An Assessment of the Impact of the Mining Industry on Soil and Plant Contamination by Potentially Toxic Elements in Boreal Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
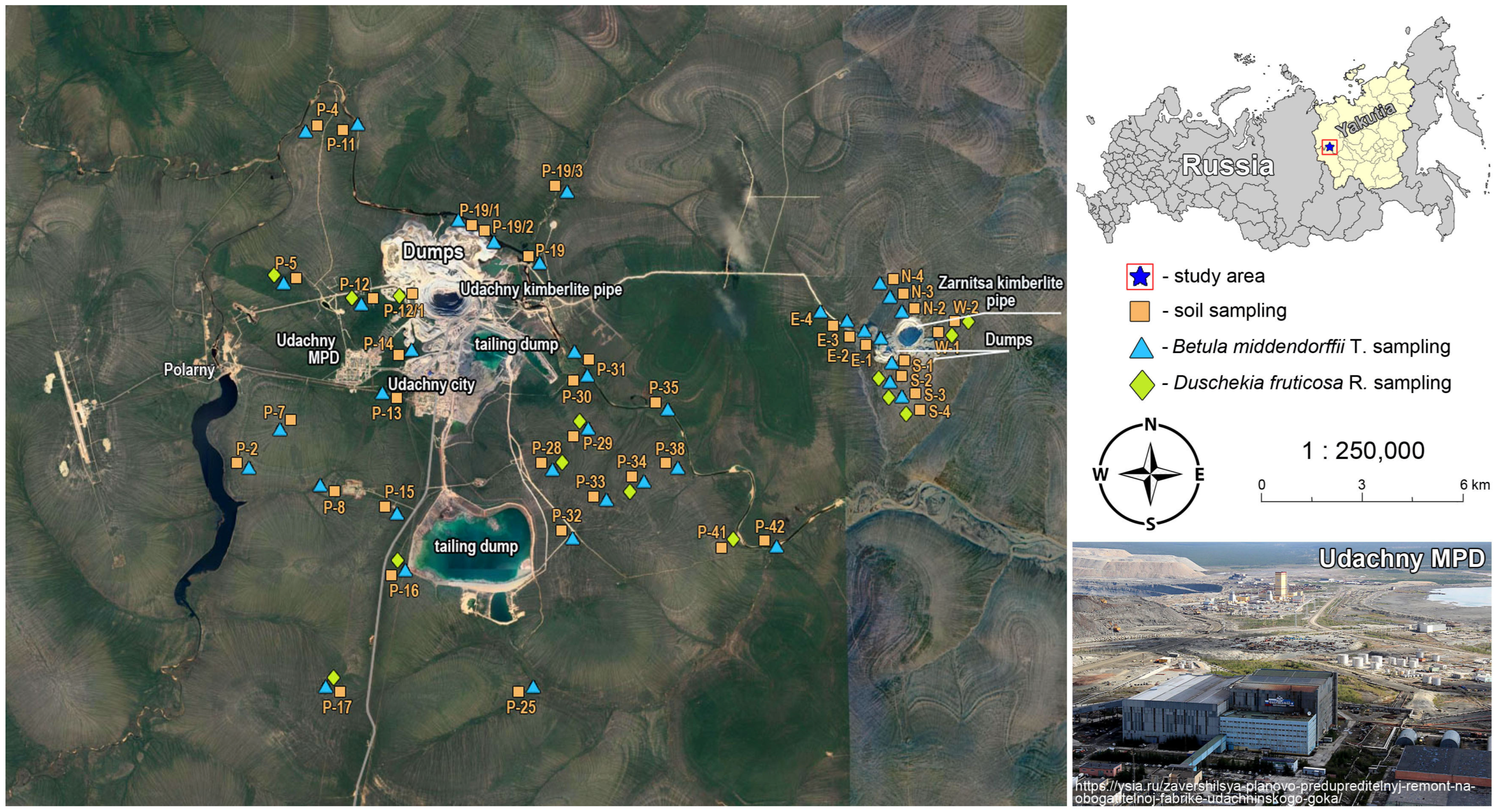
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analyses
2.3. Plant Sampling and Analyses
2.4. Quality Control
2.5. Assessment of PTE Pollution
2.6. Bioaccumulation Factor
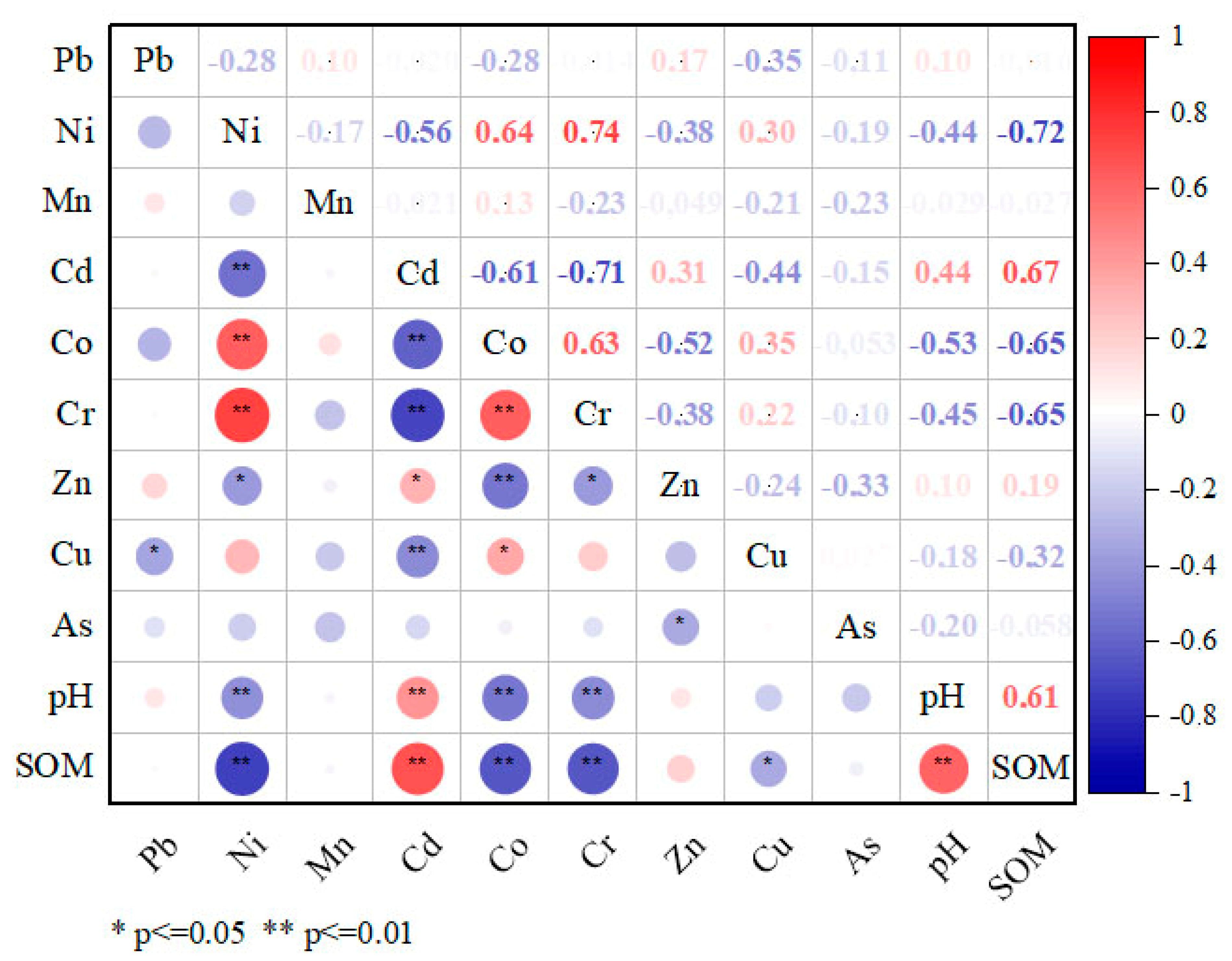
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
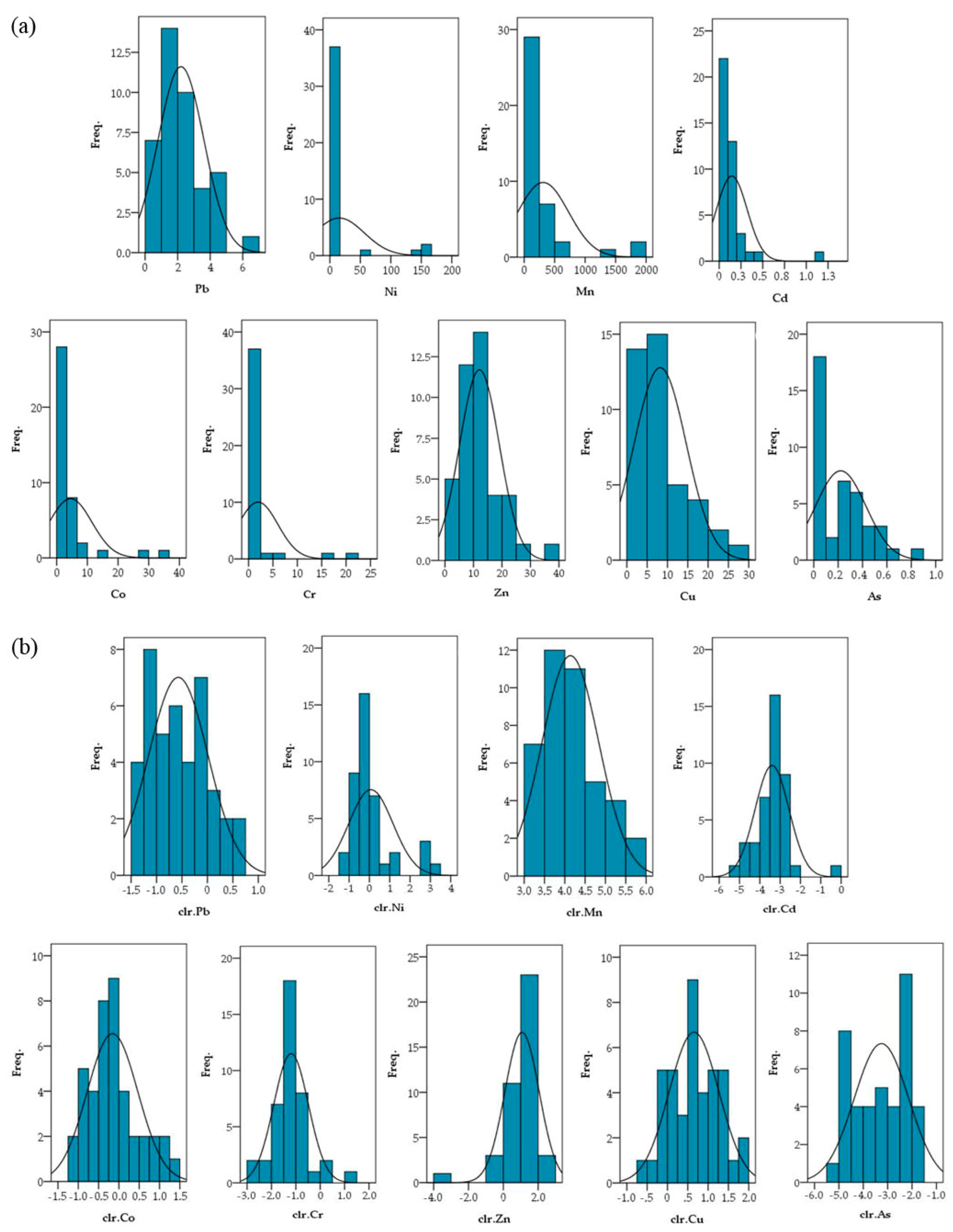
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Physicochemical Properties and PTE Concentrations in Soils
3.2. Descriptive Statistics of PTE Concentrations in Plants
3.3. Indices of Pollution
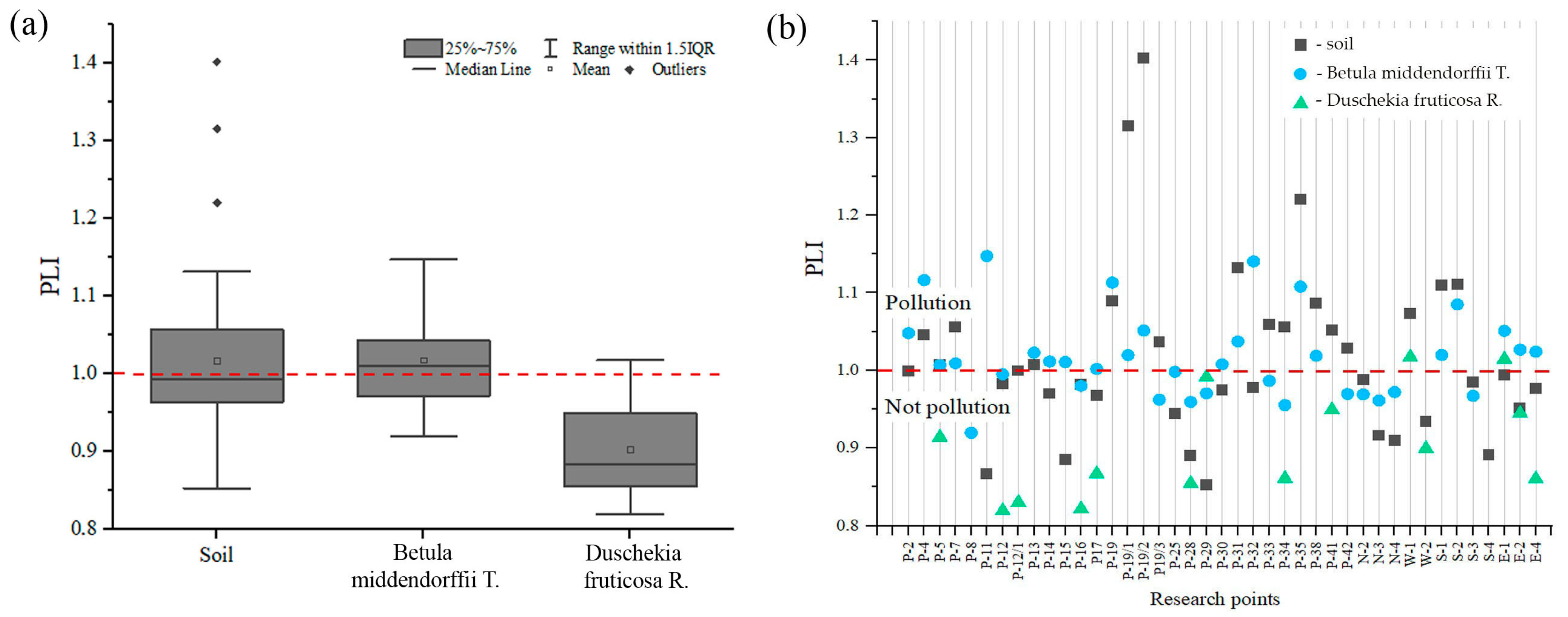
3.3.1. Pollution Index (PI) and Pollution Load Index (PLI)
3.3.2. Bioaccumulation Factor (BAF)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angulo-Bejarano, P.I.; Puente-Rivera, J.; Cruz-Ortega, R. Metal and metalloid toxicity in plants: An overview on molecular aspects. Plants 2021, 10, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. The Relative Impact of Toxic Heavy Metals (THMs) (Arsenic (As), Cadmium (Cd), Chromium (Cr)(VI), Mercury (Hg), and Lead (Pb)) On the Total Environment: An Overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seleiman, M.; Santanen, A.; Mäkelä, P. Recycling Sludge on Cropland as Fertilizer-Advantages and Risks. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 155, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Yun, L.; Jenmei, W.; Xinyu, C. The Sources Risk Assessment Combined with APCS/MLR Model for Potentially Toxic Elements in Farmland of a First-Tier City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50717–50726. [Google Scholar]
