Effects of Soil Arthropods on Non-Leaf Litter Decomposition: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Extraction and Calculation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
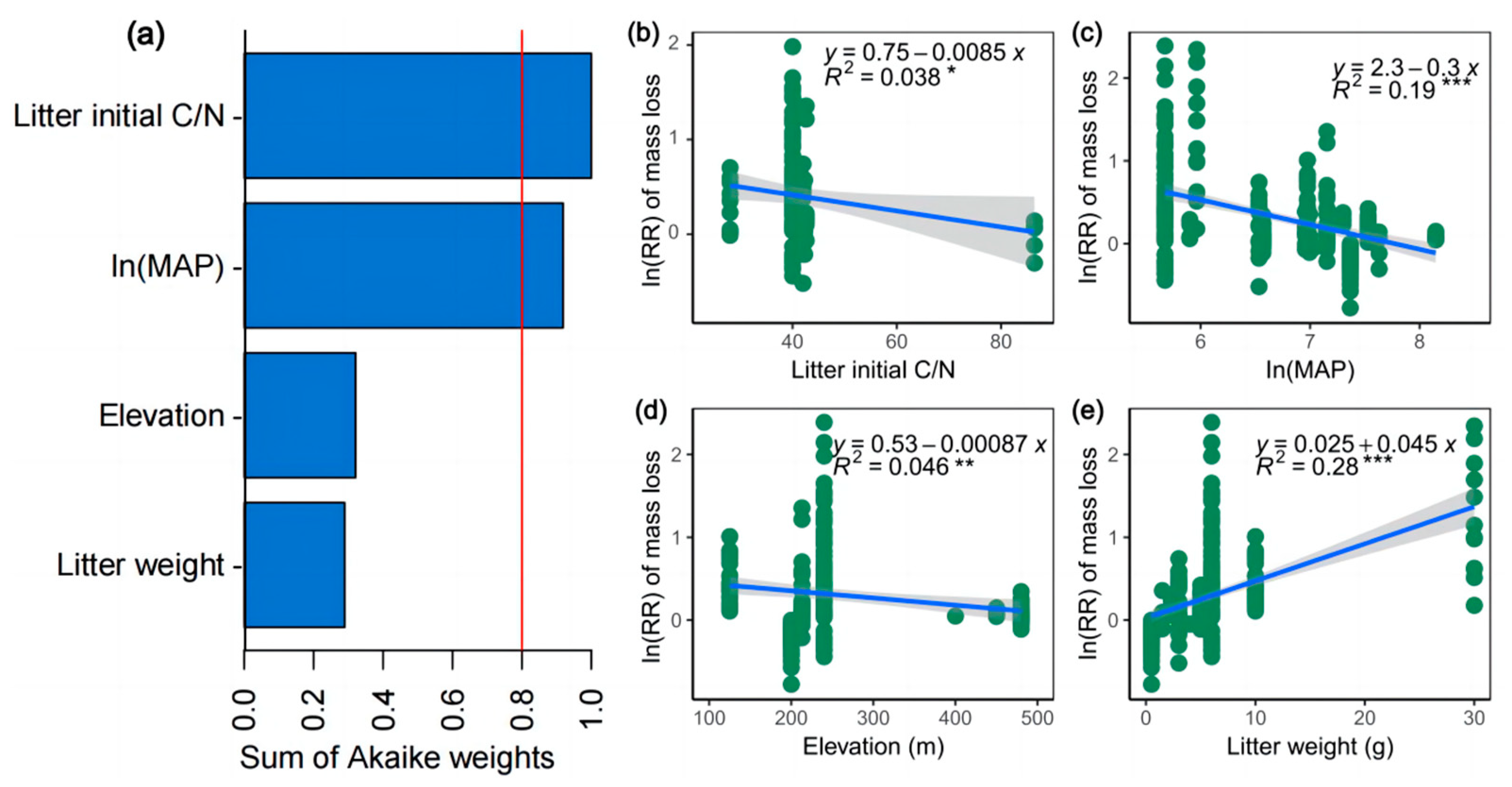
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Soil Arthropods on Non-Leaf Litter Mass Loss
3.2. Relationship between the Soil Arthropods’ Decomposition Effect and Its Potential Drivers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg, B.; Mcclaugherty, C. Plant Litter. Decomposition, Humus Formation, Carbon Sequestration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Culliney, T.W.J.A. Role of arthropods in maintaining soil fertility. Agriculture 2013, 3, 629–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.H.; Gratton, C. Insects as drivers of ecosystem processes. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 2, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrian, J. Patterns in the fate of production in plant communities. Am. Nat. 1999, 154, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, M.J.; Heal, O.W.; Anderson, J.M. Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Stud. Ecol. 1979, 5, 2772–2774. [Google Scholar]
- Parton, W.; Silver, W.L.; Burke, I.C.; Grassens, L.; Harmon, M.E.; Currie, W.S.; King, J.Y.; Adair, E.C.; Brandt, L.A.; Hart, S.C.; et al. Global-scale similarities in nitrogen release patterns during long-term decomposition. Science 2007, 315, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, Y.; Bar-On, Y.M.; Fromm, A.; Ostikar, M.; Shoshany, A.; Giz, O.; Milo, R. The global biomass and number of terrestrial arthropods. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eabq4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basset, Y.; Cizek, L.; Cuenoud, P.; Didham, R.K.; Guilhaumon, F.; Missa, O.; Novotny, V.; Odegaard, F.; Roslin, T.; Schmidl, J.; et al. Arthropod diversity in a tropical forest. Science 2012, 338, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, M.O.; Swan, C.M.; Dang, C.K.; McKie, B.G.; Bardgett, R.D.; Wall, D.H.; Hattenschwiler, S. Diversity meets decomposition. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, G.; Seastedt, T.R. Soil fauna and plant litter decomposition in tropical and subalpine forests. Ecology 2001, 82, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.J.; Cao, P.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Wang, W.F.; Ruan, H.H. Cellulose dominantly affects soil fauna in the decomposition of forest litter: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2020, 378, 114620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Gonzalez, G.; Zou, X.M. Earthworm abundance and functional group diversity regulate plant litter decay and soil organic carbon level: A global meta-analysis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 150, 103473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Vesterdal, L.; Penuelas, J.; Peguero, G.; Wu, Q.; Hedenec, P.; Yue, K.; Wu, F. Soil fauna effects on litter decomposition are better predicted by fauna communities within litterbags than by ambient soil fauna communities. Plant Soil 2023, 487, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, P.; Mao, Z.J.; Sun, T. Effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition in Chinese forests: A meta-analysis. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njoroge, D.M.; Chen, S.C.; Zuo, J.; Dossa, G.G.O.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. Soil fauna accelerate litter mixture decomposition globally, especially in dry environments. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, S.; Rammer, W.; Hothorn, T.; Seidl, R.; Ulyshen, M.D.; Lorz, J.; Cadotte, M.W.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Adhikari, Y.P.; Aragon, R.; et al. The contribution of insects to global forest deadwood decomposition. Nature 2021, 597, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.; Makita, N.; Mori, A.S.; Takeda, H. Plant species control and soil faunal involvement in the processes of above- and below-ground litter decomposition. Oikos 2016, 125, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastow, J.L.; Preisser, E.L.; Strong, D.R. Wood decomposition following a perennial lupine die-off: A 3-year litterbag study. Ecosystems 2008, 11, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milcu, A.; Manning, P. All size classes of soil fauna and litter quality control the acceleration of litter decay in its home environment. Oikos 2011, 120, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; John, K.; Arida, G.; Auge, H.; Brandl, R.; Horgan, F.G.; Hotes, S.; Marquez, L.; Radermacher, N.; Settele, J.; et al. Effects of residue management on decomposition in irrigated rice fields are not related to changes in the decomposer community. