The Impact of Predation of Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae) on Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) and Tsuga canadensis (Pinales: Pinaceae) Tree Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
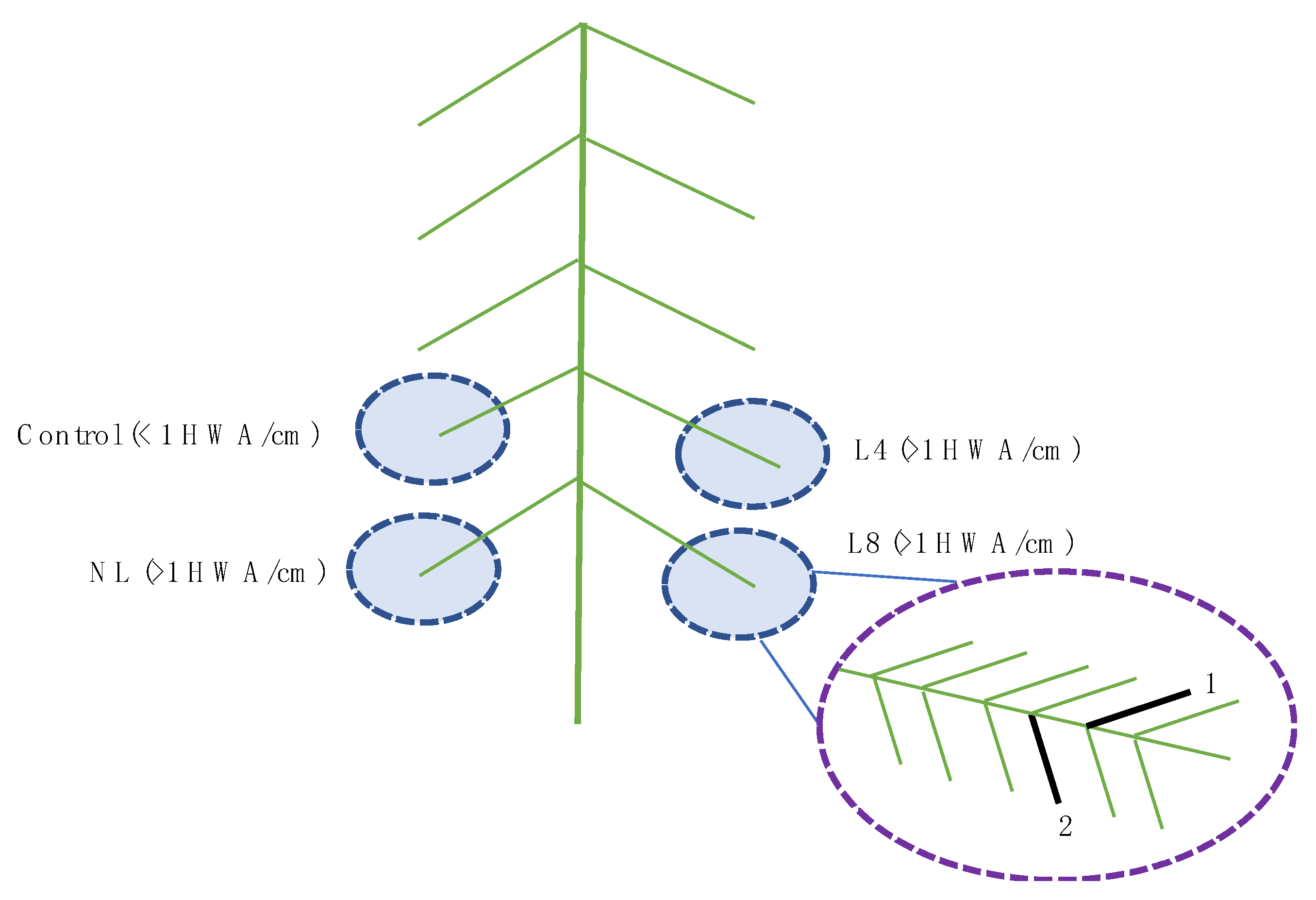
2.1. Field Site Set Up
2.2. Laricobius nigrinus Rearing
2.3. Experiment 1—L. nigrinus Impact on HWA Sistens Densities
2.4. Experiment 2—L. nigrinus Impacts on Tree Growth and Next Generation HWA Sistens Population Density
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Site Environmental Conditions
3.2. Temperature Inside vs. Outside Mesh Cages
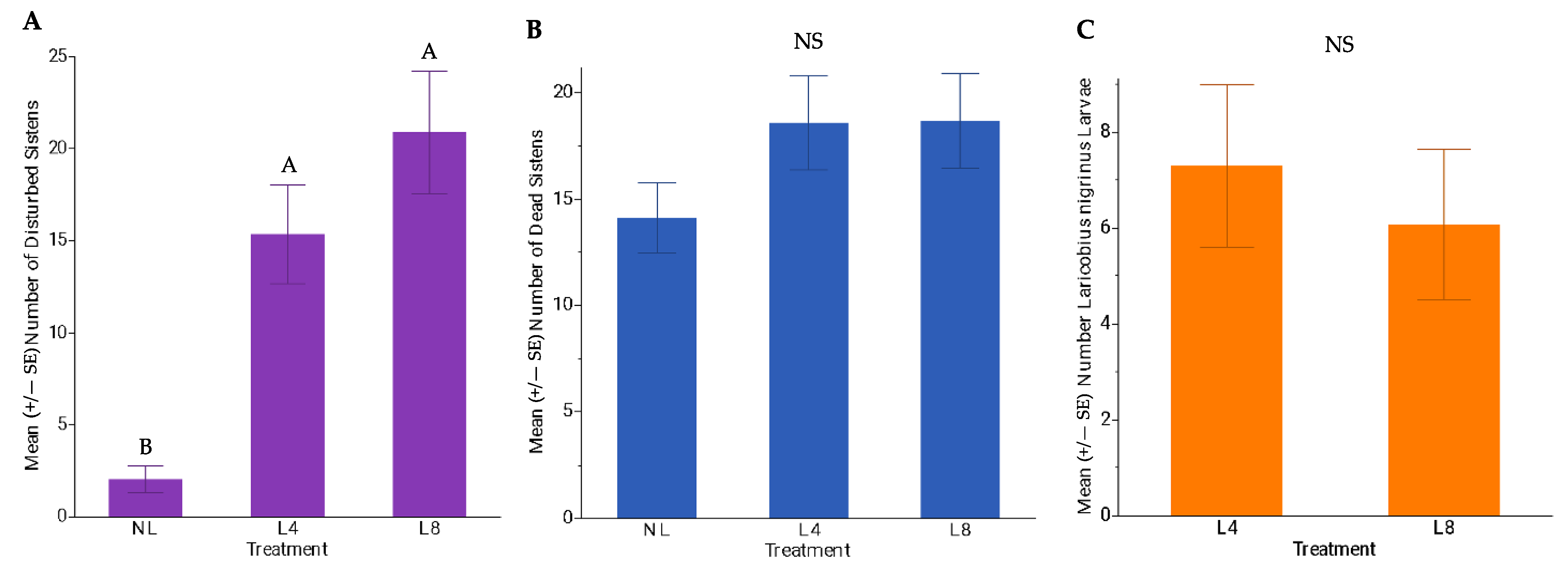
3.3. Experiment 1—L. nigrinus Impacts on HWA Sistens Densities
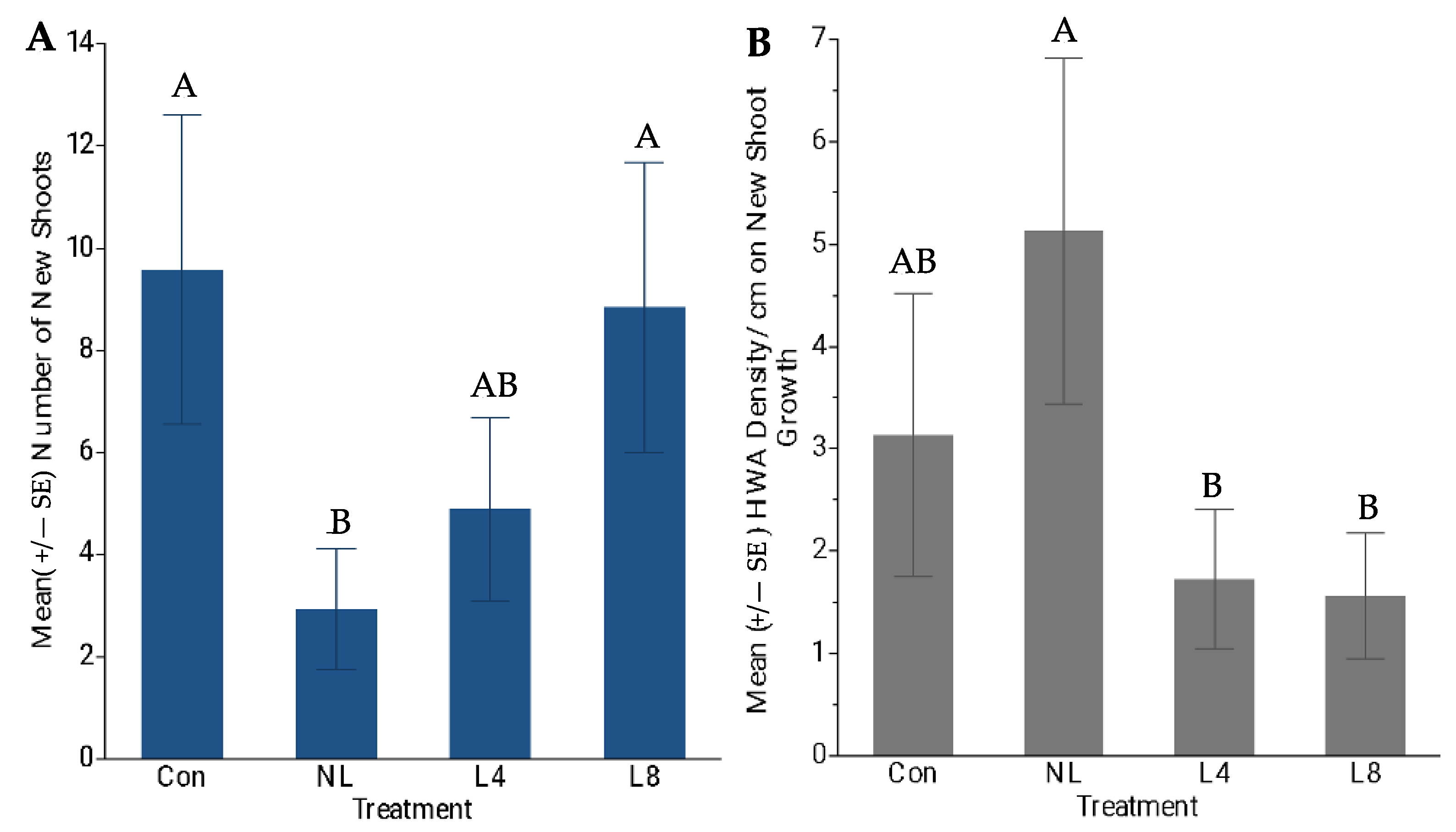
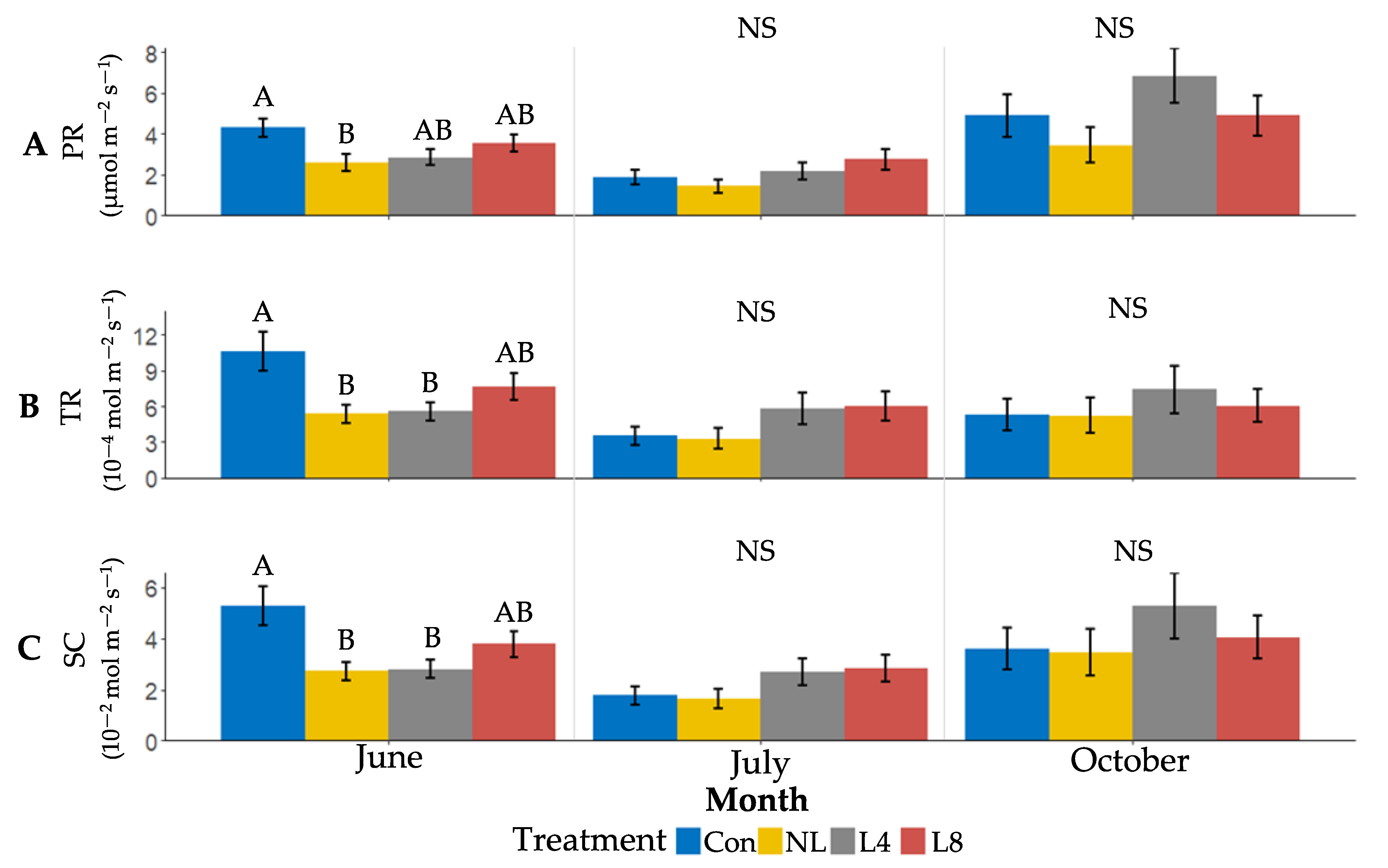
3.4. Experiment 2—L. nigrinus Impacts on Tree Growth and Next Generation HWA Sistens Population Density
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Cage Effects
4.2. Experiment 1—L. nigrinus Impacts on Winter HWA Sistens Densities
4.3. Experiment 2—L. nigrinus Impacts on External Tree Growth and Next Generation HWA Sistens Population Density
4.4. Experiment 2—L. nigrinus Impacts on Tree Physiology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellison, A.M.; Orwig, D.A.; Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Preisser, E.L. The past, present, and future of the hemlock woolly adelgid (Adelges tsugae) and its ecological interactions with eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) forests. Insects 2018, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havill, N.P.; Shiyake, S.; Lamb Galloway, A.; Foottit, R.G.; Yu, G.; Paradis, A.; Elkinton, J.; Montgomery, M.E.; Sano, M.; Caccone, A. Ancient and modern colonization of North America by hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae), an invasive insect from East Asia. