Abstract
Pine wilt disease (PWD) has caused extensive mortality in pine forests worldwide. The longicorn beetle Monochamus saltuarius, as the vector of the invasive species Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, plays an important role in the infection cycle. Although the gut microbiota and its contribution to health and disease have been extensively documented, it is unclear whether B. xylophilus affects the longicorn gut microbiota because of a lack of understanding of potential temporal changes in the microbial composition of the vector beetles. In this study, we collected beetles at the emergence and mating stages, and divided them into two groups according to whether they carried nematodes. Based on 16S rDNA sequence analysis, 174 bacterial species were identified that belonged to 112 genera, 53 families, and 8 phyla. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus increased the microflora abundance and diversity of the infected M. saltuarius. In addition, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes were more abundant in infected M. saltuarius at the same developmental stage. Some of the bacteria in these two phyla were the key species in the co-occurrence network of intestinal flora and represented a unique module in the co-occurrence network of infected M. saltuarius. We found some high abundance colonies in the intestinal tract of infected M. saltuarius during the emergence period that were mostly related to metabolism. Compared with the emergence period, there were more similar microorganisms in the intestinal tract of M. saltuarius during the mating period. With the change in growth environment and continuous feeding, the intestinal microorganisms gradually stabilized and became single species.
1. Introduction
Pines are conifers in the genus Pinus that are found in the Northern Hemisphere [1]. They have economic, ecological, and scientific importance, as they provide timber for construction, furniture, paneling, and flooring [2,3]; habitats and food for wildlife; and anticancer, antioxidant, and antimutagenic properties in their needles [4]. However, pine trees (such as P. tabuliformis Carr., P. thunbergii Parl., and P. koraiensis Siebold and Zucc.) are threatened by pine wilt disease (PWD), a devastating disease that kills trees within a few weeks to a few months from infection, with symptoms that are characterized by wilted and brown needles. PWD is caused by the pine wood nematode (PWN), Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner and Buhrer) Nickle (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae), which is vectored by longhorned beetles (Monochamus spp.) and spreads when the beetles feed on trees. Monochamus saltuarius (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) is widely distributed in Central and Eastern Europe, Siberia, the Russian Far East, and East Asia [5], and is a trunk borer of pine trees. It has been identified as an important vector of PWD in Japan, Korea, and China [6,7]. However, there are very limited studies on the intestinal microbial community of adult Monochamus, and to date, few studies have focused on the interaction between nematodes and the intestinal flora of Monochamus.
The intestinal tract of insects is usually inhabited by bacteria, archaea, viruses, fungi, and some protozoa, among which bacteria are the most important microbial groups in the intestinal tracts of insects. The bacterial community that inhabits the intestinal tracts is often collectively referred to as the intestinal flora [8]. Over their long-term evolution, a unique symbiotic relationship has been formed between insects and their intestinal microorganisms. The intestinal flora provides important nutrients for the host, assists in digesting food, helps the insect host resist the invasion of parasites [9], and improves the host’s defense and detoxification ability. The intestinal flora also affects the host insect’s life span [10], development cycle, and mating and reproductive capacity [11,12,13,14,15,16].
Although some studies on the intestinal flora of Monochamus have been conducted, knowledge gaps remain. At present, there have been few studies on M. saltuarius intestinal bacteria. Ge et al. [17] studied the intestinal bacterial diversity of M. saltuarius larvae isolated from P. koraiensis and P. sylvestris var. mongolica Litv. in 2021, but did not study its correlation with B. xylophilus. Monochamus saltuarius can only produce one generation per year, and May is the peak emergence period. In the forest, the beetles synchronously enter the mating period. These traits provided us with convenient conditions for collecting samples. In this study, 16S rDNA library technology and Illumina HiSeq sequencing technology were used to detect the effects of B. xylophilus on the bacterial community in the intestines of natural populations of M. saltuarius at the emergence and mating stages.
In this study, we compared the changes in intestinal microflora between M. saltuarius in the emergence and mating stages with and without B. xylophilus to reveal the interaction mechanism between endophyte and host. This study laid the foundation for further exploring the effects of B. xylophilus on the reproductive physiology of M. saltuarius, which could help with the development of new methods for PWD management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Dissections
Monochamus. saltuarius were collected in May 2021 from Dahuofang Forest Farm, Fushun City, Liaoning Province, China. Samples (n = 100) were collected in the forest. To obtain M. saltuarius at the eclosion stage, we cut down P. koraiensis that died in the current year, divided them into 2-m-long sections, and put these sections into a tailor-made stainless-steel cage (length × width × height = 2.5 m × 2.5 m × 2.0 m); then, the cages were regularly checked daily. Once eclosed adults were found, they were put into a 10-mL centrifuge tube and brought back to the laboratory. To obtain M. saltuarius at the mating stage, we carefully searched for M. saltuarius in areas where host trees were weak, and once we found a mating couple (a male and female M. saltuarius, usually on the trunk), they were placed in a 10-mL centrifuge tube and brought back to the laboratory.
Intestinal tracts were collected as follows: the body surface of the longicorn beetle was disinfected with 75% ethanol for 1 min, and then washed twice with sterile water. Dissection was performed under sterile conditions, and the intact intestines were removed, placed in labeled centrifuge tubes, and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Then, using the Baermann funnel method to count the number of nematodes carried by each beetle, we separated the beetles into four categories: emergence and mating beetles without nematodes (‘healthy’) and emergence and mating beetles with nematodes (‘infested’) (EH, MH, EI, and MI, respectively). Three biological replicates were used per category, and each biological replicate consisted of the gut from one beetle.
2.2. Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing of Bacterial 16S rDNA
The 16S rDNA was amplified by polymerase chain reaction with 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) primers. The 16S rDNA genes of bacteria in the intestinal microflora of M. saltuarius were sequenced and analyzed using an Illumina MiSeq sequencing platform of Meiji Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.3. Sequence Data Analysis
PE(Paired-end) reads from MiSeq sequencing were first spliced using FLASH [18]. The assembled sequences were subjected to operational taxonomic unit (OTU) clustering using USEARCH (version 7.1, http://drive5.com/uparse/ (accessed on 15 June 2022)) [19]. Each sequence was annotated by an RDP classifier (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/ (accessed on 21 June 2022)) [20], and R (version 3.3.1) was used to determine the community composition and species abundance of each sample at different classification levels. Simultaneously, a Venn diagram was drawn to infer the similarity and overlap of the OTU composition of samples.
Alpha diversity analyses were conducted to reveal the richness and diversity of microbial communities. Based on the statistical results of OTUs, Mothur was used to calculate the alpha diversity indexes [21], including Chao and Ace indexes, which reflect the community richness in samples, and Shannon and Simpson indexes, which reflect the species diversity in the samples. Additionally, a dilution curve was drawn according to the Shannon index.
2.4. Construction of Phylogenetic Interaction Networks
For interaction network analysis, we filtered out those OTUs whose relative abundance was lower than 0.03% and which appeared in fewer than two of the test samples. Based on an ensemble approach in CoNet [22], which combines the measures of several different correlations (Pearson [23], Spearman [23]), and similarity (mutual information [24]), or dissimilarity (Bray-Curtis [25], Kullback–Leibler), the phylogenetic co-occurrence networks of EH, EI, MH, and MI microbiota were inferred. We used Cytoscape (version 3.6.0) to visualize the co-occurrence network and compute its topological features, including the connectance and the average degree of co-occurrence [26]. The clustering of the submodules was manually conducted based on the involved vertices and topological structures.
2.5. Functional Analysis of Intestinal Flora
PICRUSt 2 was used to predict the function of intestinal microbiota in M. saltuarius. First, the OTU abundance table was standardized to remove the influence of the copy number of the 16S rRNA marker gene in the species genome. Then, MetaCyc Pathways functional annotation was performed according to the Greengene ID corresponding to each OTU, and the annotation information of OTUs at each functional level and their abundance information were obtained for different samples.
3. Results
3.1. General Profile of Illumina Data
In total, 761,375 raw sequencing reads were obtained by the Illumina HiSeq analysis of 16S rRNA gene amplicons from 16 samples. After quality filtering and chimera removal, 760,692 (99.91%) high-quality reads remained for analysis, with an average read length of 422 bp. Overall, 222 OTUs were clustered at 97% sequence identity (Table S1). The rarefaction curves suggested that all samples tended toward saturation (Figure S1) and the Good’s coverage of each sample was above 99%, which indicated a sufficient sequencing depth and capture of most bacterial diversity.
3.2. Alpha and Beta Diversity Analyses
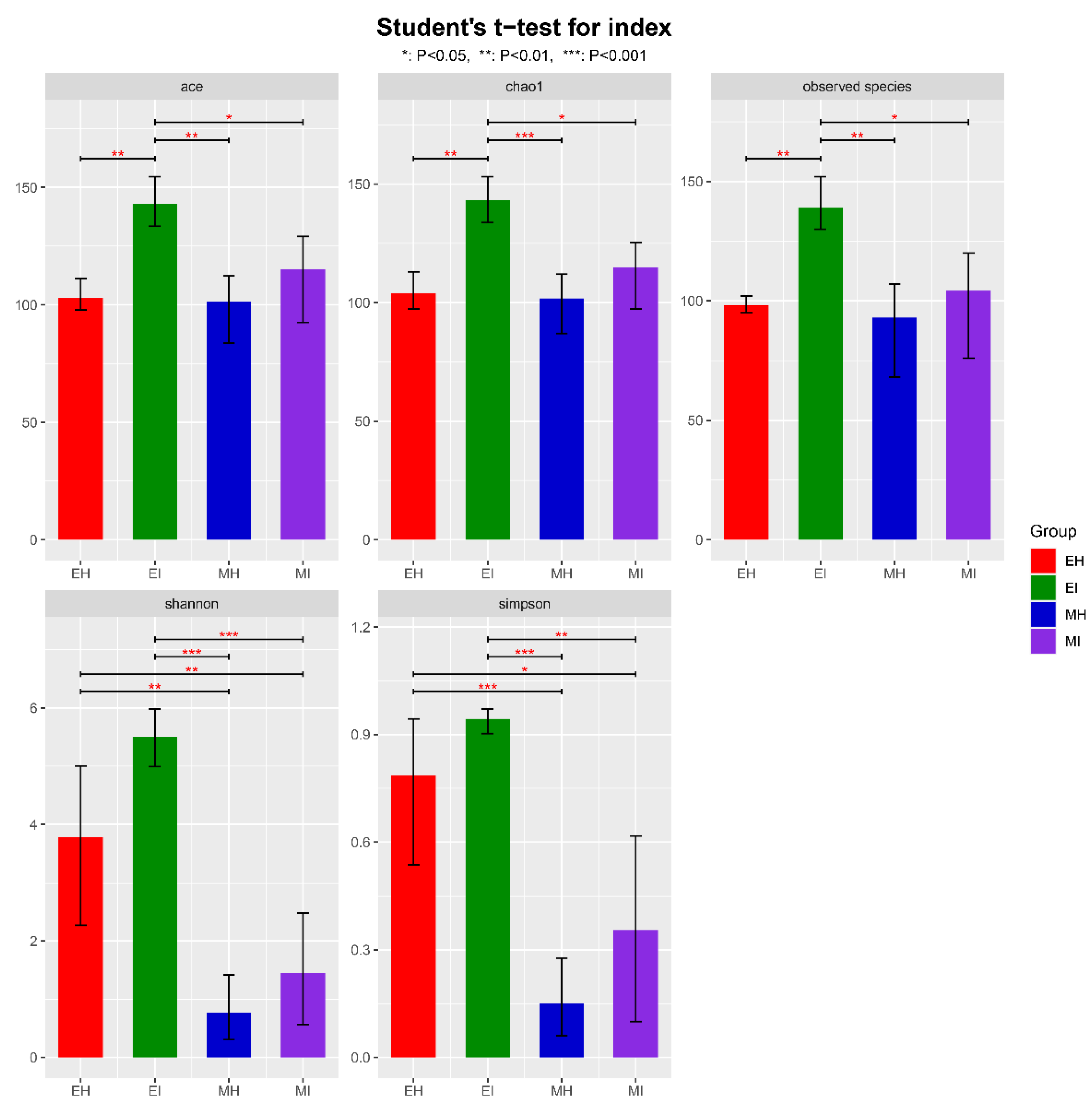
An alpha diversity index evaluation revealed the flora diversity in the samples. Five commonly used indexes, Ace, Chao1, observed species, Shannon, and Simpson, were selected to analyze the diversity of intestinal microflora of M. saltuarius (Figure 1, Table S2). The Ace index, observed species, and Chao1 index of EI were significantly higher than those of the other groups, which indicated that there were more intestinal microbial species in M. saltuarius carrying nematodes. In addition, the Shannon and Simpson indexes did not significantly differ between EH and EI, but both were significantly higher in EH and EI than MH and MI; this indicated that the species diversity of the intestinal microorganisms of M. saltuarius was higher in the emergence period. Overall, the species diversity and number in the beetles were higher in the emergence stage than in the mating stage. Therefore, the nematodes had a greater effect on beetles in the emergence stage than in the mating stage. Nematodes were associated with an increased number of intestinal microorganisms in the beetles and affected their diversity, but not significantly.
