Response of Tracheid Structure Characteristics and Lignin Distribution of Taxodium Hybrid Zhongshanshan to External Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
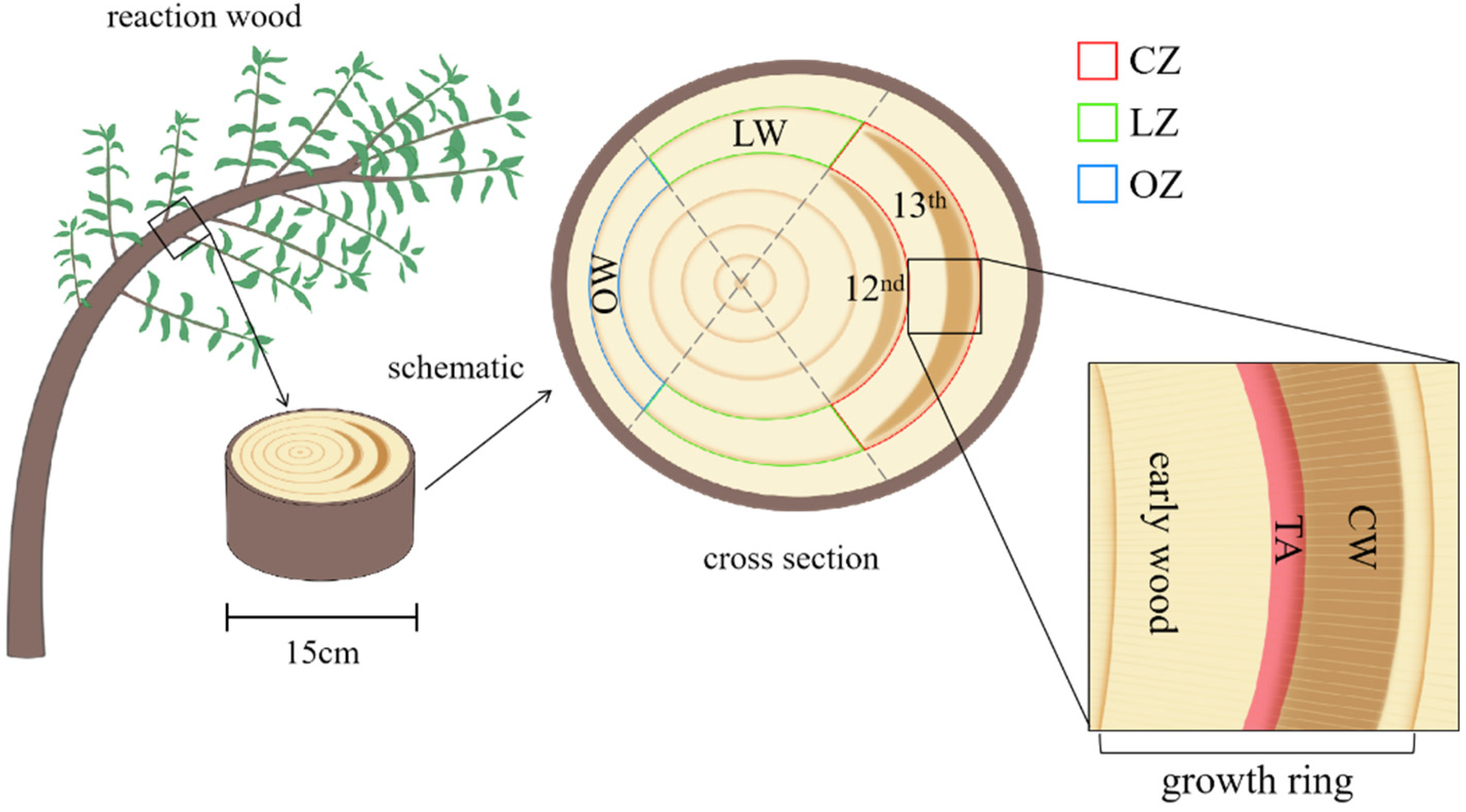
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microstructure Observation
2.3. Roundness Value of Tracheid Measurement
2.4. Tracheid Dimensions Analysis
2.5. Multilayer Structure of Cell Walls
3. Results
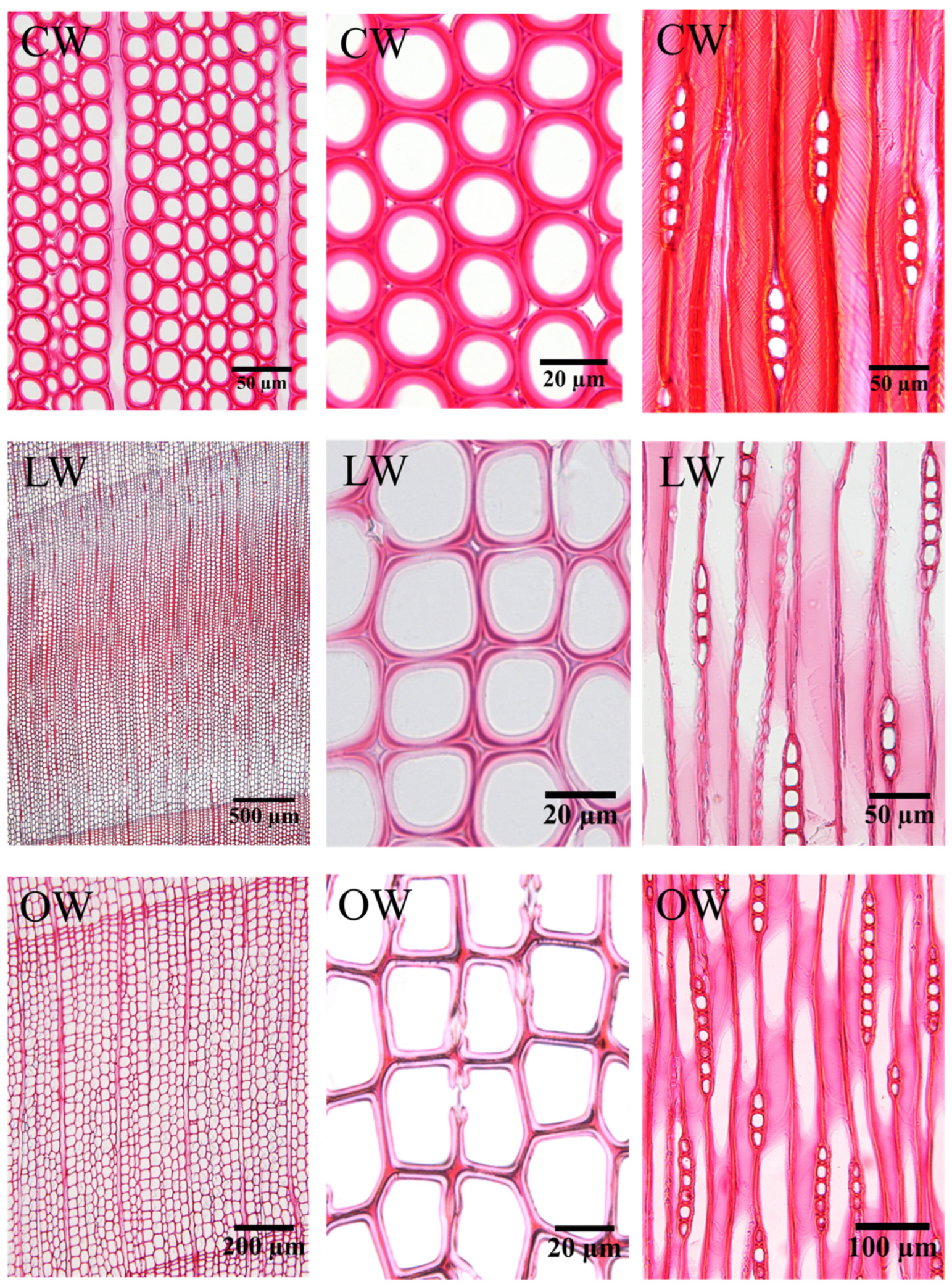
3.1. Microscopic Distribution of CW Tracheids
3.2. Anatomical Characteristics of Reaction Wood
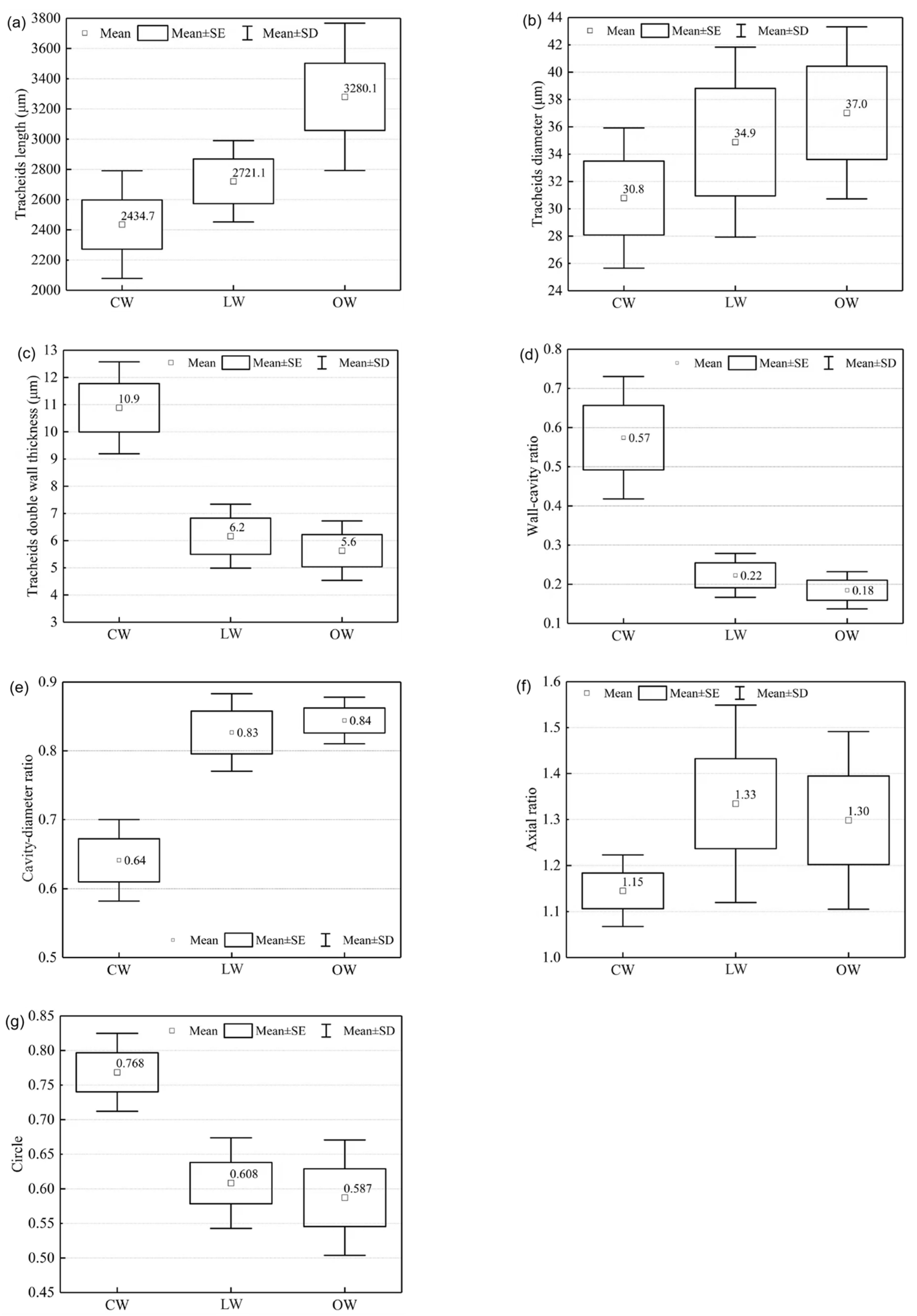
3.3. Tracheid Morphological Parameters of Reaction Wood
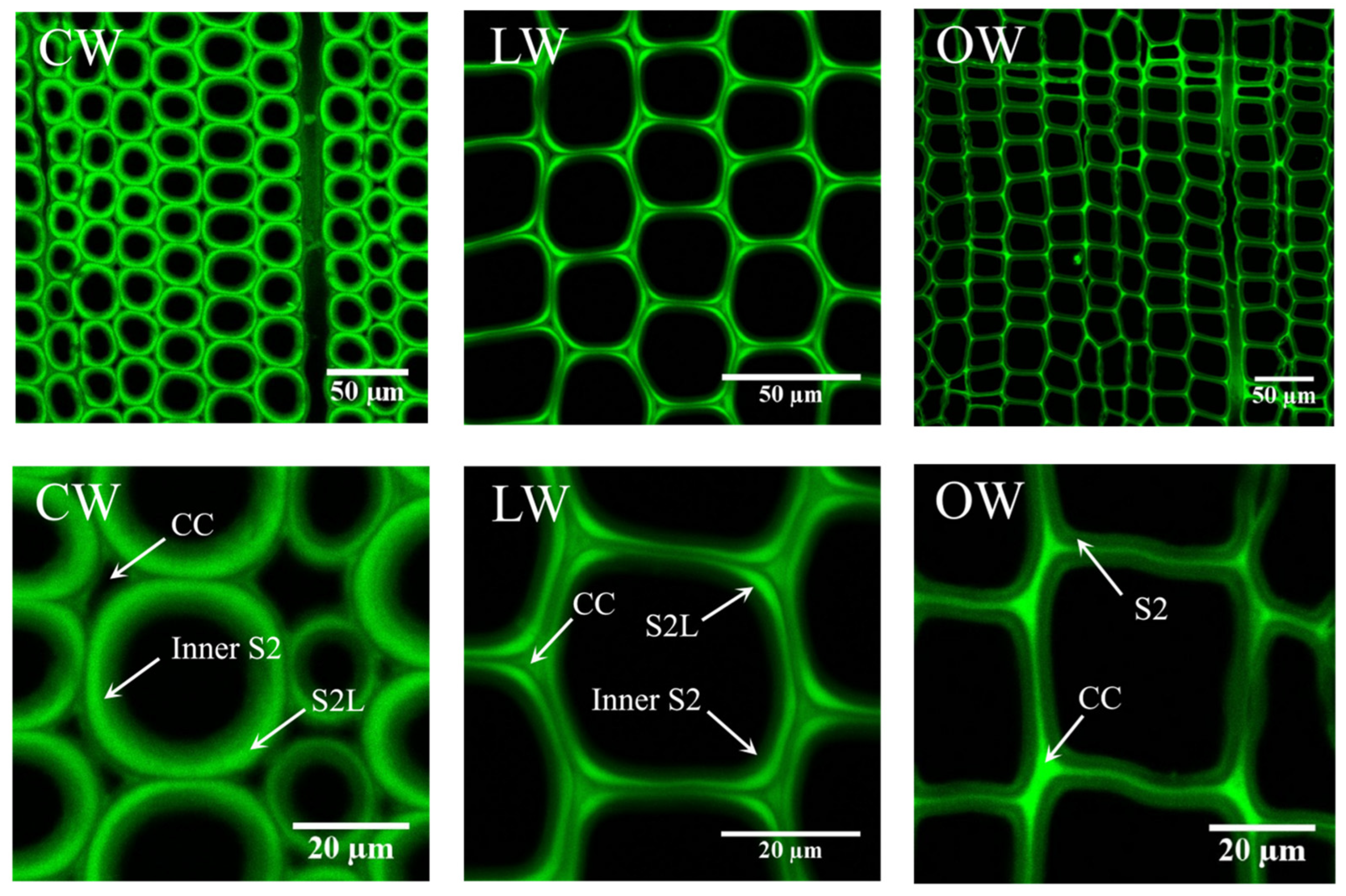
3.4. Cell Wall Structure of Reaction Wood
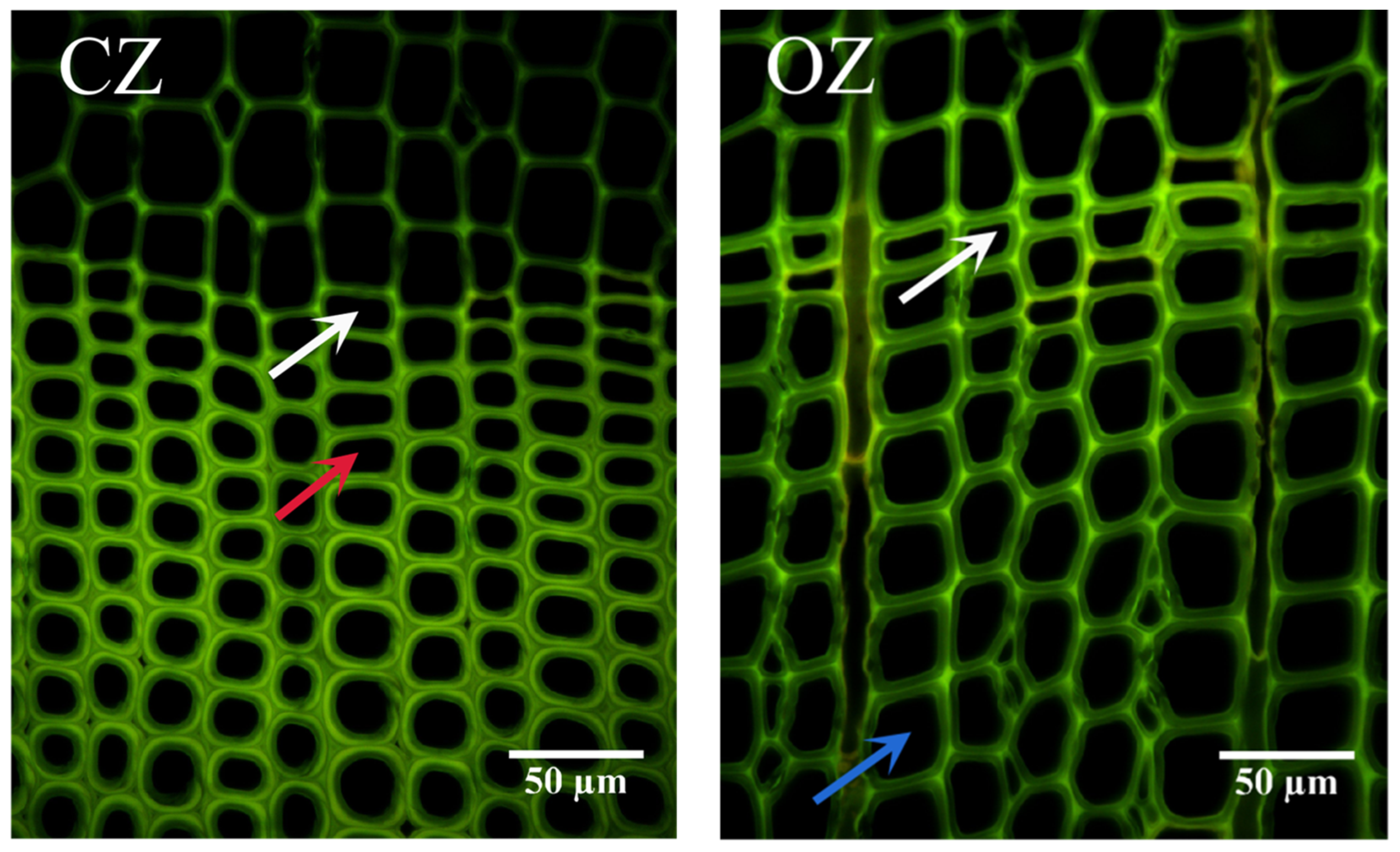
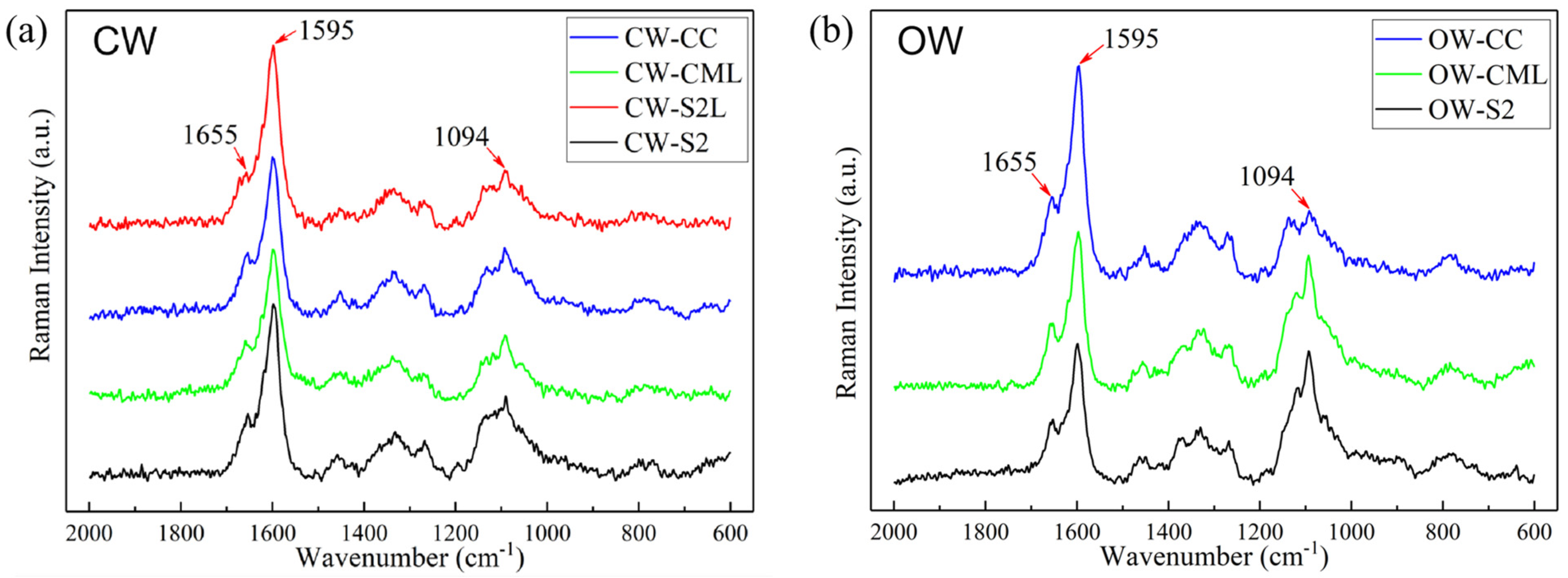
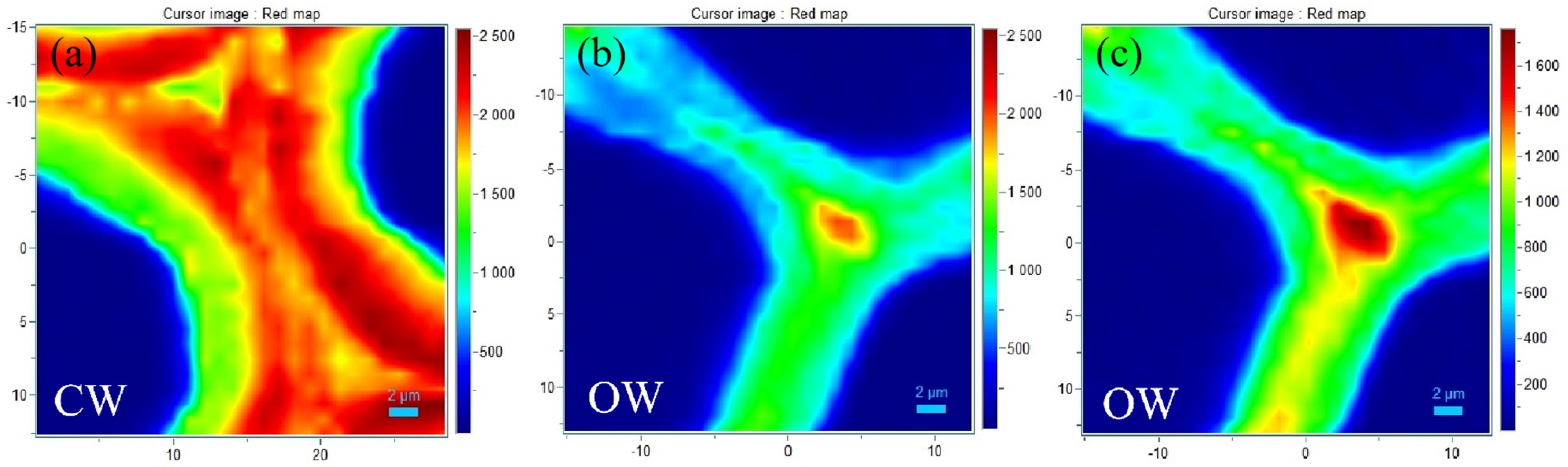
3.5. Microscopic Distribution of Lignin in Reactive Wood Tracheids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Archer, R.R. Growth Stresses and Strains in Trees; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, I.; Vilkovská, T.; Vilkovský, P.; Hýsek, Š. Structural differences between reaction wood and opposite wood with different drying temperatures. BioResources 2020, 15, 4407–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, I.; Vilkovská, T.; Uhrín, M. Color