Abstract
The stoichiometric characteristics of C, N, and P in plants result from long-term adaptation to environmental conditions. In this study, we analyzed leaf, branch, and soil C, N, and P stoichiometry in a karst primary forest plant community in China. The results showed that N and P content in leaves was higher than that in branches, while C content in the latter was higher than in leaves. Moreover, the coefficient of the variation in C, N, and P content in branches was greater than that in leaves but there was no significant difference in said coefficients in soil. The values of the C:N and C:P ratios were both branch > leaf > soil, whereas the value of the N:P ratio was leaf > branch > soil. There was also a significant positive correlation between leaf nitrogen (LN), leaf phosphorus (LP), branch nitrogen (BN), and branch phosphorus (BP) concentrations but no significant correlation between leaf carbon (LC), branch carbon (BC), and other element concentrations. We found that leaf stoichiometry was strongly influenced by species diversity, whereas branch stoichiometry was mainly influenced by leaf and species diversity; the environmental factors influencing the stoichiometric characteristics of leaves and branches were mainly altitude, soil pH, and total soil P. Finally, these results are relevant as they are helpful to understand the adaptation mechanisms and eco-geochemical processes in karst forest plants and they can also provide a scientific basis for vegetation restoration and reconstruction in these degraded ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Plant ecological stoichiometry refers to the quantitative characteristics of elements in plant organs, as well as their relationship with environmental factors and ecosystem functions [1,2]. Among these elements, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus are the most basic nutritional units to ensure plant growth and are the main constituents of biological macromolecules, such as sugars, proteins, and genetic material. Moreover, ecological stoichiometry characteristics can help characterize the growth status and nutrient utilization efficiency in plants [3] and changes in these characteristics can also limit plant growth [4]; for instance, C is a structural element and the availability of N and P plays major role in regulating C balance in ecosystems [5]. Moreover, N and P interactions are crucial and, as essential mineral nutrients for plant growth, they are functionally related in plants and often become limiting elements in their growth due to their insufficient supply in nature [6]. Lastly, soil C, N, and P ratios can directly reflect soil fertility and they indirectly reflect a plant’s nutritional status and plant community species composition [7]; therefore, it is of great theoretical and practical significance to study the conversion of C, N, and P cycles between plants and soil to determine the ecological stoichiometry of different types of vegetation.
In forest ecosystems, C, N, and P contents and their ecological stoichiometric ratios in different plant organs are influenced by phylogenetic, genetic, and environmental factors related to species characteristics [8,9,10]; there may be a phylogenetic signal in plant nutrient content [11,12] but other research has shown that the stoichiometric characteristics of C, N, and P in closely related species also change significantly and that environmental factors—such as temperature and precipitation—have a greater impact on stoichiometric characteristics than phylogeny. For example, Tang et al. [13] studied the stoichiometry of stems of terrestrial plants in China at the community level and found that they were affected by annual mean temperature and annual precipitation. Similarly, previous studies found that there is a strong coupling relationship between leaf C, N, and P [14,15,16,17] and that their stoichiometric ratios can reflect a plant’s nutrient utilization strategy: for instance, the C:N and C:P ratios reflect a plant’s growth rate, and they are related to the utilization efficiency of N and P [18,19,20]. At the same time, the N:P ratio of plant leaves can be an effective indicator used to judge a plant’s health and growth status, thereby facilitating a clear understanding of the adaptability of different plants to environments and stress [21,22]. Currently, studies on plant ecological stoichiometry still focus on leaves. Although, there are many reports on the stoichiometric characteristics of roots, there are few studies about the stoichiometric characteristics of branches and reproductive organs [23].
Our study was conducted at a karst primary forest plant community in southwestern China, which extends for approximately 550,000 km2 and is the largest contiguous exposed carbonate area in the world. Owing to the uniqueness of karst landforms and calcareous soils, the representative vegetation in this area shows unique physiological and ecological characteristics, such as calcium liking, desert resistance, and petrogenesis [24]. Moreover, because of the particularity of the karst forest habitat, the complicacy of the structure, system vulnerability, plant growth, development, and adaptation mechanisms are different from those in normal landforms under the same climate conditions. For instance, Zeng et al. [25] explored the ecological stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in the plant–litter–soil continuum of six forest types in karst areas and found that plants in these areas mainly absorbed nutrients from the soil rather than reabsorbed nutrients to meet their growth needs. Furthermore, Yu et al. and Wang et al. [1,26] contrasted the stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in plants and soils of different forest types in karst areas and the study showed that there were significant differences in the ecological stoichiometric ratios of vegetation types in different karst succession stages and that the ecological stoichiometric ratios were limited by N in the early succession stage and P in the late succession stage.
Although scholars have carried out many ecological stoichiometric ratio studies in karst areas [27,28], there is still a lack of studies on the stoichiometry of nutrients in different plant organs in karst ecosystems. Therefore, the study of element content characteristics and stoichiometric ratios of different plant organs in karst areas is helpful for understanding the adaptation mechanisms and eco-geochemical processes of these plants in this ecosystem type [29]. Thus, our study determined the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometric ratio of the leaves and branches of 101 plant species and it aimed to: (1) analyze, through chemical metrology, the “leaf–branch–soil” C, N, and P content to determine the ecological characteristics of the studied karst forest and (2) identify some of the key factors affecting the C, N, and P ecological stoichiometry of leaves and branches in this fragile region. Lastly, we believe that our study will contribute to the understanding of adaptation mechanisms and eco-geochemical processes in karst forest plants, and that it can provide scientific guidelines for the restoration and reconstruction of these fragile and degraded ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Site
The research site was located in Bannan and Xiabai Dan (107°51′–108°43′ E, 24°44′–25°33′ N, 400–600 m above sea level) in the town of Chuanshan, Huanjiang County, west of Guangxi Province, China, which is the location of the Mulun National Nature Reserve. On the basis of the records of the Huanjiang County weather station from 1961 to 2020, the annual average temperature is 15.7 °C. The average annual precipitation at the site was 1389 mm and the average annual sunshine time was 4422 during these years. The mother rock here is limestone and brown calcareous soil is the dominant substrate. Moreover, karsts are mainly distributed southwest of the county and the region is characterized as a subtropical mixed evergreen deciduous broadleaf forest with 6754 living woody plant individuals belonging to 34 families, 87 genera, and 109 species, dominated by Itoa orientalis Hemsl., Cornus macrophylla Wall., and Bridelia tomentosa Blume [30].
2.2. Field Survey
From July to September 2021, 35 quadrants (20 m × 20 m) were set up according to the different terrains and wood plants and each quadrant was further divided into 16 sub-quadrants (5 m × 5 m). In addition, based on the Center for Tropic Forest Sciences’ (CTFS) standard field protocol, we determined the diameter at breast height (DBH) and crown width of all woody plants with a DBH ≥ 1 cm in the quadrant, and then the species, quantity, height, and growth status of woody plants were recorded.
Additionally, a global positioning system (GPS) (E640+MobileMapper) was used to obtain the geographic information, such as the longitude, latitude, and altitude of the inner center of the sample square, and then to investigate and record its altitude (Alt), aspect (Asp), slope (Slo), and rock exposure (Roc). According to the species survey data in each plot, species with more than three individuals were selected for sampling. In total, 101 tree species were selected for data collection, ensuring that four intact branches and 20 to 30 leaves were taken from each tree. In addition, five soil samples from each plot were collected from the surface (0–20 cm) according to the plum-flower pattern and then fully mixed to form the sample from which we measured the amount of nutrients [31].
