Coarse Woody Debris and Carbon Stocks in Pine Forests after 50 Years of Recovery from Harvesting in Northeastern California
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
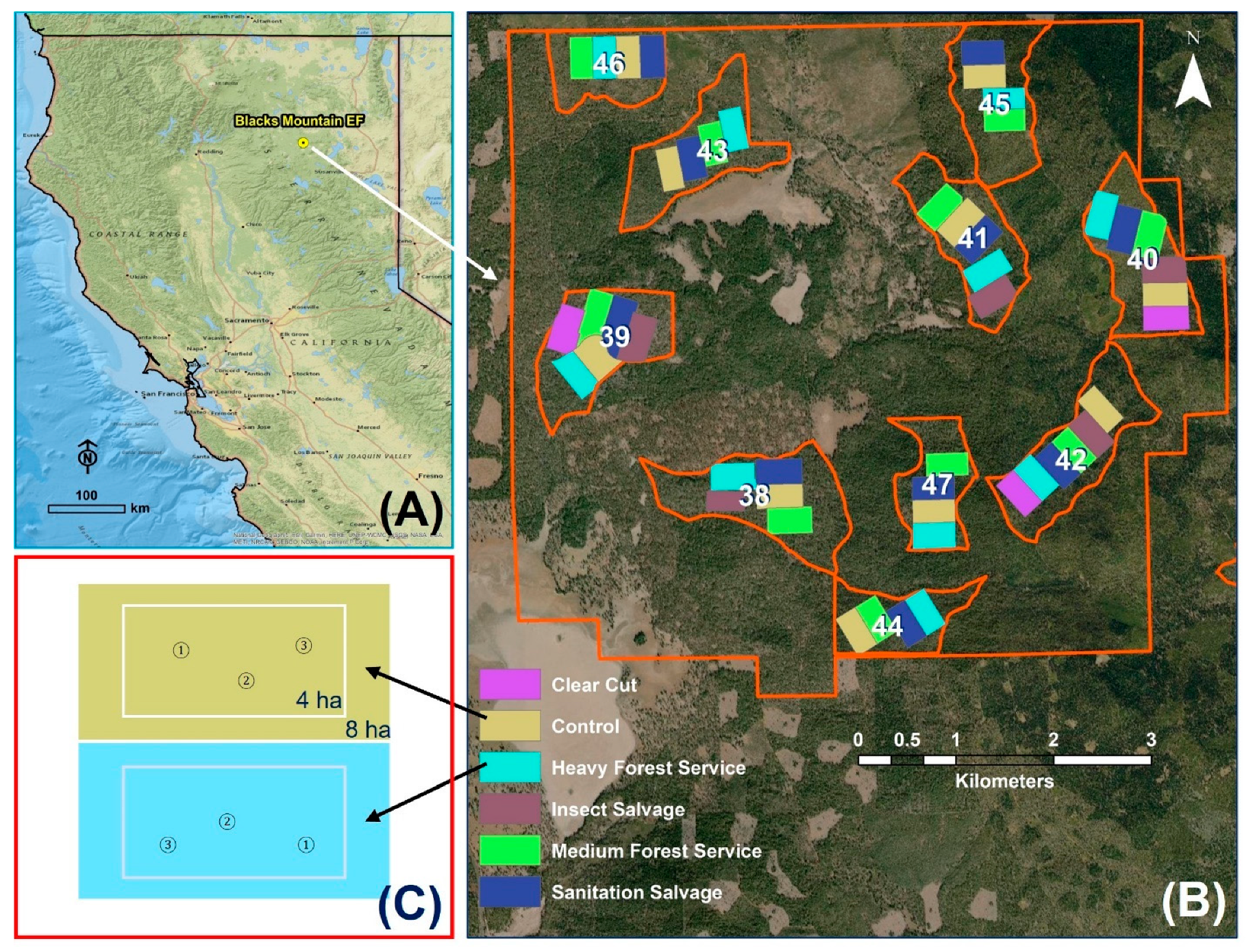
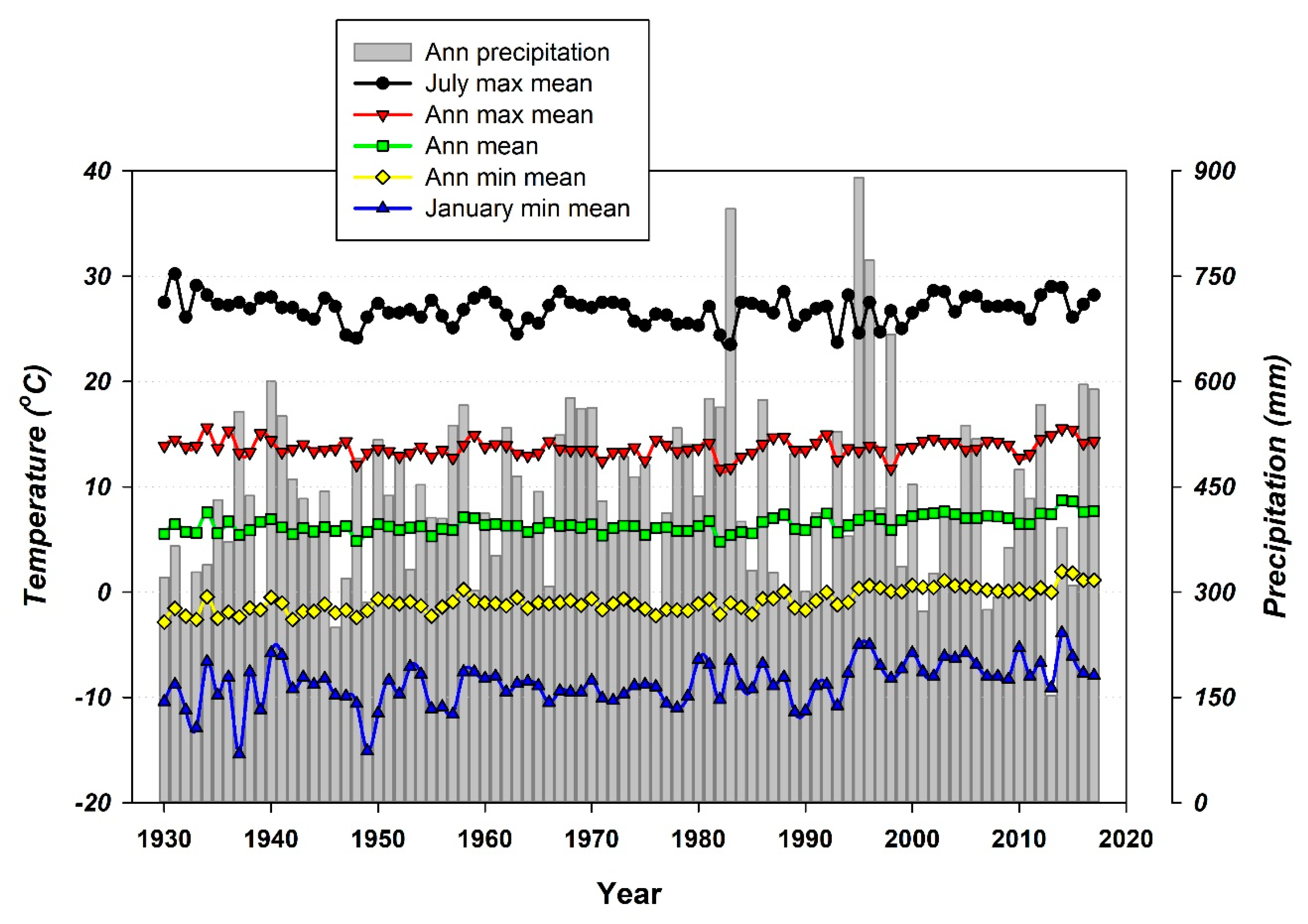
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Coarse Woody Debris (Lying and Standing Dead Wood)
2.4. Forest Floor and Soil Sampling
2.5. Laboratory Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
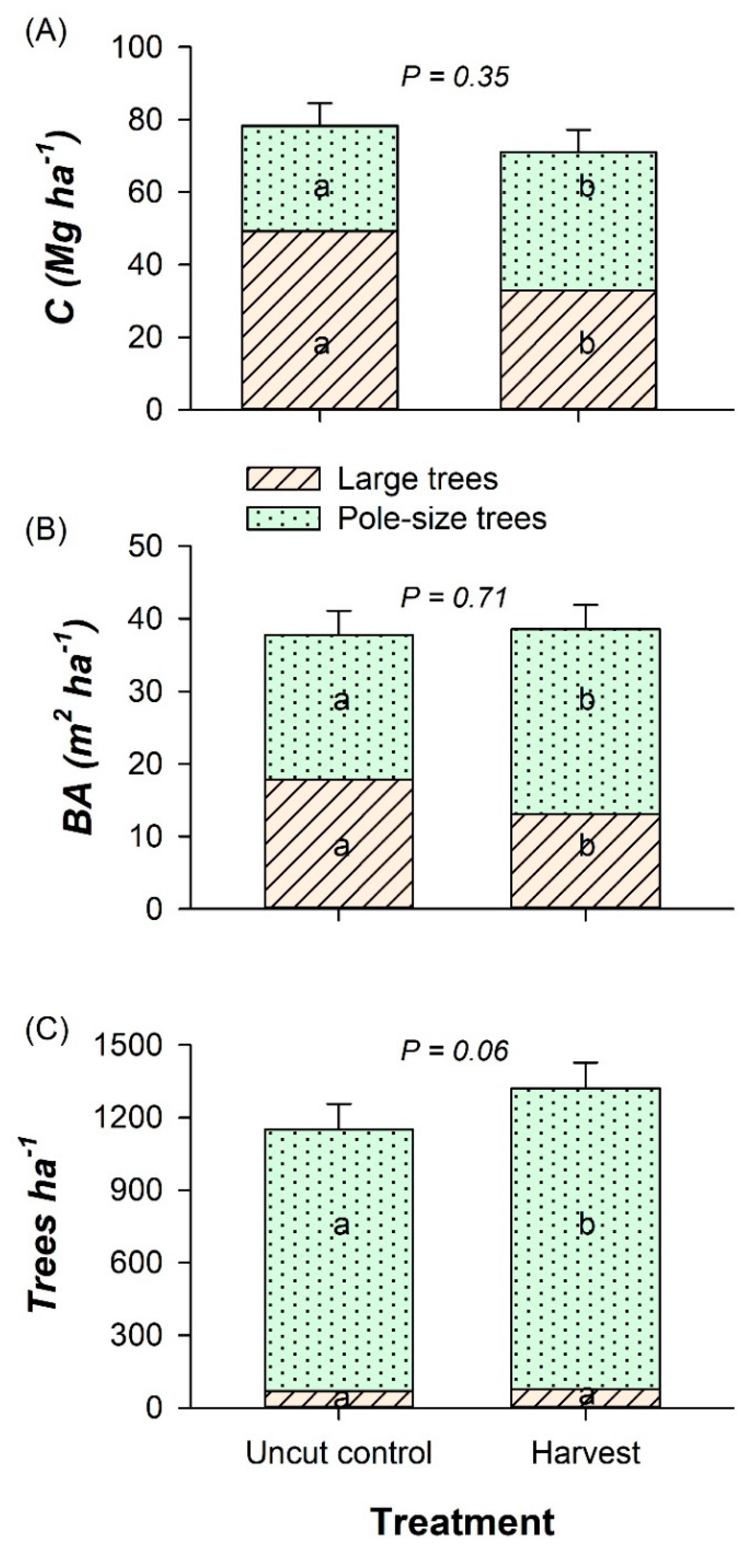
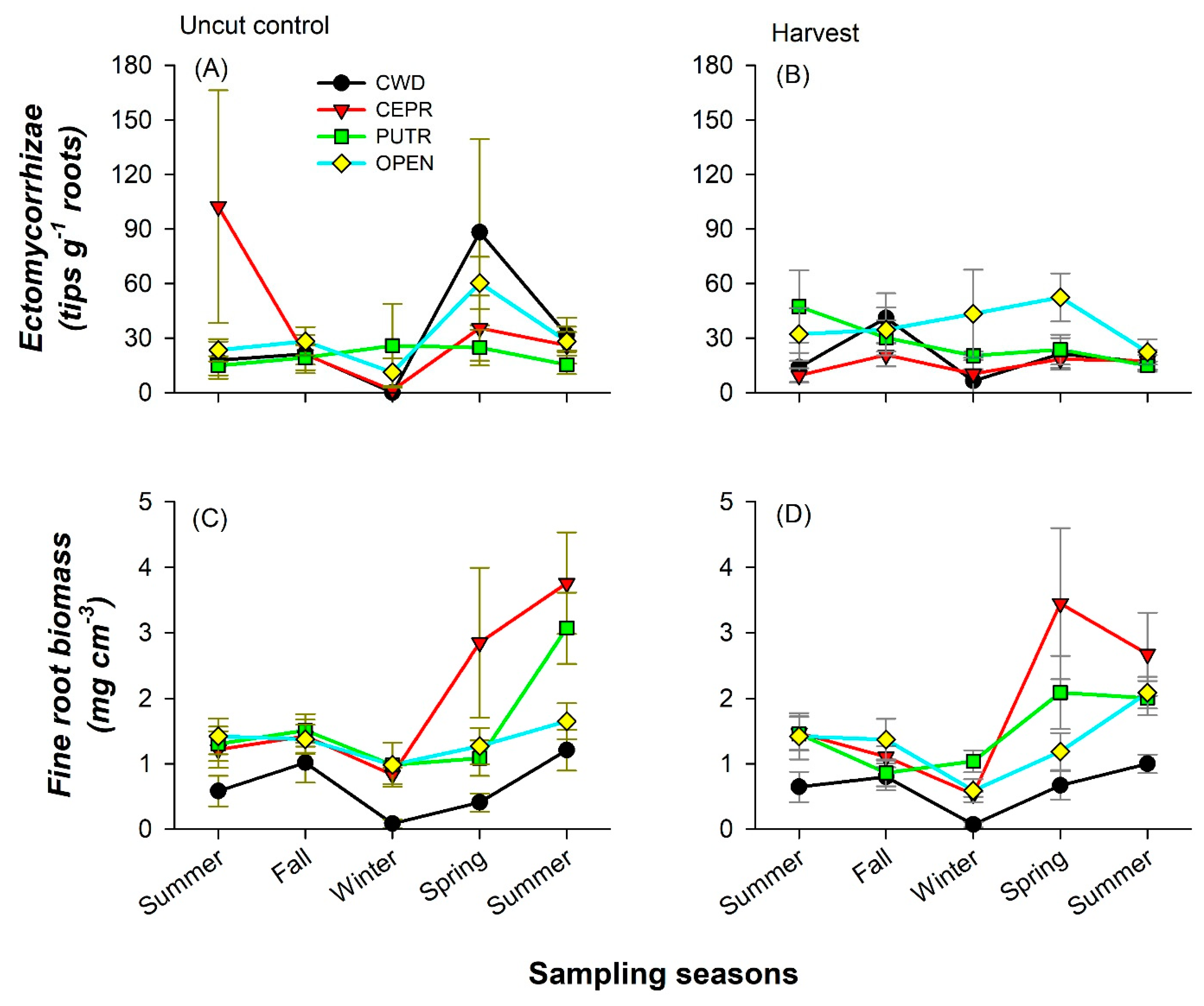
3.1. Overstory Trees, Shrubs, and Ground Cover
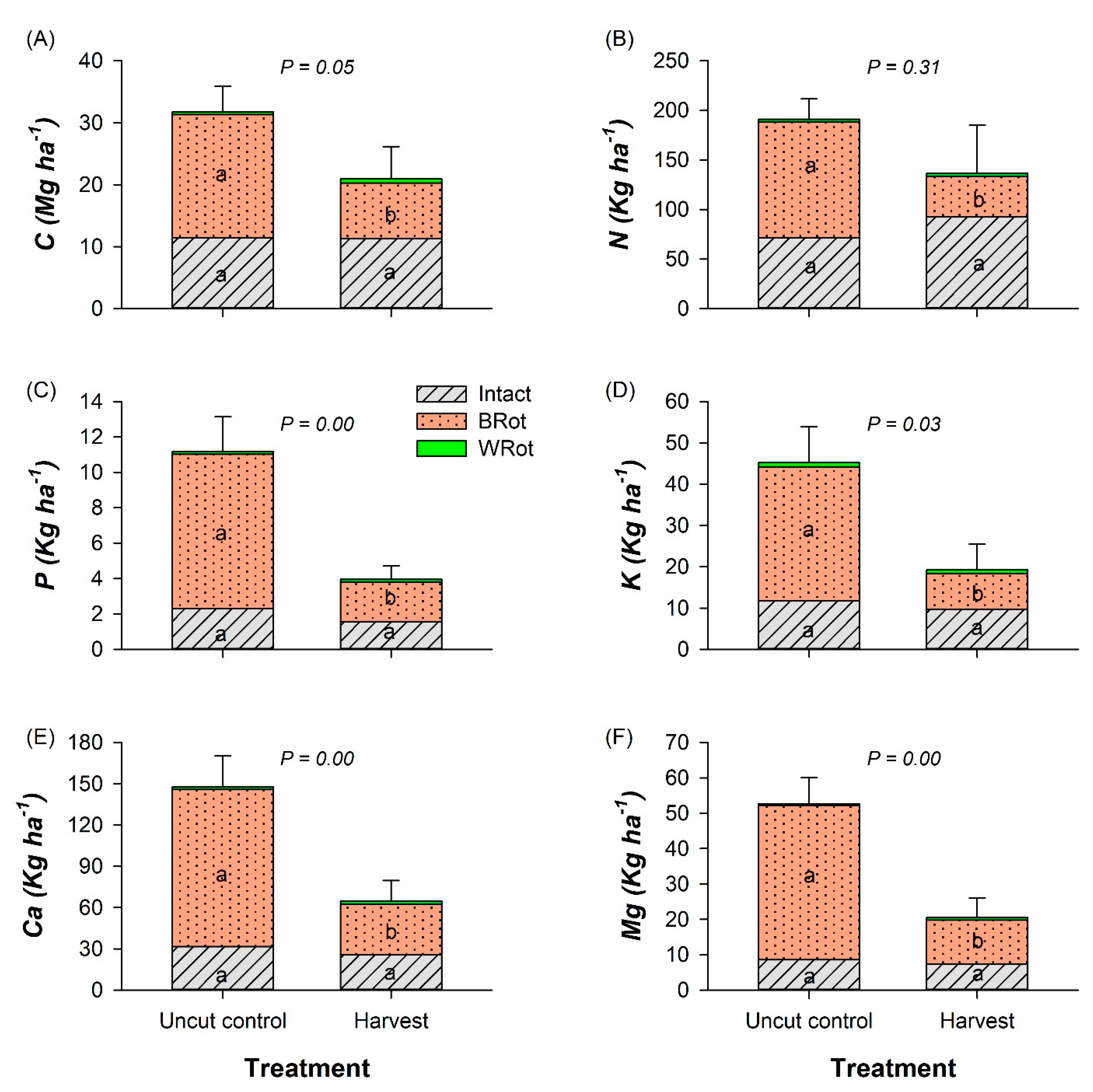
3.2. CWD and Snags
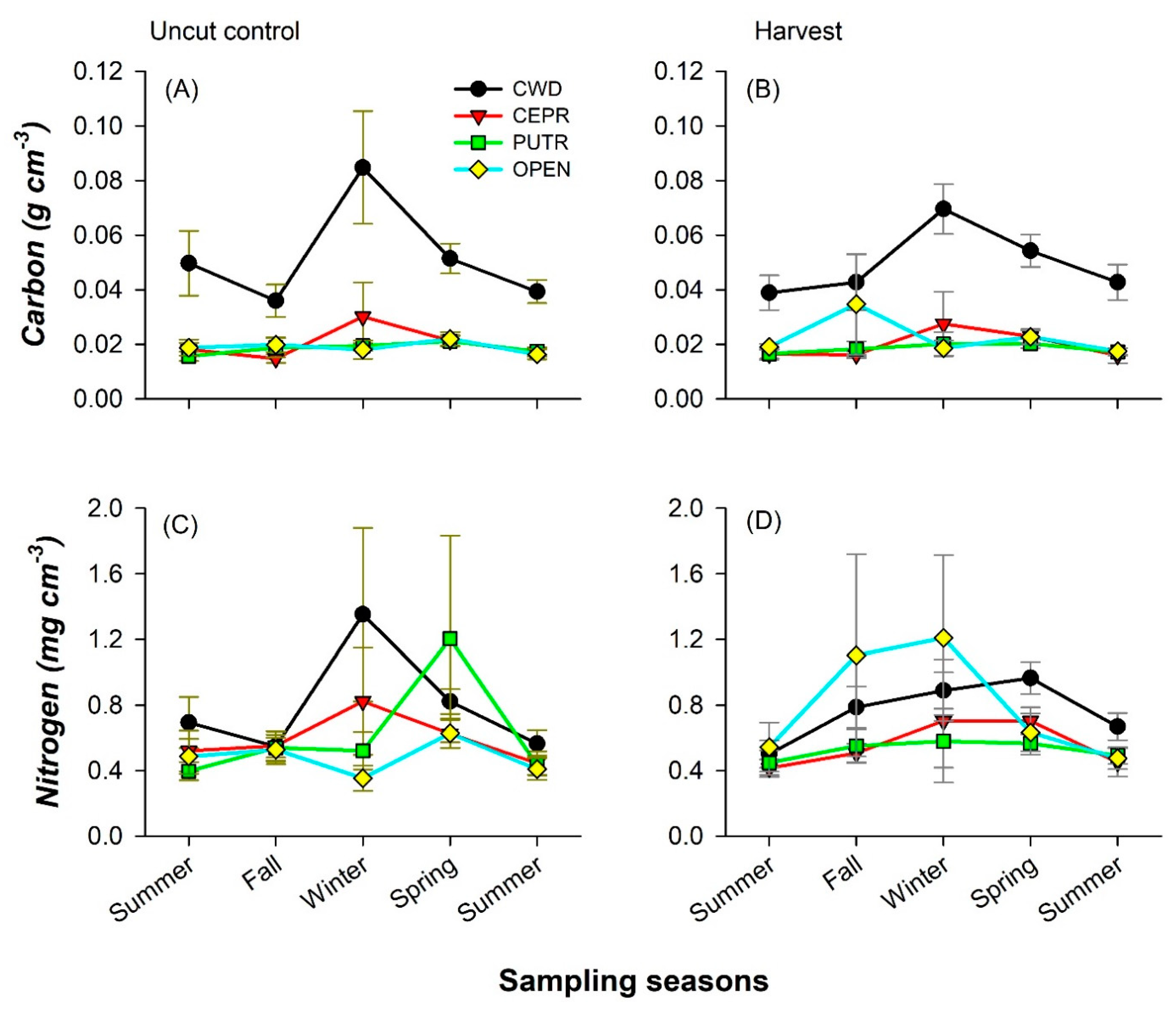
3.3. Forest Floor and Mineral Soil
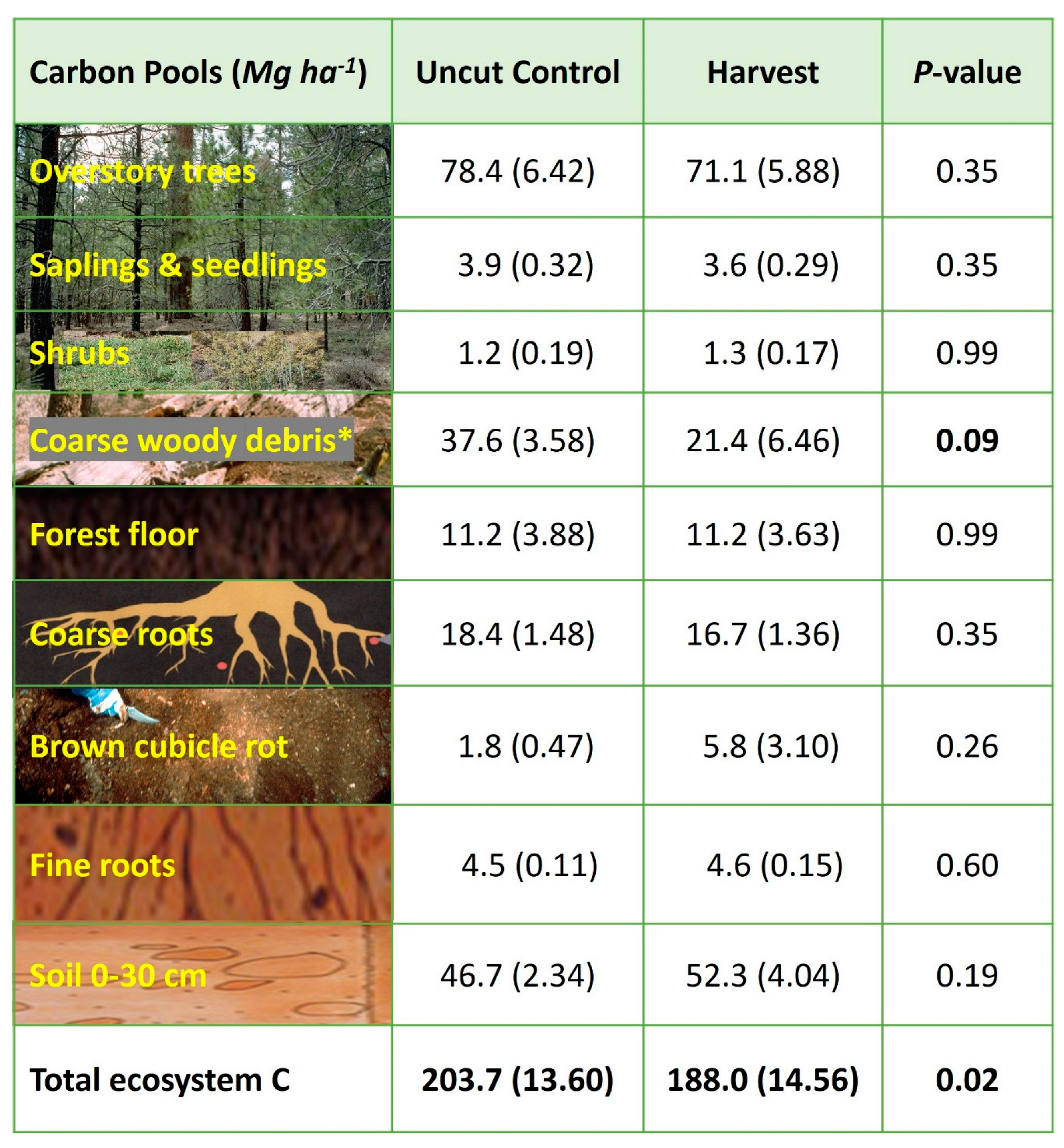
3.4. Stand-Level C Pools
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birdsey, R.; Pregitzer, K.; Lucier, A. Forest carbon management in the United States: 1600–2100. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, K.G.; Zhang, J.W. Forests in the northern Sierra Nevada of California, USA store large amounts of carbon in different patterns. Ecosphere 2019, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastin, J.