities of soil fauna [1,27,34]. (iii) traits related to chemical defense spectrum, such as cellulose, total phenol, and the concentrations of condensed tannins, these chemicals may cause leaves to decompose more slowly, thus reducing the available food for soil fauna [38,39]. Current literature concerning litter traits modulating the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition is generally based on study approaches using in situ observations. Although some studies have used meta-analysis methodology to assess this pattern [5,40,41], there is still insufficient knowledge regarding the effect of leaf size traits on the modulation of soil fauna on decomposition rates.
Here, we conducted a meta-analysis to synthesize existing research findings regarding the effects of leaf traits and soil fauna on litter decomposability on a global scale. Our objective is to (i) assess the effects of climate (temperature and precipitation), soil fauna, and litter quality on leaf litter decomposition rates and (ii) explore the patterns of economic traits, size and shape traits, and defensive traits on the soil fauna regulation of litter decomposition. Our associated hypotheses are as follows: (H1) Soil fauna enhance litter decomposition across diverse climate types, ecosystem types, and leaf characteristics, with macro-, meso-, and micro-fauna communities exerting a stronger effect compared to micro- and meso-fauna communities. (H2) Litter economics traits and size traits positively modulate the effect of soil fauna on litter decomposition, while defensive traits have a contrasting opposite effect. (H3) Higher mean annual temperature and higher mean annual precipitation amplify the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposability.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Preparation
Data were systematically collected from two prominent databases: the Web of Science (https://webofscience.clarivate.cn/) and the Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (https://kns.cnki.net/). We searched for published papers spanning from January 1996 to January 2022. Our study focused on studies that examined the contribution of soil fauna to litter decomposition, utilizing a set of keywords: (litter OR leaf OR foliar OR trait) AND (decomposition OR mass loss OR remaining mass OR decomposition rate OR breakdown OR decay or processing) AND (soil fauna OR microfauna OR mesofauna OR macrofauna OR soil invertebrate OR soil animal OR nematoda OR protozoa OR acari OR collembola OR diplura OR symphyla OR enchytraedae OR isoptera OR formicoidea OR diptera OR isoptera OR myriapoda OR arachnida OR coleoptera OR mollusca OR oligochaeta OR microarthropod OR mesoarthropod OR macroarthropod). By employing this rigorous search strategy, we aimed to capture a broad spectrum of relevant literature encompassing various aspects of litter decomposition and the role of the soil fauna therein (Figure S1).
To mitigate potential publication bias, we applied five criteria: (1) Studies were required to quantitatively compare litter mass loss or remaining mass, or to calculate the decomposing constant k in field litterbag experiments involving different soil fauna. (2) The method used to exclude soil fauna must strictly adhere to the physical litterbag method, while chemical methods were not considered in our study. Additionally, it is crucial that the size of the litterbags used in each experiment is reported, as this information is crucial for ensuring consistency and comparability across studies. (3) The experiments must include two data categories: treatments with soil fauna excluded, and treatments with soil fauna present. (4) The data for treatments with soil fauna excluded and present must include information on mean values, standard errors (SE) or standard deviations (SD), and replicates or sample sizes. (5) Published articles must cover a minimum of one of the following 19 variables: litter decomposition characteristics such as mass loss, decomposition rate, remaining mass, and residue rate; economic traits including specific leaf area (SLA), carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus concentration (P); metal elements including sodium, calcium, and magnesium concentration; and defensive traits including cellulose, hemicellulose, total phenols, and condensed tannins concentrations. For size traits, we referred to Flora of China (http://www.iplant.cn/frps, accessed on 15–30 July 2023) and China Virtual Herbarium (https://www.cvh.ac.cn/, accessed on 15–30 July 2023). Leaf length and width were averaged from mature leaves, while leaf shape was represented by the leaf shape index, calculated as the ratio of leaf length to leaf width [42]; The multiplication of leaf length and width exhibits a strong linear relationship with leaf area [43,44,45], thus, leaf length × width was employed for the estimation of leaf area. Overall, the database encompassed research from 81 articles (Supporting Information) conducted at 75 distinct locations (Figure 1)
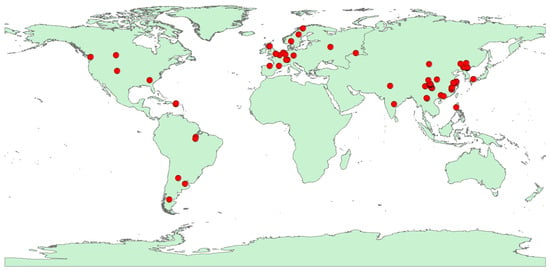
Figure 1.
