Phenotypic Variation in Leaf, Fruit and Seed Traits in Natural Populations of Eucommia ulmoides, a Relict Chinese Endemic Tree
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Morphometric Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Variation of Traits
3.2. Phenotypic Variation among and within Populations
3.3. Correlations among the 15 Traits
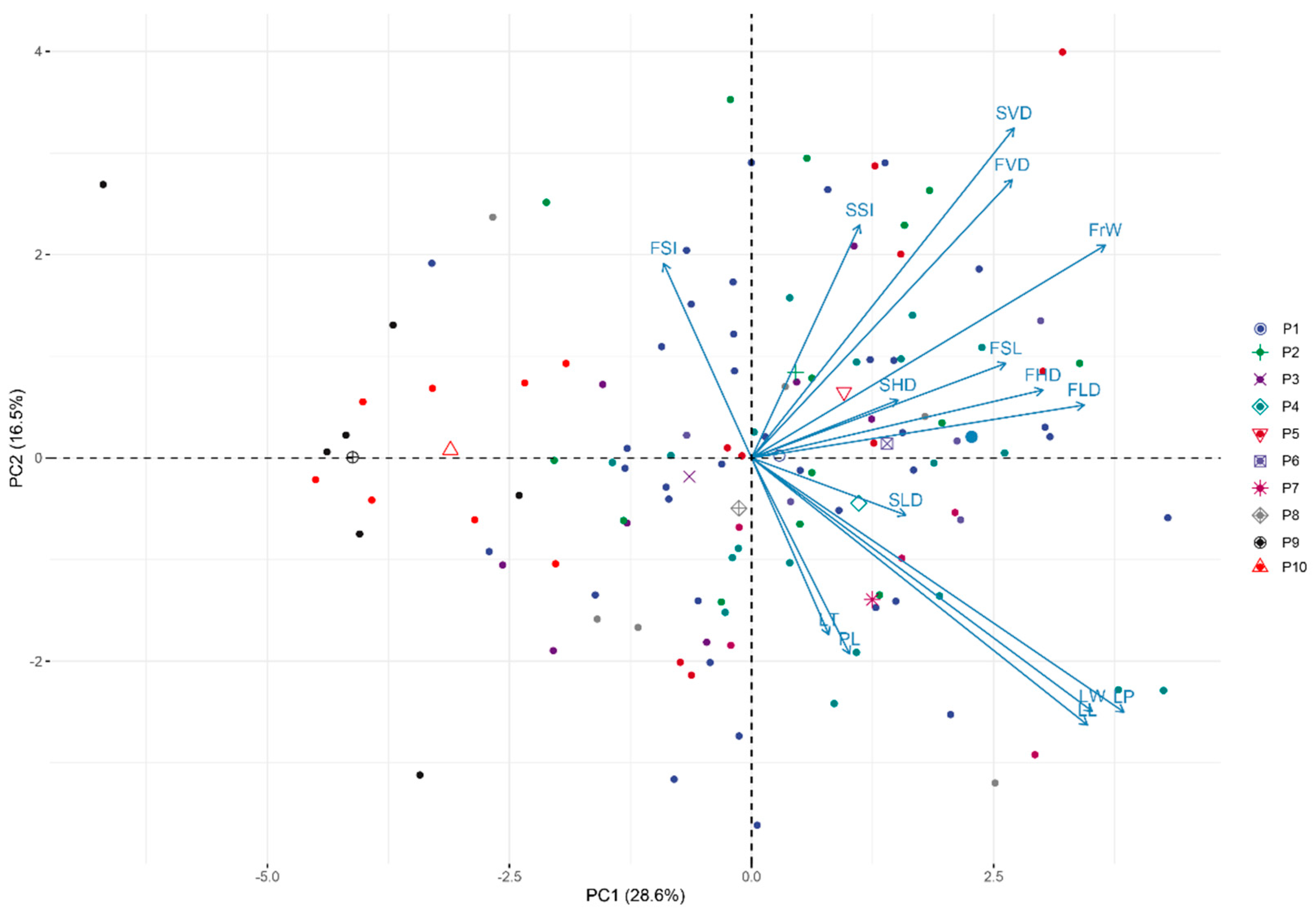
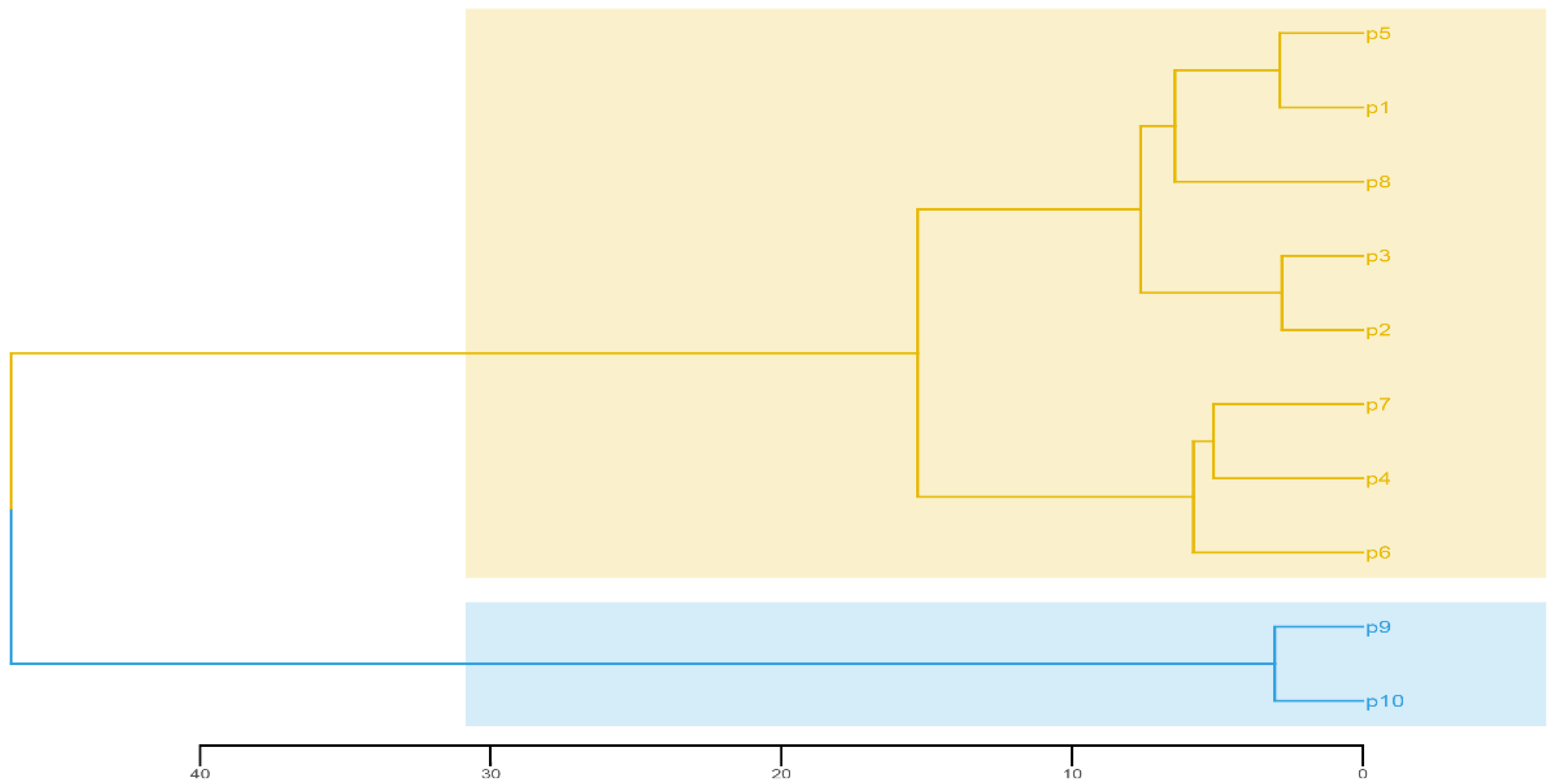
3.4. Principal Components and Cluster Analysis of the 15 Traits
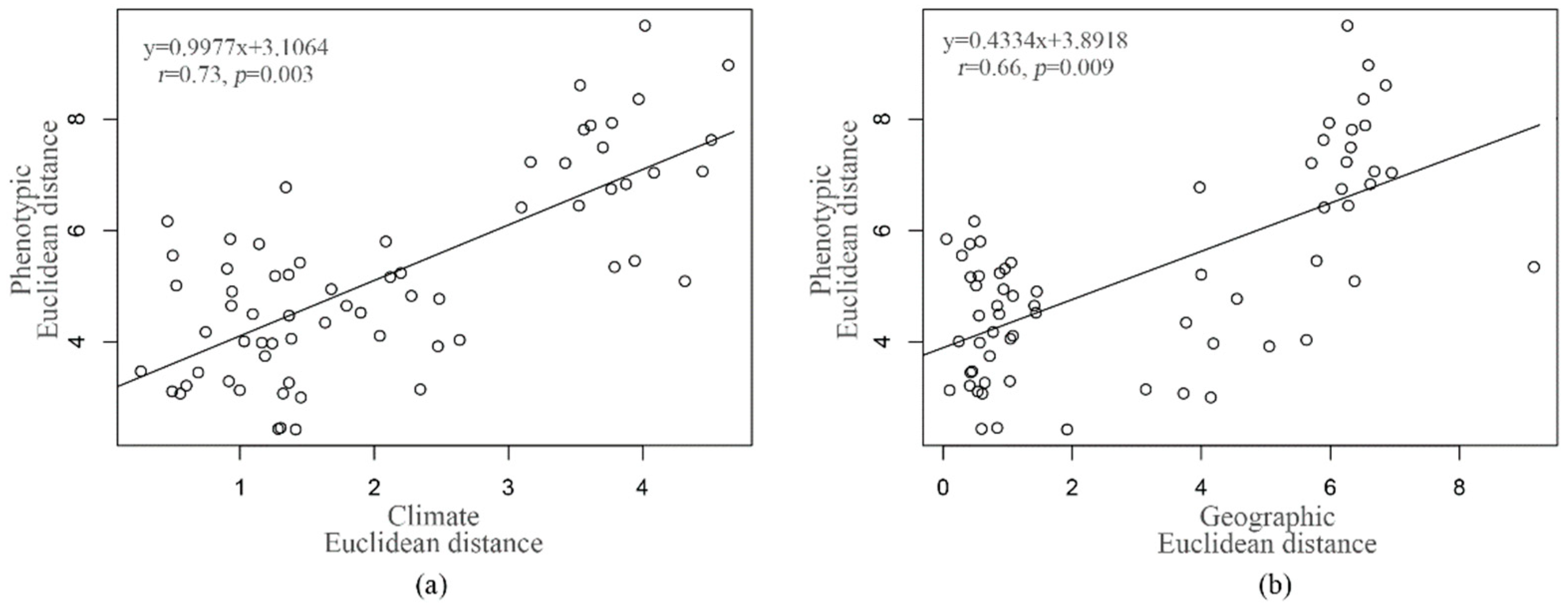
3.5. Correlations among the Morphological and Geographical or Climate Distances
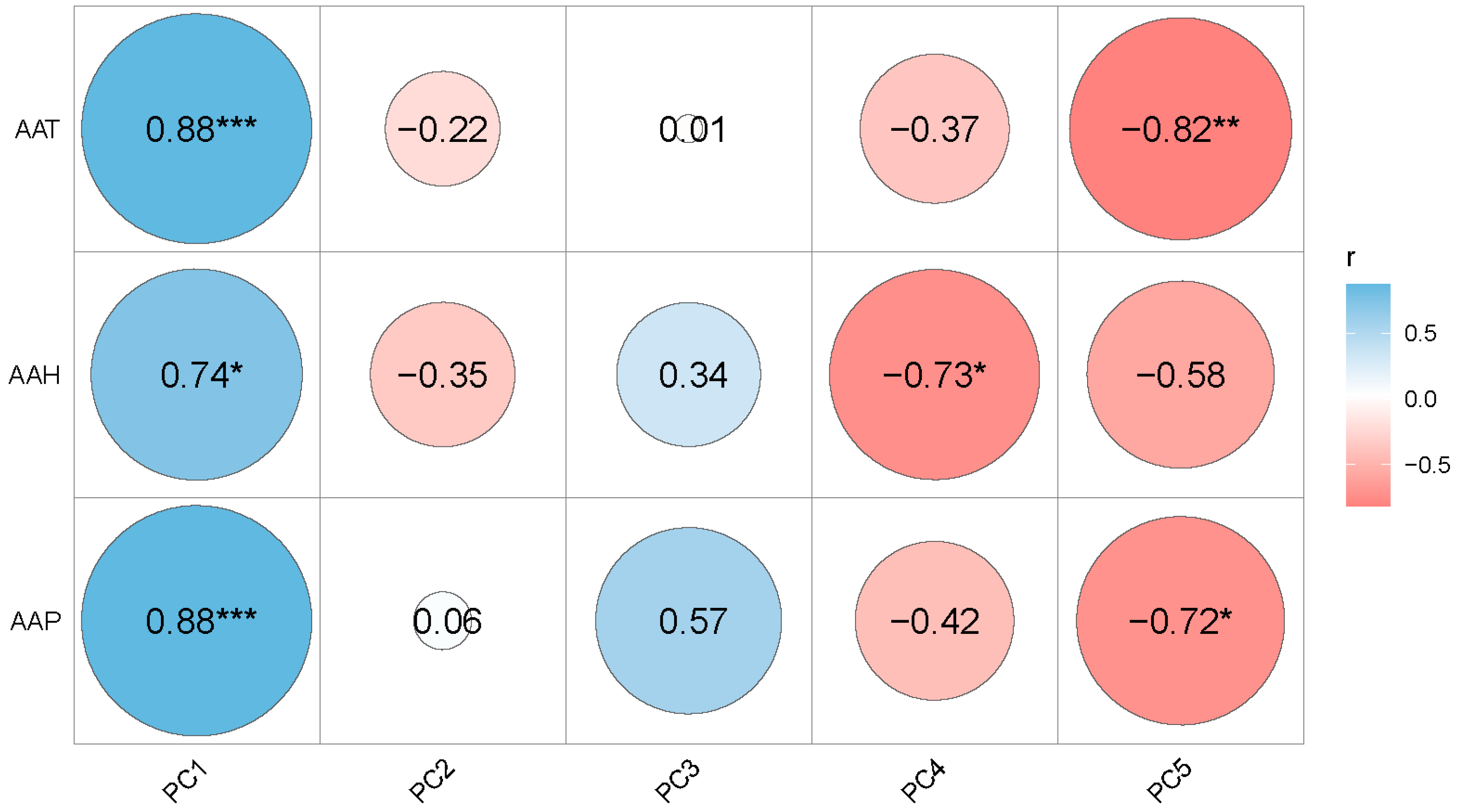
3.6. Associations among Principal Components and Climatic Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takeno, S.; Bamba, T.; Nakazawa, Y.; Fukusaki, E.; Okazawa, A.; Kobayashi, A. Quantification of trans-1,4-polyisoprene in Eucommia ulmoides by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 105, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.R.; Wang, J.H.; Li, M.X.; Hao, D.J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.L.; He, R.; Tao, R. Eucommia ulmoides oliv.: Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Tan, B.E.; Liu, G.; Oladele, O.A.; Rahu, N.; Tossou, M.C.; Yin, Y.L. Health-promoting properties of Eucommia ulmoides: A review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 5202908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Tang, L.; He, J.W.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.Z. Ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of Eucommia ulmoides: A review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 259–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Bamba, T.; Takeda, T.; Uefuji, H.; Harada, Y.; Li, X.H.; Chen, R.; Inoue, S.; Tutumi, M.; Shimizu, T.; et al. Production of eucommia-rubber from Eucommia ulmoides oliv. (hardy rubber tree). Plant Biotechnol. 2009, 26, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.D.; Zhao, Y.L.; Harrison, R.D.; Monkai, J.; Li, Y.W.; Chau, K.T.; Xu, J.C. Soil respiration in sloping rubber plantations and tropical natural forests in xishuangbanna, china. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 249, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyun, T.N.