Exploring the Role of Stumps in Soil Ecology: A Study of Microsite Organic Carbon and Enzyme Activities in a Larix olgensis Henry Plantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Site
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TOC and Active Organic C Fractions
3.2. Hydrolase Activity
3.3. Oxidase Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kappes, H.; Catalano, C.; Topp, W. Coarse woody debris ameliorates chemical and biotic soil parameters of acidified broad-leaved forests. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 36, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palviainen, M.; Finer, L.; Laiho, R.; Shorohova, E.; Kapitsa, E.; Vanha, M.I. Carbon and nitrogen release from decomposing Scots pine, Norway spruce and silver birch stumps. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschet, G.T.; Weedon, J.T.; Aerts, R.; Van, H.J.R.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. Interspecific differences in wood decay rates: Insights from a new short-term method to study long-term wood decomposition. J. Ecol. 2012, 100, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finer, L.; Mannerkoski, H.; Piirainen, S.; Starr, M. Carbon and nitrogen pools in an old-growth, Norway spruce mixed forest in eastern Finland and changes associated with clear-cutting. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 174, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnússon, R.Í.; Tietema, A.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Hefting, M.M.; Kalbitz, K. Tamm Review: Sequestration of carbon from coarse woody debris in forest soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 377, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, S.D.; Groffman, P.M. Soil nitrogen cycling under litter and coarse woody debris in a mixed forest in New York State. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 2159–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Men, X.; Sun, Z.H.; Chen, X.W. Effects of Larix olgensis Henry Stumps and Coarse Roots on Phosphorus Fractions and Availability in Plantation Microsite Soils. Forests 2022, 13, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, J.D.H.; Lajtha, K. The imprint of coarse woody debris on soil chemistry in the western Oregon Cascades. Biogeochemistry 2004, 71, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalamea, M.; Gonzalez, G.; Ping, C.L.; Michaelson, G. Soil organic matter dynamics under decaying wood in a subtropical wet forest: Effect of tree species and decay stage. Plant Soil 2007, 296, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.H.; Post, W.M.; King, A.W. Fast labile carbon turnover obscures sensitivity of heterotrophic respiration from soil to temperature: A model analysis. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R. Labile organic matter fractions as central components of the quality of agricultural soils: An overview. Adv. Agron. 2005, 5, 221–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.G.; Lou, Y.L.; Sun, X.L.; Wang, W.; Baniyamuddin, M.; Zhao, K. Soil organic carbon active fractions as early indicators for total carbon change under straw incorporation. Biol. Fert. Soils 2011, 47, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błońska, E.; Kacprzyk, M.; Spólnik, A. Effect of deadwood of different tree species in various stages of decomposition on biochemical soil properties and carbon storage. Ecol. Res. 2017, 32, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmsley, J.D.; Godbold, D.L. Stump Harvesting for Bioenergy—A Review of the Environmental Impacts. Forestry 2010, 83, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Gallo, M.E.; Lauber, C.; Waldrop, M.P.; Zak, D.R. Extracellular enzyme activities and soil organic matter dynamics for northern hardwood forests receiving simulated nitrogen deposition. Biogeochemistry 2005, 75, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, E.; Re, D.A.A.M.; Rao, M.A.; Gianfreda, L. Development and validation of numerical indexes integrating enzyme activities of soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L. Phenol oxidase, peroxidase and organic matter dynamics of soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusack, D.F.; Silver, W.L.; Torn, M.S.; Burton, S.D.; Firestone, M.K. Changes in microbial community characteristics and soil organic matter with nitrogen additions in two tropical forests. Ecology 2011, 92, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, F.; Dong, L. Individual tree diameter growth model for Larix olgensis plantation in Heilongjiang Province, China. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2018, 42, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Cheng, F.; Li, M.; He, P.; Shen, L.; Liu, H. Effect of different decay classes of Eucalyptus stump substrates on microbial resource limitation and carbon-use efficiency. Plant Soil 2022, 478, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tláskal, V.; Brabcová, V.; Větrovský, T.; Jomura, M.; López-Mondéjar, R.; Oliveira Monteiro, L.M.; Baldrian, P. Complementary roles of wood-inhabiting fungi and bacteria facilitate deadwood decomposition. Msystems 2021, 6, e01078-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, B.G. Exploring relationships between enzyme activities and leaf litter decomposition in a wet tropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 64, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Xia, D.; Yang, C.; Zhao, X. Genetic variation and superior provenances selection for wood properties of Larix olgensis at four trials. J. For. Res. 2022, 33, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Effects of thinning intensity on carbon storage of Larix olgensis plantation ecosystem. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2016, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Pang, Y. Tree species classification in an extensive forest area using airborne hyperspectral data under varying light conditions. J. For. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.M.L. Wildlife, Forests, and Forestry. Principles of Managing Forests for Biological Diversity; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990; p. 370. [Google Scholar]