Geographical distribution of the experimental sites used in this study. Red dots represent sampling spots.
2.2. Meta-Analysis
The log response ratio (lnRR), which serves as an indicator of effect size [46], was used to assess the effect of soil fauna on litter decomposition:
where and represent the average values of the variable with soil fauna present and absent, respectively. The variance (v) of each RR was calculated using:
where nt and nc represent repeated measurements of fauna present and absent, respectively. st and sc represent the standard deviation (SD) of fauna present and absent, respectively. The inverse of variance was utilized as the weighting factor (Wij) for each RR [47], which was calculated as:
The average weighted response ratio (RR++) was calculated by employing the RR from individual pairwise comparisons between fauna present and absent, RRij (i = 1, 2…, m; j= 1, 2…, k):
where m represents different treatment types, and k refers to the number of comparisons between fauna present and absent in the ith treatment type [48].
The standard error (SE) of RR++ was determined as follows:
RR++ ± 1.96 S(RR++) was used to calculate the 95% confidence interval (CI). In instances where the number of observations for evaluating RR++ was less than 20, the bootstrapping method was used [49]. The percentage change in the soil faunal variables affecting litter decomposition was calculated as follows:
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Get Data Graph Digitizer 2.24 software (http://getdata-graph-digitizer.com, accessed on 1–15 July 2023) was used to extract data from published articles. This software facilitated the extraction of numerical information from graphical representations, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data collection process. Meta-analysis and calculation of effect size and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were conducted using Meta Win 2.1.4 (Sinauer Associations Inc., Sunderland, MA, USA). Forest plots were generated using the Sigma Plot 14.0 software (Systat Software Inc., Point Richmond, CA, USA). Linear regression was used to test the relationships between effect size and litter traits. We used R (v.3.6.0) to fit the linear model of relationships between the effect size and climate parameters and selected the best model based on the AIC value [50].
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Soil Fauna on Litter Decomposition
Soil fauna significantly accelerated litter decomposition across various climate zones, ecosystems, and leaf litter types (Figure 2). The effect size value was highest in tropical regions (0.32), followed by subtropical (0.22) and alpine climate zones (0.23), with the lowest observed in temperate zones (0.06) (Figure 2a). The effect size values were comparatively higher in farmland (0.25) and grassland (0.24) compared to wetland (0.21) and forest (0.18) ecosystems (Figure 2b). When considering the different litter types of vegetation, the effect size followed the order: annual herbs (0.25) > evergreen woody plants (0.22) > deciduous woody plants (0.13) > perennial herbs (0.08) (Figure 2d). Sand (0.31) and loam (0.13) had higher effect sizes than clay (−0.16) (Figure 2c). Moreover, the effect size was the highest (0.24) when the decomposition period was less than 180 days, with minimal differences observed between 180–360 days (0.11) and in periods exceeding 360 days (0.11) (Figure 2e). The effect size for communities of micro-, meso-, and macro-fauna (0.22) was higher than that for micro- and meso-fauna communities (0.08) (Figure 2f).
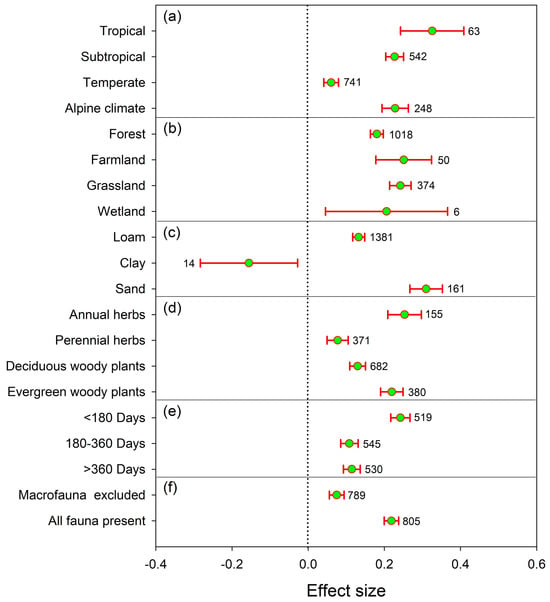
Figure 2.
Mean effect size of soil fauna presence on litter mass loss at global scale. (a–f) represent the climate, ecosystem, soil, litter type, decomposition duration, and faunal community, respectively. The numbers adjacent to each circle represent the sample sizes. For sample sizes below 20, confidence intervals were calculated using bootstrapping. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. The significance of the faunal effect was determined by the absence of overlap between the 95% confidence intervals and zero.
