Felled and Lure Trap Trees with Uncut Branches Are Only Weakly Attractive to the Double-Spined Bark Beetle, Ips duplicatus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Species Studied
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | Year | Estimate | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ips typographus | (Intercept) | 0.226 | 0.075 | 0.0028 |
| 2017 | −2.253 | 0.120 | 1.38 × 10−78 | |
| 2018 | 0.775 | 0.056 | 3.08 × 10−44 | |
| Ips duplicatus | (Intercept) | 0.864 | 0.087 | 3.32 × 10−23 |
| 2017 | 0.851 | 0.077 | 1.29 × 10−28 | |
| 2018 | −0.890 | 0.113 | 3.74 × 10−15 | |
| Pityogenes chalcographus | (Intercept) | 0.570 | 0.064 | 8.53 × 10−19 |
| 2017 | 0.327 | 0.055 | 2.71 × 10−9 | |
| 2018 | 0.686 | 0.054 | 5.25 × 10−37 |
Appendix B
| Species | Year | Estimate | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ips typographus | (Intercept) | 1.199 | 0.176 | 1.51 × 10−11 |
| 2017 | 0.650 | 0.183 | 0.00041 | |
| 2018 | −0.338 | 0.124 | 0.0065 | |
| Ips duplicatus | (Intercept) | 0.609 | 0.169 | 0.00034 |
| 2017 | −0.560 | 0.159 | 0.00043 | |
| 2018 | 3.267 | 0.468 | 4.41 × 10−12 | |
| Pityogenes chalcographus | (Intercept) | 0.592 | 0.076 | 1.35 × 10−14 |
| 2017 | −0.146 | 0.063 | 0.020 | |
| 2018 | −0.052 | 0.068 | 0.448 |
References
- Pfeffer, A. Zentral-und Westpaläarktische Borken-und Kernkäfer (Coleoptera: Scolytidae, Platypodidae); Pro Entomologia, Naturhistorisches Museum: Basel, Switzerland, 1995; p. 310. [Google Scholar]
- Piel, F.B.; Grégoire, J.C.; Knížek, M. New occurrence of Ips duplicatus Sahlberg in Herstal (Liege, Belgium). Bull. OEPP/EPPO Bull. 2006, 36, 529–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petercord, R.; Lemme, H. Der Nordische Fichtenborkenkäfer. LWF-aktuell 2019, 120, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Duduman, M.L.; Isaia, G.; Olenici, N. Ips duplicatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Scolytinae) distribution in Romania. Preliminary results. In Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Brasov; Series II; Transilvania University Press: Brasov, Romania, 2011; Volume 53, pp. 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wermelinger, B.; Mathis, D.S.; Knizek, M.; Forster, B. Tracking the spread of the northern bark beetle (Ips duplicatus [Sahlb]) in Europe and first records from Switzerland and Liechtenstein. Alp. Entomol. 2020, 4, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodzki, W. Zasieg wystepowania kornika zroslozebnego Ips duplicatus C.R. Sahlberg (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) w obszarach górskich poludniowej Polski. Sylwan 2003, 8, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Olenici, N.; Duduman, M.L.; Tulbure, C.; Rotariu, C. Ips duplicatus (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Scolytinae)—An important insect pest of Norway spruce planted outsider its natural range. Revis. Pädur. 