- Petrillo, M.; Cherubini, P.; Fravolini, G.; Marchetti, M.; Ascher-Jenull, J.; Schärer, M.; Synal, H.; Bertoldi, D.; Camin, F.; Larcher, R.; et al. Time since death and decay rate constants of Norway spruce and European larch deadwood in subalpine forests determined using dendrochronology and radiocarbon dating. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 1537–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Osawa, A.; Prokushkin, A.S.; Sofronov, M.A.; Abaimov, A.P. Root system development of Larix gmelinii trees affected by micro-scale conditions of permafrost soils in central Siberia. Plant Soil 2003, 255, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Elliott, E.T. Particulate Soil Organic-Matter Changes across a Grassland Cultivation Sequence. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Islam, K.R.; Stine, M.A.; Gruver, J.B.; Samson-Liebig, S.E. Estimating active carbon for soil quality assessment: A simplified method for laboratory and field use. Am. J. Altern. Agr. 2003, 18, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.B.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agr. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. Microbial biomass measurements in forest soils: The use of the chloroform fumigation-incubation method in strongly acid soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 19, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiya-Cork, K.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Zak, D.R. The effects of long-term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtev, P.S.; Ehrenfeld, J.G.; Huang, W.Z. Enzyme activities during litter decomposition of two exotic and two native plant species in hardwood forests of New Jersey. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, C.E.; Warnock, D.D.; Van, H.D.J.; Weintraub, M.N.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Allison, S.D. Measuring phenol oxidase and peroxidase activities with pyrogallol, L-DOPA, and ABTS: Effect of assay conditions and soil type. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 67, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.M.; Wen, D.Z.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, J. Altitudinal changes in active and recalcitrant soil carbon pools of forests in the Dinghu Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 6089–6099. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.M.; Ruan, H.H.; Fu, Y.; Yang, X.D.; Sha, L.Q. Estimating soil labile organic carbon and potential turnover rates using a sequential fumigation-incubation procedure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1923–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietl, A.J.; Jackson, C.R. Effects of the ecological restoration practices of prescribed burning and mechanical thinning on soil microbial enzyme activities and leaf litter decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 50, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, R.H.; Kennepohl, P.; Solomon, E.I. Structural and functional aspects of metal sites in biology. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2239–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, D.T.; Hanson, J.B. The mineral nutrition of higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1980, 31, 239–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zámocký, M.; Hofbauer, S.; Schaffner, I.; Gasselhuber, B.; Nicolussi, A.; Soudi, M.; Obinger, C. Independent evolution of four heme peroxidase superfamilies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 574, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, N.; Esposito, E. Potential applications of oxidative enzymes and phenoloxidase-like compounds in wastewater and soil treatment: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 28, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejirian, A.; Xu, F. Inhibition of cellulase-catalyzed lignocellulosic hydrolysis by iron and oxidative metal ions and complexes. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2010, 76, 7673–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Bora, S.; Thrall, P.H.; Richardson, A.E. Soil C and N as causal factors of spatial variation in extracellular enzyme activity across grassland-woodland ecotones. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameshwar, A.K.S.; Qin, W.S. Recent Developments in Using Advanced Sequencing Technologies for the Genomic Studies of Lignin and Cellulose Degrading Microorganisms. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.Y.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Comerford, N.B.; Sickman, J.O.; Grunwald, S. Carbon Mineralization and Labile Organic Carbon Pools in the Sandy Soils of a North Florida Watershed. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 represents the study area’s location in China, while the
represents the study area’s location in China, while the  represents the sampling location in the Forest Farm for this study.