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, X.W.; Zhang, L.S.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Li, T.Z.; Yang, L.R.; Liu, P.F.; Du, L.Y.; et al. The hardy rubber tree genome provides insights into the evolution of polyisoprene biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, P.; Wang, Y.; Hu, F.; Yu, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z. Phenotypic trait subdivision provides new sight into the directional improvement of Eucommia ulmoides oliver. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 832821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, J.; Meng, Y.D.; Liu, C.L.; Du, Q.X.; Du, H.Y.; Du, L.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Li, X.J.; Wang, L. Analysis of leaf phenotypic variation and evaluation of elite individual plant in F1 progeny of Eucommia ulmoides. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2022, 42, 18–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.J.; Bai, M.S.; Zhang, T.; Ma, X.H.; Gao, J.M. A study on the growth features of individuals and secondary metabolites of Eucommia ulmoides leaves. Sci. Silv. Sin. 2001, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Yan, L.; Fu, Y. The characteristics of habitat, functional traits and medicinal components of Eucommia ulmoides from guizhou (vol 29, pg 12629, 2022). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32299–32302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, L.; Qi, D. Variation in leaf traits at different altitudes reflects the adaptive strategy of plants to environmental changes. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 8166–8175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Call, V.B.; Dilcher, D.L. The fossil record of Eucommia (Eucommiaceae) in north america. Am. J. Bot. 1997, 84, 798–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.Y.; Manchester, S.R.; Lu, A.M. The first discovery of eucommia fruit fossil in china. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1999, 44, 1506–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Li, C.S.; Collinson, M.E.; Lin, J.; Sun, Q.G. Eucommia (Eucommiaceae), a potential biothermometer for the reconstruction of paleoenvironments. Am. J. Bot. 2003, 90, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.G.; Jia, H.Y.; Li, W.Z.; Du, H.Y.; Wuyun, T.N.; Liu, P.F.; Bao, W.Q. Genetic diversity and genetic structure of Eucommia ulmoides populations based on SSR markers. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2018, 38, 79–85, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.Y. China Eucommia Pictorial; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.Y.; Hu, W.Z.; Yu, R. The Report on Development of China’s Eucommia Rubber Resources and Industry (2014–2015); Social Sciences Academic Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.X. Eucommia Ulmoides; Guizhou People’s Press: Guizhou, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.R.; Gao, C.J.; Li, J.; Miao, Y.C.; Cui, K. Phenotypic diversity analysis and superior family selection of industrial raw material forest species-Pinus yunnanensis Franch. Forests 2022, 13, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelaar, P.; Jovani, R.; Gomez-Mestre, I. Should i change or should i go? Phenotypic plasticity and matching habitat choice in the adaptation to environmental heterogeneity. Am. Nat. 2017, 190, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.X.; Liu, P.F.; Qing, J.; Du, H.Y. Genetic diversity analysis on morphology traits of Eucommia ulmoides male flowers. For. Res. 2016, 29, 670–675. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Q.X.; Qing, J.; Liu, P.F.; Wang, L.; Du, L.Y.; He, F.; Du, H.Y. Variation in fruit traits of Eucommia ulmoides germplasm resourcesand their comprehensive evaluation. For. Res. 2021, 34, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, G.X.; Xiong, L.Z.; Huang, M.; Liu, C.; Cai, Z.X. Diversity of samara characters of Euocmmia ulmoides in western of hunan. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2014, 34, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, J.Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Pei, Z.C.; Li, B.H. A study on growth characteristics of Eucommia ulmoides oliver in different areas and the dynamic changes of main effective components in leaves. J. Agric. Univ. Hebei 2019, 42, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.C.; Li, Z.Q.; Li, Y.; Chang, L. Genetic analysis of morphological traits of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver’s hybrid offspring. J. Northwest Sci.