Abstract
Two alder species (Alnus glutinosa and A. incana) have overlapping distribution, naturally occur in Lithuania, and are considered ecologically and economically important forest tree species. The objective of our study was to estimate the likelihood of spontaneous hybridizations between native alders in natural stands of Lithuania based on leaf morphology and nuclear microsatellite markers. The sampled trees were assigned to the three taxonomic groups of A. glutinosa, A. incana, and potential hybrids based on the leaf and bark morphological traits. The genetic differentiation and potential hybridization between these three groups was tested based on 15 nSSR markers. We identified studied Alnus spp. individuals as pure species and hybrids. Two microsatellite loci were reported as discriminating well between these species. We concluded that our results showed the highest likelihood of two genetic group structures, a clear genetic differentiation between the morphology-based groups of A. glutinosa and A. incana, and rather variable likelihood values in the putative hybrid group. The results provide important implications for genetic conservation and management of Alnus spp.
1. Introduction
Spontaneous natural interspecific hybridization provides a source of genetic variation, where hybrid populations often contains higher genetic diversity than their parental species, upon which natural selection may act [1]. Thus, natural interspecific hybridization of plants has been studied for a decades, and it is common to many species [1,2,3,4,5]. Hybridization can increase allelic variability and transmit adaptively important genetic information, which can increase the fitness of an introgressed lineage [6,7,8,9,10]. Introgressive hybridization plays an important role in evolution, increasing genetic diversity by creating many new genotypes, which can lead to the creation of new strains, ecotypes, or even sexual species adapted to certain conditions [1,4,11,12,13]. However, hybridization can have a negative impact as well; for example, it can cause genetic erosion and interrupt species integrity and lead to species extinction [1,13,14,15,16].
A. incana Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. is naturally widespread across all of Europe, from mid-Scandinavia to the Mediterranean countries, including northern Morocco and Algeria [17]. A. incana (L.) Moench. is native to most of Central Europe, to the west towards France and east into Russia, the Caucasus, and is common in Scandinavia and western Siberia. A. incana distribution range overlaps with the black alder and extends further north. In contrast, its southern distribution is more limited in comparison with black alder, and it does not exist in the United Kingdom [18]. Natural hybrids between different alder species were found in Europe, North America, the Russian Far East, and Japan [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. According to Banaev and Bažant [28], hybrids between A. incana and A. glutinosa occur very seldom on the eastern border of the species areas, and there is greater frequency of hybridization in the northern boundary of their areas. However, hybrid forms are infrequently found because of the differences in flowering time, which disable matting possibilities among related species [37,42]. In Belarus, for example, A. incana begins to flower six days earlier than black alder. This is enough time for alder pollination, although later the flowering time is overlapping. According to Parfenov [37], these species hybridize in anomalous years, i.e., when the cold spring is prolonged. The hybridization process occurs more frequently at the edges of populations and at their ‘sharp’ points. The researcher explains this property by the presence of specific flowering and pollination phases and also refers to the fact that polymorphic species can change the structure of biologic processes by adaptation. According to Lučnik [43], first-generation hybrid alders growing outside the natural range retain their characteristic properties for a long time. A. glutinosa flowers from six to eighteen days. In contrast, A. incana A. incana usually flowers one to two weeks earlier [28,42,44]. It is likely that, in addition to phenological traits that interfere with the hybridization of grey and black alders, there are other mechanisms involved, as these species grow together over a large area under different climatic conditions. A geneflow over a riparian network such as that assumed for Tilia [45] may also facilitate creating sympatric populations of water-tolerant alder species.
Morphological variation in alder can occur naturally due to isolation, small population size, and because of different environmental conditions [40]. Morphological data also provide information on the ecological and evolutionary phenomena associated with hybridization, since hybrids always have new traits [46]. The emergence of new traits increases as a percentage with hybrid generations. Hybrids often have traits that the primary species lack [47]. Mejnartowicz [48,49] studied the morphological alder traits and founded that the F1 hybrids of A. incana × glutinosa have many leaf traits clearly distinguishing them from the parental species. The leaves of hybrids differ from the paternal species in the luster, and the form is rounder than maternal species. They are intermediate in the length of the petiole, the number of pairs of veins, and the distance between the veins. The bark is smooth with the texture and color more like that of A. incana. These and additional traits have been used by many authors in their work to identify hybrids [28,40,41,50,51]; however, they are unique to first-generation hybrids. In the process of introgression, when hybrid alders backcross with plants of the parent species [52], morphometric traits are not sufficient to distinguish pure alder species.
There are a number of examples where microsatellite markers (simple sequence repeats—SSRs) were used for the identification of hybridization among various trees species [5,29,31,32,33,53,54,55,56]. Thus, SSRs are short, tandemly repeated DNA sequences, which are valuable molecular tools for various eco-genetic studies such as hybrid detection, due to high abundance, co-dominance, high level of polymorphism, and easy transferability among the species and laboratories [29,57,58,59,60]. A number of different studies on genetic variation of different Alnus spp. population have been performed in the last decades, for example, A. glutinosa [27,33,61,62,63,64,65,66], A. incana [67,68], A. rubra Bong. [69,70,71,72], and A. cordata (Loisel.) Duby [27,33], among others. Furthermore, for the identification of alder species and their hybrids, various morphological traits as well as molecular marker techniques have been recorded and well-documented, for example, A. glutinosa × incana hybrids [28,29,38,40,48,73,74]. Bousquet et al. [75] have used 15 isozyme loci to study genetic diversity within and among 11 A. crispa populations based on 15 isozyme loci. Later, Bousquet et al. [26] have used 15 isozyme loci to study genetic divergence and introgressive hybridization between A. sinuata and A. crispa among 20 populations. They have found some evidence for introgressive hybridization at the overlap of their ranges in three populations. However, the width of the hybrid zone appeared tenuous and the putative hybrid populations contained mostly intermediate or backcrossed genotypes, which were found at a much lower frequency in parental populations [26]. King and Ferris [27] have used chloroplast DNA (PCR-RFLP) and nuclear DNA (ISSR) variation to study alder species A. cordata (Lois.) and A. glutinosa (L.) in Corsica and southern Italy. Some of their findings of geographically correlated cpDNA variation was explained by introgressive hybridization. Zhuk et al. [29] have tested the transferability and amplification of 15 microsatellite markers developed for Betula pendula Roth. on A. glutinosa, A. incana, and their hybrids. The transferability rate was high, and eight out of fifteen nSSR have amplified in Alnus spp. Moreover, SSR marker results confirmed the species separation but were not entirely correlated for the putative hybrids. Later, Šmid et al. [31] used nuclear microsatellites in combination with chloroplast DNA markers to find putative hybrids among A. glutinosa and A. rohlenae at a narrow hybrid zone in southern Serbia. They found that, despite the selection, which acts against the triploid hybrids, they are important for gene exchange and enrichment of haplotype diversity and serve as a bridge for introgression and development of novel genetic lineages [31]. Stanton et al. [32] was investigating the hybridization of red alder (A. rubra Bong.) and white alder (A. rhombifolia Nutt.) in Cascade Mountains. Authors have developed and tested 30 SSR markers, which successfully produced high-quality multilocus genotypes. Furthermore, they were looking for SSR markers that can identify putative species-specific alleles that could best differentiate among the red alder, white alder, and hybrid samples. TO the end, Stanton et al. [32] found four SSR markers, which amplified loci with specific alleles that could serve for species and hybrid identification. Villani et al. [33] used seven nuclear microsatellites to study hybridization and genetic variation among endemic tree species—A. cordata and A. glutinosa in southern Italy. Authors found low genetic diversity, a variable frequency of F2 interspecific hybrids, and few backcross individuals. They have concluded that hybridization among the two Alnus spp. is limited, and the risk of genetic pollution is relatively low [33].