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 2065–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingley, M.W.; Orwig, D.A.; Field, R.; Motzkin, G. Avian response to removal of a forest dominant: Consequences of hemlock woolly adelgid infestations. J. Biogeogr. 2002, 29, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vose, J.M.; Wear, D.N.; Mayfield, A.E.; Dana Nelson, C. Hemlock woolly adelgid in the southern Appalachians: Control strategies, ecological impacts, and potential management responses. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 291, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwig, D.A.; Foster, D.R. Forest response to the introduced hemlock woolly adelgid in southern New England, USA. J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 1998, 125, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, H.L.; Rieske, L.K. The aftermath of an invasion: Structure and composition of central Appalachian hemlock forests following establishment of the hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 3135–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abella, S.R. Impacts and management of hemlock woolly adelgid in national parks of the eastern United States. Southeast. Nat. 2014, 13, 16–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annand, P.N. A new species of Adelges (Hemiptera, Phylloxeridae). Pan-Pac. Entomol. 1924, 1, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Havill, N.P.; Montgomery, M.E.; Yu, G.; Shiyake, S.; Caccone, A. Mitochondrial DNA from hemlock woolly adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) suggests cryptic speciation and pinpoints the source of the introduction to eastern North America. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2006, 99, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.S. Evidence of a polymorphic life cycle in the hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae (Homoptera: Adelgidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1989, 82, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mausel, D.L.; Salom, S.M.; Kok, L.T.; Fidgen, J.G. Propagation, synchrony, and impact of introduced and native Laricobius spp. (Coleoptera: Derodontidae) on hemlock woolly adelgid in Virginia. Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, D.R.; Salom, S.M. Biology of the hemlock woolly adelgid. In Proceedings of the Technology Transfer Hemlock Woolly Adelgid: Proceedings of the First Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Review, Charlottesville, VA, USA, 12 October 1995; Volume 96, p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Oten, K.L.F.; Cohen, A.C.; Hain, F.P. Stylet bundle morphology and trophically related enzymes of the hemlock woolly adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.F.; Shields, K.S.; Berlyn, G.P. Hemlock woolly adelgid (Homoptera: Adelgidae): Stylet bundle insertion and feeding sites. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1995, 88, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbu, S.; Keena, M.A.; Whitmore, M.C. Hemlock woolly adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae): A non-native pest of hemlocks in eastern North America. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2018, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggett, B.; Savage, J.; Hao, G.-Y.; Preisser, E.; Holbrook, N. Impact of hemlock woolly adelgid (Adelges tsugae) infestation on xylem structure and function and leaf physiology in eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis). Funct. Plant Biol. 2017, 45, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, L.A.; Dillaway, D.N.; Rieske, L.K. Effect of an exotic herbivore, Adelges tsugae, on photosynthesis of a highly susceptible Tsuga host, with notes on conspecifics. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2014, 8, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, L.; Charles, S.; Sirulnik, A.G.; Tuininga, A.R.; Lewis, J.D. Invasive insect effects on nitrogen cycling and host physiology are not tightly linked. Tree Physiol. 2015, 35, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniat, C.F.; Zietlow, D.R.; Brantley, S.T.; Brown, C.L.; Mayfield, A.E., III; Jetton, R.M.; Rhea, J.R.; Arnold, P. Physiological responses of eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) to light, adelgid infestation, and biological control: Implications for hemlock restoration. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 460, 117903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domec, J.-C.; Rivera, L.N.; King, J.S.; Peszlen, I.; Hain, F.; Smith, B.; Frampton, J. Hemlock woolly adelgid (Adelges tsugae) infestation affects water and carbon relations of eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) and Carolina hemlock (Tsuga caroliniana). New Phytol. 2013, 199, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.M.; Copenheaver, C.A.; Zink-Sharp, A. radial growth changes following hemlock woolly adelgid infestation of eastern hemlock. Ann. For. Sci. 2014, 71, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda-King, L.; Radville, L.; Preisser, E.L. False ring formation in eastern hemlock branches: Impacts of hemlock woolly adelgid and elongate hemlock scale. Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, M.S. Density-dependent feedback and population cycles in Adelges tsugae (Homoptera: Adelgidae) on Tsuga canadensis. Environ. Entomol. 