-Tech. Univ. Agric. For. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 40, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.H.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, W.K.; Deng, D.M.; Zhao, D.; Xiong, H.X. Analysis of genetic diversity of cultivated Eucommia ulmoides from guizhou province by phenotypic traits and SCoT markers. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2014, 37, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Meng, C.; Ji, Z.; Wang, Y. Phenotypic diversity of leaves morphologic characteristics of Ulmus lamellosa natural populations in shanxi. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2013, 40, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Keylock, C.J. Simpson diversity and the Shannon-Wiener index as special cases of a generalized entropy. Oikos 2005, 109, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 25 June 2022).
- Koutecky, P. MorphoTools: A set of R functions for morphometric analysis. Plant Syst. Evol. 2015, 301, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, N. Detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res. 1967, 27, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Fortin, M.J. Spatial pattern and ecological analysis. Vegetatio 1989, 80, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, R.; Tian, Z.; Xu, J.; Sun, W.; Duan, R.; Fu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L. Phenotypic variation and diversity in fruit, leaf, fatty acid, and their relationships to geoclimatic factors in seven natural populations of Malania oleifera Chun et S.K. Lee. Forests 2022, 13, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Package ‘Vegan’: Community Ecology Package; Version 2.4-2. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/vegandevs/vegan (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- Miljkovic, D.; Stefanovic, M.; Orlovic, S.; Nedic, M.S.; Kesic, L.; Stojnic, S. Wild cherry (Prunus avium (L.) L.) leaf shape and size variations in natural populations at different elevations. Alp. Bot. 2019, 129, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Xie, X.C.; Long, F.Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.H.; Zhao, Z.X.; Yang, S.