Genome-Wide Analysis, Characterization, Expression and Function of SERK Gene Family in Phyllostachys edulis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
2.2. Identification and Characterization of the PeSERK Family
2.3. Analysis of Physicochemical Properties and Prediction of Transmembrane Domains of PeSERKs
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis and Collinearity Analysis
2.5. Cis-Acting Elements in PeSERK Promoter Regions
2.6. Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.7. Tissue-Specific Analysis of PeSERKs
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification of PeSERKs
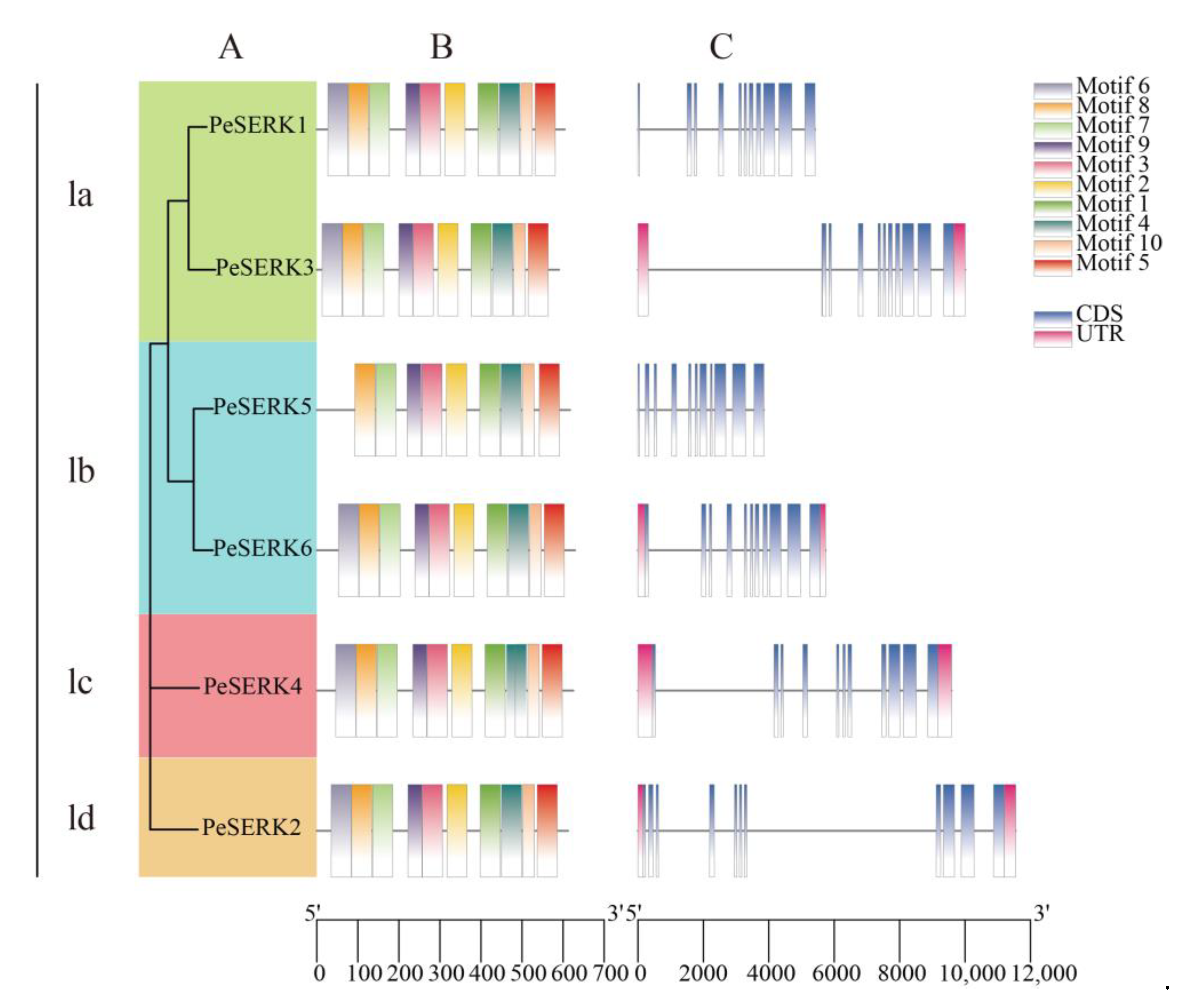
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of PeSERKs
3.3. Gene Structure and Motif Analysis of PeSERKs
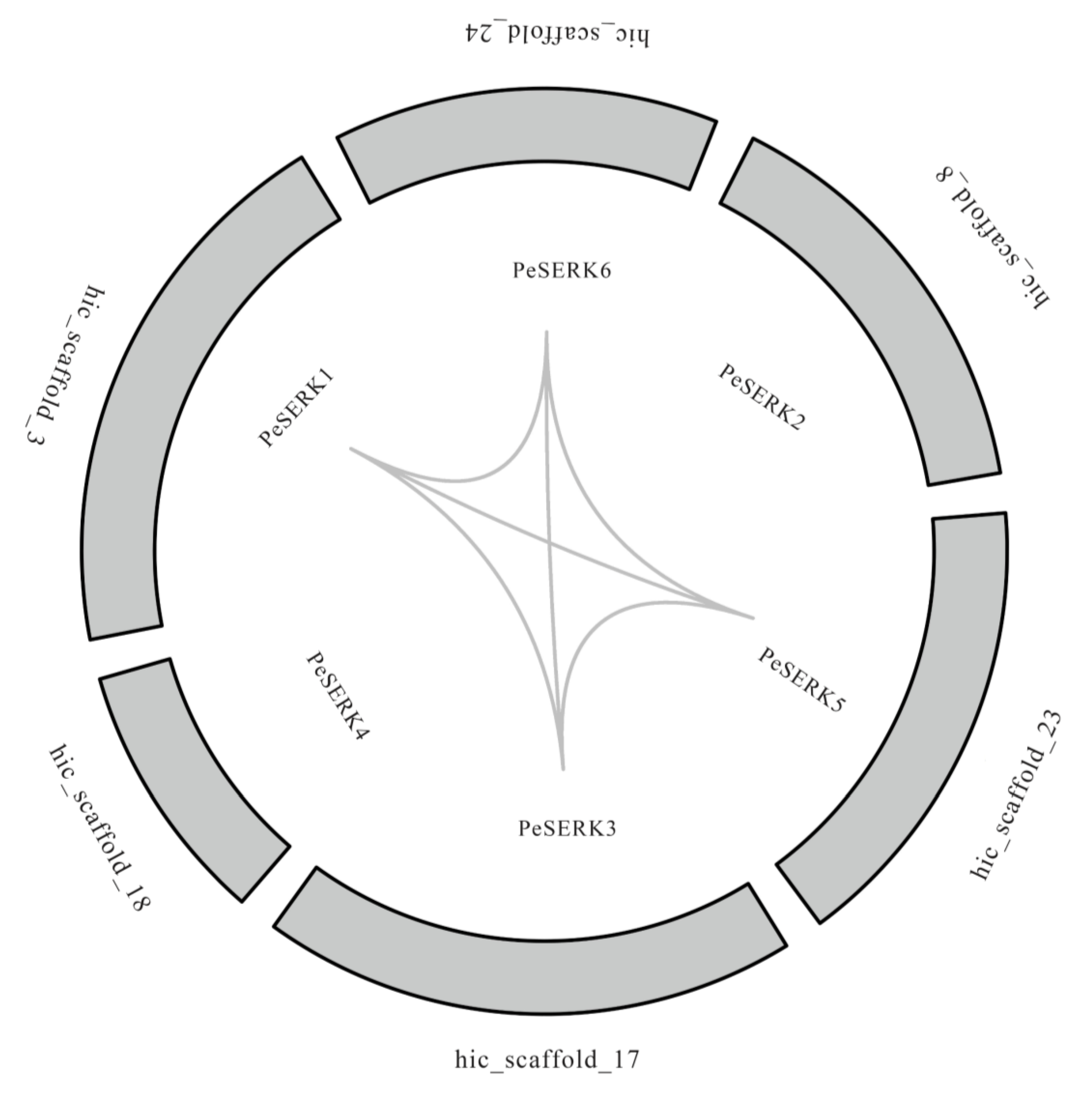
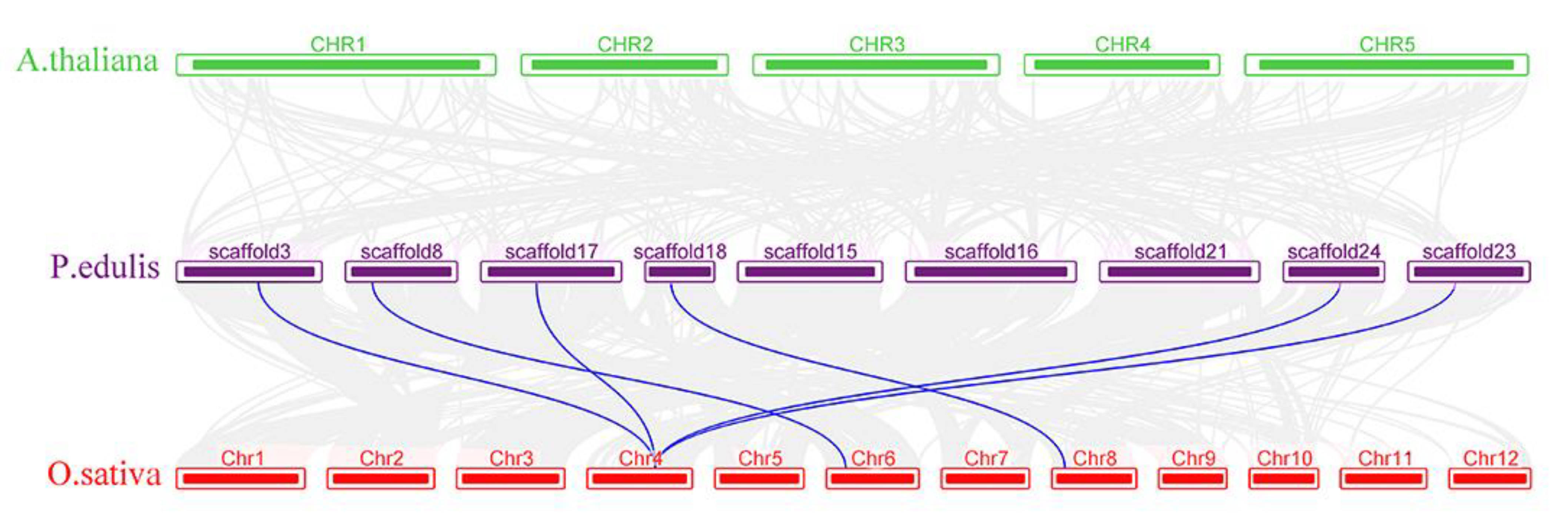
3.4. Collinearity Analysis of PeSERKs
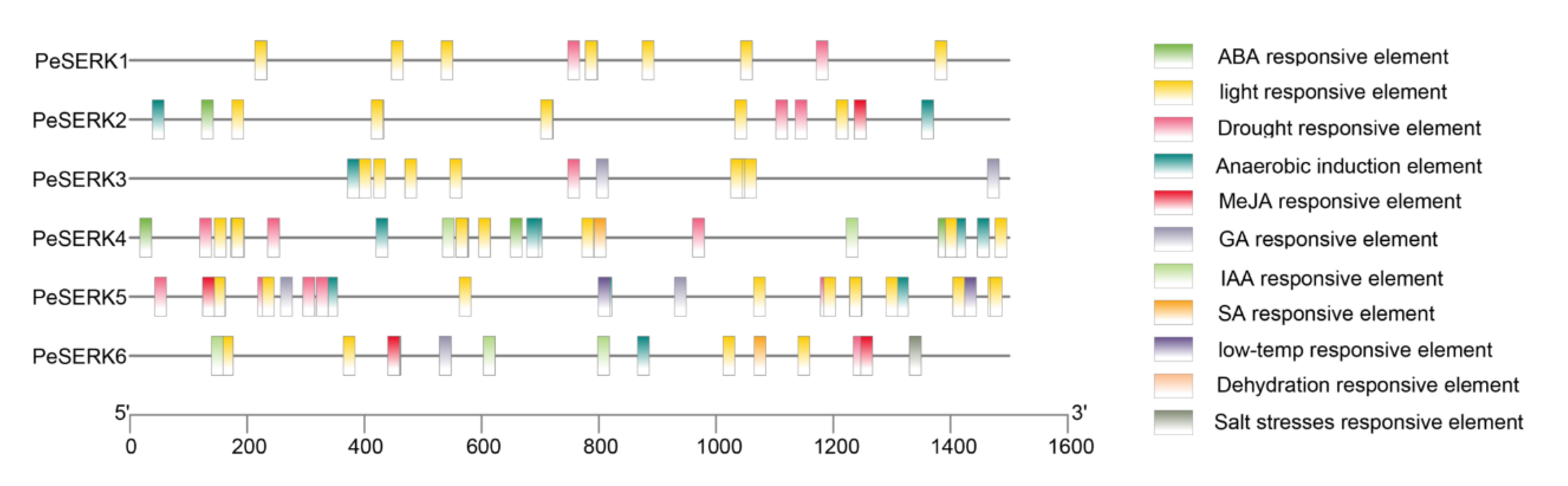
3.5. Cis-Acting Element Analysis in the Promoter Regions of PeSERKs
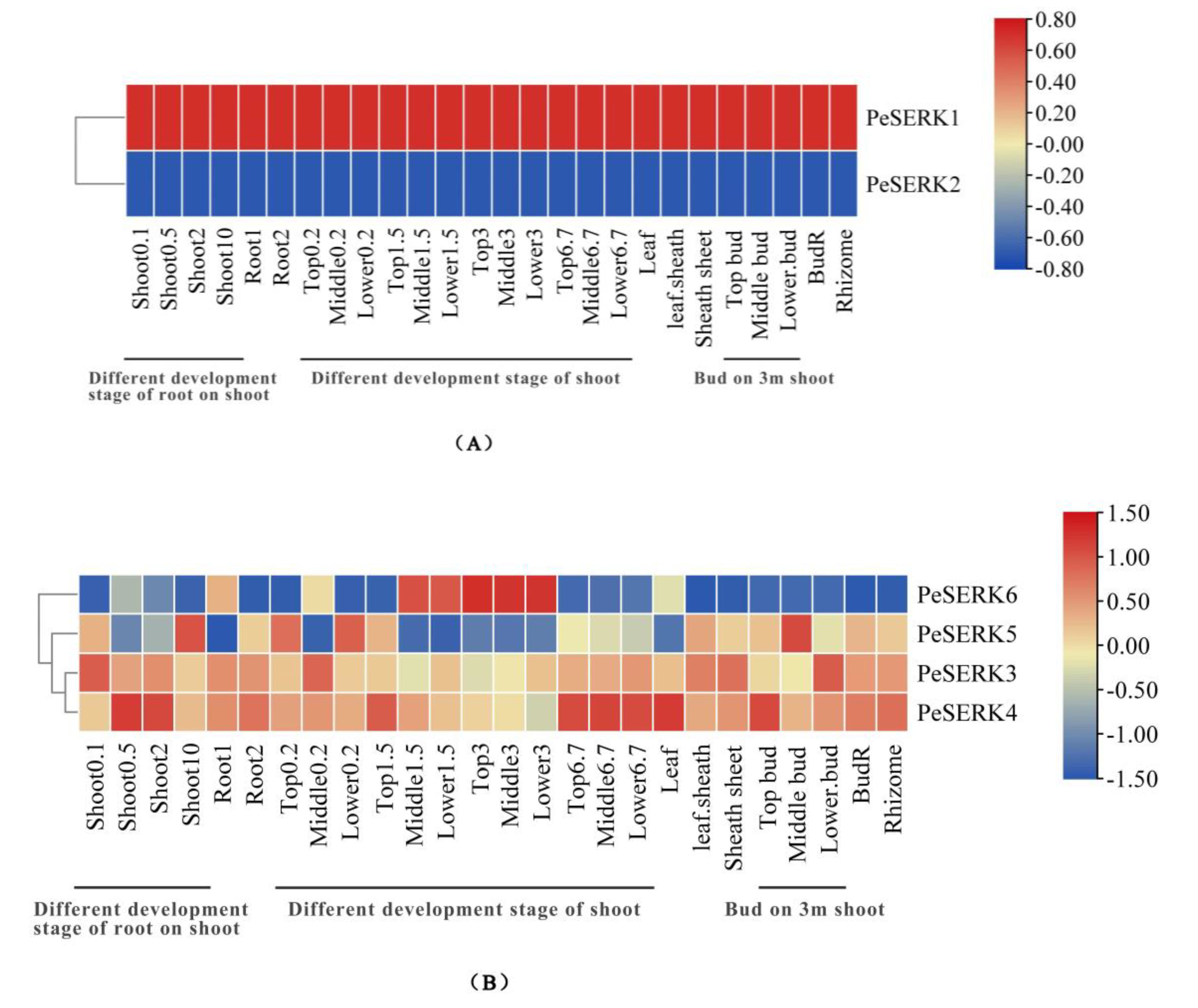
3.6. Expression Pattern of PeSERKs in Different Tissues
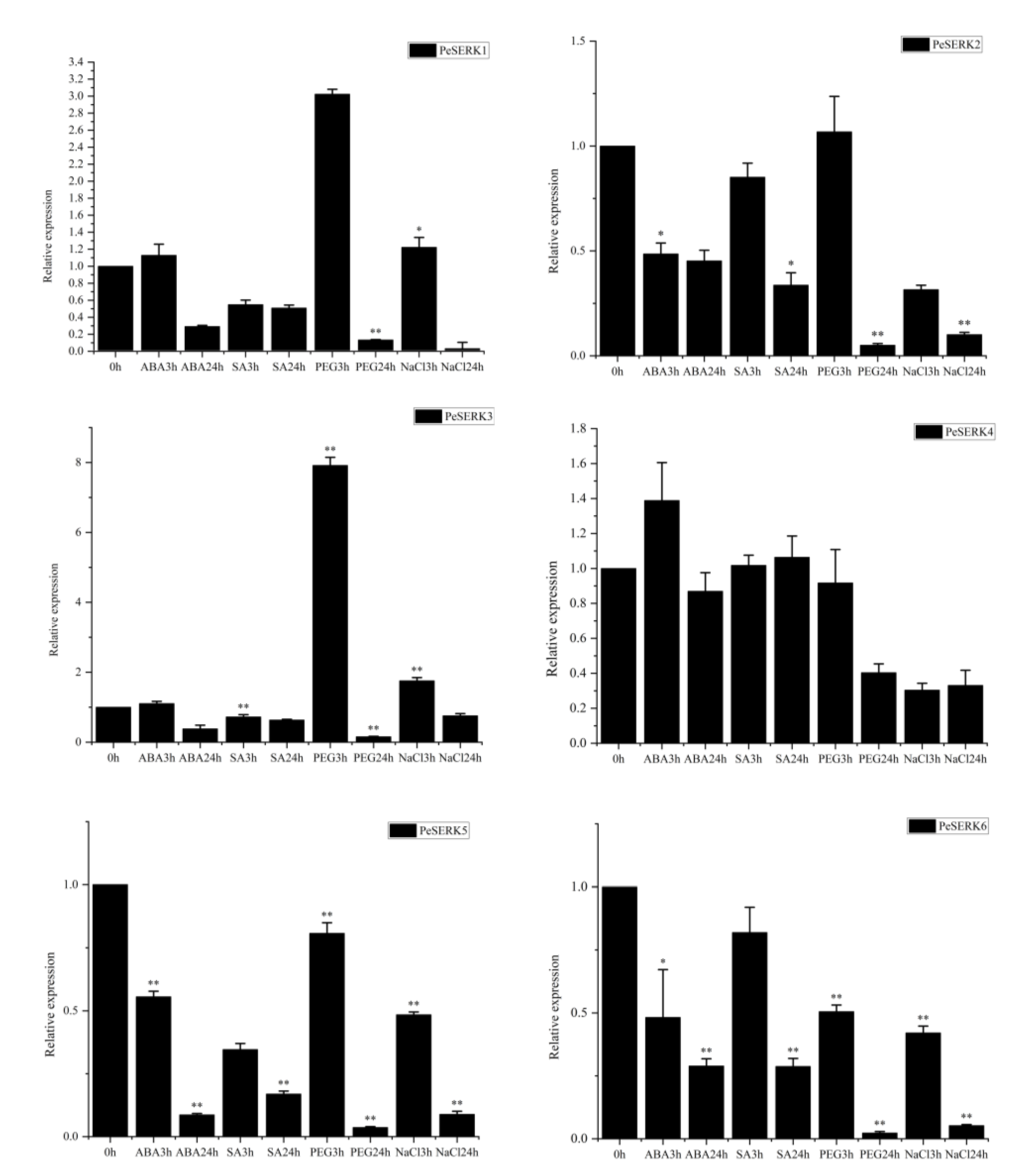
3.7. Expression Patterns of PeSERKs under Abiotic and Hormone Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shiu, S.H.; Bleecker, A.B. Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. PNAS 2001, 98, 10763–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.M.; Kou, S.J.; Liu, Y.L.; Fang, Y.N.; Xu, Q.; Guo, W.W. Genomewide analysis of small RNAs in nonembryogenic and embryogenic tissues of citrus: microRNA- and siRNA-mediated transcript cleavage involved in somatic embryogenesis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becraft, P.W. Receptor kinases in plant development. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.D.; Guzzo, F.; Toonen, M.A.; de Vries, S.C. A leucine-rich repeat containing receptor-like kinase marks somatic plant cells competent to form embryos. Development 1997, 124, 2049–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xiong, L.; Yang, Y. Rice SERK1 gene positively regulates somatic embryogenesis of cultured cell and host defense response against fungal infection. Planta 2005, 222, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, V.; Vielle-Calzada, J.P.; Hartog, M.V.; Schmidt, E.D.; Boutilier, K.; Grossniklaus, U.; de Vries, S.C. The Arabidopsis somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinases1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Khurana, P. Ectopic expression of Triticum aestivum SERK genes (TaSERKs) control plant growth and development in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Li, Y.B.; Tan, H.X.; Guo, G.M. Cloning and bioinformatics analysis of SERK gene family in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Acta Agric. Shanghai 2016, 32, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Baudino, S.; Hansen, S.; Brettschneider, R.; Hecht, V.F.; Dresselhaus, T.; Lörz, H.; Dumas, C.; Rogowsky, P.M. Molecular characterisation of two novel maize LRR receptor-like kinases, which belong to the SERK gene family. Planta 2001, 213, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.; Romano, E. Characterisation of the cacao somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase (SERK) gene expressed during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Sci. 2005, 68, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, L.J.; Ma, J.H.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, C.; Wang, W.J. Identification and expression analysis of SERK gene in Dendrobium officinale. J. Biol. 2019, 36, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, H.; Lai, Z.X. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of Cn-SERK Gene from Somatic Embryos in Camellia nitidissima. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2013, 34, 699–1707. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.L.; Wu, Y.J.; Xiao, C.B. Isolation of SERKs family genes in potato and their functions in plant immune signal. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2019, 54, 88–99. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B. Bioinformatics of soybean SERK gene family and expression analysis under salt stress. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2019, 28, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Aan den Toorn, M.; Albrecht, C.; de Vries, S. On the origin of SERKs: Bioinformatics analysis of the somatic embryogenesis receptor kinases. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 762–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lin, Q. Biological functions of plant somatic cell embryogenesis receptor-like protein kinases. Genetics 2012, 34, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y. Brassinosteroids modulate plant immunity at multiple levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.H.; He, Z.Y.; Hu, S.; Kanakala, W.T.; Xu, J.X.; Xia, C.H.; Guo, S.Q.; Lin, C.J.; Chen, C.H. Histological analysis of somatic embryogenesis in pineapple: AcSERK1 and its expression validation under stress conditions. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.W.; Ma, J.J.; Mao, J.P.; Fan, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, C.; An, N.; Han, M.Y. Genome-wide identification of SERKs in apple and analyses of their role in stress responses and growth. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Liu, C.H.; Guo, G.M.; He, T.; Chen, Z.W.; Gao, R.H. Expression analysis of three SERK-like genes in barley under abiotic and biotic stresses. J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhong, X.J.; He, J.; Jin, S.H.; Guo, H.D.; Yu, X.F.; Zhou, Y.J.; Li, X. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Stress-Responsive Expression Profiling of Genes Encoding LEA (Late Embryogenesis Abundant) Proteins in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PloS ONE 2016, 11, e0165953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F. Analysis on economic and ecological benefit of bamboo planting. Mod. Hortic. 2014, 018, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, Q.T.; Hou, D.; Lu, H.; Lin, X.C. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of NCED Gene Family in Phyllostachys edulis. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 29, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.D.; Zhang, Y.F. Development of bamboo cultural tourism resources in China. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2007, 188–191+301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M. Bamboo resources and the development direction of bamboo industry economy in Yunnan. Ecol. Econ. 1992, 4, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.F.; Sun, H.J.; Jiao, Y.B. Viral infection-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and a membrane-associated transcription factor NbNAC089 are involved in resistance to virus in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, T.; Mu, S.; Li, X.; Gao, J. Transcriptome sequencing and analysis of the fast growing shoots of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PloS ONE 2013, 8, e78944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Hu, S.L.; Cao, Y.; Xu, G. Bioinformatics analysis of NAC gene family in moso bamboo. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2015, 34, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, G.Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, M.B. Research progress on the mechanism of rapid growth of bamboo plants. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 26, 871–887. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Fei, B.; Chen, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Chromosome-level reference genome and alternative splicing atlas of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Giga Sci. 2018, 7, giy115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K. Bioinformatics and Functional Analysis of SOD Gene Family in Moso Bamboo; Zhejiang A&F University: Hang Zhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.T.; Hou, D.; Wei, H.T.; Lin, X.C. Identification and expression analysis of PP2C gene family in moso bamboo. J Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 28, 1776–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, T.T.; Wei, W. Cloning and expression analysis of PeRaf22 gene in moso bamboo. Mol. Plant Breed. 