- Sabir, M.; Baltrėnaitė-Gedienė, E.; Ditta, A.; Ullah, H.; Kanwal, A.; Ullah, S.; Faraj, T.K. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in a Soil–Plant System from an Open Dumpsite and the Associated Health Risks through Multiple Routes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendrula-Kotha, R.; Theriault, G.; Mehes-Smith, M.; Kalubi, K.; Nkongolo, K. Metal Toxicity and Resistance in Plants and Microorganisms in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Residue Rev. 2019, 249, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, X.; Ge, S.; Jiao, X.; Zhan, W.; Wang, Y. Bioaccumulation and risk assessment of potential toxic elements in the soil-vegetable system as influenced by historical wastewater irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 279, 108197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataliia, R.; Abdelhak, E.; Michelle, G.; Tian, F.; Laptev, V. Bioaccumulation of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn in Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. in the polluted area by enterprise for the production and processing of batteries. Ann. Civil. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pehoiu, G.; Murarescu, O.; Radulescu, C.; Dulama, I.D.; Teodorescu, S.; Stirbescu, R.M.; Bucurica, I.A.; Stanescu, S.G. Heavy metals accumulation and translocation in native plants grown on tailing dumps and human health risk. Plant Soil 2020, 456, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloud, S.S. Impact of Municipal and Industrial Waste on the Distribution and Accumulation of Some Heavy Metals in Sandy Soils of Al-Qassim Region at Central of Saudi Arabia. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 1, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Aloud, S.S.; Alotaibi, K.D.; Almutairi, K.F.; Albarakah, F.N. Assessment of Heavy Metals Accumulation in Soil and Native Plants in an Industrial Environment, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E.; Stoffella, P.J. Trace Elements in Agroecosystems and Impacts on the Environment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2005, 19, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, L.; Bian, X.; Zhang, W. Source Attributions of Heavy Metals in Rice Plant Along Highway in Eastern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, F.R.; Hamzah, H.A. Heavy Metals Accumulation in Suburban Roadside Plants of a Tropical Area (Jengka, Malaysia). Ecol. Process. 