Effects of Several Chemicals on the Migration Behavior of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source and Culture of PWNs
2.2. Chemicals
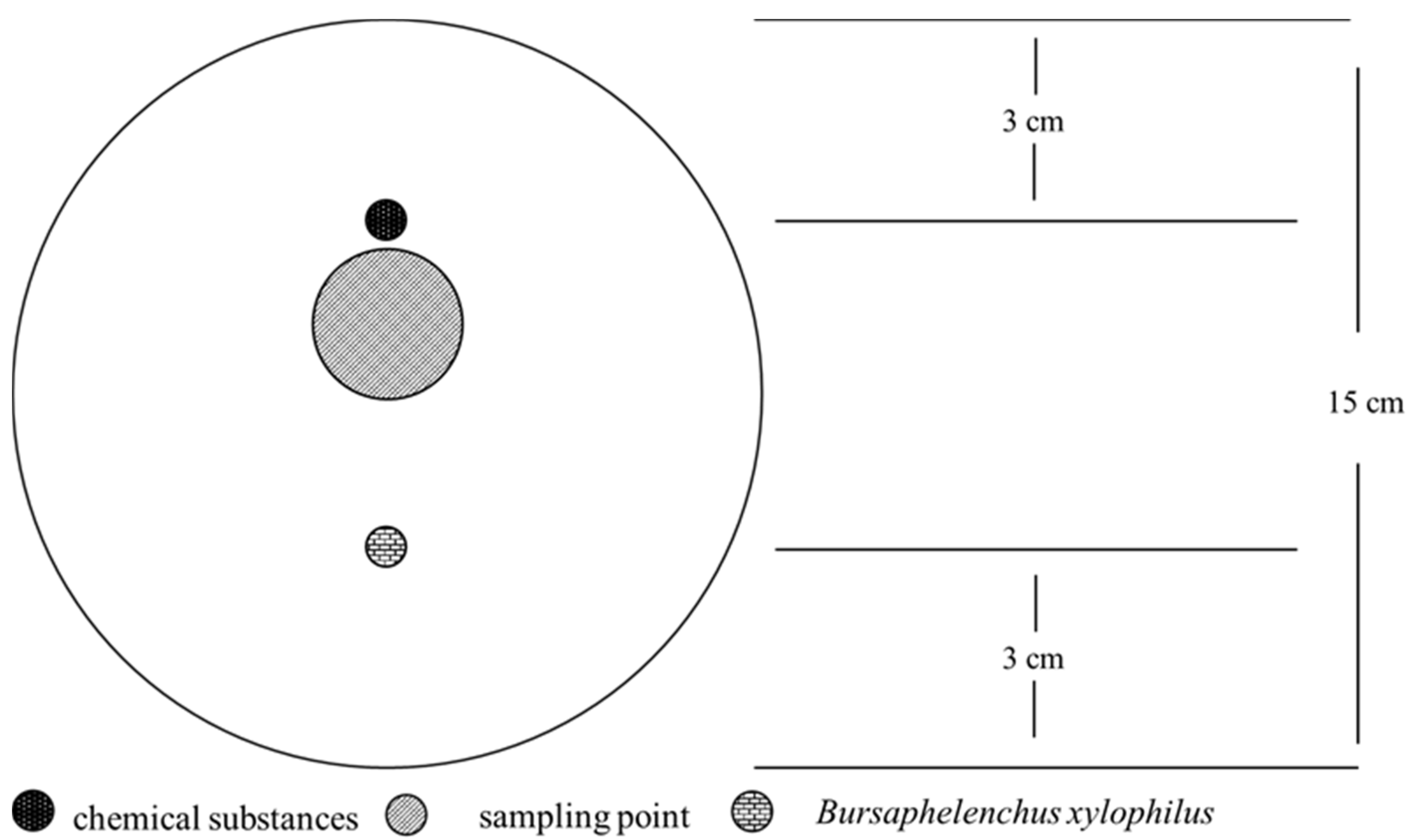
2.3. The Self-Designed Assay for Evaluating Attractive Effects of Chemicals toward PWN
2.4. Attractive Effects of Several Chemicals on PWN in Infected Wood
2.5. The Self-Designed Assay for Evaluating Repellent Effects of Chemicals toward PWN
2.6. Repellent Effect of Several Chemicals on PWN in Infected Wood
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
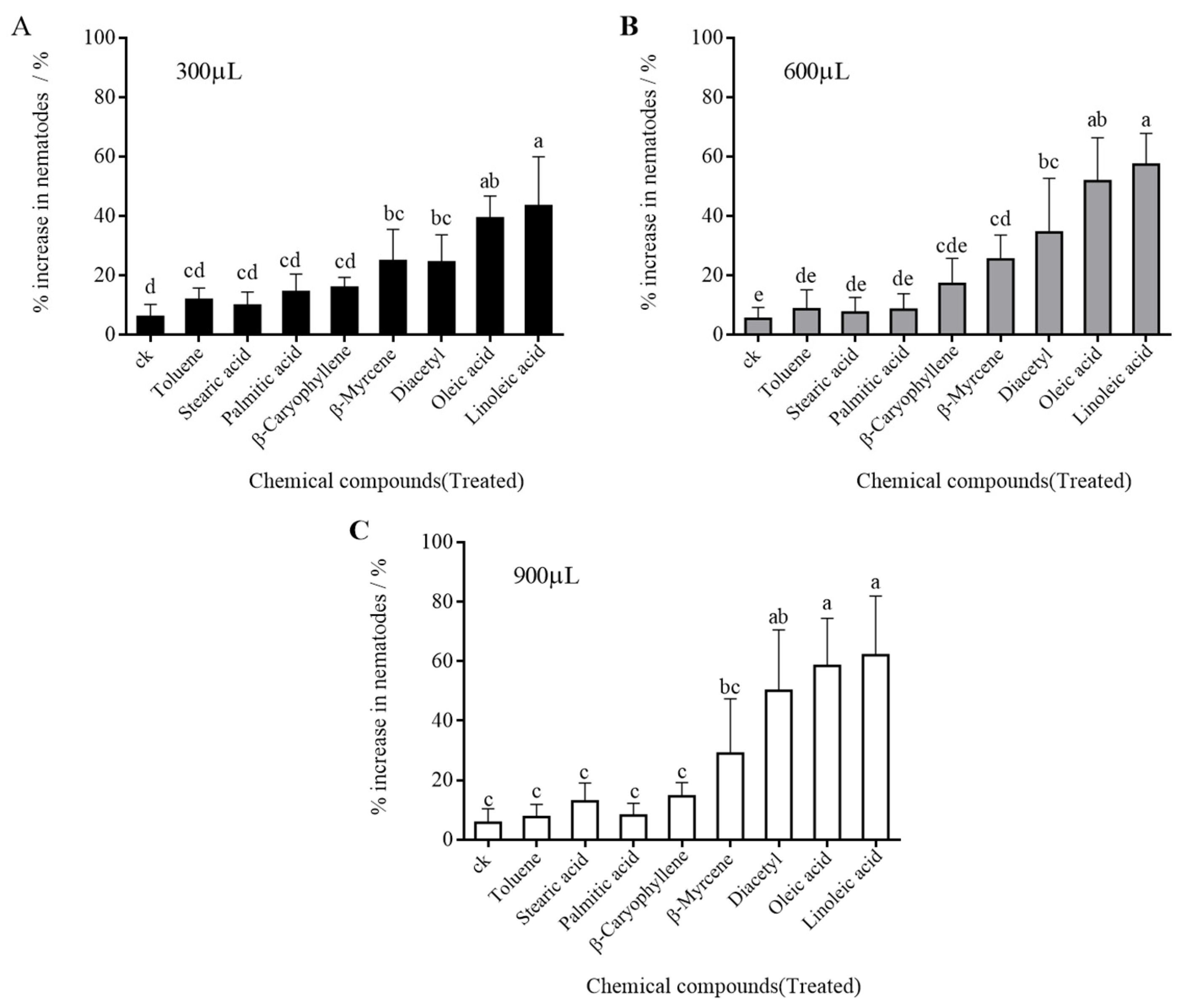
3.1. Analysis of the Attractive Effects of Several Chemicals toward PWN
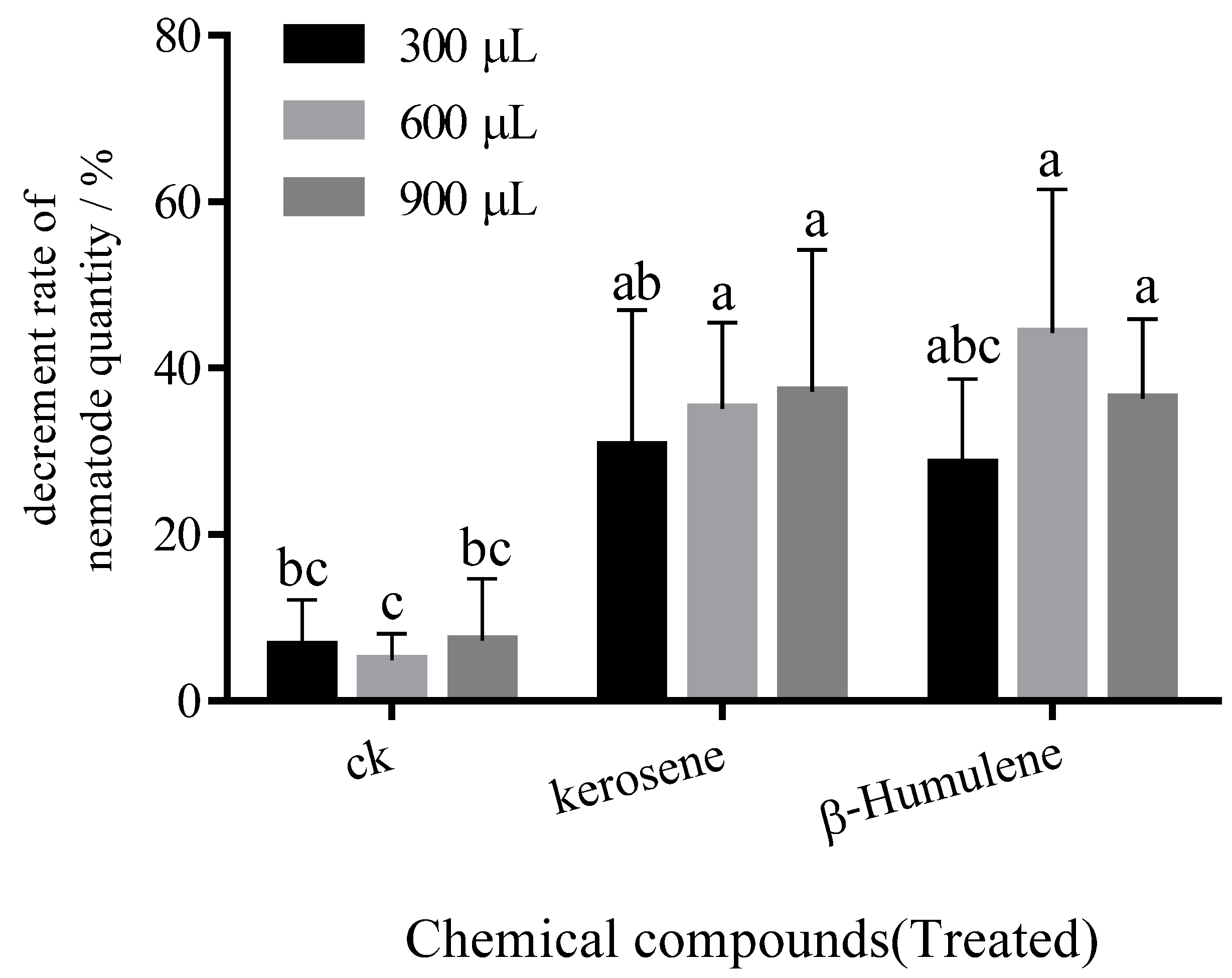
3.2. Analysis of Repellent Effects of Several Chemicals on PWN
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Qin, P.; Chinta, S.; Kong, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H. Ascarosides coordinate the dispersal of a plant-parasitic nematode with the metamorphosis of its vector beetle. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. A preliminary study on population dynamics of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in diseased trees. For. Pest Dis. 1993, 15, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, L.; Zhu, X. In A rapid β-Myrcene-attractant assisted wood sampling method for PCR-based detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus massoniana wood tissue. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering, Nanjing, China, 24–26 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liang, J.; Yan, D.; Zhang, X. Research Advances of Pine Wood Nematode Disease in China. World For. Res. 2010, 23, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Sheng, R.-C.; Sun, H.; Sun, S.-H.; Chen, F.-M. The First Record of Monochamus saltuarius (Coleoptera; Cerambycidae) as Vector of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Its New Potential Hosts in China. Insects 2020, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mota, M.; Vieira, P.; Butcher, R.A.; Sun, J. Interspecific communication between pinewood nematode, its insect vector, and associated microbes. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Wei, W.; Hao, H.; Zhang, B.; Butcher, R.A.; Sun, J. Chemical Signals Synchronize the Life Cycles of a Plant-Parasitic Nematode and Its Vector Beetle. Curr. Biol. CB 2013, 23, 2038–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, L.; Chinta, S.; Singh, P.; Wang, Y.; Nunnery, J.K.; Butcher, R.A. Acyl-CoA oxidase complexes control the chemical message produced by Caenorhabditis elegans. Pro. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3955–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, R.; Xie, B. The role of chemical communication in the infection and spread of pine wood nematodes (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 22, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, F. Transmission of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) through feeding activity of Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2019, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.L. The Pathogenic Mechanism and Virulence Variations Analyses of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Based on high-Throughput Sequencing. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.X.; Kong, Q.; Li, Y.; Jing, Y.M. Effects of chemicals with different toxicity levels on the perceptual behavior of nematodes. J. Toxicol. 2014, 28, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wicks, S.R.; Vries, C.J.D.; Luenen, H.G.A.M.; Plasterk, R.H.A. CHE-3, a cytosolic dynein heavy chain, is required for sensory cilia structure and function in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 2000, 221, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.L. Chemotaxis of Two Kinds of Nematodes Induced by Rhizosphere Bacteria. Master Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.R. Epidemic Status of Pine Wilt Disease in China and Its Prevention and Control Techniques and Counter. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2019, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.C.; Zeng, F.L.; Ben, A.L.; Han, Z.M. Pathogenicity and repulsion for toxin-producing bacteria of dominant bacteria on the surface of American Pine Wood Nematodes. Phytopathology 2017, 165, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Cao, Y.F.; Wang, L.F.; Piao, C.G.; Li, C.L. Current status of pine wilt disease and its control status. J. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 40, 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.P. Technology for in situ control of pine wilt nematode disease in forest. Modern. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 2, 106–107. [Google Scholar]
- FUTAI, K. Population Dynamics of Bursaphelenchus lignicolus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) and B. mucronatus in Pine Seedlings. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1980, 15, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.H.; Ye, J.R.; Negi, S.; Xu, X.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Ji, J.Y. Pathogenicity of Aseptic Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38095. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Lu, M.; Ahmad, F.; Tian, H.; Ning, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Sun, J. Chemical Signals of Vector Beetle Facilitate the Prevalence of a Native Fungus and the Invasive Pinewood Nematode. J. Nematol. 2017, 49, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Shuto, Y.; Watanabe, H. Attractants from a vector, Monochamus alternatus, for the pine wood nematode. J. Agric. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 51, 1457–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Bolla, J.A. Attraction of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, Pathotype MPSy-1, to Monochamus carolinensis Larvae. Jpn. J. Nematol. 1989, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.L.; Yao, H.W. Analysis of the epidemic situation of pine wilt disease in China in 2019. For. Pest Dis. 2020, 40, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y. Effect of Rhizosphere Microbe on Chemotaxis of Root-Knot Nematode. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J. Analysis effects of Several Pine Volatiles on Behavior of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Farmers Consult. 2020, 98, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.J.; Hao, D.J. Effects of Several Pine Volatiles on Behavior of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2009, 12, 58–59. [Google Scholar]


| Compound | Purity (%) | CAS No. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaClO | 5.2% | 7681-52-9 | Damas-beta. |
| C2HCL3O2 | >99% | 200-663-8 | Damas-beta |
| Clycerol | >99% | 56-81-5 | Damas-beta |
| Lactic acid | ≥97.5% | 50-21-5 | General-reagent |
| Palmitic acid | 98% | 57-10-3 | General-reagent |
| Stearic acid | 40% | 57-11-4 | General-reagent |
| β-Caryophyllene | 30% | 123-35-3 | General-reagent |
| β-Myrcene | ≥75% | 123-35-3 | Mackin |
| Toluene | ≥99.5% | 108-88-3 | Mackin |
| Oleic acid | 90% | 112-80-1 | Mackin |
| Linoleic acid | ≥98% | 60-33-3 | Mackin |
| Diacetyl | ≥98.0% | 431-03-8 | Mackin |
| KCl | ≥99.8% | 7447-40-7 | Nanjing Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| NaC1 | ≥99.5% | 7647-14-5 | Nanjing Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| MnC12 | 98% | 7773-01-5 | Nantong agro-chemical co. LTD |
| CrCl2·2.5H2O | ≥99.0% | 7790-78-5 | Ourchen |
| NaF | ≥99.0% | 7681-49-4 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| Atropine sulfate | 100 mμg/mL | 5908-99-6 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| DDVP | 200 g/L | 203645-53-8 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| CuSO4·5H2O | ≥99.0% | 7758-99-8 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| Kerosene | 1 L | 8008-20-6 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| Diquat dibromide | 100 μg/mL | 85-00-7 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| β-Humulene | ≥90% | 116-04-1 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| PWN | AmA3 | AA3 | Yw4 |
Average Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemicals | |||||
| Control | 70 ± 5.60 h A | 71 ± 14.93 g A | 69 ± 2.08 g A | 70 ± 0.81 g | |
| NaClO | 89 ± 5.29 gh A | 85 ± 6.06 fg A | 76 ± 2.49 fg A | 83 ± 5.43 fg | |