3.2. Effects of Litter Quality on Soil Fauna Modulate Litter Decomposition
Regarding economics traits, P (p < 0.01) and SLA (p < 0.001) had a significant positive correlation with the response ratio of fauna in modulating litter decomposition, whereas C and N showed no significant correlation (Figure 3). In terms of size and shape traits, leaf length (p < 0.05), width (p < 0.01), and area (p < 0.001) had significant positive correlations with the response ratio, but leaf shape had no significant correlation (Figure 4). In contrast to economics and size traits, defensive traits such as cellulose (p < 0.001), hemicellulose (p < 0.01), total phenols (p < 0.05), and condensed tannins concentrations (p = 0.001) were negatively correlated with the response rate (Figure 5). Furthermore, metal elements, such as sodium (p < 0.001), calcium (p < 0.001), and magnesium concentrations (p < 0.001), exhibited significantly positive correlation with the response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss (Figure 6).
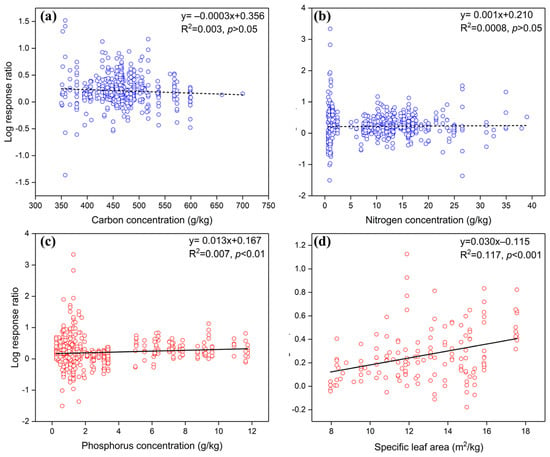
Figure 3.
Effects of initial economics traits on soil fauna regulation of litter decomposition. (a, b, c, d) represent carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus concentration, and specific leaf area, respectively. Blue circles and dashed lines present that there is no statistically significant correlation between the economics traits and response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss, while red circles and solid lines indicate a significant correlation between the economics traits and the response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss.
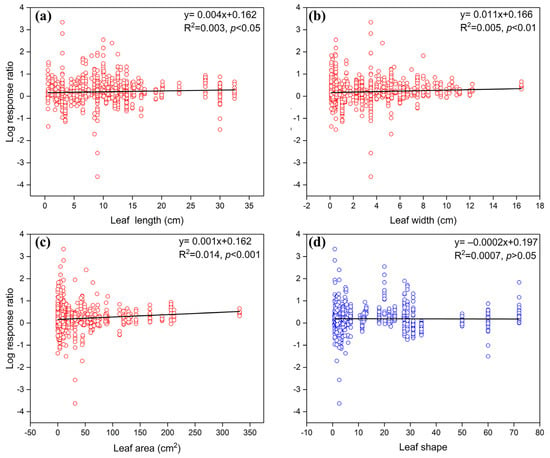
Figure 4.
Effects of initial size and shape traits on soil fauna regulation of litter decomposition. (a, b, c, d) represent leaf length, width, area, and shape, respectively. Blue circles and dashed lines indicate that there is no significant correlation between size–shape traits and the response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss, while red circles and solid lines indicate a significant correlation between size and shape traits and the response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss.
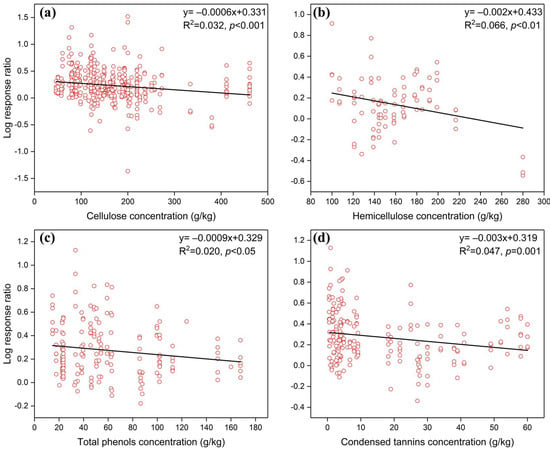
Figure 5.
Effects of initial defense traits on soil fauna regulation of litter decomposition. (a, b, c, d) represent cellulose, hemicellulose, total phenols, and condensed tannins concentrations, respectively. Solid lines indicate a significant correlation between the defensive trait response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss.