Changes of Compression and Opposite Spruce Wood (Picea abies L. Karst.) Affected by Different Drying Conditions. BioResources 2019, 14, 6697–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malan, F.S.; Gerischer, G.F.R. Wood property differences in South African grown Eucalyptus grandis trees of different growth stress intensity. Holzforschung 1987, 41, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Fei, B.; Yu, H.; Liu, J. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Taxodium ’zhongshansha 302’ and Taxodium distichum Wood. J.-Northeast. For. Univ.-Chin. Ed. 2007, 35, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, R.; Johansson, M. Effects of reaction wood on the performance of wood and wood-based products. In The Biology of Reaction Wood; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadenbäck, J.; Clapham, D.; Gellerstedt, G.; von Arnold, S. Variation in content and composition of lignin in Young Wood of norway spruce. Holzforschung 2004, 58, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindl, W. Comparing mechanical properties of normal and compression wood in Norway spruce: The role of lignin in compression parallel to the grain. Holzforschung 2002, 56, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Altaner, C.M. Properties of young Araucaria heterophylla (Norfolk Island pine) reaction and Normal Wood. Holzforschung 2014, 68, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, L.A.; Nanayakkara, B.; Radotić, K.; Djikanovic-Golubović, D.; Mitrović, A.; Bogdanović Pristov, J.; Simonović Radosavljević, J.; Kalauzi, A. Xylem parenchyma cell walls lack a gravitropic response in conifer compression wood. Planta 2015, 242, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timell, T.E. Origin and evolution of Compression Wood. Holzforschung 1983, 37, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, L.A.; Singh, A.P. Formation and structure of Compression Wood. In Plant Cell Monographs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 225–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelbourne, C.J.; Ritchie, K.S. Relationships between degree of compression wood development and specific gravity and Tracheid characteristics in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). Holzforschung 1968, 22, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumoto, M.; Ishida, S.; Fukazawa, K. Gradation of the Severity of Compression Wood Tracheids. In Studies on the Formation and Structure of the Compression Wood Cells Induced by Artificial Inclination in Young Trees of Picea glauca; Research Bulletins of the College Experiment Forests Hokkaido University: Sapporo, Japan, 1983; pp. 409–454. [Google Scholar]