2009, 124, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Holusa, J.; Lubojacký, J.; Knížek, M. Distribution of the double-spined spruce bark beetle Ips duplicatus in the Czech Republic: Spreading in 1997–2009. Phytoparasitica 2010, 38, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duduman, M.L.; Vasian, I. Effects of volatile emissions of Picea abies fresh debris on Ips duplicatus response to characteristic synthetic pheromone. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2020, 40, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vakula, J.; Galko, J.; Gubka, A.; Kunca, A.; Zúbrik, M.; Nikolov, C.H.; Rell, S. Výsledky monitoringu lykožrúta severského (Ips duplicatus) v roku 2016. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference, Národné lesnícke centrum—Lesnícky výskumný ústav Zvolen, Nový Smokovec, Slovakia, 26–27 January 2017; pp. 144–147. (In Slovakia). [Google Scholar]
- Kausrud, K.; Okland, B.; Skarpaas, O.; Gregoire, J.C.; Erbilgin, N.; Stenseth, N.C. Population dynamics in changing environments: The case of an eruptive forest pest species. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, J.C.; Evans, H.F. Damage and control of BAWBILT organisms—An overview. In Bark and Wood Boring Insects in Living Trees in Europe, a Synthesis; Lieutier, F., Day, K.R., Battisti, A., Grégoire, J.C., Evans, H., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Holuša, J.; Hlásny, T.; Modlinger, R.; Lukášová, K.; Kula, E. Felled trap trees as the traditional method for bark beetle control: Can the trapping performance be increased? For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 404, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaider, Z.; Sierpiński, Z. Z biologii kornika zrosłozębnego (Ips duplicatus Sahlb.) (From the biology of Ips duplicatus). Roczn. Nauk. Leśn. 1955, 13, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Grodzki, W. Możliwości kontroli liczebności populacji kornika zrosłozębnego Ips duplicatus C.R. Sahlb. na południu Polski. Sylwan 1997, 11, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Szabla, K. Instrukcja Ochrony Lasu, cz. I, III, IV, t. I; PGL Lasy Państwowe: Bedoń, Poland, 2012; pp. 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, J. Neues zur Bekämpfung des Buchdruckers (Ips typographus L.). Anz. Schädl. 1948, 21, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prell, H. Kampf dem Fichtenborkenkäfer; Neumann: Radebeul, Germany; Berlin, Germany, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Chararas, C. L’influence des conditions climatiques sur l´évolution des scolytidae. Ann. Éc. Eaux Univ. Nancy 1959, 16, 135–167. [Google Scholar]
