Abstract
Thinning is an important management practice for reducing plant competition and improving wood production in forests. The residues from thinning can contain large amounts of carbon (C) and nitrogen (N), and the management methods applied directly after thinning can affect the input of nutrients to soil, change the availability of substrates to soil bacterial communities, and thus affect soil bacterial community structure. Our objective was to determine the effects of different thinning residue treatments on soil bacterial community structure and diversity. Illumina high-throughput sequencing technology was used to sequence the bacterial 16SrRNA V3–V4 variable region of the soil (0–10 cm) of a Larix olgensis plantation to compare the composition and diversity of soil bacterial communities following removal of thinning residues (tree stems plus tree crowns) (RM) and retention of thinning residues (crowns retained with stem removal) (RT) treatments. Total soil carbon (TC) and nitrogen (TN) content in the residue retention treatment were significantly greater than in residue removal treatments (p < 0.05). The relative abundance of the dominant soil bacteria phyla were, in descending order: Proteobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Acidobacteria, Chloroflexi, Actinobacteria, Nitrospirae, Planctomycetes, Gemmatimonadetes, and Bacteroidetes, with a total relative abundance of more than 80%. Acidobacteria were enriched in the RM treatment, while Proteobateria, Actinobacteria and Bacteroidetes were greater in the RT treatment. Rhizobiales and Rhodospirillales (belonging to the α-Proteobacteria) were enriched in the RM treatment. Soil bacteria α diversity was not significantly different among different treatments. Spearman correlation analysis showed that the α diversity index was significantly negatively correlated with TC and TN. Lefse analysis revealed that 42 significant soil bacteria from phylum to genus were found in the two different thinning residue treatments. Redundancy analysis showed that soil TC and TN were the major drivers of variation in soil bacterial community structure. Overall, thinning residue retention increased the availability of resources to the soil bacterial community, thus changing bacterial community structure. This research provides a theoretical basis for the regulation of plantation forest soil fertility and quality.
1. Introduction
Forest plantations play an important role in both timber production and ecological protection since China has the most extensive and largest plantation program in the world. Thinning is the most widely employed plantation management practice, being a major tool for achieving the goal of increasing tree growth or improving tree quality and species composition on a sustainable basis [1]. With increasing demand for bioenergy production, the use of forest residues as energy sources has become common, but this will cause serious ecological problems [2]. Although most logging residue harvested for energy use comes from clear-felled areas, part of it is harvested in connection with the thinning of young stands [3,4]. As an important forest management method, forest thinning is of great significance to the sustainable and healthy development of forests and wood products [5]. Thinning produces a large amount of nutrient-rich residues which are important resources for soil organisms in terrestrial ecosystems, impact soil nutrient inputs through decomposition, and provide energy and nutrients for soil microbial decomposition and metabolism [6,7,8]. However, removal or retention of harvesting residues can produce significant contrasting effects on topsoil nutrients [3,9,10]. In particular, when harvest residues were removed, a large quantity of nutrients will be exported [9,10]. In Nordic countries, residue removal during commercial thinning results in the removal of nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from the forest [2,4,11,12,13]. In one Norwegian study of thinning in a spruce forest, rates of soil net N and C mineralization after removal of the whole tree following thinning were both lower than when only the stems were removed following thinning [12]. Therefore, removal of thinning residues may be considered as negative fertilization, where nutrients are removed from the forest. A previous study showed that soil carbon and nitrogen contents increase during the residues retention process [14], and the contents of soil total carbon (TC) and total nitrogen (TN) increased by 45% and 32%, respectively, over 12–24 months [15]. In contrast, whole-tree removal tended to cause losses in soil C, N and the soil organic matter (SOM) labile fraction was reduced [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Additionally, as residue retention quantity increases, the content of water extractable organic carbon (WEOC) and water extractable total nitrogen (WEON) increases accordingly [15,23,24], which is due to the decomposition of the labile C and N from leaves and branches in the residue. Therefore, relative to the removal of forest residues, their retention improves the quality of the resource and compensates for the loss of soil nutrients caused by thinning, which promotes plant growth and maintains the forest nutrient balance [3,25].
Soil microorganisms are an important part of nature; they, akin to other organisms, require nutrients to maintain cellular morphology and to decompose organic materials for energy [26]. When exogenous organic materials are added to the soil, microbes will respond to this new food supply. Plant residues are the primary source of soil organic matter [25,27,28,29,30], and their decomposition will stimulate the increase in the availability of carbon and nitrogen for microorganisms, thereby stimulating microbial metabolic activity. The rate of microbial decomposition also varies with residue C/N. Microbial competition for available nitrogen increases when decomposing plant residues have high C/N, reducing the availability of N for plant growth, and is therefore not conducive to the growth of higher plants. As plants mature, the ratio of protein in their tissues decreases, while the concentrations of lignin and cellulose increase. This results in poorer substrate quality for microbial communities. Clear-felling mainly occurs in mature forests, and residues from this activity are of poorer quality than those from thinning operations [31,32]. In fast-growing plantations, thinning generally occurs at a time when nutrient demand is at a peak, resulting in a large demand for nutrients from the remaining trees. Therefore, recently thinned stands may be sensitive to nutrient removal if residues are removed from thinned stands [33,34]. The extent of the impact of this nutrient removal in thinning residues is unknown with respect to that which happens with clear fell harvesting. Whole-tree removal following thinning may result in a decrease in the availability of soil nutrients, in turn reducing tree growth, and thereby reducing litter cycling and potentially impacting on the composition of the soil microbial community. Soil microbial communities are responsible for crucial soil functions, including nutrient cycling and availability, transformation and breakdown of harvesting residues, and disease suppression or susceptibility. However, the effects of changes in resource quality on soil bacterial communities due to different management of thinning residues have been rarely studied [14,27]. Therefore, an in-depth understanding of how soil bacterial communities respond to the retention or removal of thinning residues is critical to maintaining forest productivity.
