Species Differentiation of Prunus serrulata and Prunus xueluoensis Based on Combined Analysis of SSR and cpDNA Markers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification, Sequencing, and Sequence Alignment
2.3. SSR Polymorphism Analysis
2.4. CpDNA Haplotypes Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity of SSR Microsateilite Locus and Gene Flow
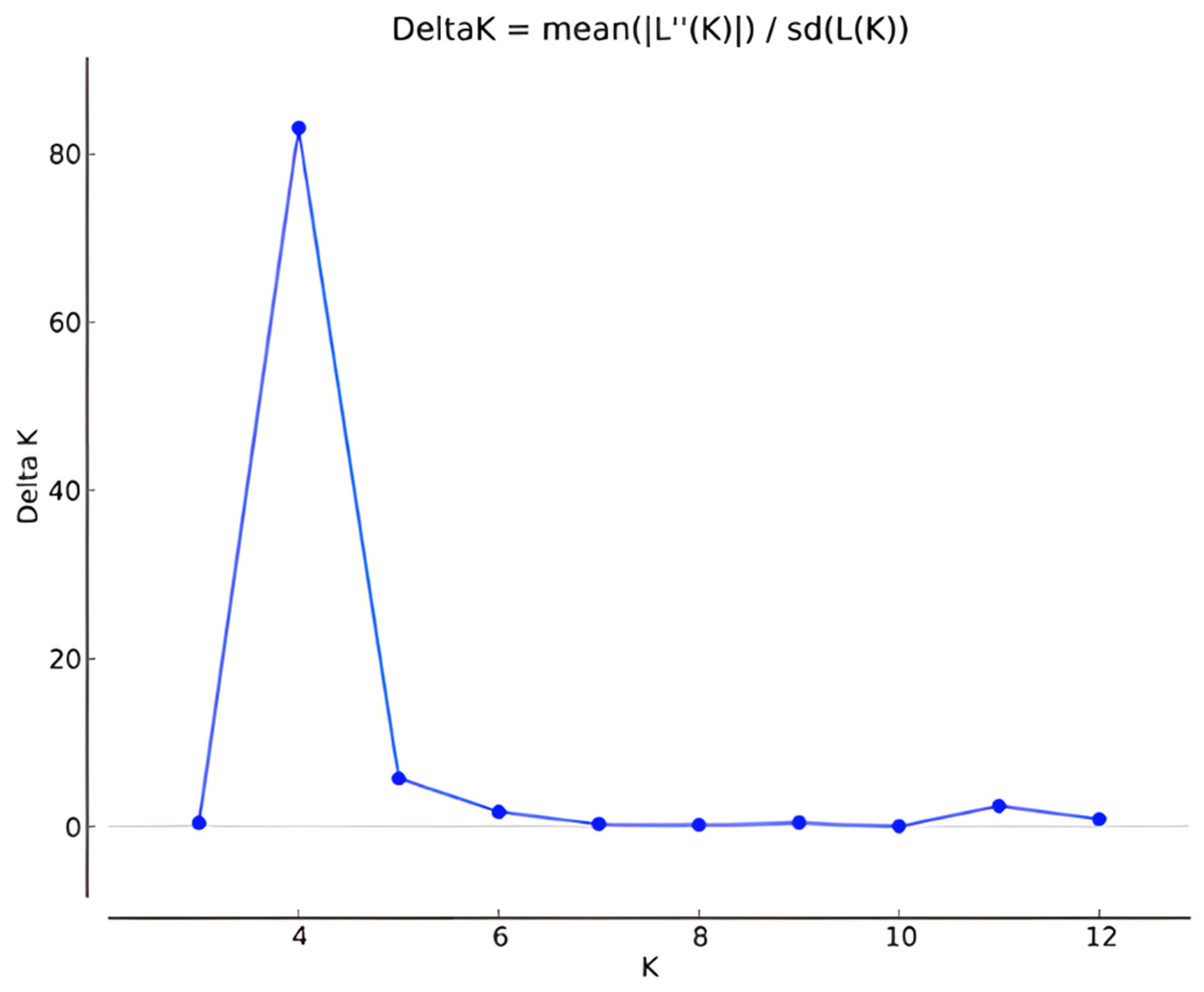
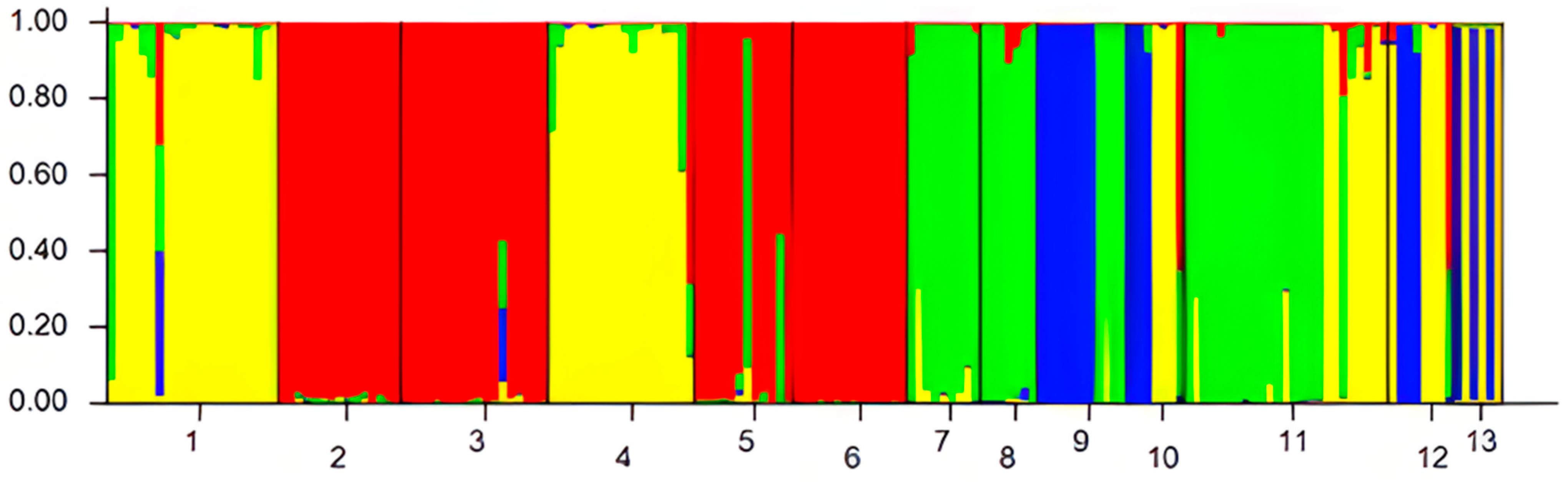
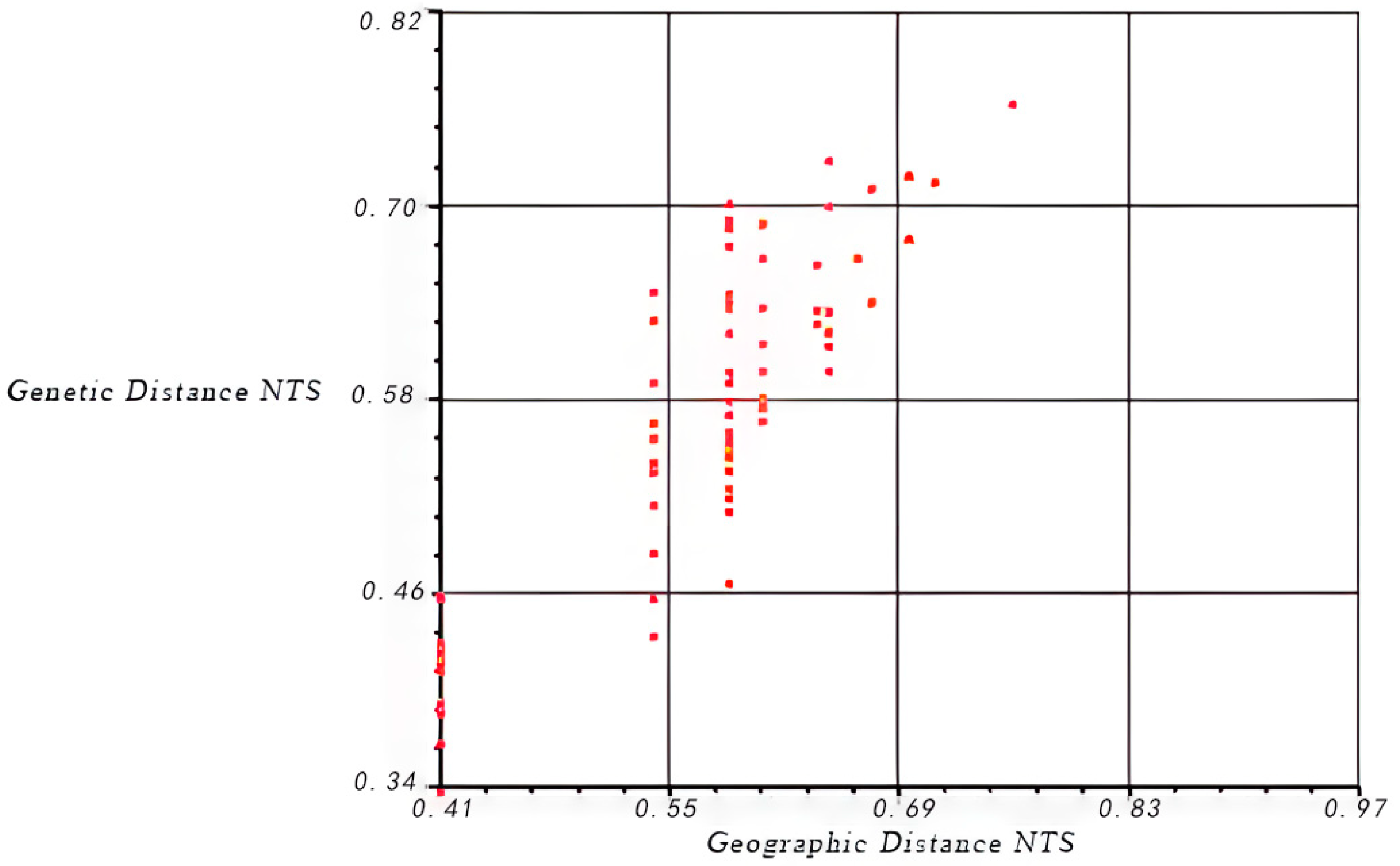
3.2. Genetic Differentiation, Structure, and Cluster Analysis
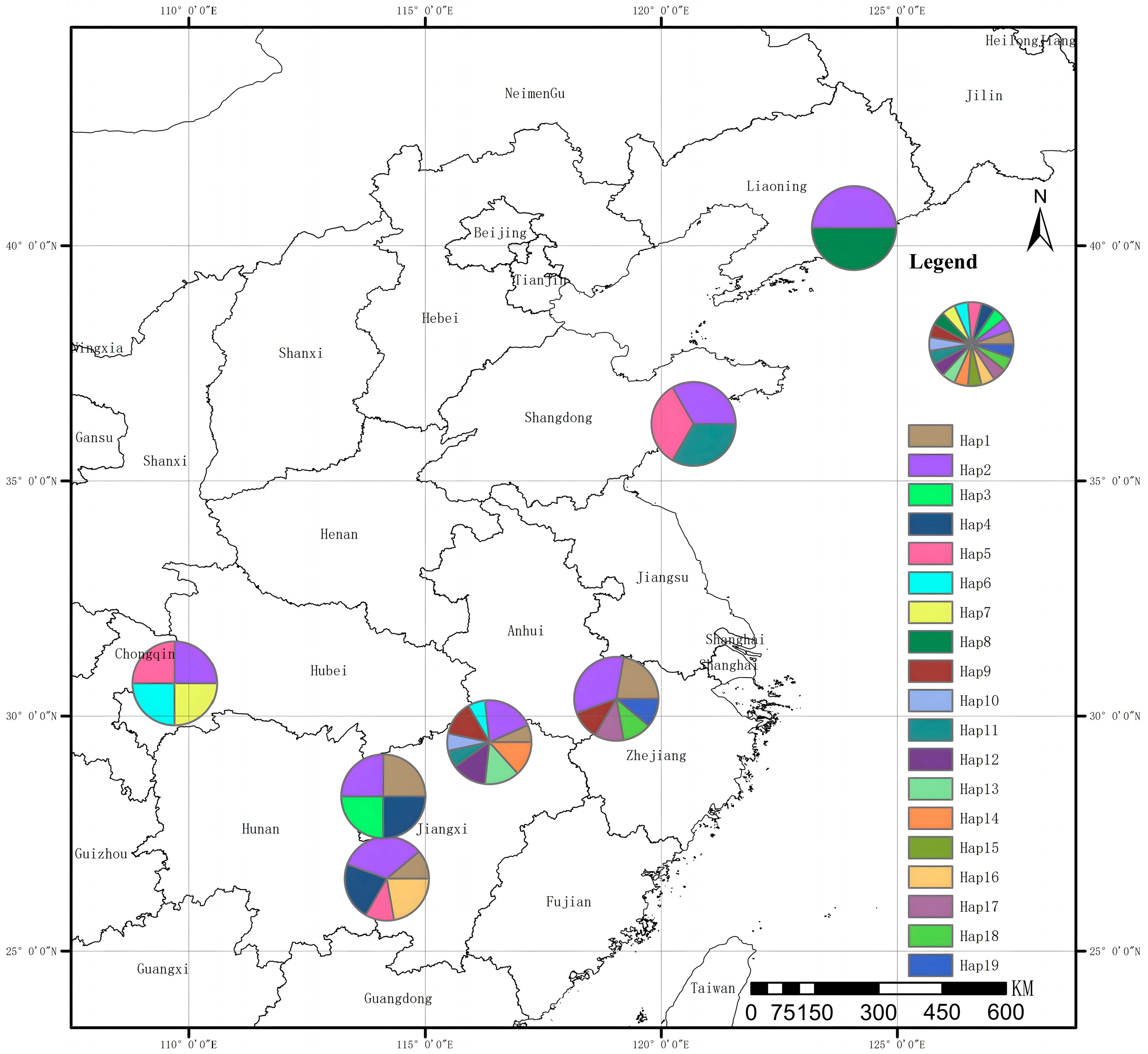
3.3. CpDNA Genetic Diversity and Structure
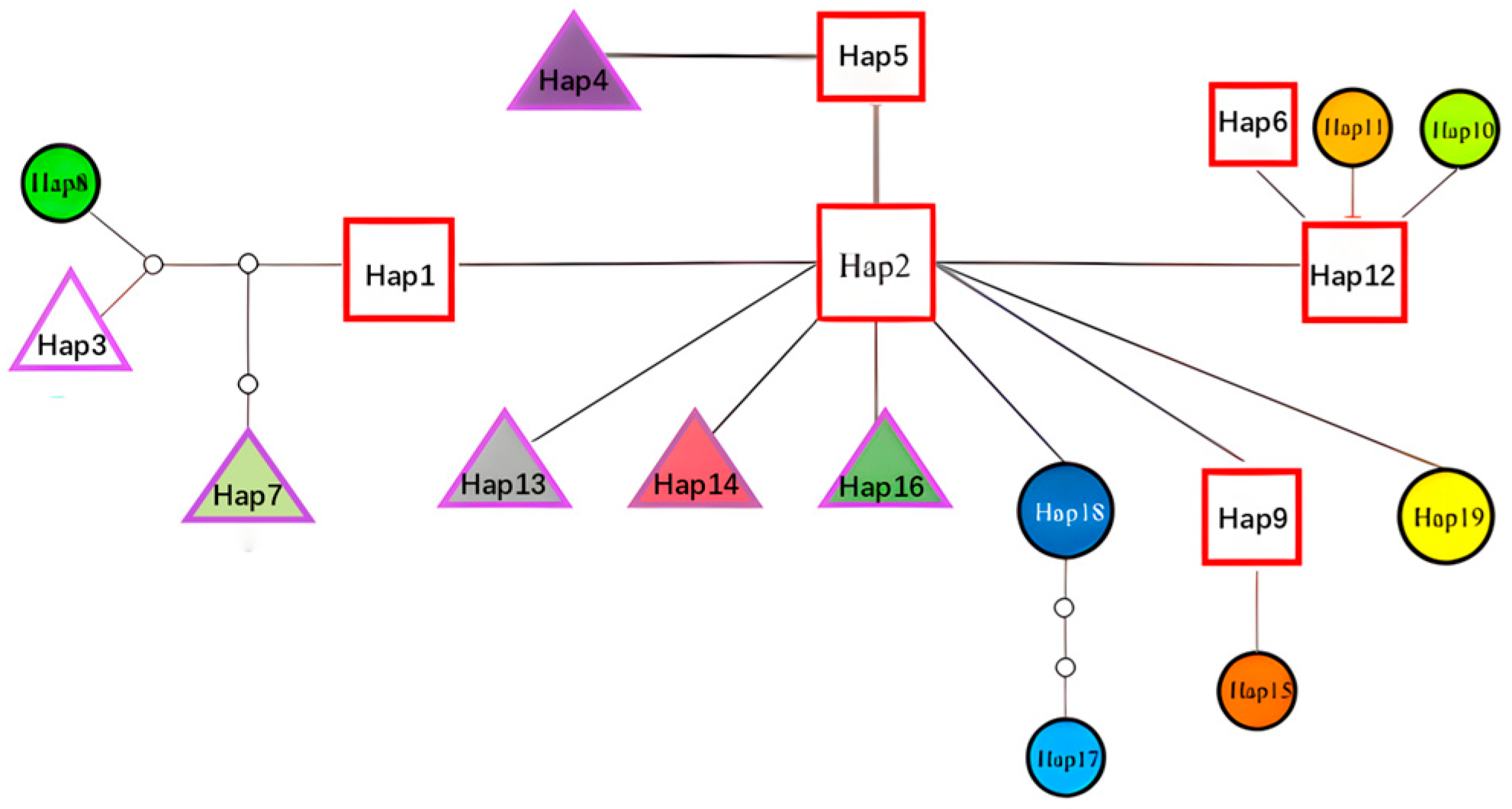
3.4. Haplotype Network
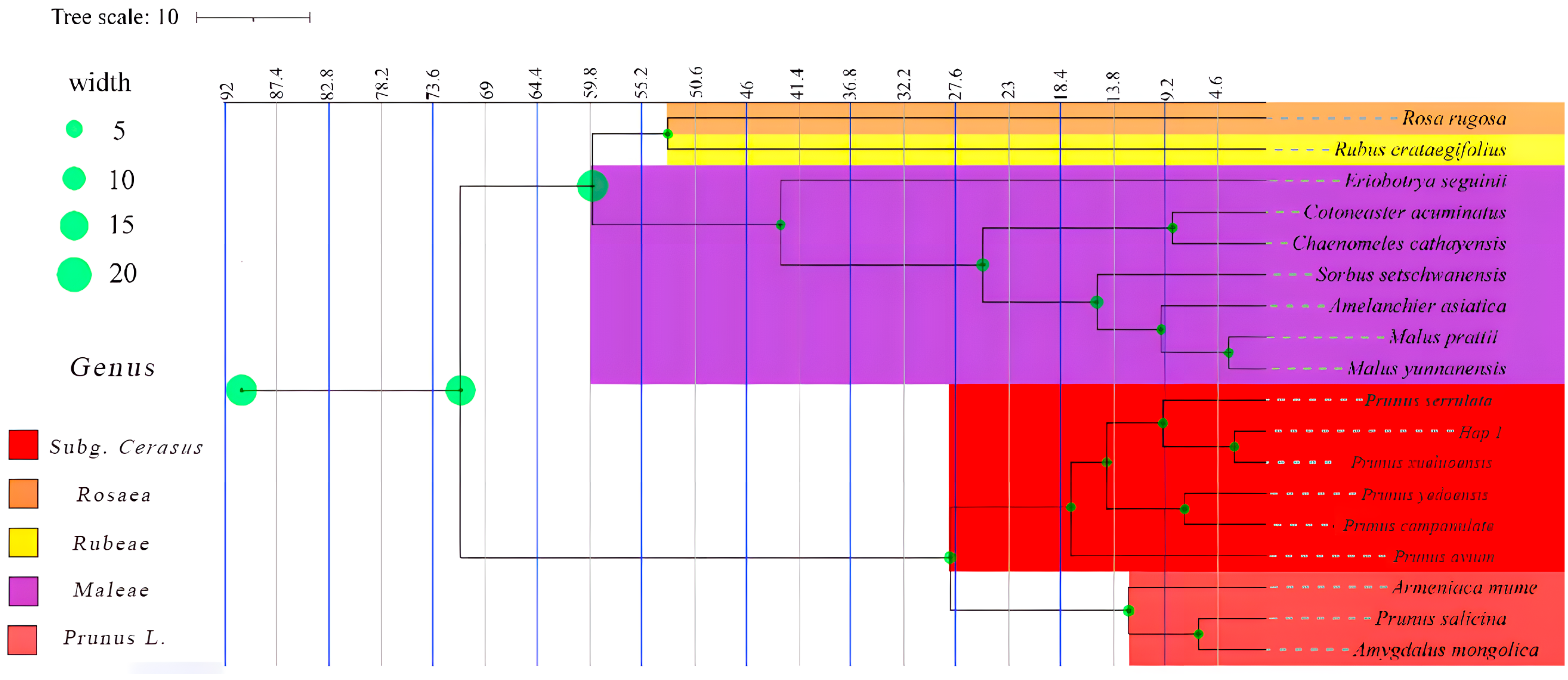
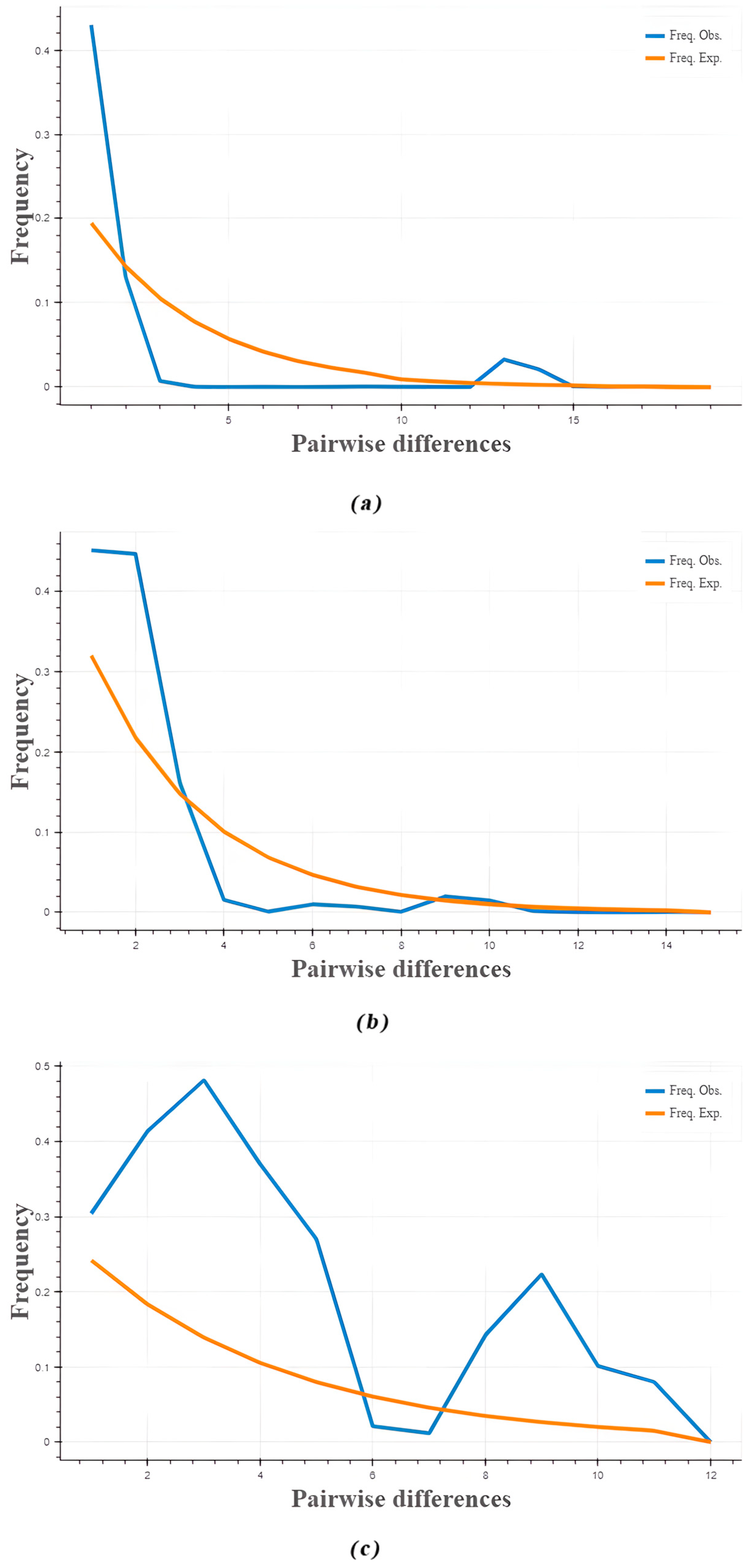
3.5. Phylogenetic Tree, Temporal Differentiation, and Collective Historical Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Diversity and Variation
4.2. Genetic Differentiation and Evolution
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nan, C.H.; Wang, X.R.; Tang, G.G.; Yi, X.G.; Luo, S.J. Cerasus xueluoensis (Rosaceae), a new species from China. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 2013, 50, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Queiroz, K. Species concepts and species delimitation. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scudder, G.G.E. Species concepts and speciation. Can. J. Zool. 1954, 9, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, E.O. The Evolutionary Species Concept Reconsidered. Syst. Zool. 1978, 27, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Liu, B.B.; Wang, J.R.; Tong, R.C.; Ren, C.; Chang, Z.Y.; Zhao, L.; Potter, D.; Wen, J. On the species delimitation of the Maddenia group of Prunus (Rosaceae): Evidence from plastome and nuclear sequences and morphology. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 743643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, Z.H.; Shang, Q.H.; Sa, W.; Wang, L. The Complete chloroplast genome of Prunus Triloba Var. plena and comparative analysis of Prunus species: Genome structure, sequence divergence, and phylogenetic analysis. Braz. J. Bot. 2021, 44, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Yang, X.C.; Wang, M.C.; Zhong, L.L.; Ma, R.; Ma, T.; Liu, J.Q.; Davis, C.C.; Xi, Z.X. Species delimitation of north American Nyssa species. J. Syst. Evol. 2022, 60, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steier, J.E.; Mandakova, T.; Wojciechowski, M.F.; Steele, K.P. Insights into species delimitation of selected species in the flowering plant genus Medicago section Buceras (Leguminosae). Syst. Bot. 2022, 47, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.N.; Zhang, D.Y. Current status and future directions in plant phylogeography. Chin. Bull. Life Sci. 2014, 26, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.S.; Chang, C.S.; Park, T.Y.; Roh, M.S. Reconsideration of the Prunus serrulata complex (Rosaceae) and related taxa in eastern Asia. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2007, 154, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, C.H. Study on Population Variation and Reproductive Biology of Cerasus discoidea Yü et Li; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.G. Studies on Investigation and Exploitation of the Resources of Cerasus Mill. In Wuyi Mountain; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H. Phylogenetic Position and Population Biogeography of Cerasus dielsiana (Rosaceae); Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, D.K. Cerasus Laoshanensis (Rosaceae), a new species from Shandong, China. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 2017, 54, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.X.; Zhang, F.G.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, F.; Chen, Z.H. Noteworthy plants in prunoideae of Rosaceae from Zhejiang. J. Hangzhou Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 16, 518–521. [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki, T. A new species, Cerasus kumanoensis from the southern Kii Peninsula, Japan. Acta Phytotaxon. Geobot. 