Sorption Characteristic of Thermally Modified Wood at Varying Relative Humidity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Vapour Sorption Test
2.3. Hailwood–Horrobin Model and Data Fitting
2.4. 1H NMR Experiments
3. Results
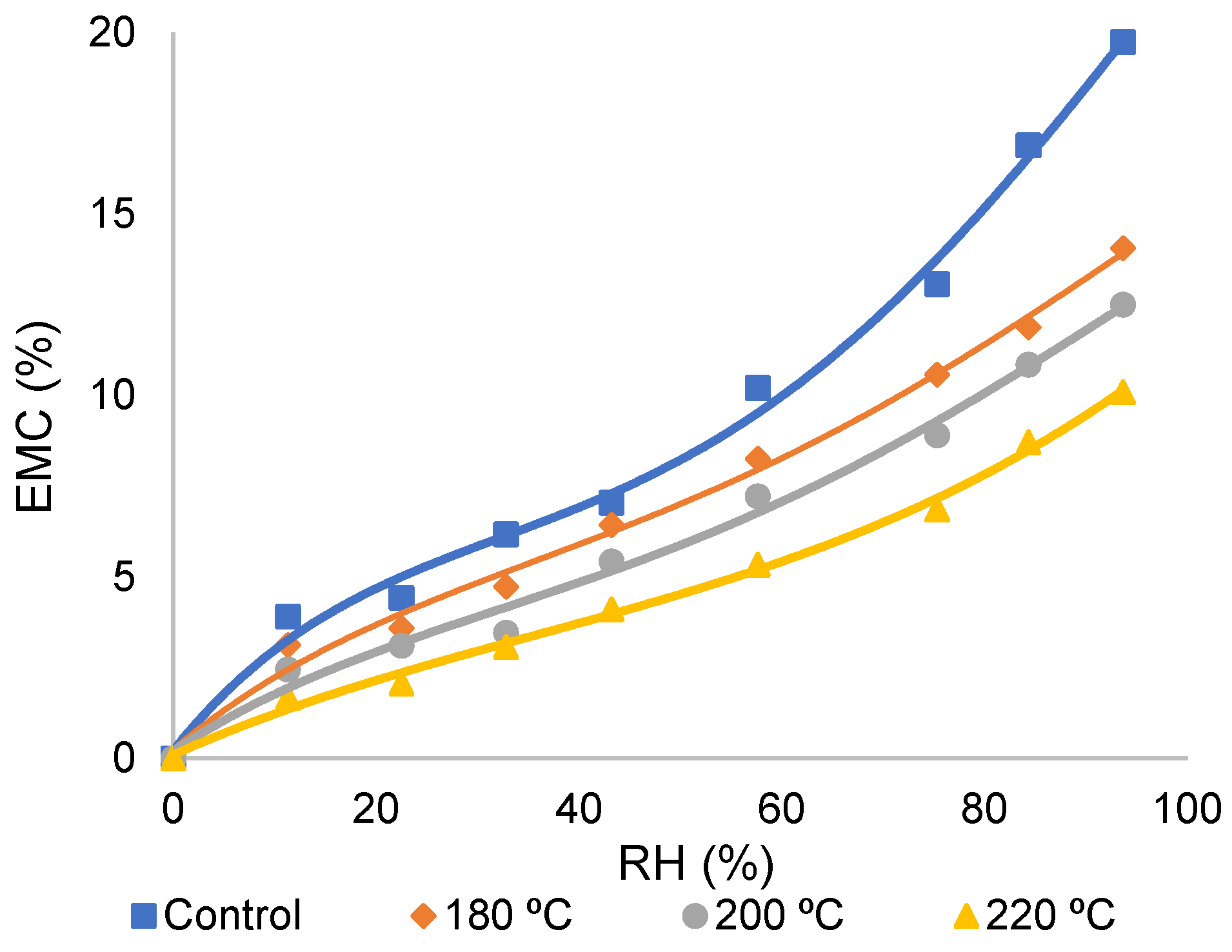
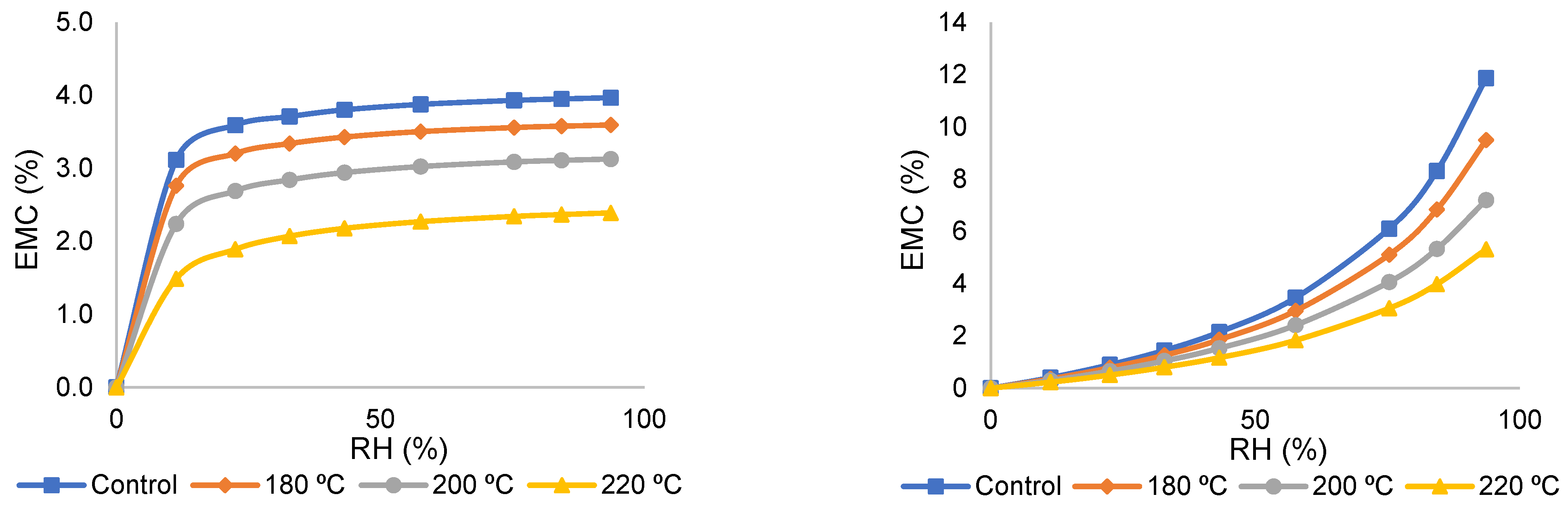
3.1. The Sorption Isotherms of TMW at Various RHs
3.2. Isotherm Model Fit
3.3. T2 and Moisture Distribution of Specimens under Different RHs
4. Discussion
4.1. The Sorption Isotherms of TMW
4.2. Isotherm Model Fit and Adsorption Properties
4.3. T2 and Moisture Distribution of Specimens under Different RHs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, C.A.S. Wood Modification-Chemical, Thermal and Other Processes; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Esteves, B.; Pereira, H. Wood modification by heat treatment: A review. BioResources 2009, 4, 370–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Liu, N.; Guan, H. Optimal design of a furniture frame by reducing the volume of wood. Drewno 2019, 62, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Wan, H.; Guan, H. Size effect on the elastic mechanical properties of beech and its application in finite element analysis of wood structures. Forests 2019, 10, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jin, H.H. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Physic-Mechanical Characteristics of Eucalyptus urophylla ST Blake. Materials 2021, 14, 6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Ma, J.W.; Xu, W.; Fei, B.H.; Lian, C.P.; Sun, F.B. Effect of bending on radial distribution density, MFA and MOE of bent bamboo. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, H.H. Effect of a Combination of Moderate-Temperature Heat Treatment and Subsequent Wax Impregnation on Wood Hygroscopicity, Dimensional Stability, and Mechanical Properties. Forests 2020, 11, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Fu, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhou, Y. Changes in the wood-water interactions of mahogany wood due to heat treatment. Holzforschung 2020, 74, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Iruela, A.; Esteban, L.G.; García, F.F.; de Palacios, P.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.B.; Martín-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M.E. Changes in cell wall components and hygroscopic properties of Pinus radiata caused by heat treatment. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2021, 79, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Zhong, T.H.; Zhang, W.F.; Shi, J.J.; Fei, B.H.; Chen, H. Comparison of colors, microstructure, chemical composition and thermal properties of bamboo fibers and parenchyma cells with heat treatment. J. Wood Sci. 2021, 67, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.Y.; Cheng, S.; Cao, S.; Cai, J.B. Evaluation of Color Changes, Wettability, and Moisture Sorption of Heat-Treated Blue-Stained Radiata Pine Lumber. BioResoures 2022, 17, 4952–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailwood, A.J.; Horrobin, S. Absorption of water by polymers: Analysis in terms of a simple model. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1946, 42, B084–B092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, W. Sorption theories applied to wood. Wood Fiber Sci 1980, 12, 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, A.N.; Hill, C.A.S. The sorption of water vapour by anhydride modified softwood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patcharawijit, A.; Choodum, N.; Yamsaengsung, R. Effects of superheated steam treatment on moisture adsorption and mechanical properties of pre-dried rubberwood. Drying Techno. 2019, 37, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucur, V. Nondestructive Characterization and Imaging of Wood; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kekkonen, P.M.; Ylisassi, A.; Telkki, V.V. Absorption of water in thermally modified pine wood as studied by NMR. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 2146–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownstein, K.R.; Tarr, C.E. Importance of Classical Diffusion in NMR Studies of Water in Biological Cells. Phys. Rev. A 1979, 19, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.Y.; Javed, M.A.; Komulainen, S.; Telkki, V.-V.; Haapala, A.; Heräjärvi, H. Effect of natural weathering on water absorption and pore size distribution in thermally modified wood determined by nuclear magnetic resonance. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4235–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.Y.; Zhou, F.D.; Cai, J.B. Bound Water Content and Pore Size Distribution of Heat-treated Wood Studied by NMR. Forests 2020, 11, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A.S.; Keating, B.A.; Jalaludin, Z.; Mahrdt, E. A rheological description of the water vapour sorption kinetics behaviour of wood invoking a model using a canonical assembly of Kelvin-Voigt elements and a possible link with sorption hysteresis. Holzforschung 2012, 66, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Cheng, S.; Cai, J. Research progress and prospects of wood high-temperature heat treatment technology. BioResources 2022, 17, 3702–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.R.; Fang, L.; Xu, W.; Xiong, X.Q.; Wang, X.D. Effect of Laser Irradiation on the Surface Wettability of Poplar Wood. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2019, 11, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Liu, H.H. Research Progress of Wood Cell Wall Modification and Functional Improvement: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, M.; Thybring, E.E. On sorption hysteresis in wood: Separating hysteresis in cell wall water and capillary water in the full moisture range. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, L.G.; Engelund, E.T.; Hoffmeyer, P. Water sorption in wood and modified wood at high values of relative humidity—Part 1: Results for untreated, acetylated, and furfurylated Norway spruce. Holzforschung 2010, 64, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelund, E.T.; Thygesen, L.G.; Hoffmeyer, P. Water sorption in wood and modified wood at high values of relative humidity—Part 2. Theoretical assessment of the amount of capillary water in wood microvoids. Holzforschung 2010, 64, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakano, T. Effect of Thermal Treatment on Fracture Properties and Adsorption Properties of Spruce Wood. Materials 2013, 6, 4186–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezici-Koç, Ö.; Erich, S.; Huinink, H.; Ven, L.; Adan, O. Bound and free water distribution in wood during water uptake and drying as measured by 1D magnetic resonance imaging. Cellulose 2017, 24, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauer, M.; Kretzschmar, J.; Grossmann, L.; Pfriem, A.; Wagenfuhr, A. Analysis of the pore-size distribution and fiber saturation point of native and thermally modified wood using differential scanning calorimetry. Wood Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.Y.; Haapala, A.; Rahman, M.H.; Tiitta, M.; Tiitta, V.; Tomppo, L.; Lappalainen, R.; Herajarvi, H. Effect of two-year Natural Weathering on Chemical and Physical Properties of Thermally Modified Picea abies, Pinus sylvestris and Fraxinus Excelsior Wood. Can. J. Forest. Res. 2020, 50, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Salt Solutions | LiCl | CH3COOK | MgCl2 | K2CO3 | NaBr | NaCl | KCl | KNO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RH (%) | 11.3 | 22.5 | 32.8 | 43.2 | 57.6 | 75.3 | 84.3 | 93.6 |
| A | B | C | K1 | K2 | W | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.86 | 22.91 | 18.67 | 34.64 | 0.791 | 436.9 | 0.98 |
| 180 °C | 1.04 | 25.08 | 19.83 | 32.32 | 0.766 | 480.2 | 0.97 |
| 200 °C | 1.57 | 27.94 | 21.30 | 25.36 | 0.732 | 544.3 | 0.98 |