- Švihra, P. Über die Wirksamkeit von mit eigenen Ästen zugedeckten Fangbäumen. Les. Čas. 1968, 41, 363–374. [Google Scholar]
- Kula, E.; Šotola, V. Lýkožrout smrkový na neodvětvených a odvětvených smrkových lapácích. Zpr. Les. Výzk. 2017, 62, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer, A. Kůrovec lýkožrout smrkový a boj proti němu. In Lesnická Knihovna 12; SZN: Praha, Czech Republic, 1952; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Zumr, V. Lýkožrout Smrkový—Biologie Prevence a Metody Boje; Matice lesnická: Písek, Czech Republic, 1995; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Lubojacký, J.; Liška, J.; Knížek, M. Atraktivita stromových lapáků pro lýkožrouta severského, Ips duplicatus Sahlberg (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Zpr. Les. Výzk. 2018, 63, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Holuša, J.; Grodzki, W.; Lukášová, K. Porównanie skuteczności dyspenserów feromonowych ID Ecolure, Pheagr IDU i Duplodor na kornika zrosłozębnego (Ips duplicatus). Sylwan 2010, 154, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Mrkva, R.; Vala, V. Lýkožrout severský: Obrana proti významnému invaznímu škůdci. Les. Prace 2009, 88, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Knížek, M.; Liška, J.; Modlinger, R. Zpravodaj Ochrany Lesa. Supplementum: Výskyt Lesních Škodlivých Činitelů v Roce 2016 a Jejich Očekávaný Stav v Roce 2017; Výzkumný Ústav Lesního Hospodářství a Myslivosti, v. v. i.: Strnady, Czech Republic, 2017; p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- Knížek, M.; Liška, J. Zpravodaj Ochrany Lesa. Supplementum: Výskyt Lesních Škodlivých Činitelů v Roce 2017 a Jejich Očekávaný Stav v Roce 2018; Výzkumný Ústav Lesního Hospodářství a Myslivosti, v. v. i.: Strnady, Czech Republic, 2018; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Knížek, M.; Liška, J. Zpravodaj Ochrany Lesa. Supplementum: Výskyt Lesních Škodlivých Činitelů v Roce 2018 a Jejich Očekávaný Stav v Roce 2019; Výzkumný Ústav Lesního Hospodářství a Myslivosti. v. v. i.: Strnady, Czech Republic, 2019; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Olenici, N.; Duduman, M.L.; Olenici, V.; Bouriaud, O.; Tomescu, R.; Rotariu, C. The first outbreak of Ips duplicatus in Romania. In Working Party 7.03.10 Methodology of Forest Insect and Disease Survey in Central Europe, Proceedings of the 10th Workshop, 20–23 September 2010; Delb, H., Pontuali, S., Eds.; Fakultät für Forst- und Umweltwissenschaften der Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg and Forstliche Versuchs- und Forschungsanstalt (FVA) Baden-Württemberg: Freiburg, Germany, 2011; Volume 89, pp. 