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Fan, R.S.; Li, Z.Q. Trait variations and probability grading index system on leaf-related traits of Eucommia ulmoides oliver germplasm. Plants 2021, 10, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.X.; Qing, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, P.F.; He, F.; Zhu, L.L.; Du, H.Y. Variation and probability grading of main quantitative traits of fruits for Eucommia ulmoides germplasm. Bull. Bot. Res. 2019, 39, 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.D.; Du, H.Y.; Wang, L.; Lv, G.X.; Qing, J.; He, F.; Huang, H.Y.; Du, Q.X. Diversity analysis of leaf phenotypic traits of Eucommia ulmoides germplasm resources. For. Res. 2022, 35, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.Y.; Du, H.Y.; Wuyun, T.N.; Zhu, G.P. Establishment of genetic diversity system of Eucommia ulmoides based on SSR molecular markers. For. Res. 2013, 26, 795–799. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.Y. Gutta-Percha-Content Character, Its Variance and Selection of Superior Clone Associated with Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Hunan, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.G. Genetic Diversity Analysis, Core Collection Construction and Molecular Identification of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. Ph.D. Thesis, China Academy of Forestry Sciences, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M. Development of Genomic SSR Makers and Genetic Diversity Evaluation of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Master’s Thesis, China Academy of Forestry Sciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.M. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Eucommia ulmoides in Anhui Province Based on ISSRs. Master’s Thesis, School of Forestry & Landscape Architecture, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Q.; Reich, P.B.; Schmid, B.; Shrestha, N.; Feng, X.; Lyu, T.; Maitner, B.S.; Xu, X.T.; Li, Y.C.; Zou, D.T.; et al. Leaf size of woody dicots predicts ecosystem primary productivity. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Wang, W.N.; Wang, S.Z.; Yang, L.X.; Gu, J.C. Intraspecific variations of anatomical, morphological and chemical traits in leaves and absorptive roots along climate and soil gradients: A case study with Ginkgo biloba and Eucommia Ulmoides. Plant Soil 2021, 469, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