- Altaner, C.M.; Tokareva, E.N.; Wong, J.C.; Hapca, A.I.; McLean, J.P.; Jarvis, M.C. Measuring compression wood severity in spruce. Wood Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, L.A.; Singh, A.P.; Yoshinaga, A.; Takabe, K. Lignin distribution in mild compression wood of Pinus radiata. Can. J. Bot. 1999, 77, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Terashima, N. Heterogeneity in formation of lignin. Wood Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, J.D. Helical fissures in compression wood cells: Causative factors and mechanics of development. Wood Sci. Technol. 1973, 7, 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Ji, Z.; Xu, F. Comparison of anatomy and composition distribution between normal and compression wood of Pinus bungeana zucc. revealed by Microscopic Imaging Techniques. Microsc. Microanal. 2012, 18, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, B.; Manley-Harris, M.; Suckling, I.D.; Donaldson, L.A. Quantitative chemical indicators to assess the gradation of Compression Wood. Holzforschung 2009, 63, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiso-Sanada, H.; Ishiguri, F.; Irawati, D.; Wahyudi, I.; Yokota, S. Reaction wood anatomy and lignin distribution in gnetum gnemon branches. J. Wood Sci. 2018, 64, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, R.A.; Côté, W.A. Distribution of lignin in normal and compression wood of Pinus taeda L. Wood Sci. Technol. 1971, 5, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, U.P. Raman imaging to investigate ultrastructure and composition of plant cell walls: Distribution of lignin and cellulose in black spruce wood (Picea mariana). Planta 2006, 224, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Xu, F. Chemical characteristics of wood cell wall with an emphasis on ultrastructure: A mini-review. Forests 2022, 13, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, L.A.; Radotic, K. Fluorescence lifetime imaging of lignin autofluorescence in normal and Compression Wood. J. Microsc. 2013, 251, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarmian, A.; Azadfallah, M. Variation of cell features and chemical composition in spruce consisting of opposite, normal, and compression wood. BioResources 2008, 4, 194–204. [Google Scholar]
- Timell, T.E. Compression Wood in Gymnosperms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; Volume 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Purusatama, B.D.; Kim, N.H. Quantitative anatomical characteristics