The objectives of our study were (i) to identify spontaneous hybridization events among A. glutinosa and A. incana species based on the morphology and DNA markers, (ii) to evaluate the genetic diversity and morphological traits of A. glutinosa and A. incana and their spontaneous hybrids, (iii) and to assess the growth characteristics of the hybrids in common habitats of both pure alder species.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
The material for laboratory analysis was collected in several study sites all over the country based on the presence of alder species and the alder hybrid swarms (Figure 1). In total, om two alders seed orchards (I—black alders, II—black, grey, and hybrid alders), two black alder progeny field trials, and the natural mixed forests of Lithuania, four temporary research plots (500 m2) of juvenal alders and individually selected black, grey, and hybrid alders were sampled for the study. During summer 2015, in each sample plot, 5–10 leaves were collected from the southern side at height of 5–8 m from the selected alder trees.
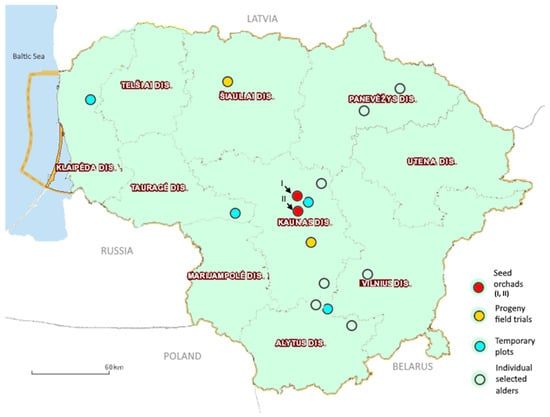
Figure 1.
The leaf collection sites of alder species (Alnus spp.) in Lithuania.
In total, for laboratory analysis, we used leaves from 162 putative spontaneous hybrids between black (Alnus glutinosa L) and gray (A. incana (L.) Moench.) alders as well as 13 and 14 individuals of A. glutinosa and A. incana. We collected leaves only from trees that looked like hybrids in seed orchard I, progeny field trials, and temporary research plots. Some hybrids and the pure alders leaves were collected in seed orchard II and individual selected plots. The putative hybrid alders were identified onsite based on a visual examination of the leaf morphology traits and stem morphotype [28,48]. After the morphological evaluation of the leaves was performed in the second half of the summer, we used the degree of leaf injury by alder leaf beetle (Agelastica alni L.) as an additional trait for the morphological discrimination between the species groups. The degree of the leaf injury by A. alni was the highest in A. incana (damaged > 50% leaf), lowest in black alder (damaged < 30% leaf), and often reached an intermediate level in the group of putative hybrids. This injury may be related to phenolic compound concentration, which is the highest in black alder leaves [76]. Nevertheless, we used these pest injury scores as a pure species indicator, but not for the determination of the hybridization degree.
2.2. Morphology Traits
In total, leaf morphology/morphometric traits of 192 alder trees with 5 to 10 leaves per tree were scanned and assessed: A. glutinosa (13 trees), A. incana (14 trees), and Alnus putative hybrids (162 trees). The mean values of the leaf traits were used in the data analysis. For the morphological investigation, we chose the key leaf traits for identifying the alder species [28,48,50]. The WinFolia 2016 Leaf analyzer program (Regent Instruments Inc.) was used to score six leaf traits: blade length (A, mm), blade maximum width (B, mm), length to position where maximum blade (D, mm), petiole length (I, mm), blade width measured at 90% blade length (E, mm), and upper angle of leaf (W) (Figure 2). One trait was assessed visually: secondary veins pairs (N, un). The pubescence of the lower half of the blade was determined in the five-point scale by [28] and was scored on a microscope (4× digital zoom) (P, 0–5). Four leaf traits were derived (D/A, E/B, I/A, and B/A).
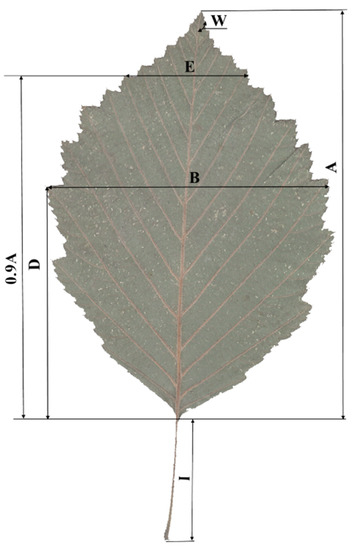
Figure 2.
Morphological traits of leaves (by [28]). A—blade length, mm; B—blade maximum width, mm; D—length to position where maximum blade, mm; I—petiole length, mm; E—blade width measured at 90% blade length, mm; W—upper angle of leaf, degrees.
2.3. DNA Extraction and Microsatellite Genotyping
Total genomic DNA was extracted from frozen leaf material according to an adjusted ATMAB DNA extraction method [77]. In total, DNA was successfully extracted from 189 samples, which were further used for DNA analysis with 15 microsatellite markers (nSSR): A2 [78], A7 [79]; A10 [80]; A22 [81]; A26 [82]; A35, A37 and A38 [83]; Ag01, Ag05, Ag09, Ag10, Ag13, Ag20, and Ag30 [84] (Table S1). Polymerase chain reactions were performed in two multiplexes (A and B) in a final volume of 15 μL containing 1.0 μL of genomic DNA (about 10 ng), 5.5 μL H2O RNase-free water, 7.5 μL of Qiagen Multiplex PCR Master Mix 2×, and 1.0 μL of 10× primer mix (thermal cycler from GeneAmp® PCR System 9700, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Multiplex A used loci Ag01, Ag05, Ag09, Ag10, Ag13, Ag20, and Ag30, and it comprised an initial denaturalization step of 5 min at 95 °C, followed by 30 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 3 min at 58 °C, 30 s at 72 °C, and a final extension step of 60 °C for 30 min. Multiplex B used loci A2, A7, A10, A22, A26, A35, A37, and A38, and it comprised an initial denaturalization step of 15 min at 95 °C, followed by 28 cycles of 30 s at 94 °C, 30 s at 56 °C, 30 s at 58 °C, 30 s at 60 °C, and 1 min at 72 °C, with a final extension step of 72 °C for 10 min. Amplified PCR products were separated by capillary electrophoresis using an ABI PRISMTM 310 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). GeneScan-500 LIZ (Applied Biosystems) was used as an internal size standard. Allele sizing was performed on a binset by using the program GeneMapper (Applied Biosystems version 4.0, Foster City, CA, USA).
2.4. Molecular Data Analysis
We have used 15 microsatellite loci (nSSR) for Alnus species differentiation and putative hybrid identification analysis. We use the Bayesian clustering approach as the model-based clustering algorithm in STRUCTURE ver. 2.3.4 software [85] to assess the genetic structure within the sampled groups of alders with the number of genetic clusters (K) ranging from 1 to 6 and using 100,000 Markov chain Monte Carlo iterations with a burn-in period of 100,000 and 20 replicates per run. We used the admixture model with correlated allele frequencies among the species groups. To determine the most likely number of clusters (K), the Delta K method by Evanno et al. [86] was applied using STRUCTURE HARVESTER software v0.6.94 [87].
