Linking Soil Bacterial Communities to Soil Aggregates after Afforestation in a Karst Rocky Desertification Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Experimental Design
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Composition of the Soil Aggregates and Soil Properties
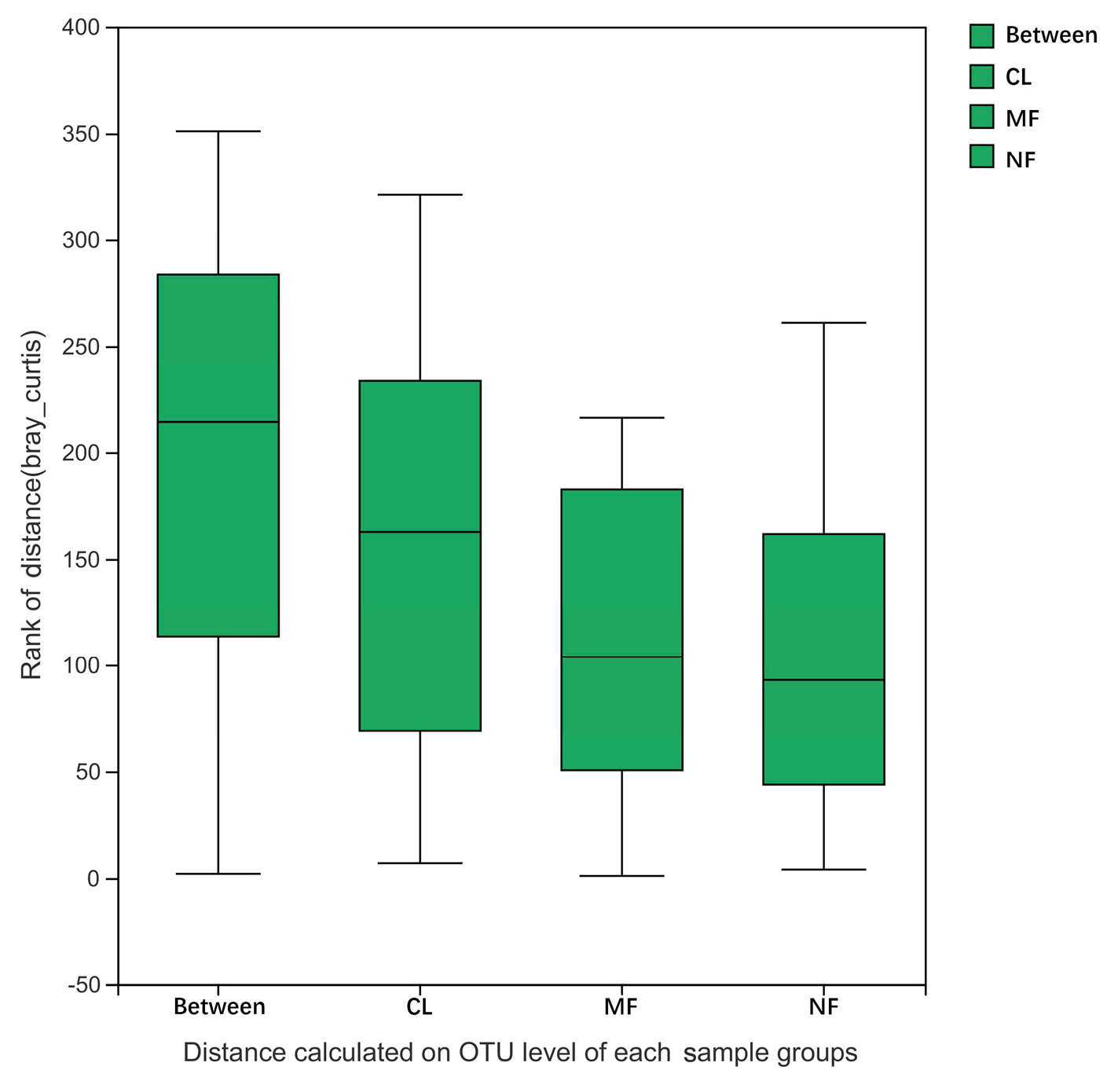
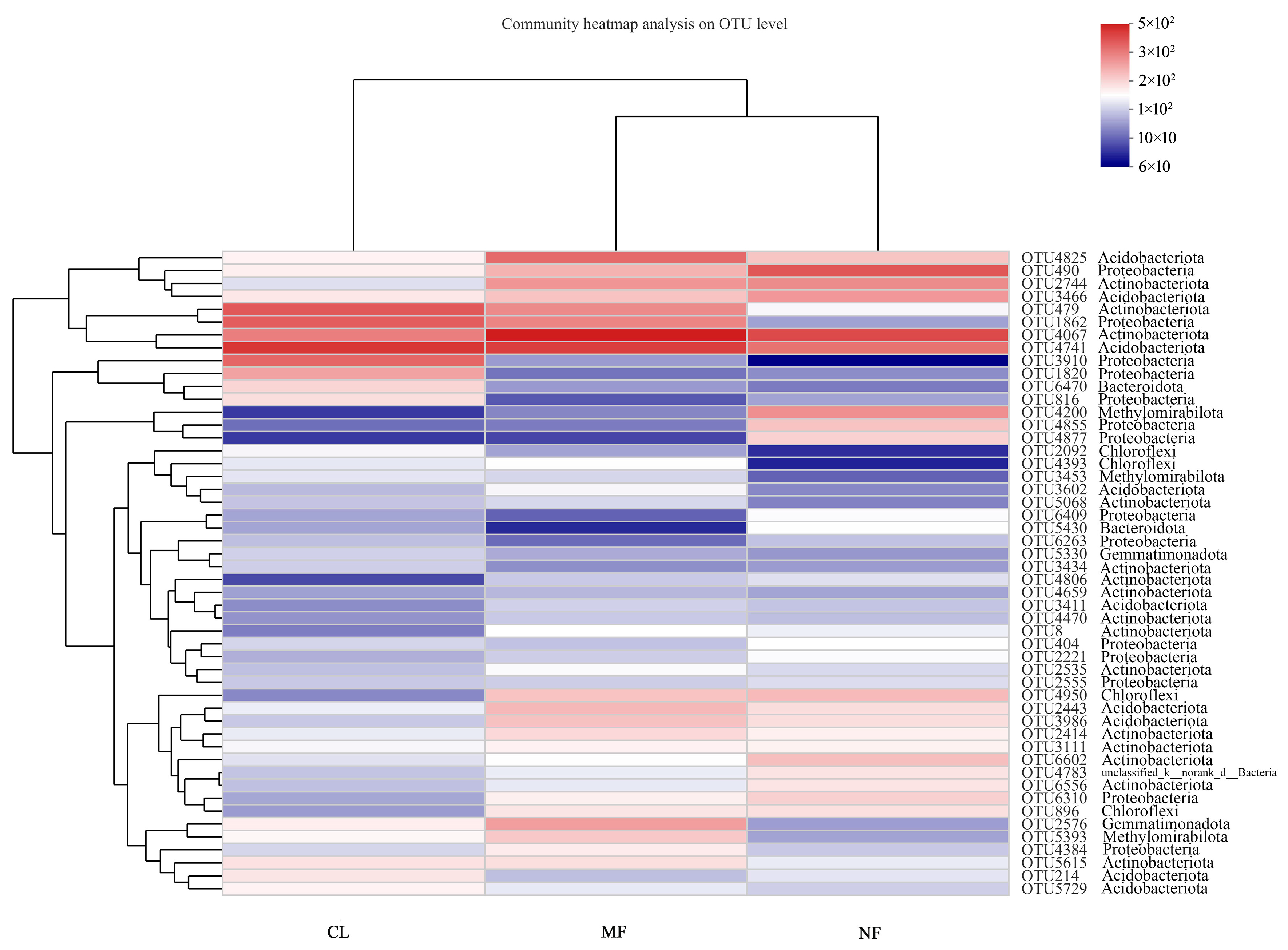
3.2. Soil Bacterial Quantity and Community Compositions
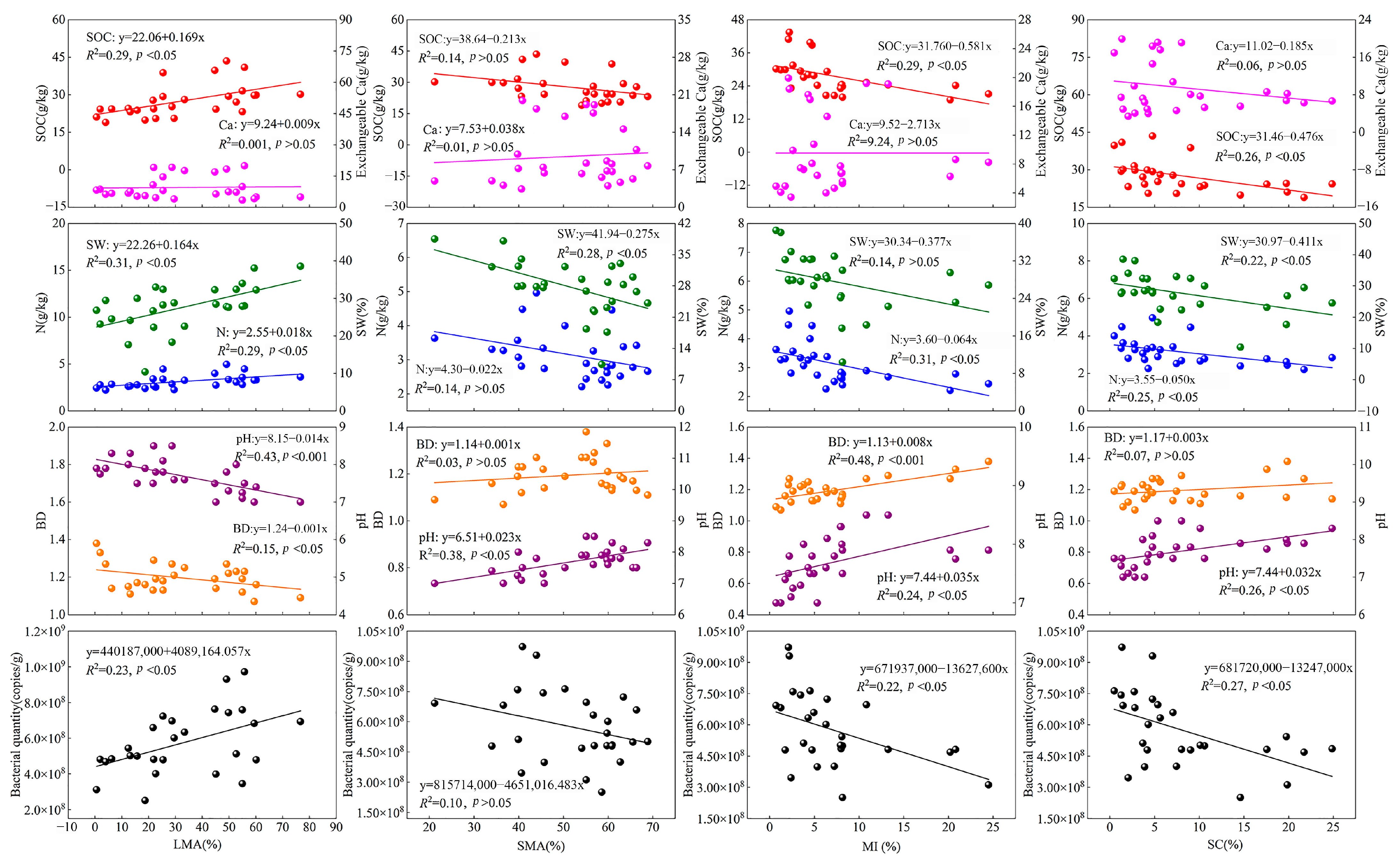
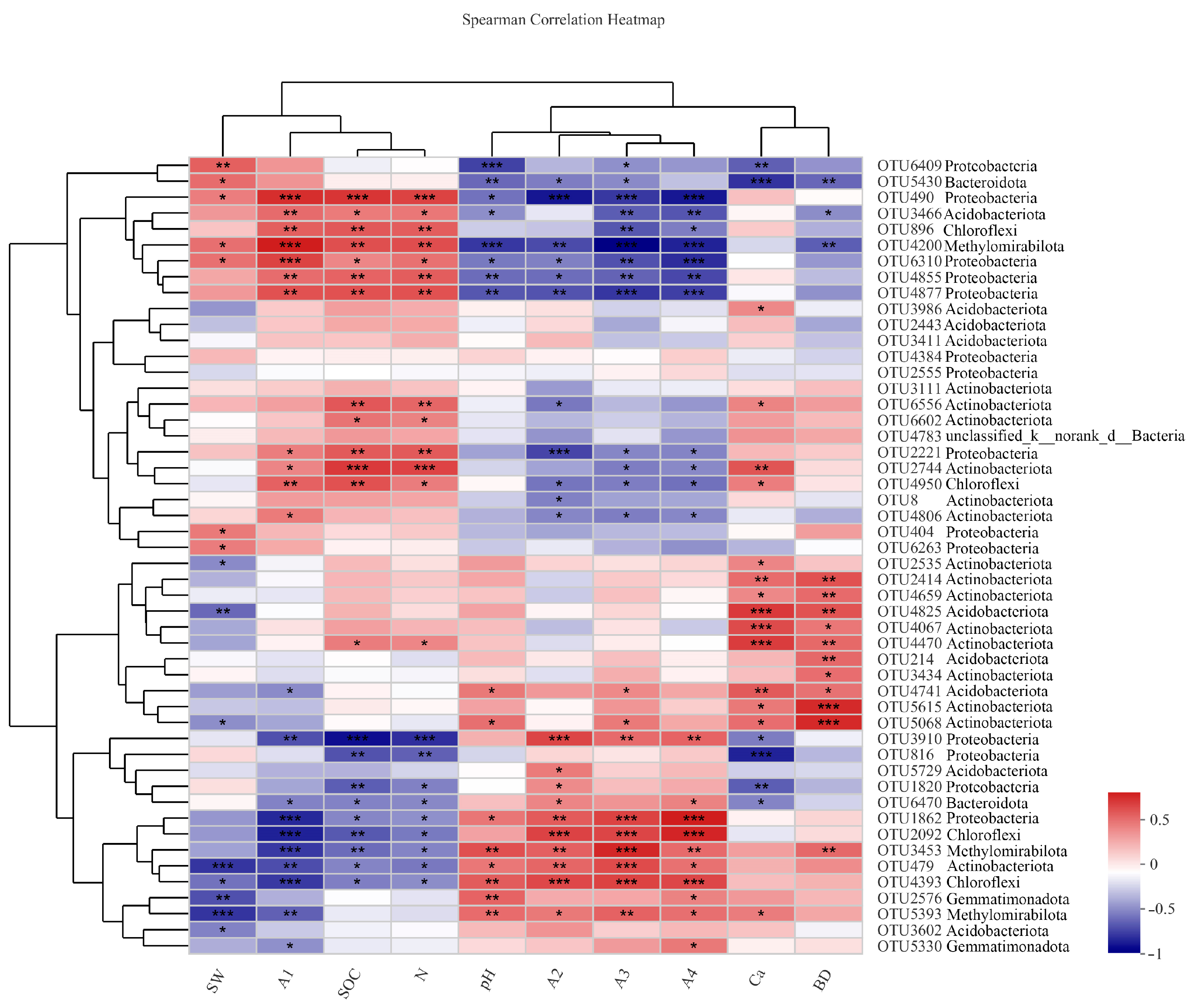
3.3. Relationships between the Aggregates, and Bacteria and the Soil Properties
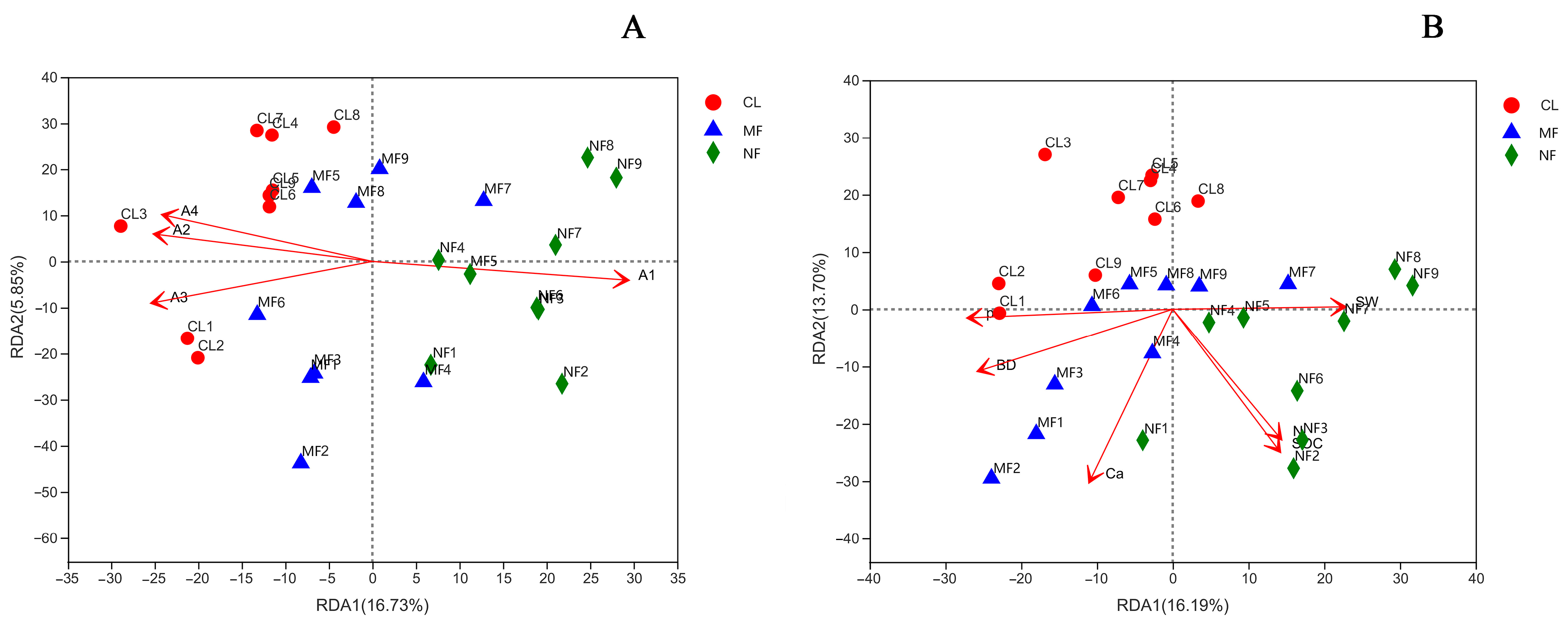
3.4. Relationships between the Soil Properties and Quantities, and Bacterial Communities
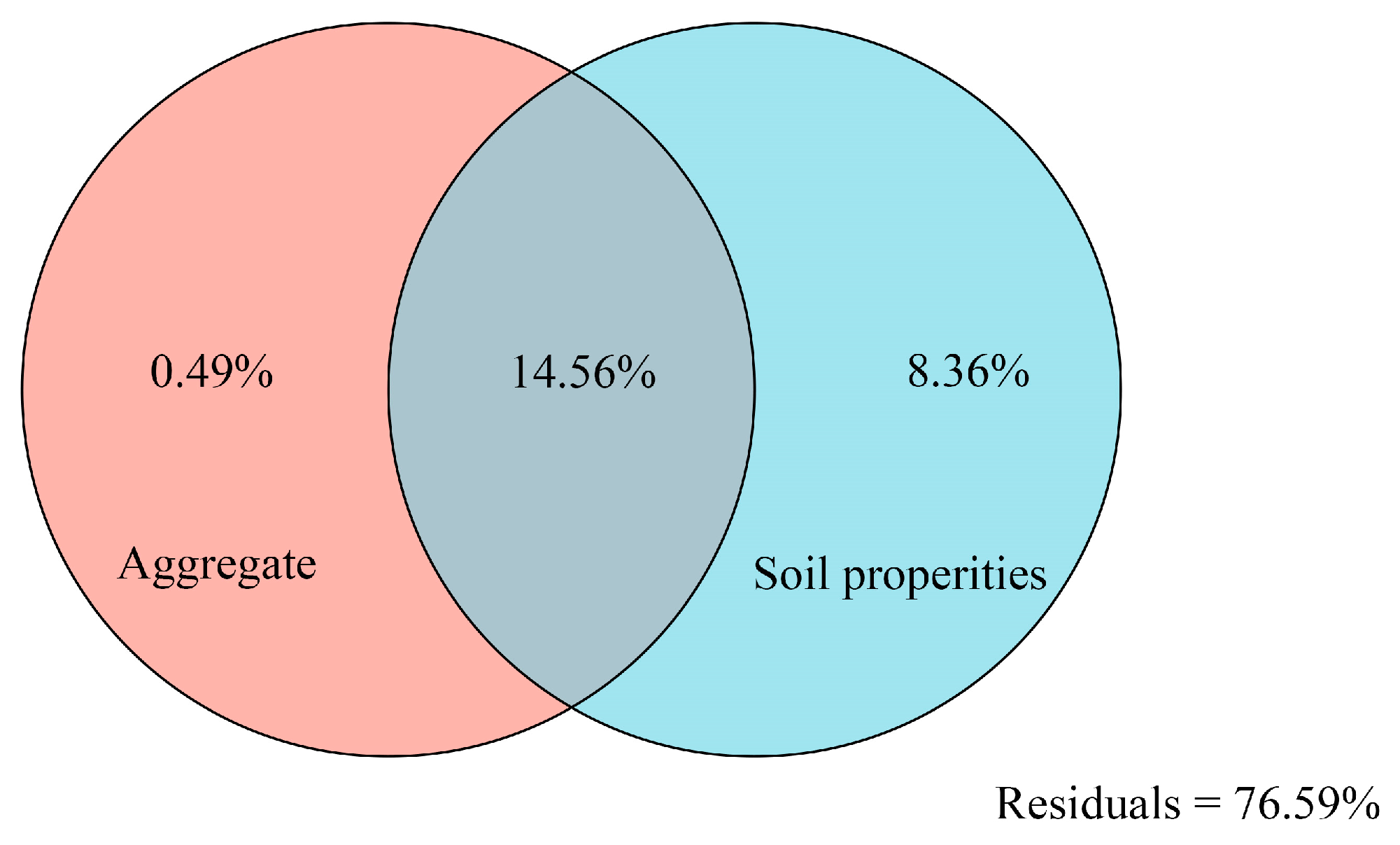
3.5. Variation-Partitioning Analysis (VPA) of the Soil Bacterial Community, Soil Aggregation, and Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Aggregation and Bacterial Composition Structure
4.2. Linking Aggregates to Soil Bacteria
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delgado Baquerizo, M.; Reich, P.B.; Khachane, A.N.; Campbell, C.D.; Thomas, N.; Freitag, T.E.; AlSoud, W.A.; Sorensen, S.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Singh, B.K. It is elemental: Soil nutrient stoichiometry drives bacterial diversity. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 19, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horner-Devine, M.C.; Leibold, M.A.; Smith, V.H.; Bohannan, B.J.M. Bacterial diversity patterns along a gradient of primary productivity. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Franco, N.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Goberna, M.; Albaladejo, J. Changes in soil aggregation and microbial community structure control carbon sequestration after afforestation of semiarid shrublands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 87, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Fan, X.D.; Ren, C.J.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Wang, J.; Doughty, R. Changes of the organic carbon content and stability of soil aggregates affected by soil bacterial community after afforestation. Catena 2018, 171, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Lu, X.; Yang, Y.; Hartley, I.P.; Zhang, W.; Mo, J.; Yu, G.; Zhou, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Long-term nitrogen addition modifies microbial composition and functions for slow carbon cycling and increased sequestration in tropical forest soil. Globle Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 3267–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Direct and indirect linkages between soil aggregates and soil bacterial communities under tillage methods. Geoderma 2019, 354, 113879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, F.; Xu, M.; Cai, P.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. Contrasting responses of bacterial and fungal communities to aggregate-size fractions and longterm fertilizations in soils of northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 635, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Long, Q.; Huang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, N. Afforestation-induced large macroaggregate formation promotes soil organic carbon accumulation in degraded karst area. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 505, 119884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, R.; Luo, W. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil quality in degraded karst landscapes of southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lin, C.; Guo, B.; Yu, J.; Ding, H.; Peng, S.; Sveen, T.R.; Zhang, Y. Effects of re-vegetation restoration on soil bacterial community structure in degraded land in subtropical China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 98, 103184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil structure and soil organic matter II. A normalized stability index and the effect of mineralogy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Xiao, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, H.; Guggenberger, G.; Wang, K. Tillage induces rapid loss of organic carbon in large macroaggregates of calcareous soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, G.