2018, 69, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oginuma, K. Karyomorphological studies on Prunus in Japan. J. Sci. Hiroshima Univ. Ser. B. Div. Bot. 1987, 21, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mowrey, B.D.; Werner, D.J. Phylogenetic relationships among species of Prunus as inferred by isozyme markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1990, 80, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, A.R.; Clarke, G.R.; Jackson, J.F. Sweet cherry cultivar identification by leaf isozyme polymorphism. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1993, 86, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.L.; Chen, F.; Miao, J.G.; Han, D.D.; Li, C.L. Identification of 19 Cerasus cultivars on esterase isozyme in Qingdao. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2008, 23, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yi, X.G.; Gu, Y.; Wang, X.R. The genome size determination of Cerasus serrulata. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2014, 38, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.L.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Tang, M.Q.; Fu, M.Q.; Jin, X.F. Prunus pananensis (Rosaceae), a new species from Pan’an of central Zhejiang, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.X.; Lu, Y.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.L.; Jin, X.F. Cerasus fengyangshanica (Rosaceae), a new species from Zhejiang. J. Hangzhou Norm. Univ. 2017, 16, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.S.; Jiang, Z.L.; Yusupov, Z.; Zhang, M.H.; Zhang, D.G.; Tojibaev, K.; Meng, Y.; Deng, T. Prunus sunhangii: A new species of Prunus from central China. Plant Divers. 2019, 41, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.H.; Qin, B.; Huang, Y.H.; Tang, L.M.; Zhang, Z.J.; Li, C.; He, Y.H.; Jiang, R.H.; Li, J.L. Prunus quanzhouensis: A newly discovered species of Prunus subgen. Cerasus (Rosaceae) from northeastern Guangxi, China. Phytotaxa 2023, 622, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.G.; Dong, J.J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, H.J.; Wu, T.; Gao, S.C.; Chen, X.Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X.R. Molecular and morphological evidence support a new species of Rosaceae Prunus subg. Cerasus from Wuyishan National Park, Southeast China. PhytoKeys 2024, 237, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, T.; Wang, X.R.; Nan, C.H.; Zhang, Q. Genetic diversity in natural populations of Cerasus discoidea based on SSR markers. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2013, 48, 104–109+115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, R.; Zhang, K.W.; Yi, X.G.; Li, M.; Wang, X.R. Construction of DNA fingerprinting with SSR markers for 201 Kangding cherry (Cerasus tatsienensis) accessions. Mol. Plant Breed. 2020, 18, 6776–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, K.C.; Zhang, X.M.; Yan, G.H.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, X.W.; Chen, L. Identification of new polymorphic SSRs, fingerprinting and cluster analysis in sweet cherry. J. Fruit Sci. 2019, 36, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueller, E.; Fernandez, F.F.; Antanaviciute, L.; Anhalt-Bruederl, U.; Spornberger, A.; Forneck, A. Autochthonous Austrian Varieties of Prunus Avium L. represent a regional gene pool, assessed using SSR and AFLP markers. Genes 2021, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals Using the Software structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.G. The Variation and Phylogeography of Cerasus serrulata Mill. Populations; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in excel. population genetic software for teaching and research an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, Y.; Kimura, M.; Kato, S.; Katsuki, T.; Mukai, Y.; Tsumura, Y. Genetic structure of Cerasus Jamasakura, a Japanese flowering cherry, revealed by nuclear SSRs: Implications for conservation. J. Plant. Res. 2009, 122, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S.; Katsuki, T.; Tanaka, T.; Hayashi, T.; Sato, Y.; Yamamoto, T. Genetic variation in flowering cherries (Prunus Subgenus Cerasus) characterized by SSR markers. Breed. Sci. 2005, 55, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirlewanger, E.; Cosson, P.; Tavaud, M.; Aranzana, J.; Poizat, C.; Zanetto, A.; Arús, P.; Laigret, F. Development of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q. Genetic Diversity Among Populations of Cerasus campanulate; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.X. Genetic Diversity and Breeding Strategy of Cerasus campanulata Maxim; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.L. Genetic Diversity and Populations Genetic Structure of Wild Prunus tomentosa in Northern China Using Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs) Markers; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Yang, W.K.; Wang, X.Y.; Hou, Y.G. High genetic diversity in an endangered medicinal plant, Saussurea Involucrata (Saussurea, Asteraceae), in western Tianshan mountains, China. Conserv. Genet. 2017, 18, 1435–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.D.; Jin, J.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Chase, M.W.; Soltis, D.E.; Li, H.T.; Yang, J.B.; Li, D.Z.; Yi, T.S. Diversification of Rosaceae since the late cretaceous based on plastid phylogenomics. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.G.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.F.; Li, X.X.; Li, M.; Duan, Y.F.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.R. Phylogeography and the population genetic structure of flowering cherry Cerasus serrulata (Rosaceae) in subtropical and temperate China. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 11262–11276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.W. Molecular Phylogeography of Prunus subgenus Cerasus; Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.M. Phylogeography of Prunus subgenus Cerasus and Genetic Diversity of P. pscudocerasas; Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.; Choi, K.; Kim, G.B.; Yu, H.J.; Cho, A.; Jang, H.; Kim, C.