represents the sampling location in the Forest Farm for this study.
 represents the study area’s location in China, while the
represents the study area’s location in China, while the  represents the sampling location in the Forest Farm for this study.
represents the sampling location in the Forest Farm for this study.




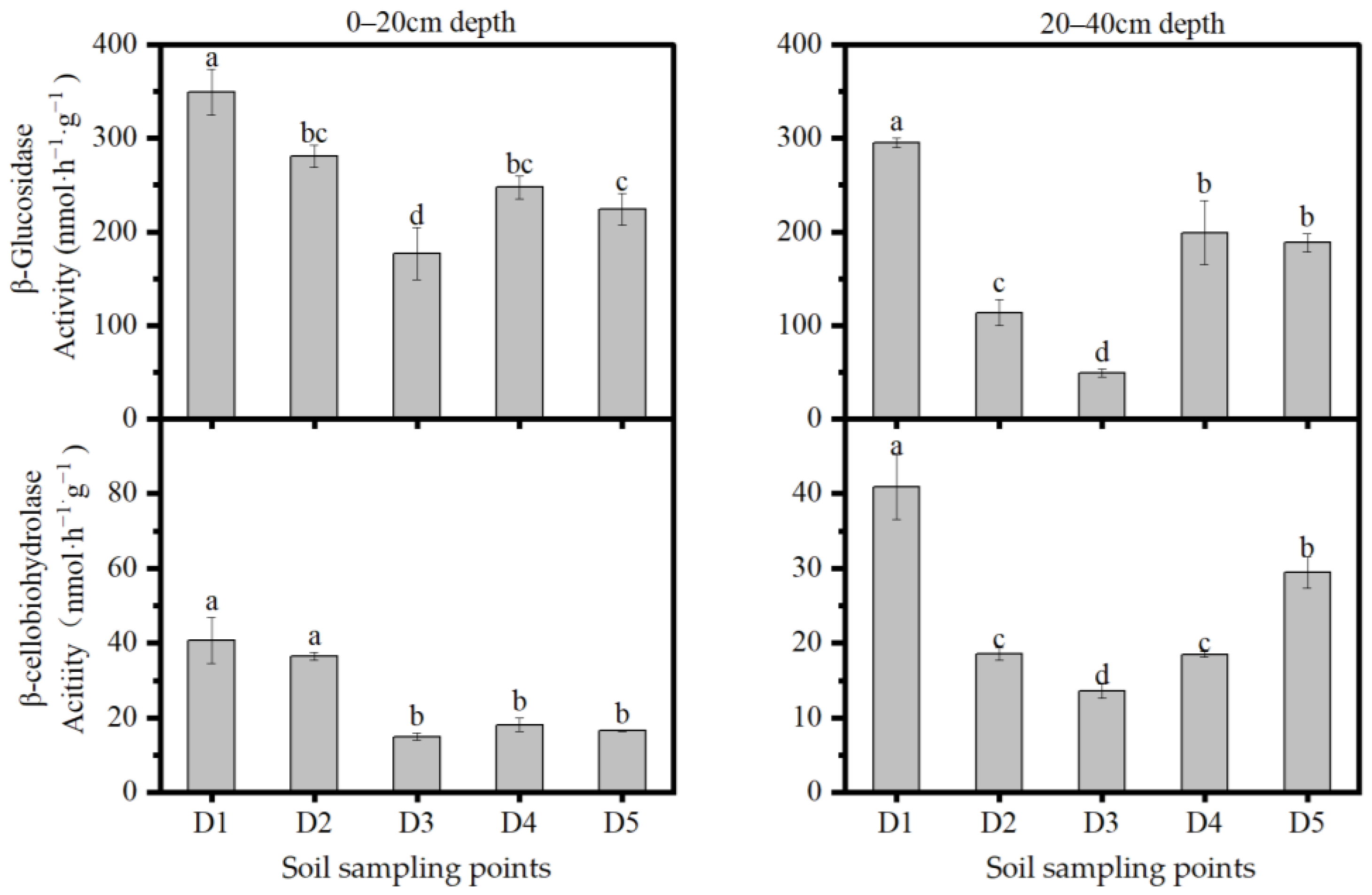
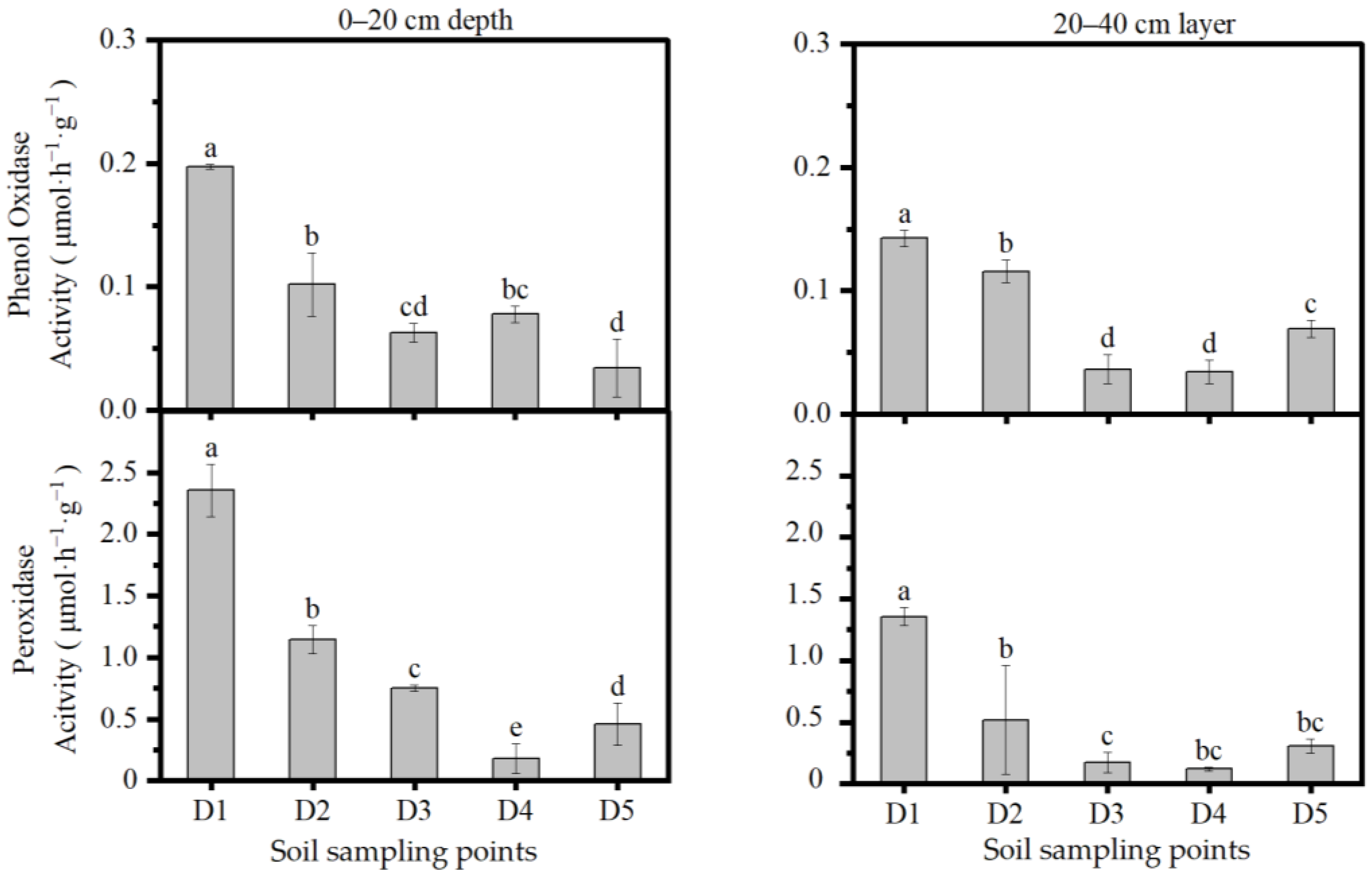
| Soil Depths | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | pH | SOC (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | TP (mg/kg) | NH4+ (g/kg) | NO3– (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 1.10 ± 0.05 | 5.8 ± 0.02 | 49.02 ± 0.42 | 3.24 ± 0.03 | 610.94 ± 6.29 | 1.57 ± 0.10 | 1.37 ± 0.01 |
| 20–40 cm | 1.56 ± 0.02 | 5.6 ± 0.06 | 5.67 ± 0.21 | 0.63 ± 0.05 | 322.21 ± 8.06 | 1.67 ± 0.09 | 0.43 ± 0.02 |
| Enzymes Type | Enzyme | EC Number | Substrate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrolase | β-glucosidase | EC 3.2.1.21 | 4-Methylumbelliferyl-β-D-glucoside |