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, L.; Ge, N.; Wei, X.; Shao, M. Dynamics of new- and old- organic carbon and nitrogen in bulk soils and aggregates following afforestation on farmland. Catena 2020, 195, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xin, X.; Zhu, A.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ding, S.; Mu, L.; Shao, L. Linking macroaggregation to soil microbial community and organic carbon accumulation under different tillage and residue managements. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaud, A.; Lerch, T.Z.; Chevallier, T.; Nunan, N.; Chenu, C.; Brauman, A. Dynamics of bacterial communities in relation to soil aggregate formation during the decomposition of 13C-labelled rice straw. Apply Soil Ecol. 2012, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ren, Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, K.; Sun XPeng, S. Contribution of soil variables to bacterial community composition following land use change in Napahai plateau wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Lin, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Impacts of forest conversion on soil bacterial community composition and diversity in subtropical forests. Catena 2019, 175, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Shangguan, Z.; Chang, F.; Jia, F.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Shi, W.; Deng, L. Effects of grassland afforestation on structure and function of soil bacterial and fungal communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Alharbi, H.; Wang, J.; Dang, P.; Chen, X.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Yan, W. Soil organic matter, nitrogen and pH driven change in bacterial community following forest conversion. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 477, 118473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Lee, X.; Theng, B.K.G.; Zhang, L.; Fang, B.; Li, F. Biomass accumulation and carbon sequestration in an age-sequence of Zanthoxylum bungeanum plantations under the Grain for Green Program in karst regions, Guizhou province. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 203, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.; Elliott, E. Carbon and nitrogen distributions in aggregates from cultivated and grassland soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Soil Argrochemistry Analysis Protocoes, 1st ed.; China Agriculture Science Press: BeiJing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Qi, X.; Long, Q.; Huang, M. The shift of soil bacterial community after afforestation influence soil organic carbon and aggregate stability in karst region. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 901126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.; Zhang, Q. Effects of agricultural abandonment on soil aggregation, soil organic carbon storage and stabilization: Results from observation in a small