Determine the Optimal Vegetation Type for Soil Wind Erosion Prevention and Control in the Alpine Sandy Land of the Gonghe Basin on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location
2.2. Research Method
2.2.1. Sample Site Selection
2.2.2. Experimental Design
Wind Speed Profile and Sediment Transport Measurement
Wind Erosion Depth Measurement
2.2.3. Index Calculation
Windbreak Effect
The Sediment Transport Rate
Sand Fixation Effect
Erosion Intensity
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
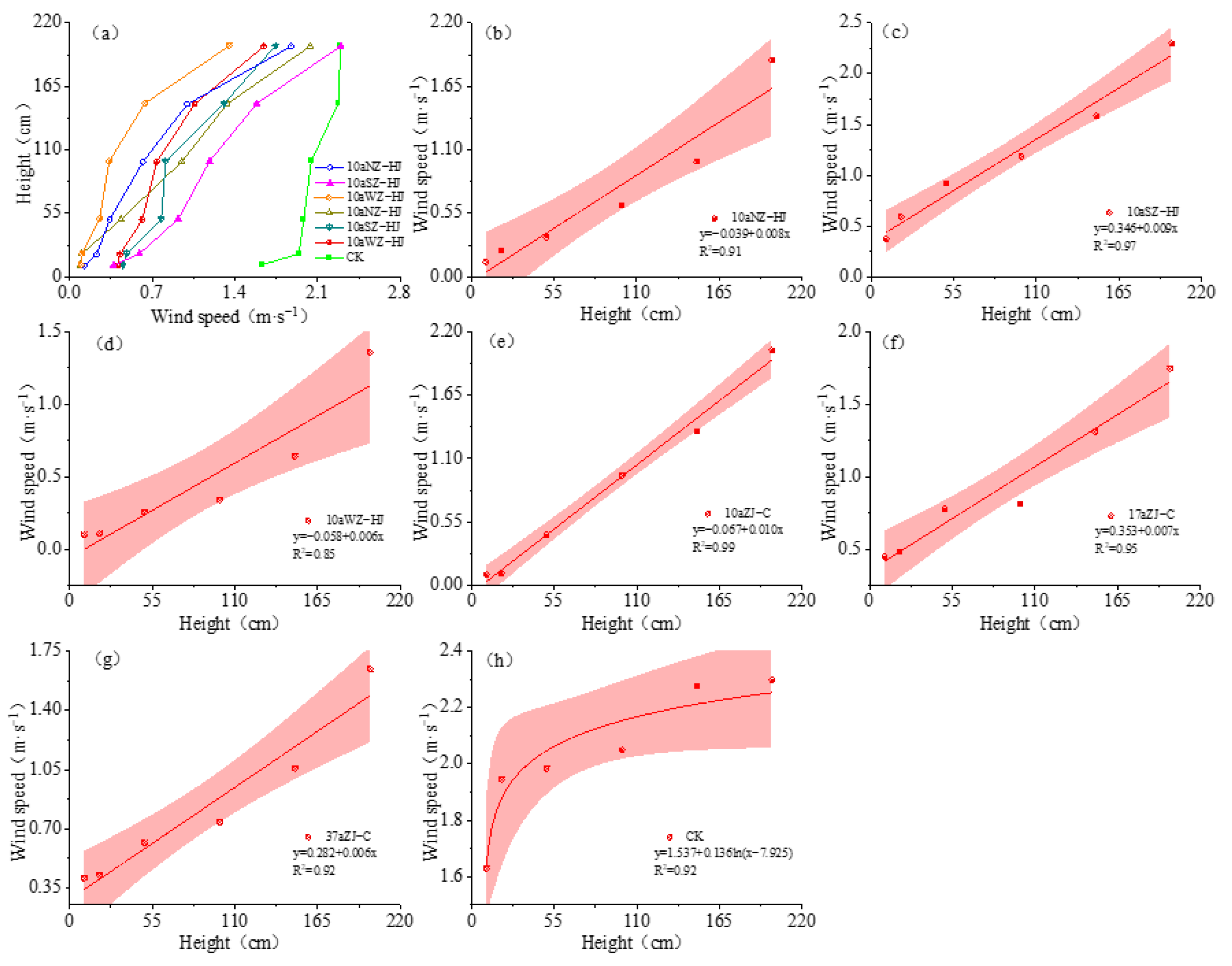
3.1. Characteristics of Wind Speed Profile Variation and Its Windproof Effect in Protective Forests
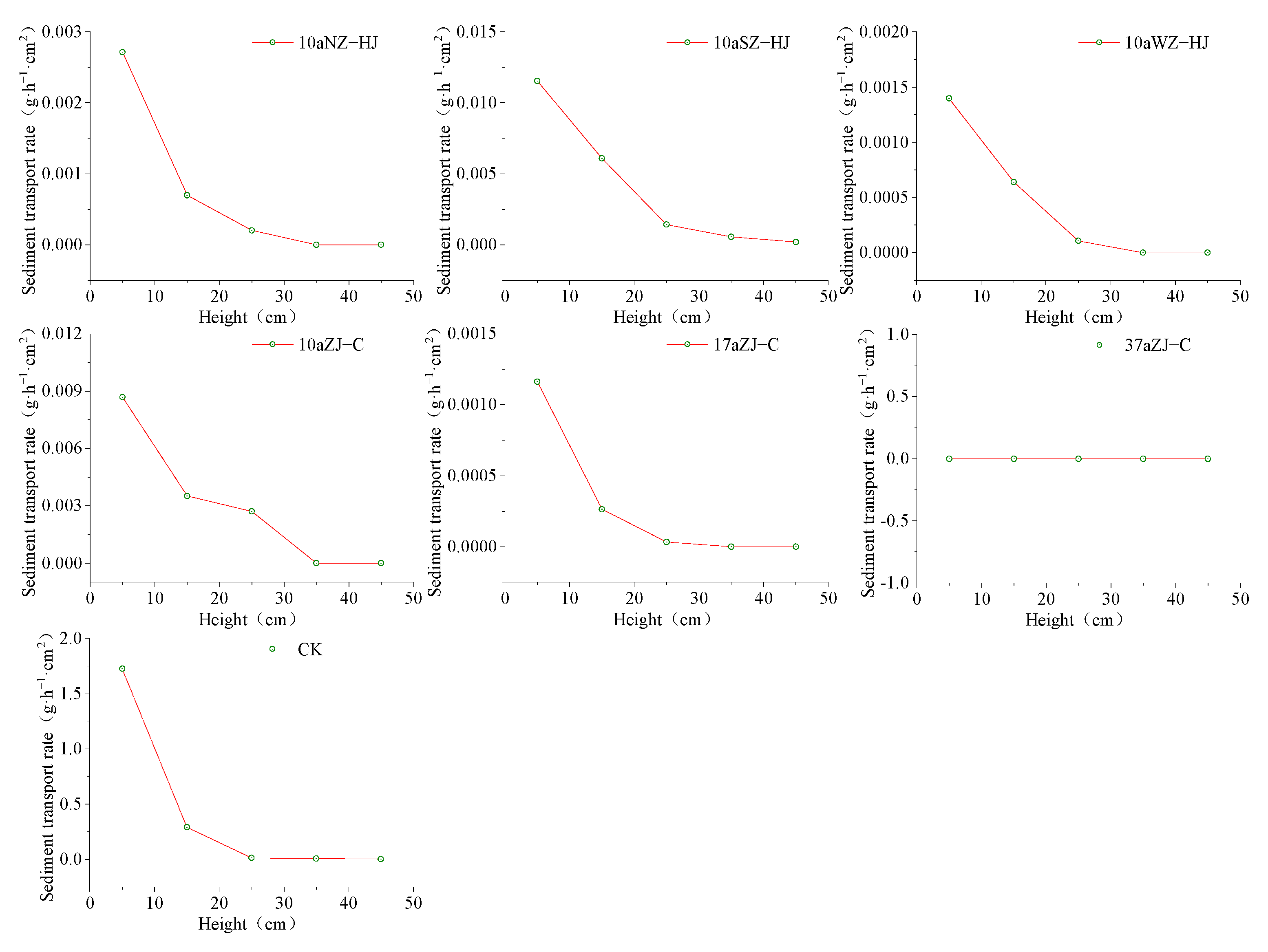
3.2. Sediment Transport Rate and Its Vertical Distribution in the Protective Forest
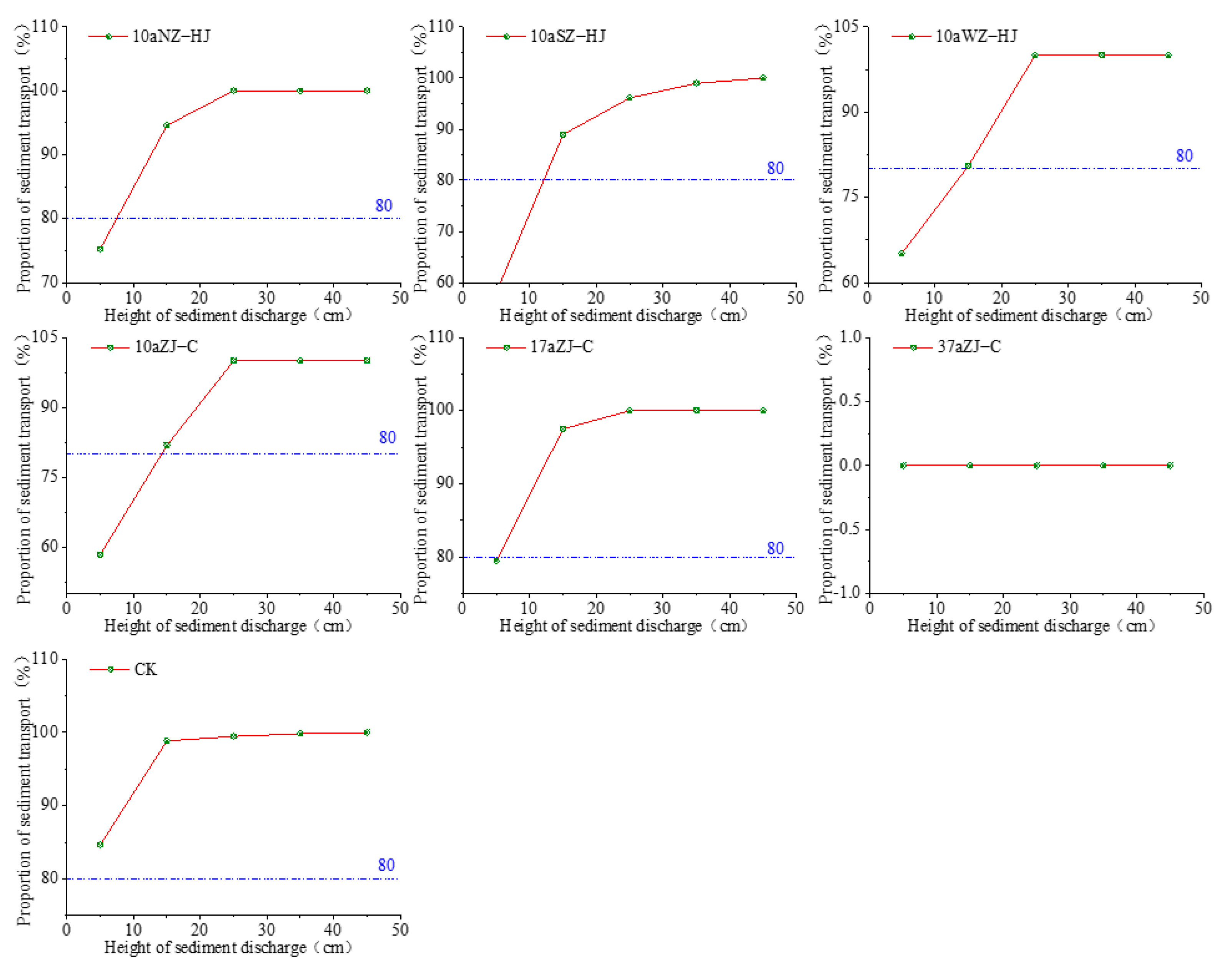
3.3. Cumulative Sand Transport Rate and Sand Blocking Effect of Shelter Forest
3.4. Shelter Forest Surface Erosion Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Wind Protection Efficiency of Different Stand Types
4.2. Redistribution of Different Stand Types on Near-Surface Aeolian Sand Flows
4.3. Morphological Characteristics of Forest Surface in Forests of Different Stand Types
4.4. Areas for Improvement
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akbari, M.; Shalamzari, M.J.; Memarian, H.; Gholami, A. Monitoring desertification processes using ecological indicators and providing management programs in arid regions of Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Abulimiti, M.; Fan, J.L.; Wang, H.F. Ecologic service, economic benefits, and sustainability of the man-made ecosystem in the Taklamakan Desert. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Chan, F.K.S.; Togtokh, C.; Ochir, A.; Davaasuren, D. Research progress of desertification and its prevention in Mongolia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fussell, J.C.; Kelly, F.J. Mechanisms underlying the health effects of desert sand dust. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106790–106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, J.R. Quantifying the impact of cropland wind erosion on air quality: A high-resolution modeling case study of an Arizona dust storm. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 263, 118658–118680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Shi, P.; Han, G.; Liu, L.; Guo, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, G. Desertification control practices in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.T.; Davis, K.M.; Abad, H.; McClung, M.R.; Moran, M.D. Ecosystem services of the Big Bend region of the Chihuahuan Desert. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 27, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torshizi, M.R.; Miri, A.; Shahriari, A.; Dong, Z.; Davidson-Arnott, R. The effectiveness of a multi-row Tamarix windbreak in reducing aeolian erosion and sediment flux, Niatak area, Iran. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110486–110498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.W.; Huang, N.; Zhang, J.; Dun, H.C. Investigations into the design of sand control fence for Gobi buildings. Aeolian Res. 2021, 49, 100662–100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.X.; Gong, W.; Xie, H.; Liu, B.L.; Chen, H.L. Chemical sand stabilization: A review of material, mechanism, and problems. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2015, 4, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirfam, H.; Asadzadeh, F. Stabilizing sand from dried-up lakebeds against wind erosion by accelerating biological soil crust development. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 98, 103189–103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, S.M.; Soroush, A.; Huang, N. Wind erosion control using inoculation of aeolian sand with cyanobacteria. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2104–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Sherman, D.J. Aerodynamics and morphodynamics of sand fences: A review. Aeolian Res. 2015, 17, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Ma, J.; Na, L. Synthesis and swelling behaviors of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(AA-co-AM-co-AMPS)/MMT superabsorbent hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Kimura, R.; Miyawaki, M.; Kinugasa, T. Effects of plants with different shapes and coverage on the blown-sand flux and roughness length examined by wind tunnel experiments. Catena 2021, 197, 104976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, W.W.; Ding, J.Y.; Ferreira, C.S.S. Soil erodibility for water and wind erosion and its relationship to vegetation and soil properties in China’s drylands. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagib, N.A.; Al-Saidi, M. Balancing the benefits from the water–energy–land–food nexus through agroforestry in the Sahel. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhech, A.; Ouahmane, L.; Hafidi, M. Analysis of symbiotic microbial status of Atlantic sand dunes forest and its effects on Acacia gummifera and Retama monosperma (Fabaceae) to be used in reforestation. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danin, A. Plant adaptations in desert dunes. J. Arid. Environ. 1991, 21, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsutdinov, Z.S.; Shamsutdinov, N.Z. Biogeocenotic principles and methods of environmental restoration of desert pasture ecosystems in Central Asia. Arid. Ecosyst. 2012, 2, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; Yu, X.X.; Jia, G.D.; Liu, Z.Q. Determination of optimum vegetation type and layout for soil wind erosion control in desertified land in North China. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 171, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.J.; Wu, B.; Jia, X.H.; Xie, S.B. Wind-proof and sand-fixing effects of Artemisia ordosica with different coverages in the Mu Us Sandy Land, northern China. J. Arid. Land 2022, 14, 877–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.X.; Wang, X.F.; Feng, X.M.; Ma, J.H.; Wang, X.X.; Zhang, X.R.; Zhou, J.T.; Sun, Z.C.; Yao, W.J.; Tu, Y. Exploring the spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem services and influencing factors on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Q.; Shao, Q.Q.; Ning, J.; Liu, G.B.; Liu, S.C.; Niu, L.N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, H.B. Analysis on Ecological Restoration in Different Ecogeographical Divisions of the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2023, 31, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M. The Changing of Important Factors in The Landscape Planning Occur Due to Global Climate Change in Temperature, Rain and Climate Types: A Case Study of Mersin City. Turk. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 8, 2695–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.H.; Jiao, L.M.; Hu, Y.C.; Liu, Z.J. Future climate imposes pressure on vulnerable ecological regions in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.Y.; Wu, Q.B.; Fu, Z.T.; Jiang, G.L.; Liu, Y.L.; Xu, K.M. Aeolian sand accumulation and land desertification over the past 1500 years as revealed by two aeolian dunes in the Beiluhe Basin on interior Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, SW China. Quat. Int. 2022, 613, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.H.; Wu, W.Y.; Zhang, D.S.; Yu, Y. Airflow field around Hippophae rhamnoides in alpine semi-arid desert. Land 2020, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Jia, Y.H.; Tian, S.M. Impacts of artificially planted vegetation on the ecological restoration of movable sand dunes in the Mugetan Desert, northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 32, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jiao, J.Y.; Li, J.J.; Qi, H.K.; Bai, L.C.