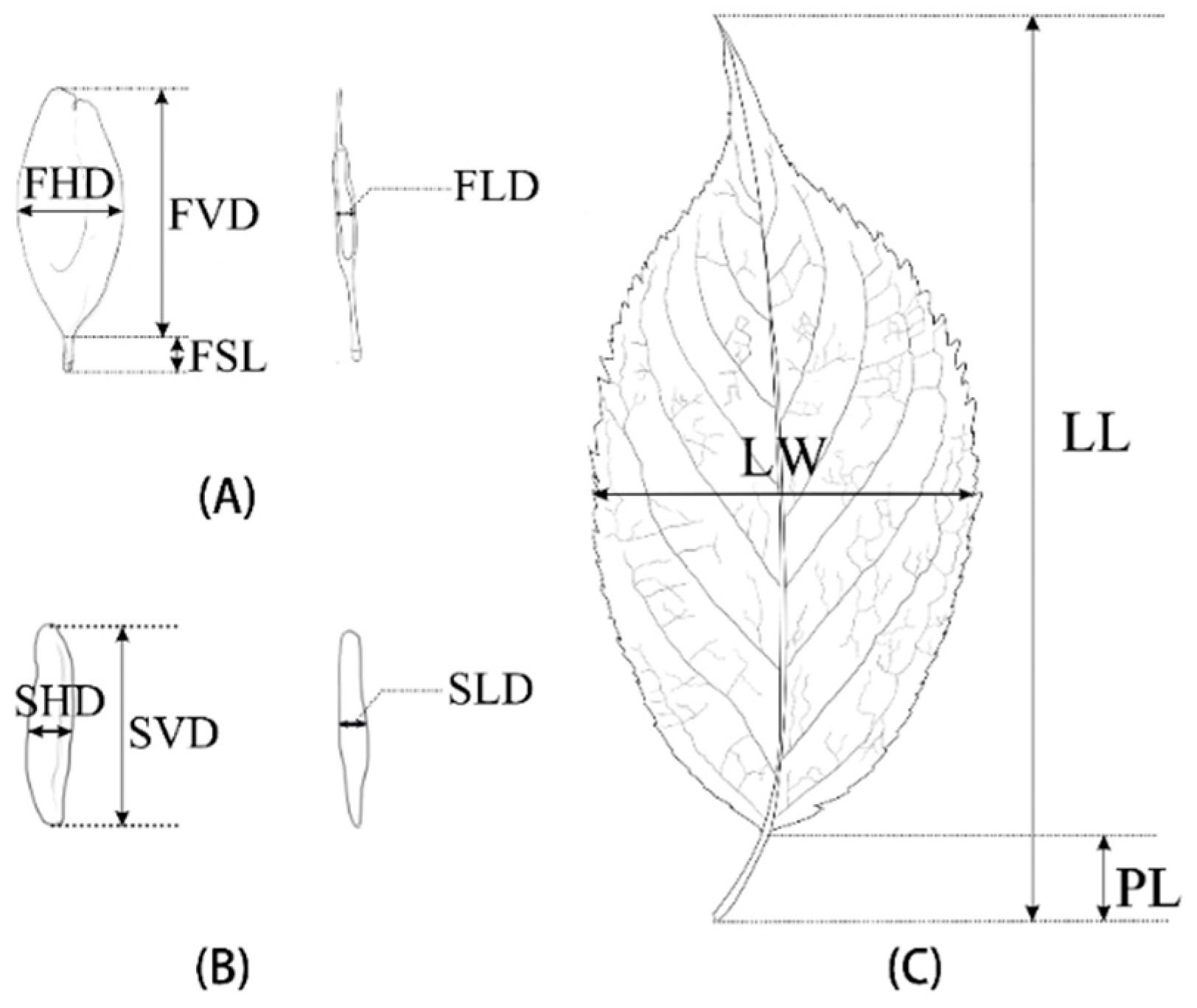

| Population | Sample Size (Number of Trees Sampled) | Longitude (°E, LON) | Latitude (°N, LAT) | Altitude (m, ALT) | Average Annual Temperature (°C, AAT) | Average Annual Precipitation (mm, AAP) | Average Annual Humidity (%, AAH) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cljy (P1) | 36 | 110.70 | 29.16 | 212–808 | 16.3 | 1340.4 | 75.8 |
| Clylp (P2) | 14 | 110.17 | 29.57 | 96–590 | 15.6 | 1349.2 | 74.4 |
| Clgfq (P3) | 8 | 110.18 | 29.43 | 243–588 | 16.4 | 1396.9 | 78.6 |
| Cljylc (P4) | 19 | 110.77 | 29.52 | 71–370 | 16.6 | 1301.7 | 75.8 |
| Cldx (P5) | 9 | 110.78 | 29.12 | 450–778 | 15.0 | 1430.9 | 80.2 |
| Ydtms (P6) | 5 | 110.49 | 29.10 | 179–621 | 18.0 | 1411.7 | 73.4 |
| Tyrs (P7) | 5 | 111.25 | 29.37 | 250–253 | 16.4 | 1431.6 | 70.8 |
| Hcgq (P8) | 6 | 106.88 | 27.72 | 924–978 | 15.2 | 1059.8 | 80.5 |
| Lyjjh (P9) | 7 | 106.26 | 33.55 | 696–705 | 9.6 | 754.8 | 74.4 |
| Wxgjz (P10) | 8 | 111.37 | 35.60 | 468–481 | 13.2 | 524.9 | 65.6 |
| Traits | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf length (LL) (mm) | 44.80 | 239.80 | 118.02 | 28.32 | 23.99 |
| Leaf width (LW) (mm) | 21.70 | 120.10 | 59.90 | 12.56 | 20.96 |
| Leaf thickness (LT) (mm) | 0.04 | 1.64 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 49.00 |
| Petiole length (PL) (mm) | 5.50 | 38.20 | 15.49 | 3.78 | 24.41 |
| Leaf perimeter (LP) (mm) | 59.20 | 295.30 | 145.10 | 33.10 | 22.81 |
| Fruit vertical diameter (FVD) (mm) | 16.15 | 41.36 | 32.22 | 3.13 | 9.72 |
| Fruit horizontal diameter (FHD) (mm) | 6.87 | 19.96 | 11.66 | 1.39 | 11.94 |
| Fruit lateral diameter (FLD) (mm) | 0.16 | 5.44 | 2.40 | 0.46 | 19.14 |
| Fruit stalk length (FSL) (mm) | 1.26 | 10.21 | 4.85 | 1.19 | 24.60 |
| Fruit shape index (FSI) | 1.35 | 4.79 | 2.79 | 0.31 | 11.03 |
| Seed vertical diameter (SVD) (mm) | 7.51 | 18.74 | 13.05 | 1.48 | 11.30 |
| Seed horizontal diameter (SHD) (mm) | 1.66 | 4.60 | 2.94 | 0.36 | 12.25 |
| Seed lateral diameter (SLD) (mm) | 0.22 | 2.12 | 1.17 | 0.24 | 20.51 |
| Seed shape index (SSI) | 2.26 | 7.59 | 4.49 | 0.65 | 14.52 |
| 100-fruit weight (FrW) (g) | 4.24 | 13.42 | 8.41 | 1.67 | 19.84 |