The STRUCTURE analysis as described above was performed on all samples from the three species groups: the group of A. glutinosa, the group of A. incana, and the group of potential hybrids—189 individuals in total. To detect the putative interspecific hybrids among the studied individuals, the genetically pure individuals of the two respective parental species (A. glutinosa and A. incana) were used as the reference samples. This method has been used in several studies [5,54,56] to identify intra- and inter-specific hybridization in trees. The sampled individuals were sorted according to leaf and stem traits into the most probably pure individuals of each species and into one group of putative hybrids. Then, we used the program STRUCTURE to assign individuals to pure species or identify possible hybrids when pools were mixed. When two pure parental species were sampled as references, it was expected that the optimal value of K would consist of two genetic clusters (K = 2). This could be confirmed by testing values of K from one up to the number of populations in the respective groups using the STRUCTURE HARVESTER software [87], and we selected the optimum K following the method of Evanno et al. [86]. The program STRUCTURE generates an admixture coefficient (q) that represents the proportion of an individual’s genotype that originates from each of the K genetic clusters. STRUCTURE can be run with the option ANCESTDIST, which computes the 95% posterior probability for each q value, equivalent to a 95% confidence interval. Following Blair and Hufbauer [88], individuals were classified as hybrids if their q value was <0.90. If an individual’s proportion did not include one, introgression likely occurred. The online software CLUMPAK was used to identify clustering modes and packaging population structure inferences across the K values, as well as for graphical representation of the STRUCTURE results [89].
Finally, we used the Bayesian algorithms provided in NewHybrids v.1.1 beta [90], which estimate the posterior probability, and performed the independent classification of individuals as Alnus glutinosa and Alnus incana, or a hybrid based on their DNA genotypes. We considered the following categories: AI—A. incana, AG—A. glutinosa, F1 and F2 first- and second-generation hybrids, and two backcrosses: first to A. incana (0_Bx) and second to A. glutinosa (1_Bx). The NewHybrids algorithm was run with Jeffreys-like priors with 500,000 iterations following a 500,000-iteration burning. At the end, we combined the information obtained from Structure and NewHybrids to determine the specific hybrid class to which an individual tree was most likely to belong.
Finally, when the putative hybrids and pure species individuals were identified, the genetic diversity parameters were calculated for the three Alnus spp. groups: number of different alleles (Na), number of effective alleles (Ne), observed (Ho)/expected (He)/unbiased (uHe) heterozygosity, and fixation index (F) based on 15 microsatellite loci using the GenAlEx 6.5 software [91]. Pairwise Nei’s genetic distance [92] was estimated among three groups identified by STRUCTURE analysis [91,93]. The assessment and visualization the number of private alleles were performed in the Poppr R package [94]. Allelic richness (Ar) was estimated with the FSTAT 2.9.3. software [95], the lowest number of samples (23) was used for rarefaction. The software estimates allelic richness per locus, sample, and samples overall. Allelic richness is a measure of the number of alleles independent of sample size, thus allowing for comparison between different sample sizes among populations. Missing data were assessed among the loci and three groups of Alnus spp. and visualized by the R package poppr [94]. Putative species-specific alleles were identified by a manual examination of the GenAlEx output and GeneMapper profiles (data not shown). Discriminant analysis of principal components (DAPC) was used to proof the clustering of individuals based on results from STRUCTURE analysis (R package adegent 2.0.0 [96,97]). To test the associations among the species groups based on traditional Nei’s [98] genetic distances, we ran UPGMA cluster analysis with the R package poppr with 10,000 bootstrap replicates.
2.5. Statistical Analysis of Leaf Morphometric Traits
We used an analysis of variance (ANOVA XLSTAT 2020.3.1, Addinsoft [99]) to estimate differentiation in leaf morphology traits among the species groups as assigned by the DNA analyses. The traits with the highest F-values were used for further PCA analysis aimed to cluster the individuals based on the morphology traits (PC-ORD5 soft [100]). We used variance/covariance cross-products matrix and, for scores for variant, used distance-based biplot in PCA calculation. Significance of PCA scores of morphological traits was calculated using Pearson (R) and Kendell (tau) correlations. Based on this analysis, we identified the key leaf morphology traits for the discrimination among and identification of hybrids of alder species.
3. Results
3.1. Species Genetic Differentiation
Based on the on-site morphologic identification according to leaves and stem traits, we grouped all alder individuals into three groups: A. glutinosa (13 trees), A. incana (14 trees), and putative A. × hybrid (162 trees). In total, 189 trees from the three target groups were analyzed using 15 microsatellite loci. All the microsatellite loci were polymorphic and amplified 162 alleles in total. The mean number of alleles varied from 2.67 at loci A2 to 12.33 at loci A26 (Table S2).
The STRUCTURE Bayesian clustering revealed two genetic clusters that best explain the molecular variation (delta K = 975.007; Figure S1 and Table S3). A clear separation of Alnus glutinosa (AG) and A. incana (AI) as pure reference samples was observed with a few exceptions and among the remaining group of alder hybrids (AH), they were clearly visible (Figure 3). The STRUCTURE program identified 24 individuals as A. incana, 132—A. glutinosa, and 33—hybrids, of which five individuals are closer to A. glutinosa, six to A. incana, and 22 are F1 hybrids (Table S4).
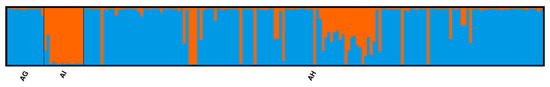
Figure 3.
Genetic differentiation of the alder species groups based on the Bayesian admixture clustering with K = 2 (highest delta K value of 975.007 was for K = 2; Figure S1 and Table S3). In the plot, individuals are represented by a thin vertical bar divided into K = 2 colored segments that represent the individual’s estimated membership fractions. The black vertical lines separate the three species groups.
The analysis by NewHybrids program allowed us to verify the species and hybrids assignment. NewHybrids have identified 20 individuals of A. incana, 132 of A. glutinosa and 37 of hybrids, of which 15 are pure F1 hybrids (q > 0.9), 9 are F1 hybrids with 0.9 < q > 0.7, 3 are hybrids are closer to A. incana, 5 are closer to A. glutinosa, and the other 5 hybrids as backcrosses to A. incana or to A. glutinosa (Table S4).
After species identification based on the Bayesian clustering, we used the discriminant analysis of principal components (DAPC) to further confirm the A. incana, A. glutinosa, and A. × hybrid genetic differentiation on the ordination axes based on SSR scores (Figure 4). The results showed a clear speciation of the tree species groups as identified by the NewHybrids analyses (Figure 4).
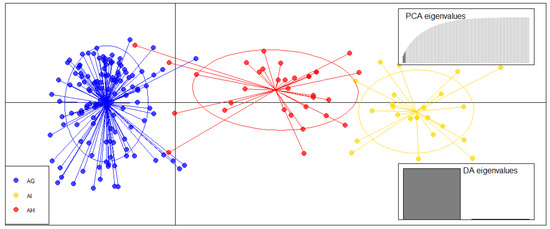
Figure 4.
Discriminant analysis of principal components (DAPC) of three Alnus spp. groups based on fifteen microsatellite markers. The graph shows the individuals as dots and the groups as inertia ellipses. Eigenvalues of the PCs are displayed in the upper left bar chart (R package adegent 2.0.0). AG—Alnus glutinosa, AI—A. incana, AH—hybrids.
The UPGMA clustering based on Nei’s [98] genetic distances showed closer genetic ties between the hybrid group and A. incana (Figure 5). Similar results were obtained based on pairwise genetic distance according to Nei [92] (Table S5).
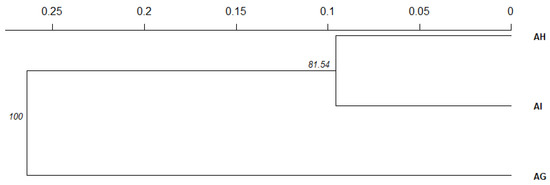
Figure 5.