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.C. Morphometric characteristics and sand intercepting capacity of dominant perennial plants in the Eastern Qaidam Basin: Implication for aeolian erosion control. Catena 2022, 210, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Y.; Zhang, D.S.; Tian, L.H.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhou, X. Ecological responses of Hippophae rhamnoides to wind-sand hazard in alpine sand land. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Wang, K.J.; Gu, J.C.; Liu, Q.G.; Cui, Y. Windbreak effect model of forest belts with different structure. J. Desert Res. 2019, 39, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.X.; Yang, D.F.; Jia, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Feng, L.L.; He, L.X.Z.; Yang, K.Y.; Dai, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Changes in soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks along a chronosequence of Caragana liouanaa plantations in alpine sandy land. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 133, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.Y.; Jia, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.H.; Li, Q.X.; He, L.X.Z.; Dai, J.; Chen, J. Study on spatial distribution characteristics of soil water in typical plantation of Alpine sandy land. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2019, 33, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Jia, Z.Q.; Li, Q.X.; He, L.X.Z.; Yang, K.Y.; Gao, Y. Effects of Natural Rainfall on Soil Respiration of Caragana Plantation in Alpine Sandland. For. Res. 2020, 33, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jia, Z.; He, L.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X. The Allocation and Cycling Characteristics of Main Nutrients for Caragana intermedia With Different Stand Age on Alpine Sandy Land. For. Res. 2023, 36, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y. The quantity and intensity of regional aeolian sand erosion and deposition: The case of shanxi-sha an xi-nei monggol region. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1999, 54, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.L.; Wang, D.J.; Feng, Y.X.; Zhang, H.W.; Chen, H.X.; Zhao, C.Y. Intensity of Wind Erosion and Deposition in Patch Vegetation Area of Desert Oasis Ecotone in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River of China. J. Desert Res. 2016, 36, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.K.; Li, J.R.; Dong, L.; Luo, X.Y.; Han, Z.E.; Wang, R. The wind and sand resistance effect of four vegetation types in Ulan Buhe Desert. J. Dessert Res. 2022, 42, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tian, L.H.; Zhang, D.S.; Wu, W.