Soil bacteria are highly valued as they are the most abundant and widely distributed microbial group in soils. They play an important role in the biogeochemistry cycle as they are involved in the decomposition of organic matter [35,36], humus formation and energy transfer processes [27,32], which have become the focus of increasing research. The diversity and composition of soil bacteria can regulate the health and stability of soil ecosystems. Therefore, it is of great potential significance to study the classification and characteristics of the soil bacterial community to maintain ecosystem stability and sustainable utilization. In the past, bacterial community studies used traditional culture methods, which were unable to isolate and culture a large number of bacteria, so our understanding of bacterial community diversity and structure was severely limited. In recent years, with the development of molecular biology, 16sRNA high-throughput sequencing technology has been widely used in microbial identification and typing. It enables those soil bacteria that cannot be cultured to be identified by sequencing their genomic DNA fragments, thus achieving a more comprehensive understanding of the soil bacterial community [37,38].
Larch (Larix spp.) is a fast-growing deciduous coniferous tree, and one of the main plantation tree species in northeast China. The Chinese planting area and volume for larch are approximately 3.14 million ha and 18.4 million m3, respectively [39,40], and make a great contribution to the provision of timber products, as well as soil and water conservation of the forest region. Presently, research on different Larch residue treatments following thinning mainly focuses on changes in soil nutrient content. Interestingly, the effects of different thinning residue treatments on soil microbial properties have been largely ignored. Therefore, we investigated soil bacterial community composition and diversity in a Korean larch (Larix olgensis) plantation using a 16sRNA high-throughput sequencing technique. Our objective was to determine (1) whether different residue treatments following thinning lead to changes in the quality of soil resources, (2) how such changes affect the composition and diversity of soil bacterial communities, and (3) how these changes relate to each other. Our findings will hopefully provide a scientific basis for the sustainable management and maintenance of ecological function of plantations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
The experiment was established in MengJiagang National Forest Farm, Heilongjiang Province, Northeastern China (46°20′16″–46°30′50″ N, 130°32′42″–130°52′36″ E). The study site climate is continental monsoon, with a mean annual air temperature and mean annual precipitation of 2.7 °C and 535 mm, respectively. The average altitude is approximately 250 m and the soil type is Alfisol. The main vegetation types are plantation coniferous forest and secondary deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest with Quercus mongolica, Betula davurica, Populus davidiana, and Betula platyphylla as the major tree species.
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sample Collection
The Larix olgensis plantation was manually felled with an intensity of ~20% (calculated based on the standing trees before thinning) in August 2016 at an age of 21 years. At the time of thinning, stand density was 1440 trees/ha, average Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) was 13.9 cm, and average tree height was 14 m. The average DBH of the thinned trees was 10.5cm, and the average amount of thinning residues produced was 11.3 m3/ha. Different treatments included: retention of thinning residues (tree stem was removed but the crown residues were retained) (RT); removal of thinning residues (tree stems plus tree crowns) (RM). Three (20 × 20 m) study plots were set up for each treatment. In August 2018, 0–10 cm soil samples were randomly collected at 5 points in each plot. Five samples in each plot were homogenized into a composite sample, which was passed through a 2 mm sterile soil sieve to remove roots, wood fragments and bark. Each treatment had three composite samples. The soil was divided into two parts—one was taken back to the laboratory for determination of soil pH, water content, TC and TN, and the other was placed in a sterile centrifuge tubes and kept in an ice box. On the same day, these latter soil samples were taken back to the laboratory and kept in a refrigerator at −80 °C for later DNA extraction and bacterial diversity analysis.
2.3. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Biological Analysis
2.3.1. Physicochemical Analysis
Soil total carbon content was determined by a multi N/C2100S analyzer (Analytik Jena, Germany) [41]. Total nitrogen concentration was determined by the semi-micro-Kjeldahl method [42]. Soil pH was measured using a potentiometric pH meter (soil: water ratio of 1:2.5, w/v). Soil moisture was determined by the drying method (105 °C, 24 h) [43].
2.3.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
Total soil DNA was extracted from all samples using an E.Z.N.A.®DNA isolation kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Omega Bio-Tek Co., LTD, Norcross, GA, USA), and DNA quality was evaluated on a 0.8% agarose gel, with a Nano Drop ND-1000 UV spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, MA, USA). The extracted DNA samples were stored at −20 °C prior to further analysis. Total DNA from each soil sample was used as a template for PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification of the highly variable V3~V4 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA. The bacterial 16s rRNA gene was amplified using primers 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTCHVCCCTNHTCTAAT-3′), which target the V3–V4 regions of the 16S rRNA gene. PCRs were performed in triplicate with a 25 μL mixture containing 5 μL of 5× Reaction buffer, 5 μL of 5× GC buffer, 2 μL of dNTP (2.5 mM), 1 μL of forward primer (10 uM), 1 μL of reverse primer (10 uM), 0.25 μL of Q5 high-fidelity DNA polymerase, 3 μL of DNA template, and 7.75 mL of ultrapure water (ddH2O). The PCR thermocycling conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 98 °C for 5 min, followed by 25 cycles of 30 s at 98 °C, 30 s at 52 °C, 60 s at 72 °C and finally, at 72 °C for 5 min. The PCR amplicons were extracted from 2% agarose gels. Target fragments were then cut from the gel and purified using an Axygen DNA gel kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, USA) and the PCR amplicons were quantified with a Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and microplate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA, FLx800). All successfully amplified PCR products were prepared for sequencing libraries using the TruSeq Nano LT DNA Library Prep Kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. To assess library quality, we used an Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Analysis Kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), and libraries were quantified using a Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Libraries were performed on the Illumina Miseq PE250 instrument with 2 × 300bp paired-end chemistry using the MiSeq Reagent Kit V3 (600 cycles). All 16S rRNA gene sequence data sets derived from Illumina MiSeq sequencing were submitted to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession number SRP274251.