-F.; Finegold, Y.; Garcia, C.; Mollicone, D.; Rezende, M.; Routh, D.; Zohner, C.M.; Crowther, T.W. The global tree restoration potential. Science 2019, 365, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domke, G.M.; Oswalt, S.N.; Walters, B.F.; Morin, R.S. Tree planting has the potential to increase carbon sequestration capacity of forests in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24649–24651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, T.A.; Harden, J.W. Effect of timber harvest on soil carbon storage at Blodgett Experimental Forest, California. Can. J. For. Res. 1995, 25, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, S.; Kolb, T.E.; Montes-Helu, M.; Eckert, S.E.; Sullivan, B.W.; Hungate, B.A.; Kaye, J.P.; Hart, S.C.; Koch, G.W.; Finkral, A. Carbon and water fluxes from ponderosa pine forests disturbed by wildfire and thinning. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 663–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgensen, M.F.; Larsen, M.J.; Mroz, G.D.; Harvey, A.E. Timber harvesting, soil organic matter, and site productivity. In Proceedings of the 1986 Symposium on the Productivity of Northern Forests Following Biomass Harvesting, Durham, NH, USA, 1–2 May 1986; Smith, C.T., Martin, C.W., Tritton, L.M., Eds.; USDA Forest Service NE Experiment Station NE-GTR-115. [Google Scholar]