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, K.S.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Draft genome sequence of wild Prunus yedoensis reveals massive inter-specific hybridization between sympatric flowering cherries. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.Q.; Dong, P.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, S.X.; Dong, J.-J.; Zhong, Y.Q.; Zhai, F.F.; Zheng, A.C.; Wang, X.R.; Yi, X.G. Analyses of Cerasus serrulata population structure and point patterns in Yuntai mountain, Jiangsu. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2021, 45, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yi, X.G.; Wang, H.C.; Shang, T.; Gu, Y.; Wang, X.R. Studies on the relationship between Cerasus serrulata distribution region and the environmental factors. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2014, 38, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.C. Study on Living Environment and Seed Charateristics of Cerasus xueluoensisin Dawei Mountain in Hunan Province; Nanjing Forestry Univeristy: Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L. Seed Predation and di Spersal of Cherry (Cerasus pseudocerasus) by Animals in a Dujiangyan Subtropical Forest; SiChuan University: Chengdu, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.X. Study on Stem Andleaf Structure and SSR Genetic Diversity of Cerasus; Central South University of Forestry and Technology: Changsha, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Li, J.L.; Sun, J.K.; Yu, J.; Zhou, S.L. Phylogeny and classification of Prunus Sensu Lato (Rosaceae). J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2013, 55, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Cerasus serrulata Populations Based on SSR Markers; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, R. Genetic Diversity of Cerasus tatsienensis (Batal.) Yu et Li Populations by SSR Markers; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