karst catchment, Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 288, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, W.; Hu, P.; Xiao, D.; Yang, R.; Ye, Y.; Wang, K. The formation of large macroaggregates induces soil organic carbon sequestration in short-term cropland restoration in a typical karst area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Lan, J. Impact of vegetation restoration on soil organic carbon stocks and aggregates in a karst rocky desertification area in Southwest China. J. Soils Sed. 2019, 20, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, X.; Jia, X.; Shao, M. Accumulation of soil organic carbon in aggregates after afforestation on abandoned farmland. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 49, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wei, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X. Dynamics of soil aggregate-associated organic carbon along an afforestation chronosequence. Plant Soil 2015, 391, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Wen, X.; Quine, T.A.; Wang, Q. Changes in the biological N2-fixation rates and diazotrophic community as vegetation recovers on abandoned farmland in a karst region of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 158, 103808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Luo, C.; Jiang, L.; Song, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ostle, N.J.; Zhang, G. Land-use changes alter soil bacterial composition and diversity in tropical forest soil in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Ren, H.; Li, S.; Leng, X.; Yao, X. Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Co-occurrence Pattern during Vegetation Restoration in Karst Rocky Desertification Area. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, A.; Yang, H.; Müller, W.E.G. Impact of Rocky Desertification Control on Soil Bacterial Community in Karst Graben Basin, Southwestern China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilpiszeski, R.L.; Aufrecht, J.A.; Retterer, S.T.; Sullivan, M.B.; Graham, D.E.; Pierce, E.M.; Zablocki, O.D.; Palumbo, A.V.; Elias, D.A. Soil aggregate microbial communities: Towards understanding microbiome interactions at biologically relevant scales. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00324-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Land-Use Type | CL | MF | NF |
|---|---|---|---|
| LMA/% | 12.40 ± 3.34 c | 29.69 ± 4.11 b | 56.14 ± 3.06 a |
| SMA/% | 59.59 ± 1.17 a | 57.08 ± 3.14 a | 39.18 ± 2.77 b |
| MI/% | 12.37 ± 2.40 a | 6.84 ± 1.08 ab | 2.33 ± 0.38 b |
| SC/% | 15.63 ± 2.31 a | 6.40 ± 9.76 b | 2.35 ± 0.47 b |
| SOC/(g kg−1) | 22.02 ± 0.73 b | 27.59 ± 1.56 a | 33.17 ± 2.23 a |
| N/(g kg−1) | 2.54 ± 0.08 b | 3.17 ± 0.19 a | 3.71 ± 0.22 a |
| Exchangeable Ca/(g kg−1) | 6.25 ± 0.51 b | 12.31 ± 1.78 a | 10.01 ± 2.21 ab |
| SW/% | 24.88 ± 2.35 b | 26.18 ± 1.58 ab | 31.85 ± 1.46 a |