2.3. Analyses of Elemental Concentrations
Total carbon and nitrogen concentrations (g·kg−1) in leaf and branch were measured by a multi N/C 2100 automatic analyzer (Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany), whereas phosphorus concentration (g·kg−1) was measured by molybdenum-antimony colorimetric methods after digestion using a microwave digestion system (μPREP-A, MLS, Leutkirch, Germany). Soil pH was determined in a 1:5 soil-water slurry and measured using a combination glass electrode; soil organic matter was determined by the chloride potassium dichromate volumetric-external heating method; soil total nitrogen was determined using the semi-micro Kjeldahl determination of nitrogen method; soil total phosphorus was determined using sodium hydroxide (NaOH) fusion-ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry; soil total potassium was determined by NaOH fusion-flame spectrophotometry; soil available nitrogen was determined using the diffusion–absorption method; soil available phosphorus was determined by NaHCO3 extraction-ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry; and soil available potassium was determined by (NH4)2CO3 extraction-flame spectrophotometry [32].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The coefficient of variation (CV = (standard deviation SD/mean M) × 100%) was used to calculate C, N, and P concentrations and the stoichiometric ratio variations. Furthermore, a Pearson correlation analysis was used to test the correlation between leaf, branch, and soil CNP ratios and species diversity indices and a Student’s t-test was used to analyze the correlation. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used for the dimension reduction of soil properties and the PCA score coefficients were used for a regression analysis of leaf and branch C, N, and P stoichiometric ratios.
At the species diversity level (SD), we applied the Shannon–Wiener, Simpson, Pielou, and richness indexes and, at the topographic level (Top), the altitude, slope, aspect, and rock exposure rate were selected as indices. Furthermore, at the soil property level (SPP), soil pH, available N, P, and K, as well as total N, P, and K, and organic matter were selected as indices. The community-level weighted means of trait values (CWM), the average value of functional traits in the community, was obtained by weighted average based on relative abundance. Finally, the impact factors of leaf and branch C, N, and P concentrations and stoichiometric ratios were analyzed using a random forest model and structural equation models. All statistical analyses and mapping were computed using R 4.1.1 (FD [33], vegan [34], randomForest [35], and lavaan packages [36]) and Origin 2021.
3. Results
3.1. Leaf-Branch-Soil Elemental C, N, and P Characteristics
The general characteristics of leaf-branch-soil elemental C, N, and P in the karst plant community are shown in Table 1. Leaf N and P concentrations were higher than those in branches and soil P concentrations were slightly higher than those in branches and leaves. The overall coefficient of variation ranged from 4.62% to 128.06% and the coefficients for branch C, N, and P concentrations were larger than those in leaves. In contrast, the coefficient of variation for soil C, N, and P concentrations showed little difference. The order of C:N and C:P ratios was branch > leaf > soil, whereas the order of the N:P ratio was leaf > branch > soil. Meanwhile, the variation coefficients of branch C:N, C:P, and N:P ratios were also larger than those of the leaves and soil.

Table 1.
Contents and stoichiometric ratios of C, N, and P in leaf, branch, and soil. Statistics of leaf and branch stoichiometric traits of the studied karst primary forest species. LC, leaf carbon concentration (g·kg−1); LN, leaf nitrogen concentration (g·kg−1); LP, leaf phosphorus concentration (g·kg−1); BC, branch carbon concentration (g·kg−1); BN, branch nitrogen concentration (g·kg−1); BP, branch phosphorus concentration (g·kg−1); SC, soil carbon concentration (g·kg−1); SN, soil nitrogen concentration (g·kg−1); SP, soil phosphorus concentration (g·kg−1); LC:N, ratio of leaf carbon to nitrogen concentration in leaf; LC:P, ratio of leaf carbon to phosphorus concentration in leaf; LN:P, ratio of leaf nitrogen to phosphorus concentration in leaf. BC:N, ratio of leaf carbon to nitrogen concentration in branch; BC:P, ratio of leaf carbon to phosphorus concentration in branch; BN:P, ratio of leaf nitrogen to phosphorus concentration in branch; SC:N, ratio of leaf carbon to nitrogen concentration in soil; SC:P, ratio of leaf carbon to phosphorus concentration in soil; SN:P, ratio of leaf nitrogen to phosphorus concentration in soil.
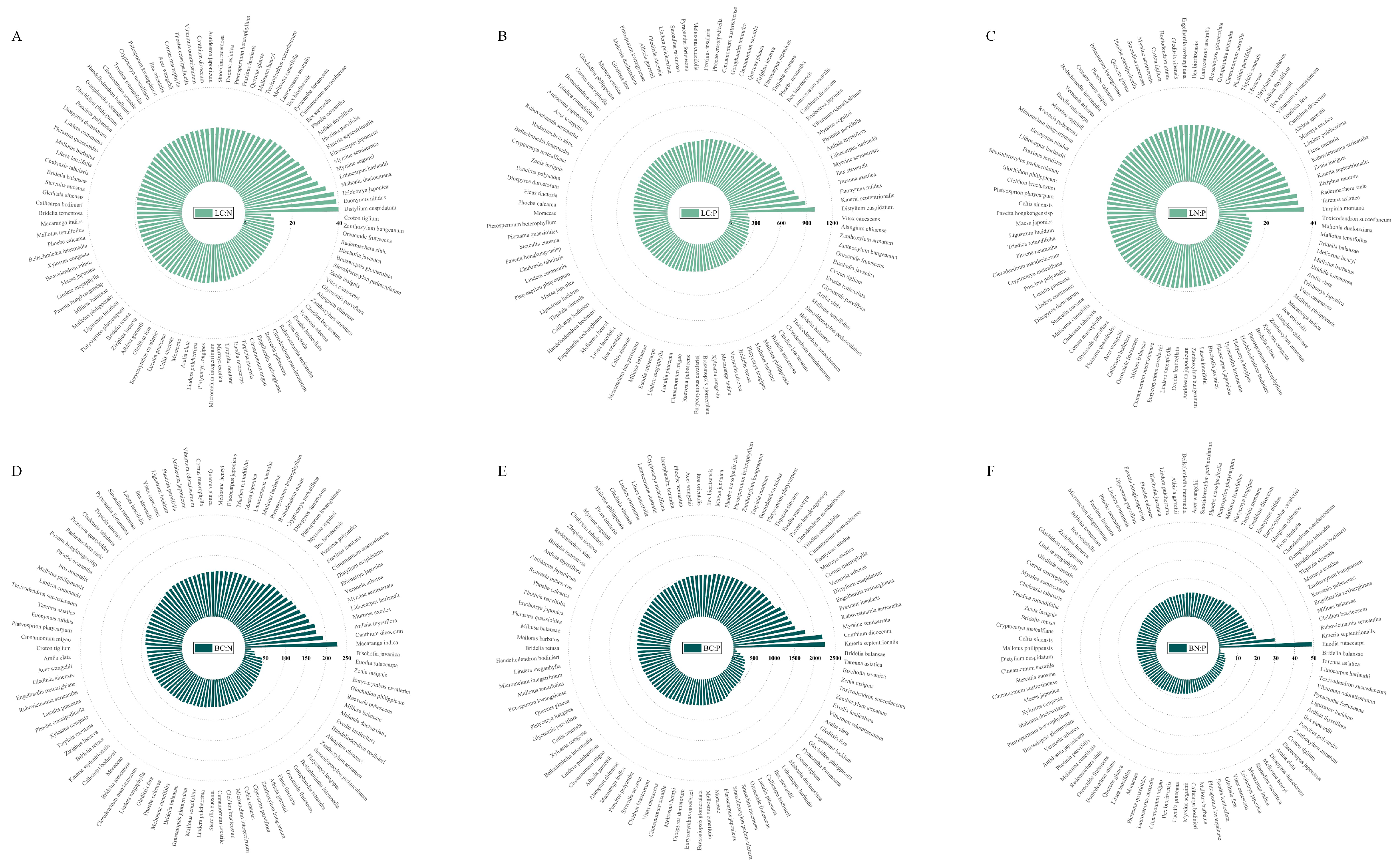
At the species level, the three species with the highest leaf C:N ratio were Distylium cuspidatum, Euonymus nitidus, and Eriobotrya japonica; for branch C:N ratio, Macaranga indica, Canthium dicoccum, and Ardisia thyrsiflora; for leaf C:P ratio, D. cuspidatum, Kmeria septentrionalis, and Euonymus nitidus; for branch C:P ratio, K. septentrionalis, C. dicoccum, and Myrsine semiserrata; for leaf N:P ratio Turpinia montana, Tarenna asiatica, and Radermachera sinic; and for branch N:P ratio, Euodia rutaecarpa, K. septentrionalis, and Rubovietnamia sericantha (Figure 1).