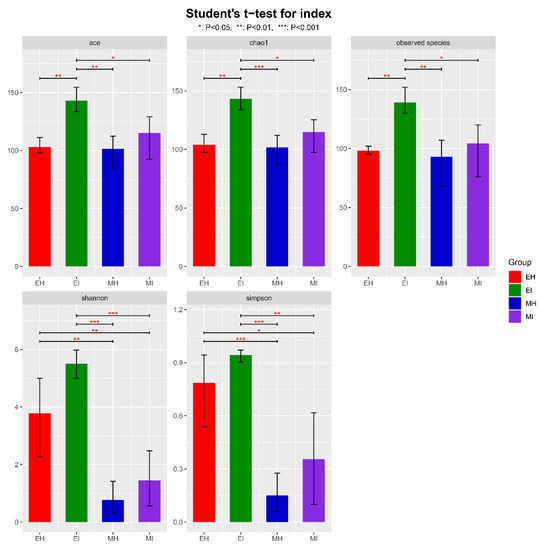
Figure 1.
Alpha diversity of bacterial communities in intestinal samples of M. saltuarius. (EH: emergence period, healthy; EI: emergence period, infested; MH: mating period, healthy; MI: mating period, infested. All of these abbreviations apply to the following figures. Student’s t-test; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).
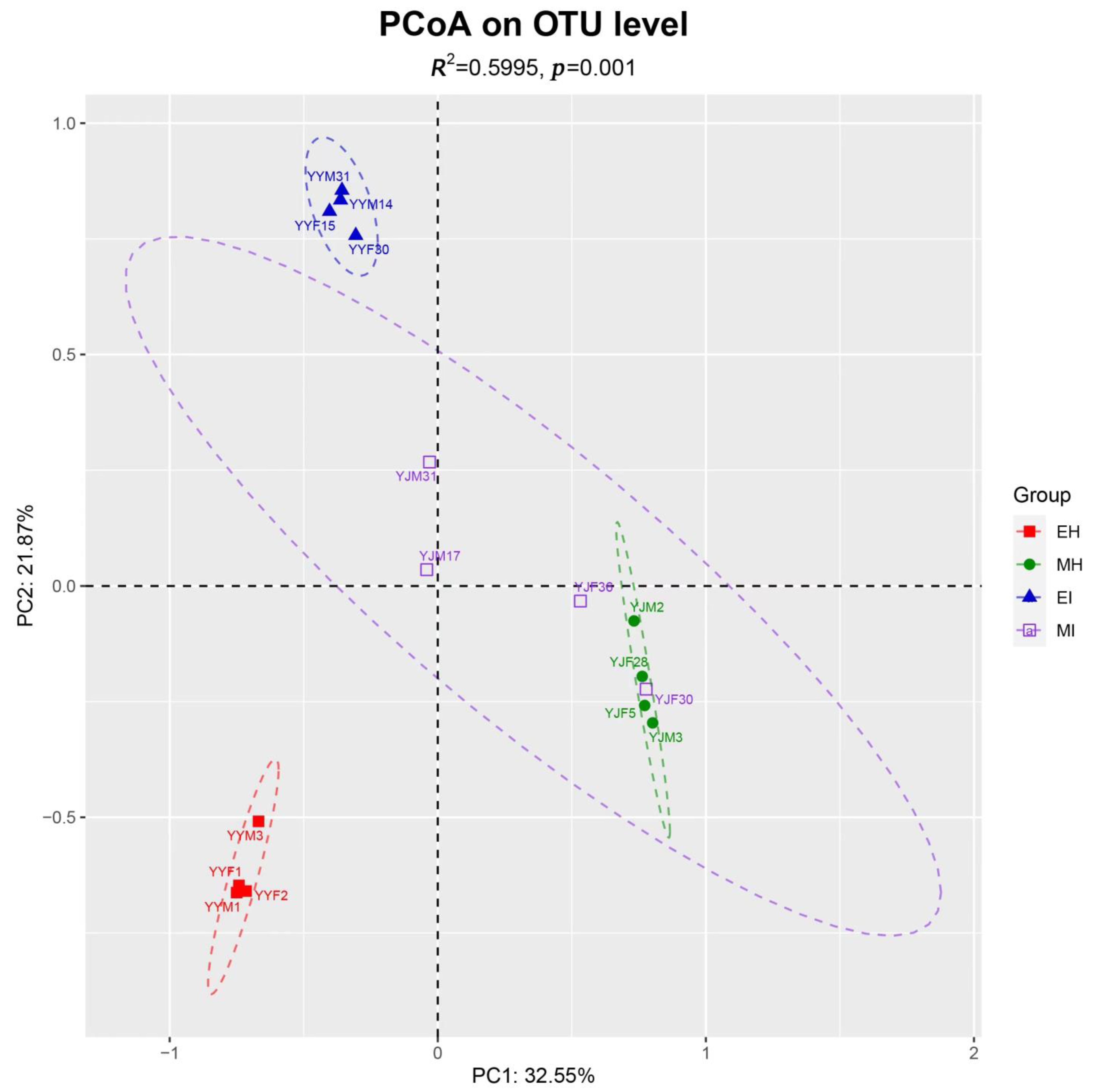
The beta diversity of the samples at the OTU level illustrated the similarities and differences in species composition and community structure. According to the main principal coordinate analysis (Figure 2), the microbial communities in all samples were grouped into four relatively independent groups (Adonis, R2 = 0.5995, p = 0.001). We found that MI was scattered, MH was basically contained in the MI group, and EH was far from EI and had no intersection. These results indicated that there were more similar microorganisms in the intestinal tract of beetles during the mating stage than during the emergence stage, and the species of these microorganisms changed as the beetles fed after emergence. Therefore, the effect of B. xylophilus on the emergence stage was greater than that on the mating stage.
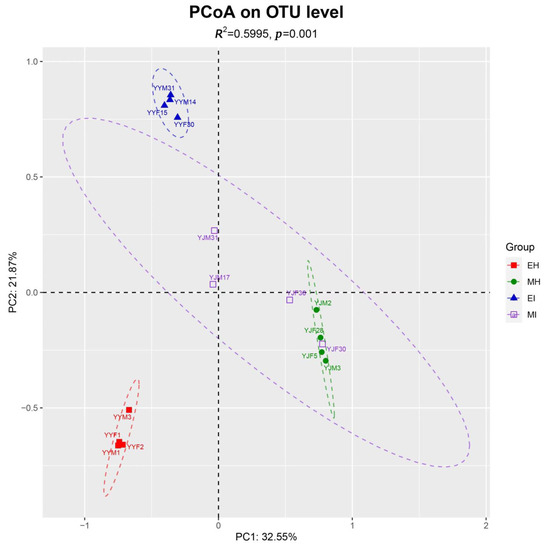
Figure 2.
Principal coordinate analysis based on Bray-Curtis distances generated from the OTU table. Differently colored ovals represent different groupings. (EH: emergence period, healthy; EI: emergence period, infested; MH: mating period, healthy; MI: mating period, infested).