2018, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabulo, G.; Oryem-Origa, H.; Diamond, M. Assessment of Lead, Cadmium, and Zinc Contamination of Roadside Soils, Surface Films, and Vegetables in Kampala City, Uganda. Environ. Res. 2006, 101, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Schreck, E.; Xiong, T.; Niazi, N.K. Foliar Heavy Metal Uptake, Toxicity and Detoxification in Plants: A Comparison of Foliar and Root Metal Uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Shen, L.F.; Liu, J.W.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, S.R. Uptake of Toxic Heavy Metals by Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivated in Agricultural Soil near Zhengzhou city, People Republic of China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koz, B.; Cevik, U. Lead Adsorption Capacity of Some Moss Species Used for Heavy Metal Analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boularbah, A.; Schwartz, C.; Bitton, G.; Aboudrar, W.; Ouhammou, A.; Morel, J.L. Heavy metal contamination from mining sites in South Morocco: 2. Assessment of metal accumulation and toxicity in plants. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yan, X.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, C.; Devkota, L.P. Factorial analysis of heavy metal concentration in roadside farmland plants around Kathmandu, Nepal. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 178–181, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, P.P.; Legostaeva, Y.B.; Savvinov, G.N. Technogenic Landscapes and Their Influence on The Natural Soil Cover of Western Yakutia. Vestn. NEFU 2005, 2, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- JV Udachninsky GOK AK «ALROSA» (PJSC). Monitoring of Sustainable Development. Available online: https://monitoring-esg.ru/esg-analitika/analitika-po-kompaniyam/sp-ak-alrosa-pao-udachninskij-gorno-obogatitelnyj-kombinat (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Legostaeva, Y.; Kozlova, I.; Popov, V.; Noev, D. Geoecological Situation in the Area of Aikhal MPD. In Proceedings of the Geology and Mineral Resources of the North-East of Russia, Yakutsk, Russia, 8 April 2020; pp. 482–485. [Google Scholar]
- Drozdov, A.V.; Popov, V.F. Removal of drainage brines into the bowels of the permafrost zone during the development of diamond deposits in Yakutia. Explor. Prot. Miner. Resour. 2013, 12, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Gololobova, A.G. Investigation of The Spatial Distribution of Microelements in Soils by the Method of Multivariate Statistical Analysis (on the Example of The Territory of the Daldyn Kiberlite Field, Northwestern Yakutia). Bull. Tomsk. Polytech. 2023, 334, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Mironova, S.I. Plant Successions in the Natural-Technogenic Landscapes of Western Yakutia and their Optimization; Academy of Natural History Publ. House: Moscow, Russia, 2016; p. 140. [Google Scholar]
- Poiseeva, S.I. The current state of vegetation in the zone of technogenesis (on the example of North-Western Yakutia). Probl. Reg. Ecol. 2008, 2, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Legostaeva, Y.B.; Gololobova, A.G. Features of the distribution of trace elements in the soils of the background and impact zones at diamond mining sites in the northwest of the Siberian Platform. Bull. Tomsk. Polytech. 2021, 332, 142–153. [Google Scholar]
- International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS). IUSS Working Group WRB, 4th ed.; World Reference Base for Soil Resources. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10390; Soil Quality—Determination of pH. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- GOST-26483-85; State Standard of the Union of SSR. Soils. Preparation of Salt Extract and Determination of Its pH by CINAO Method. Standards Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 1985.