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Schlyter, F.; Anderbrant, O. Competition and niche separation between two bark beetles: Existence and mechanisms. Oikos 1993, 68, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, A.; Knížek, M. Expanze lýkožrouta Ips duplicatus (Sahlb.) ze severské tajgy. Zpr. Ochr. Lesa 1995, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bakke, A. Aggregation pheromone in the bark beetle Ips duplicatus (Sahlberg). Nor. J. Entomol. 1975, 22, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Byers, J.A.; Schlyter, F.; Birgersson, G.; Francke, W. E-Myrcenol In Ips duplicatus: An aggregation pheromone component new for bark beetles. Experientia 1990, 46, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holuša, J.; Zahradník, P.; Knížek, M.; Drápela, K. Seasonal flight activity of the double-spined spruce bark beetle Ips duplicatus (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Scolytinae) in Silesia (Czech Republic). Biologia 2003, 58, 935–941. [Google Scholar]
- Mrkva, R. Nové poznatky o bionomii, ekologii a hubení lykožrouta severského. Les. Prace 1995, 74, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, L.M.; Weslien, J.; Lindelöw, Å.; Lindhe, A. Attacks by bark- and wood-boring Coleoptera on mechanically created high stumps of Norway spruce in the two years following cutting. For. Ecol. Manag. 1999, 123, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holuša, J.; Liška, J. Hypotéza hynutí smrkových porostů ve Slezsku (Česká republika). Zpr. Les. Výz. 2002, 47, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Erbilgin, N.; Krokene, P.; Kvamme, T.; Christiansen, E. A host monoterpene influences Ips typographus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Scolytinae) responses to its aggregation pheromone. Agric. For. Entomol. 2007, 9, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, A.J.; Debruyne, C.; Grégoire, J.C. Recapture of Ips typographus L. (Col., Scolytidae) with attractants of low release rates: Localized dispersion and environmental influences. Agric. For. Entomol. 2000, 2, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, D.; Gershenzon, J.; Andersson, M.N.; Hammerbacher, A. Volatile organic compounds infuence the interaction of the Eurasian spruce bark beetle (Ips typographus) with its fungal symbionts. ISME J. 2009, 13, 1788–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raffa, K.F.; Andersson, M.N.; Schlyter, F. Host selection by bark beetles: Playing the odds in a high-stakes game. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Blomquist, G., Tittinger, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016; Volume 50, pp. 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Schlyter, F.; Birgersson, G. Forest Beetles. In Pheromones of Non-Lepidopteran Insects Associated with Agricultural Plants; Hardie, J., Minks, A.K., Eds.; CAB International: Walingford, UK, 1999; pp. 113–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Schlyter, F. Olfactory recognition and behavioural avoidance of angiosperm nonhost volatiles by conifer-inhabiting bark beetles. Agric. For. Entomol. 