Identification of the HbZAR1 Gene and Its Potential Role as a Minor Gene in Response to Powdery Mildew and Anthracnose of Hevea brasiliensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of HbZAR1 Gene Family Members in Rubber Tree
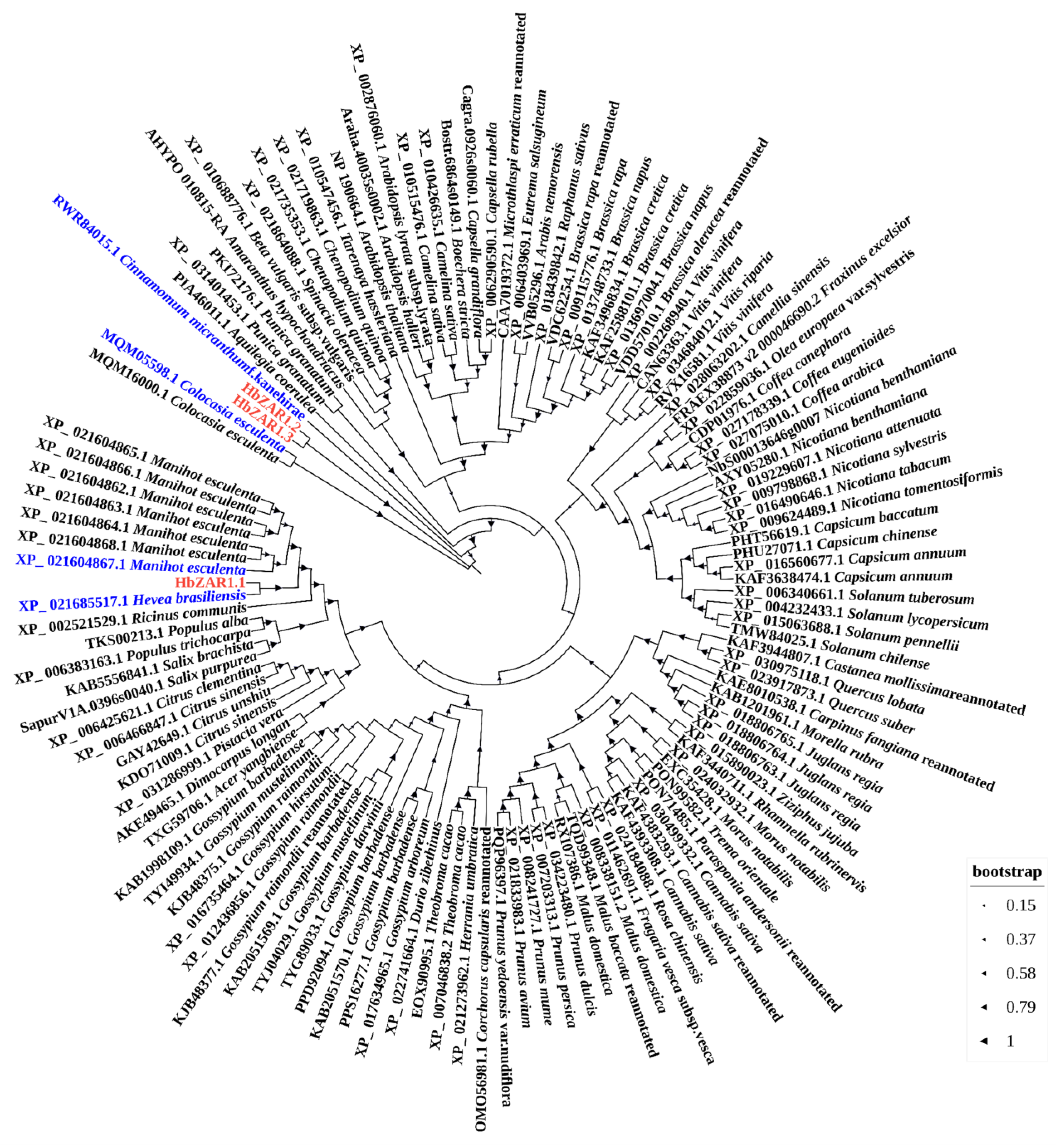
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of HbZAR1s
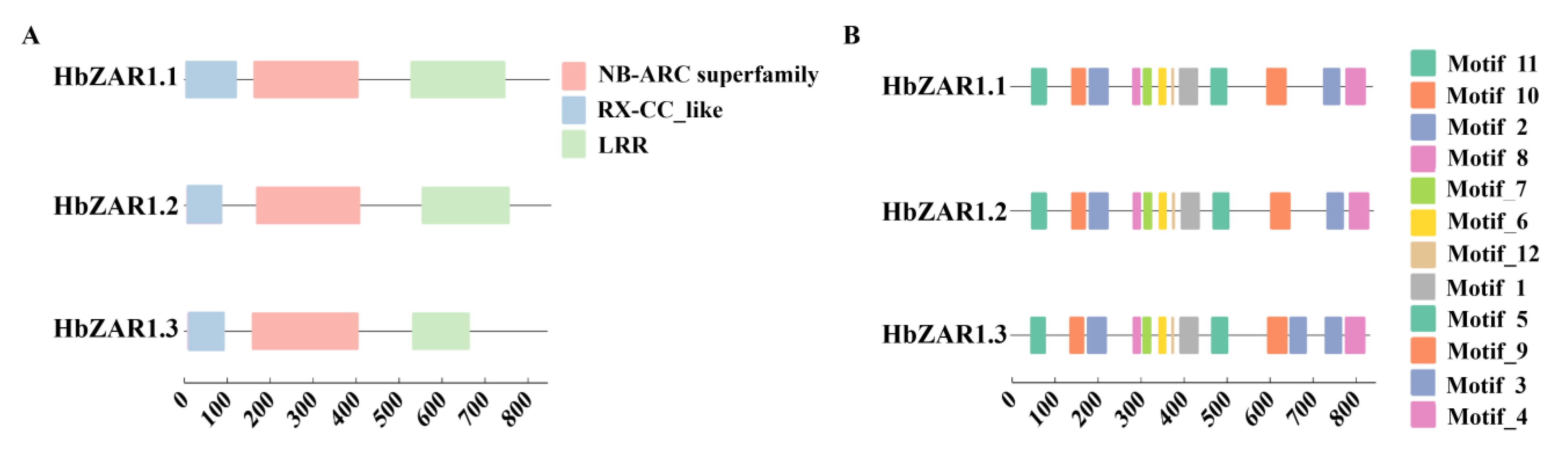
2.3. Conserved Domain and Motifs of HbZAR1 Proteins in Rubber Tree
2.4. Structure and Putative Cis-Acting Element Analysis of HbZAR1s in Rubber Tree
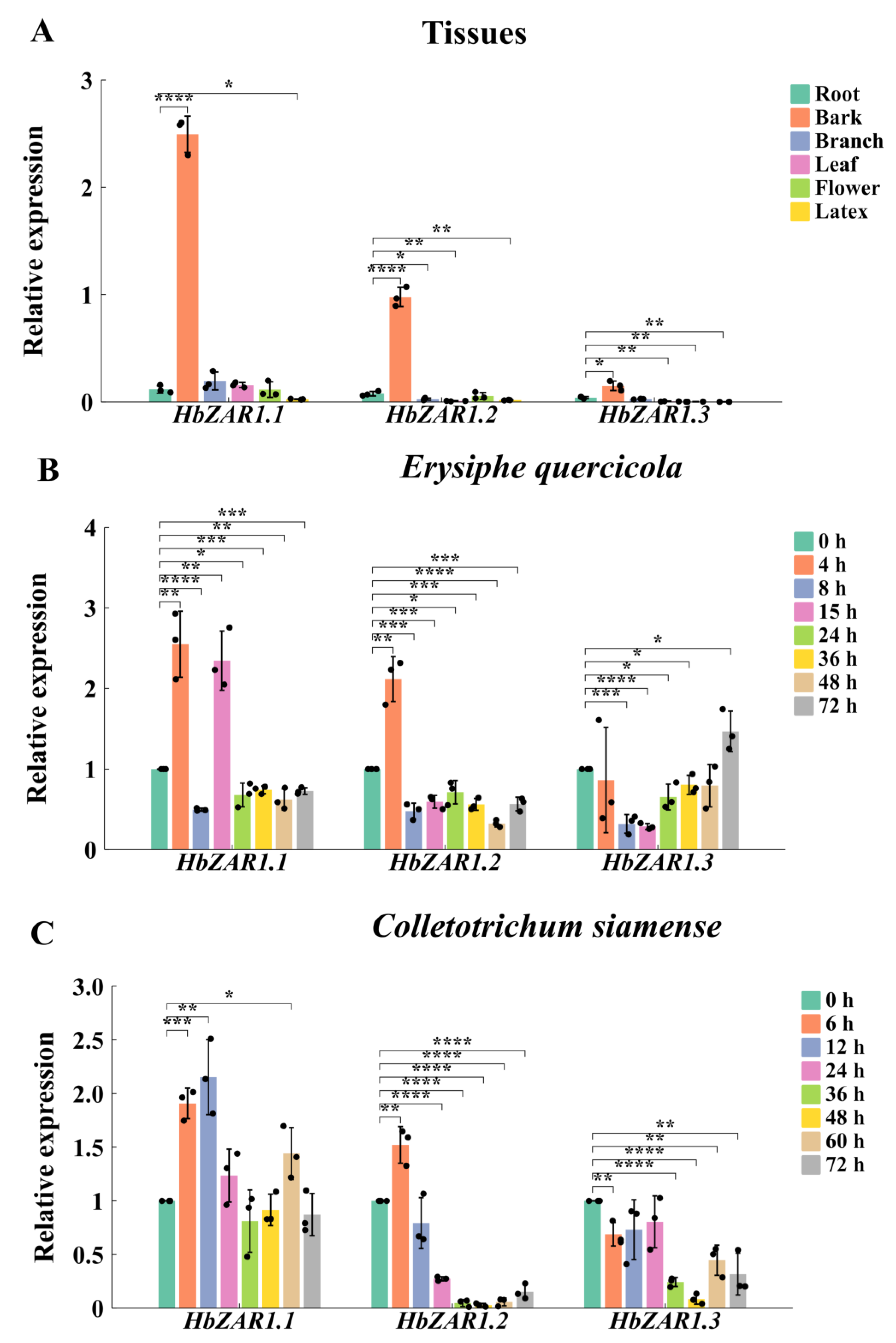
2.5. Expression Patterns of HbZAR1s in Different Tissues
2.6. Expression of HbZAR1 Genes Under Infection of E. quercicola and C. siamense
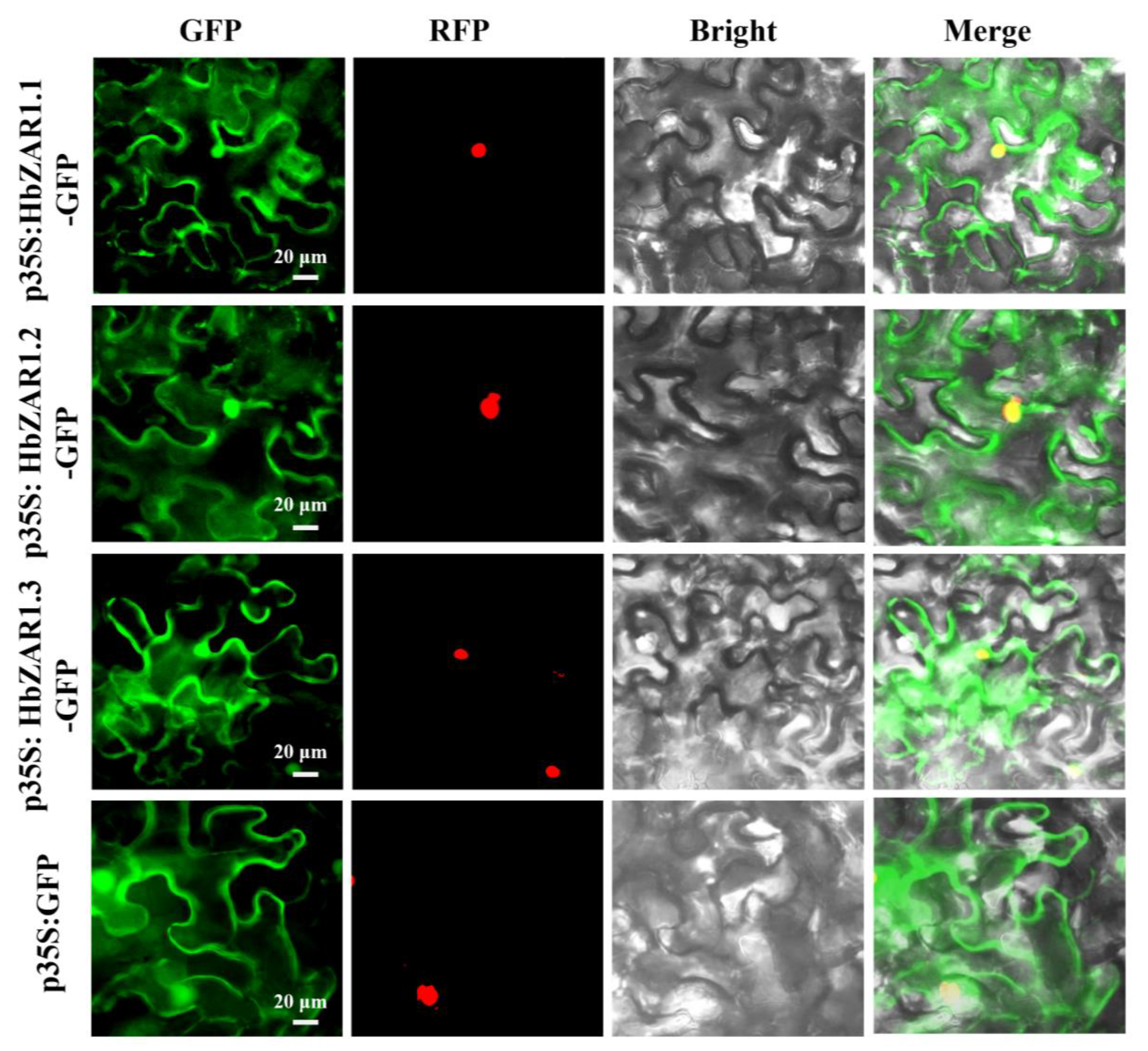
2.7. Subcellular Localization of the HbZAR1 Genes
2.8. HbZAR1 Does Not Induce ROS Burst and Cell Death in Tobacco
3. Discussion
3.1. Detailed Characterization and Evolution of HbZAR1s in Rubber Tree
3.2. The HbZAR1s Responds to Biological Stress
3.3. Function and Mechanism of HbZAR1 Genes
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of HbZAR1 Gene Family Members in Rubber Tree
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of HbZAR1s
4.4. Conserved Domain and Motifs of HbZAR1 Proteins in Rubber Tree
4.5. Structure and Putative Cis-Acting Element Analysis of HbZAR1 Genes in Rubber Tree
4.6. Expression of HbZAR1s Using qRT–PCR
4.7. The HbZAR1 Genes Subcellular Localization
4.8. The HbZAR1 Genes Transiently Overexpressed in Tobacco
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Locci, F.; Parker, J.E. Plant NLR immunity activation and execution: A biochemical perspective. Open Biol. 2024, 14, 230387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, K.S.; Carella, P. Taking the lead: NLR immune receptor N-terminal domains execute plant immune responses. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wan, L. Molecular insights into the biochemical functions and signalling mechanisms of plant NLRs. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 23, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Jia, A.; Ma, S.; Sun, Y.; Chang, X.; Han, Z.; Chai, J. NLR signaling in plants: From resistosomes to second messengers. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2023, 48, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, H.; Kamoun, S. NLR receptor networks in plants. Essays Biochem. 