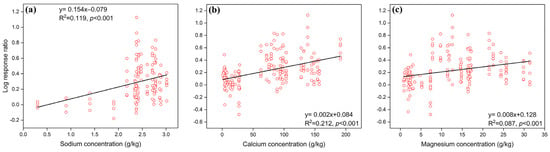
Figure 6.
Effects of initial metal elements on soil fauna regulation of litter decomposition. (a, b, c) represent sodium, calcium, and magnesium concentrations, respectively. Solid lines indicate a significant correlation between metal elements and the response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss.
3.3. Effects of Climate on Soil Fauna Modulate Litter Decomposition
Mean annual temperature and mean annual precipitation had positive effect on the modulation of litter decomposition by soil fauna. There was a significant correlation between the mean annual temperature, mean annual precipitation, and the response ratio of soil fauna regulating litter decomposition (Figure 7, p < 0.001). Linear model analysis and its AIC value showed that the mean annual temperature (p < 0.001), mean annual precipitation (p < 0.001), and the interaction between mean annual temperature and mean annual precipitation (p < 0.05) together affect the response ratio of fauna to leaf litter decomposition (Table 1).
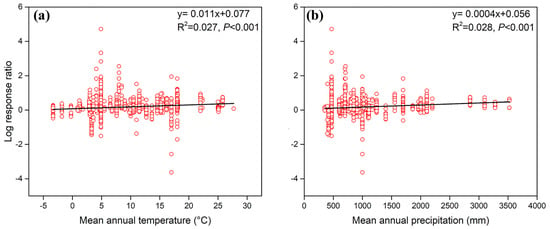
Figure 7.
Effects of mean annual temperature (a) and precipitation (b) on soil fauna regulation of litter decomposition. Solid lines indicate that there is a significant correlation between the mean annual temperature or precipitation and the response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss.

Table 1.
Effects of mean annual temperature, precipitation, and their interactions on the response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss based on a linear model.
4. Discussion
4.1. Positive Effect of Soil Fauna on Litter Decomposition
Our meta-analysis revealed that soil fauna significantly accelerated the decomposition of leaf litter globally across various climate types, ecosystem categories, and leaf litter types (Figure 2a,b,d). In a case study meta-analysis, Kampichler and Bruckner [51] reported a significant negative effect of microarthropods on litter decomposition. But more studies are consistent with our findings: a meta-analysis of forests, grasslands, and farmland by García-Palacios et al. [5] confirmed the positive influence of soil fauna on litter decomposition rates, but the 95% confidence interval in coniferous forests overlaps with the zero line. Zan et al. [41] reported that in a meta-analysis of Chinese forests, soil fauna also increased the litter decomposition rate in forest ecosystems, with the greatest effect on tropical forests and the least effect on boreal forests, but in temperate forests the 95% confidence interval overlaps with the zero line. Additionally, Xu et al. [40] found that soil fauna significantly increased decomposition in various forest ecosystems worldwide. With more data from in situ litterbag experiments in recent years, our study reinforces the notion that soil fauna play a positive role in leaf litter decomposition.
In various soil types, our analysis revealed that sand and loam had higher effect size com-pare to clay (Figure 2c). This result may be because the soil textures can affect the soil fauna community [52]; on the other hand, it may also be affected by the small sample size, warranting further investigation with more detailed data. In this study, we considered the duration of decomposition and the different groups of soil fauna. Our findings indicate that the response ratio during the early stages of decomposition (<180 days) exceeded that of the middle and late stages (Figure 2e), which is consistent with previous studies [53,54]. Furthermore, we observed a better decomposition effect in the presence of soil macro-fauna, and the effect of micro- and meso-fauna communities was much lower than that of micro-, meso-, and macro-fauna communities (Figure 2f). These results generally support the first hypothesis that the soil fauna enhances the litter decomposition across diverse climate types, ecosystem types, and leaf characteristics, with macro-, meso-, and micro-fauna communities exerting a stronger effect compared to micro- and meso-fauna communities. However, Data from Siedento [55] and Bradford et al. [56] indicated that coarse meshes had a considerable effect on litter mass loss (25%). Additionally, Kampichler and Bruckner [51] reported in their meta-analysis that microarthropods had no effect on mass loss when considering the litterbag size effect. Therefore, further exploration of the effect of litterbag size should be considered in studies investigating the regulation of leaf litter decomposition by soil fauna.
