A Digital Management System for Monitoring Epidemics and the Management of Pine Wilt Disease in East China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. The Data Collection
2.2.1. Manual Survey
2.2.2. UAV-Based Survey
2.2.3. Satellite Remote Sensing
2.3. Data Input into the DFP SYSTEM
2.4. Data Processing Within the DFP
2.5. Orleans Distributed Map Service System in DFP System
2.6. Establishment of Native Libraries of DFP System
2.7. Nacos Dynamic Configuration Service in DFP System
2.8. PWD Detection from UAV Images Based on Deep-Learning Algorithms
3. Results
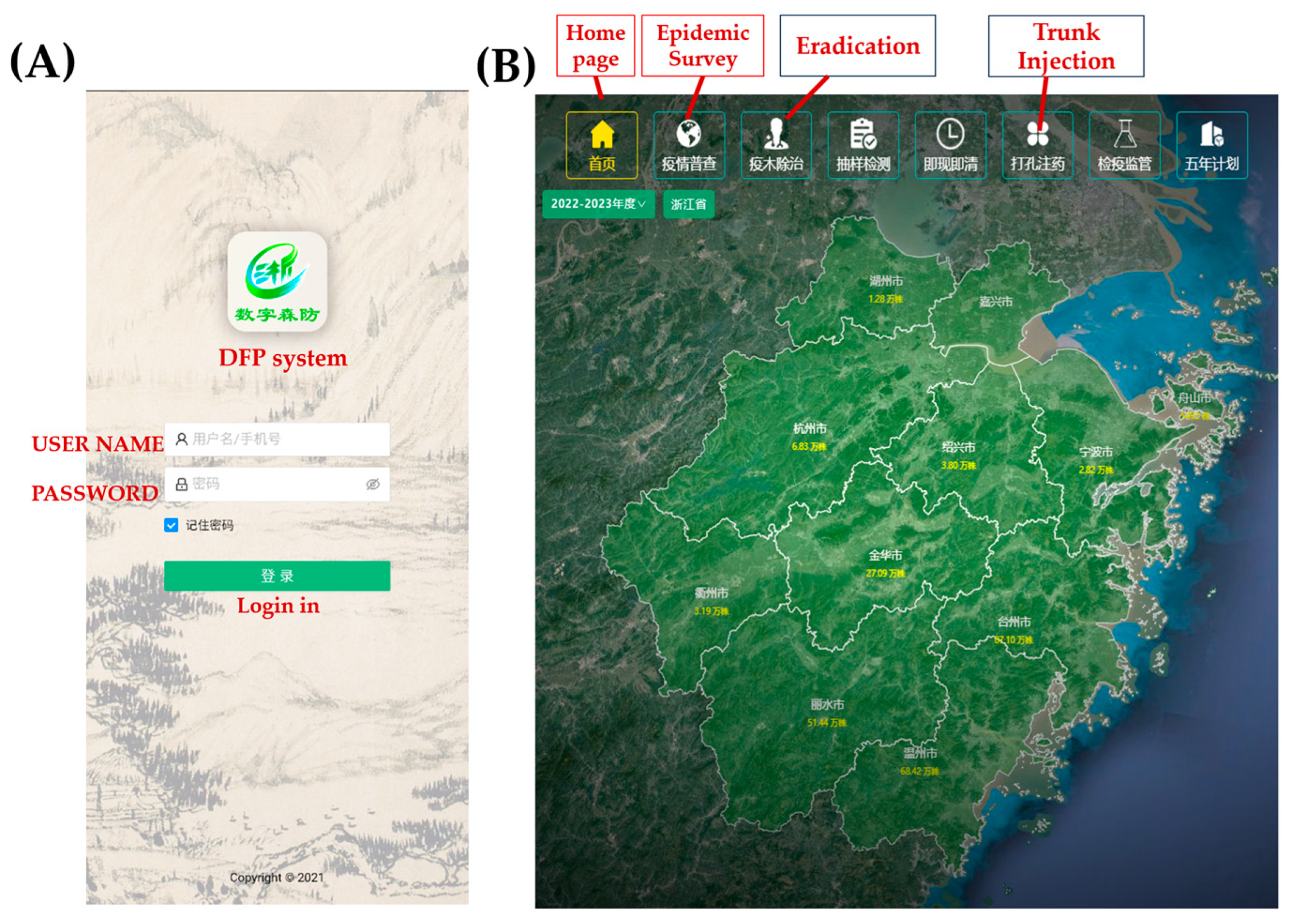
3.1. Development of DFP System
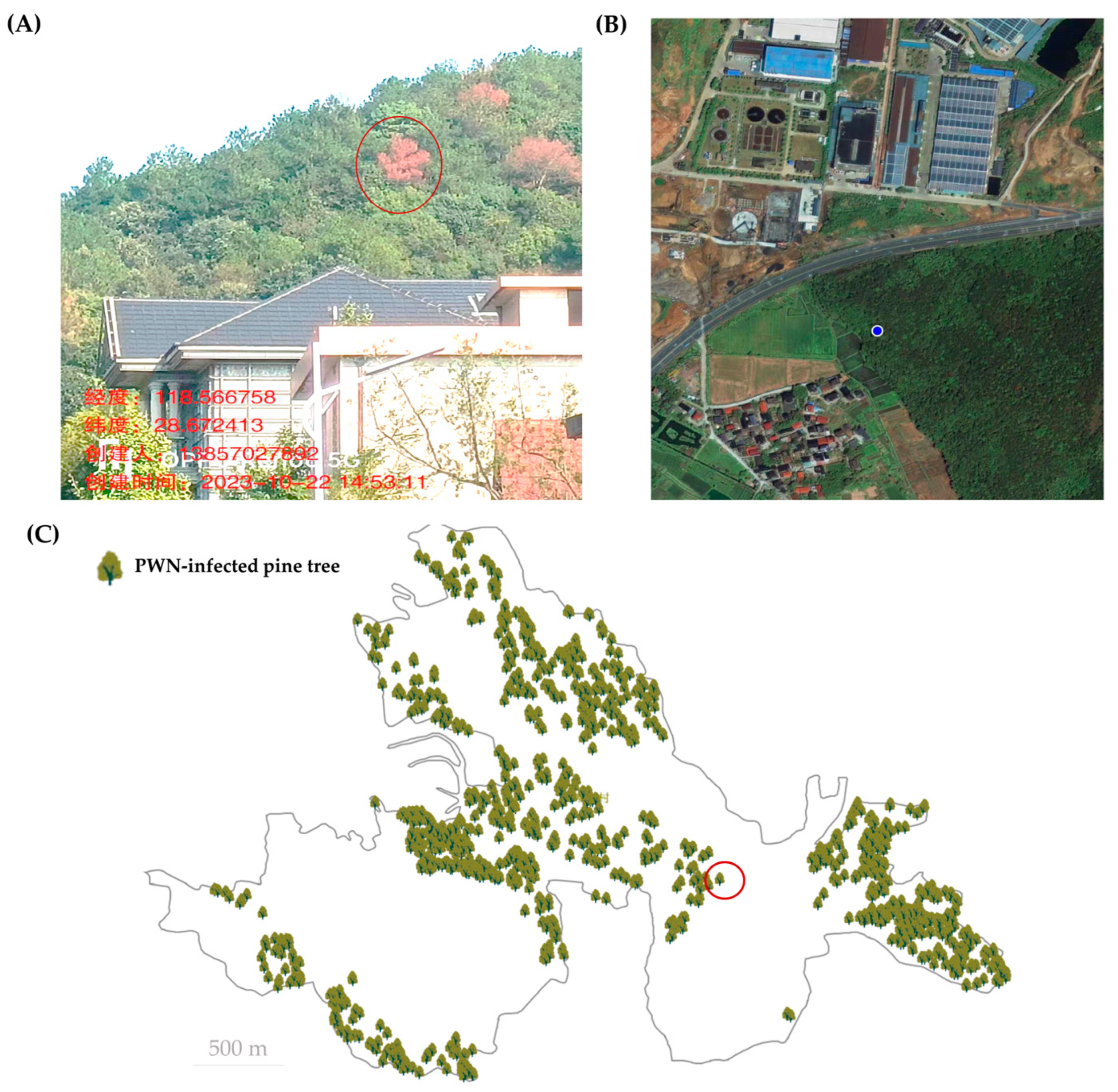
3.2. Data Collection Using Manual Epidemic Survey Module in DFP System
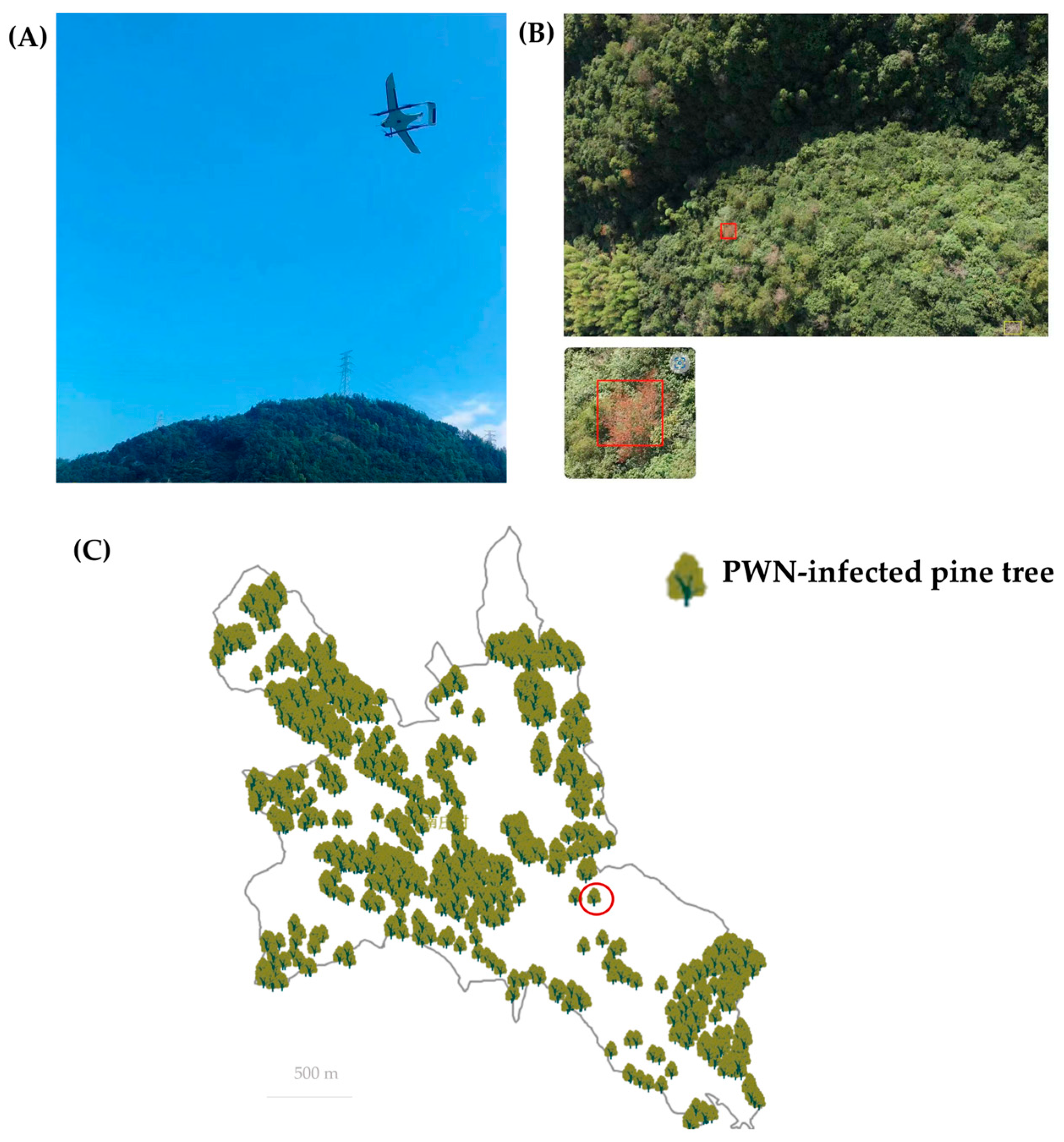
3.3. Data Collection Using UAV Epidemic Survey Module in DFP System
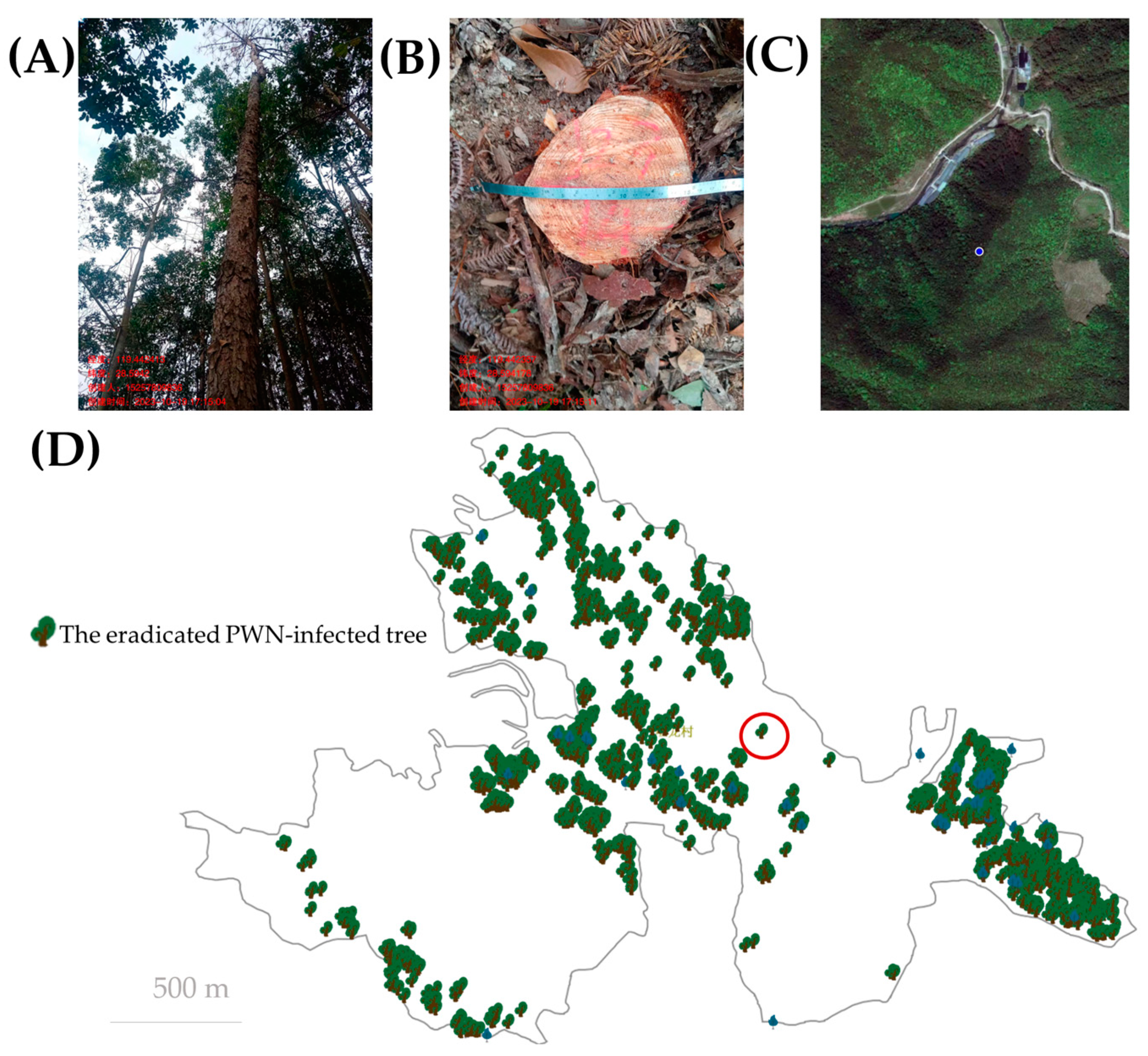
3.4. Eradication Monitoring and Data Collection Module in DFP System
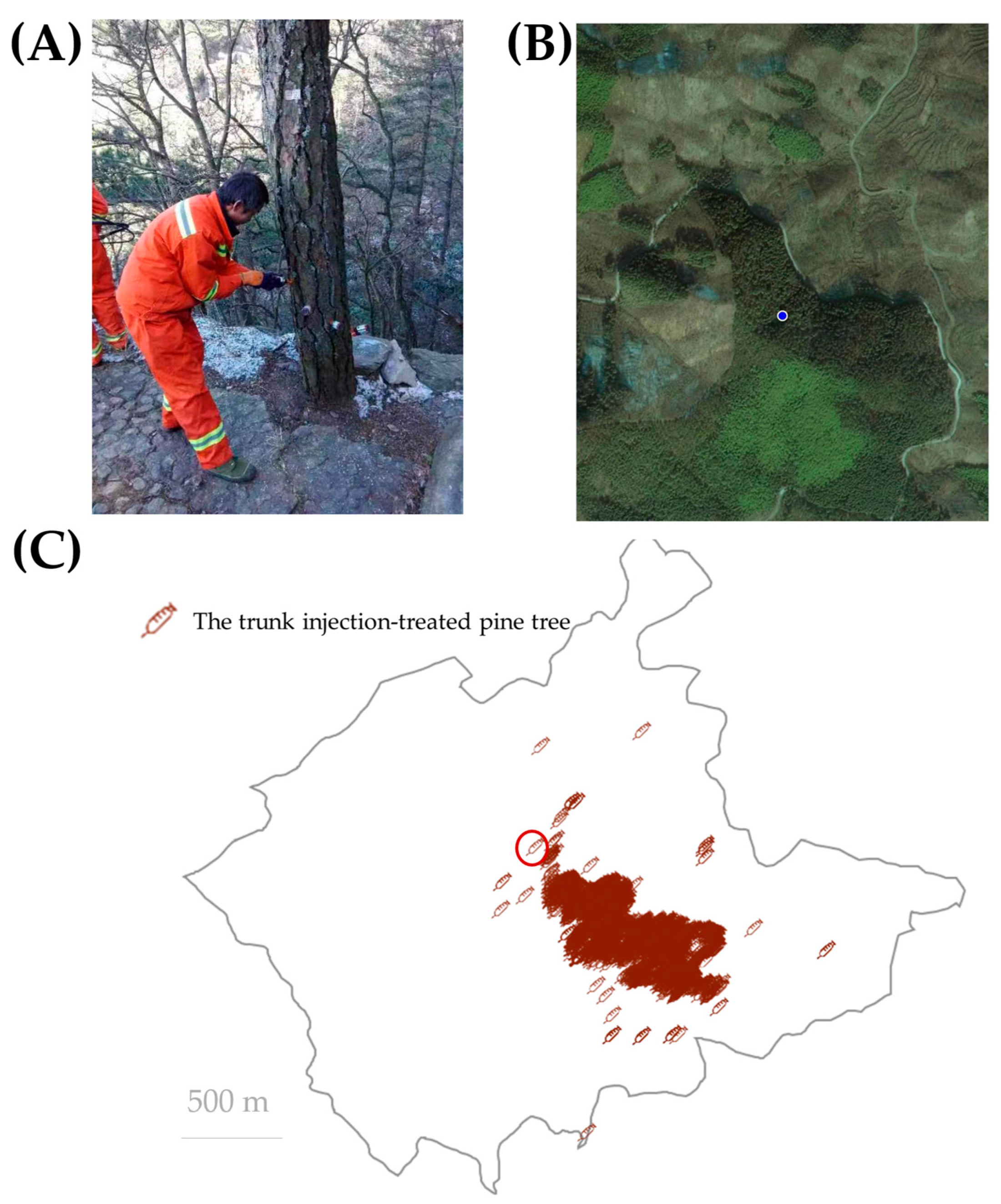
3.5. Trunk Injection Monitoring and Data Collection Module in DFP System
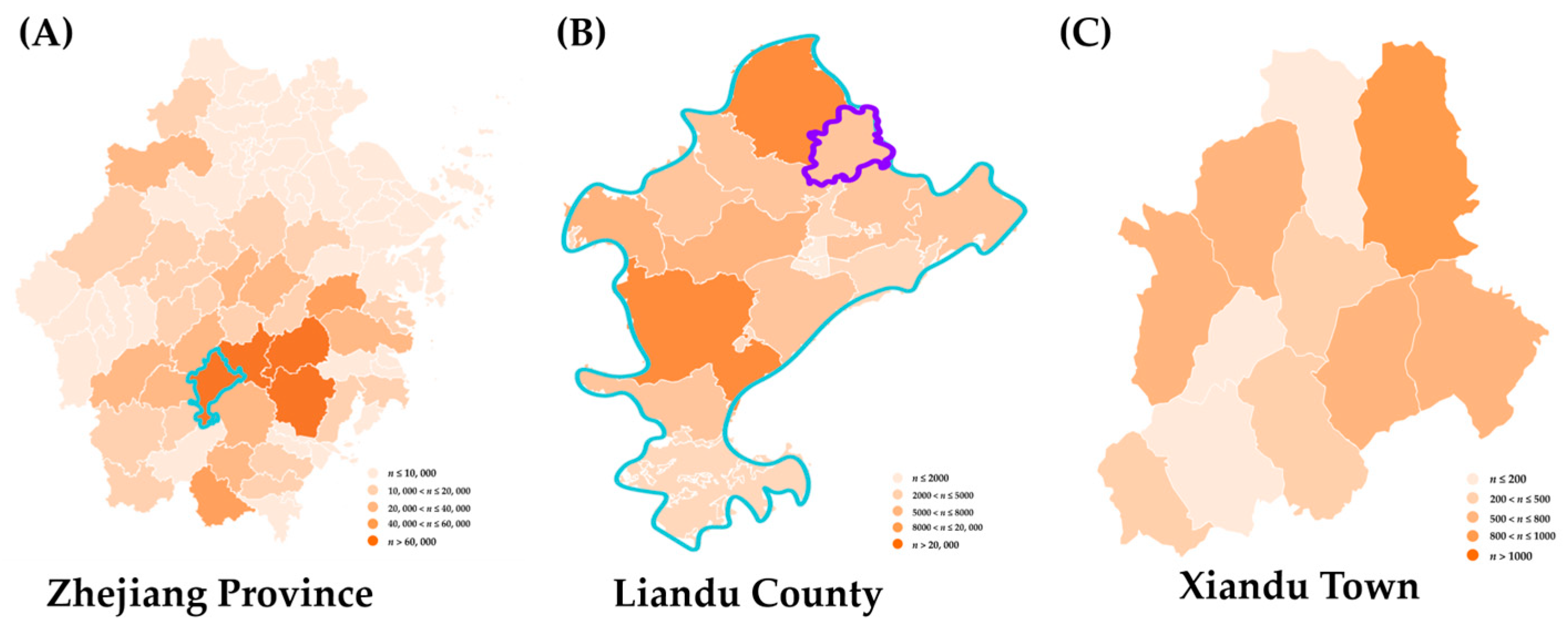
3.6. Epidemic Dynamic of PWD in Different Geographical Scale Based on the DFP System
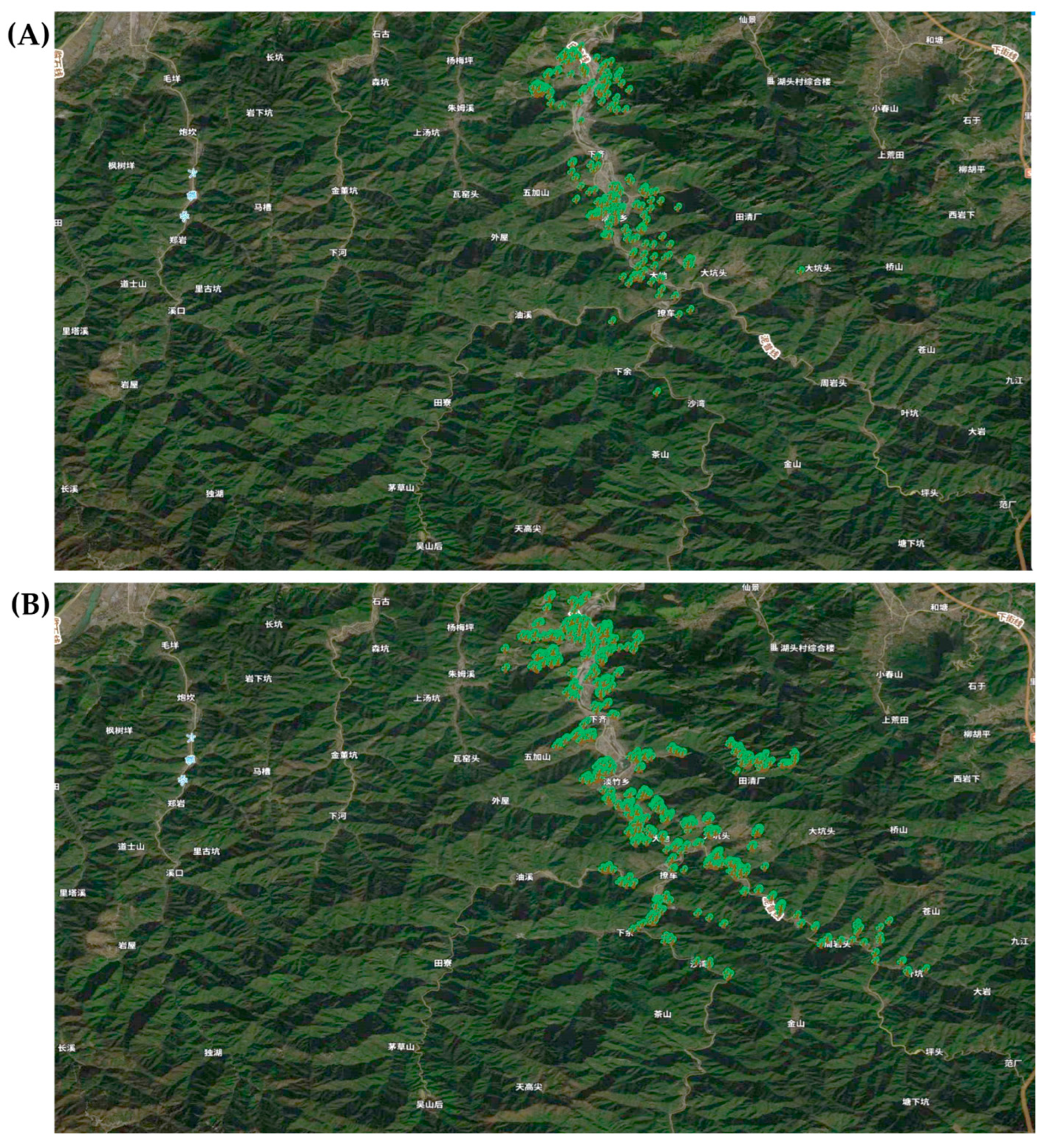
3.7. Spatial Trajectory of PWD Epidemic Based on the DFP System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mariette, N.; Hotte, H.; Chappé, A.-M.; Grosdidier, M.; Anthoine, G.; Sarniguet, C.; Colnard, O.; Kersaudy, E.; Paris, M.-T.; Koen, E.; et al. Two decades of epidemiological surveillance of the pine wood nematode in France reveal its absence despite suitable conditions for its establishment. Ann. For. Sci. 2023, 80, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPPO. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and its vectors: Procedures for official control. EPPO Bull. 2012, 42, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, C.; Espada, M.; Vieira, P.; Mota, M. Pine wilt disease: A threat to European forestry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2011, 133, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.R. Epidemic status of pine wilt disease in China and its prevention and control techniques and counter measures. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2019, 55, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.L.; Mota, M.; Vieira, P.; Butcher, R.A.; Sun, J.H. Interspecific communication between pinewood nematode, its insect vector, and associated microbes. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Su, H.J.; Ding, T.T.; Huang, J.X.; Liu, T.; Ding, N.; Fang, G.F. Refined assessment of economic loss from pine wilt disease at the subcompartment scale. Forests 2023, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futai, K. Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rands, S.; Robinet, C.; Roques, A.; Pan, H.; Fang, G.; Ye, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Role of human-mediated dispersal in the spread of the pinewood nematode in China. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Ding, X.L.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, F.M. The detection of pine wilt disease: A literature review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, M.A.; Bonifácio, L.; Inacio, M.L.; Mota, M.; Boa, E. Pine wilt disease: A global threat to forestry. Plant Pathol. 2024, 73, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzman, M.; Bàrberi, P.; Birch, A.N.E.; Boonekamp, P.; Dachbrodt-Saaydeh, S.; Graf, B.; Hommel, B.; Jensen, J.E.; Kiss, J.; Kudsk, P.; et al. Eight principles of integrated pest management. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1199–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, S.; Stamps, W.T. Insect vectors of the pinewood nematode: A review of the biology and ecology of Monochamus species. For. Pathol. 2012, 42, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, A.; Rasinmäki, J.; Eyvindson, K.; Chambers, P. A mobile phone application for the collection of opinion data for forest planning purposes. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Mora, S.; Preisler, Y.; Duarte, F.; Prasad, V.; Ratti, C. Tools and methods for monitoring the health of the urban greenery. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, R.F.; Wempe, A.M.; Becker, R.M.; Zimbelman, E.G.; Nagler, E.S.; Gilbert, S.L.; Caudill, C.C. Positioning methods and the use of location and activity data in forests. Forests 2019, 10, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, M.D.; Mantas, V.; Baltazar, E.; Pauly, K.; Lewyckyj, N. A machine learning approach to detecting pine wilt disease using airborne spectral imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.K.; Park, S.B.; Shim, B.S. Diagnosis of pine wilt disease using remote wireless sensing. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Luo, Y.Q.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.D.; Wu, D.W.; Ren, L.L. Early detection of pine wilt disease using deep learning algorithms and UAV-based multispectral imagery. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2021, 497, 119493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.D.; Liu, Z.Y.; Shen, W.X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Ge, C.K.; Sun, F.G.; Lan, P. A remote sensing and airborne edge-computing based detection system for pine wilt disease. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 66346–66360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; Choi, K.; Cho, W.; Chang, B.; Ko, D.W. Efficient dead pine tree detecting method in the forest damaged by pine wood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus) through utilizing unmanned aerial vehicles and deep learning-based object detection techniques. For. Sci. Technol. 2022, 18, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.L.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, H.C. Identifying pine wood nematode disease using UAV images and deep learning algorithms. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Ye, H.C.; Lu, W.; Huang, W.J.; Wu, B.; Hao, Z.Q.; Sun, H. A spatiotemporal change detection method for monitoring pine wilt disease in a complex landscape using high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.; Hassan, S.S.; Yang, L.; Ma, M.; Li, C. Detection Methods for Pine Wilt Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Plants 2024, 13, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Tong, Z.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Z. Detection and location of dead trees with pine wilt disease based on deep learning and UAV remote sensing. AgriEngineering 2020, 2, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, L.Y.; Zhuo, R.; Chen, W.D.; Duan, R.; Wang, G.S. A dataset for forestry pest identification. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 857104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.W.; Kong, X.N.; Xie, L.; Chen, K.Y.; Liao, Y.Y.; Fan, B.W.; Wang, K.L. Forest pest identification based on a new dataset and convolutional neural network model with enhancement strategy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.W.; Xie, M.; Koski, T.M.; Li, Y.S.; Zhou, H.; Song, J.Y.; Gong, C.Q.; Fang, G.F.; Sun, J.H. Epidemiological model including spatial connection features improves prediction of the spread of pine wilt disease. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Lin, Q.N.; Du, H.Q.; Chen, C.; Hu, M.C.; Chen, J.J.; Huang, Z.H.; Xu, Y.X. Detection of the infection stage of pine wilt disease and spread distance using monthly UAV-based imagery and a deep learning approach. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syifa, M.; Park, S.J.; Lee, C.W. Detection of the pine wilt disease tree candidates for drone remote sensing using artificial intelligence techniques. Engineering 2020, 6, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Research progress on the early monitoring of pine wilt disease using hyperspectral techniques. Sensors 2020, 20, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Zhai, J.; Zhou, C.; Xia, Z. The first detection of pine wilt disease in Xiangshan county, Zhejiang Province. Plant Quar. 1993, 1, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, T. Integrated pest management of Japanese pine wilt disease. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 2007, 14, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.W.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, J.X.; Ren, J.R.; Ren, L.L.; Luo, Y.Q. Pine wilt disease in Northeast and Northwest China: A comprehensive risk review. Forests 2023, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.Q.; Huang, J.X.; Li, X.D.; Sun, H.; Fang, G.F. A multi-point aggregation trend of the outbreak of pine wilt disease in China over the past 20 years. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2022, 505, 119890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xian, X.; Yang, N.; Guo, J.; Zhao, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, W.-X. Risk assessment framework for pine wilt disease: Estimating the introduction pathways and multispecies interactions among the pine wood nematode, its insect vectors, and hosts in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Yan, E.P.; Jiang, J.W.; Zhang, G.Z.; Mo, D.K. An efficient approach to monitoring pine wilt disease severity based on random sampling plots and UAV imagery. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, L.; Yao, Z.; Li, N.; Long, L.; Zhang, X. Intelligent Identification of Pine Wilt Disease Infected Individual Trees Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.N.; Lindberg, E.; Bohlin, J.; Persson, H.J. Assessing the detectability of European spruce bark beetle green attack in multispectral drone images with high spatial- and temporal resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 287, 113484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiya, Y. Pathology of the pine wilt disease caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1983, 21, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, K.; Shigesada, N. Spread of the pinewood nematode vectored by the Japanese pine sawyer: Modeling and analytical approaches. Popul. Ecol. 2006, 48, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo, L.F.; Kim, Y. A simulation of the effects of early eradication of nematode infected trees on spread of pine wilt disease. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 132, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, P. Eradications of invasive alien species in Europe: A review. Biol. Invasions 2005, 7, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.M. National Eradication Programme for the Pinewood Nematode. In Pine Wilt Disease: A Worldwide Threat to Forest Ecosystems; Mota, M.M., Vieira, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Tang, G.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Chen, A.L. Advanced research of trunk injection against pine wild disease. For. Pest Dis. 2022, 41, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kawazu, K. Development and preventative effect against pine wilt disease of a novel liquid formulation of emamectin benzoate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Wu, X.Q.; Ye, J.R.; Li, C.Q.; Hu, L.J.; Rui, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.F.; Wang, L. Toxicity of an emamectin benzoate microemulsion against and its effect on the prevention of pine wilt disease. Forests 2023, 14, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Huang, J.X.; Li, X.D.; Fang, G.F.; Liu, D.Q. The interaction of environmental factors increases the risk of spatiotemporal transmission of pine wilt disease. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Jung, J.M.; Hwang, J.; Park, Y.; Lee, W.H. Ensemble evaluation of the spatial distribution of pine wilt disease mediated by insect vectors in South Korea. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2023, 529, 120677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuhashi, S.; Hirata, A.; Akiba, M.; Nakamura, K.; Oguro, M.; Takano, K.T.; Nakao, K.; Hijioka, Y.; Matsui, T. Developing a point process model for ecological risk assessment of pine wilt disease at multiple scales. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2020, 463, 118010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, L.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Luo, Y. Impact of stand- and landscape-level variables on pine wilt disease-caused tree mortality in pine forests. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, F. Individual-based modeling of the spread of pine wilt disease: Vector beetle dispersal and the Allee effect. Popul. Ecol. 2009, 51, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xie, N.; Yuan, G.; Liao, M.; Gui, Q.; Ding, G. Predicting the global potential distribution of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus using an ecological niche model: Expansion trend and the main driving factors. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2024, 24, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.Q.; Huang, J.X.; Zhou, Y.T.; Fang, G.F. Spatiotemporal pattern of pine wilt disease in the Yangtze river basin. Forests 2021, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Kawasaki, K.; Takasu, F.; Togashi, K.; Futai, K.; Shigesada, N. Modeling the spread of pine wilt disease caused by nematodes with pine sawyers as vector. Ecology 1999, 80, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Hwang, J.; Park, Y.; Lee, W.H. Analysis of the spread distance of pine wilt disease based on a high volume of spatiotemporal data recording of infected trees. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2024, 553, 121612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y. A Digital Management System for Monitoring Epidemics and the Management of Pine Wilt Disease in East China. Forests 2024, 15, 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122174
Zhang Y, Chen W, Hu J, Wang Y. A Digital Management System for Monitoring Epidemics and the Management of Pine Wilt Disease in East China. Forests. 2024; 15(12):2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122174
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanjun, Weishi Chen, Jiafu Hu, and Yongjun Wang. 2024. "A Digital Management System for Monitoring Epidemics and the Management of Pine Wilt Disease in East China" Forests 15, no. 12: 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122174
APA StyleZhang, Y., Chen, W., Hu, J., & Wang, Y. (2024). A Digital Management System for Monitoring Epidemics and the Management of Pine Wilt Disease in East China. Forests, 15(12), 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122174