3.3. Distribution of OTUs in Different Sample Populations
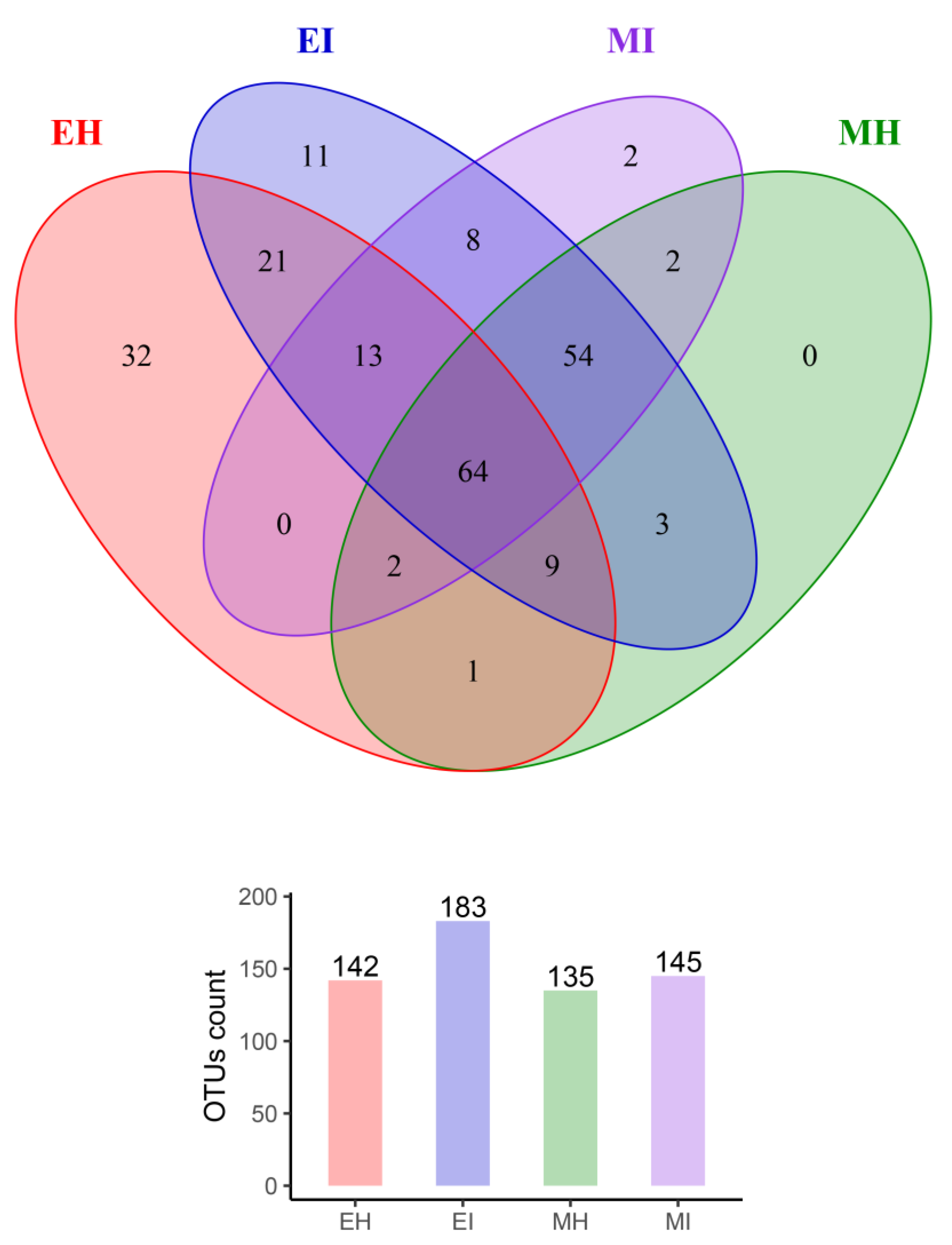
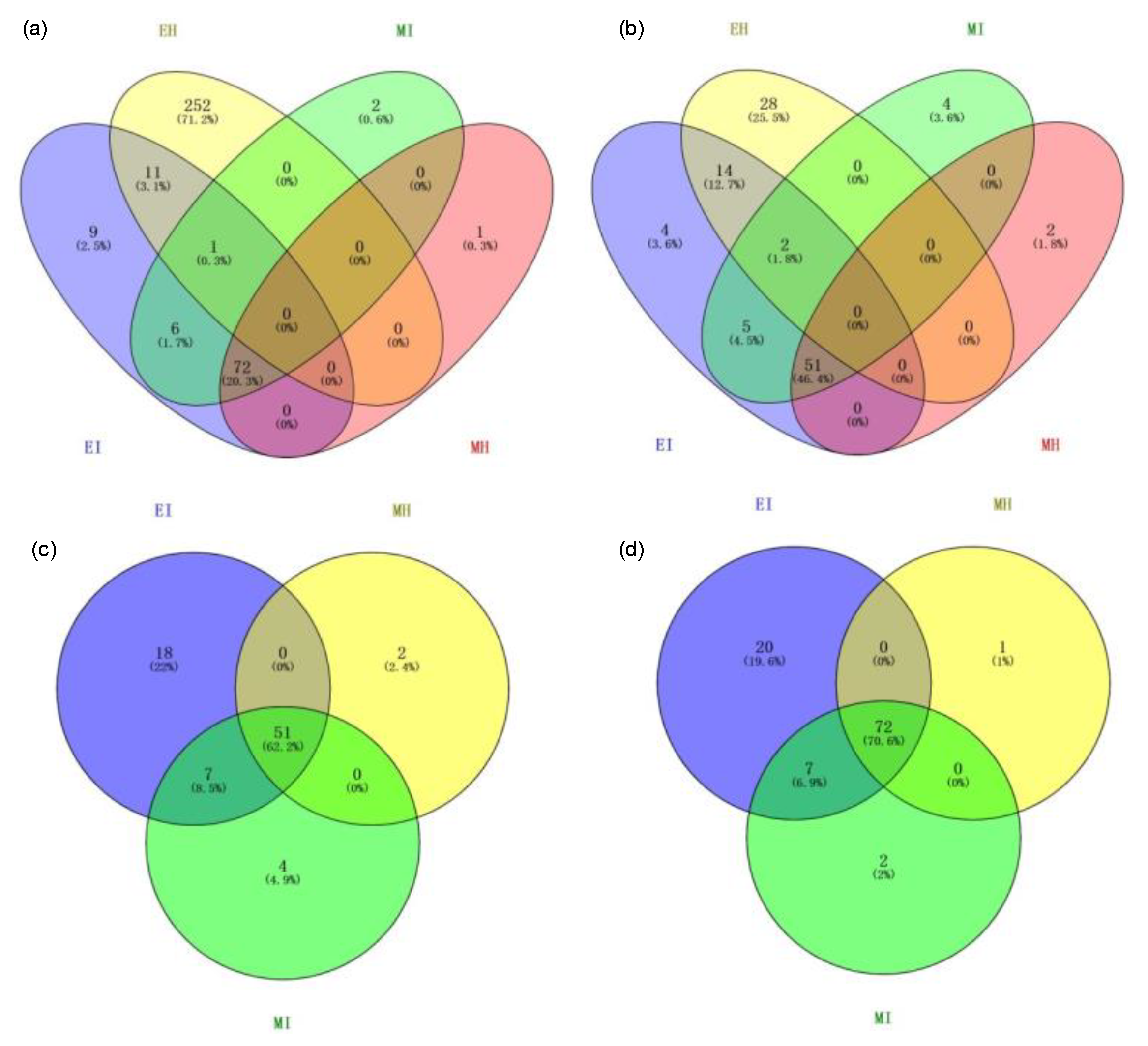
To study the similarity of microbial composition in different samples (eclosion and mating, healthy and infested), we constructed an OTU-level Venn diagram (Figure 3) and found that the number of OTUs in EI was the highest, and was 1.3, 1.3, and 1.4 times that in EH, MH, and MI, respectively. By comparing EH and EI in the eclosion stage, we observed the number of OTUs in the intestinal tract of infested M. saltuarius was much higher than that of healthy M. saltuarius in the eclosion stage.
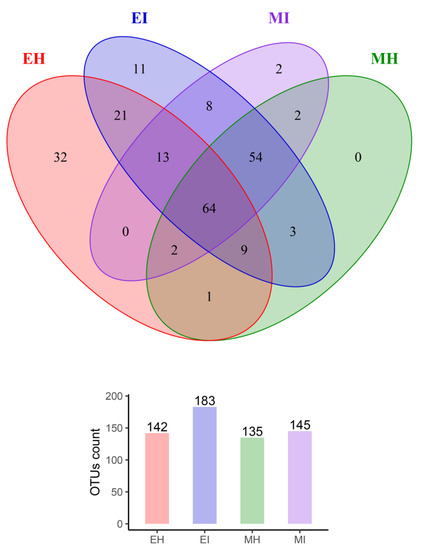
Figure 3.
Venn diagrams of shared OTUs among different sample groups. (EH: emergence period, healthy; EI: emergence period, infested; MH: mating period, healthy; MI: mating period, infested).
In total, 107 OTUs were analyzed in the two groups, 32 of which were unique to EH and 11 of which were unique to EI. Therefore, there was a great difference in the composition of intestinal bacterial communities between the two groups. The healthy population was richer than the infested population, and there was a significant difference between them. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus had a significant effect on the intestinal microbial flora during the eclosion stage. In the mating stage, the number of OTUs in the intestinal tract of the healthy group was almost the same as that of the infested group, with a total of 122 OTUs in the two groups; two of which were only found in MI, which indicated that the effect of B. xylophilus on intestinal microorganisms was reduced in the mating stage compared with the eclosion stage.
Interestingly, we found that 64 OTUs were consistently present in the intestines of all M. saltuarius at different times, and they may have colonized and become autochthonous microbes in the intestines of M. saltuarius. In addition, eight OTUs were present in the intestinal tract of infested M. saltuarius from eclosion to mating, and these colonies were all from the phyla Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and Bacteroides. These OTUs were not found in the intestinal tract of healthy M. saltuarius during eclosion and mating, and their presence likely reflects the effect of B. xylophilus on intestinal microbial flora.
3.4. Analysis of M. saltuarius Intestinal Bacterial Community Structure
All samples were annotated to 8 phyla, 14 classes, 31 orders, 53 families, 112 genera, and 174 species (Table S3). We analyzed the community composition of each sample at the phylum and genus levels. Proteobacteria and Firmicutes were the dominant phyla in the intestinal microflora of the larva (Figure S2). Proteobacteria accounted for 37% and 31.1% of EH and EI, respectively, whereas Firmicutes accounted for 48.3% and 57.1%, respectively. Proteobacteria was the dominant phylum of the beetles at the mating stage, accounting for 95.5% and 91.7% of MH and MI, respectively. Additionally, the abundance of Proteobacteria in the intestine significantly increased over time.