1991, 20, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwig, D.A. Stand dynamics associated with chronic hemlock woolly adelgid infestations in southern New England. In Proceedings of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid in the Eastern United States Symposium, East Brunswick, NJ, USA, 5–7 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zilahi-Balogh, G.M.G.; Kok, L.T.; Salom, S.M. Host specificity of Laricobius nigrinus Fender (Coleoptera: Derodontidae), a potential biological control agent of the hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae Annand (Homoptera: Adelgidae). Biol. Control 2002, 24, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilahi-Balogh, G.M.G.; Salom, S.M.; Kok, L.T. Development and reproductive biology of Laricobius nigrinus, a potential biological control agent of Adelges tsugae. Biocontrol 2003, 48, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.A.; Salom, S.M.; Brewster, C.C.; Onken, B.P.; Kok, L.T. Spatiotemporal distribution of the hemlock woolly adelgid predator Laricobius nigrinus after release in eastern hemlock forests. Agric. For. Entomol. 2012, 14, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.R.; McAvoy, T.J.; Dorman, S.; Bekelja, K.; Kring, T.J.; Salom, S.M. Establishment and distribution of Laricobius spp. (Coleoptera: Derodontidae), a predator of hemlock woolly adelgid, within the urban environment in two localities in Southwest Virginia. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubb, C.S.; McAvoy, T.J.; Stanley, K.E.; Heminger, A.R.; Salom, S.M. Establishment of the predator Laricobius nigrinus, introduced as a biological control agent for hemlock woolly adelgid in Virginia, USA. Biocontrol 2021, 66, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mausel, D.L.; Salom, S.M.; Kok, L.T.; Davis, G.A. Establishment of the hemlock woolly adelgid predator, Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae), in the eastern United States. Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubb, C.S.; Heminger, A.R.; Mayfield, A.E.; Elkinton, J.S.; Wiggins, G.J.; Grant, J.F.; Lombardo, J.A.; McAvoy, T.J.; Crandall, R.S.; Salom, S.M. Impact of the introduced predator, Laricobius nigrinus, on ovisacs of the overwintering generation of hemlock woolly adelgid in the eastern United States. Biol. Control 2020, 143, 104180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, A.E.; Reynolds, B.C.; Coots, C.I.; Havill, N.P.; Brownie, C.; Tait, A.R.; Hanula, J.L.; Joseph, S.V.; Galloway, A.B. Establishment, hybridization and impact of Laricobius predators on insecticide-treated hemlocks: Exploring integrated management of the hemlock woolly adelgid. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 335, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumpter, K.L.; McAvoy, T.J.; Brewster, C.C.; Mayfield, A.E.; Salom, S.M. Assessing an integrated biological and chemical control strategy for managing hemlock woolly adelgid in southern Appalachian forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 411, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewski, S.L. Using Tree-Ring Analysis to Determine the Effectiveness of Predator Beetle Laricobius spp. to Treat Hemlock Woolly Adelgid on Eastern Hemlock. Master’s Thesis, Indiana University of Pennsylvania, Indiana, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schomaker, M.E.; Zarnoch, S.J.; Bechtold, W.A.; Latelle, D.J.; Burkman, W.G.; Cox, S.M. Crown-Condition Classification: A Guide to Data Collection and Analysis; General Technical Report SRS-102; USDA Forest Service, Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2007.