2004, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudinsky, J.A. Ecology of Scolytidae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1962, 7, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D. The role of pheromones, kairomones, and allomones in the host selection and colonization behavior of bark beetles. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1982, 27, 411–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomquist, G.J.; Figueroa-Teran, R.; Aw, M.; Song, M.; Gorzalsky, A.; Abbot, M.L.; Chang, E.; Tittiger, C. Pheromone production in bark beetles. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudinsky, J.A.; Novak, V.; Svihra, P. Pheromone and terpene attraction in the bark beetle Ips typographus L. Experientia 1971, 27, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, P.; Bader, R.; Rosner, S. Monoterpene content and monoterpene emission of Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst.) bark in relation to primary attraction of bark beetles (Col., Scolytidae). In Proceedings of the Physiology and Genetics of Tree-Phytophage Interactions International Symposium, Gujan, France, 31 August–5 September 1997; Lieutier, F., Mattson, W.J., Wagner, M.R., Eds.; Institut National de la Recherche Agronomiqu: Paris, France, 1999; pp. 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Byers, J.A. Wind-aided dispersal of simulated bark beetles fying through forests. Ecol. Model. 2000, 125, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duduman, M.L. Field response of the northern spruce bark beetle Ips duplicatus (Sahlberg) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Scolytinae) to different combinations of synthetic pheromone with (−)-α-pinene and (+)-limonene. Agric. For. Entomol 2014, 16, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.-T.; Zhou, X.; Niu, J.; Schlyter, F. Catching Ips duplicatus (Sahlberg) (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) with pheromone-baited traps: Optimal trap type, colour, height and distance to infestation. Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 66, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutelje, J. On the anatomical structure, moisture content, density, shrinkage, and resin content of the wood in and around knots in Swedish pine (Pinus silvestris L.), and in Swedish spruce (Picea abies Karst.). Sven. Papperstidn. 1966, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kimland, B.; Norin, T. Wood extractives of common spruce, Picea abies (L.) Karts. Sven. Papperstidn. 1972, 75, 403–409. [Google Scholar]