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analyses
The QIIME (quantitative insights into microbial ecology) pipeline (version 1.8.0) was used to conduct quality screening on the offline data using the sliding window method; then, the chimeras were checked and removed to obtain individual sample effective sequences using USEARCH (version 5.2.236) tools. Subsequently, obtained sequences based on 97% similarity level were merged, and OTUs were clustered using the UCLUST sequence comparison tool of QIIME. The BLAST method was used to compare the representative sequences with the SILVA database, and finally each sample OTU’s abundance matrix was obtained. Soil bacterial α-diversity indices (Shannon index, Simpson index, ACE index, Chao1 index) were calculated based on the OTU’s table in QIIME. Significant differences in soil physical and chemical properties and bacterial α-diversity indices for different treatments were tested by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). We used the Shapiro–Wilk test to assess whether the data were normally distributed (p > 0.05). The homogeneity of variances was assessed by Levene’s test for equality of variances (p > 0.05). The correlation between bacterial α-diversity and physical and chemical properties of soil were tested with Spearman correlation analyses. The Bray–Curtis distance matrix based on OTU level was constructed and used for nonmetric multidimensional scale (NMDS) analysis to intuitively reflect similarities of thinning residue treatments on soil bacterial community structures. Adonis analysis was used to determine whether bacterial community structure was significantly influenced by different thinning residue treatments. A distance-based RDA (db-RDA) was used to examine the effect of each physical and chemical soil parameter on the bacterial community (based on OTU composition). The above analyses were conducted in statistical program R 3.6.3. The relative abundance at the genus level matrix was submitted on the Galaxy web http://huttenhower.sph.harvard.edu/galaxy/ (accessed on Saturday 6 February 2021 05:46:27 AM (UTC)). platform for LEfSe analysis to further uncover taxa distribution differences between different treatment groups from the phylum to the genus level.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical and Physical Properties
Soil total carbon content (TC) and total nitrogen content (TN) were significantly greater in residue retention (RT) than in residue removal (RM) treatments (p < 0.05, Table 1). However, pH and soil water content (WC) showed no significant differences. Since TC and TN contents in the residue retention treatment were all greater than in the removal treatment, the carbon to nitrogen ratio (C:N) did not show a significant difference.

Table 1.
Soil physicochemical properties in different harvesting residue treatments.
3.2. OTU Statistics and Bacterial Community Diversity
After the original sequence of the paired-end sequencing of the PCR product was optimized by filtering and removing the low-quality portion, a total of 253,542 effective sequences were obtained. Each sample had an average of 42,257 subsamples, and 99.96% of the sequence reads were between 400 and 450 bp. A total of 6226 OTUs were obtained after removing rare OTUs, and the abundance of OTU units between different treatments was compared (analyzing only the presence or absence of the OTU unit). The OTUs found in both treatments were shared (3182), and those that were found in only one treatment were considered unique (Figure 1). In total, 4494 OTUs were found in the RT treatment, of which 1312 (21.07%) were unique, and 4914 OTUs were found in the RM treatment, of which 1732 (27.82%) were unique.
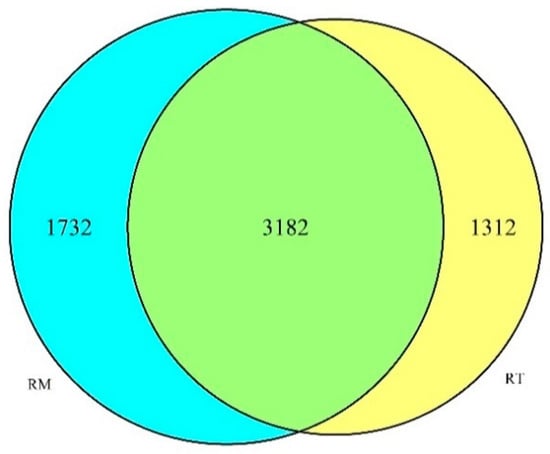
Figure 1.
The numbers of shared and unique bacteria species OTUs obtained from soil of the residue retention (RT) and residue removal (RM) treatments.
Based on these OTUs, alpha diversity analysis was conducted. Simpson, Chao1, ACE and Shannon indices were used to characterize species richness and diversity (Table 2). The Simpson diversity index focuses on the probability of species in the population and the Shannon Wiener Diversity Index focuses on describing the disorder and uncertainty of individuals—the greater the uncertainty, the greater the diversity index. The Chao1 index estimates the number of species contained in the sample, and the ACE index assesses the richness and uniformity of species composition in the sample. Although the four diversity indices from the RM treatment were greater than those of the RT treatment, there were no significant differences between them (p > 0.05).

Table 2.
Soil bacteria α-diversity indices for different thinning residue treatments.
Spearman correlation analysis was conducted between the soil physical and chemical characteristics and the bacterial diversity index. Simpson and Shannon indices were negatively correlated with TC (r = −0.89, p < 0.01; r = −0.77, p < 0.01) and TN (r = −0.89, p < 0.01; r = −0.77, p < 0.01), respectively (Figure 2). In contrast, the soil carbon: nitrogen ration (C:N) was positively correlated with Simpson (r = 0.66, p < 0.05), Chao1 (r = 0.6, p < 0.05), ACE (r = 0.66, p < 0.05) and Shannon index (r = 0.6, p < 0.05).
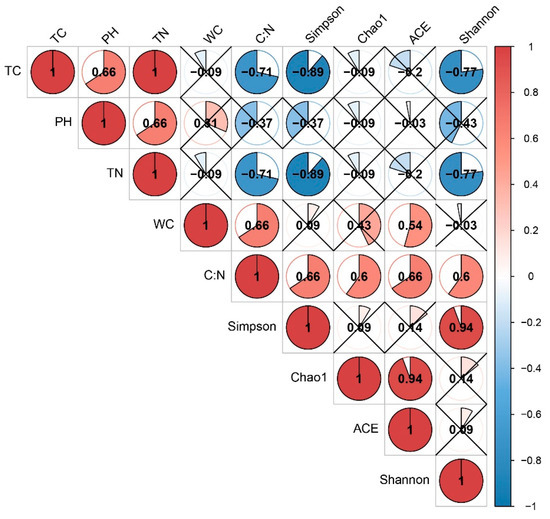
Figure 2.
Correlations among soil properties and soil bacterial diversity indices. Blue and red indicate positive and negative correlations, respectively; the extent of circle shading represents the strength of the correlation coefficient, and crosses in the circles indicate insignificant correlations (p > 0.05).