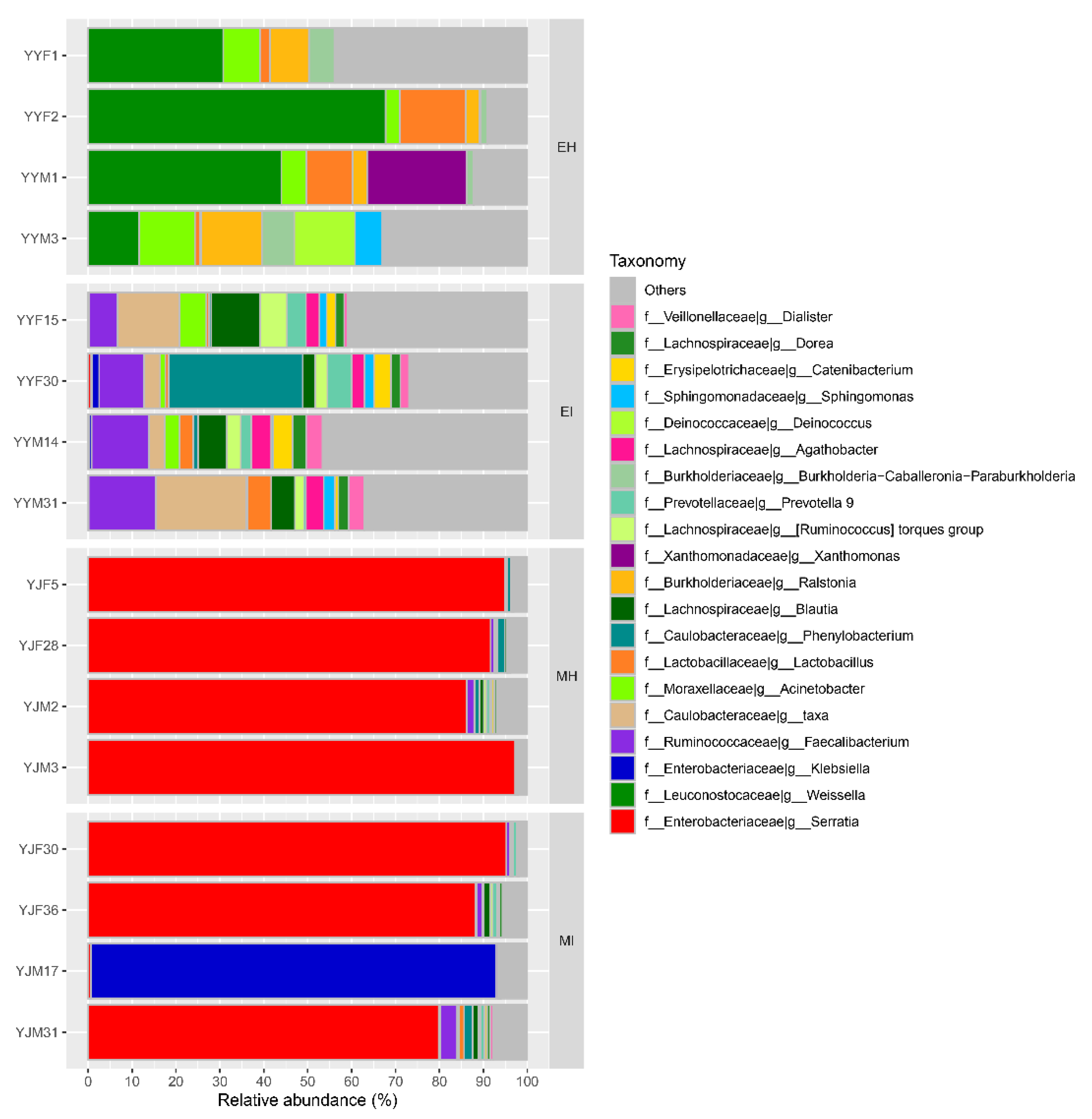
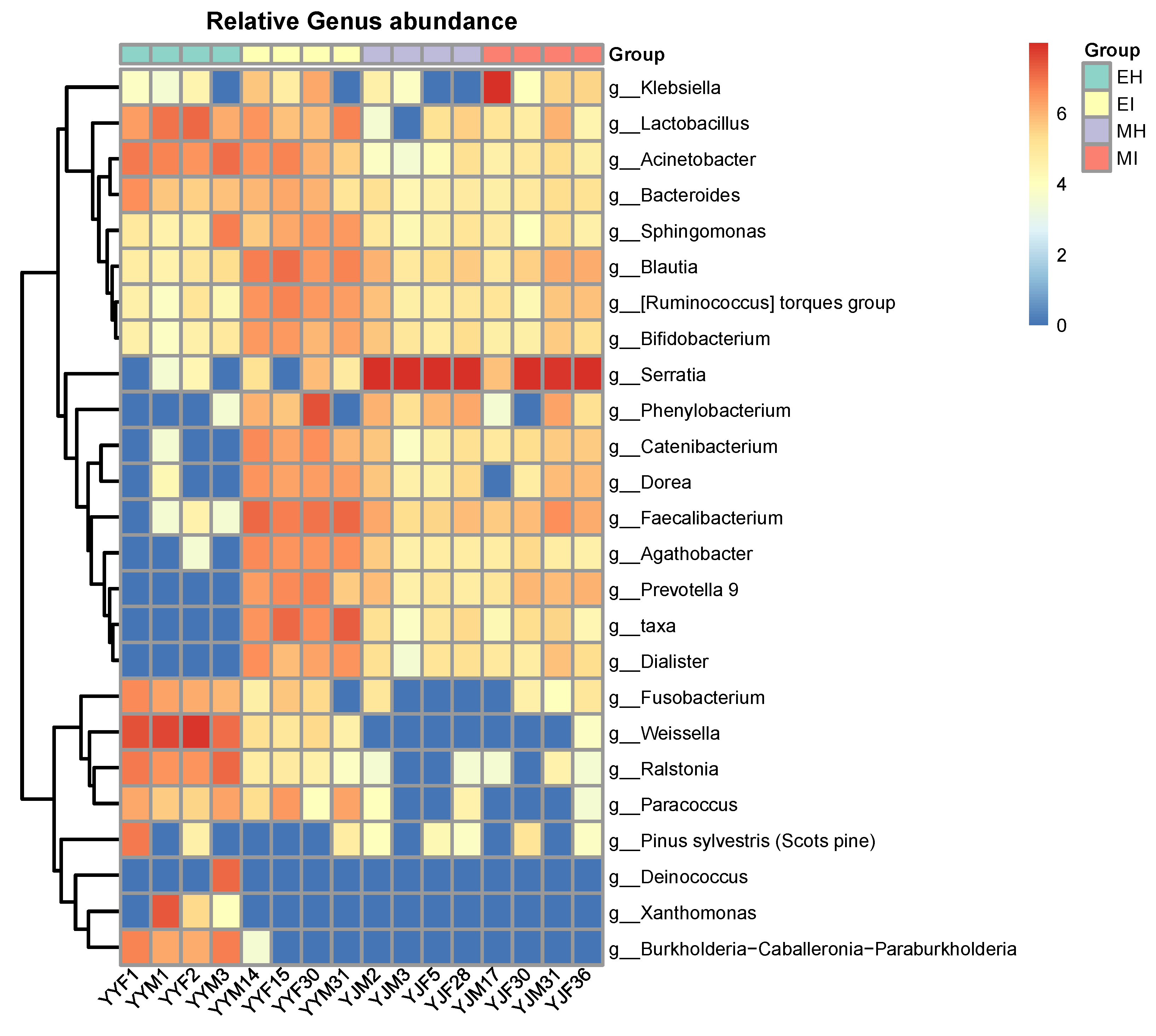
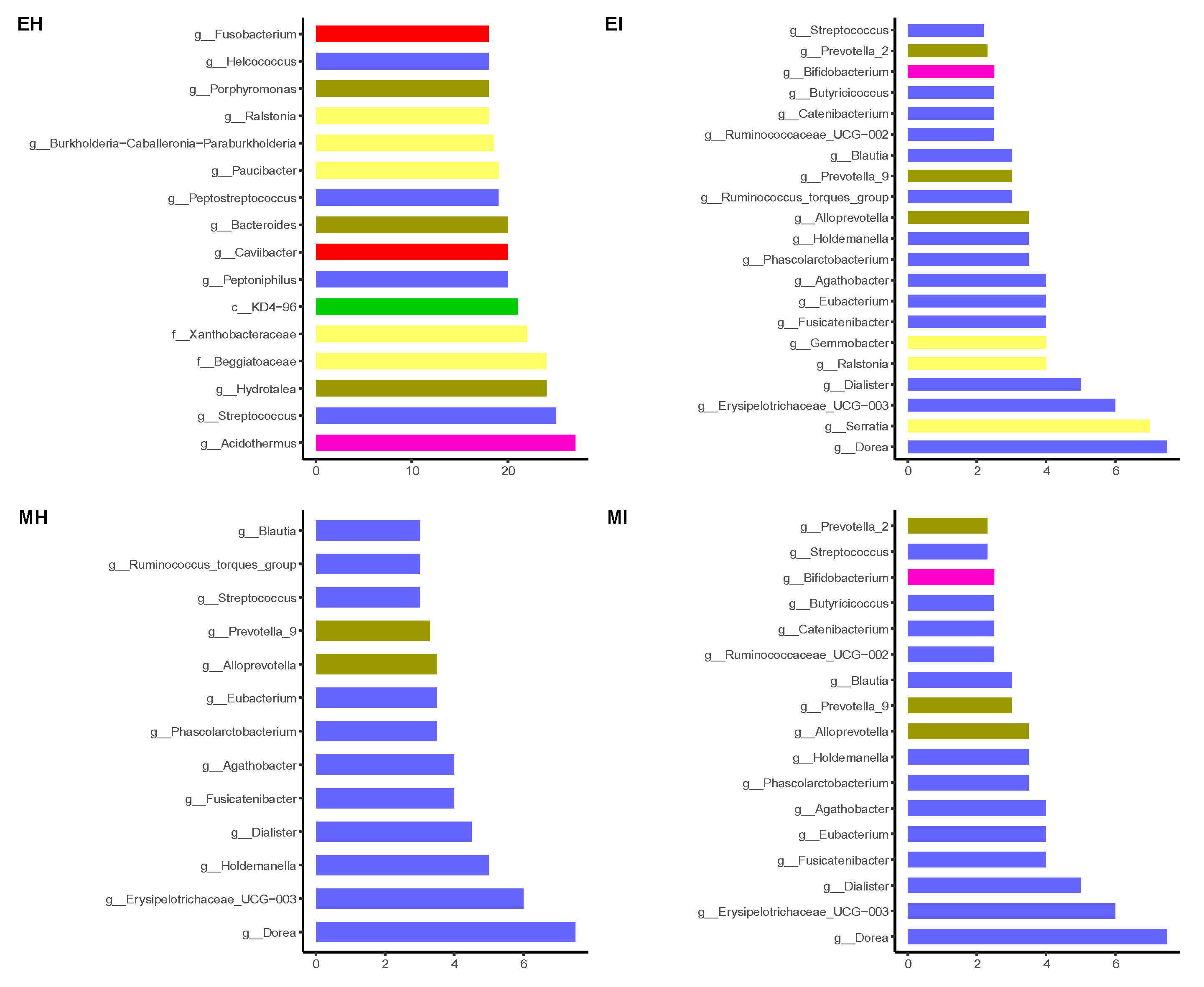
At the genus level, the intestinal bacteria genera of M. saltuarius showed different distributions in the four types of samples (Figure 4). In general, there were more genera with high abundance in M. saltuarius at the emergence stage than at the mating stage, and there were also great differences depending on whether they carried nematodes. The genera with an average abundance ≥ 2% in EH were Weissella (38.5%), Acinetobacter (7.5%), Lactobacillus (7.2%), Ralstonia (7.2%), Xanthomonas (5.7%), Burkholderia-Caballeronia-Paraburkholderia (4.1%), Deinococcus (3.5%), and Fusobacterium (2.1%). The genera with an average abundance ≥ 2% in EI were Faecalibacterium (11.3%), Phenylobacterium (8%), Blautia (6.5%), Agathobacter (3.7%), Ruminococcus_torques_group (3.5%), Prevotella (3.2%), Catenibacterium (2.8%), Acinetobacter (2.8%), Dialister (2.5%), Lactobacillus (2.5%), Dorea (2.4%), Holdemanella (2%), Bifidobacterium (2%), and Subdoligranulum (2%). The genus with an average abundance ≥ 2% in MH was Serratia (92.5%), and the genera with an average abundance ≥ 2% in MI were Serratia (66%) and Klebsiella (23.2%).