of compression wood, lateral wood, and opposite wood in the stem wood of Ginkgo biloba L. BioResources 2018, 13, 8076–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, Y.; Butterfield, B.G. Anatomical comparisons of compression, opposite, and lateral woods in New Zealand radiata pine (Pinus radiata D. Don). J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 1997, 25, 88–99. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.M. Within-tree variation in anatomical properties of compression wood in Radiata Pine. IAWA J. 2004, 25, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, O.M.; Velín, A.; García, A.; Arroyo, C.R.; Barrigas, H.L.; Vizuete, K.; Debut, A. Representative Hardwood and Softwood Green Tissue-Microstructure Transitions per Age Group and Their Inherent Relationships with Physical–Mechanical Properties and Potential Applications. Forests 2020, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.; Donaldson, L.; Hill, S.; Hitchcock, K. Safranine fluorescent staining of wood cell walls. Biotech. Histochem. 2008, 83, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, N.; Itoh, T.; Shimaji, K. Variation in features of compression wood among gymnosperms. Bull. Utunomiya Univ. For. 1982, 16, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Saka, S.; Whiting, P.; Fukazawa, K.; Goring, D.A. Comparative studies on lignin distribution by UV microscopy and bromination combined with EDXA. Wood Sci. Technol. 1982, 16, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, L.A. Lignification and lignin topochemistry—An ultrastructural view. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Guo, D.; Jiang, P.; Li, G.; Yang, S.; Chu, F. Reaction mechanisms of furfuryl alcohol polymer with wood cell wall components. Holzforschung 2021, 75, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Ma, J.-F.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.-C. Distribution of lignin and cellulose in compression wood tracheids of pinus yunnanensis determined by fluorescence microscopy and confocal Raman microscopy. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 47, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.M. Shrinkage and density of radiata pine compression wood in relation to its anatomy and mode of formation. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 1977, 7, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Hu, Z.; Chang, H.; Li, B. Micro analytical methods for determination of compression wood content in loblolly pine. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2007, 27, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Salmén, L.; Stevanic, J.S.; Lu, J. Structural Organization of the cell wall polymers in compression wood as revealed by FTIR microspectroscopy. Planta 2019, 250, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yong, L.; Bi, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Pan, B. Response of Tracheid Structure Characteristics and Lignin Distribution of Taxodium Hybrid Zhongshanshan to External Stress. Forests 2022, 13, 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13111792
Yong L, Bi Y, Shi J, Wang X, Pan B. Response of Tracheid Structure Characteristics and Lignin Distribution of Taxodium Hybrid Zhongshanshan to External Stress. Forests. 2022; 13(11):1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13111792
Chicago/Turabian StyleYong, Lu, Yujin Bi, Jiangtao Shi, Xinzhou Wang, and Biao Pan. 2022. "Response of Tracheid Structure Characteristics and Lignin Distribution of Taxodium Hybrid Zhongshanshan to External Stress" Forests 13, no. 11: 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13111792
APA StyleYong, L., Bi, Y., Shi, J., Wang, X., & Pan, B. (2022). Response of Tracheid Structure Characteristics and Lignin Distribution of Taxodium Hybrid Zhongshanshan to External Stress. Forests, 13(11), 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13111792