3.3. Composition and Soil Bacterial Community Differences between Different Thinning Residue Treatments
A total of 37 phyla were detected in the RT and RM treatment soil samples (Figure 3A). The dominant phyla (with a relative abundance of at least 1% in each treatment) were Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Chloroflexi, Actinobacteria, Nitrospirae, Planctomycetes, Gemmatimonadetes, and Bacteroidetes, with a total relative abundance of more than 80%. The top three relative abundances at the phyla level were: Proteobacteria (RT—34.9%, RM—33.5%), Acidobacteria (19%, 20.6%) and Verrucomicrobia (23.4%, 21.7%), respectively. The relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobia in the RT treatment was greater than in the RM treatment, but the relative abundance of Acidobacteria was lower.
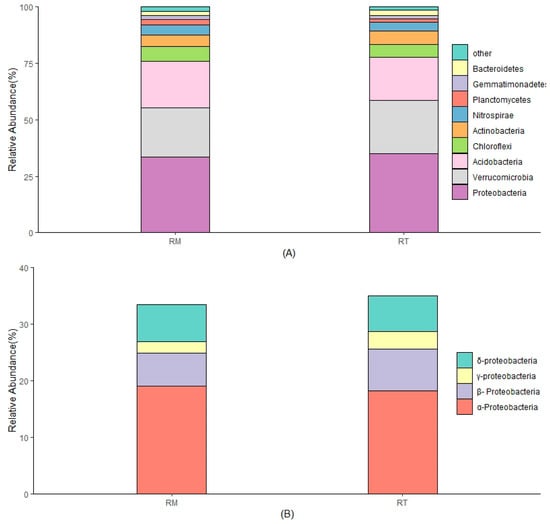
Figure 3.
The relative abundance of soil bacterial communities at the phylum level (A), and class composition of Proteobacteria (B). RT: residue retention; RM: residue removal.
Proteobacteria, which ranked first in phyla relative abundance, was investigated further. The α-Proteobacteria are the main class of Proteobacteria, with the highest relative abundance in both treatments (Figure 3B). The relative abundance of β-Proteobacteria was lower than α-Proteobacteria, and it was greater in RT (7.38%) than in RM (5.87%).
Burkholderiales and Pseudomonadales belong to β-Proteobacteria, and γ-Proteobacteria, respectively, and were enriched in the RT treatment (Figure 4). Rhizobiales and Rhodospirillales belong to α-Proteobacteria and were enriched in the RM treatment. In contrast, Sphingomonadales was enriched in the RT treatment. The relative abundances of these five bacteria were 4.28%, 1.59%, 11.09%, 5.38%, and 0.96% in the RT group and 2.27%, 0.65%,11.45%, 6.67%, and 0.64% in the RM treatment, respectively.
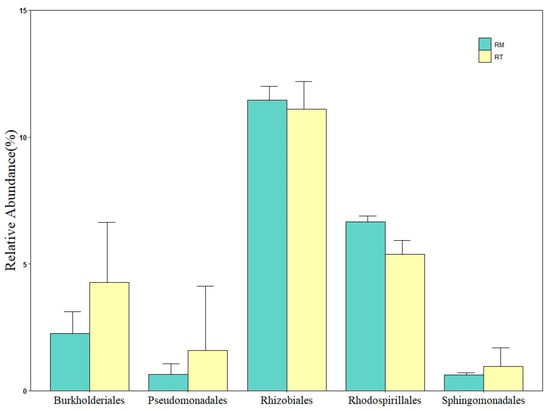
Figure 4.
The relative abundance of bacterial class groups. Values are mean ± SE; residue retention—RT; residue removal—RM.
A LEfSe (LDA Effect Size) analysis was performed on 268 genera to reveal significant differences in bacteria from the phylum to genus level between the two treatments (Figure 5). Forty-two significant bacteria were identified as belonging to different taxonomic levels—19 were enriched in the RT treatment and 23 in the RM treatment. At the phylum level, there were three bacteria—Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Planctomycetes—and at the class level, there were five—Planctomycetacia, Bacilli, Sphinggobacteriia, Flavobacteriia, Acidimicrobiia. At the order level, there were eight species—Rhizobiales, Acidimicrobiales, Streptomycetales, Frankiales, Planctomycetales, Bacillales, Sphingobacteriales, and Flavobacteriales—and at the family level, there were 10—Acidimicrobiacea, Flavobacteriaceae, Bacillaceae, Planctomycetaceae, Sphingobacteriaceae, Acidothermaceae, Bdellovibrionaceae, Streptomycetaceae, Erythrobacteraceae, and Chitinophagaceae. The remaining 16 significant bacteria were at the genus level.
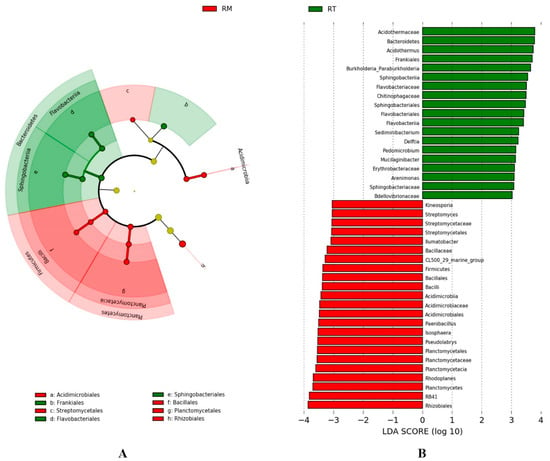
Figure 5.
Significant bacteria in soils with different thinning residue treatments, for which the threshold on the logarithmic LDA score was 3.0 according to the LEfSe method. Cladogram, indicating the phylogenetic distribution of microbial lineages associated with two treatments (only display from the phylum to the order level), and taxonomic units with significant differences are represented in the color of the most abundant class (red RM, green RT) (A). The vertical coordinate is the taxonomic unit with significant differences between two treatments, while the horizontal coordinate is a bar chart to visually show the linear discriminant analysis (LDA) score (log 10) of the corresponding taxonomy unit. Bar graph reports the group of samples with a higher abundance corresponding to the taxonomy unit (B).
3.4. Comparison of Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors
A nonsimilarity matrix between two treatments was established based on the Bray–Curtis distance similarity coefficient at the OTU abundance level. Then, the similarity of bacterial community structure was obtained by nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis (Figure 6A). The Adonis nonparametric test showed that there was no significant difference in bacterial community structure among the RT and RM treatments (r2 = 31%, p = 0.1), and the two-dimensional NMDS was in good agreement with the actual samples (stress = 0.025).