Results of UPGMA clustering based on Nei’s 1978 genetic distances [98]. The significance of branch nodes was tested with 10,000 bootstraps among loci (indicated by percentage of bootstraps separating a given branch).
Finally, after successful hybrid identification based on genetic markers, we sorted all the individuals into three groups of pure A. glutinosa (132 individuals), A. incana (24 individuals), and A. × hybrid (33 individuals) and identified two microsatellite loci discriminating A. incana from A. glutinosa and their hybrids. Putative species-specific alleles were identified by manual examination of the GenAlEx output of loci Ag01 and Ag30. Locus Ag01 was monomorphic and amplified only one allele (129/129) in A. incana. In A. glutinosa and their hybrids, this locus amplified 11 and 8 alleles, respectively, and locus Ag30 amplified only two alleles for A. incana (96 and 98) and for A. glutinosa, and their hybrids seven and six, respectively.
3.2. Genetic Diversity
The genetic diversity indices were calculated after the Bayesian assignment of 189 individuals into three groups of pure A. glutinosa (132 individuals), A. incana (24 individuals), and A. × hybrid (33 individuals) (Table 1). Interestingly, the hybrid group possessed marked higher values for most of the genetic diversity indexes, including the observed and expected heterozygosity (Table 1). The mean number of alleles (Na) varied from 5.07 in A. incana to 10.07 in A. glutinosa, with an overall average of Na = 7.76. The mean number of effective alleles (Ne) varied from 2.96 in A. incana to 4.47 in A. × hybrid, with an overall average of Ne = 3.94. Allelic richness (Ar) varied from 5.03 in A. incana to 7.58 in A. × hybrid, with an overall average of Ar = 6.63. Unbiased expected heterozygosity (uHe) varied from 0.586 in A. incana to 0.726 in A. × hybrid with an overall average 0.649. Most of the allelic diversity parameters were markedly lower in A. incana in comparison with the other alder species (Table 1 and Figure S2). The inbreeding coefficient (FIS) was highest in A. incana followed by A. glutinosa (FIS = 0.057) and A. × hybrid (FIS = −0.066) with an overall average 0.063 (Table 1). In total, 39 private alleles were present and differently distributed over three alder species groups, with the highest number of private alleles observed in the group of A. glutinosa (Np = 34) (Table 1 and Figures S2 and S3). When comparing the two pure species of A. glutinosa and A. incana, for all the genetic diversity indices, A. incana had the lowest values.

Table 1.
The within-population genetic diversity parameters estimated based on 15 nSSR loci.
3.3. Leaf Morphology Variation
After assigning the individuals into the species groups based on the DNA markers, morphological analysis of leaves according to twelve morphological traits was performed. The ANOVA revealed significant species effects on all the leaf morphology traits except for A and I/A (blade length and ratio of petiole length and blade length) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Description statistics and results of ANOVA on the effect of species on the leaf morphology traits of alders and their hybrids. The model R2, F value, and Pr > F from ANOVA are given for n = 189 individuals.
The PCA analysis was performed on the morphology traits with the highest values of R2 and F from the ANOVA (Table 2, rows 1–6). The PCA results showed high correlation and determination coefficients between the above-mentioned leaf traits and the PC1 from the PCA (Table 3).

Table 3.
Description of three main principal components (PCs) from the PCA on leaf traits with the highest R2 from the ANOVA. Pearson’s (R) and Kendall’s (tau) correlations with the PCA ordination axes; n = 189.
The PCA plots of the individual tree values against two major PCs accounted for 95.55%, 4.10%, and 0.28% of the total variance in the first, second, and third PC axes, respectively. Based on leaf morphology traits, pure alder species obtained extreme PC1 scores and clustered onto the opposite ends of the PC1 axis, whereas the putative spontaneous hybrids were mainly located in between the pure species (Figure 6a,b).
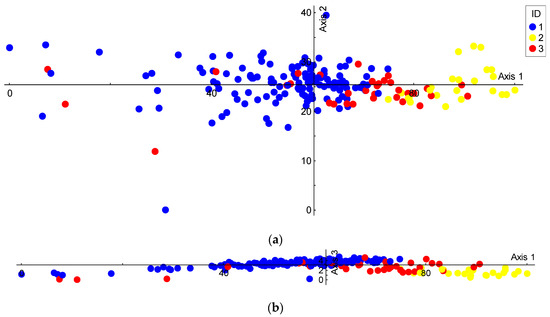
Figure 6.
Ordination plots (PCAs) of six leaf morphology traits of alder species. (a) Distribution of trees on axes 1 and 2; (b) distribution of trees on axes 1 and 3. Species ID: 1—Alnus glutinosa, 2—A. incana, 3—A. × hybrid.
For black alder, the values for all investigated leaf morphology traits were high, except for the pubescence (P), secondary veins pairs (N), and blade width and length ratio (B/A). Though the hybrid alder were found to occupy intermediate positions between A. glutinosa and A. incana. The A. incana had more pubescens and secondary veins pairs (Table 2, Figure S4). Variety of alder leaf shapes within the species can be seen in Figure 7.
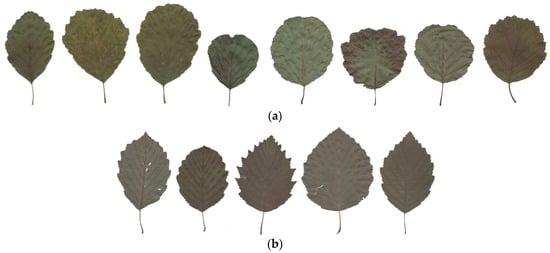

Figure 7.
Variation of leaf forms of the parental species Alnus glutinosa (a), A. incana (b), and their hybrids (c). The leaves numbered 1, 6, 7, 8, and 9 in the c row are of the F1 hybrids, the leaves numbered 2 and 9 are of the hybrids that have backcrosses with A. incana, and the leaves numbered 3 and 4 are of the hybrids that have backcrosses with A. glutinosa; all have nine pairs of veins, less pubescence, and a blade maximum width greater than A. incana.
4. Discussion
Our study focused on two autochthonous Alnus genus (Betulaceae) species—A. glutinosa and A. incana, with overlapping ranges in Lithuania. A. incana is inhabiting drier sites than A. glutinosa and is less common in the southern part and more frequent in the north-eastern part of the country. Meanwhile, A. glutinosa is most common on wet sites in the lowlands of central Lithuania and in the southwestern part of the country. However, warming climates often alter the site moisture regime, thus providing better chances for co-occurrence and hybridization among tree species that may lead to sympatric speciation events following the global environmental change [101]. Our study provides strong evidence for such sympatric speciation events among alder species complex in overlapping natural habitats. Assuming climatic predictions for northern Europe of frequent incidence of high precipitation over a short time in otherwise dry ecosystems, we may expect a diverse moisture regime within a single site. Here, a desiccation and moisture stress may occur on the same site, where alders possessing integrated gene pools of A. glutinosa × incana could be an example of an adaptive species introgression for better tolerance of such complex stresses [102].
For this study, we collected leaves mainly from those alders that were morphologically different from the usual morphometric traits of A. glutinosa and A. incana (bark color, number of leaf vein pairs, and tooths of leaf edging) [28,36,48]. The leaves of most of the trees that were assigned to the A. × hybrid group had 7–9 vein pairs, the leaf edge was slightly serrated and double-toothed, and the form of leaf was not traits of pure A. glutinosa or A. incana. However, only about 30 trees of the morphology-based 162 putative hybrids proved to be such based on the DNA markers. Thus, the accuracy of the onsite morphology identification of alder hybrids is low.