- Jurgensen, M.F.; Harvey, A.E.; Graham, R.T.; Page-Dumroese, D.S.; Tonn, J.R.; Larsen, M.J.; Jain, T.B. Impacts of timber harvesting on soil organic matter, nitrogen, productivity, and health of inland northwest forests. For. Sci. 1997, 43, 234–251. [Google Scholar]
- Nave, L.E. Harvest impacts on soil carbon storage in temperate forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.; Harrison, R. The effect of harvest on forest soil carbon: A meta-analysis. Forests 2016, 7, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, C.I.; Stephenson, N.L. Temperature forest health in an era of emerging megadisturbance. Science 2015, 349, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidl, R.; Thom, D.; Kautz, M. Forest disturbances under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyssaert, S.; Schulze, E.; Börner, A.; Knohl, A.; Hessenmöller, D.; Law, B.E.; Ciais, P.; Grace, J. Old-growth forests as global carbon sinks. Nature 2008, 455, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, P.; Thybring, E.E.; Nord-Larsen, T.; Vesterdal, L.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Johannsen, V.K. Old-growth forest carbon sinks overestimated. Nature 2021, 591, E21–E23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, B.J.; Régnière, J.; Fettig, C.J.; Hansen, E.M.; Hayes, J.L.; Hicke, J.A.; Kelsey, R.G.; Negrón, J.F.; Seybold, S.J. Climate