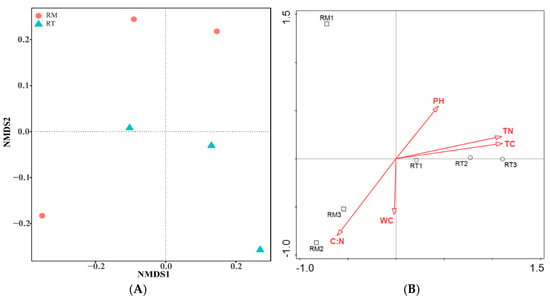
Figure 6.
Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis of soil bacterial community (A) and Redundancy analysis (B) based on Bray–Curtis distance. The numbers 1, 2, 3 are repetitions in the same treatment.
The RDA (db-RDA) analysis using the OTU abundance matrix of bacteria based on the Bray distance was performed to determine the effects of environmental factors on soil bacterial communities (Figure 6B). The first two axes explained 56.14% of the variability of the bacterial community structure. The first axis was positively correlated with TC, TN and pH, and was negatively correlated with C:N. The second axis was negatively correlated with C:N and WC, and positively correlated with TC, TN and pH. RT treatment bacterial communities were located in the positive region of the first axis, while the RM group was located in the negative area of the first axis. The envfit function was used to analyze whether the explanatory quantity of environmental factors on the distribution of bacterial communities was significant, as shown in Table 3. A smaller r2 indicates that the environmental factors have less influence on the distribution of bacterial communities. TC (r2 = 0.97) and TN (r2 = 0.9798) had the largest impacts on the distribution of bacterial communities and reached a significant level (p < 0.01) and therefore are dominant factors driving bacterial community variation.

Table 3.
Significance test of the correlation between environmental factors and bacterial community distribution.
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Soil Bacterial Community Composition to the Different Thinning Residue Treatments
Soil bacteria play an important role in the decomposition of organic matter and the formation of humus in a variety of biogeochemistry soil processes [44,45]. The community composition of soil bacteria is also influenced by the environment. It is well known that Proteobacteria and Firmicutes respond rapidly to labile C sources and exhibit rapid growth in a carbon-rich environment [10,46,47]. Two years after thinning a 21-year-old stand of Larix olgenis, there were significant differences between our residue removal treatments, which included whole-tree removal vs. stem only removal. Our results showed that Firmicutes abundance was significantly different in the two treatments. However, Proteobacteria tended to accumulate in the residue retention treatment (RT), although there was no significant difference between RT and RM. Alphaproteobacteria, the main class of Proteobacteria, was also not significantly more abundant in RT or RM. Although the relative abundances of Burkholderiales, Pseudomonadales and Sphingomonadales, which belong to the class Alphaproteobacteria, were greater in RT than RM, the relative abundance of Rhizobiales was lower in RT. This is because the Rhizobiales order has beneficial properties of nitrogen fixation, decomposition promotion of organic matter and plant growth [48,49]. In the RM treatment, the relatively low nitrogen environment stimulated the growth of nitrogen-fixing bacteria and increased their accumulation. The wax and wane of bacteria at the order level could be one of the reasons for the lack of a significant difference in Proteobacteria between RT and RM.
Bacteroidetes is a copiotrophic bacterium and can take advantage of simple carbon sources, usually occurring in cases of high resource utilization [46,47]. The LEfSe analysis showed that the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes was significantly different at the phylum level for two management treatments (Figure 5). Additionally, the relative abundances of Flavobacteriia, Flavobacteriales, and Flavobacteriaceae belonging to Bacteroidetes were also significantly different for both management treatments, and their relative abundances were greater in the RT treatment. Changes in the relative abundances of these bacteria under residue management were consistent with changing in soil TC and TN contents. The β-Proteobacteria, including Bacteroidetes, are copiotrophic bacteria, and β-Proteobacteria growth is closely associated with soil nutrient quantity and quality, and we observed that its relative abundance in the RT treatment was greater than in the RM treatment.
Moreover, the relative abundance of Acidobacteria in RT was lower than that of RM. This is due to the fact that Acidobacteria is an oligotrophic bacteria, its relative abundance tends to be greater in the case of low resource utilization, especially in the case of low soil carbon concentration [50,51], and so the increase in available carbon in the RT treatment leads to a decline in Acidobacteria abundance. It also shows that residue treatment changes the soil nutrient input, which leads to changes in soil bacterial community composition. We attribute this change in bacterial community composition to changes in resource availability. The redundancy analysis of soil physical and chemical properties to the bacterial community showed that TC and TN have the greatest influence on bacterial communities (Table 3). The residue content was 11.3 m3/ha, which is not high; however, there was a big difference between the nutrient element composition of the harvesting residue and the litter. The branches and leaves of the harvesting residue are mostly growing tissues, which contain more nutrient elements that are beneficial to microorganism decomposition. Nonstructural materials (leaves, fine roots, and twigs) of harvest residues have high decomposition rates during residue decomposition, and thus the nutrient release rate is fast in the early decomposition stages. This may be the cause of differences in the abundance of microorganisms that prefer a nutrient-rich environment [18]. However, structurally complex residues (stumps, coarse roots and branches) have higher proportions of resistant organic substrates compared with nonstructural residues, and thus it takes several years or even decades for the C and N in the structurally complex residues to be released [52,53].
Additionally, the removal of trees can immediately modify the microclimate, i.e., forest soils receive more solar radiation, and then the soil temperature rises after thinning, also reducing evapotranspiration due to loss of canopy trees, consequently increasing soil water availability. The increased soil temperature and water content can enhance organic matter decomposition [5]. Microorganisms need to input a certain amount of nitrogen in the process of organic matter decomposition. However, the soil after residue removal in thinning lacks the intake of exogenous nitrogen so that the microorganisms will consume the soil nitrogen when decomposing organic matter, resulting in soil nitrogen decline, thus stimulating the increase in nitrogen-fixing bacteria to meet the nitrogen demand of soil microorganisms [54]. At the same time, after thinning, the forest will distribute more photosynthates to the growth of the underground root system and improve the root system’s ability to absorb water and nutrients to meet the growing needs of above-ground plants, increase the fine root biomass of the remaining wood, and provide more decomposing substances. When the soil is relatively nitrogen deficient, the organic matter decomposition process will be slow, and nutrient release time will be prolonged. Residue retention has more exogenous nitrogen intake than residue removal, and the nutrient return rate of above-ground biomass is faster, which increases organic matter input. This may also be the reason for the change in eutrophic microbial groups.