- ISO 14235; Soil Quality—Determination of Organic Carbon by Sulfochromic Oxidation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- GOST-26213-91; State Standard of the Union of SSR. Soils. Methods for Determination of Organic Matter. Standards Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 1991.
- Method M 03-07-2014; Measurement of the Mass Fraction of Elements (As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb, V, Zn) in Samples of Soil, Subsoil, Bottom Sediments and Sewage Sludge, FER 16.1:2:2.2:2.3.63-09. FGU “Federal Center for Analysis and Evaluation technogenic impact”: Moscow, Russia, 2014.
- Ilyin, V.B. Heavy Metals in the Soil-Plant System; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1991; p. 150. [Google Scholar]
- Ladonin, D.V. Compounds of heavy metals in soils—problems and methods of study. Soil Sci. 2002, 6, 682–692. [Google Scholar]
- Syso, A.I. Mechanisms of Distribution of Chemical Elements in Soil-Forming Rocks and Soils of the Western Siberia; SB RAS; Publishing House of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2007; Volume 227. [Google Scholar]
- Šmejkalová, M.; Mikanová, O.; Borůvka, L. Effects of heavy metal concentrations on biological activity of soil micro-organisms. Plant Soil Environ. 2003, 49, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelova, S.V.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Gorbunov, A.V.; Lyapunov, S.M.; Okina, O.I. Bioindication and monitoring of atmospheric deposition using trees and shrubs. In Proceedings of the 27th Task Force Meeting of the UNECE ICP Vegetation, Paris, France, 28–30 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Petrunina, N.S.; Ermakov, V.V. Modern aspects of plant geochemical ecology. Probl. Biogeochem. Geochem. Ecol. 2012, 1, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Neverova, O.A.; Kolmogorova, E.Y. Woody Plants and the Urbanized Environment: Ecological and Biotechnological Aspects; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2003; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination—A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, V.; Gulan, L.; Milenković, B.; Valjarević, A.; Zeremski, T.; Penjišević, I. Environmental Risk Assessment of Radioactivity and Heavy Metals in Soil of Toplica Region, South Serbia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2101–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, N.; Parsa, M.; Lentz, D.R.; Sobhanverdi, J. Identification of heavy metal pollution sources and its associated risk assessment in an industrial town using the K-means clustering technique. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 135, 105113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Zhang, T.X.; Wang, H.; Yu, X.J.; Zheng, X.N.; Li, H.Y. Characteristics of temperature and precipitation change in Xinjiang during 1961–2017. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2020, 14, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Rizova, V.A. Assessment of phytoremediation potential of indigenous plants growing around the solid waste open dumpsite. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 24, 234. [Google Scholar]
- Ladislas, S.; El-Mufleh, A.; Gérente, C.; Chazarenc, F.; Andres, Y.; Béchet, B. Potential of aquatic macrophytes as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution in urban stormwater runoff. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessalew, G.; Beyene, A.; Nebiyu, A.; Astatkie, T. Effect of brewery spent diatomite sludge on trace metal availability in soil and uptake by wheat crop, and trace metal risk on human health through the consumption of wheat grain. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitchison, J. The Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1986; 416p. [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison, J. The Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data; Blackburn Press: Caldwell, NJ, USA, 2003; 460p. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Buccianti, A. (Eds.) Compositional Data Analysis: Theory and Applications; Wiley: Chichester, UK; West Sussex, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Desyatkin, R.V.; Lesovaya, S.N.; Okoneshnikova, M.V.; Ivanova, A.Z. Cryozems and pale-yellow poorly differentiated soils of the tundra and taiga of Yakutia: Properties, mineralogical composition and classification. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 12, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Ershov, Y.I. Cryogenic soils on the rocks of the trap formation of Central Siberia. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2022, 6, 657–672. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, A.Z.; Okoneshnikova, M.V.; Desyatkin, A.R.; Filippov, N.V. Soils of cryogenic forms of the microrelief of the tundra and forest-tundra zones of North-Eastern Yakutia. Nat. Resour. Arct. Subarct. 2022, 1, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Desyatkin, R.V.; Lesovaya, S.N.; Okoneshnikova, M.V.; Ivanova, A.Z.; Platonova, N.V. Permafrost soils of the river basin. Alazeya: Properties, mineralogical composition and classification. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2023, 2, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Gololobova, A.G. Ecogeochemical monitoring of soil cover at diamond mining sites in Western Yakutia. Bull. Tomsk Polytech. 2020, 331, 146–157. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.S.; Han, Q.; Gui, C.L.; Cao, J.L.; Liu, Y.P.; He, X.D.; He, Y.C. Differences in the risk assessment of soil heavy metals between newly built and original parks in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRS Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; 548p. [Google Scholar]
- Ganpat, L.; Rajpaul, Y.; Atul, B.P.; Ravindra, K.R.; Anil, K.V.; Dinesh, K.Y. Heavy metals distribution and their correlation with physico-chemical properties of different soil series of northwestern India. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 90, 1742–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Nuralykyzy, B.; Wang, P.; Deng, X.; An, S.; Huang, Y. Heavy Metal Contents and Assessment of Soil Contamination in Different Land-Use Types in the Qaidam Basin. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Parvez, L.; Islam, M.A.; Dampare, S.B.; Suzuki, S. Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.J.; Taylor, K.G.; Hoon, S.R. Geochemical and mineral magnetic characterisation of urban sediment particulates, Manchester, UK. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, J.; Dai, B.; Zhu, Y. Identifying the origins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in soils of Ju country (Eastern China) using multivariate and geostatistical approach. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.J.A.; Arias, M.L.; Corbi, J.M.G. Heavy metals contents in agricultural topsoils in the Ebro basin (Spain). Application of the multivariate geoestatistical methods to study spatial variations. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gololobova, A.; Legostaeva, Y.; Popov, V.; Makarov, V.; Shadrinova, O. Geochemical Characteristics of Soils to the Impact of Diamond Mining in Siberia (Russia). Minerals 2022, 12, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, D.; Xu, F.; Lai, J.; Shao, L. Assessment of soil and maize contamination by TE near a coal gangue–fired thermal power plant. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Yaftian, M.R.; Parizanganeh, A. Statistical evaluation of topsoil heavy metal pollution around a lead and zinc production plant in Zanjan province, Iran. Caspian J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 13, 349–361. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabizadeh, Z.; Sodaeizadeh, H.; Hakimzadeh, M.A.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Ghanei Bafghi, M.J. A statistical approach to study the spatial heavy metal distribution in soils in the Kushk Mine, Iran. Geosci. Data J. 2022, 10, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Patra, A.; Singh Jatav, H.; Singh Jatav, S.; Kumar Singh, S.; Sathyanarayana, E.; Verma, S.; Singh, P. Toxicity of Cadmium in Soil-Plant-Human Continuum and Its Bioremediation Techniques. Soil Contamination—Threats and Sustainable Solutions; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; p. 298. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Liao, Q.; Chillrud, S.N.; Yang, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Yan, B. Environmental Exposure to Cadmium: Health Risk Assessment and its Associations with Hypertension and Impaired Kidney Function. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, M.A.; Hezmee, M.N.M.; Haron, A.W.; Sabri, M.Y.; Rajion, M.A. The detrimental effects of lead on human and animal health. Vet. World 2016, 9, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irshad, S.; Xie, Z.; Mehmood, S.; Nawaz, A.; Ditta, A.; Mahmood, Q. Insights into conventional and recent technologies for arsenic bioremediation: A systematic review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18870–18892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameters | Background Values, mg/kg | Mean | Median | Min | Max | CV | SD | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 7.31 | 7.60 | 4.32 | 8.70 | 0.99 | 1.00 | −1.38 | 1.74 |
| SOM | - | 23.74 | 30.00 | 2.20 | 30.00 | 96.29 | 9.81 | −1.29 | 0.04 |
| Pb | 1.79 | 2.21 | 1.96 | 0.33 | 6.60 | 1.99 | 1.41 | 1.13 | 1.08 |
| Ni | 3.12 | 15.39 | 2.40 | 1.00 | 163.8 | 1678.4 | 40.97 | 3.17 | 8.82 |
| Mn | 189 | 311.6 | 184.9 | 34.76 | 1856.0 | 172.61 | 415.5 | 3.00 | 8.49 |
| Cd | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 1.12 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 4.56 | 24.00 |
| Co | 2.64 | 4.53 | 2.69 | 0.53 | 34.65 | 47.94 | 6.92 | 3.47 | 12.20 |
| Cr | 0.93 | 1.94 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 21.45 | 16.62 | 4.08 | 4.08 | 16.70 |
| Zn | 9.47 | 12.10 | 11.46 | 0.05 | 36.46 | 48.91 | 6.99 | 1.17 | 2.53 |
| Cu | 5.81 | 8.21 | 5.73 | 0.82 | 28.44 | 40.95 | 6.40 | 1.33 | 1.37 |
| As | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.84 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 1.03 | 0.62 |
| Plant Species | Parameters | Pb | Ni | Mn | Cd | Co | Cr | Zn | Cu | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betula middendorffii (n = 36) | Mean | 3.03 | 8.08 | 144.8 | 0.04 | 0.39 | 12.30 | 42.94 | 4.73 | n/d |
| Minimum | 1.51 | 4.00 | 14.67 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 9.92 | 25.00 | 2.92 | n/d | |
| Maximum | 7.33 | 15.90 | 2237.2 | 0.26 | 2.71 | 15.62 | 97.54 | 8.83 | n/d | |
| SD | 1.15 | 2.61 | 408.5 | 0.04 | 0.46 | 1.67 | 24.18 | 1.27 | n/d | |
| Duschekia fruticosa (n = 14) | Mean | 3.09 | 6.81 | 31.5 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 12.08 | 25.00 | 5.16 | n/d |
| Minimum | 2.14 | 3.45 | 9.65 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 9.60 | 25.00 | 4.13 | n/d | |
| Maximum | 4.58 | 9.02 | 98.9 | 0.05 | 0.44 | 14.49 | 25.00 | 7.04 | n/d | |
| SD | 0.86 | 1.47 | 24.2 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 1.59 | 0.00 | 0.97 | n/d | |
| Background values, mg/kg | 2.88 | 7.39 | 44.82 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 12.13 | 33.46 | 4.72 | n/d | |
| Plant Species | Parameters | Pb | Ni | Mn | Cd | Co | Cr | Zn | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betula middendorffii (n = 36) | Mean | 2.07 | 3.26 | 2.32 | 0.36 | 0.16 | 18.85 | 10.15 | 1.02 |
| Median | 1.39 | 3.00 | 0.22 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 13.70 | 3.22 | 0.76 | |
| GM | 1.62 | 2.25 | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 12.30 | 3.77 | 0.76 | |
| Minimum | 0.39 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.52 | 0.99 | 0.18 | |
| Maximum | 9.64 | 8.40 | 64.36 | 1.07 | 0.78 | 135.6 | 210.0 | 4.27 | |
| SD | 1.76 | 1.91 | 10.75 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 22.89 | 34.60 | 0.84 | |
| Duschekia fruticosa. (n = 14) | Mean | 1.86 | 3.24 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 15.97 | 3.43 | 1.21 |
| Median | 2.15 | 2.73 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 14.46 | 2.39 | 0.88 | |
| GM | 1.58 | 2.68 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 15.01 | 2.71 | 0.95 | |
| Minimum | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 8.05 | 1.05 | 0.24 | |
| Maximum | 3.23 | 8.59 | 0.97 | 0.41 | 0.24 | 26.66 | 10.55 | 2.90 | |
| SD | 0.98 | 2.05 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 5.92 | 2.83 | 0.81 |
| № | Index | Research Point | PLI | PI | Hi, % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Plant | Soil | Plant | Soil | Plant | |||
| 1 | PLI ˂ 1 | P-8 | 0.96 | 0.92 | Zn2.7→As1.8 | PI ˂ 1 | Zn(52) > Mn(43) > Cd(43), Pb(43) > As(33) > Cr(24), Co(24) > Cu(19) | Co(38) > Zn(29) > Mn(19), Ni(19) > Cr(14), Cd(14) > Pb(10) |