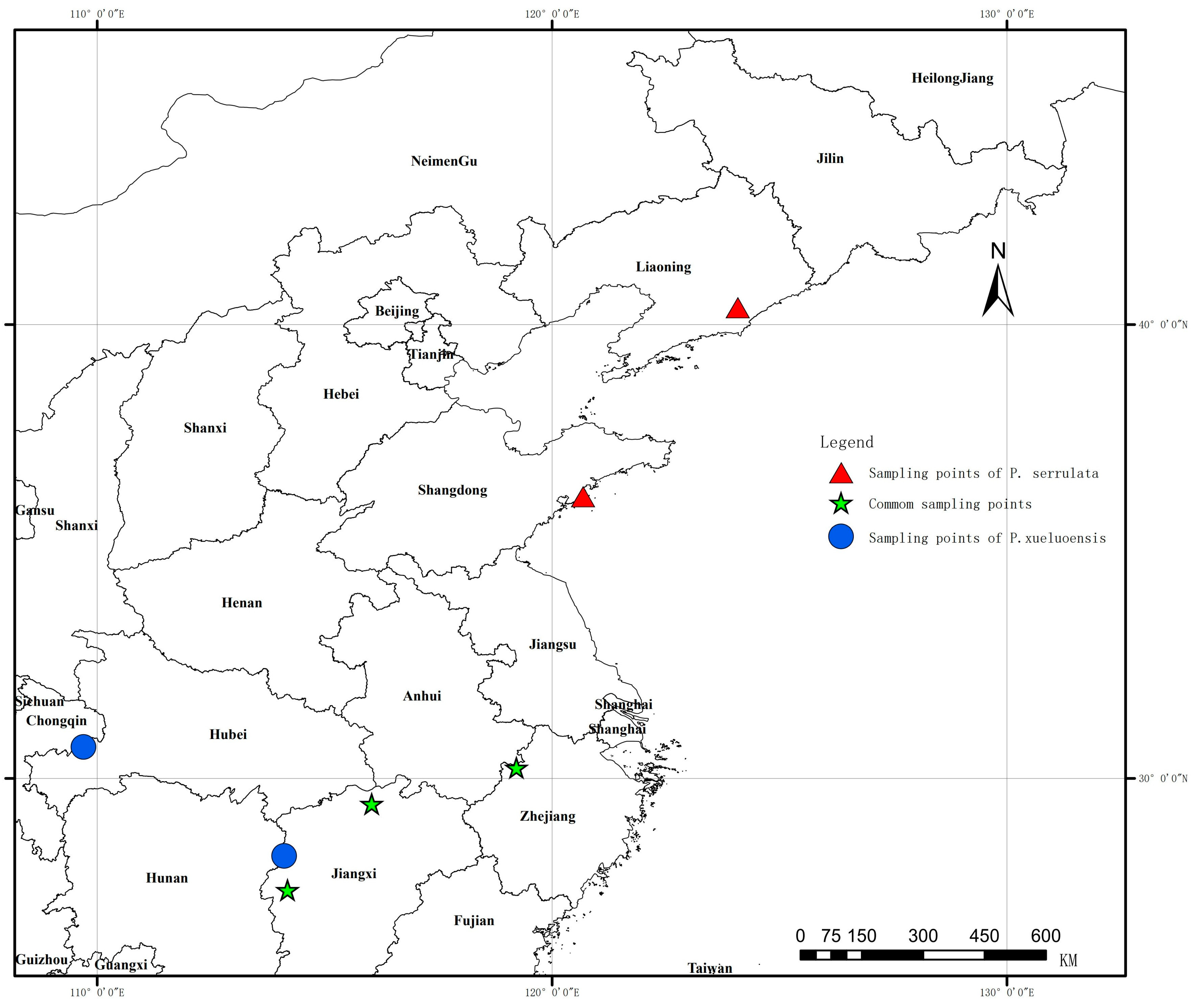


| Population Label | Place, Province | Species | Sample Size | Altitude (m) | Northern Latitude (° ′ ″) | Eastern Longitude (° ′ ″) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QLFs | Qingliang Feng, Zhejiang | P. serrulata | 31 | 950–1376 m | 30°22′01″ | 119°02′47″ |
| QLFx-U | Qingliang Feng, Zhejiang | P. xueluoensis | 30 | 1311–1500 m | 30°14′22″ | 119°12′57″ |
| QLFx-D | Qingliang Feng, Zhejiang | P. xueluoensis | 30 | 1500–1743 m | 30°14′32″ | 118°51′57″ |
| LuSs | Lushan Jiangxi | P. serrulata | 23 | 111–1311 m | 29°26′41″ | 116°02′08″ |
| LuSx-U | Lushan Jiangxi | P. xueluoensis | 30 | 1300–1410 m | 29°31′07″ | 115°58′11″ |
| LuSx-D | Lushan Jiangxi | P. xueluoensis | 43 | 1147–1300 m | 29°31′13″ | 115°57′14″ |
| MYSs | Mingyue Shan, Jiangxi | P. serrulata | 24 | 786–939 m | 27°32′36″ | 114°11′01″ |
| MYSx-U | Mingyue Shan, Jiangxi | P. xueluoensis | 30 | 1500–1611 m | 27°32′31″ | 114°11′09″ |
| MYSx-D | Mingyue Shan, Jiangxi | P. xueluoensis | 15 | 1398–1500 m | 27°32′16″ | 114°11′01″ |
| FHSs | FenghuangShan Liaoning | P. serrulata | 16 | 387–539 m | 40°22′36″ | 124°04′53″ |
| LaoSs | Lao Shan, Shandong | P. serrulata | 16 | 511–835 m | 36°12′38″ | 120°40′53″ |
| DWSx | Dawei Shan Hunan | P. xueluoensis | 25 | 1321–1483 m | 28°17′31″ | 114°06′36″ |
| ESx | Enshi City, Hubei | P. xueluoensis | 28 | 1465–1578 m | 30°41′41″ | 109°41′49″ |
| Primers | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| AM287648 | F: ATGATGCTACCACAAGGGACTCGT |
| R: GTTTAGCTGCACATACGCTTTTACCTCC | |
| AM287842 | F: ATTTGACAGTGAGGACATGACCGA |
| R: GTTTACAATTAAAGGTGGGTTAGGGCCA | |
| BP040 | F: ATGAGGACGTGTCTGAATGG |
| R: AGCCAAACCCCTCTTATACG | |
| BPPCTO28 | F: TCAAGTTAGCTGAGGATCGC |
| R: GAGCTTGCCTATGAGAAGACC | |
| BPPCTO41 | F: CAATAAGGCATTTGGAGGC |
| R: CAGCCGAACCAAGGAGAC | |
| CPSCT044 | F: CCAGCACAGAGAAAACGATG |
| R: GAGCTCCTACTCTGAGTCTGTAAAA | |
| DN554499 | F: ATAGTGCAGTTGAGAAACGAGCAG |