- Salom, S.M.; Kok, L.T.; Lamb, A.B.; Jubb, C. Laboratory rearing of Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae): A predator of the hemlock woolly adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae). Psyche 2012, 2012, e936519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.R.; Jubb, C.S.; Cole, D.A.; Mausel, D.; Galloway, A.L.; Brooks, R.; Salom, S.M. Historic assessment and analysis of the mass production of Laricobius spp. (Coleoptera: Derodontidae), biological control agents for the hemlock woolly adelgid, at Virginia Tech. J. Insect Sci. 2021, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, A.B.; Salom, S.M.; Kok, L.T. Survival and reproduction of Laricobius nigrinus Fender (Coleoptera: Derodontidae), a predator of hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae Annand (Homoptera: Adelgidae) in field cages. Biol. Control 2005, 32, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mausel, D.L.; Kok, L.T.; Salom, S.M. Numerical response and impact of Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae) on Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) in their native range. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 46, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RC Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M. GlmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, F. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models; R Package Version 0.4.5; 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=DHARMa (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Climate Data Online (CDO). Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/cdo-web/ (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Nelson, L.A.; Rieske, L.K. Microclimatic variation within sleeve cages used in ecological studies. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, L.C.; Salom, S.M.; Kok, L.T. Functional and numerical response of Laricobius spp. predators (coleoptera: Derodontidae) on hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae (hemiptera: Adelgidae). Biol. Control 2012, 61, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda-King, L.; Gómez, S.; Martin, J.L.; Orians, C.M.; Preisser, E.L. Tree responses to an invasive sap-feeding insect. Plant Ecol. 2014, 215, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Pierce, M.R.; Orwig, D.A.; Preisser, E. Effects of hemlock woolly adelgid and elongate hemlock scale on eastern hemlock growth and foliar chemistry. Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, K.M. Eastern Hemlock Need Physiology as Impacted by Hemlock Woolly Adelgid and Treatment with Imidacloprid. Master’s Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Grubin, S.M.; Ross, D.W.; Wallin, K.F. Prey suitability and phenology of Leucopis spp. (Diptera: Chamaemyiidae) associated with hemlock woolly adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) in the Pacific Northwest. Environ. Entomol. 2011, 40, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietschler, N.J.; Bittner, T.D.; Trotter, R.T., III; Fahey, T.J.; Whitmore, M.C. Biological control of hemlock woolly adelgid: Implications of adult emergence patterns of two Leucopis spp. (Diptera: Chamaemyiidae) and Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae) larval drop. Environ. Entomol. 2021, 50, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crandall, R.S.; Jubb, C.S.; Mayfield, A.E.; Thompson, B.; McAvoy, T.J.; Salom, S.M.; Elkinton, J.S. Rebound of Adelges tsugae spring generation following predation on overwintering generation ovisacs by the introduced predator Laricobius nigrinus in the eastern United States. Biol. Control 2020, 145, 104264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, J.L. Understory microclimate and photosynthetic response of saplings in an old-growth eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis L.) Forest. Écoscience 2000, 7, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.S.; Loucks, O.L. Summer air temperatures as a factor affecting net photosynthesis and distribution of eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis L. (Carriere)) in southwestern Wisconsin. Am. Midl. Nat. 1971, 85, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjon, A. A Handbook of the World’s Conifers (2 Vols.); BRILL: Leiden-Boston, MA, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-90-04-17718-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.S.; Montgomery, M.E.; Cheah, C.; Onken, B.P.; Cowles, R.S. Eastern Hemlock Forests: Guidelines to Minimize the Impacts of Hemlock Woolly Adelgid, 1st ed.; Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station: New Haven, CT, USA, 2004; pp. 1–24.