- Uçar, G.; Balaban, M.; Usta, M. Volatile needle and wood extracts of oriental spruce Picea orientalis (L.) Link. Flavour Fragr. J. 2003, 18, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisula, L. Wood Extractives in Conifers: A Study of Stemwood and Knots of Industrially Important Species; Åbo Akademi University Press: Turku, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Führer, E.; Wiener, L.; Hausmann, B. Dynamik von Terpen-Mustern und Borkenkäfer- befall an Fangbaum-Fichten unterschiedlichen Kronen-zustandes. Entomol. Gen. 1992, 17, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hietz, P.; Baier, P. Tree temperatures, volatile organic emissions, and primary attraction of bark beetles. Phyton. Ann. Rei. Bot. A. 2005, 45, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.M.; Vasconcelos, T.; Mateus, E.; Farrall, M.H.; Gomes Da Silva, M.D.; Paiva, M.R.; Branco, M. Characterization of the volatile fraction emitted by phloems of four pinus species by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 2006, 1105, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlyter, F.; Birgersson, G.; Byers, J.A.; Bakke, A. The aggregation pheromone of Ips duplicatus and its role in competitive interactions with I. typographus (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Chemoecology 1992, 3, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgersson, G.; Schlyter, F.; Löfqvist, J.; Bergström, G. Quantitative variation of pheromone components in the spruce bark beetle Ips typographus from diferent attack phases. J. Chem. Ecol. 1984, 10, 1029–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnle, U.; Vité, J.P.; Baader, E.J.; Meyer, H.; Francke, W. Chirality of ipsdienol and ipsenol indicates a frass pheromone system in the spruce engraver, Ips typographus. Naturwissenschaften 1991, 78, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlyter, S. Aggregation pheromone system in the spruce bark beetle Ips typographus. Ph.D. Thesis, Department Animal Ecology, University of Lund, Lund, Sweden, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Bakke, A.; Fröyen, P.; Skatteböl, L. Field response to a new pheromonal compound isolated from Ips typographus. Naturwissenschaften 1977, 64, 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlyter, F.; Anderbrant, O. Mass attack of trees by Ips typographus induced by sex-specific pheromone: A model of attack dynamics author(s). Holarct. Ecol. 1989, 12, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulock, P.; Christiansen, E. The threshold of successful attack by Ips typographus on Picea abies: A field experiment. For. Ecol. Manag. 1986, 14, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, K. The effect of carrion smell on the catching-efficiency of spruce bark beetle traps. Anz. Schädl. Pflanzenschutz Umweltschutz 1990, 63, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