In managed young forests, thinning occurs at least once before they reach commercial dimensions and then one to three times before clear-felling [4]. As the number of thinning treatments increases, the amount of accumulated thinning residues increases, and the removal of these residues will cause more nutrients to flow out of the forest. Additionally, in the final harvest (i.e., clear-felling), the removal of residues will result in a lack of physical soil protection, and temperature and humidity may also change, which is very unfavorable for microorganism growth [2,11]. However, our study was based on one thinning and medium-intensity thinning measures. Therefore, in subsequent forestland practice, the impact of harvest residues retention and removal on forest land nutrients and microbial communities will be greater than we documented.
Nutrient changes lead to changes in bacterial community composition; however, there was no significant difference in soil bacterial community structure between the two thinning residue treatments (Figure 6A). This may be because many bacteria are not dependent on their symbiotic hosts and have a high tolerance and flexibility to soil environmental variations, which may lower their sensitivity. Therefore, the resistance of bacteria to a reduction in survival resources caused by environmental changes can be improved [19,55]. In Hartmann’s study, it was also found that there was a relatively small difference in soil bacteria community structure in whole-tree vs. stem-only harvesting treatments in the taiga [30,56]. Overall, our study indicates that thinning residue retention or residue removal had little effect on soil microbial community structure but had an impact on soil bacterial composition; however, whether it has an effect on the ecosystem function remains to be determined.
4.2. Effects of Different Thinning Residue Treatments on Soil Bacterial α-Diversity
Using DNA sequences obtained by OTU to calculate microbial diversity indices is an effective method to evaluate microbial community diversity. Qualitative and quantitative change in a soil microbial community is a sensitive index for monitoring change in soil quality [37]. Assessing soil bacterial community diversity under different thinning residue treatments is a useful approach to understand soil bacterial community structure and function and is an index of soil ecosystem health. Our study found that there were no significant differences in OTU number and diversity index between thinning residue retention and removal treatments, the number of OTUs in the RT treatment was 1312, which was less than in the RM treatment (1732). Although the four diversity indexes show no significant differences between the two treatments, they are all reduced in the RT treatment, which is contrary to Peng Su’s study showing that organic matter addition promoted soil biological diversity [57], but are similar to Che et al.’s and Fernandez et al.’s studies, showing that fertilizer treatments reduced bacterial α-diversity and litter addition decreased microbial α-diversity, respectively [25,58]. Previous studies show that environmental heterogeneity can affect microbial diversity and for example, habitat types, vegetation cover, soil nutrient content and land use types [59]. Factors affecting microbial diversity are not singular, but rather the result of combined effects of a variety of complex ecological processes. Soil pH, water content and nutrient contents are the main environmental factors affecting soil microbial diversity in forest soils. Studies by Quanchao Zeng [60], Han Meng [61] and Miaojing Meng [62] show that pH has a strong effect on bacterial growth and survival, and the growth of some soil microorganisms can be inhibited or stimulated in different pH ranges, and it is considered to be the most important factor affecting soil bacterial community diversity. In Zhou’s study [63], the majority of microorganisms could not survive below a certain pH, but some acidophilic microorganisms showed an extremely high tolerance. In forest soils, greater soil water content reduces oxygen content, leading to the formation of anaerobic microhabitats, thus reducing microbial diversity [61]. In both treatments in our study, soil pH was about 5.5 and soil water content about 30%, and they were not significantly different (Table 1). Hence, this may be the reason for the lack of a significant difference in bacterial community diversity between the two treatments. However, in addition to soil pH and water content, soil quality (SOC, TC, TN, C:N, etc.) is also an important factor affecting soil bacterial diversity [62]. Due to the survival strategy of soil microorganisms, some bacteria will have a preference for resource quality—for example, copiotrophic bacteria are thought to be found under nutrient-rich conditions. The relative abundances of copiotrophic bacteria such as Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes and β-Proteobacteria in our study were consistent with soil TC and TN variation, which is also consistent with previous studies [25,28,64]. Therefore, there were no significant differences in the soil bacterial diversity among different thinning residue treatments. Moreover, the reason why the RT treatment diversity was lower than the RM treatment was that there were no significant differences in soil pH and water content. Nevertheless, residue retention improves soil quality and makes the environment more conducive to the growth of the copiotrophic taxa, thus reducing the diversity and evenness of the communities.
5. Conclusions
We demonstrated that retention of thinning residues (tree crowns) increased soil TC and TN contents, increased the availability of substrates for soil bacteria, and changed the soil bacteria community structure. Copiotrophic taxa such as Bacteroidetes and β-Proteobacteria were enriched in the soil environment where the stem was removed but the crown residues were retained, and nitrogen-fixing Rhizobiales increased in the soil after whole-tree removal. Changes in the soil bacterial community are mainly caused by soil nutrient change. There was no significant difference in bacterial community diversity among different thinning residue treatments, but residue retention treatment diversity tended to be lower than that of the residue removal treatment. We attribute this to the absence of significant differences in environmental factors such as soil pH and water content, which can drive bacterial community diversity. Residue retention improves soil quality and makes the environment more conducive to the growth of copiotrophic taxa, thus reducing the diversity and evenness of bacterial communities. Generally, to some extent, residue retention can alleviate the adverse effects of harvesting on soil nutrient loss.