| Tree # | Class | DBH (cm) | Crown Density | Live Crown Ratio | Transparency | Foliage Density | Dieback |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | Suppressed | 11.7 | 85 | 90 | 15 | 85 | 5 |
| 13 | Suppressed | 9.9 | 90 | 90 | 5 | 95 | 5 |
| 14 | Intermediate | 25.9 | 80 | 80 | 15 | 80 | 15 |
| 15 | Suppressed | 10.7 | 80 | 95 | 15 | 85 | 5 |
| 16 | Suppressed | 14.5 | 80 | 90 | 15 | 85 | 5 |
| 17 | Intermediate | 25.7 | 95 | 95 | 5 | 95 | 5 |
| 18 | Suppressed | 14 | 75 | 90 | 15 | 75 | 10 |
| 19 | Suppressed | 12.2 | 80 | 95 | 10 | 85 | 10 |
| 20 | Suppressed | 5.1 | 85 | 80 | 10 | 90 | 10 |
| 21 | Suppressed | 13.5 | 75 | 90 | 20 | 70 | 10 |
| 22 | Suppressed | 13.5 | 85 | 95 | 10 | 85 | 5 |
| 23 | Suppressed | 24.9 | 75 | 80 | 20 | 75 | 15 |
| 24 | Suppressed | 14.2 | 75 | 80 | 20 | 75 | 10 |
| 25 | Suppressed | 13.7 | 90 | 95 | 5 | 95 | 5 |
| Temperature (°C) | Precipitation (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Sampling Date a | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Mean |
| January | 0.66 | −11.90 | 29.70 | 3.28 | |
| February | 1.51 | −11.90 | 29.50 | 3.95 | |
| March | 7.53 | −10.20 | 36.20 | 4.09 | |
| April | 10.70 | −8.58 | 38.30 | 2.75 | |
| May | 14.20 | −1.57 | 37.20 | 1.39 | |
| June | 14 June 2021 | 18.70 | 3.58 | 30.20 | 0.17 |
| July | 30 July 2021 | 19.90 | 9.28 | 30.00 | 3.97 |
| August | 20.30 | 9.96 | 30.90 | 3.25 | |
| September | 15.70 | 1.22 | 28.30 | 3.08 | |
| October | 1 October 21 | 13.30 | 3.68 | 25.00 | 3.79 |
| November | 5.72 | −5.37 | 27.00 | 3.50 | |
| December | 1.07 | −12.20 | 26.90 | 2.62 | |
| Year | Month | Location | Mean Temperature (°C) | SE (±) | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | December | Inside | 1.36 | 0.204 | AB |
| Outside | 0.78 | 0.204 | BC | ||
| 2021 | January | Inside | 0.89 | 0.204 | AB |
| Outside | 0.42 | 0.204 | A | ||
| 2021 | February | Inside | 1.74 | 0.21 | C |
| Outside | 1.28 | 0.21 | BC | ||
| 2021 | March | Inside | 7.77 | 0.204 | D |
| Outside | 7.3 | 0.204 | D | ||
| 2021 | April | Inside | 11.02 | 0.206 | E |
| Outside | 10.45 | 0.206 | E | ||
| 2021 | May * | Inside | 13.47 | 0.233 | F |
| Outside | 14.65 | 0.204 | G |
| Treatment | Zero Model | Shoot Length Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Probability (%) a | Standard Error (+/–) | Mean New Shoot Length (cm) b | Standard Error (+/–) | |
| Control | 11.52 | 10.82 | 28.3 | 8.94 |
| NL | 49.13 | 21.15 | 13.9 | 11.15 |
| L4 | 18.67 | 14.65 | 21.4 | 9.33 |
| L8 | 6.15 | 6.96 | 32.2 | 8.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Preston, C.E.; Arneson, A.; Seiler, J.R.; Salom, S.M. The Impact of Predation of Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae) on Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) and Tsuga canadensis (Pinales: Pinaceae) Tree Health. Forests 2023, 14, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040698
Preston CE, Arneson A, Seiler JR, Salom SM. The Impact of Predation of Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae) on Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) and Tsuga canadensis (Pinales: Pinaceae) Tree Health. Forests. 2023; 14(4):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040698
Chicago/Turabian StylePreston, Carrie E., Alicia Arneson, John R. Seiler, and Scott M. Salom. 2023. "The Impact of Predation of Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae) on Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) and Tsuga canadensis (Pinales: Pinaceae) Tree Health" Forests 14, no. 4: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040698
APA StylePreston, C. E., Arneson, A., Seiler, J. R., & Salom, S. M. (2023). The Impact of Predation of Laricobius nigrinus (Coleoptera: Derodontidae) on Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) and Tsuga canadensis (Pinales: Pinaceae) Tree Health. Forests, 14(4), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040698