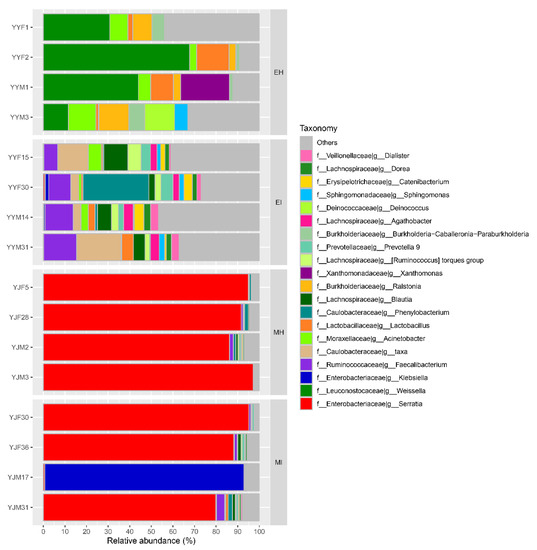
Figure 4.
Relative abundance of dominant microbial genera (abundance ≥ 2%). The relative percentage of abundance of bacterial genera is represented by different colors. (EH: emergence period, healthy; EI: emergence period, infested; MH: mating period, healthy; MI: mating period, infested).
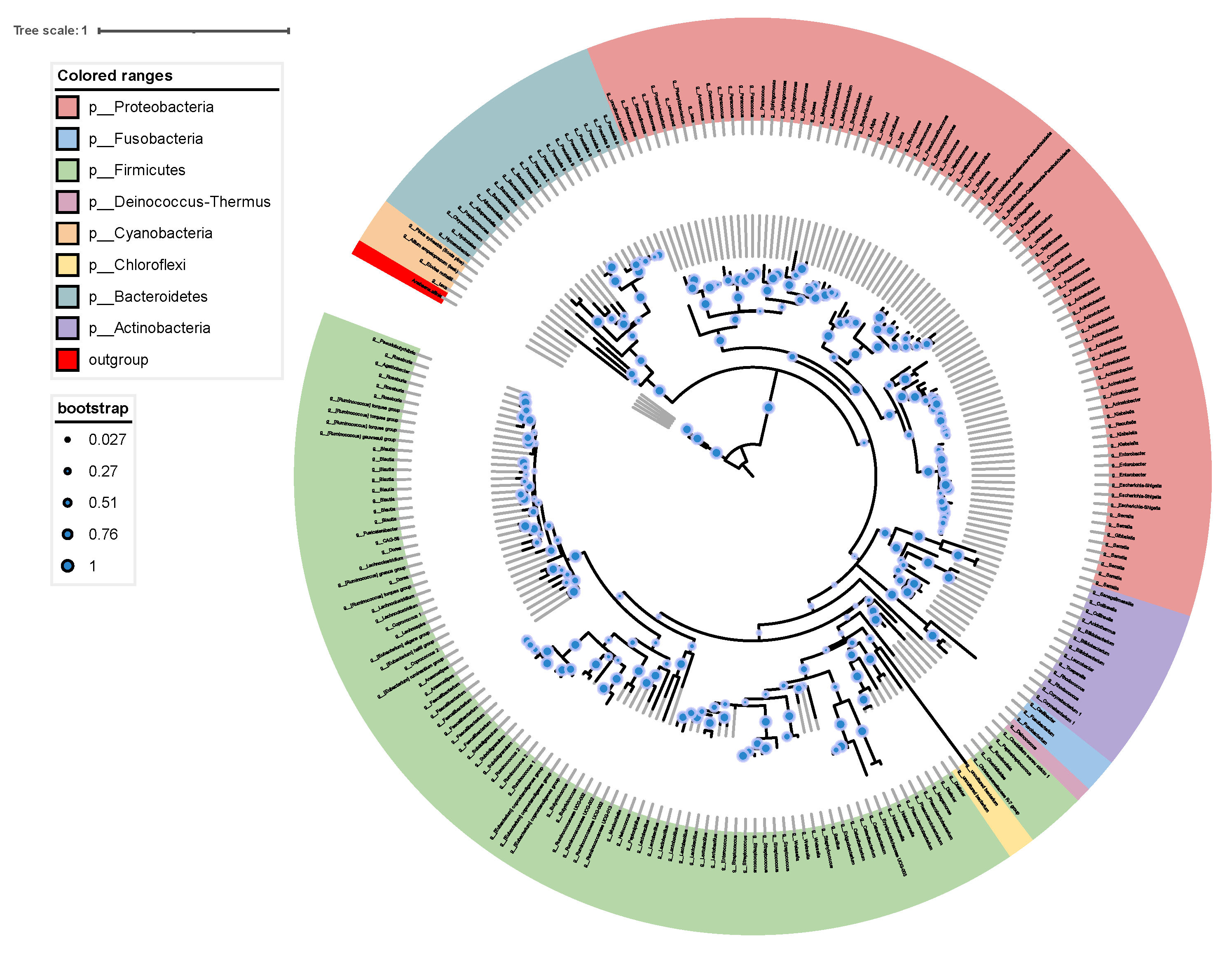
The constructed phylogenetic tree shows the relationship between the gut microbiota of M. saltuarius (Figure 5). Most of the 222 OTUs belonged to Proteobacteria and Firmicutes. A total of 82 OTUs belonged to Proteobacteria and 97 OTUs belonged to Firmicutes.
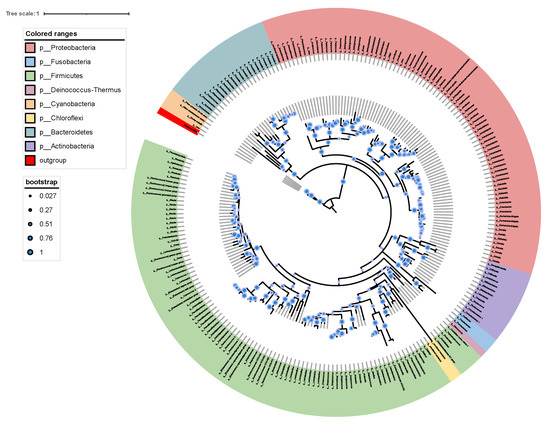
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic tree showing the placement of 222 OTUs based on 16S rDNA sequence. The phylogenetic tree was produced by maximum likelihood methods with 1000 bootstrap replicates.
3.5. Effect of B. xylophilus on Intestinal Bacteria
To explore the relationship between the intestinal microorganisms of different groups of M. saltuarius, we investigated the top 25 species of total abundance at the taxonomic level and constructed a heat map of species abundance (Figure 6). A dendrogram was prepared using the Bray-Curtis index to compare the similarity of the bacterial communities. Each column represents an individual insect, and columns were clustered according to the similarity of bacterial abundance profiles. Each row represents an OTU assigned to the genus level (Figure 6). Although microbial population shifts in both abundant and less abundant genera were detected in individuals, we found that the samples still clustered based on development and pine wood nematode presence, which resulted in highly distinct microbial communities. Individuals of the same group were associated with a common bacterial community composed of the same dominant members.
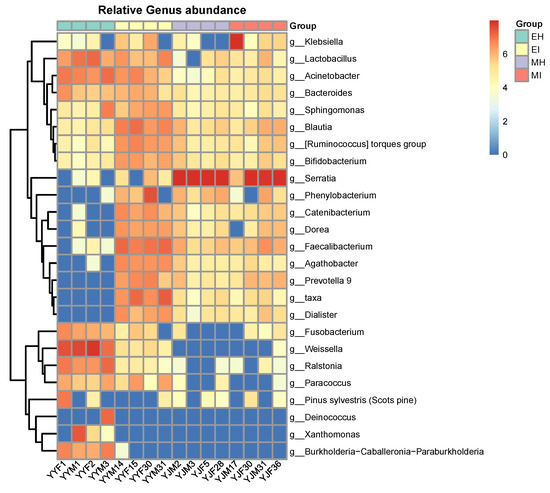
Figure 6.
Heatmap showing the relative abundance of dominant taxa in each group. Cluster analysis used the Bray-Curtis distance and complete-linkage method. Each bar or column corresponds to a group (three individuals per species). (EH: emergence period, healthy; EI: emergence period, infested; MH: mating period, healthy; MI: mating period, infested).
Abundant Serratia (MH: 92.50%; MI: 65.97%) were present in the mating stage, and some bacteria, such as Fusobacterium and Weissella, varied within the developmental stage, and therefore may represent transient microbes. Some bacterial taxa were consistent colonizers of the M. saltuarius gut, including Acinetobacter, Bacteroides, Sphingomonas, Blautia, Ruminococcus_torques_group, and Bifidobacterium. Compared with the other three groups, a highly diverse gut microbiota was found in MI, whereas MH showed significant differences compared with the other three groups. Interestingly, Catenibacterium, Dorea, Faecalibacterium, Prevotella 9, and Dialister were the most common genera in the infected M. saltuarius. However, in the healthy M. saltuarius at the eclosion stage, the abundance of these bacteria was very low. In contrast, the genera Deinococcus, Xanthomonas, and Burkholderia-Caballeronia-Paraburkholderia only existed in MH.
3.6. Dynamic Changes of Interaction Networks of M. saltuarius Intestinal Bacteria
To evaluate the dynamic changes of potential interaction networks among bacterial taxa in different groups, phylogenetic interaction networks were constructed using 44, 76, 53, and 62 key OTUs for EH, EI, MH, and MI, respectively. From the topological structure parameters of the coexistence network, it was seen that the complexity of the intestinal flora coexistence network topology differed among the four groups. The EI, MH, and MI groups shared 70.6% of the edges (72) and 62.2% of the nodes (51) (Figure 7), which indicated that there was a certain proportion of the same interactions among the three groups. Compared with the other three groups, the coexistence network of the intestinal flora of healthy M. saltuarius in the eclosion period had 252 edges (accounting for 71.2% of the coexistence network) and 28 nodes (accounting for 25.5% of the coexistence network); therefore, EH was the most complex among the four groups and had the greatest difference from the other three groups, which was consistent with the other analyses.
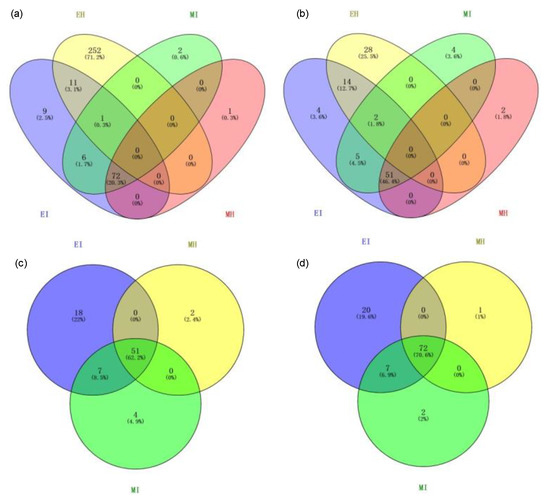
Figure 7.