2021, 19, 815–819. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.L.; Kong, B.; Gao, Z.M. Identification and expression analysis of APX family genes in moso bamboo. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2020, 28, 255–264. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.X.; Vasupalli, N.; Hou, D.; Stalin, A.; Wei, H.T.; Zhang, H.C.; Lin, X.C. Genome-wide identification and evolution of WNK kinases in Bambusoideae and transcriptional profiling during abiotic stress in Phyllostachys edulis. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghai, D.; Alok, A.; Himani; Upadhyay, S.K.; Sembi, J.K. Genome wide characterization of the SERK/SERL gene family in Phalaenopsis equestris, Dendrobium catenatum and Apostasia shenzhenica (Orchidaceae). Comput. Biol. Chen. 2020, 85, 107210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.M.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Peng, A.Y.; Cheng, F.J.; Luo, D.F. Genome-wide identification and phylogenetic analysis of SERK gene family in Brassica napus. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2021, 43, 783–794. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Yin, H.; He, K.; Du, J.; Yi, J.; Xu, S. Genetic evidence for an indispensable role of somatic embryogenesis receptor kinases in brassinosteroid signaling. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.G.; Cui, B.M.; Peng, M. Advanced study on SERK genes family. Hereditas 2007, 29, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganko, E.W.; Meyers, B.C.; Vision, T.J. Divergence in expression between duplicated genes in Arabidopsis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 2298–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, A.D.; Irsigler, A.S.T.; Carneiro, V.T.C.; Cabral, G.B.; Rodrigues, J.C.M.; Gomes, A.C.M.M. SERK