| C2HCL3O2 | 96 ± 5.60 gh A | 97 ± 14.93 fg A | 87 ± 2.08 fg AB | 93 ± 4.49 fg | |
| Clycerol | 113 ± 2.06 fg A | 89 ± 5.60 fg B | 96 ± 6.33 fg B | 98 ± 10.07 fg | |
| Lactic acid | 121 ± 8.62 fg A | 116 ± 3.56 fg AB | 124 ± 10.39 fg A | 120 ± 3.29 fg | |
| Palmitic acid | 151 ± 8.62 e A | 148 ± 3.56 ef A | 145 ± 8.36 ef A | 148 ± 2.45 ef | |
| Stearic acid | 154 ± 11.49 fg A | 150 ± 3.39 ef A | 159 ± 6.06 ef A | 154 ± 3.68 ef | |
| β-Caryophyllene | 173 ± 3.39 ef A | 164 ± 10.43 ef B | 169 ± 6.06 ef A | 168 ± 3.68 ef | |
| β-Myrcene | 272 ± 2.49 cd A | 253 ± 10.43 de B | 268 ± 10.37 de A | 264 ± 8.18 cd | |
| Toluene | 292 ± 6.06 cd A | 284 ± 6.33 cd A | 298 ± 2.08 cd A | 291 ± 5.73 cd | |
| Oleic acid | 337 ± 11.49 c A | 346 ± 2.83 bc AB | 333 ± 5.06 bc A | 338 ± 5.44 bc | |
| Linoleic acid | 441 ± 4.22 b A | 451 ± 3.74 b AB | 442 ± 3.85 b A | 444 ± 4.49 b | |
| Diacetyl | 513 ± 8.72 a AB | 523 ± 2.08 a AB | 509 ± 11.4 a A | 515 ± 5.89 a | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.-F.; Ding, X.-L.; Shi, L.-N.; Wang, Q.-T.; Ye, J.-R. Effects of Several Chemicals on the Migration Behavior of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle. Forests 2021, 12, 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12060771
Shi X-F, Ding X-L, Shi L-N, Wang Q-T, Ye J-R. Effects of Several Chemicals on the Migration Behavior of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle. Forests. 2021; 12(6):771. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12060771
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xiu-Feng, Xiao-Lei Ding, Li-Na Shi, Qing-Tong Wang, and Jian-Ren Ye. 2021. "Effects of Several Chemicals on the Migration Behavior of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle" Forests 12, no. 6: 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12060771
APA StyleShi, X.-F., Ding, X.-L., Shi, L.-N., Wang, Q.-T., & Ye, J.-R. (2021). Effects of Several Chemicals on the Migration Behavior of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle. Forests, 12(6), 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12060771