2022, 66, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, H.; Sakai, T.; Kourelis, J.; Pai, H.; Gonzalez Hernandez, J.L.; Utsumi, Y.; Seki, M.; Maqbool, A.; Kamoun, S. Jurassic NLR: Conserved and dynamic evolutionary features of the atypically ancient immune receptor ZAR1. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 3662–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastedo, D.P.; Khan, M.; Martel, A.; Seto, D.; Kireeva, I.; Zhang, J.; Masud, W.; Millar, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, A.H.; et al. Perturbations of the ZED1 pseudokinase activate plant immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, M.; Martin, E.C.; Sass, C.; Hassan, J.A.; Bendix, C.; Sauceda, R.; Diplock, N.; Specht, C.D.; Petrescu, A.J.; Lewis, J.D. A natural diversity screen in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals determinants for HopZ1a recognition in the ZAR1-ZED1 immune complex. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diplock, N.; Baudin, M.; Xiang, D.; Liang, L.Y.; Dai, W.; Murphy, J.M.; Lucet, I.S.; Hassan, J.A.; Lewis, J.D. Molecular dissection of the pseudokinase ZED1 expands effector recognition to the tomato immune receptor ZAR1. Plant Physiol. 2024, 196, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, M.; Hassan, J.A.; Schreiber, K.J.; Lewis, J.D. Analysis of the ZAR1 immune complex reveals determinants for immunity and molecular interactions. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 2038–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diplock, N.; Baudin, M.; Harden, L.; Silva, C.J.; Erickson-Beltran, M.L.; Hassan, J.A.; Lewis, J.D. Utilising natural diversity of kinases to rationally engineer interactions with the angiosperm immune receptor ZAR1. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 2238–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Cui, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, N.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Xu, E.; Hu, Z.; Ren, D.; Tang, D.; et al. Two Arabidopsis Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases SZE1 and SZE2 associate with the ZAR1-ZED1 complex and are required for effector-triggered immunity. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, G.; Su, M.; Li, N.; Liang, Y.; Dang, S.; Xu, J.; Hu, M.; Wang, J.; Zou, M.; Deng, Y.; et al. The ZAR1 resistosome is a calcium-permeable channel triggering plant immune signaling. Cell 2021, 184, 3528–3541.