4.2. Climate and Litter Quality Moderate the Effects of Soil Fauna on Litter Decomposition
Climate and initial litter quality are the primary factors affecting decomposition rates globally, with models indicating that they account for approximately 60–70% of the variability in decomposition rates [9,11]. This study delves deeper into the impact of climate and initial litter traits on the regulation of litter decomposition by soil fauna. We found that both mean annual temperature and precipitation had significant positive effects on the fauna’s regulation of litter decomposition (Figure 7), consistent with the global-scale findings of García-Palacios et al. [5] and Xu et al. [40]. Further linear model analysis revealed that mean annual temperature, precipitation, and their interaction together affect the modulation of soil fauna on litter decomposition (Table 1), thus validating our third hypothesis that higher mean annual temperature and precipitation amplify the effects of fauna on litter decomposability. García-Palacios et al. [5] demonstrated through a structural equation model that climate characteristics, SLA, and the C/N ratio were the primary drivers of differences in litter decomposition rates. The climate characteristics (mean annual temperature and precipitation), SLA, C, and N were verified in our study. Thus, litter traits, such as size and defensive traits. serves as a valuable complement by incorporating essential size and defensive functional traits.
Initial C, N, P, and SLA are key traits of the economic spectrum [31,33]. Our study revealed that SLA and P significantly influence the effect of soil fauna on litter decomposition, whereas C and N did not modulate the effect of soil fauna on decomposition (Figure 3). Similar findings were observed in moist tropical forests and dry tropical forests, C had a significant effect in deciduous forests and N in evergreen broad-leaved forests [40], which indicates that the impact of initial C and N on the regulation of decomposition rates by soil fauna varies across different vegetation types. N and carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratios have been identified as modulators of faunal effects on litter decomposition in Chinese forests [41]. While C/N ratios were not considered in this study, it may be that the C/N ratio of litter leaves reflects the impact of soil fauna on decomposition. Although a meta-analysis in global forests found that initial P had no effect on soil fauna regulating litter decomposition rates [40]. This disparity can be attributed to the fact that our meta-analysis also considered farmland, grassland, and wet ecosystems, covering a wider range of ecosystem types.
Leaf length, width, area, and shape are essential traits of the size and shape spectrum [1]. In this study, we used data from the Flora of China to evaluate the average length and width of litter leaves, subsequently calculating the leaf area and shape index [45], which is a pioneering effort to investigate the relationship between size–shape traits and soil fauna regulating litter decomposability. Notably, our findings demonstrate that leaf length, width, and area significantly influence the effect of soil fauna on decomposition, while leaf shape does not exert a modulating effect (Figure 4). Hence, future research endeavors should emphasize the initial size traits of leaf litter. Furthermore, our results highlight the significant positive effect of sodium, calcium, and magnesium concentrations in the initial litter (Figure 6) on the regulation of litter decomposition by soil fauna. These findings underscore the crucial role of metal elements in mediating the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition, necessitating further investigation in subsequent research.
Cellulose, hemicelluloses, total phenols, and condensed tannins are constituents of the defense spectrum [36,57,58,59], all of which had a significant negative correlation with the influence of fauna on litter decomposition (Figure 5). Cellulose, characterized by its complex structure, plays a pivotal role in regulating the later stages of forest litter decomposition, and litter with high cellulose and hemicellulose contents is usually difficult to decompose [60,61]. In an analysis of forest ecosystems worldwide, Xu et al. [40] reported that cellulose predominant impact on soil fauna in forest litter decomposition, aligning with the findings of our study (Figure 5a). Meanwhile, the same effect was also found for the initial hemicellulose concentration (Figure 5b). Total phenols and condensed tannins, as chemicals with intricate structures, were also found to significantly inhibit the effects of fauna on litter decomposition in this study. Zan et al. [41] reported a similar inhibitory effect of tannins on litter decomposition in Chinese forest ecosystems. It can be concluded that these defensive traits exert negative effects, not only altering the decomposition rate of leaf litter, but also affecting the ability of fauna to regulate litter decomposability.
The correlations between the response ratio of soil fauna to mass loss and economics traits (e.g., P and SLA), size traits (e.g., leaf length, width, and area), defensive traits (e.g., cellulose, hemicellulose, total phenols, and condensed tannins concentrations), and climate (e.g., mean annual temperature and precipitation) although significant, are very weak (about 1%). This is due to the large number of studies used [62,63], the predictive value of such weak dependencies is possibly small, which sometimes gave opposite results. In our study, although there was such a weak dependence, the results are basically consistent with those of previous studies. A meta-analysis of Xu et al. [40] reported that cellulose, temperature, and precipitation predominantly affect the soil fauna involved in forest litter decomposition. García-Palacios et al. [5] found that litter quality and climate conditions regulate the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition through a global scale meta-analysis. Zan et al. [41] reported that the correlation between the soil fauna’s effect size and cellulose content was negative in Chinese forests. In this study, we classified according to the type of litter quality such as economics traits, size and shape traits, and defensive traits, which are trade-off core traits for LES, SSS, and a defense spectrum [1,35,36,64]. That is, each type of trait has similar regulatory mechanism, thus our results for each trait type had similar trends and these values are reliable. Moreover, the published articles do not have enough data to explore the spectra and faunal regulation of litter decomposition, while the traits used to construct the spectra (LES, SSS, and defense spectrum) can be determined using economics traits, size and shape traits, and defensive traits.