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, M.T.; Sabatte, M.L.; Rubin, M.A.R.; Sfeir, A.J.; Massobrio, M.J. Litter decomposition by soil fauna: Effect of land use in agroecosystems. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Zou, X.M. Exotic earthworms accelerate plant litter decomposition in a Puerto Rican pasture and a wet forest. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Palacios, P.; Shaw, E.A.; Wall, D.H.; Hattenschwiler, S. Temporal dynamics of biotic and abiotic drivers of litter decomposition. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Kang, B.T.; Brussaard, L. Biological effects of plant residues with contrasting chemical-compositions under humid tropical conditions—Decomposition and nutrient release. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Du, M.; Chen, J.; Tie, L.; Zhou, S.; Buckeridge, K.M.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Huang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Microbial necromass under global change and implications for soil organic matter. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 3503–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrer, C.; Vicca, S.; Hungate, B.A.; Phillips, R.P.; Prentice, I.C. Mycorrhizal association as a primary control of the CO2 fertilization effect. Science 2016, 353, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Palacios, P.; Maestre, F.T.; Kattge, J.; Wall, D.H. Climate and litter quality differently modulate the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition across biomes. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, D.H.; Bradford, M.A.; St John, M.G.; Trofymow, J.A.; Behan-Pelletier, V.; Bignell, D.D.E.; Dangerfield, J.M.; Parton, W.J.; Rusek, J.; Voigt, W.; et al. Global decomposition experiment shows soil animal impacts on decomposition are climate-dependent. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2661–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.C.; Bradford, M.A.J.A.S.E. Litter quality impacts on grassland litter decomposition are differently dependent on soil fauna across time. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2003, 24, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Huerta, R.A.; Falco, L.B.; Sandler, R.V.; Coviella, C.E. Differential contribution of soil biota groups to plant litter decomposition as mediated by soil use. PeerJ 2015, 3, e826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Auge, H.; Brandl, R.; Heong, K.L.; Hotes, S.; Settele, J.; Villareal, S.; Schaedler, M. Small-scale variability in the contribution of invertebrates to litter decomposition in tropical rice fields. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2015, 16, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Brussaard, L.; Kang, B.T.J.A.S.E. An index for assessing the quality of plant residues and evaluating their effects on soil and crop in the (sub-) humid tropics. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1995, 2, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Takeda, H. Dominant effects of litter substrate quality on the difference between leaf and root decomposition process above- and belowground. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2224–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, L.G.; David, A.W.; Stephen, M.S.; Mark, E.H.; William, J.P. Long-term dynamics of pine and hardwood litter in contrasting environments: Toward a global model of decomposition. Glob. Change Biol. Bioenergy 2000, 6, 751–765. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Hui, D.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, G. Rates of litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: Global patterns and controlling factors. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickings, K.; Grandy, A.S.; CReed, S.; Cleveland, C.C. The origin of litter chemical complexity during decomposition. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, S.E. Plant species effects on nutrient cycling: Revisiting litter feedbacks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouz, J. Effects of soil macro- and mesofauna on litter decomposition and soil organic matter stabilization. Geoderma 2018, 332, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Lu, X.G.; Jiang, M.; Bao, X. Impacts of soil fauna on litter decomposition at different succession stages of wetland in Sanjiang Plain, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tie, L.; Fu, R.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, S.; Hu, J.; Huang, C. The additions of nitrogen and sulfur synergistically decrease the release of carbon and nitrogen from litter in a subtropical forest. Forests 2020, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Harguindeguy, N.; Díaz, S.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Vendramini, F.; Cabido, M.; Castellanos, A.J.P. Chemistry and toughness predict leaf litter decomposition rates over a wide spectrum of functional types and taxa in central Argentina. Plant Soil 2000, 218, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, L.; Wei, S.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Peguero, G.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; Hu, J.; Huang, C. Phosphorus addition reverses the negative effect of nitrogen addition on soil arthropods during litter decomposition in a subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, L.; Wei, S.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; Bose, A.K.; Huang, C. N and P combined addition accelerates the release of litter C, N, and most metal nutrients in a N-rich subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Yin, X.Q.; Wang, H.X. Soil fauna effect on dryas octopetala litter decomposition in an alpine tundra of the Changbai Mountains, China. Alp. Bot. 2019, 129, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, C.; Corbara, B.; Dezerald, O.; Trzcinski, M.K.; Carrias, J.-F.; Dejean, A.; Cereghino, R. What drives detrital decomposition in neotropical tank bromeliads? Hydrobiologia 2017, 802, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Liu, Q.; Tian, S.Y.; Potapov, A.; Zhu, B.A.; Yang, K.J.; Li, Z.J.; Zhuang, L.Y.; Tan, B.; Zhang, L.; et al. Nitrogen deposition stimulates decomposition via changes in the structure and function of litter food webs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 166, 108522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.; Healey, I.J.P. Improvements in the gelatine-embedding technique for woodland soil and litter samples. Pedobiologia 1970, 10, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D. Regulation of deciduous forest litter decomposition by soil arthropod feces. In The Role of Arthropods in Forest Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1977; pp. 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C.; Heath, G.J.S.O. The role of soil animals in breakdown of leaf material. Soil Org. 1962, 1962, 76–84. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, W.; Tie, L.; Zhou, S.; Hu, J.; Ouyang, S.; Huang, C. Effects of Soil Arthropods on Non-Leaf Litter Decomposition: A Meta-Analysis. Forests 2023, 14, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081557
Cheng W, Tie L, Zhou S, Hu J, Ouyang S, Huang C. Effects of Soil Arthropods on Non-Leaf Litter Decomposition: A Meta-Analysis. Forests. 2023; 14(8):1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081557
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Wei, Liehua Tie, Shixing Zhou, Junxi Hu, Shengnan Ouyang, and Congde Huang. 2023. "Effects of Soil Arthropods on Non-Leaf Litter Decomposition: A Meta-Analysis" Forests 14, no. 8: 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081557
APA StyleCheng, W., Tie, L., Zhou, S., Hu, J., Ouyang, S., & Huang, C. (2023). Effects of Soil Arthropods on Non-Leaf Litter Decomposition: A Meta-Analysis. Forests, 14(8), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081557