genes identification and expression analysis during somatic embryogenesis and sporogenesis of sexual and apomictic Brachiaria brizantha (Syn. Urochloa brizantha). Planta 2020, 252, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Expression Pattern and Antibody Preparation of LaSERK1 Gene Related to Somatic Embryogenesis in Larch; Chinese Academy of Forestry: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.Q. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Embryonic Related Genes such as SERK during Longan Somatic Embryogenesis; Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University: Fuzhou, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- You, C.R. Characterization of Somatic Embryogenesis, Development and Expression of SERK Gene during Somatic Embryogenesis in Cyclamen D; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, P.W. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Somatic Embryogenesis Marker Genes in Liriodendron Hybrid; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, C.; Meyer, D.; Himber, C.; Steinmetz, A. Spatial expression of a sunflower SERK gene during induction of somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2004, 42, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehan, M.R.; Almonte, M.; Slaten, E.; Freimer, N.B.; Rao, P.N.; Ophoff, R.A. Analysis of segmental duplications reveals a distinct pattern of continuation-of-synteny between human and mouse genomes. HUM Genet. 2007, 121, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehan, M.R.; Freimer, N.B.; Ophoff, R.A. A genome-wide survey of segmental duplications that mediate common human genetic variation of chromosomal architecture. HUM Genet. 2004, 1, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Hirabayashi, T.; Endo, T. Isolation and characterization of the somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase gene homologue (CitSERK1) from Citrus unshiu Marc. Sci. Hortic. 