Edge and node discrepancies between the four gut microbiome networks. (a,c): node discrepancies among the four gut microbiome networks; (b,d): edge discrepancies among the four gut microbiome networks. (EH: emergence period, healthy; EI: emergence period, infested; MH: mating period, healthy; MI: mating period, infested).
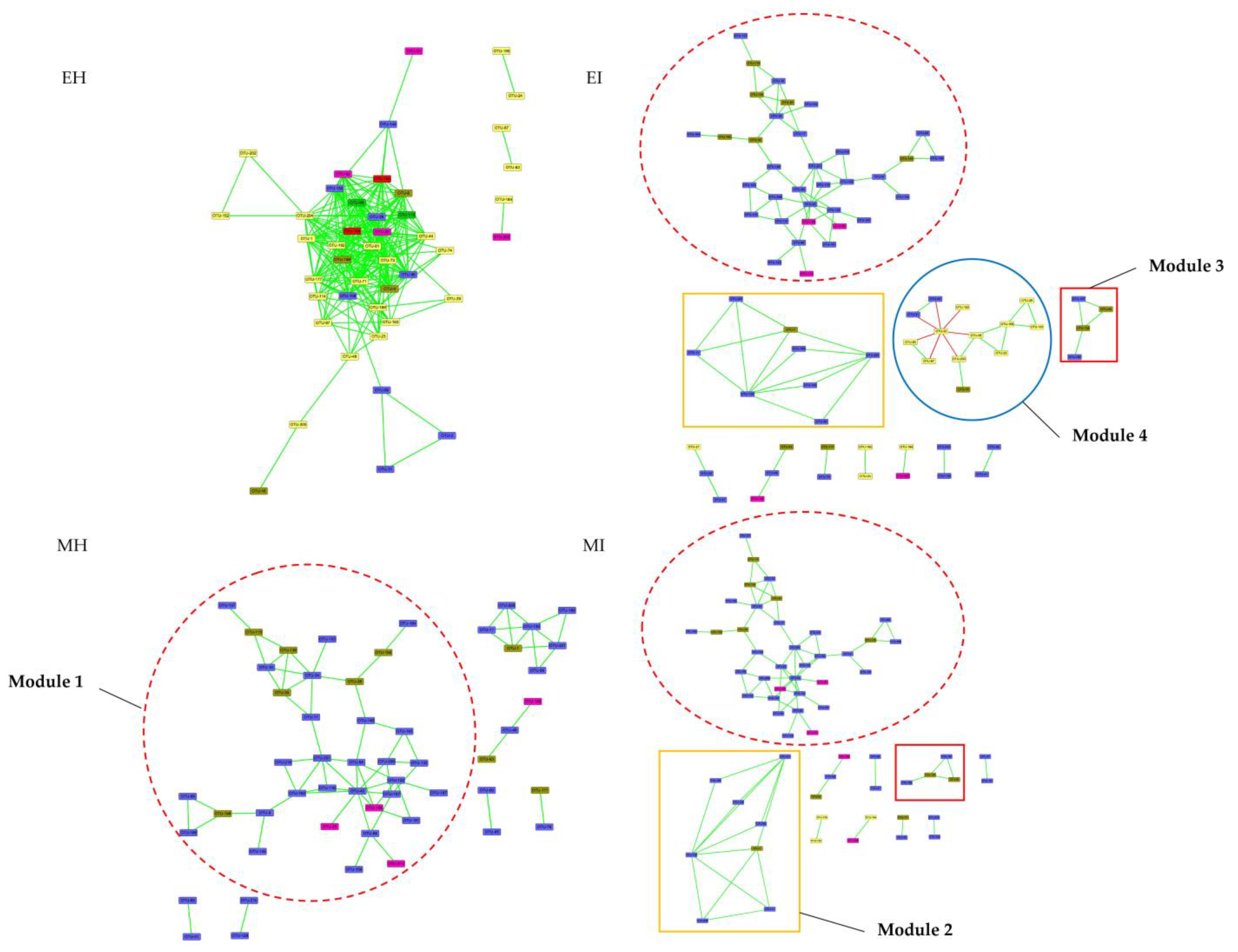
The coexistence network of intestinal flora in the four M. saltuarius groups had a modular structure, and most of the nodes were positively correlated (Figure 8). The analysis of modules containing four or more nodes showed that this phylogenetic interaction network was divided into four distinct modules, including two infected M. saltuarius-specific modules (modules 2 and 3) that were unique to the intestines of infected longicorn beetles. These two modules were mainly composed of 12 bacteria from Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes (three and nine species, respectively). Module 4 was specific to the infected gut during emergence (Table S4) and consisted of 13 bacteria from the three phyla Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and Bacteroidetes. Module 1 showed high stability in EI, MI, and MH groups, and consisted of 35 bacteria from Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria. There was a greater degree of interaction among species that were more evolutionarily divergent (from different phyla).
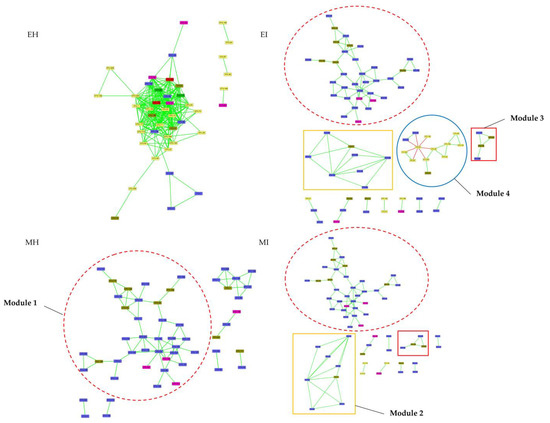
Figure 8.
Phylogenetic co-occurrence networks of intestinal bacterial microbiota in four groups. The networks were constructed at the OTU level. The edge color represents positive (green) and negative (red) correlations. The edge thickness indicates the correlation values, and only the high-confidence interactions with absolute sparse correlations greater than 0.55 were selected. (EH: emergence period, healthy; EI: emergence period, infested; MH: mating period, healthy; MI: mating period, infested).
Based on the average degree and connectivity of the nodes, the importance of the nodes in the four groups of intestinal flora coexistence networks was ranked (Figure 9, Table S5). Streptococcus had a high degree in the four groups of intestinal flora coexistence networks, and its presence was strongly correlated with other species. In this study, the important nodes in the coexistence networks of the intestinal flora of the two groups of infected M. saltuarius were highly similar. Proteobacteria were more important in the emergence period and were closely associated with the presence of other species, but less important in the mating period. The phyla Fusobacteria and Chloroflexi only showed a strong association with other species in the eclosion stage of M. saltuarius.
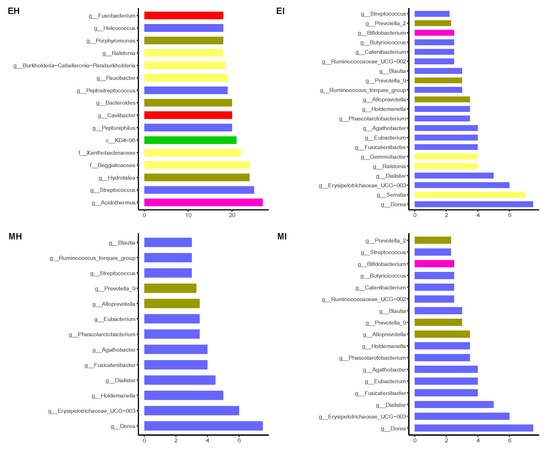
Figure 9.
Ranking of important nodes in the gut microbiome network. (EH: emergence period, healthy; EI: emergence period, infested; MH: mating period, healthy; MI: mating period, infested).
3.7. Functional Predictions for M. saltuarius
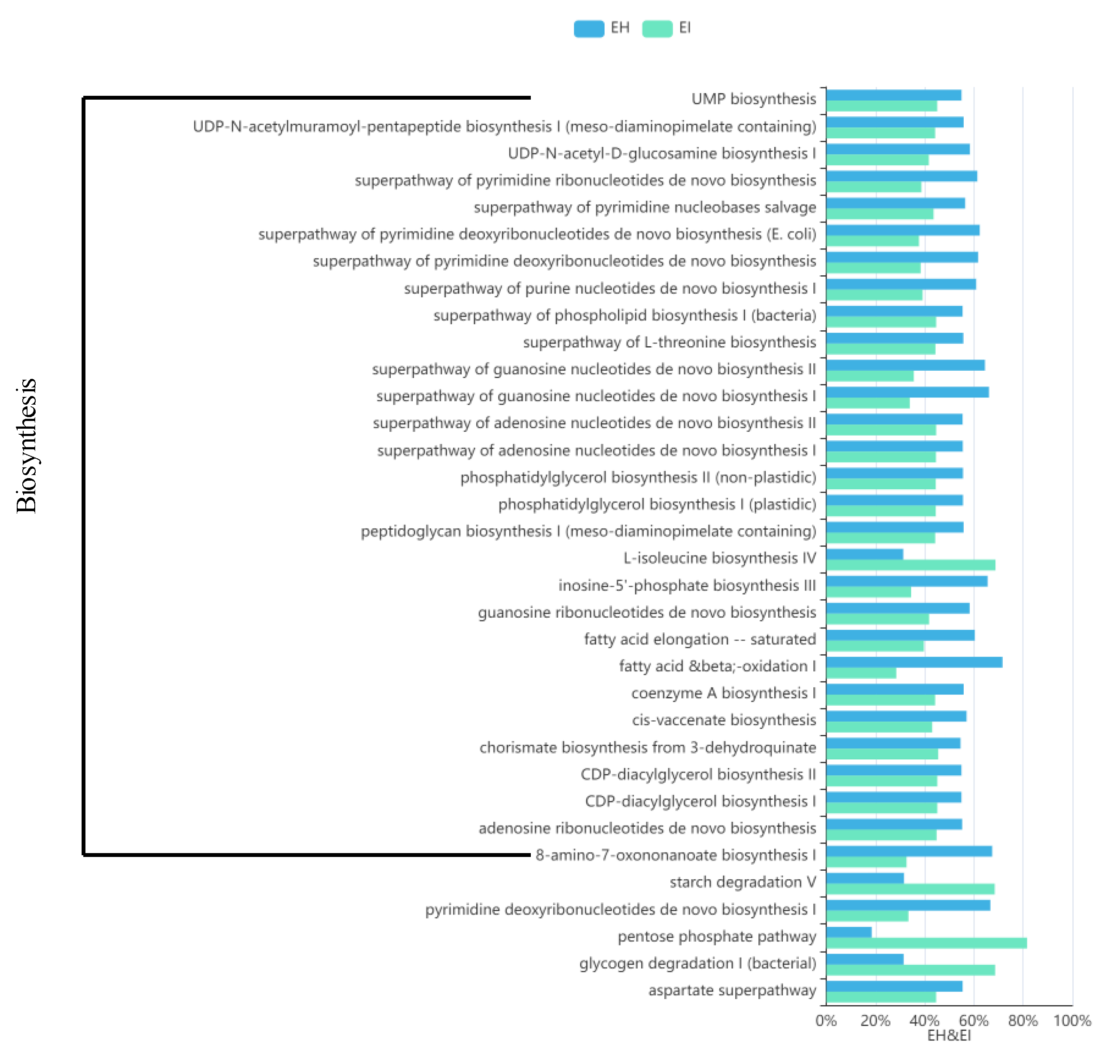
A comparison of the differences between the top 100 pathways in abundance revealed that 34 pathways showed significant differences, and 29 of the 34 pathways belonged to the “Biosynthesis” pathway (Figure 10). EI and EH had the largest difference in the levels of association with MetaCyc “Biosynthesis” pathways. EI was significantly less associated with the primary biosynthesis pathways than EH, but other secondary pathways related to biosynthesis, such as glycogen degradation, the pentose phosphate pathway, and starch degradation, were significantly more associated with EI than EH.