change and bark beetles of the western United States and Canada: Direct and indirect effects. BioScience 2010, 60, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverkus, A.B.; Buma, B.; Wagenbrenner, J.; Burton, P.J.; Lingua, E.; Marzano, R.; Thorn, S. Tamm review: Does salvage logging mitigate subsequent forest disturbances? For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 481, 118721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerling, A.L. Warming and earlier spring increase western U.S. forest wildlife activity. Science 2006, 313, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulakowski, D.; Seidl, R.; Holeksa, J.; Kuuluvainen, T.; Nagel, T.A.; Panayotov, M.; Svoboda, M.; Thorn, S.; Vacchiano, G.; Whitlock, C.; et al. A walk on the wild side: Disturbance dynamics and the conservation and management of European mountain forest ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 388, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, D.; Seidl, R. Natural disturbance impacts on ecosystem services and biodiversity in temperate and boreal forests. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2016, 91, 760–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, D.C.; Simard, M.; Romme, W.H.; Harvey, B.J.; Turner, M.G. Evaluating post-outbreak management effects on future fuel profiles and stand structure in bark beetle-impacted forests of Greater Yellowstone. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 303, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Burton, P.J.; Franklin, J.F. Salvage Logging and Its Ecological Consequences; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, S.M.; Baker, S.; Sala, A. Fortifying the forest: Thinning and burning increase resistance to a bark beetle outbreak and promote forest resilience. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 1984–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.; Parrott, L.; Hawkins, C.D.B. Aftermath of mountain pine beetle outbreak in British Columbia: Stand dynamics, management response and ecosystem resilience. Forests 2016, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverkus, A.B.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Thorn, S.; Gustafsson, L. Salvage logging in the world’s forests: Interactions between natural disturbance and logging need recognition. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.N.; Page-Dumroese, D.S.; Busse, M.; Palik, B.J.; Zhang, J.; Eaton, B.; Slesak, R.A.; Tirocke, J.; Kwon, H. Effects of forest harvesting and biomass removal on soil carbon and nitrogen: Two complementary meta-analyses. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 485, 118935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzoh, F.; Skinner, C. Effects of creating two forest structures and using prescribed fire on coarse woody debris in northeastern California, USA. Fire Ecol. 2009, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderwel, M.C.; Thorpe, H.; Shuter, J.L.; Caspersen, J.P.; Thomas, S.C. Contrasting downed woody debris dynamics in managed and unmanaged northern hardwood stands. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 2850–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, M.D.; Grigal, D.F. Effects of timber harvesting on coarse woody debris in red pine forets across the Great Lakes states, U.S.A. J. For. Res. 1999, 29, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum, M.U.F. Will changes in soil organic carbon act as a positive or negative feedback on global warming? Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 21–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, E.B. Insect-Caused Mortality in Relation to Methods of Cutting in Ponderosa Pine in the Blacks Mountain Experimental Forest; USDA Forest Service Technical Paper PSW-43; Pacific Southwest Forest and Range Experiment Station: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1959; 33p.