5. Conclusions
This study conducted a meta-analysis of litter quality modulating the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposability. Our findings demonstrate that soil fauna significantly accelerated the decomposition rate across diverse climates (e.g., tropical, subtropical, temperate, and alpine climate zones), ecosystems (e.g., forest, grassland, wetland, and farmland), and litter types (e.g., evergreen woody plants, deciduous woody plants, annual herbs, and perennial herbs), respectively. Furthermore, we show that the combined influence of climate factors (mean annual temperature and precipitation) and litter quality serves as a robust predictor of the contribution of soil fauna to litter decomposability across different biomes. Climate change, particularly warming temperatures and increasing precipitation patterns, exerts a moderating effect on the role of soil fauna in litter decomposition. It highlights that leaf size traits (e.g., leaf length, width and area) and SLA positively modulate the effect of soil fauna on litter decomposition. Conversely, defensive traits such as cellulose, hemicellulose, total phenols, and the concentration of condensed tannins exert a counteractive effect compared to size traits. Our results emphasize the importance of soil fauna and litter quality in shaping leaf litter decomposition, suggesting that leaf size and defensive traits differently modulate the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://doi.org/10.57760/sciencedb.10380 and https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f15030481/s1, Figure S1. Steps taken in a systematic quantitative literature review in meta-analysis. Supporting Information Article List.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.W. and J.Z.; methodology, D.W.; formal analysis, D.W.; investigation, F.Y., W.X. and D.W.; writing—original draft preparation, D.W.; visualization, D.W.; supervision, J.Z. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Knowledge Innovation Program of Wuhan–Basic Research (2022020801010166); China Scholarship Council (No. 202104910380, for D.W.).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to the administrative staff of the host laboratory (UMR AMAP 0931, France) for their support in making the first author’s one-year stay as a visiting researcher possible. We are also very grateful to Zhun MAO (INRAE) for his suggestions on this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Dias, A.T.C.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Berg, M.P. Litter for life: Assessing the multifunctional legacy of plant traits. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.P.; Fornara, D.; Yang, H.; Yu, R.P.; Callaway, R.M.; Li, L. Plant litter strengthens positive biodiversity–ecosystem functioning relationships over time. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2023, 38, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.B.; Sims, R.E.H. Litter decomposition and nutrient release via litter decomposition in New Zealand eucalypt short rotation forests. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 75, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giweta, M. Role of litter production and its decomposition, and factors affecting the processes in a tropical forest ecosystem: A review. J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 44, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Palacios, P.; Maestre, F.T.; Kattge, J.; Wall, D.H. Climate and litter quality differently modulate the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition across biomes. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Palacios, P.; Shaw, E.A.; Wall, D.H.; Hättenschwiler, S. Temporal dynamics of biotic and abiotic drivers of litter decomposition. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butenschoen, O.; Scheu, S.; Eisenhauer, N. Interactive effects of warming, soil humidity and plant diversity on litter decomposition and microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1902–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Gulledge, J.M.; Clein-Curley, J.S.; Lindstrom, J.E.; Braddock, J.F. Moisture effects on microbial activity and community structure in decomposing birch litter in the Alaskan taiga. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, W.K.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Amatangelo, K.; Dorrepaal, E.; Eviner, V.T.; Godoy, O.; Hobbie, S.E.; Hoorens, B.; Kurokawa, H.; Pérez-Harguindeguy, N.; et al. Plant species traits are the predominant control on litter decomposition rates within biomes worldwide. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djukic, I.; Kepfer-Rojas, S.; Schmidt, I.K.; Larsen, K.S.; Beier, C.; Berg, B.; Verheyen, K.; Caliman, A.; Paquette, A.; Gutiérrez-Girón, A.; et al. Early stage litter decomposition across biomes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 1369–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parton, W.; Silver, W.L.; Burke, I.C.; Grassens, L.; Harmon, M.E.; Currie, W.S.; King, J.Y.; Adair, E.C.; Brandt, L.A.; Hart, S.C.; et al. Global-scale similarities in nitrogen release patterns during long-term decomposition. Science 2007, 315, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Peñuelas, J.; Vesterdal, L.; Yue, K.; Peguero, G.; Fornara, D.A.; Hedenec, P.; Steffens, C.; Wu, F.Z. Responses of soil fauna communities to the individual and combined effects of multiple global change factors. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 25, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.H.; Bradford, M.A. Assessing the functional implications of soil biodiversity in ecosystems. Ecol. Res. 2001, 16, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.C.; Whitman, W.B. Linking species richness, biodiversity and ecosystem function in soil systems. Pedobiologia 2005, 49, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaëns, T. Macroecological patterns in soil communities. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, E. Spare a thought for the teeming ecosystem beneath your feet. Science 2020, 370, 1255–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Wang, F.; Fanin, N.; Pang, M.; Dou, P.; Wang, H.; Qian, S.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.; Mi, X.; et al. Soil fauna promote litter decomposition but do not alter the relationship between leaf economics spectrum and litter decomposability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 107519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, M.; Kautz, G.; Topp, W. Do woodlice and earthworms interact synergistically in leaf litter decomposition? Funct. Ecol. 2005, 19, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcamo, H.A.; Abe, T.A.; Prescott, C.E.; Holl, F.B.; Chanway, C.P. Influence of millipedes on litter decomposition, N mineralization, and microbial communities in a coastal forest in British Columbia, Canada. Can. Eur. J. For. Res. 2000, 30, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M. Succession, diversity and trophic relationships of some soil animals in decomposing leaf litter. J. Anim. Ecol. 1975, 44, 475–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.P.; Ferran, A.; Gambier, J.; Meyran, J.C. Taste sensitivity of detritivorous mosquito larvae to decomposed leaf litter. J. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 28, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, P.M.; McNamara, N.P.; Chaplow, J.; Stott, A.W.; Black, H.I.J. Translocation of surface litter carbon into soil by Collembola. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Z.; Warren, M.W.; Chen, J. Mechanical fragmentation enhances the contribution of Collembola to leaf litter decomposition. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2012, 53, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickings, K.; Grandy, A.S. The oribatid mite Scheloribates moestus (Acari: Oribatida) alters litter chemistry and nutrient cycling during decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, N.Z.; Whitford, W.G. The role of microarthropods and nematodes in decomposition in a semi-arid ecosystem. Oecologia 1982, 55, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Koenning, S.R.; Hu, S. Root-parasitic nematodes enhance soil microbial activities and nitrogen mineralization. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 46, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.J.; Heal, O.W.; Anderson, J.M. Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. In The Quarterly Review of Biology; Anderson, D.J., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkely, CA, USA, 1979; Volume 56, p. 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seastedt, T.R. The role of microarthropods in decomposition and mineralization processes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1984, 29, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresch, S.; Frey, D.; Le Bayon, R.C.; Zanetta, A.; Rasche, F.; Fliessbach, A.; Moretti, M. Litter decomposition driven by soil fauna, plant diversity and soil management in urban gardens. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1614–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristok, C.; Leppert, K.N.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Niklaus, P.A.; Bruelheide, H. Soil macrofauna and leaf functional traits drive the decomposition of secondary metabolites in leaf litter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.J.; Reich, P.B.; Westoby, M.; Ackerly, D.D.; Baruch, Z.; Bongers, F.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Chapin, T.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Diemer, M.; et al. The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 2004, 428, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, L.S. Extending the leaf economics spectrum to decomposition: Evidence from a tropical forest. Ecology 2007, 88, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Riva, E.G.; Prieto, I.; Villar, R. The leaf economic spectrum drives leaf litter decomposition in Mediterranean forests. Plant Soil 2019, 435, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.S.; Ota, A.T.; Fujii, S.; Seino, T.; Kabeya, D.; Okamoto, T.; Ito, M.T.; Kaneko, N.; Hasegawa, M. Biotic homogenization and differentiation of soil faunal communities in the production forest landscape: Taxonomic and functional perspectives. Oecologia 2015, 177, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Berg, M.P.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. Living litter: Dynamic trait spectra predict fauna composition. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.W.N.; Schrodt, F.; Allard, P.M.; Defossez, E.; Jassey, V.E.J.; Schuman, M.C.; Alexander, J.M.; Baines, O.; Baldy, V.; Bardgett, R.D.; et al. Leaf metabolic traits reveal hidden dimensions of plant form and function. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossa, G.G.O.; Schaefer, D.; Zhang, J.L.; Tao, J.P.; Cao, K.F.; Corlett, R.T.; Cunningham, A.B.; Xu, J.C.