| 220 °C | 3.08 | 33.97 | 25.91 | 16.39 | 0.716 | 690.9 | 0.96 |
| RHs | Control | 180 °C | 200 °C | 220 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11.3% | 0.215 | 0.168 | 0.164 | 0.149 |
| 22.5% | 0.293 | 0.173 | 0.171 | 0.162 |
| 32.8% | 0.477 | 0.316 | 0.302 | 0.253 |
| 43.2% | 0.525 | 0.503 | 0.497 | 0.178 |
| 57.6% | 0.692 | 0.607 | 0.494 | 0.352 |
| 75.3% | 0.813 | 0.611 | 0.641 | 0.639 |
| 84.3% | 0.876 | 0.725 | 0.657 | 0.644 |
| 93.6% | 0.883 | 0.738 | 0.684 | 0.679 |
| RH | Control | 180 °C | 200 °C | 220 °C | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | EMC (%) | IP (a.u.) | IPbw (a.u.) | Pbw (%) | EMC (%) | IP (a.u.) | IPbw (a.u.) | Pbw (%) | EMC (%) | IP (a.u.) | IPbw (a.u.) | Pbw (%) | EMC (%) | IP (a.u.) | IPbw (a.u.) | Pbw (%) |
| 11.3 | 3.90 | 884 | 816 | 92.3 | 3.12 | 871 | 759 | 87.2 | 2.44 | 460 | 399 | 86.8 | 1.66 | 310 | 265 | 85.6 |
| 22.5 | 4.42 | 1600 | 1501 | 93.8 | 3.58 | 1381 | 1281 | 92.8 | 3.10 | 770 | 702 | 91.2 | 2.06 | 678 | 609 | 89.9 |
| 32.8 | 6.17 | 2422 | 2323 | 95.9 | 4.73 | 1752 | 1640 | 93.6 | 3.46 | 1196 | 1128 | 94.3 | 3.07 | 850 | 780 | 91.8 |
| 43.2 | 7.04 | 2540 | 2472 | 97.3 | 6.43 | 2122 | 2013 | 94.9 | 5.42 | 1202 | 1129 | 93.9 | 4.11 | 945 | 888 | 93.9 |
| 57.6 | 10.21 | 3452 | 3407 | 98.7 | 8.25 | 2435 | 2352 | 96.6 | 7.22 | 1595 | 1500 | 94.1 | 5.53 | 1287 | 1203 | 93.5 |
| 75.3 | 13.07 | 4883 | 4829 | 98.9 | 10.57 | 3013 | 2962 | 98.3 | 8.90 | 2330 | 2235 | 95.9 | 6.85 | 1862 | 1822 | 97.9 |
| 84.3 | 16.89 | 6073 | 6006 | 98.9 | 11.88 | 3845 | 3779 | 98.3 | 10.85 | 3341 | 3294 | 98.6 | 8.71 | 2671 | 2637 | 98.7 |
| 93.6 | 19.74 | 8609 | 8549 | 99.3 | 14.06 | 5821 | 5774 | 99.2 | 12.50 | 5086 | 5030 | 98.9 | 10.09 | 4221 | 4187 | 99.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, C.; Zhou, F. Sorption Characteristic of Thermally Modified Wood at Varying Relative Humidity. Forests 2022, 13, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13101687
Cai C, Zhou F. Sorption Characteristic of Thermally Modified Wood at Varying Relative Humidity. Forests. 2022; 13(10):1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13101687
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Chenyang, and Fanding Zhou. 2022. "Sorption Characteristic of Thermally Modified Wood at Varying Relative Humidity" Forests 13, no. 10: 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13101687
APA StyleCai, C., & Zhou, F. (2022). Sorption Characteristic of Thermally Modified Wood at Varying Relative Humidity. Forests, 13(10), 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13101687