- Hallin, W.E. The Application of Unit Area Control in the Management of Ponderosa-Jeffrey Pine at Blacks Mountain Experimental Forest; USDA Technical Bulletin No. 1191; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1959; 96p.
- Dolph, K.L.; Mori, S.R.; Oliver, W.W. Long-term response of old-growth stands to varying levels of partial cutting in the eastside pine type. West. J. Appl. For. 1995, 10, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, M.; Jurgensen, M.F.; Page-Dumroese, D.S.; Powers, R.F. Contribution of actinorhizal shrubs to site fertility in a Northern California mixed pine forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 244, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.W. Ecological Research at the Blacks Mountain Experimental Forest in Northeastern California; USDA Forest Service General Technical Report PSW GTR-179; Pacific Southwest Research Station: Albany, CA, USA, 2000; 66p.
- Maser, C.; Anderson, R.; Cromack, K.; Williams, J.T.; Martin, R.G. Dead and down woody material. In Wildlife Habitats in Managed Forests the Blue Mountains of Oregon and Washington; Agriculture Handbook No. 553; Thomas, J.W., Ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1979; 512p.
- Powers, E.M.; Marshall, J.D.; Zhang, J.W.; Wei, L. Post-fire management regimes affect carbon sequestration and storage in a Sierra Nevada mixed conifer forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 291, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Ritchie, M.W.; Oliver, W.W. Vegetation responses to stand structure and prescribed fire in an interior ponderosa pine ecosystem. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrill, E.A.; Wilson, A.M.; Turner, J.A.; Pugh, S.A.; Menlove, J.; Christensen, G.; Conklin, B.L.; David, W. The Forest Inventory and Analysis Database: Database Description and User Guide for Phase 2 (Version 7.0.1); U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; 588p.
- Brown, J.K. Handbook for Inventorying Downed Woody Material; USDA Forest Service General Technical Report INT-16, Intermountain Research Station: Ogden, UT, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Cowling, E.B. Comparative Biochemistry of the Decay of Sweetgum Sapwood by White-Rot and Brown-Rot Fungi; Technical Bulletin No. 1258; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; p. 79.
- Zhang, J.W.; Ritchie, M.W.; Maguire, D.A.; Oliver, W.W. Thinning ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa) stands reduces mortality while maintaining stand productivity. Can. J. For. Res. 2013, 43, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgensen, M.F.; Larsen, M.J.; Harvey, A.E. A Soil Sampler for Steep, Rocky Slopes; Research Note INT-RN-217; USDA Forest Service, Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station: Ogden, UT, USA, 1977; 5p.
- Larsen, M.J.; Harvey, A.E.; Jurgensen, M.F. Residue decay processes and associated environmental functions in northern Rocky Mountain forests. In Proceeding Environmental Consequences of Timber Harvesting in Rocky Mountain Forests; Technical Report INT-90; Intermountain Forest and Range Experimental Station, USDA Forest Service: Ogden, UT, USA, 1980; pp. 157–174. [Google Scholar]
- Triska, F.J.; Cromack, K., Jr. The role of woody debris in forests and streams. In Forests: Fresh Perspectives from Ecosystem Analysis; Waring, R.H., Ed.; Oregon State University Press: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1979; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Page-Dumroese, D.S.; Jurgensen, M.F.; Miller, C.A.; Pickens, J.B.; Tirocke, J.M. Wildfire alters belowground and surface wood decomposition on two national forests in Montana, USA. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2019, 28, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page-Dumroese, D.S.; Brown, R.E.; Jurgensen, M.F.; Mroz, G.D. Comparison of methods for determining bulk densities of rocky forest soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.B.; Adams, A.B.; Licata, C.; Flaming, B.; Wagoner, G.L.; Carpenter, P.; Vance, E.D. Quantifying deep-soil and coarse-soil fractions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, N.; Zabowski, D. Total soil nitrogen in the coarse fraction and at depth. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J. Use of Detergents in the Analysis of Fibrous Feeds. II. A Rapid Method for the Determination of Fiber and Lignin. J. AOAC Int. 1963, 46, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS User’s Guide; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Page-Dumroese, D.S. Soil physical property changes at the North American Long-Term Soil Productivity study sites: 1 and 5 years after compaction. Can. J. For. Res. 2006, 36, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, J.; Mattson, K.G.; Zhang, W.; Weber, T.A. Sample Sizes to Control Error Estimates in Determining Soil Bulk Density in California Forest Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Page-Dumroese, D.; Jurgensen, M.; Tirocke, J.; Liu, Y. Effect of forest thinning and wood quality on the short-term wood decomposition rate in a Pinus tabuliformis plantation. J. Plant Res. 2018, 131, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnússon, R.Í.; Tietema, A.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Hefting, M.M.; Kalbitz, K. Tamm Review: Sequestration of carbon from coarse woody debris in forest soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 377, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, B.E.; Sun, O.J.; Campbell, J.; Van Tuyl, S.; Thornton, P.E. Changes in carbon storage and fluxes in a chronosequence of ponderosa pine. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 510–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, B.E. Carbon storage and fluxes in ponderosa pine forests at different developmental stages. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2001, 7, 755–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithwick, E.A.H.; Harmon, M.E.; Remillard, S.M.; Acker, S.A.; Franklin, J.F. Potential upper bounds of carbon stores in forests of the pacific northwest. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agee, J.K. Fire as a coarse filter for snags and logs. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the Ecology and Management of Dead Wood in Western Forests, Reno, Nevada, 2–4 November 1999; Laudenslayer, W.F., Jr., Shea, P.J., Valentine, B.E., Weatherspoon, C.P., Lisle, T.E., Eds.; General Technical Report PSW-GTR-181. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station: Albany, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 359–368. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon, M.E.; Cromack, K., Jr.; Smith, B.G. Coarse woody debris in mixed-conifer forests, Sequoia National Park, California. Can. J. For. Res. 1987, 17, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, W.W.; Offord, H.R. Logging Slash: Its Breakdown and Decay at Two Forests in Northern California; Research Paper PSW-RP-083; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station: Albany, CA, USA, 1972; 20p.