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhang, P. Study on wind—Prevention and sand—Fixing benefits of different vegetation on the east coast dune of Qinghai Lake. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2018, 32, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Ullah, A.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, F.J.; Graciano, C.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, W.Q.; Ahmed, Z.; Ali, S.; Zhang, Z.H.; et al. Alhagi sparsifolia: An ideal phreatophyte for combating desertification and land degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Qiu, X.N.; Xu, G.X.; Shang, W.; Yang, X.M.; Zhao, P.; Chai, C.G.; Hu, X.K.; Zhang, Y.N.; et al. Wind tunnel study of the effect of planting Haloxylon ammodendron on aeolian sediment transport. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 208, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutto, S.L.; Miri, A.; Zhang, Y.; Danish, A.B.; Cao, Q.Q.; Xin, Z.M.; Xiao, H.J. Experimental study on the effect of four single shrubs on aeolian erosion in a wind tunnel. Catena 2022, 212, 106097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.D.; Chen, Y.P.; Li, Y.Q.; Yan, Z.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Niu, Y.Y.; Gong, X.W. Influence of Vegetation Coverage on Sand Flow Structure and Wind Erosion Yield with Wind Tunnel Experiment as a Case. J. Desert Res. 2019, 39, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Davidson-Arnott, R. The effectiveness of a single Tamarix tree in reducing aeolian erosion in an arid region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 300, 108324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.W.; Liu, C.H.; Chow, H.L.; Lam, M.K.; Lok, Y.H.; Ma, S.W.; Wong, F.L.; Yip, P.Y. Roughness sublayer over vegetation canopy: A wind tunnel study. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 316, 108880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.A.; Nickling, W.G. The protective role of sparse vegetationin wind erosion. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1993, 17, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, N.P.; McCord, S.E.; Edwards, B.L.; Herrick, J.E.; Kachergis, E.; Okin, G.S.; Van Zee, J.W. Vegetation canopy gap size and height: Critical indicators for wind erosion monitoring and management. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 76, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Dragovich, D.; Dong, Z. Wind-borne sand mass flux in vegetated surfaces—Wind tunnel experiments with live plants. Catena 2018, 172, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.M.; Cao, C.Y.; Toshio, O.; Li, X.H.; Li, M. Study on the Effects of Protection against Wind, Sand-fixation and Soil Improvement of Caragana microphylla Plantations in Horqin Sand Land. Arid. Zone Res. 2008, 25, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Dosmanbetov, D.A.; Guo, H.; Xin, Z.M.; Liu, P.F.; Liu, M.H. Wind tunnel experiment on protection benefits of arbor-shrub mixed forest belts in different configurations. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Y.; Zhang, D.S.; Tian, L.H.; Wei, D.S.; Zhao, C.; Jia, F.F. Mechanism and benefit of wind-prevention and sand-fixation of Hippophae rhamnoides forestation in Ketu Sandy Land around Qinghai Lake. Arid. Land Geogr. 2014, 37, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Zhao, W.Z.; Su, P.X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, T.; Ram, R. Ecological effects of desertification control and desertified land reclamation in an oasis–desert ecotone in an arid region: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Hu, G.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; He, Z.B. Shielding effect of oasis-protection systems composed of various forms of wind break on sand fixation in an arid region: A case study in the Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 33, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Li, J.R.; Ma, Y.J.; Shan, L.S.; Li, X.L.; Wei, L.Y. A wind tunnel study of the airflow field and shelter efficiency of mixed windbreaks. Aeolian Res. 2019, 41, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z. Aeolian Geomorphology and Sand Control Engineering; Chinese Science Publishing: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Ning, W.X.; Wang, Z.T. Aeolian Sand Structure at the Brink of Barchans. J. Desert Res. 2019, 39, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Hu, S.R.; Gao, Y.; Sun, X.R.; Liu, B.; Yang, L.M.; Shen, G.L. Shelter Effect of the Forest Shelterbelt System around Jilantai Salt Lake after 35y’s Running. J. Desert Res. 2019, 39, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condit, R.; Ashton, S.P.; Baker, P.; Yamakura, T. Spatial Patterns in the Distribution of Tropical Tree Species. Science 2000, 288, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Liu, C.C.; Zou, X.Y.; Li, H.R.; Kang, L.Q.; Liu, B.; Li, J.F. Wind erosion rate for vegetated soil cover: A prediction model based on surface shear strength. Catena 2020, 187, 104398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, R.J.; Hyde, R. Factors determining desert dune type. Nature 1984, 304, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, A.A.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Poesen, J.; Tsubo, M.; Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Vanmaercke, M.; Broeckx, J.; Yasuda, H.; et al. Land susceptibility to water and wind erosion risks in the East Africa region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesp, P.A.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, H.; Booth, J.L. Wind flow and sedimentation in artificial vegetation: Field and wind tunnel experiments. Geomorphology 2019, 337, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.L.; Lei, J.Q.; Zeng, F.J.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Zaynulla, R. Sand erosion and deposition on different underlying land surfaces in the desertoasis ecotone in Cele, Xinjiang, China. J. Desert Res. 2014, 34, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Ma, Y.; Tan, T.Z. Spatial heterogeneity of soil grain size on Tamarix ramosissima nebkhas and interdune in desert-oasis ecotone. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2015, 37, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.Z.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, H.F.; Xu, J.R.; Yuan, X.X. Wind tunnel simulation on distribution change of erosion and deposition around nebkhas and interdune under different background vegetation coverage. Arid. Zone Res. 2018, 41, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
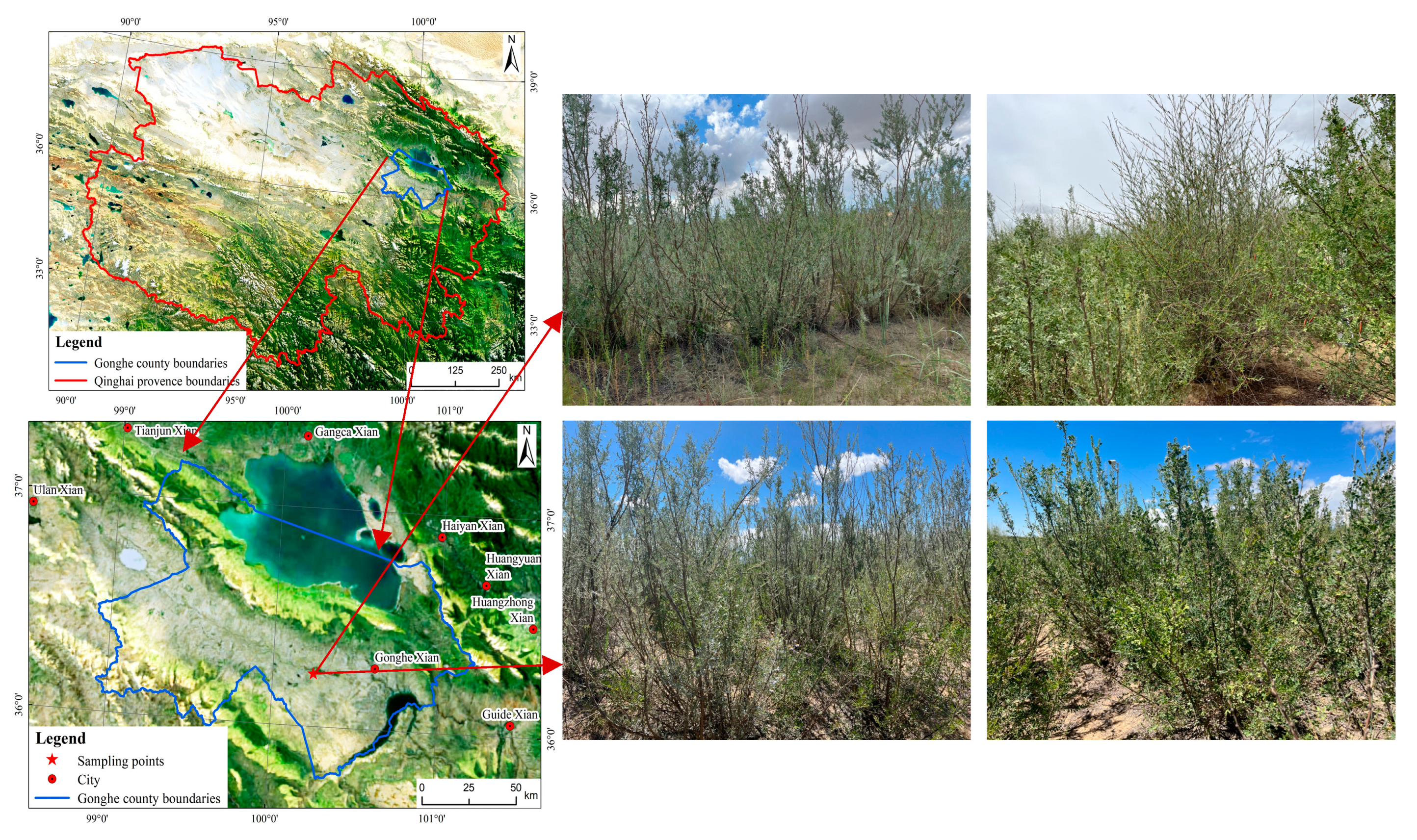




| Type of Protection Forest | Caragana liouana | Caragana korshinskii | Artemisia desertorum | Salix cheilophila | Vegetation Coverage (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Tree Height (cm) | Average Crown Width (cm) | Average Tree Height (cm) | Average Crown Width (cm) | Average Tree Height (cm) | Average Crown Width (cm) | Average Tree Height (cm) | Average Crown Width (cm) | ||
| 10aNZ-HJ | 104.16 | 95.45 | 194.25 | 110.38 | 75 | ||||
| 10aSZ-HJ | 63.69 | 69.65 | 58.19 | 85.64 | 48.8 | ||||
| 10aWZ-HJ | 102.91 | 102.28 | 126.70 | 93.55 | 78.2 | ||||
| 10aZJ-C | 111.49 | 107.94 | 68.8 | ||||||
| 17aZJ-C | 142.92 | 114.46 | 61 | ||||||
| 37aZJ-C | 230.17 | 224.63 | 59 | ||||||