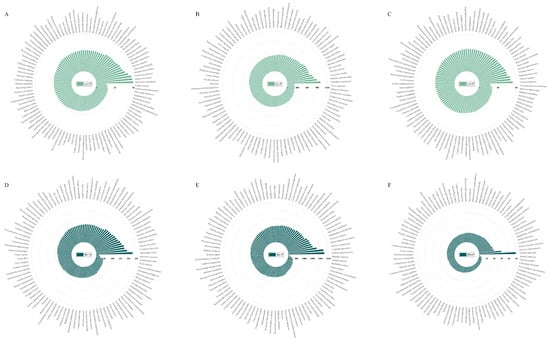
Figure 1.
The stoichiometric ratios of C:N (A,D), C:P (B,E), and N:P (C,F) in leaf and branch of different species. The abbreviations are shown in Table 1. The axes represent the values of stoichiometric ratios.
3.2. Correlations of C, N, and P Concentrations and Ratios among Leaf, Branch, and Soil
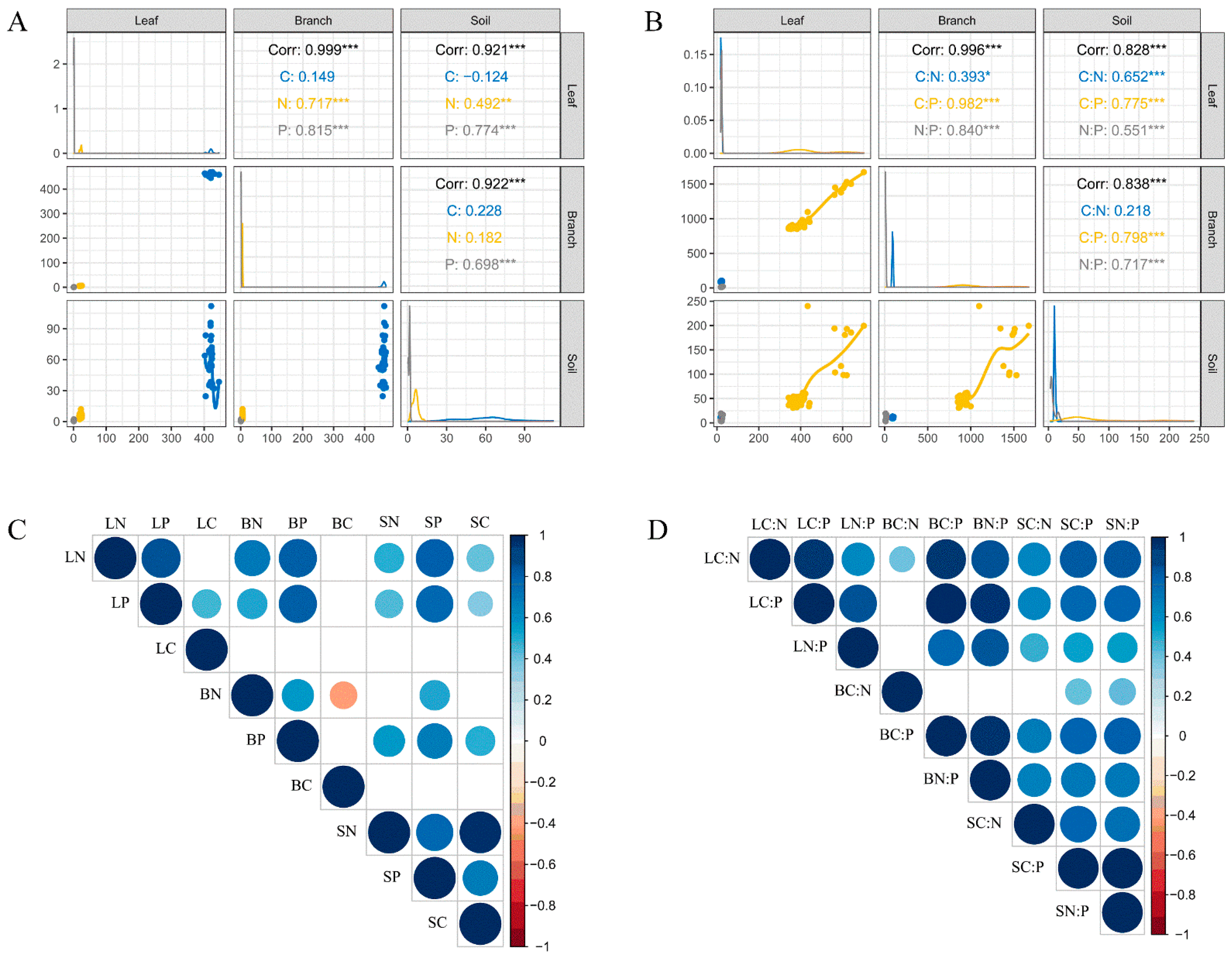
As shown in Figure 2C,D, there was a strong coupling relationship between the leaf and branch. Leaf nitrogen (LN) was significantly positively correlated with leaf phosphorus (LP), branch nitrogen (BN), and branch phosphorus (BP) (p < 0.001) but not with leaf carbon (LC) and branch carbon (BC) (p > 0.05). LP was also significantly positively correlated with BP (p < 0.001) with no significant correlations between LC and LP, BC, and BN (p < 0.01), whereas there were no significant correlations between LC, BC, and other chemical elements.
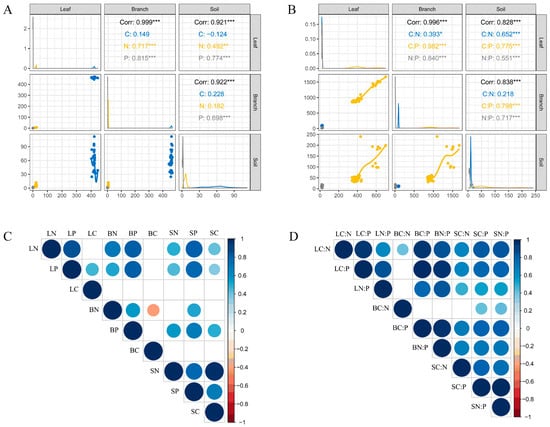
Figure 2.
Correlations of C, N, and P stoichiometric characteristics in plant leaf, branch, and soil. Correlations between leaf, branch, and soil (A,B), C, N, and P stoichiometry (C,D). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Lastly, as shown in Figure 2A,B, there were significant or extremely significant positive correlations between LC:N and BC:N (p < 0.01), LC:P and BC:P (p < 0.001), as well as LN:P and BN:P (p < 0.001). Moreover, there was no significant correlation between BC:N and the other stoichiometric ratios, except for BC:N and LC:N. Leaf C:N was positively correlated with soil C:N and LN, whereas BN was positively correlated with SN.