| 2 | P-11 | 0.87 | 1.15 | Cd1.2 | B: Mn49,9→Cd3,1→Co2,0 | |||
| 3 | P-12 | 0.98 | 1.00 | Pb1.8→As1.8→Zn1.5 | B: Co2.4/D: Cu1.5→Cr1.2 | |||
| 4 | P-14 | 0.97 | 1.01 | Cu1.8→Zn1.5→Cd1.1→Cr1.0 | B: Mn2.6 | |||
| 5 | P-15 | 0.89 | 1.01 | As1.5→Co1.4→Mn1.0 | B: Co1.9→Mn1.7→ Zn1.6 | |||
| 6 | P-16 | 0.98 | 0.98 | As2.1→Co1.2→Cd1.1 | B: Zn1.7→Co1.6/D: Cr1.2 | |||
| 7 | P-17 | 0.97 | 1.00 | Co1.8→Cr1.1 | B: Zn1.5/D: Pb1.3→Cr1.0 | |||
| 8 | P-25 | 0.94 | 1.00 | Zn3.9→Cd1.9→Mn1.5→Cu1.1 | B: Zn2.4 | |||
| 9 | P-28 | 0.89 | 0.96 | Zn1.2→Cd1.2 | PI ˂ 1 | |||
| 10 | P-29 | 0.85 | 0.97 | Zn2.2 | D: Mn2.2→Ni1.2→Pb1.2 | |||
| 11 | P-30 | 0.97 | 1.01 | Cu3.1→Cd1.5→Zn1.4 | B: Co1.7→Zn1.6 | |||
| 12 | P-32 | 0.98 | 1.14 | Mn3.0→Cd2.2→ Zn2.1 | B: Cd8.7→Zn2.6→Cu1.6 | |||
| 13 | N-2 | 0.99 | 0.97 | As2.5→Mn1.3→Pb1.0 | PI ˂ 1 | |||
| 14 | N-3 | 0.92 | 0.96 | Pb1.1→Zn1.1 | PI ˂ 1 | |||
| 15 | N-4 | 0.91 | 0.97 | Pb1.3→Mn1.3→Zn1.1 | PI ˂ 1 | |||
| 16 | E-2 | 0.93 | 0.90 | Cu3.2→Cd1.3 | D: Cu1.1→Ni1.0 | |||
| 17 | S-3 | 0.98 | 0.97 | Pb2.8→As2.5→Co1.3→Cr1.0 | PI ˂ 1 | |||
| 18 | S-4 | 0.89 | 0.86 | Zn1.6→Mn1.2→Pb1.1 | D: Cu1.1 | |||
| 19 | W-1 | 0.99 | 1.05 | As4.2→Pb1.7→Mn1.1→Cd1.0 | B: Co3.6→Cd2.1 | |||
| 20 | W-2 | 0.95 | 1.03 | Mn1.9→Pb1.9→Cr1.1 | B: Co3.9→Ni1.5 | |||
| 21 | W-4 | 0.98 | 1.02 | Pb2.4→Mn2.3→Co1.5→Cr1.3 | B: Co2.3→Ni1.6 | |||
| 22 | PLI > 1 | P-2 | 1.00 | 1.05 | Cd1.4→Zn1.3→Cr1.2→As1.1→Cu1.0 | B: Cd3.3→Zn2.9 | Co(75), Cu(75) > Zn(70), Pb(70), As(70) > Cr(60), Cd(60) > Mn(55) > Ni(40) | Co(45) > Zn(40) > Cu(35) > Mn(30), Ni(30) > Cd(25) > Pb(15) > Cr(10) |
| 23 | P-12/1 | 1.00 | 0.83 | Ni3.2→Zn1.4 | D: Cr1.1→Cu1.0 | |||
| 24 | P-4 | 1.05 | 1.12 | As4.2→Co1.3→Pb1.3→Cr1.3→Zn1.2→Cu1.1→Cd1.0 | B: Mn27.1→Cd1.7→Co1.6 | |||
| 25 | P-5 | 1.01 | 1.01 | Cd3.2→Cr1.6→Zn1.3→Pb1.2→Co1.1 | B: Zn2.3→Mn1.9/D: Pb1.6→Cr1.2 | |||
| 26 | P-7 | 1.06 | 1.01 | As2.7→Cu1.7→Cr1.5→Co1.4→Zn1.4 | B: Zn2.7→Mn1.8 | |||
| 27 | P-13 | 1.01 | 1.02 | Cu2.3→As1.7→Ni1.3→Zn1.2→Pb1.1→Cr1.0 | B: Co2.6→Cu1.6 | |||
| 28 | P-19 | 1.09 | 1.11 | Ni20.2→Co3.6→Cr3.5→As1.8→Cu1.7 | B: Co12.3→Ni2.0→Cu1.9 | |||
| 29 | P-19/1 | 1.32 | 1.02 | Ni49.2→Cr23.1→Co11.1→Cu4.9→As1.5→Pb1.4→Mn1.1 | B: Co3.1→Zn1.5 | |||
| 30 | P-19/2 | 1.4 | 1.05 | Ni47.6→Cr11.7→Co13.1→Mn9.4→As3.2→Cu3.1→Zn1.5→Pb1.3 | B: Co4.6→Zn1.7→Ni1.7 | |||
| 31 | P-19/3 | 1.04 | 0.96 | Mn3.1→As2.7→Co1.7→Cu1.5→Pb1.3 | PI ˂ 1 | |||
| 32 | P-31 | 1.13 | 1.04 | Mn7.7→Co3.6→As2.9→Cu2.8→Cd1.2→Zn1.2 | B: Mn2.8→Zn1.9 | |||
| 33 | P-33 | 1.06 | 0.99 | As4.1→Cd2.3→Zn2.0→Mn1.7→Cu1.3→Pb1.2 | B: Co1.6 | |||
| 34 | P-34 | 1.06 | 0.96 | As6.5→Cu3.6→Ni1.1→Mn1.1→Zn1.0 | D: Cu1.1 | |||
| 35 | P-35 | 1.22 | 1.11 | Ni52.5→Cr7.3→Co6.3→Cu3.6→Zn2.0→Pb1.5→Mn1.2 | B: Co3.2→Ni2.2→Zn1.8→Cd1.7 | |||
| 36 | P-38 | 1.09 | 1.02 | As5.1→Pb1.6→Zn1.6→Cu1.4→Cd1.3→Cr1.2→Co1.1 | B: Zn2.8 | |||
| 37 | P-41 | 1.05 | 0.95 | Pb3.7→As2.9→Cu1.6→Cr1.0→Co1.0 | D: Pb1.5→Ni2.2→Cu1.0 | |||
| 38 | P-42 | 1.03 | 0.97 | Ni3.2→Pb2.4→Cu2.1→Cr2.1→Mn1.3→ Co1.2 | PI ˂ 1 | |||
| 39 | E-1 | 1.07 | 1.02 | As3.2→Pb1.9→Cu1.9→Ni1.7→Cr1.5→Mn1.4→Co1.3→Cd1.2 | D: Cd1.8→Mn1.5→Cu1.3→Ni1.1 | |||
| 40 | S-1 | 1.11 | 1.02 | Cd3.5→Pb2.6→Zn2.2→Mn2.1→Cr1.8→Ni1.7→Co1.2 | B: Co1.8 | |||
| 41 | S-2 | 1.11 | 1.08 | Mn9.8→Cd4.0→Zn2.5→Pb2.5→Co1.2 | B: Mn3.1→Co1.9→Cd1.7/D: Pb1.5→Cu1.2→Ni1.0 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gololobova, A.; Legostaeva, Y. An Assessment of the Impact of the Mining Industry on Soil and Plant Contamination by Potentially Toxic Elements in Boreal Forests. Forests 2023, 14, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081641
Gololobova A, Legostaeva Y. An Assessment of the Impact of the Mining Industry on Soil and Plant Contamination by Potentially Toxic Elements in Boreal Forests. Forests. 2023; 14(8):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081641
Chicago/Turabian StyleGololobova, Anna, and Yana Legostaeva. 2023. "An Assessment of the Impact of the Mining Industry on Soil and Plant Contamination by Potentially Toxic Elements in Boreal Forests" Forests 14, no. 8: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081641
APA StyleGololobova, A., & Legostaeva, Y. (2023). An Assessment of the Impact of the Mining Industry on Soil and Plant Contamination by Potentially Toxic Elements in Boreal Forests. Forests, 14(8), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081641