| β-cellobiohydrolase | EC 3.2.1.91 | 4-Methylumbelliferyl-β-D-cellobioside | |
| Oxidase | Peroxidase | EC 1.11.1.7 | L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine and H2O2 |
| Phenol oxidase | EC 1.10.3.2 | L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| POC | EOC | MBC | BG | CBH | PER | POX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC | 0.996 ** | 0.979 ** | 0.827 ** | 0.547 | 0.083 | 0.405 | 0.195 |
| POC | - | 0.993 ** | 0.814 ** | 0.562 * | 0.114 | 0.436 | 0.216 |
| EOC | - | - | 0.796 ** | 0.551 * | 0.141 | 0.464 | 0.241 |
| MBC | - | - | - | 0.114 | −0.301 | 0.019 | −0.102 |
| BG | - | - | - | - | 0.773 ** | 0.730 ** | 0.645 * |
| CBH | - | - | - | - | - | 0.801 ** | 0.800 ** |
| PER | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.891 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Y.; Men, X.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X. Exploring the Role of Stumps in Soil Ecology: A Study of Microsite Organic Carbon and Enzyme Activities in a Larix olgensis Henry Plantation. Forests 2023, 14, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14051027
Yue Y, Men X, Sun Z, Chen X. Exploring the Role of Stumps in Soil Ecology: A Study of Microsite Organic Carbon and Enzyme Activities in a Larix olgensis Henry Plantation. Forests. 2023; 14(5):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14051027
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Yang, Xiuli Men, Zhihu Sun, and Xiangwei Chen. 2023. "Exploring the Role of Stumps in Soil Ecology: A Study of Microsite Organic Carbon and Enzyme Activities in a Larix olgensis Henry Plantation" Forests 14, no. 5: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14051027
APA StyleYue, Y., Men, X., Sun, Z., & Chen, X. (2023). Exploring the Role of Stumps in Soil Ecology: A Study of Microsite Organic Carbon and Enzyme Activities in a Larix olgensis Henry Plantation. Forests, 14(5), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14051027