3.3. Relationship between Leaf-Branch C:N:P Ratios and Environmental Factors
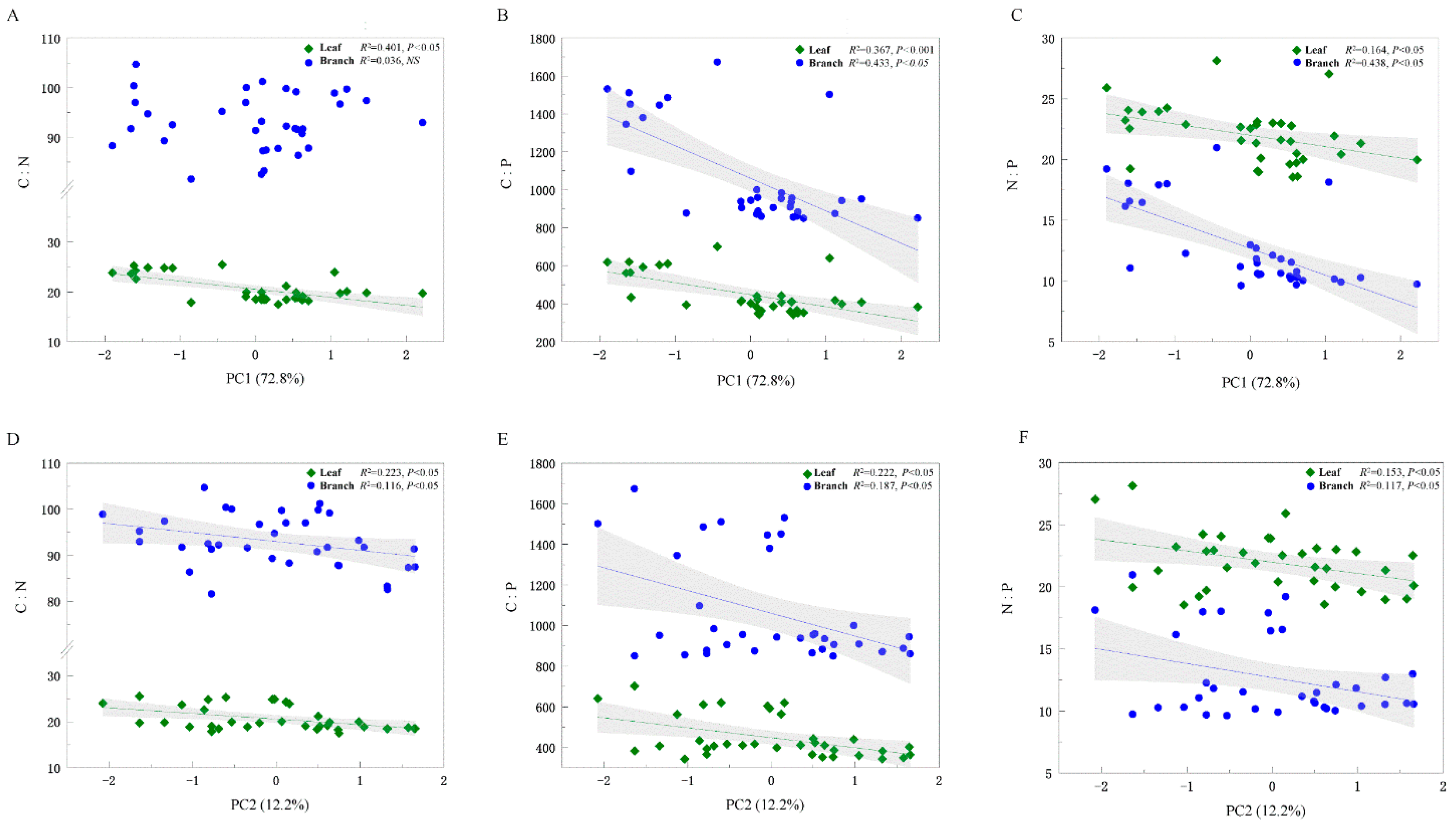
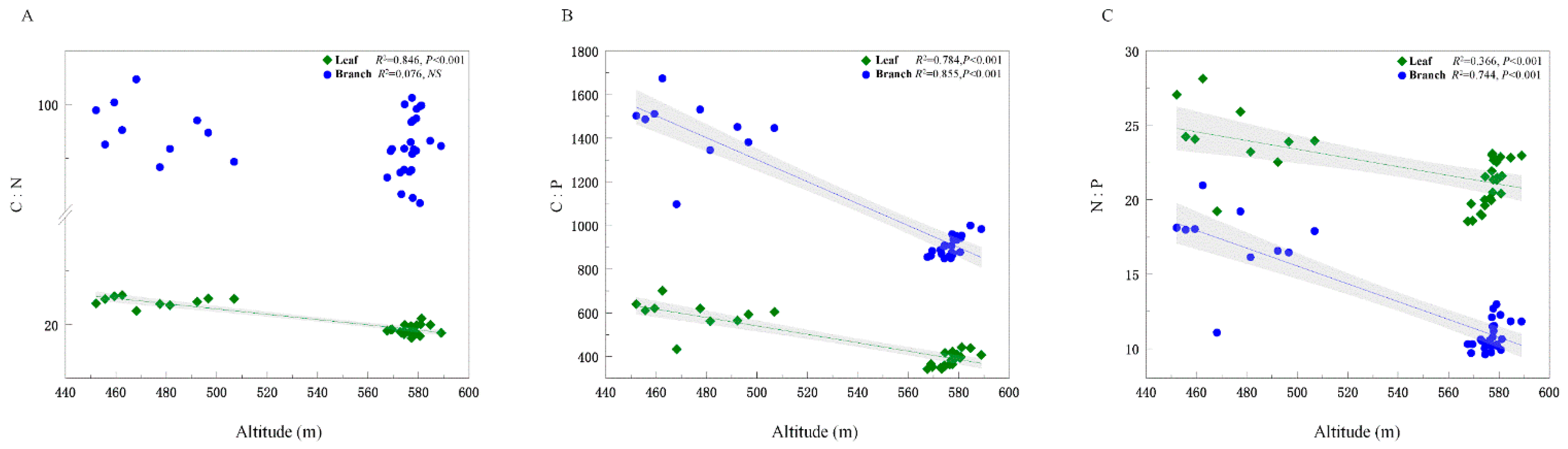
To reduce the effect of multicollinearity among the explanatory variables and the number of variables, a principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted on eight soil property variables. The PC1 (explaining 72.8% of the total variability) and PC2 axis scores (explaining 12.2% of the total variability) were included in the subsequent analysis (Table S1). The leaf C:N ratio was negative for PC1 (R2 = 0.433, p < 0.05) but there was no relationship with the branch C:N ratio (p > 0.05) (Figure 3A,D). Moreover, the explanation rate of PC1 to branch C:P (R2 = 0.433, p < 0.05) and N:P (R2 = 0.438, p < 0.05) ratios was higher than that of leaves (R2 = 0.367, p < 0.05; R2 = 0.164, p < 0.05) (Figure 3B,C); however, the explanation rate for PC2 showed an opposite trend (leaf C:N:P > branch C:N:P) (Figure 3D–F). Finally, leaf C:N, C:P, and N:P ratios, as well as branch C:P and N:P ratios, tended to decrease from low to high altitudes (Figure 4), although on scales ranging from 440 to 600 m above sea level, we found that branch C:N was not significantly corelated to altitude (Figure 4A).
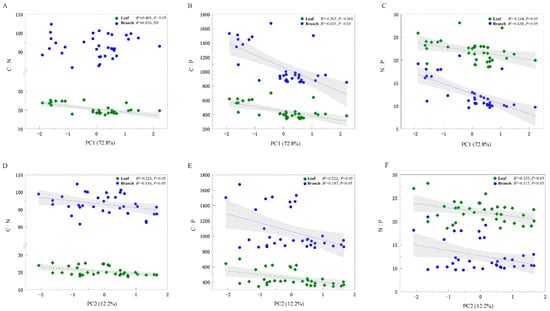
Figure 3.
C, N, and P stoichiometric ratios related to soil properties’ PCA scores. C:N, ratio of carbon to nitrogen concentration (A,D); C:P, ratio of carbon to phosphorus concentration (B,E); N:P, ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus concentration (C,F).
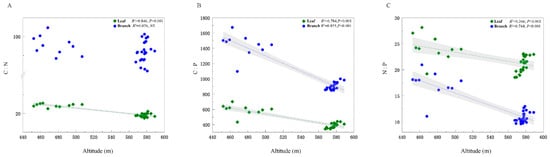
Figure 4.
C, N, and P stoichiometric ratios related to altitude. C:N, ratio of carbon to nitrogen concentration (A); C:P, ratio of carbon to phosphorus concentration (B); N:P, ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus concentration (C). The abbreviations are shown in Figure 3.