- Herrmann, S.; Prescott, C.E. Mass loss and nutrient dynamics of coarse woody debris in three Rocky Mountain coniferous forests: 21 year results. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, M.D. Downed bole-wood decomposition in lodgepole pine forests of central oregon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, L.C.; Palmer, M. California’s Forest Resources, 2006–2015: Ten-Year Forest Inventory and Analysis Report; General Technial Report PNW-GTR-983; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 2020; 60p.
- Herrero, C.; Krankina, O.; Monleon, V.J.; Bravo, F. Amount and distribution of coarse woody debris in pine ecosystems of north-western Spain, Russia and the United States. Iforest—Biogeosci. For. 2014, 7, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, R.D.; Currie, W.S.; Goodale, C.L. Soil carbon dynamics after forest harvest: An ecosystem paradigm reconsidered. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, M.D.; Sanchez, F.G.; Ratcliff, A.W.; Butnor, J.R.; Carter, E.A.; Powers, R.F. Soil carbon sequestration and changes in fungal and bacterial biomass following incorporation of forest residues. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, M.E.; Franklin, J.F.; Swanson, F.J. Ecology of coarse woody debris in temperate ecosystems. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1986, 15, 133–302. [Google Scholar]
- Forrester, J.A.; Mladenoff, D.J.; Gower, S.T.; Stoffel, J.L. Interactions of temperature and moisture with respiration from coarse woody debris in experimental forest canopy gaps. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 265, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.L.; Lang, G.E.; Reiners, W.A. Loss of mass and chemical change in decaying boles of a subalpine balsam fir forest. Ecology 1980, 61, 1460–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, K.G.; Swank, W.T. Wood decomposition following clearcutting at Coweeta Hydrologic Laboratory. In Long-Term Response of a Forest Watershed Ecosystem; Swank, W.T., Webster, J.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; Chapter 7; pp. 118–133. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, R. Carbon sequestration. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2008, 363, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.L.; Wheeler, C.E.; Mitchard, E.T.A.; Koch, A. Restoring natural forests is the best way to remove atmospheric carbon. Nature 2019, 568, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansley, J.-A.S.; Battles, J.J. Forest composition, structure, and change in an old-growth mixed conifer forest in the Northern Sierra Nevada. J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 1998, 125, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, S.L.; Lydersen, J.M.; Collins, B.M.; Fry, D.L.; Meyer, M.D. Historical and current landscape-scale ponderosa pine and mixed conifer forest structure in the Southern Sierra Nevada. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, C.N. Influence of fire on the dynamics of dead woody material in forests of California and southwestern Oregon. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the Ecology and Management of Dead Wood in Western Forests, Reno, Nevada, 2–4 November 1999; Laudenslayer, W.F., Jr., Shea, P.J., Valentine, B.E., Weatherspoon, C.P., Lisle, T.E., Eds.; General Technical Report PSW-GTR-181. USDA Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station: Albany, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 445–454, 949p. [Google Scholar]

| Treatment | Decay Type | Lignin (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Uncut control | Intact | 47.5 (2.0) |
| White rot | 43.4 (2.1) | |
| Brown rot | 73.6 (4.3) | |
| Harvest | Intact | 46.0 (2.0) |
| White rot | 44.6 (2.1) | |
| Brown rot | 67.2 (4.4) |
| Source of Variation | Num df | Den df | Soil C | Soil N | Fine Roots | Ecto-mycorrhizae |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment (TRT) | 1 | 4 | 0.961 | 0.781 | 0.690 | 0.523 |
| Ground Cover (GC) | 3 | 253 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.117 |
| TRT * GC | 3 | 253 | 0.888 | 0.353 | 0.927 | 0.486 |
| Sampling season (SS) | 4 | 253 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.114 |
| TRT * SS | 4 | 253 | 0.961 | 0.808 | 0.340 | 0.601 |
| GC * SS | 12 | 253 | 0.285 | 0.988 | 0.126 | 0.630 |
| TRT * GC * SS | 12 | 253 | 1.000 | 0.581 | 0.820 | 0.867 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Page-Dumroese, D.S.; Jurgensen, M.F.; Busse, M.; Mattson, K.G. Coarse Woody Debris and Carbon Stocks in Pine Forests after 50 Years of Recovery from Harvesting in Northeastern California. Forests 2023, 14, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030623
Zhang J, Page-Dumroese DS, Jurgensen MF, Busse M, Mattson KG. Coarse Woody Debris and Carbon Stocks in Pine Forests after 50 Years of Recovery from Harvesting in Northeastern California. Forests. 2023; 14(3):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030623
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jianwei, Deborah S. Page-Dumroese, Martin F. Jurgensen, Matt Busse, and Kim G. Mattson. 2023. "Coarse Woody Debris and Carbon Stocks in Pine Forests after 50 Years of Recovery from Harvesting in Northeastern California" Forests 14, no. 3: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030623
APA StyleZhang, J., Page-Dumroese, D. S., Jurgensen, M. F., Busse, M., & Mattson, K. G. (2023). Coarse Woody Debris and Carbon Stocks in Pine Forests after 50 Years of Recovery from Harvesting in Northeastern California. Forests, 14(3), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030623