Author Contributions
X.D. (Xue Dong) conceived and designed the experiments; X.-W.C. and Z.-H.S. supervised the design of experiments; X.D. (Xue Dong) and X.D. (Xin Du) performed the data collection of experiments; X.D. (Xue Dong) analyzed the data; X.D. (Xue Dong) wrote the first draft of the manuscript; X.-W.C. led the writing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31770670).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their valuable comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lei, X.; Lu, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhang, X.; Chang, J.; Hong, L. Growth and structure development of semi-natural larch-spruce-fir (Larix olgensis-Picea jezoensis-Abies nephrolepis) forests in northeast China: 12-year results after thinning. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 240, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolander, A.; Kitunen, V.; Tamminen, P.; Kukkola, M. Removal of logging residue in Norway spruce thinning stands: Long-term changes in organic layer properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.H.T.; Gonçalves, J.L.d.M.; Brandani, C.B.; de Ferraz, A.V.; Franci, A.F.; Marques, E.R.G.; Arthur Junior, J.C.; Hubner, A. Forest residue removal decreases soil quality and affects wood productivity even with high rates of fertilizer application. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 430, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamminen, P.; Saarsalmi, A.; Smolander, A.; Kukkola, M.; Helmisaari, H.S. Effects of logging residue harvest in thinnings on amounts of soil carbon and nutrients in Scots pine and Norway spruce stands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 263, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Z. Impacts of thinning on soil carbon and nutrients and related extracellular enzymes in a larch plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 450, 117523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Oliva, F.; Sveshtarova, B.; Oliva, M. Seasonal effects on soil organic carbon dynamics in a tropical deciduous forest ecosystem in western Mexico. J. Trop. Ecol. 2003, 19, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A.V.; Pereira e Silva, M.C.; Szturc-Koestsier, A.E.; Schmitt, H.; Falcão Salles, J.; Van Elsas, J.D. Impact of incorporated fresh 13C potato tissues on the bacterial and fungal community composition of soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 49, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhu, A.N.; Zhang, X.K.; Zhang, H.W.; Liang, W.J. Effects of tillage and residue management on soil microbial communities in north china. Plant Soil Environ. 2012, 58, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, J.W.; Wieder, W.R.; Taylor, P.G.; Townsend, A.R.; Nemergut, D.R.; Grandy, A.S.; Cleveland, C.C. Experimental litterfall manipulation drives large and rapid changes in soil carbon cycling in a wet tropical forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 2969–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.H.; Huang, Z.Q.; He, Z.M.; Yu, Z.P.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, R.Q.; Zheng, L.J. Changes of above- and belowground carbon input affected soil microbial biomass and community composition in two tree species plantations in subtropical China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 3582–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.; Kukkola, M.; Mälkönen, E.; Tveite, B. Impact of whole-tree harvesting and compensatory fertilization on growth of coniferous thinning stands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 129, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolander, A.; Levula, T.; Kitunen, V. Response of litter decomposition and soil C and N transformations in a Norway spruce thinning stand to removal of logging residue. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 256, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, O.; Jacobson, S. Effects of repeated slash removal in thinned stands on soil chemistry and understorey vegetation. Silva Fenn. 2004, 38, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, C.R.; Xu, Z.H. Soil carbon and nitrogen pools and microbial properties in a 6-year-old slash pine plantation of subtropical Australia: Impacts of harvest residue management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 206, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutua, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Blumfield, T. Residue retention mitigated short-term adverse effect of clear-cutting on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics in subtropical Australia. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3786–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, L.E.; Vance, E.D.; Swanston, C.W.; Curtis, P.S. Harvest impacts on soil carbon storage in temperate forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, N.J.; Xu, Z. Solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy: Characterization of soil organic matter under two contrasting residue management regimes in a 2-year-old pine plantation of subtropical Australia. Geoderma 2003, 114, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumfield, T.J.; Xu, Z.H.; Saffigna, P.G. Carbon and nitrogen dynamics under windrowed residues during the establishment phase of a second-rotation hoop pine plantation in subtropical Australia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 200, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.F.; Scott, D.A.; Sanchez, F.G.; Voldseth, R.A.; Page-Dumroese, D.; Elioff, J.D.; Stone, D.M. The North American long-term soil productivity experiment: Findings from the first decade of research. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 220, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaill, S.J.; Clinton, P.W.; Greenfield, L.G. Postharvest organic matter removal effects on FH layer and mineral soil characteristics in four New Zealand Pinus radiata plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 256, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Clinton, P.W.; Davis, M.R. Post-harvest residue management effects on recalcitrant carbon pools and plant biomarkers within the soil heavy fraction in Pinus radiata plantations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaraswamy, S.; Mendham, D.S.; Grove, T.S.; O’Connell, A.M.; Sankaran, K.V.; Rance, S.J. Harvest residue effects on soil organic matter, nutrients and microbial biomass in eucalypt plantations in Kerala, India. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 328, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lull, C.; Bautista, I.; Lidón, A.; del Campo, A.D.; González-Sanchis, M.; García-Prats, A. Temporal effects of thinning on soil organic carbon pools, basal respiration and enzyme activities in a Mediterranean Holm oak forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 464, 118088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tang, L.; Che, R.; Chen, H.; Blumfield, T.; Boyd, S.; Nouansyvong, M.; Xu, Z. Long-Term Harvest Residue Retention Could Decrease Soil Bacterial Diversities Probably Due to Favouring Oligotrophic Lineages. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.L.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Wyse, D.L.; Staley, C.; Gould, T.J.; Sadowsky, M.J. Structure of bacterial communities in soil following cover crop and organic fertilizer incorporation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9331–9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.L.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Wyse, D.L.; Staley, C.; Gould, T.J.; Sadowsky, M.J. Associations between soil bacterial community structure and nutrient cycling functions in long-term organic farm soils following cover crop and organic fertilizer amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendham, D.S.; O’Connell, A.M.; Grove, T.S.; Rance, S.J. Residue management effects on soil carbon and nutrient contents and growth of second rotation eucalypts. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 181, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz-Barrón, M.; Cruz-Mendoza, A.; Navarro–Noya, Y.E.; Ruiz-Valdiviezo, V.M.; Ortíz-Gutiérrez, D.; Ramírez-Villanueva, D.A.; Luna-Guido, M.; Thierfelder, C.; Wall, P.C.; Verhulst, N.; et al. The Bacterial Community Structure and Dynamics of Carbon and Nitrogen when Maize (Zea mays L.) and Its Neutral Detergent Fibre Were Added to Soil from Zimbabwe with Contrasting Management Practices. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H.S.; Garrett, L.G.; Beets, P.N.; Kimberley, M.O.; Oliver, G.R. Impacts of Harvest Residue Management on Soil Carbon Stocks in a Plantation Forest. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannam, K.D.; Quideau, S.A.; Kishchuk, B.E. Forest floor microbial communities in relation to stand composition and timber harvesting in northern Alberta. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Mooshammer, M.; Peñuelas, J.; Richter, A.; Sardans, J.; Wanek, W. The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant-microbial-soil organic matter transformations. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 85, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, K.; Bengtson, P.; Falkengren-Grerup, U.; Bengtsson, G. Plant-microbial competition for nitrogen uncoupled from soil C:N ratios. Oikos 2009, 118, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiro, J.; Kukkola, M.; Saarsalmi, A.; Tamminen, P.; Helmisaari, H.S. Logging residue removal after thinning in boreal forests: Long-term impact on the nutrient status of Norway spruce and Scots pine needles. Tree Physiol. 2010, 30, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Helmisaari, H.S.; Hanssen, K.H.; Jacobson, S.; Kukkola, M.; Luiro, J.; Saarsalmi, A.; Tamminen, P.; Tveite, B. Logging residue removal after thinning in Nordic boreal forests: Long-term impact on tree growth. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 261, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Cao, J.; Lan, G.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Q. The influence of land use patterns on soil bacterial community structure in the karst graben basin of Yunnan province, China. Forests 2020, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Deng, J.J.; Yin, Y.; Qin, S.J.; Zhu, W.X.; Zhou, Y.B.; Wang, B.; Ruan, H.; Jin, L. Bacterial community changes associated with land use type in the forest montane region of northeast China. Forests 2020, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X.; Li, M.; Mu, L.; Lei, J.; Sui, X. Conversion from natural wetlands to forestland and farmland alters the composition of soil fungal communities in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Wang, G.; Jin, J.; Sui, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Comparison of microbial community structures in four black soils along a climatic gradient in northeast China. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 92, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X. Biomass modeling of larch (Larix spp.) plantations in China based on the mixed model, dummy variable model, and Bayesian hierarchical model. Forests 2017, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Xu, S.; Zheng, X. Conversion from temperate secondary forests into plantations (Larix spp.): Impact on belowground carbon and nutrient pools in northeastern China. L. Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4129–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Carbon and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis-Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Page, A.L., Mille, R.H., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 561–579. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.L.; Sheard, R.W.; Moyer, J.R. Comparison of Conventional and Automated Procedures for Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Analysis of Plant Material Using a Single Digestion. Agron. J. 1967, 59, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, B. Determination of chemical and physical soil properties. In Monitoring and Assessing Soil Bioremediation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 47–95. [Google Scholar]
- Aneja, M.K.; Sharma, S.; Fleischmann, F.; Stich, S.; Heller, W.; Bahnweg, G.; Munch, J.C.; Schloter, M. Microbial colonization of beech and spruce litter—Influence of decomposition site and plant litter species on the diversity of microbial community. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bezemer, T.M.; Yang, J.; Lü, X.; Li, X.; Liang, W.; Han, X.; Li, Q. Changes in litter quality induced by N deposition alter soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 130, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenstein, M.D.; McMahon, S.; Schimel, J. Bacterial and fungal community structure in Arctic tundra tussock and shrub soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Noya, Y.E.; Gómez-Acata, S.; Montoya-Ciriaco, N.; Rojas-Valdez, A.; Suárez-Arriaga, M.C.; Valenzuela-Encinas, C.; Jiménez-Bueno, N.; Verhulst, N.; Govaerts, B.; Dendooven, L. Relative impacts of tillage, residue management and crop-rotation on soil bacterial communities in a semi-arid agroecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, W.T.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.K.; Ten, L.N.; Lee, S.T. Pleomorphomonas koreensis sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing species in the order Rhizobiales. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1663–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, S.A.; Myrold, D.D.; Högberg, M.N. Termination of belowground C allocation by trees alters soil fungal and bacterial communities in a boreal forest. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 70, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cong, J.; Lu, H.; Li, G.; Qu, Y.; Su, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, D. Community structure and elevational diversity patterns of soil Acidobacteria. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krankina, O.N.; Harmon, M.E.; Griazkin, A.V. Nutrient stores and dynamics of woody detritus in a boreall forest: Modeling potential implications at the stand level. Can. J. For. Res. 1999, 29, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvönen, R.; Olsson, B.A.; Lundkvist, H.; Staaf, H. Decomposition and nutrient release from Picea abies (L.) Karst. and Pinus sylvestris L. logging residues. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 126, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, P.; Mo, J. Global pattern and controls of biological nitrogen fixation under nutrient enrichment: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 3018–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, T.M. Impacts of forest management on northern forest soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 133, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Howes, C.G.; Vaninsberghe, D.; Yu, H.; Bachar, D.; Christen, R.; Henrik Nilsson, R.; Hallam, S.J.; Mohn, W.W. Significant and persistent impact of timber harvesting on soil microbial communities in Northern coniferous forests. ISME J. 2012, 6, 2199–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Lou, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Luo, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, J. Taxon-specific responses of soil microbial communities to different soil priming effects induced by addition of plant residues and their biochars. J. Soils Sedim. 2017, 17, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.; Liu, D.; Qin, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Hu, J.; Tahmasbian, I.; Cui, X. Increased litter input significantly changed the total and active microbial communities in degraded grassland soils. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2804–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; He, Z.; Wilson, M.J.; Campbell, C.D. Microbial biomass and community structure in a sequence of soils with increasing fertility and changing land use. Microb. Ecol. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; An, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Biogeography and the driving factors affecting forest soil bacteria in an arid area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 680, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Li, K.; Nie, M.; Wan, J.R.; Quan, Z.X.; Fang, C.M.; Chen, J.K.; Gu, J.D.; Li, B. Responses of bacterial and fungal communities to an elevation gradient in a subtropical montane forest of China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, M.; Lin, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Impacts of forest conversion on soil bacterial community composition and diversity in subtropical forests. Catena 2019, 175, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y. Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceja-Navarro, J.A.; Rivera, F.N.; Patiño-Zúñiga, L.; Govaerts, B.; Marsch, R.; Vila-Sanjurjo, A.; Dendooven, L. Molecular characterization of soil bacterial communities in contrasting zero tillage systems. Plant Soil 2010, 329, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).