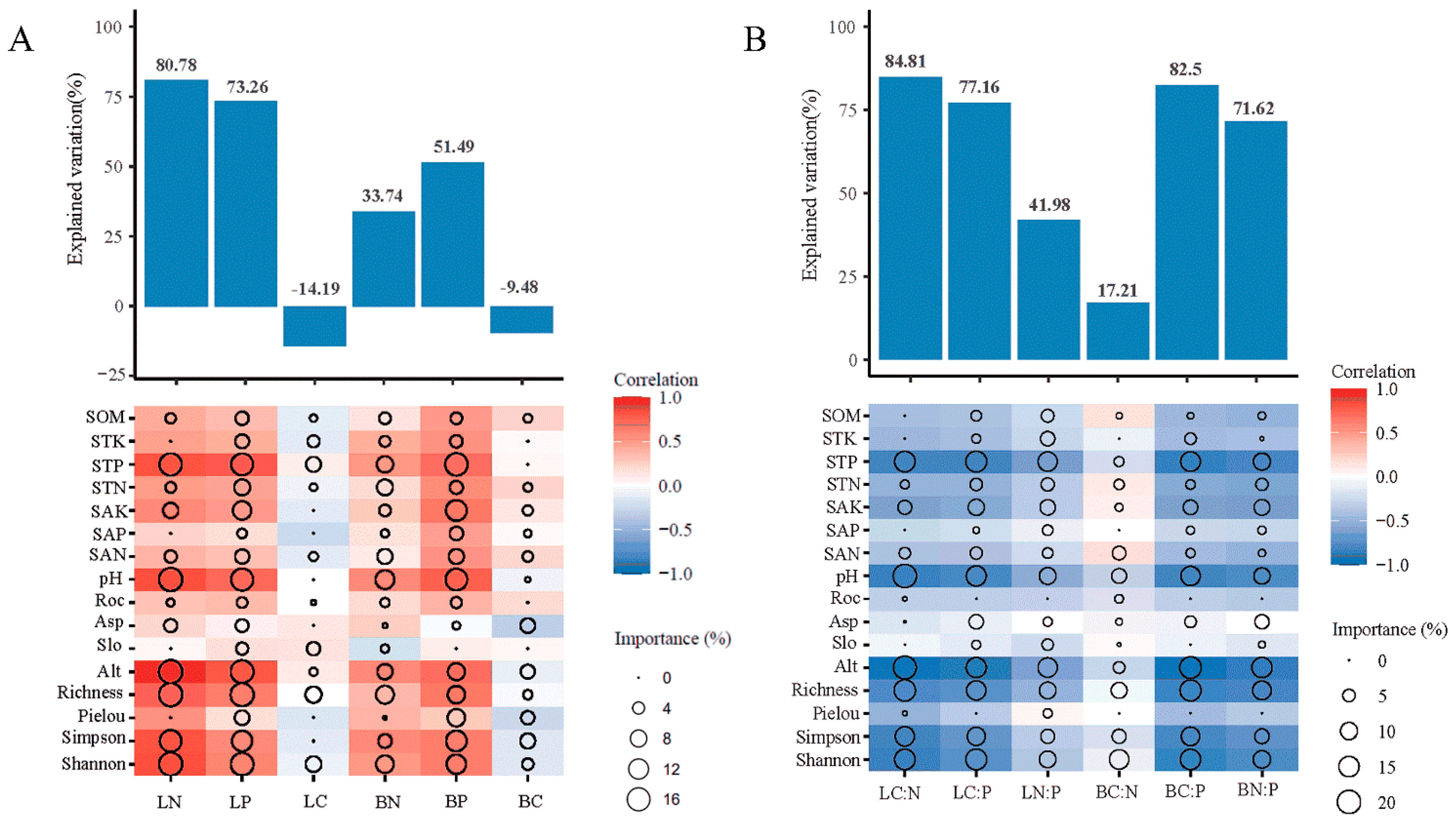
3.4. Influencing Factors of Leaf-Branch Elemental CNP and Its Ecological Stoichiometric Ratio
The importance of different factors on the elemental CNP was determined based on the random forest model. Species diversity, topography, and soil properties had higher explained rates of the leaf C:N ratio (84.81%) than branch C:N (17.21%) and higher explaining rates of branch C:P and N:P ratios (82.5% and 41.98%) than in leaves (77.16% and 41.98%, respectively) (Figure 5A). Elemental C, N, and P ratios, except the branch C:N ratio, were predominantly affected by Alt, soil pH, STP, richness, and Shannon. In addition, the leaf C:N ratio was mainly affected by soil pH (%IncMSE = 20.03%), Alt (%IncMSE = 19.31%), richness (%IncMSE = 16.62%), STP (%IncMSE = 15.20%), Shannon (%IncMSE = 15.17%), and Simpson (%IncMSE = 12.85%). Branch C:N was affected by Shannon index (%IncMSE = 13.63%). Leaf and branch C:P ratios were predominantly affected by soil pH (%IncMSE = 14.38%; %IncMSE = 13.32%), Alt (%IncMSE = 14.49%; %IncMSE = 16.87%), richness (%IncMSE = 13.33%; %IncMSE = 15.97%), STP (%IncMSE = 15.78%; %IncMSE = 13.72%), and Shannon (%IncMSE = 15.68%; %IncMSE = 14.86%). Moreover, the leaf N:P ratio was less affected by species diversity than the branch N:P ratio; however, it was more affected by topography and soil property factors. The leaf and branch C concentrations were less affected by species diversity, topography, and soil properties (Figure 5B). For instance, the leaf C concentration was mainly affected by richness (%IncMSE = 7.66%) and Shannon (%IncMSE = 7.28%). The branch C concentration was mainly affected by Simpson (%IncMSE = 6.46%) and Asp (%IncMSE = 6.25%).
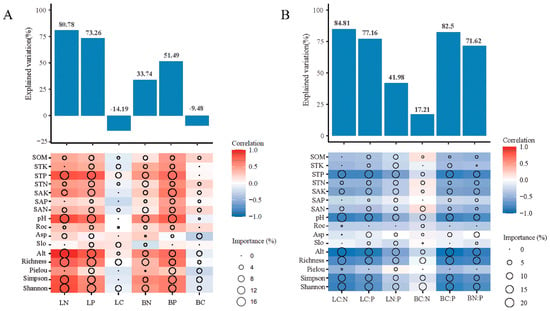
Figure 5.
Influencing factors of leaf and branch stoichiometry was analyzed using a random forest model. The dependent variables are the concentrations (A) and ratios (B) of C, N, and P. The bar graph shows the explained variation for each factor. Circles indicate the importance of independent variables.