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdett, H.; Bentham, A.R.; Williams, S.J.; Dodds, P.N.; Anderson, P.A.; Banfield, M.J.; Kobe, B. The Plant “resistosome”: Structural insights into immune signaling. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Han, Q.; Xiao, Y.; He, J.; Chuan, X.; Jiang, G.; West, J.S.; Xu, X. Population genetic structure of the rubber tree powdery mildew pathogen (Erysiphe quercicola) from China. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.L.; Thaler, P.; Worthy, F.R.; Xu, J. Rubber latex yield is affected by interactions between antecedent temperature, rubber phenology, and powdery mildew disease. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2023, 67, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunupolagama, D.M.; Chandrasekharan, N.V.; Wijesundera, W.S.S.; Kathriarachchi, H.S.; Fernando, T.; Wijesundera, R.L.C. Unveiling Members of Colletotrichum acutatum species complex causing colletotrichum leaf disease of Hevea brasiliensis in Sri Lanka. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, B.; Cai, J.; Zheng, X.; Feng, Y.; Huang, G. Colletotrichum species causing anthracnose of rubber trees in China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C. Tracing the evolution of the ZAR1 resistosome back to the Jurassic era. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 3629–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, M.; Schreiber, K.J.; Martin, E.C.; Petrescu, A.J.; Lewis, J.D. Structure-function analysis of ZAR1 immune receptor reveals key molecular interactions for activity. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 101, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wersch, S.; Tian, L.; Hoy, R.; Li, X. Plant NLRs: The whistleblowers of plant immunity. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Qi, J.; Hu, M.; Bi, G.; Zhou, J.M.; Han, G.Z. The origin and evolution of a plant resistosome. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 1600–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, H.; Contreras, M.P.; Harant, A.; Wu, C.H.; Derevnina, L.; Sakai, T.; Duggan, C.; Moratto, E.; Bozkurt, T.O.; Maqbool, A.; et al. An N-terminal motif in NLR immune receptors is functionally conserved across distantly related plant species. Elife 2019, 8, e49956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.; Mazo-Molina, C.; Prokchorchik, M.; Zhang, N.; Kim, B.; Mang, H.; Koehler, N.; Kim, J.; et al. Ptr1 and ZAR1 immune receptors confer overlapping and distinct bacterial pathogen effector specificities. New Phytol. 2023, 239, 1935–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Qi, J.; Bi, G.; Zhou, J.M. Bacterial effectors induce oligomerization of immune receptor ZAR1 in vivo. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.D.; Lee, A.H.; Hassan, J.A.; Wan, J.; Hurley, B.; Jhingree, J.R.; Wang, P.W.; Lo, T.; Youn, J.Y.; Guttman, D.S.; et al. The Arabidopsis ZED1 pseudokinase is required for ZAR1-mediated immunity induced by the Pseudomonas syringae type III effector HopZ1a. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18722–18727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.D.; Wu, R.; Guttman, D.S.; Desveaux, D. Allele-specific virulence attenuation of the Pseudomonas syringae HopZ1a type III effector via the Arabidopsis ZAR1 resistance protein. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, Z.; Hu, M.; Ahn, Y.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, G.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, J.; et al. Two plant NLR proteins confer strain-specific resistance conditioned by an effector from Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae. J. Genet. Genom. 2022, 49, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, S.; Leonard, A.; Lauer, M.; Panangipalli, G.; Norman, B.; Hou, Z.; Llaca, V.; Hu, W.N.; Qi, X.; Jaqueth, J.; et al. The northern corn leaf blight resistance gene Ht1 encodes an nucleotide-binding, leucine-rich repeat immune receptor. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 24, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, L.; Lanver, D.; Schweizer, G.; Tanaka, S.; Liang, L.; Tollot, M.; Zuccaro, A.; Reissmann, S.; Kahmann, R. Fungal effectors and plant susceptibility. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015, 66, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Dong, S.; Liu, W. Structures of plant resistosome reveal how NLR immune receptors are activated. Abiotech 2020, 1, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hu, M.; Wang, J.; Qi, J.; Han, Z.; Wang, G.; Qi, Y.; Wang, H.W.; Zhou, J.M.; Chai, J. Reconstitution and structure of a plant NLR resistosome conferring immunity. Science 2019, 364, eaav5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, D.; Koulena, N.; Lo, T.; Menna, A.; Guttman, D.S.; Desveaux, D. Expanded type III effector recognition by the ZAR1 NLR protein using ZED1-related kinases. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, D.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Xin, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Ren, D.; Tang, D.; et al. Arabidopsis ZED1-related kinases mediate the temperature-sensitive intersection of immune response and growth homeostasis. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, A.; Laflamme, B.; Seto, D.; Bastedo, D.P.; Dillon, M.M.; Almeida, R.N.D.; Guttman, D.S.; Desveaux, D. Immunodiversity of the Arabidopsis ZAR1 NLR is conveyed by receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase sensors. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngou, B.P.M.; Ding, P.; Jones, J.D.G. Channeling plant immunity. Cell 2021, 184, 3358–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Fu, Z.Q. ZAR1 resistosome and helper NLRs: Bringing in calcium and inducing cell death. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1234–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harant, A.; Pai, H.; Sakai, T.; Kamoun, S.; Adachi, H. A vector system for fast-forward studies of the HOPZ-ACTIVATED RESISTANCE1 (ZAR1) resistosome in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Physiol. 2022, 188, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruta, N.; Burdett, H.; Lim, B.Y.J.; Hu, X.; Desa, S.; Manik, M.K.; Kobe, B. Structural basis of NLR activation and innate immune signalling in plants. Immunogenetics 2022, 74, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ma, Z.; Ke, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Qin, B.; Tang, C.; Liu, M.; Xian, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analyses reveal cellular and molecular patterns of rubber tree response to early powdery mildew infection. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 2222–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Ke, Y.; Xian, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y. Identification of HbHSP90 gene family and characterization HbHSP90.1 as a candidate gene for stress response in rubber tree. Gene 2022, 827, 146475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ooijen, G.; Mayr, G.; Kasiem, M.M.; Albrecht, M.; Cornelissen, B.J.; Takken, F.L. Structure-function analysis of the NB-ARC domain of plant disease resistance proteins. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daudi, A.; O’Brien, J.A. Detection of hydrogen peroxide by DAB staining in Arabidopsis leaves. Bioprotocol 2012, 2, e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Gene ID | Length of CDS (bp) | Number of Exons | Predicted Protein | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siza (aa) | MW (Da) | PI | Subcellular Localization | ||||
| HbZAR1.1 | 110668533 | 2532 | 1 | 843 | 96,350.36 | 6.37 | M/N/Cyto |
| HbZAR1.2 | 110644474 | 2541 | 1 | 846 | 97,467.88 | 7.93 | M/N/Cyto |
| HbZAR1.3 | 110671616 | 2514 | 1 | 837 | 95,889.91 | 8.06 | M/N/Cyto |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Qiao, A.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Qin, B.; Wang, M.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y. Identification of the HbZAR1 Gene and Its Potential Role as a Minor Gene in Response to Powdery Mildew and Anthracnose of Hevea brasiliensis. Forests 2024, 15, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111891
Liu Q, Qiao A, Zhou S, Lu Y, Yang Y, Wang L, Qin B, Wang M, Liang X, Zhang Y. Identification of the HbZAR1 Gene and Its Potential Role as a Minor Gene in Response to Powdery Mildew and Anthracnose of Hevea brasiliensis. Forests. 2024; 15(11):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111891
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qifeng, Anqi Qiao, Shaoyao Zhou, Yiying Lu, Ye Yang, Lifeng Wang, Bi Qin, Meng Wang, Xiaoyu Liang, and Yu Zhang. 2024. "Identification of the HbZAR1 Gene and Its Potential Role as a Minor Gene in Response to Powdery Mildew and Anthracnose of Hevea brasiliensis" Forests 15, no. 11: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111891
APA StyleLiu, Q., Qiao, A., Zhou, S., Lu, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, L., Qin, B., Wang, M., Liang, X., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Identification of the HbZAR1 Gene and Its Potential Role as a Minor Gene in Response to Powdery Mildew and Anthracnose of Hevea brasiliensis. Forests, 15(11), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111891