| Type of Protection Forest | Regression Equation of Sediment Transport Rate | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10aNZ-HJ | y = 0.005e−0.135x | 1.00 | <0.001 |
| 10aSZ-HJ | y = 0.018e−0.083x | 0.98 | <0.01 |
| 10aWZ-HJ | y = 0.003e−0.001x | 1.00 | <0.001 |
| 10aZJ-C | y = 0.013e−0.081x | 0.96 | <0.01 |
| 17aZJ-C | y = 0.002e−0.153x | 1.00 | <0.001 |
| CK | y = 4.284e−0.182x | 1.00 | <0.001 |
| Type of Protection Forest | Grouping of Erosion Depth Range (cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −4~−3 | −3~−2 | −2~−1 | −1~0 | 0~1 | 1~2 | 2~3 | |
| 10aNZ-HJ | 0 | 0 | 12.00 | 20.00 | 36.00 | 32.00 | 0 |
| 10aSZ-HJ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16.00 | 44.00 | 36.00 | 4.00 |
| 10aWZ-HJ | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 8.00 | 36.00 | 32.00 | 20.00 |
| 10aZJ-C | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.00 | 44.00 | 32.00 | 0 |
| 17aZJ-C | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.00 | 48.00 | 24.00 | 4.00 |
| 37aZJ-C | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32.00 | 44.00 | 24.00 | 0 |
| CK | 4.00 | 8.00 | 36.00 | 52.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Jia, Z.; Li, Q.; He, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Han, D. Determine the Optimal Vegetation Type for Soil Wind Erosion Prevention and Control in the Alpine Sandy Land of the Gonghe Basin on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Forests 2023, 14, 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14122342
Zhang J, Jia Z, Li Q, He L, Zhao X, Wang L, Han D. Determine the Optimal Vegetation Type for Soil Wind Erosion Prevention and Control in the Alpine Sandy Land of the Gonghe Basin on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Forests. 2023; 14(12):2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14122342
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiapeng, Zhiqing Jia, Qingxue Li, Lingxianzi He, Xuebin Zhao, Long Wang, and Dong Han. 2023. "Determine the Optimal Vegetation Type for Soil Wind Erosion Prevention and Control in the Alpine Sandy Land of the Gonghe Basin on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau" Forests 14, no. 12: 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14122342
APA StyleZhang, J., Jia, Z., Li, Q., He, L., Zhao, X., Wang, L., & Han, D. (2023). Determine the Optimal Vegetation Type for Soil Wind Erosion Prevention and Control in the Alpine Sandy Land of the Gonghe Basin on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Forests, 14(12), 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14122342