In the current study, we have identified a set of 15 nuclear microsatellite markers for an efficient genetic discrimination within the Alnus species complex. Our findings agree with a number of studies where microsatellites or other DNA markers were used to study the level of genetic diversity and hybridization in Alnus species [26,27,29,31,33]. First, based on Bayesian clustering analysis (STRUCTURE soft.), everyone was assigned to either pure A. incana, pure A. glutinosa, or a hybrid; thus, we have identified 24 individuals as A. incana, 132 as A. glutinosa, and 33 as putative hybrids. The analysis with NewHybrids software assigned everyone to either pure species of A. incana or A. glutinosa and different orders of hybrids (F1, F2 and Backcrosses) as follows: 20, 132, and 37 individuals as A. incana, A. glutinosa, and putative hybrids, respectively. For the hybrid populations, 24 individuals were F1 hybrids and 13 have F2, backcrosses, or mixed traits. These multiple backcrossing events usually complicate the morphology-based identification of the hybrids. However, most of the hybrids identified in our study belonged to the F1 generation. In contrast, Villani et al. [33] in southern Italy have not found any F1 hybrids, and most of the hybrids were F2 hybrids among A. cordata and A. glutinosa with a low frequency of backcrosses toward the parental species. According to some authors [49,103], hybrids between A. incana and A. glutinosa most commonly occur when the mother tree is A. incana. It was proven by artificial crosses and was found that successful hybridization takes a place only when the mother tree was A. incana. In contrast, hybridization was unsuccessful when the mother tree was A. glutinosa. Moreover, in pilot plantation, where we have collected alders as a putative hybrid, genetic data analysis recognized only one hybrid. All other trees were identified as black alders. Furthermore, from other leaf collection sites, we identified 82 putative hybrids by morphometric traits; however, genetic analysis determined 32 hybrids. These results shows that their morphological and genetic boundaries do not fit and are much wider than the phenotypic or vice versa. The variation of hybridization rate among the sampled trees suggests that natural crossing between the two species occurs at lower frequency than we were expecting and probably depends on diverse local factors such as synchronization, which favors hybridization.
Overall, in our study, evidence for hybridization between A. glutinosa and A. incana was found from morphological and genetic backgrounds; however, it was inconsistent. Based on Bayesian clustering results, putative hybrids constituted 17.5% (33 out of 189 individuals), which was comparable with the results of Villani et al. [33], which identified significant introgression (from 9.1% to 50.0%) in some natural Alnus spp. populations in southern Italy.
However, the initial number of pure reference samples per parental species was not high in our study (e.g., A. glutinosa—13 trees and A. incana—14 trees), which may influence the genetic assignment into hybrid groups. Furthermore, morphological leaf traits typically used to identify alders in the field did not reliably distinguish taxonomy within the Alnus complex [28]. However, our results show that a combination of molecular data and morphological traits has high potential and could help the classification of the genus Alnus, especially in hybrid individuals. Therefore, further autochthonous Alnus species conservation, breeding, and management measures should take a more detailed genetic examination to enable better species discrimination, which is the basis for in situ and ex situ conservation and for successful breeding programs.
After clear pure species and hybrids identification, the level of genetic diversity was assessed on the three groups: A. glutinosa, A. incana, and their hybrids were compared based on 15 nSSR markers. Our results agreed with previous studies of Alnus spp. and showed a moderate level of genetic diversity among three groups. In the group of pure A. incana trees, the inbreeding coefficient (FIS = 0.197) was highest, and all genetic variation indices were lower (e.g., mean values of mean number of alleles (Na), mean number of effective alleles (Ne), allelic richness (Ar), and expected heterozigosity (He)) in comparison to A. glutinosa and their hybrids. Overall, despite unequal sample size, Alnus spp. hybrids contained higher values of Na, Ne, Ar, and He. In comparison, results presented by Šmid et al. [31], which used nuclear and chloroplast DNA markers to study hybridization zone and find putative hybrids among A. glutinosa and A. rohlena, showed clear separation of the two Alnus species based on both marker types. Genetic diversity was moderate (Na = 4.78 and He = 0.72) but the inbreeding coefficient was high (FIS = 0.33–0.42). The results presented by Villani et al. [33] showed low genetic diversity among and within A. cordata, endemic tree species, populations in comparison with A. glutinosa or A. cordata × glutinosa hybrids. For example, A. cordata × glutinosa hybrids showed higher values for the number of alleles (Na = 6.904) and observed heterozygosity (Ho = 0.489), compared to pure populations of A. cordata and A. glutinosa (Na = 3.107, Ho = 0.396, Na = 5.286, and Ho = 0.468, respectively). Furthermore, all populations with admixture of putative hybrids indicated significant positive inbreeding coefficient (FIS = 0.237–0.461). However, when comparing the results, we should consider the peculiarities of each species and the variation in sample size, geography, and number of loci used.
A. glutinosa leaves vary in their shape, and they are emarginate, rounded, or acute at tip and cuneate, obtuse, or acute at base, and their margins are entire, serrate with a slightly wavy edge, or double serrate (Figure S5). Many interesting morphological forms were found between alders in our sampling sites (Figure S6). These results may be related to natural variability within the species, or they might be the consequence of backcross-breeding or heritability. Morphological investigations in our study were carried out to help to distinguish the species of A. glutinosa from A. incana and their hybrids. We can highlight that F1 A. hybrids in their morphometric traits are closer to A. incana and have about nine pairs of veins (N), pubescence (P) less than A. incana, and a blade maximum width (B) greater than A. incana. However, morphometric data gives just first insights into interspecific hybridization but are not sufficient to assess the level of hybridization among the alder species. Although our morphological assessment in many cases showed alders as pure A. glutinosa or A. incana, the genetic analysis showed that it is a putative hybrid (Table S4, alders id J9, 17BtPL25, BL1, BM1, B3).
In the temporary research plots, A. glutinosa accounted for 88.4%, A. incana for 10.3%, and alder hybrids for 1.3% of all alders (results not shown). Similarly, hybridization events have been reported in other studies on A. glutinosa and A. incana [25,28,36,39,48,50,51,73,84]. Our results are in line with other studies showing that, by a complex of morphometric traits, hybrids of alders hold an intermediate position (e.g., Villani et al. [33] found from 9.1% to 50% of hybrids between A. cordata and A. glutinosa in different populations in Italy).
5. Conclusions
We used DNA makers to untangle the complex morphology of pure A. incana and A. glutinosa species and their hybrid swarms in natural stands. The result showed that most were F1 hybrids, and other had backcrosses to parental species or mixed traits. It is these multiple backcrossing events that complicated morphology-based recognition of the hybrids. Two microsatellite loci (Ag01 and Ag30) discriminate well between these species. DNA markers supported clear genetic differentiation between the groups based on the morphology of A. glutinosa and A. incana and quite variable values of the probable envelope in the putative hybrid group.