| pH | 7.85 ± 0.08 a | 7.92 ± 0.17 a | 7.32 ± 0.09 b |
| BD/(g cm−3) | 1.22 ± 0.03 a | 1.19 ± 0.02 a | 1.17 ± 0.02 a |
| Bacterial quantity/(copies g−1) | 2.93 × 108 ± 4.30 × 107 b | 5.02 × 108 ± 7.19 × 107 ab | 5.88 × 108 ± 5.46 × 107 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Long, Q.; Qi, X.; Yue, K.; Liu, L. Linking Soil Bacterial Communities to Soil Aggregates after Afforestation in a Karst Rocky Desertification Region. Forests 2023, 14, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020326
Lan J, Huang M, Wang J, Wang S, Long Q, Qi X, Yue K, Liu L. Linking Soil Bacterial Communities to Soil Aggregates after Afforestation in a Karst Rocky Desertification Region. Forests. 2023; 14(2):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020326
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Jiacheng, Mingzhi Huang, Junxian Wang, Shasha Wang, Qixia Long, Xue Qi, Kunqian Yue, and Lei Liu. 2023. "Linking Soil Bacterial Communities to Soil Aggregates after Afforestation in a Karst Rocky Desertification Region" Forests 14, no. 2: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020326
APA StyleLan, J., Huang, M., Wang, J., Wang, S., Long, Q., Qi, X., Yue, K., & Liu, L. (2023). Linking Soil Bacterial Communities to Soil Aggregates after Afforestation in a Karst Rocky Desertification Region. Forests, 14(2), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020326