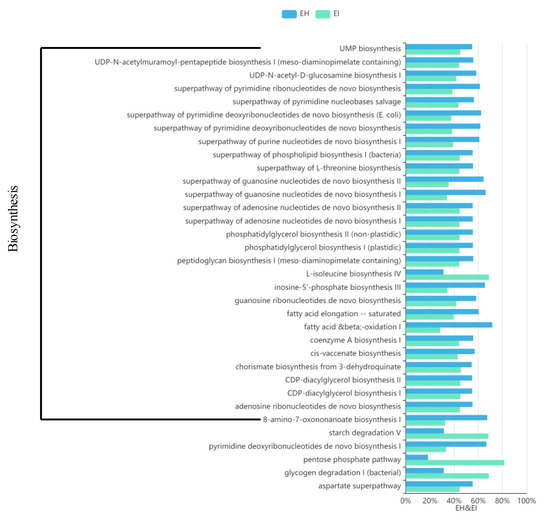
Figure 10.
Map of predicted MetaCyc functional pathway differences. The abscissa represents the abundance of functional pathways (relative abundance); the left side of the ordinate shows the MetaCyc functional pathway. (EH: emergence period, healthy; EI: emergence period, infested).
4. Discussion
Some studies have reported the intestinal bacterial composition of the genus Monochamus [17,27,28] and analyzed the microbial composition of infected pine tree pupal chambers and of the trachea of M. alternatus harboring B. xylophilus [29]. However, as far as we know, to date, there have been no studies on the interaction between B. xylophilus and the intestinal flora of the vector M. saltuarius. This study is the first to describe and analyze the effects of B. xylophilus on the intestinal microbiota of M. saltuarius based on high-throughput sequencing. To continuously observe the correlation between B. xylophilus and intestinal flora, we selected two time points for comparative analysis, the emergence and mating periods, and provided a comprehensive overview of changes in the intestinal microbiome of M. saltuarius affected by B. xylophilus.
Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria are the dominant phyla in the intestinal tract of M. saltuarius. These isolates were previously found to be common in the genus Monochamus [26,27]. The presence of a variety of bacteria, including Firmicutes and Proteobacteria, indicates their ecological importance [30]. Most of the bacteria that belong to these phyla are facultative anaerobes that ferment sugars and tolerate acidic environments. The identified bacterial isolates are commonly found in soil and water, and a few have clinical relevance to humans. It is not uncommon for these bacteria to occur in insect intestines, which was previously described.
Our study showed that the intestinal flora was not evenly distributed because of the activities of B. xylophilus and the changes in the living environment of M. saltuarius. At the same developmental stage, there were greater proportions of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in the infected M. saltuarius, and some of the bacteria in these two phyla became the key species in the coexistence network of intestinal flora; moreover, they represented a unique module in the phylogenetic interaction network of infected longhorn beetles. Additionally, the intestinal microflora of M. saltuarius substantially differed between the mating and eclosion stages. Proteobacteria and Firmicutes were dominant in the emergence stage of the beetle; however, the abundance of Firmicutes sharply decreased in the mating stage, and Proteobacteria became the main phyla and far exceeded other phyla in abundance. Food and environmental factors can affect the diversity of the intestinal microorganisms of insects [31]. During the emergence period, M. saltuarius had just emerged from the pupal chamber and had not yet eaten, and the intestinal microorganisms are more diverse. With the change in the growth environment and continuous feeding, the intestinal microorganisms gradually stabilized and became single species.
At lower taxonomic levels, differences in gut bacterial composition between samples were more pronounced. In infected longhorn beetles in the eclosion period, Faecalibacterium, Phenylobacterium, Blautia, Agathobacter, Ruminococcus_torques_group, Catenibacterium, Acinetobacter, Dialister, Dorea, Holdemanella, Bifidobacterium, and Subdoligranulum exhibited higher abundances than in the other three groups. Interestingly, these groups are not mentioned in the other literature on the intestinal microbiota of Monochamus. Most of these bacteria are related to digestion. Some studies have found that Faecalibacterium is a beneficial gut microbe in humans and has anti-inflammatory properties [32,33].
Enterobacteriaceae accounted for more than 90% of the total intestinal microflora of mating M. saltuarius, and was also the dominant family (52.2%) in the trachea of M. galloprovincialis and M. alternatus [34], and this finding was consistent with a previous report on M. alternatus [28]. Among Enterobacteriaceae, Serratia and Klebsiella were most abundant. Serratia is found in more than 70 insect species [35], including crickets, grasshoppers, bees, aphids, and fruit flies [36]. Most Serratia form mutualistic symbioses with their hosts. In aphids, S. symbiotica strains play a key nutritional role by providing vitamins and amino acids to the host [37]. The nutritional role of Serratia has mostly been assessed in the context of obligate mutualism. The discovery of this bacterium in the gut of M. saltuarius carrying nematodes provides a new perspective on the potential role of Serratia. A strain of S. marcescens isolated from the gut of Periplaneta americana may have the ability to protect the host against disease by producing secondary metabolites. Prodigiosin, a red secondary metabolite produced by Serratia can induce apoptosis of HeLa cells, and its mechanism may be related to the up-regulation of Bax and Caspase-3, down-regulation of Bcl-2 level, and triggering of the exogenous apoptosis signaling pathway [38]. In addition, large amounts of prodigiosin have also been detected in the gut of cockroaches [39,40]. Therefore, Serratia may have the ability to protect the host against disease by producing secondary metabolites.
Intestinal bacterial diversity and its metabolic role in functional metabolism have been studied in 12 species of three subfamilies of Araneidae from five states in India. Among the spider species, Prevotella spp. was only observed in Cyclosa mulmeinensis [41], which indicated that Prevotella spp. may exhibit some host selectivity. Although a high abundance of Serratia was not detected in our samples during the emergence period, Serratia was dominant in the midgut of adult M. alternatus reared in the laboratory. Because we did not detect the microorganisms in the living environment of M. saltuarius, we could not confirm whether Serratia originated from the pupal chamber or from feeding after eclosion. However, Enterobacteriaceae eventually occupied the niche and became the absolute dominant flora in the intestinal tract during mating, which needs further study.
To evaluate the effect of B. xylophilus on the dynamics of the potential interaction network of intestinal bacteria, phylogenetic interaction networks were constructed for each of the four groups. The phylogenetic interaction networks were mainly divided into four different modules, including two modules specific to infected longhorn beetles (modules 2 and 3), one module only appearing in the early stage of infection (module 4), and a relatively stable module 1.
Module 1 was made up of 35 OTUs that belonged to the three phyla Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria, and Firmicutes mainly included Ruminococcaceae and Lachnospiraceae. These two bacterial families have a large number of glycoside hydrolase genes and specific metabolic pathways to cleave the cellulose and hemicellulose components of complex plant material and degrade a wide variety of polysaccharides [42,43]. Therefore, Ruminococcaceae and Lachnospiraceae are often found in the intestines of herbivores, such as the rumen of cattle, and in red colobus (Procolobus gordonorum) [44,45]. Although Ruminococcaceae and Lachnospiraceae are both diverse groups, they share a common role as active plant degraders. Bacteroidetes mainly included Prevotellaceae. Some researchers have found, through co-occurrence network analysis, that Prevotellaceae and Ruminococcaceae were the central nodes of the luminal microbial network. Functional analyses demonstrated that Prevotella, Veillonellaceae, Lachnospiraceae, and Ruminococcaceae were positively correlated with gene functions related to amino acid, energy, cofactor, and vitamin metabolism [46]. Therefore, module 1 is probably related to food digestion and absorption, which is indispensable for M. saltuarius.
Module 2 consisted of eight OTUs that belonged to Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes. In Firmicutes, most OTUs belonged to Lachnospiraceae and Streptococcaceae. A study showed that, after long-term high-fat feeding, intestinal inflammation occurs in mice, and Lachnospiraceae and Streptococcaceae abundance increases [47]. This module also included Prevotellaceae, which are often considered opportunistic pathogens. We speculate that module 2 plays a role in regulating intestinal performance.
Module 3 was composed of four OTUs from Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, and it was a unique module in the infected M. saltuarius during emergence. Prevotella is a non-cellulosic carbohydrate-degrading bacterium that digests cell wall polysaccharides such as xylan [48] and also has protease activity. It is a major resident of the bark beetle gut microbiota [49], and its abundance is positively correlated with dietary fiber intake. However, it is also considered an indicator of certain diseases. Qi et al. [50] showed intestinal dysbiosis in gastric cancer patients associated with peripheral cellular immunity, and the combination of Veillonella, Streptococcus, and Lachnospira was sufficient to distinguish gastric cancer patients from healthy subjects. CD3+ T cell counts were associated with the relative abundance of Lactobacillus and Streptococcus, whereas CD3+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, and NK cells were associated with Lactobacillus.
The presence of module 2 may be associated with microbial dysbiosis. Lachnospira taxa can produce beneficial metabolites for their hosts and are involved in carbohydrate metabolism; associated fermentation leads to the production of acetate and butyrate, which provide the main source of energy for the host. However, the increase in Lachnospira may be related to the imbalance of the microbial ecology. Wang et al. [51] confirmed that the composition and function of intestinal flora differed between people with chronic spontaneous urticaria and healthy people, and the relative abundance of Faecalibacterium, Lachnospira, Prevotella, and Bifidobacterium increased in the chronic spontaneous urticaria patients. Interestingly, we also detected similar changes in the number of bacteria in the intestines of M. saltuarius carrying pine wood nematodes. The flora coexistence network analysis showed that there was a synergistic effect among the intestinal flora of M. saltuarius, and the colonies in the same module showed the same or opposite trends. Additionally, changes in lower abundance colonies were easier to detect, whereas changes in the higher abundance colonies were often overlooked. Faecalibacterium and Bifidobacterium had high abundances in EH and EI; therefore, it is possible that these two bacteria cooperate with module 3.