2005, 103, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, C.; Russinova, E.; Hecht, V.; Baaijens, E.; de Vries, S. The Arabidopsis thaliana somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinases1 and 2 control male sporogenesis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 3337–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colcombet, J.; Boisson-Dernier, A.; Ros-Palau, R.; Vera, C.E.; Schroeder, J.I. Arabidopsis somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinases1 and 2 are essential for tapetum development and microspore maturation. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 3350–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhao, J.; He, C. Distinct subfunctionalization and neofunctionalization of the B-class MADS-box genes in Physalis floridana. Planta 2015, 241, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liao, L.; Xu, S.; Ren, F.; Zhao, J.; Ogutu, C.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Han, Y. Two amino acid changes in the R3 repeat cause functional divergence of two clustered MYB10 genes in peach. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 98, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.J.; Liu, J.P.; Han, Q.Z.; Gao, J.H. Effect of N-terminal signal peptide of Cry1Ia protein on its protein expression. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 694–698. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, R.; Zhao, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Calmodulin and Calmodulin-like Genes Family in Tea Plant and Their Roles under Abiotic Stress. Forests 2022, 13, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| PeSERK1 | F: GCCATCTGAACAACCGCTTG R: CACAACTGCCTCGAAGTCCT |
| PeSERK2 | F: CACATTGCTCCTGAGTACCTGT R: CCAGTGTCTCCACCTTCTTCTC |
| PeSERK3 | F: ACCTCCTCCATACAATCCTCCA R: GCAATAGCAGGAACAGCAAACA |
| PeSERK4 | F: GAACCTCCACTCGATTGGCA R: TATTCCGGTGCGATATGCCC |
| PeSERK5 | F: AATGGTTCATTTTCGCGCTTCA R: CACTACAACAGGAGCAGCAAAC |
| PeSERK6 | F: CTGGTGCTGCATTGCTGTTT R: AGGCGTGCGTTCCTCTTTTA |
| NTB | F: TCTTGTTTGACACCGAAGAGGAG R: AATAGCTGTCCCTGGAGGAGTTT |