| Traits | Proportion of Variance Components (%) | Population Differentiation Coefficient (%) | F Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among Populations | Among Trees within Populations | Within Trees (Residual) | Among Populations | Among Trees within Populations | ||
| Leaf length (LL) (mm) | 9.81 | 21.66 | 68.53 | 31.17 | 4.0 *** | 10.5 *** |
| Leaf width (LW) (mm) | 16.15 | 25.33 | 58.52 | 38.94 | 5.0 *** | 13.9 *** |
| Leaf thickness (LT) (mm) | 5.88 | 52.94 | 41.18 | 10.00 | 2.4 *** | 42.6 ** |
| Petiole length (PL) (mm) | 9.33 | 39.69 | 50.98 | 19.02 | 2.8 ** | 23.4 ** |
| Leaf perimeter (LP) (mm) | 19.07 | 18.47 | 62.46 | 50.80 | 7.8 *** | 9.9 *** |
| Fruit vertical diameter (FVD) (mm) | 3.02 | 71.11 | 25.87 | 4.07 | 1.2 | 84.8 |
| Fruit horizontal diameter (FHD) (mm) | 2.19 | 67.04 | 30.77 | 3.17 | 1.5 | 65.2 |
| Fruit lateral diameter (FLD) (mm) | 53.75 | 20.16 | 26.09 | 72.73 | 19.9 *** | 24.3 *** |
| Fruit stalk length (FSL) (mm) | 10.55 | 47.29 | 42.15 | 18.25 | 2.6 ** | 34.7 ** |
| Fruit shape index (FSI) | 12.38 | 51.43 | 36.19 | 19.40 | 1.4 | 42.9 |
| Seed vertical diameter (SVD) (mm) | 13.17 | 61.78 | 25.06 | 17.57 | 2.5 *** | 75.8 *** |
| Seed horizontal diameter (SHD) (mm) | 3.05 | 53.44 | 43.51 | 5.41 | 1.4 | 38.3 |
| Seed lateral diameter (SLD) (mm) | 37.10 | 22.58 | 40.32 | 62.16 | 14.3 *** | 17.6 *** |
| Seed shape index (SSI) | 13.42 | 47.62 | 38.96 | 21.99 | 1.9 * | 38.4 * |
| 100-fruit weight (FrW) (g) | 40.10 | 41.49 | 18.41 | 49.15 | 6.7 *** | 7.8 *** |
| Mean | 16.60 | 42.80 | 40.6 | 28.26 | ||
| Traits | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf length (LL) (mm) | 0.707 | −0.535 | 0.238 | −0.124 | 0.049 |
| Leaf width (LW) (mm) | 0.717 | −0.508 | 0.218 | −0.034 | −0.011 |
| Leaf thickness (LT) (mm) | 0.163 | −0.354 | 0.329 | 0.488 | −0.491 |
| Petiole length (PL) (mm) | 0.207 | −0.393 | 0.183 | 0.463 | 0.486 |
| Leaf perimeter (LP) (mm) | 0.784 | −0.509 | 0.230 | −0.115 | −0.021 |
| Fruit vertical diameter (FVD) (mm) | 0.548 | 0.558 | 0.082 | 0.323 | 0.416 |
| Fruit horizontal diameter (FHD) (mm) | 0.613 | 0.136 | −0.508 | 0.456 | 0.088 |
| Fruit lateral diameter (FLD) (mm) | 0.700 | 0.106 | −0.097 | −0.392 | −0.144 |
| Fruit stalk length (FSL) (mm) | 0.535 | 0.190 | 0.072 | 0.043 | 0.214 |
| Fruit shape index (FSI) | −0.185 | 0.390 | 0.689 | −0.206 | 0.308 |