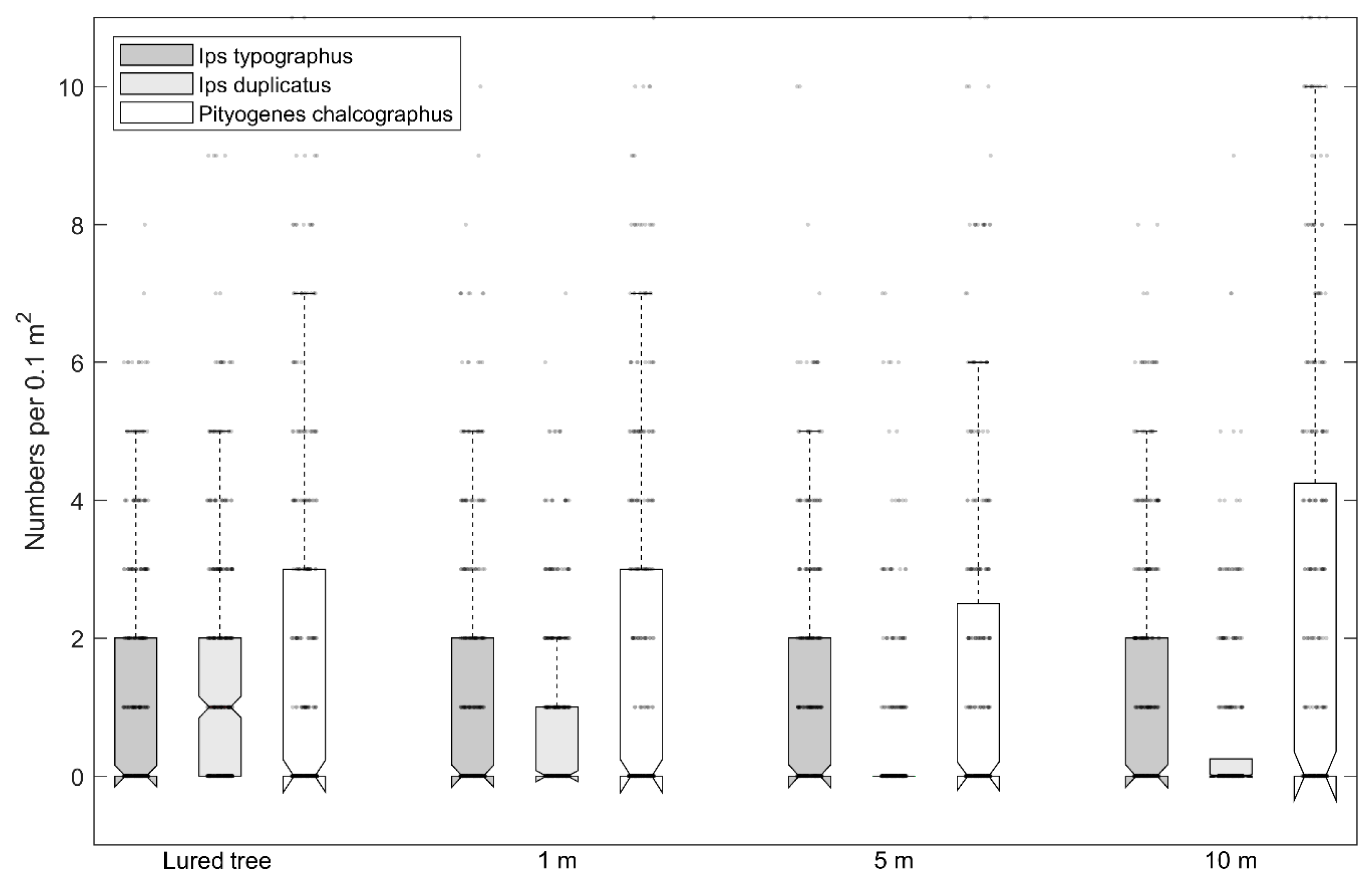
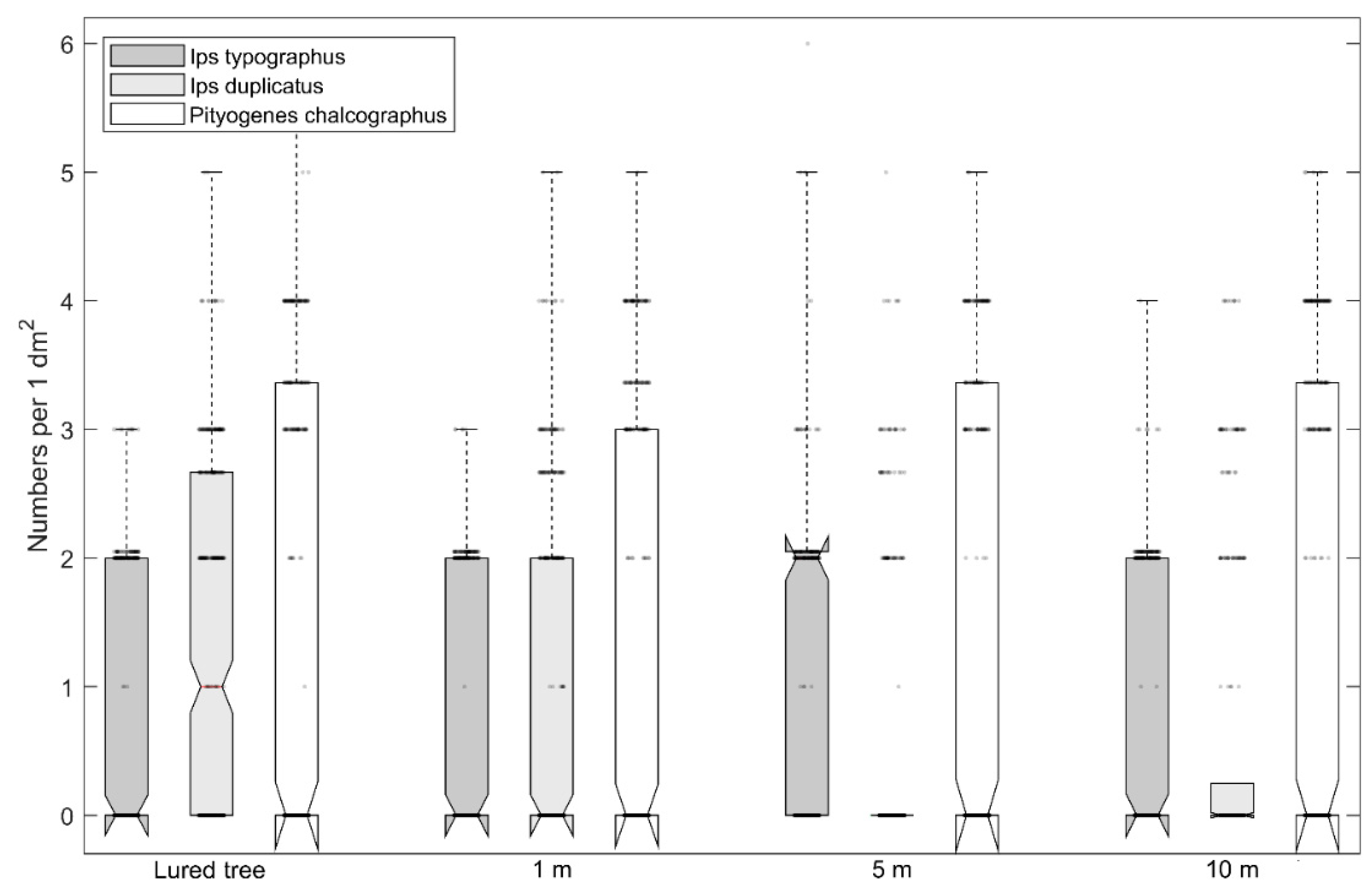
| Location | Latitude (°); Longitude (°) | Year of Study | Altitude (m asl) | Age of Spruce Forest | Proportion of Spruce (%) | Mean DBH (cm) | Stock Volume (m3/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dvorce | 49.8339; 17.5956 | 2016 | 610 | 60 | 83 | 28 | 317 |
| Guntramovice | 49.7824; 17.5536 | 2017 | 710 | 60 | 65 | 29 | 264 |
| Svatý Kopeček | 49.6392; 17.3431 | 2018 | 420 | 60 | 75 | 29 | 301 |
| Species | Type | Estimate | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ips typographus | (Intercept) | −0.921 | 0.173 | 1.1 × 10−7 |
| 1 | 0.028 | 0.066 | 0.66 | |
| 5 | −0.053 | 0.066 | 0.42 | |
| 10 | 0.098 | 0.065 | 0.13 | |
| Ips duplicatus | (Intercept) | 1.120 | 0.133 | 3.43 × 10−17 |
| 1 | −0.539 | 0.070 | 8.86 × 10−15 | |
| 5 | −0.860 | 0.085 | 3.95 × 10−24 | |
| 10 | −0.867 | 0.083 | 1.52 × 10−25 | |
| Pityogenes chalcographus | (Intercept) | −0.817 | 0.186 | 1.08 × 10−5 |
| 1 | 0.024 | 0.054 | 0.65 | |
| 5 | −0.070 | 0.055 | 0.21 | |
| 10 | 0.433 | 0.049 | 2.00 × 10−18 |
| Species | Term | Estimate | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ips typographus | (Intercept) | 1.864 | 0.644 | 0.004 |
| 1 | 0.054 | 0.242 | 0.82 | |
| 5 | −0.344 | 0.184 | 0.061 | |
| 10 | −0.081 | 0.225 | 0.72 | |
| Ips duplicatus | (Intercept) | 0.425 | 0.305 | 0.16 |
| 1 | 0.102 | 0.112 | 0.36 | |
| 5 | 0.501 | 0.224 | 0.026 | |
| 10 | 0.413 | 0.194 | 0.034 | |
| Pityogenes chalcographus | (Intercept) | 2.159 | 0.374 | 9.3 × 10−9 |
| 1 | 0.038 | 0.074 | 0.61 | |
| 5 | 0.006 | 0.074 | 0.94 | |
| 10 | −0.076 | 0.067 | 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šotola, V.; Holuša, J.; Kuželka, K.; Kula, E. Felled and Lure Trap Trees with Uncut Branches Are Only Weakly Attractive to the Double-Spined Bark Beetle, Ips duplicatus. Forests 2021, 12, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070941
Šotola V, Holuša J, Kuželka K, Kula E. Felled and Lure Trap Trees with Uncut Branches Are Only Weakly Attractive to the Double-Spined Bark Beetle, Ips duplicatus. Forests. 2021; 12(7):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070941
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠotola, Vojtěch, Jaroslav Holuša, Karel Kuželka, and Emanuel Kula. 2021. "Felled and Lure Trap Trees with Uncut Branches Are Only Weakly Attractive to the Double-Spined Bark Beetle, Ips duplicatus" Forests 12, no. 7: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070941
APA StyleŠotola, V., Holuša, J., Kuželka, K., & Kula, E. (2021). Felled and Lure Trap Trees with Uncut Branches Are Only Weakly Attractive to the Double-Spined Bark Beetle, Ips duplicatus. Forests, 12(7), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070941