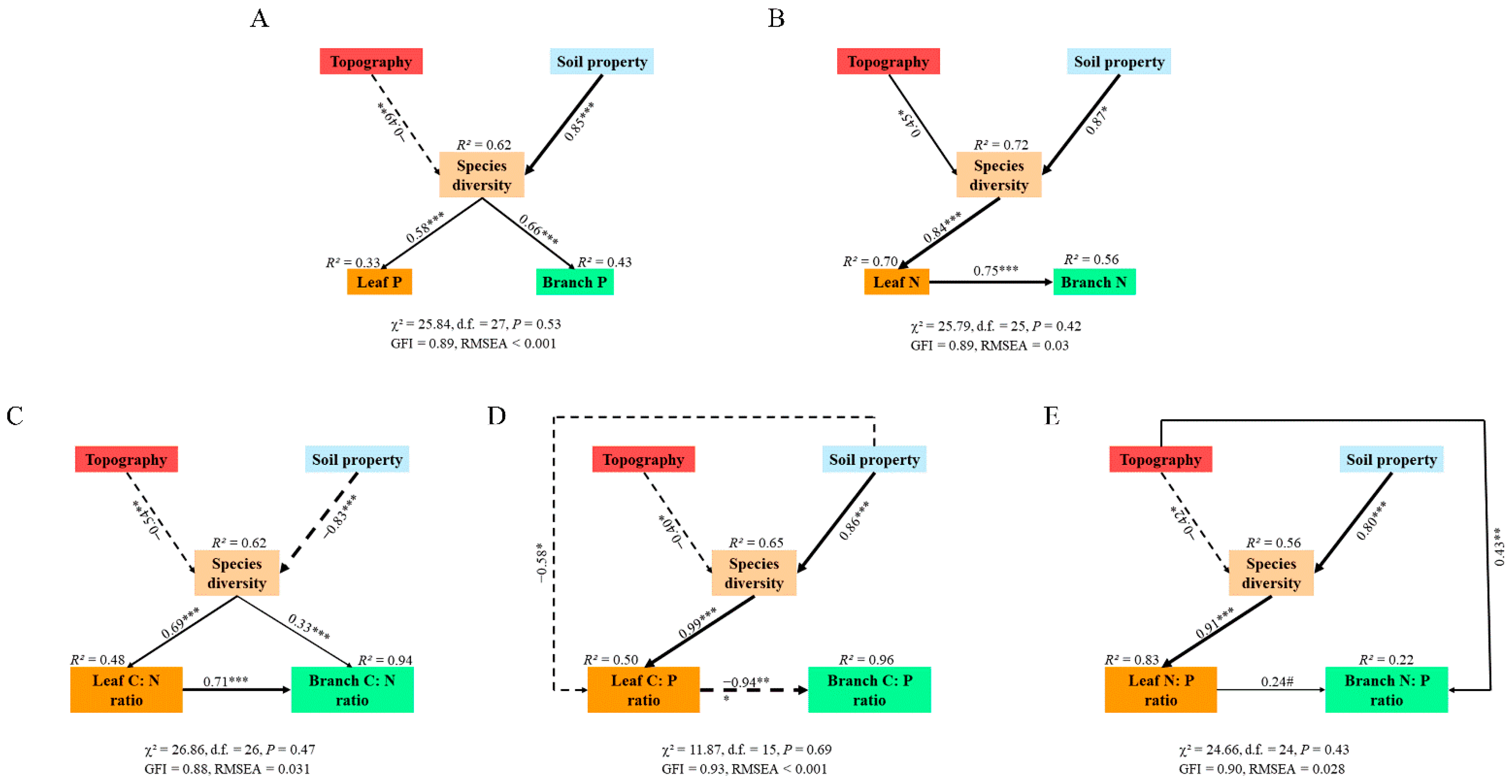
Soil properties, topography, and species diversity simultaneously included in the models predicted 48% and 94% variability in LC:N and BC:N, respectively (Figure 6C). Species diversity showed strong direct effects (0.69 and 0.33) and soil properties and topography showed weak indirect (−0.54 and −0.83) effects on LC:N and BC:N, respectively. The direct effect of LC:N on BC:N was the largest (0.71), while the indirect effects of topography and soil properties were −0.44 and −0.68, respectively. The path equation is as follows: ZLC:N = −0.37ZTop − 0.57ZSPP + 0.69ZSD(R2 = 0.48), ZBC:N = −0.44ZTop − 0.68ZSPP + 0.82ZSD + 0.71ZLC:N(R2 = 0.94). Similarly, other path equations can be obtained as follows: ZLC:P = −0.40ZTop + 0.27ZSPP + 0.99ZSD(R2 = 0.50), ZBC:P = 0.37ZTop−0.26ZSPP − 0.93ZSD – 0.94ZLC:P(R2 = 0.96); ZLN:P = −0.38ZTop + 0.73ZSPP + 0.91ZSD(R2 = 0.83), ZBN:P = 0.34ZTop + 0.17ZSPP + 0.22ZSD + 0.24ZLN:P(R2 = 0.22); ZLN = 0.38ZTop + 0.73ZSPP + 0.84ZSD(R2 = 0.70), ZBN = 0.28ZTop + 0.55ZSPP + 0.63ZSD + 0.75ZLN(R2 = 0.56); ZLP = −0.28ZTop + 0.49ZSP + 0.58ZSD(R2 = 0.33), ZBP = −0.32ZTop + 0.56ZSP + 0.66ZSD(R2 = 0.43).
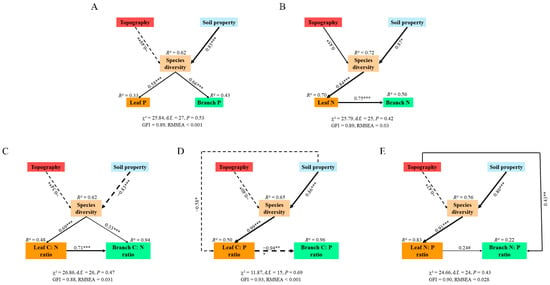
Figure 6.
The strength of direct and indirect effects (standardized path coefficients) of topography, soil property, and species diversity on (A) leaf and branch P, (B) leaf and branch N, (C) leaf and branch C:N ratio, (D) leaf and branch C:P ratio, and (E) leaf and branch N:P ratio. Solid arrows indicate a positive relationship, and dotted arrows indicate a negative relationship. The numbers adjacent to the arrows are the standardized path coefficients and the arrow width indicates the strength of the standardized path coefficient. R2 values represent the proportion of the variance explained for each endogenous variable. χ2, chi-squared values; d.f., degree of freedom; GFI, goodness-of-fit index; RMSEA, the root mean square error of approximation. # p < 0.10, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
4.1. C, N, and P Stoichiometric Characteristics of Leaf–Branch–Soil Continuum in the Karst Primary Forest
Structural C and N and P, the limiting elements, interact to regulate plant growth. In addition, soil, the main source of nutrients, regulates plant growth [37]. Our findings show that the average C content in the leaves of karst primary forest plants is 418.23 g·kg−1, which is lower than that of leaves in the karst ecosystem of southwestern China (449.95 mg·g−1) [38] and the average C content of leaves of different forest types in karst peak cluster depression (496.15 g·kg−1) [39]. This may be because of the sampling time used in this study: in September, C in deciduous tree species was returned to the soil in the form of litter and the content of C in leaves was low during this time. We found that the leaf N content of the karst region was higher than that of the global [13] and Chinese terrestrial vegetation [40] (22.93, 18.74, and 20.2 mg·g−1, respectively), whereas the opposite was true for the P content (1.15, 1.21, and 1.46 mg·g−1, respectively). The results show that the leaf N content of the karst region was higher than that of the global and Chinese terrestrial vegetation, whereas the opposite was true for the P content; this may be due to seasonal drought and soil nutrient shortages in the study area and increasing leaf N input may be an effective adaptation strategy under conditions of water and nutrient limitation. Moreover, increasing leaf N content can increase the amount of photosynthetic enzymes in leaves and further improve their photosynthetic rate [41].
Furthermore, the content of vegetative elements in plant leaves is closely related to their structure and growth rate and it varies greatly across different growth stages. Optimal plant growth requires a certain N:P ratio; when this value in plant leaves is <14, plant growth is limited by N; when N:P is >16, it is limited by P; when 14 < N:P < 16, it is limited by either N or P or is lacking both N and P [42]. In this study, the average leaf N:P of plants was 21.41, which is higher than the reported average leaf N:P for land plants in China (14.4) [40] and worldwide (13.8) [6], indicating that plant growth in karst regions is limited by P, which is consistent with the conclusions of Zeng et al. [25]. Moreover, because of the different nutrient acquisition strategies of different species, the leaf N:P ratio of a few species cannot be used to evaluate the nutrient limitation of the whole plant community; therefore, it is necessary to further study this species and explore the nutrient limitations of karst rock desertification ecosystems (Figure S1).
In this study, the C, N, and P contents in the branches of karst primary forest trees were lower than those of subtropical monsoon evergreen trees [43]. This may be because nutrient elements in plants mainly originate from the soil; moreover, their content is closely related to soil nutrient status [1,44]. In addition, plants in karst regions have developed adaptive strategies to invest more resources into the leaves of plants growing in degraded habitats. Currently, there are relatively few studies on the CNP characteristics of plant branches, which are limited to some plant groups and certain regions. Furthermore, there are few studies on the C, N, and P stoichiometry of branches in karst regions, so we should strengthen the research in this field.