| R: GTTTAAGGTGCAGTTCGTTGTCGATGT | |
| DY640849 | F: ATAGGCCAGGCAAATAGCGAAGTA |
| R:GTTTCCTCTGTAGCTCCCAAGTTTTCG | |
| DY647422 | F: AGACACCCTATCACAATGTCGCAA |
| R: GTTTGCGAACAGCGATAACCTTAATCC | |
| EMPA026 | F: ATTGAAAAAGCCAAAGAGCG |
| R: TTCACGGTTTGAAGCAAGTG | |
| EMPaS02B | F: CTACTTCCATGATTGCCTCAC |
| R: AACATCCAGAACATCAACACAC | |
| MA007a | F: GTGCATCGTTAGGAACTGCC |
| R: GCCCCTGAGATACAACTGCA | |
| MA016b | F: TGGCTGGTGGAGACGGAGGA |
| R: ATGATACCCAGCCTCCCGGG | |
| pchgms1 | F: GGGTAAATATGCCCATTGTGCAATC |
| R: GGATCATTGAACTACGTCAATCCTC | |
| pchgm3 | F: ACGCTATGTCCGTACCATCTCCATG |
| R: CAACCTGTGATTGCTCCTATTAAAC | |
| PMS2 | F: CACTGTCTCCCAGGTTAAACT |
| R: CCTGAGCTTTTGACACATGC | |
| UDPGA96-018 | F: TTCTAATCTGGGCTATGGCG |
| R: GAAGTTCACATTTACGACAGGG | |
| UDPGA98-412 | F: AGGGAAAGTTTCTGCTGCAC |
| R: GCTGAAGACGACGATGCTGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, S.; Chen, X.; Peng, Z.; Zeng, X.; Yun, Y.; Wang, X.; Yi, X. Species Differentiation of Prunus serrulata and Prunus xueluoensis Based on Combined Analysis of SSR and cpDNA Markers. Forests 2024, 15, 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111927
Gao S, Chen X, Peng Z, Zeng X, Yun Y, Wang X, Yi X. Species Differentiation of Prunus serrulata and Prunus xueluoensis Based on Combined Analysis of SSR and cpDNA Markers. Forests. 2024; 15(11):1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111927
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Shucheng, Xiangzhen Chen, Zhiqi Peng, Xinglin Zeng, Yingke Yun, Xianrong Wang, and Xiangui Yi. 2024. "Species Differentiation of Prunus serrulata and Prunus xueluoensis Based on Combined Analysis of SSR and cpDNA Markers" Forests 15, no. 11: 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111927
APA StyleGao, S., Chen, X., Peng, Z., Zeng, X., Yun, Y., Wang, X., & Yi, X. (2024). Species Differentiation of Prunus serrulata and Prunus xueluoensis Based on Combined Analysis of SSR and cpDNA Markers. Forests, 15(11), 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111927