| Seed vertical diameter (SVD) (mm) | 0.552 | 0.661 | 0.146 | −0.015 | −0.222 |
| Seed horizontal diameter (SHD) (mm) | 0.308 | 0.116 | −0.727 | −0.026 | −0.009 |
| Seed lateral diameter (SLD) (mm) | 0.324 | −0.114 | −0.155 | −0.692 | 0.222 |
| Seed shape index (SSI) | 0.228 | 0.467 | 0.751 | 0.009 | −0.197 |
| 100-fruit weight (FrW) (g) | 0.744 | 0.426 | −0.201 | 0.031 | −0.229 |
| Eigen value | 4.295 | 2.475 | 2.232 | 1.473 | 1.012 |
| Contribution rate | 28.636 | 16.500 | 14.877 | 9.822 | 6.746 |
| Cumulative Contribution rate | 28.636 | 45.136 | 60.013 | 69.835 | 76.581 |
| Independent Effect of Climate | Independent Effect of Geography | |
|---|---|---|
| Morphological distance | r = 0.31, p = 0.034 | r = 0.16, p = 0.214 |
| Models | Fit Statistics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized Coefficients | R2 | AIC | RMSE | p | |||
| AAT | AAH | AAP | |||||
| PC1 | 0.454 | 0.459 | 0.845 | −18.05 | 0.36 | p < 0.001 | |
| PC2 | −0.226 | 0.456 | −0.351 | 0.246 | −18.51 | 0.34 | p = 0.219 |
| PC3 | −0.330 | 0.447 | 0.636 | −28.62 | 0.21 | p = 0.012 | |
| PC4 | −0.49 | 0.477 | −12.71 | 0.48 | p = 0.016 | ||
| PC5 | −0.453 | 0.626 | −19.88 | 0.94 | p = 0.003 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Gong, H.; Feng, M.; Tian, C. Phenotypic Variation in Leaf, Fruit and Seed Traits in Natural Populations of Eucommia ulmoides, a Relict Chinese Endemic Tree. Forests 2023, 14, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030462
Wang C, Gong H, Feng M, Tian C. Phenotypic Variation in Leaf, Fruit and Seed Traits in Natural Populations of Eucommia ulmoides, a Relict Chinese Endemic Tree. Forests. 2023; 14(3):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030462
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chaochun, Huimin Gong, Miao Feng, and Chunlian Tian. 2023. "Phenotypic Variation in Leaf, Fruit and Seed Traits in Natural Populations of Eucommia ulmoides, a Relict Chinese Endemic Tree" Forests 14, no. 3: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030462
APA StyleWang, C., Gong, H., Feng, M., & Tian, C. (2023). Phenotypic Variation in Leaf, Fruit and Seed Traits in Natural Populations of Eucommia ulmoides, a Relict Chinese Endemic Tree. Forests, 14(3), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030462