Module 4 was made up of 13 OTUs that belonged to the three phyla Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and Bacteroidetes. This module only appeared in EI. Serratia (Proteobacteria) and many other bacteria showed a mutual exclusion relationship because Serratia is an opportunistic pathogen. A previous study suggested that Rhodobacteraceae could be applied to shrimp to reduce the influence of cold stress [52]. Moreover, Acinetobacter have been shown to confer nutritional benefits, including nitrogen removal and intestinal nutrient substance metabolism [53].
The B. xylophilus microbiome may also have an impact on the M. saltuarius gut microbiota [54], which is currently attributed to changes in nematodes that may be due to nematode microbes. This needs to be clarified by further research.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we described the intestinal bacterial communities of adult M. saltuarius and analyzed the differences in the intestinal bacterial communities according to the presence of B. xylophilus and the developmental stage of M. saltuarius. The results showed that the microflora abundance and diversity were increased in the intestinal tract of M. saltuarius carrying nematodes. Additionally, some bacteria of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes played unique roles in the intestinal tract of M. saltuarius and were only found in the intestinal tract of beetles carrying pine wood nematodes. In the future, we will study the functions of these intestinal bacteria.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f13101673/s1, Table S1: OTU table. Table S2: Alpha-diversity of bacterial communities in intestine samples of M. saltuarius. Table S3: taxonomy-summary. Table S4: Summary of annotation information of node OTUs from biologically important modules in the phylogenetic co-occurrence networks of three categories. Table S5: the importance of the nodes in the four groups of intestinal flora coexistence networks was ranked. Figure S1. Rarefaction curves of bacterial communities in the intestinal samples of M. saltuarius. Figure S2. Relative abundance of dominant microbial phyla (abundance ≥ 1%). The relative percent abundance of bacterial genera is represented by different colors.
Author Contributions
X.-Z.W. and L.-F.W. designed the study; X.W. and Y.-F.C. performed the experiments and analyzed the results; S.-F.Z. and Y.-L.Z. assisted with the research; X.-Z.W. and X.W. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Non-profit Research Institution of CAF: CAFYBB2018SZ006.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hao, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.Y.; Nazaire, M.; Wei, X.X.; Wang, X.Q. Molecular phylogenetics and evolutionary history of sect. Quinquefoliae (Pinus): Implications for Northern Hemisphere biogeography. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2015, 87, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, R.A.; Canales, J.; Muñoz-Hernández, C.; Granados, J.M.; Ávila, C.; García-Martín, M.L.; Cánovas, F.M. Understanding developmental and adaptive cues in pine through metabolite profiling and co-expression network analysis. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3113–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B.; Kim, S.M.; Kang, M.K.; Kuzuyama, T.; Lee, J.K.; Park, S.C.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, S.U. Regulation of resin acid synthesis in Pinus densiflora by differential transcription of genes encoding multiple 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase and 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate reductase genes. Tree Physiol. 2009, 29, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, C.S.; Moon, S.C.; Lee, M.S. Antioxidant, antimutagenic, and antitumor effects of pine needles (Pinus densiflora). Nutr. Cancer 2006, 56, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Marescalchi, O.; Francardi, V.; Mantovani, B. Taxonomy and phylogeny of European Monochamus species: First molecular and karyological data. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2005, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, H. New host plants and new vector insects of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus were found in Liaoning Province. For. Pest Dis. 2018, 37, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, W.S.; Koo, H.N.; Yun, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, D.H.; Kang, W.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.K.; Han, J.H.; Kwon, Y.D.; et al. Electron beam-induced sterility and inhibition of ovarian development in the sakhalin pine longicorn, Monochamus saltuarius (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-J.; Brey, P.T. How microbiomes influence metazoan development: Insights from history and Drosophila modeling of gut-microbe interactions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 29, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, H.; Schmid-Hempel, P. Socially transmitted gut microbiota protect bumble bees against an intestinal parasite. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19288–19292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummel, T.; Ching, A.; Seroude, L.; Simon, A.F.; Benzer, S. Drosophila lifespan enhancement by exogenous bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12974–12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, J.R.; Breznak, J.A. Physiology and nutrition of Treponema primitia, an H2/CO2-acetogenic spirochete from termite hindguts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Tokuda, G. Cellulolytic systems in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 609–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, G.; Defaye, A.; Erkosar, B.; Hols, P.; Royet, J.; Leulier, F. Lactobacillus plantarum promotes Drosophila systemic growth by modulating hormonal signals through TOR-dependent nutrient sensing. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Hayatsu, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Nagayama, A.; Tago, K.; Fukatsu, T. Symbiont-mediated insecticide resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, A.; Yuval, B.; Jurkevitch, E. Gut bacterial communities in the Mediterranean fruit fly (Ceratitis capitata) and their impact on host longevity. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.C.; Kim, S.H.; You, H.; Kim, B.; Kim, A.C.; Lee, K.A.; Yoon, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, W.J. Drosophila microbiome modulates host developmental and metabolic homeostasis via insulin signaling. Science 2011, 334, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Shi, F.M.; Pei, J.H.; Hou, Z.H.; Zong, S.X.; Ren, L.L. Gut bacteria associated with Monochamus saltuarius (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) and their possible roles in host plant adaptations. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. CoNet app: Inference of biological association networks using Cytoscape. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.; Alm, E.J. Inferring correlation networks from genomic survey data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.D.; Gloor, G.B. Mutual information is critically dependent on prior assumptions: Would the correct estimate of mutual information please identify itself? Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricotta, C.; Podani, J. On some properties of the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity and their ecological meaning. Ecol. Complex. 2017, 31, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hao, D.; Wei, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, T. Bacterial communities associated with the pine wilt disease insect vector Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) during the larvae and pupae stages. Insects 2020, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, M.; Raffa, K.F.; Luo, Q.; Fu, H.; Wu, S.; Liang, G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F. Bacterial communities associated with the pine wilt disease vector Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) during different larval instars. J. Insect Sci. 2017, 17, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Koski, T.M.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J. Invasion History of the Pinewood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Influences the Abundance of Serratia sp. in Pupal Chambers and Tracheae of Insect-Vector Monochamus alternatus. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 856841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.K.; Moran, N.A. Gut microbial communities of social bees. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Huang, Y.P. Symbiosis between gut microbiota and insects. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2008, 45, 687–693. [Google Scholar]
- Prévoteau, A.; Geirnaert, A.; Arends, J.; Lannebère, S.; Van de Wiele, T.; Rabaey, K. Hydrodynamic chronoamperometry for probing kinetics of anaerobic microbial metabolism—Case study of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, H.; Pigneur, B.; Watterlot, L.; Lakhdari, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Gratadoux, J.J.; Blugeon, S.; Bridonneau, C.; Furet, J.P.; Corthier, G.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16731–16736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, M.; Pereira, A.; Matos, P.; Henriques, J.; Vicente, C.; Aikawa, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Nascimento, F.; Mota, M.; Correia, A.; et al. Bacterial community associated to the pine wilt disease insect vectors Monochamus galloprovincialis and Monochamus alternatus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkenawy, N.M.; Yassin, A.S.; Elhifnawy, H.N.; Amin, M.A. Optimization of prodigiosin production by Serratia marcescens using crude glycerol and enhancing production using gamma radiation. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 14, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, M. The Prokaryotes: Proteobacteria: Gamma Subclass; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 6, pp. 219–244. [Google Scholar]
- Renoz, F.; Pons, I.; Vanderpoorten, A.; Bataille, G.; Noël, C.; Foray, V.; Pierson, V.; Hance, T. Evidence for gut-associated Serratia symbiotica in wild aphids and ants provides new perspectives on the evolution of bacterial mutualism in insects. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.B.; Shen, J.; Ou, P.Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Chu, F.J.; Wang, J.; Jin, X.B. Prodigiosin isolated from Serratia marcescens in the Periplaneta americana gut and its apoptosis—Inducing activity in HeLa cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 3377–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbanoglu, E.B.; Ozdal, M.; Ozdal, O.G.; Algur, O.F. Enhanced production of prodigiosin by Serratia marcescens MO-1 using ram horn peptone. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H.; Chen, W.C. Enhanced production of prodigiosin-like pigment from Serratia marcescens SMΔR by medium improvement and oil-supplementation strategies. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, K.; Tyagi, I.; Kumar, V. Insights into the gut bacterial communities of spider from wild with no evidence of phylosymbiosis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5913–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, A.; Stewart, L.; Blanchard, J.; Leschine, S. Untangling the genetic basis of fibrolytic specialization by Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae in diverse gut communities. Diversity 2013, 5, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulc, J.M.; Antonopoulos, D.A.; Miller, M.E.B.; Wilson, M.K.; Yannarell, A.C.; Dinsdale, E.A.; Edwards, R.E.; Frank, E.D.; Emerson, J.B.; Wacklin, P.; et al. Gene-centric metagenomics of the fiber-adherent bovine rumen microbiome reveals forage specific glycoside hydrolases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1948–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barelli, C.; Albanese, D.; Donati, C.; Pindo, M.; Dallago, C.; Rovero, F.; Cavalieri, D.; Tuohy, K.M.; Hauffe, H.C.; De Filippo, C. Habitat fragmentation is associated to gut microbiota diversity of an endangered primate: Implications for conservation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Su, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Liu, D.; Zheng, H.; et al. Metatranscriptomic analyses of plant cell wall polysaccharide degradation by microorganisms in the cow rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; Lee, Y.K.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H. Spatial heterogeneity and co-occurrence of mucosal and luminal microbiome across swine intestinal tract. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Ishaq, S.L.; Zhao, F.Q.; Wright, A.D.G. Colonic inflammation accompanies an increase of β-catenin signaling and Lachnospiraceae/Streptococcaceae bacteria in the hind gut of high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 35, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Duncan, S.H.; Louis, P.; Forano, E. Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Roblero, C.I.; Hernández-García, J.A.; Gonzalez-Escobedo, R.; Soto-Robles, L.V.; Rivera-Orduña, F.N.; Zúñiga, G. Structure and dynamics of the gut bacterial microbiota of the bark beetle, Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) across their life stages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.F.; Sun, J.N.; Ren, L.F.; Cao, X.L.; Dong, J.H.; Tao, K.; Guan, X.M.; Cui, Y.N.; Su, W. Intestinal microbiota is altered in patients with gastric cancer from Shanxi Province, China. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yi, W.; He, L.; Luo, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; Long, H.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Q. Abnormalities in gut microbiota and metabolism in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 691304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Jin, Z.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, D. Strain-specific changes in the gut microbiota profiles of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in response to cold stress. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; He, Y.L.; Hughes, J.; Zhang, X.F. Heterotrophic nitrogen removal by a newly isolated Acinetobacter calcoaceticus HNR. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5194–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Berg, M.; Dierking, K.; Félix, M.A.; Shapira, M.; Samuel, B.S.; Schulenburg, H. Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for microbiome research. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).