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Harrison, R.D. The cover uncovered: Bark control over wood decomposition. J. Ecol. 2018, 106, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, M.E.; Lamont, B.B.; Fairbanks, M.M.; Rafferty, C.M. Plant structural traits and their role in anti-herbivore defence. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2007, 8, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.C.; Wang, L.; Cao, T.T.; He, W.H.; Lu, S.X.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Chang, T.; Tian, X.J. Legacy effect of plant chemical defence substances on litter decomposition. Plant Soil 2023, 487, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.J.; Cao, P.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Wang, W.F.; Ruan, H.H. Cellulose dominantly affects soil fauna in the decomposition of forest litter: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2020, 378, 114620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, P.; Mao, Z.; Sun, T. Effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition in Chinese forests: A meta-analysis. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.J.; Liu, M.D.; Yu, X.J.; Gielis, J.; Ratkowsky, D.A. Proportional relationship between leaf area and the product of leaf length and width of four types of special leaf shapes. Forests 2019, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, V.; Rouphael, Y.; Gyves, E.M.D.; Bignami, C. A simple model for estimating leaf area of hazelnut from linear measurements. Sci. Hortic. 2007, 113, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L. Leaf shape alters the coefficients of leaf area estimation models for Saussurea stoliczkai in central Tibet. Photosynthetica 2012, 50, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Zou, D.T.; Shrestha, N.; Xu, X.T.; Wang, Q.G.; Jia, W.; Wang, Z.H. Spatiotemporal variation in leaf size and shape in response to climate. J. Plant Ecol. 2020, 13, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, I.A.; Dieleman, W.; Luyssaert, S.; Subke, J.A.; Reichstein, M.; Ceulemans, R.; Ciais, P.; Dolman, A.J.; Grace, J.; Matteucci, G.; et al. Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Zhou, X.H.; Zhang, B.C.; Lu, M.; Luo, Y.Q.; Liu, L.L.; Li, B. Different responses of soil respiration and its components to nitrogen addition among biomes: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.J.; Zhou, H.K.; Yao, B.Q.; Wang, W.Y.; Dong, S.K.; Shang, Z.H.; She, Y.D.; Ma, L.; Huang, X.T.; Zhang, Z.H.; et al. Effects of nutrient addition on degraded alpine grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Kampichler, C.; Bruckner, A. The role of microarthropods in terrestrial decomposition: A meta-analysis of 40 years of litterbag studies. Biol. Rev. 2009, 84, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. Effects of macrofauna on soil properties in tropical ecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1988, 24, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couteaux, M.M.; Bottner, P.; Berg, B. Litter decomposition, climate and liter quality. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1995, 10, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Zhao, R.D.; Tian, Q.X.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, F. Predominant effects of litter chemistry on lignin degradation in the early stage of leaf litter decomposition. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhorst, S.; Wardle, D.A. Microclimate within litter bags of different mesh size: Implications for the ‘arthropod effect’ on litter decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.A.; Tordoff, G.M.; Jones, T.H.; Newington, J.E. Microbiota, fauna, and mesh size interactions in litter decomposition. Oikos 2002, 99, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.N.; Wallsgrove, R.M. Secondary metabolites in plant defence mechanisms. New Phytol. 1994, 127, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Tsukamoto, J.; Rahman, M.M.; Yoneyama, A.; Mostafa, K.M. Lignin and its effects on litter decomposition in forest ecosystems. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 29, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Liu, J.F.; Gao, W.Q.; Deng, Y.P.; Ni, Y.Y.; Xiao, Y.H.; Kang, F.F.; Wang, Q.; Lei, J.P.; Jiang, Z.P. Defense pattern of Chinese cork oak across latitudinal gradients: Influences of ontogeny, herbivory, climate and soil nutrients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClaugherty, C.; Berg, B. Cellulose, lignin and nitrogen concentrations as rate regulating factors in late stages of forest litter decomposition. Pedobiologia 1987, 30, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretto, A.; Di Nardo, C.; Papa, S.; Fuggi, A. Lignin and cellulose degradation and nitrogen dynamics during decomposition of three leaf litter species in a Mediterranean ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, R.; Rubin, D.B. A simple, general purpose display of magnitude of experimental effect. J. Educ. Psychol. 1982, 74, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G.; Fidler, F.; Kalinowski, P.; Lai, J. The statistical recommendations of the American Psychological Association Publication Manual: Effect sizes, confidence intervals, and meta-analysis. Aust. J. Psychol. 2012, 64, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarelli, D.; Bona, C.; Carta, A. Coordination between leaf and root traits in Mediterranean coastal dune plants. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 25, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).