In conclusion, our study provides strong evidence for spontaneous hybridization between sympatric species of A. incana and A. glutinosa in natural forests of northern Europe. The hybrid alders seem to be genetically closer to A. incana and are of a markedly greater genetic diversity than the corresponding parental species. There are concerns for genetic drift effects in the populations of A. incana.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f12111504/s1, Table S1: List of nuclear microsatellite markers (nSSR’s) used in our study; Table S2: The genetic diversity parameters for each of the loci (GenAlex6.5 software [91,93]). Allelic richness (FSTAT 2.9.3 [95]); Figure S1: The results of Bayesian clustering (soft. STRUCTURE2.3.4 [85]) on the most likely number of genetic clusters within the studied three Alnus spp. groups, indicated by the highest delta K value at K = 2 (STRUCTURE HARVESTER soft. [87]); Table S3: The Evanno table output results of Bayesian clustering (soft. STRUCTURE2.3.4 [85]) on the most likely number of genetic clusters within the studied populations, indicated by the highest delta K value (STRUCTURE HARVESTER soft. [87]); Table S4: Identification of putative hybrids by STRUCTURE and NewHybrids programs; Table S5: Pairwise genetic distance according to Nei [92] (GenAlEx6.5 [91,93]; Figure S2: Distribution of genetic diversity among three sampled Alnus spp. groups (Na—Mean no. of Different Alleles; Ne—Mean no. of Effective Alleles; Ar—Mean allelic richness (based on min. sample size of 23 diploid individuals.), Npriv—No. of Private Alleles; He—Expected Heterozygosity) (soft. GenAlEx 6.5 [91,93,94]). Groups abbreviations in Table 1; Figure S3: Private alleles distribution among the studied three Alnus spp. groups (189 individuals) (R package poppr [94]); Figure S4: The PCA ordination plots of alder trees given separately for species-specific leaf morphology traits. The symbol size indicates the relative size of the morphology traits in the entity. The minimum value (zero) is shown on an overlay as the smallest size for that symbol. Abbreviations shown in Table 2, species ID—in Figure 6. (a) Distribution of trees on axes 1 and 2; (b) Distribution of trees on axes 1 and 3; Figure S5: The varieties of black alder (Alnus glutinosa) forms; Figure S6: Different forms of Alnus glabra, A. incana and their hybrids.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.B. and S.T.; methodology, V.B. and S.T.; formal analysis, G.J. and D.K.; investigation, S.T., G.J. and J.B.; resources, G.J. and J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, G.J. and D.K.; writing—review and editing, G.J., D.K. and D.D.; visualization, S.T.; supervision, V.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Acknowledgments
The material presented in the article was collected during the long-term LAMMC research program “Sustainable Forestry and Global Change”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Neale, D.B.; Wheeler, N.C. Hybridization and Introgression. In The Conifers: Genomes, Variation and Evolution; Neale, D.B., Wheeler, N.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 387–429. ISBN 978-3-319-46807-5. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, E. Introgressive Hybridization. In Introgressive Hybridization; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, M.L. Natural Hybridization as an Evolutionary Process. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1992, 23, 237–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seehausen, O. Hybridization and Adaptive Radiation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamošaitis, S.; Jurkšienė, G.; Petrokas, R.; Buchovska, J.; Kavaliauskienė, I.; Danusevičius, D.; Baliuckas, V. Dissecting Taxonomic Variants within Ulmus Spp. Complex in Natural Forests with the Aid of Microsatellite and Morphometric Markers. Forests 2021, 12, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choler, P.; Erschbamer, B.; Tribsch, A.; Gielly, L.; Taberlet, P. Genetic Introgression as a Potential to Widen a Species’ Niche: Insights from Alpine Carex curvula. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.H.; Bouck, A.C.; Arnold, M.L. Detecting Adaptive Trait Introgression Between Iris Fulva and I. brevicaulis in Highly Selective Field Conditions. Genetics 2006, 172, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castric, V.; Bechsgaard, J.; Schierup, M.H.; Vekemans, X. Repeated Adaptive Introgression at a Gene under Multiallelic Balancing Selection. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Cui, M.-L.; Cubas, P.; Gillies, A.; Lee, K.; Chapman, M.A.; Abbott, R.J.; Coen, E. Regulatory Genes Control a Key Morphological and Ecological Trait Transferred Between Species. Science 2008, 322, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twyford, A.D.; Ennos, R.A. Next-Generation Hybridization and Introgression. Heredity 2012, 108, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.L.; Hodges, S.A. Are Natural Hybrids Fit or Unfit Relative to Their Parents? Trends Ecol. Evol. 1995, 10, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.L. Natural Hybridization and Evolution; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; ISBN 978-0-19-509975-1. [Google Scholar]
- Van Droogenbroeck, B.; Kyndt, T.; Romeijn-Peeters, E.; Van Thuyne, W.; Goetghebeur, P.; Romero-Motochi, J.P.; Gheysen, G. Evidence of Natural Hybridization and Introgression between Vasconcellea Species (Caricaceae) from Southern Ecuador Revealed by Chloroplast, Mitochondrial and Nuclear DNA Markers. Ann. Bot. 2006, 97, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, D.A.; Francisco-Ortega, J.; Jansen, R.K. Hybridization and the Extinction of Rare Plant Species. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E. The Role of Hybridization in Plant Speciation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 561–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vít, P.; Wolfová, K.; Urfus, T.; Tájek, P.; Suda, J. Interspecific Hybridization between Rare and Common Plant Congeners Inferred from Genome Size Data: Assessing the Threat to the Czech Serpentine Endemic Cerastium alsinifolium. Preslia 2014, 86, 95–117. [Google Scholar]
- Claessens, H.; Oosterbaan, A.; Savill, P.; Rondeux, J. A Review of the Characteristics of Black Alder (Alnus Glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.) and Their Implications for Silvicultural Practices. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2010, 83, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, T.H.; de Rigo, D.; Caudullo, G. Alnus Incana in Europe: Distribution, Habitat, Usage and Threats. In European Atlas of Forest Tree Species; San-Miguel Ayanz, J., de Rigo, D., Caudullo, G., Houston Durrant, T., Mauri, A., Eds.; EU Publication Office: Luxembourg, 2016; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Hylander, N. Leaved and Small-Leaved Forms of Alnus Glutinosa and A. Incana. Sven. Bot. Tidskr. 1957, 51, 437–453. [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima, M. On a Hybrid of Alnus. J. Jpn. Bot. 1957, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, F.L. Introgression of Alnus Serrulata and Alnus Rugosa. Rhodora 1961, 63, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Furlow, J.J. The Systematics of the American Species of Alnus (Betulaceae). Rhodora 1979, 81, 1–121. [Google Scholar]