Soil C content in karst primary forests was higher than that in non-karst forests, which is consistent with the results of another karst forest soil study [32]. Although the C content of karst forest soil is high, the C reserve of karst forest soil is still lower than that of non-karst forest soil because of the shallow soil and low total soil amount and the N and P reserves are much lower than those of non-karst forest soil [1,43]. The soil C:N ratio is considered a predictor of organic matter decomposition in forests [45]. In this study, the average soil C:N ratio was 10.07, which was lower than the Chinese average (14.4) and global average (12.40) [16,46]. A low soil C:N ratio often indicates rapid decomposition of SOM and relatively high soil N content [47,48], indicating that the decomposition of organic matter in karst soil is faster than the average level. This difference may be caused by the unique geological conditions of limestone soil in karst regions.
4.2. Correlation Analysis of C, N, and P in Different Organs of Karst Primary Forest
From the perspective of ecology and evolution, nutrient allocation patterns among different plant organs are closely related to their corresponding functional traits [49]. In this study, there was a close coupling relationship between the C, N, and P contents and their stoichiometric ratios in different organs (Figure 2A,B). The C content of leaves was lower than that of branches, mainly because of the preferential allocation of C assimilated by leaves to branches as a physiological adjustment. Meanwhile, leaf N and P were significantly positively correlated with branch N and P [50], indicating that their nutrient utilization efficiency was closely related, which may be because plant growth requires a large amount of ATP to synthesize proteins and has a synergistic effect on N and P absorption [49,51].
The N and P contents in branches is lower than those in leaves, which may be because leaves are the main sites for photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration, and require more photosynthetic pigments, proteins, nucleic acids, enzymes, and other compounds containing N and P. The branches support the leaves, transport water and nutrients, and contain large amounts of lignin and cellulose, thus preventing excessive N and P from being stored in them. This is consistent with previous findings that plants allocate more N and P to photosynthetic organs than to stems and roots [52]. The ratios of C:N, C:P, and N:P of leaves and branches were significantly or extremely significantly positively correlated, which is consistent with the results of Zhang et al. [53], indicating that the absorption and utilization of nutrients by various organs in plants also showed a synergistic proportional relationship during the growth process. Moreover, during plant organ formation, the efficiencies of C, N, and P are the same, and none of the elements are indispensable [54].
Leaf C:N was positively correlated with soil C:N and LN, whereas BN was positively correlated with soil N. This is largely because the soil provides plants with the nutrients they need to grow and when plant litter breaks down, plant nutrients return to the soil. However, some studies have shown that the stoichiometric characteristics of C, N, and P in the soil-vegetation system are weakly correlated [55], which may be due to the fact that plant nutrient content is restricted by environmental conditions and different study areas lead to differences in such correlations.
4.3. Species and Environmental Factors Affecting Plant Stoichiometry in Karst Primary Forest
Organisms require a specific amount and proportion of nutrients to maintain autogenic growth. Different species have different biochemical structures and specific physiological and metabolic functions owing to their different functions and life strategies; therefore, they have different element requirements; that is, different species have different biogeochemical niches [56,57,58]. In addition to LC and BC:N, in this study, C, N, P, and other stoichiometric ratios were affected by different altitudes. Temperature and water levels also have a corresponding effect on plant light and moisture. Thus, the variation in C, N, and P contents in leaves and branches leads to different survival strategies of plants. However, the degree of variation in C content in branches and leaves was low, which may be due to the stability of C in plants. These conclusions are consistent with previous studies [57]. Second, in this study, soil pH also had significant effects on C, N, P, and their stoichiometric ratios in leaves and branches, which was consistent with the results of Both et al. [59] and Tao et al. [60]. This may be due to the direct effect of soil pH on the conversion of elements in the soil, affecting the turnover and availability of key mineral nutrients needed for plant growth, especially N and P, which are closely related to the soil properties in karst regions.
Reich proposed the species composition hypothesis in 2004 [6], suggesting that differences in species or life-type composition affect biogeographic patterns of plant leaf stoichiometry. Han et al. [61] studied the biogeographic patterns of the contents of 11 nutrient elements of terrestrial plants in China and found that the latitude and longitude patterns of the contents of these elements were mainly driven by climate, soil, and plant functional group types among which plant functional group types played the most important role. He et al. [62] also showed that temperature indirectly affected the variation in the stoichiometric characteristics, mainly by changing the species composition. The results of this study are consistent with those of a previous study. For branches and leaves, the variation in stoichiometric characteristics was mainly driven by species diversity, which is consistent with the species composition hypothesis. This study shows that the nutrient content of plants is not only restricted by environmental conditions but also by the plant species itself.
5. Conclusions
We investigated leaf, branch, and soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry in a karst primary forest plant community in China. The results showed that in addition to C content, the N and P content in leaves was higher than that in branches. There was a close coupling relationship between the C, N, and P contents and their stoichiometric ratios in different organs, indicating that their nutrient utilization efficiency was closely related. We found that leaf stoichiometry was strongly influenced by species diversity, whereas branch stoichiometry was mainly influenced by leaf and species diversity. The environmental factors influencing the stoichiometric characteristics of leaves and branches were mainly altitude, soil pH, and soil total P. Although this research studied the ecological stoichiometric characteristics of plants with both species and environmental factors, their changes were also affected by time scale. Therefore, in the future, we need to study factors, such as phylogeny and seasonal variation, to promote the application and development of the ecological stoichiometry theory in karst ecosystems and provide a reference for ecological function restoration and vegetation reconstruction in karst regions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f13121990/s1, Figure S1: Leaf and branch N:P ratio and DBH distribution; Table S1: Principal component analyses of soil properties.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z. and C.Z.; funding acquisition, F.Z., H.Z. and H.D.; investigation, C.Z., Z.Z., H.D., L.S., L.Z. and M.L.; methodology, F.Z.; writing—original draft, C.Z. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870712, 32071846, 42071073), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2020GXNSFAA259031), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ30764), State Key Laboratory of Environmental Geochemistry (SKLEG2021207), and Hechi City Program of Distinguished Experts in China.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Sheng, M.; Tian, J. Ecological stoichiometry and environmental influencing factors of soil nutrients in the karst rocky desertification ecosystem, southwest China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normand, A.E.; Smith, A.N.; Clark, M.W.; Long, J.R.; Reddy, K.R. Chemical Composition of Soil Organic Matter in a Subarctic Peatland: Influence of Shifting Vegetation Communities. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Song, X.L.; Lu, X.G.; Xue, Z.S. Ecological stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in estuarine wetland soils: Influences of vegetation coverage, plant communities, geomorphology, and seawalls. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperfeld, E.; Wagner, N.D.; Halvorson, H.M.; Malishev, M.; Raubenheimer, D. Bridging Ecological Stoichiometry and Nutritional Geometry with homeostasis concepts and integrative models of organism nutrition. Funct. Ecol. 2017, 31, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusewell, S.; Freeman, C. Nutrient limitation and enzyme activities during litter decomposition of nine wetland species in relation to litter N:P ratios. Funct. Ecol. 2005, 19, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Chen, H.M.; Zhang, X.H.; Shi, F.X.; Song, C.C. Effects of P addition on plant C:N:P stoichiometry in an N-limited temperate wetland of Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Kang, M. Untangling the influence of phylogeny, soil and climate on leaf element concentrations in a biodiversity hotspot. Funct. Ecol. 2015, 29, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Grau, O.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Janssens, I.A.; Ciais, P.; Piao, S.; Penuelas, J. Changes in nutrient concentrations of leaves and roots in response to global change factors. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 3849–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Janssens, I.A.; Alonso, R.; Veresoglou, S.D.; Rillig, M.C.; Sanders, T.G.M.; Carnicer, J.; Filella, I.; Farre-Armengol, G.; Penuelas, J. Foliar elemental composition of European forest tree species associated with evolutionary traits and present environmental and competitive conditions. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Zhang, J.L.; Slik, J.W.F.; Cao, K.F. Leaf element concentrations of terrestrial plants across China are influenced by taxonomy and the environment. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. C: N: P stoichiometry of Artemisia species and close relatives across northern China: Unravelling effects of climate, soil and taxonomy. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Kattge, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, W.; Luo, Y.; He, J.; Hu, H.; Tang, Z.; Ma, S.; Yan, Z.; et al. A global database of paired leaf nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations of terrestrial plants. Ecology 2019, 100, e02812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agren, G.I. The CN:P stoichiometry of autotrophs–theory and observations. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, M.R.; Goransson, A. Terrestrial plants require nutrients in similar proportions. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGroddy, M.E.; Daufresne, T.; Hedin, L.O. Scaling of C:N:P stoichiometry in forests worldwide: Implications of terrestrial redfield-type ratios. Ecology 2004, 85, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklas, K.J.; Cobb, E.D. N, P, and C stoichiometry of Eranthis hyemalis (Ranunculaceae) and the allometry of plant growth. Am. J. Bot. 2005, 92, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minden, V.; Kleyer, M. Internal and external regulation of plant organ stoichiometry. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Bao, W.; Pang, X. Consistent profile pattern and spatial variation of soil C/N/P stoichiometric ratios in the subalpine forests. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2054–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.; Elser, J.J.; Hessen, D.O. Stoichiometry and population dynamics. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Alonso, R.; Carnicer, J.; Fernandez-Martinez, M.; Vivanco, M.G.; Penuelas, J. Factors influencing the foliar elemental composition and stoichiometry in forest trees in Spain. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2016, 18, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Alonso, R.; Janssens, I.A.; Carnicer, J.; Vereseglou, S.; Rillig, M.C.; Fernandez-Martinez, M.; Sanders, T.G.M.; Penuelas, J. Foliar and soil concentrations and stoichiometry of nitrogen and phosphorous across European Pinus sylvestris forests: Relationships with climate, N deposition and tree growth. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Yan, Z.; Fang, J. Review on characteristics and main hypotheses of plant ecological stoichiometry. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 45, 682–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Liu, C.; Dong, M. Ecological adaptation of plants and control of rocky-desertification on karst region of South-west China. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 2011, 35, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Zeng, F.; Song, T.; Peng, W.; Zhang, H.; Du, H. Stoichiometric characteristics of plants, litter and soils in karst plant communities of Northwest Guangxi. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2015, 39, 682–693. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; He, T.; Zeng, C.; Song, T.; Peng, W.; Wei, C.; Su, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, S. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry in plants, litter, soil, and microbes in degraded vegetation communities in a karst area of southwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 935–946. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; Wang, K.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Song, X. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of plants, soil, and microbes of Pennisetum purpureum cv. Guimu-1 pastures at different rehabilitation ages in a karst rocky desertification region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 896–905. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Zeng, S.; Qin, H.; Zhou, K.; Yang, H.; Lan, F.; Huang, F.; Cao, J.; Mueller, C. Low nitrate retention capacity in calcareous soil under woodland in the karst region of southwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, G.; Du, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, H.; Huang, T. Characteristics of Element Contents and Ecological Stoichiometry in Leaves of Common Calcicole Species in Maolan Karst Forest. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zeng, F.; Zeng, Z.; Du, H.; Su, L.; Zhang, L.; Lu, M.; Zhang, H. Impact of Selected Environmental Factors on Variation in Leaf and Branch Traits on Endangered Karst Woody Plants of Southwest China. Forests 2022, 13, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Peng, W.X.; Song, T.Q.; Zeng, F.P.; Wang, K.L.; Song, M.; Zhang, H. Spatial pattern of woody plants and their environmental interpretation in the karst forest of southwest China. Plant Biosyst. 2015, 149, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Yao, H.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y.; An, S.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Chang, S.X. Plant and soil elemental C:N:P ratios are linked to soil microbial diversity during grassland restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavorel, S.; Grigulis, K.; McIntyre, S.; Williams, N.S.G.; Garden, D.; Dorrough, J.; Berman, S.; Quetier, F.; Thebault, A.; Bonis, A. Assessing functional diversity in the field–methodology matters! Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rosseel, Y. lavaan: An R Package for Structural Equation Modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.S.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Sheng, M.; Bai, Y.; Jie, Y.; Xiao, H. Response of C, N, and P stoichiometry characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera to altitude gradients and soil nutrients in the karst rocky ecosystem, SW China. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Peng, W.; Song, T.; Zeng, F.; Wang, K.; Wen, L.; Fan, F. Stoichiometric characteristics of plant and soil C, N and P in different forest types in depressions between karst hills, southwest China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 947–954. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Guo, D.L.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, Q.; Chen, M.; Kuang, W.; Chang, L.; Hu, Q. C, N and P stoichiometry in different organs of Vitex rotundifolia in a Poyang Lake desertification hill. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 461–470. [Google Scholar]
- Tessier, J.T.; Raynal, D.J. Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.R.; An, S.S. Ecological stoichiometry in leaves, roots, litters and soil among different plant communities in a desertified region of Northern China. CATENA 2018, 166, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lai, Y.; Tang, S.; Qin, Z.; Liu, J.; Kang, F.; Kuang, Y. Climatic and edaphic variables determine leaf C, N, P stoichiometry of deciduous Quercus species. Plant Soil 2022, 474, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Lu, X.T.; Zhang, H.Y.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Jiang, Y.G.; Wang, X.B.; Lu, J.Y.; Wuyunna; Wang, Z.W.; Han, X.G. Changes in soil C:N:P stoichiometry along an aridity gradient in drylands of northern China. Geoderma 2020, 361, 114087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; MacKay, N.A.; Schampel, J.H. Organism size, life history, and N:P stoichiometry. Bioscience 1996, 46, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Long, M.; He, X.; Guo, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, P.; Hu, T. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and water availability affect biomass and C:N:P ecological stoichiometry in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) during regrowth. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Yin, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q. Stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus of Sibiraea angustata shrub on the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, K.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. Patterns of nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry among leaf, stem and root of desert plants and responses to climate and soil factors in Xinjiang, China. CATENA 2020, 199, 105100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Han, W.; Fang, J. Nutrient allocation strategies of woody plants: An approach from the scaling of nitrogen and phosphorus between twig stems and leaves. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, K. Ecological stoichiometry of various organs in the tree layer of subalpine forests in central Yunnan, China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2019, 38, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ji, P.; Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X. Ecological CN and P stoichiometry of the needles, twigs and fine roots in pure and mixed stands of Larix principis-rupprechtii. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2020, 34, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Tipping, E.; Somerville, C.J.; Luster, J. The C:N:P:S stoichiometry of soil organic matter. Biogeochemistry 2016, 130, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courbaud, B.; Vieilledent, G.; Kunstler, G. Intra-specific variability and the competition-colonisation trade-off: Coexistence, abundance and stability patterns. Theor. Ecol. 2012, 5, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, N.J.B.; Valencia, R.; Ackerly, D.D. Functional traits and niche-based tree community assembly in an amazonian forest. Science 2008, 322, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, N.J.B.; Adler, P.B.; Godoy, O.; James, E.C.; Fuller, S.; Levine, J.M. Community assembly, coexistence and the environmental filtering metaphor. Funct. Ecol. 2015, 29, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, S.; Riutta, T.; Paine, C.E.T.; Elias, D.M.O.; Cruz, R.S.; Jain, A.; Johnson, D.; Kritzler, U.H.; Kuntz, M.; Majalap-Lee, N.; et al. Logging and soil nutrients independently explain plant trait expression in tropical forests. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 1853–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zuo, J.; He, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. Traits including leaf dry matter content and leaf pH dominate over forest soil pH as drivers of litter decomposition among 60 species. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 1798–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Reich, P.B.; Woodward, F.I.; Wang, Z.H. Biogeography and variability of eleven mineral elements in plant leaves across gradients of climate, soil and plant functional type in China. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, D.; Flynn, D.F.B.; Geng, Z. Stoichiometry and large-scale patterns of leaf carbon and nitrogen in the grassland biomes of China. Oecologia 2006, 149, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).