| ID | ID Rename | AA 1 | Chromosomal Locus | DMW 2 | pI 3 | Aliphatic Index | GRAVY 4 | Signal Peptide | Subcellular Localization Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH02Gene43060.t1 | PeSERK1 | 612 | Scaffold3 | 67,448.23 | 6.34 | 99.14 | −0.071 | Yes | Cell membrane. |
| PH02Gene08597.t1 | PeSERK2 | 617 | Scaffold8 | 67,924.45 | 5.23 | 95.28 | −0.146 | Yes | Cell membrane. |
| PH02Gene24988.t1 | PeSERK3 | 590 | Scaffold17 | 65,128.33 | 5.53 | 93.19 | −0.229 | No | Cell membrane. |
| PH02Gene31627.t1 | PeSERK4 | 625 | Scaffold18 | 68,804.66 | 5.63 | 95.62 | −0.618 | Yes | Cell membrane |
| PH02Gene18379.t1 | PeSERK5 | 604 | Scaffold23 | 67,779.39 | 5.31 | 92.62 | −0.291 | NO | Cell membrane. |
| PH02Gene02205.t1 | PeSERK6 | 629 | Scaffold24 | 69,287.06 | 5.54 | 94.85 | −0.167 | Yes | Cell membrane |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhuo, J.; Wei, H.; Hou, D.; Lin, X. Genome-Wide Analysis, Characterization, Expression and Function of SERK Gene Family in Phyllostachys edulis. Forests 2023, 14, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030540
Zhang P, Huang Z, Zhang H, Lu H, Li Q, Zhuo J, Wei H, Hou D, Lin X. Genome-Wide Analysis, Characterization, Expression and Function of SERK Gene Family in Phyllostachys edulis. Forests. 2023; 14(3):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030540
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Pengwei, Zhinuo Huang, Huicong Zhang, Haiwen Lu, Qimin Li, Juan Zhuo, Hantian Wei, Dan Hou, and Xinchun Lin. 2023. "Genome-Wide Analysis, Characterization, Expression and Function of SERK Gene Family in Phyllostachys edulis" Forests 14, no. 3: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030540
APA StyleZhang, P., Huang, Z., Zhang, H., Lu, H., Li, Q., Zhuo, J., Wei, H., Hou, D., & Lin, X. (2023). Genome-Wide Analysis, Characterization, Expression and Function of SERK Gene Family in Phyllostachys edulis. Forests, 14(3), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030540