- Bobrov, E.G. Some Traits of Modern History of Flora and Vegetation of the Southern Part of the Russian Far East. Bot. Zhurnal 1980, 65, 172–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bousguet, I.; Cheliar, W.M.; Lalonde, M. Allozyme Divergence and Introgressive Hybridization between Alnus Crispa and Alnus Sinuata (Betulaceae). Am. J. Bot. 1989, 76, 228–229. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R.B.; Burgess, D. Evaluation of Alnus Species and Hybrids. Biomass 1990, 22, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Cheliak, W.M.; Wang, J.; Lalonde, M. Genetic Divergence and Introgressive Hybridization Between Alnus Sinuata andA. Crispa (Betulaceae). Pl. Syst. Evol. 1990, 170, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.A.; Ferris, C. Chloroplast DNA and Nuclear DNA Variation in the Sympatric Alder Species, Alnus Cordata (Lois.) Duby and A. Glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2000, 70, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaev, E.; Bažant, V. Study of Natural Hybridization between Alnus Incana (L.) Moench. and Alnus Glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. J. For. Sci. 2007, 53, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuk, A.; Veinberga, I.; Daugavietis, M.; Rungis, D. Cross-Species Amplification of Betula Pendula Roth. Simple Sequence Repeat Markers in Alnus Species. Balt. For. 2008, 14, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Jurkšienė, G.; Baliuckas, V. Natural Hybridization and Features between Alnus Incana (L.) Moenc. and Alnus Glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. in Lithuania. In Book of Abstracts, Proceedings of the Agrosym 2019: X International Scientific Agriculture Symposium, Jahorina, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 3–6 October 2019; Kovacevic, D., Ed.; University of East Sarajevo, Faculty of Agriculture: Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Šmíd, J.; Douda, J.; Krak, K.; Mandák, B. Analyses of Hybrid Viability across a Hybrid Zone between Two Alnus Species Using Microsatellites and CpDNA Markers. Genes 2020, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, B.J.; Best, T.; Islam-Faridi, N.; Gantz, C.; Haiby, K.; Johnson, L.J.; Shuren, R.; Stanish, A.; Staton, M.; Weathers, T.C.; et al. Inter-Specific Hybridization of Alnusrubra and Alnus Rhombifolia:Preliminary Report of a New Taxon and DNA Marker Resources for Bioenergy Feedstockproduction. Tree Genet. Genomes 2020, 16, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, F.; Castellana, S.; Beritognolo, I.; Cherubini, M.; Chiocchini, F.; Battistelli, A.; Mattioni, C. Genetic Variability of Alnus Cordata (Loisel.) Duby Populations and Introgressive Hybridization with A. Glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. in Southern Italy: Implication for Conservation and Management of Genetic Resources. Forests 2021, 12, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobendza, R. Meiszance Naturalne Olszy Szarej i Czarnej w Polsce (Alnus Incana Moench.× Alnus Glutinosa Gaertn.–Alnus Hybrida Alex. Braun.). Rocznik Dendrol. 1956, 56, 57–62. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kundzinsh, A.V. Hybrids of Alnus Glutinosa and A. Incana in the Forests of the Latvian SSR. Izv. AN Latv. SSR 1957, 2, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Voronova, A.; Lazdina, D.; Korica, A.; Veinberga, I.; Liepins, K.; Rungis, D. Evaluation of Allelic Content in an Experimental Alder (Alnus Spp.) Plantation. Acta Biol. Univ. Daugavp. 2015, 15, 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Parfenov, V.I. Dependence of Distribution and Adaptation of Plant Species on the Area Borders; Nauka i Tekhnika: Minsk, Belarus, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Parnell, J. Variation and Hybridisation of Alnus Miller in Ireland. Watsonia 1994, 20, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Olshansky, I.G. Genus Alnus Mill. (Betulaceae SF Gray) in the flora of Ukraine (Piд Alnus Mill. (Betulaceae SF Gray) y флopi Уkpaїни). Бioлoгічні Cucmeми 2014, 6, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Mijnsbrugge, K. Morphological Dissection of Leaf, Bud and Infructescence Traits of the Interfertile Native A. Glutinosa and Non-Native A. Incana in Flanders (Northern Part of Belgium). Trees 2015, 29, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidaković, V.; Stefanović, M.; Novaković, M.; Jadranin, M.; Popović, Z.; Matić, R.; Tešević, V.; Bojović, S. Inter-and Intraspecific Variability of Selected Diarylheptanoid Compounds and Leaf Morphometric Traits in Alnus Glutinosa and Alnus Incana. Holzforschung 2018, 72, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkevich, I.D.; Geltman, V.S.; Lovcij, N.F. Types and Associations of Black Alder Forests (Tunы u Accoцuaцuu Чернooльхoвых Лecoв); Nauka i Tiechnika: Minsk, Belarus, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Lučnik, Z.I. Introduction of Trees and Shrubs in Shrubs in the Altai Krai; Kolos: Moscow, Russia, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanauskas, V. Dendrologija (Dendrology); Mintis: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Danusevičius, D.; Kembrytė, R.; Buchovska, J.; Baliuckas, V.; Kavaliauskas, D. Genetic Signature of the Natural Gene Pool of Tilia Cordata Mill. in Lithuania: Compound Evolutionary and Anthropogenic Effects. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 6260–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieseberg, L.H.; Ellstrand, N.C.; Arnold, D.M. What Can Molecular and Morphological Markers Tell Us About Plant Hybridization? Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1993, 12, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieseberg, L.H. The Role of Hybridization in Evolution: Old Wine in New Skins. Am. J. Bot. 1995, 82, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejnartowicz, L. Morphology and Growth of Alnus Incana× Glutinosa Hybrids. Arbor. Kórnickie Rocz. XXVI 1982, 26, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Mejnartowicz, L. Evidence for Long-Term Heterosis Phenomenon in the Alnus Incana× Glutinosa F-1 Hybrids. Silvae Genet. 1999, 48. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?request_locale=en&recordID=DE1999T30143&sourceQuery=&query=&sortField=&sortOrder=&countryResource=&agrovocString=&advQuery=¢erString=&enableField= (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Bašić, N.; Selimović, E.; Pustahija, F. Morphological Identification of Nothospecies Alnus × Pubescens Tausch. and Their New Localities in Central Bosnia. Rad. Šumarskog Fak. Univ. Sarajev. 2014, 44, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Viljevac, B. Morfološki i Genetički Dokazi Hibridizacije Izmedju Bijele (Alnus Incana (L.) Moench) i Crne Johe (A. Glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.) u Podravini. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zagreb, Faculty of Science, Department of Biology, Zagreb, Croatia, 2020. (In Croatian). [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.G.; Larson, E.L. Hybridization, Introgression, and the Nature of Species Boundaries. J. Hered. 2014, 105, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalapa, J.E.; Brunet, J.; Guries, R.P. Original Article: The Extent of Hybridization and Its Impact on the Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of an Invasive Tree, Ulmus Pumila (Ulmaceae). Evol. Appl. 2010, 3, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, J.; Zalapa, J.E.; Pecori, F.; Santini, A. Hybridization and Introgression between the Exotic Siberian Elm, Ulmus Pumila, and the Native Field Elm, U. Minor, in Italy. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buiteveld, J.; Vanden Broeck, A.; Cox, K.; Collin, E. Human Impact on the Genetic Diversity of Dutch Field Elm (Ulmus Minor) Populations in the Netherlands: Implications for Conservation. Plant Ecol. Evol. 2016, 149, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.; Brunet, J.; Zalapa, J.E.; von Wehrden, H.; Hartmann, M.; Kleindienst, C.; Schlautman, B.; Kosman, E.; Wesche, K.; Renison, D.; et al. Intra- and Interspecific Hybridization in Invasive Siberian Elm. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 1889–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.J.; Pádua, J.G.; Zucchi, M.I.; Vencovsky, R.; Vieira, M.L.C. Origin, Evolution and Genome Distribution of Microsatellites. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2006, 29, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbará, T.; Palma-Silva, C.; Paggi, G.M.; Bered, F.; Fay, M.F.; Lexer, C. Cross-Species Transfer of Nuclear Microsatellite Markers: Potential and Limitations. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 3759–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.R.; Burke, J.M. EST-SSRs as a Resource for Population Genetic Analyses. Heredity 2007, 99, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Barkley, N.A.; Jenkins, T.M. Microsatellite Markers in Plants and Insects. Part I: Applications of Biotechnology. Genes Genomes Genom. 2009, 3, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Prat, D.; Leger, C.; Bojovic, S. Genetic Diversity among Alnus Glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. Populations. Acta Oecologica 1992, 13, 469–477. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.A.; Ferris, C. Chloroplast DNA Phylogeography of Alnus Glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejnartowicz, L. Genetic Variation within and among Naturally Regenerating Populations of Alder [Alnus Glutinosa]. Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae 2008, 77, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lepais, O.; Muller, S.D.; Saad-Limam, S.B.; Benslama, M.; Rhazi, L.; Belouahem-Abed, D.; Daoud-Bouattour, A.; Gammar, A.M.; Ghrabi-Gammar, Z.; Bacles, C.F.E. High Genetic Diversity and Distinctiveness of Rear-Edge Climate Relicts Maintained by Ancient Tetraploidisation for Alnus Glutinosa. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havrdová, A.; Douda, J.; Krak, K.; Vít, P.; Hadincová, V.; Zákravský, P.; Mandák, B. Higher Genetic Diversity in Recolonized Areas than in Refugia of Alnus Glutinosa Triggered by Continent-Wide Lineage Admixture. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 4759–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubry, P.; Gallagher, E.; O’Connor, E.; Kelleher, C.T. Phylogeography and Population Genetics of Black Alder (Alnus Glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.) in Ireland: Putting It in a European Context. Tree Genet. Genomes 2015, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandák, B.; Havrdová, A.; Krak, K.; Hadincová, V.; Vít, P.; Zákravský, P.; Douda, J. Recent Similarity in Distribution Ranges Does Not Mean a Similar Postglacial History: A Phylogeographical Study of the Boreal Tree Species Alnus Incana Based on Microsatellite and Chloroplast DNA Variation. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljak, I.; Idžojtić, M.; Šapić, I.; Korijan, P.; Vukelić, J. Diversity and Structure of Croatian Continental and Alpine-Dinaric Populations of Grey Alder (Alnus Incana /L./ Moench Subsp. Incana); Isolation by Distance and Environment Explains Phenotypic Divergence. Šumarski List 2018, 142, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ager, A.A.; Heilman, P.E.; Stettler, R.F. Genetic Variation in Red Alder (Alnusrubra) in Relation to Native Climate and Geography. Can. J. For. Res. 1993, 23, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.L.; Xie, C.Y.; Ying, C.; Guy, R.D. Genetic Variation of Ecophysiological Traits in Red Alder (Alnusrubra Bong.). Can. J. For. Res. 1994, 24, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, A.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Koshy, M.P.; Namkoong, G. Multivariate Analysis of Allozymic and Quantitative Trait Variation in Alnus Rubra: Geographic Patterns and Evolutionary Implications. Can. J. For. Res. 1998, 28, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.-Y.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Ying, C.C. Genetics of Red Alder (Alnus Rubra Bong.) Populations in British Columbia and Its Implications for Gene Resources Management. New For. 2002, 24, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paus-Glowacki, W.; Meinartowicz, L. Serological Investigation of Alnus Incana x Glutinosa Hybrids and Their Parental Species. Silvae Genet. 1992, 41, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Poljak, I.; Idžojtić, M.; Šapić, I.; Vukelić, J.; Zebec, M. Variability of Populations of White (Alnus Incana /L./ Moench) and Black Alder (A. Glutinosa /L./ Gaertn.) In the Mura and Drava Area According to Leaf Morphological Characteristics (Varijabilnost Populacija Bijele (Alnus Incana/L./Moench) i Crne Johe (A. Glutinosa/L./Gaertn.) Na Području Mure i Drave Prema Morfološkim Obilježjima Listova). Šumarski List 2014, 138, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet, J.; Cheliak, W.M.; Lalonde, M. Allozyme Variability in Natural Populations of Green Alder (Alnus Crispa) in Quebec. Genome 1987, 29, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peev, C.I.; Vlase, L.; Antal, D.S.; Dehelean, C.A.; Szabadai, Z. Determination of Some Polyphenolic Compounds in Buds of Alnus and Corylus Species by HPLC. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2007, 43, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumolin, S.; Demesure, B.; Petit, R.J. Inheritance of Chloroplast and Mitochondrial Genomes in Pedunculate Oak Investigated with an Efficient PCR Method. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 1995, 91, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Lian, C.; Hogetsu, T. Development of Microsatellite Markers in White Birch (Betula Platyphylla Var. Japonica). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2002, 2, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogyu, K.; Tsuda, Y.; Sugaya, T.; Yoshimaru, H.; Ide, Y. Identification and Characterization of Microsatellite Loci in Betula Maximowicziana Regel. Molecular Ecology Notes 2003, 3, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulju, K.K.M.; Pekkinen, M.; Varvio, S. Twenty-Three Microsatellite Primer Pairs for Betula Pendula (Betulaceae). Molecular Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürcan, K.; Mehlenbacher, S.A. Development of Microsatellite Marker Loci for European Hazelnut (Corylus Avellana L.) from ISSR Fragments. Mol. Breeding 2010, 26, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, S.L.; Jones, K.L.; Hagen, C.; Glenn, T.C.; Jones, J.M.; Gibson, J.P. Development and Characterization of Nineteen Polymorphic Microsatellite Loci from Seaside Alder, Alnus Maritima. Conserv. Genet. 2009, 10, 1907–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, Y.; Ueno, S.; Ide, Y.; Tsumura, Y. Development of 14 EST-SSRs for Betula Maximowicziana and Their Applicability to Related Species. Conserv. Genet. 2009, 10, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepais, O.; Bacles, C.F.E. De Novo Discovery and Multiplexed Amplification of Microsatellite Markers for Black Alder (Alnus Glutinosa) and Related Species Using SSR-Enriched Shotgun Pyrosequencing. J. Hered. 2011, 102, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of Population Structure Using Multilocus Genotype Data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the Number of Clusters of Individuals Using the Software Structure: A Simulation Study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A.; vonHoldt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A Website and Program for Visualizing STRUCTURE Output and Implementing the Evanno Method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, A.C.; Hufbauer, R.A. Hybridization and Invasion: One of North America’s Most Devastating Invasive Plants Shows Evidence for a History of Interspecific Hybridization. Evol. Appl. 2010, 3, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopelman, N.M.; Mayzel, J.; Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Mayrose, I. Clumpak: A Program for Identifying Clustering Modes and Packaging Population Structure Inferences across K. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.C.; Thompson, E.A. A Model-Based Method for Identifying Species Hybrids Using Multilocus Genetic Data. Genetics 2002, 160, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research-an Update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Genetic Distance between Populations. Am. Nat. 1972, 106, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. Genalex 6: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamvar, Z.N.; Tabima, J.F.; Grünwald, N.J. Poppr: An R Package for Genetic Analysis of Populations with Clonal, Partially Clonal, and/or Sexual Reproduction. PeerJ 2014, 2, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudet, J. FSTAT, a Program to Estimate and Test Gene Diversities and Fixation Indices, Version 2.9.3. 2001. Available online: http://www2.unil.ch/popgen/softwares/fstat.htm (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Jombart, T. An Introduction to Adegent 2.0. 0. R-Tutorial; Imperial College London, MRC Centre for Outbreak Analysis and Modelling: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jombart, T.; Collins, C. A Tutorial for Discriminant Analysis of Principal Components (DAPC) Using Adegenet 2.0.0; Imperial College London, MRC Centre for Outbreak Analysis and Modelling: London, UK, 2015; Volume 43. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M. Estimation of Average Heterozygosity and Genetic Distance from a Small Number of Individuals. Genetics 1978, 89, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addinsoft XLSTAT Statistical and Data Analysis Solution; Addinsoft: New York, NY, USA, 2020.
- McCune, B.; Mefford, M.J. PC-ORD. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data; MjM Software: Gleneden Beach, OR, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wei, G.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Fang, Y. Hybridization and Introgression in Sympatric and Allopatric Populations of Four Oak Species. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.H.; Scher, C.L. Exploring the Potential of Gametic Reconstruction of Parental Genotypes by F1 Hybrids as a Bridge for Rapid Introgression. Genome 2017, 60, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzinsh, A.V. Experiments on Artificial Hybridization of Alder. In Gain in Forest Productivity; Zinatne: Riga, Latvia, 1968; pp. 69–99. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).