Abstract
The hygroscopicity and thermodynamic properties of Pinus sylvestris L. wood from a coffin allegedly holding the remains of famous Spanish author Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra (1547–1616) were studied using the 15 °C and 35 °C isotherms fitted to the Guggenheim–Anderson–de Boer model and comparing them with the isotherms of recently felled wood of the same species. In addition, using infrared spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR) and X-ray diffractograms, the functional groups were determined and the crystallinity and organization of the cell wall components were analyzed. The absence of the 1740 cm−1 group indicates hemicellulose degradation in the archaeological wood, and the X-ray diffractograms show a considerable decrease in cellulose crystallinity and disorganization of the cellulose crystallites. The greater availability of active –OH groups means that the archaeological wood isotherms are above the juvenile and mature wood isotherms, and therefore the thermodynamic balance in the sorption of the archaeological wood is greater.
1. Introduction
For thousands of years, humans have used wood as a material for applications such as civil and naval construction, architecture, carpentry, furniture making and sculpture, and many pieces of wood have helped to write the history of humanity. As it is a biomaterial, wood is exposed to biotic and/or abiotic degradation capable of endangering constructions and cultural heritage assets of outstanding value. The study of how the cell wall components respond at chemical and ultrastructural level provides information about the sorption mechanisms of aged wood in various environments and helps to ensure proper protection, conservation, and restoration of timber.
Wood is made up mainly of cellulose microfibrils embedded in a matrix of lignin and hemicellulose [1] and each component degrades differently depending on the environmental conditions: by oxidation, hydrolyzation, depolymerization, and other chemical processes (Blanchette, 2000).
Signs of biotic deterioration in archaeological wood are mainly caused by fungi and bacteria that degrade cell wall components. These degrading agents and their effects have been widely studied [2,3,4,5], and because they selectively degrade cell wall components, a hygroscopic study of archaeological wood must take into account possible attacks by fungi or bacteria to properly compare its chemical composition with that of reference wood, normally recently felled wood.
Archaeological wood, regardless of the nature of the site (buried, submerged, exposed, etc.) continues to provide new data through the study of its chemical composition, crystallinity, and hygroscopicity. For example, the authors of [6] studied the chemical composition of Picea abies (L.), Abies alba (Mill.), and Fagus sylvatica (L.) wood in a Bronze Age mine under long-term storage surrounded by salt for 300 years, reporting that a deacetylation process had taken place. Another study of wood in contact with salt [7] examined the chemical composition, crystallinity, hygroscopicity, and thermodynamic properties of Pinus sylvestris L. wood, observing that, except in the first isotherm interval, equilibrium moisture content (EMC) was higher in the wood surrounded by salt than in the reference wood, probably due to mechanical blocking of the –OH groups by salt crystals. In addition, the cellulose and hemicellulose content and the crystallinity index were significantly lower in the wood surrounded by salt. In wood of Populus spp. aged BP 690–790 years, the authors of [1] reported that hemicellulose showed a decrease in the carbonyl group content in the glucuronic acid of xylan and partial depolymerization of lignin and glucomannan. Crystallinity also decreased, explaining, in conjunction with the chemical composition, the higher EMC in the archaeological wood.
Increased EMC was reported in other studies of archaeological wood, associated with the larger cellulose amorphous area and the consequent greater availability of active sites, e.g., [8,9,10,11]. However, not all exposures of archaeological wood cause an increase in EMC. Buried wood dated from 1100 years BC exposed to volcanic ash had lower EMC than that of control wood because of the high temperatures the wood was subjected to [12], causing it to undergo a similar effect to heat treated wood.
Although archaeological wood is not always altered by the passage of time, such as bristlecone pine (Pinus aristata (Engelm.)) dated at around 8000 years [13], wood is normally modified either in its chemical composition or its ultrastructure, and its hygroscopic response varies.
Studying new samples of wood subjected to conditions that are similar to or different from previously studied exposures therefore adds to our knowledge of the mechanisms of the hygroscopic response of the cell wall. These response mechanisms remain unknown, probably because the participation of the complex cell wall structure in water exchange is not fully understood.
The initial hypothesis of this work is that wood buried for more than 400 years will have different EMC from recently felled reference wood of the same species. However, each time wood with these characteristics is studied, it is not known whether the EMC trend will be higher or lower, because burial conditions cause selective degradation of the cell wall components that has a considerable impact on this trend.
This study compares the hygroscopic response of Pinus sylvestris L. wood that was initially buried then held in a crypt for 400 years with the response of recently felled juvenile and mature wood of the same species by plotting the 15 °C and 35 °C isotherms and determining any changes in the functional groups, cellulose crystallinity, cellulose orientation in relation to the longitudinal direction of the cell, and the thermodynamic properties of the wood.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Archaeological Wood
On 24 January 2015, archaeologist Almudena García Rubio and forensic anthropologist Francisco Etxeberría announced the finding of a coffin bearing the initials M.C., possibly that of Spain’s greatest writer, Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra, author of Don Quixote. Miguel de Cervantes died on 23 April 1616 and was buried in the Convent of the Barefoot Trinitarians, in Madrid. One hundred years later, his remains and those of 16 other people were moved to the convent crypt, where they have lain ever since. These circumstances have greatly hindered any attempt to identify Cervantes.
The wood of the coffin shows clear signs of deterioration, except where it bears the initials M.C.
2.2. Wood Identification
To identify the wood and determine whether it had suffered any attacks, part of one of the samples taken (Figure 1A–C) was used, with orientations in three sections—transverse, tangential, and radial. The process of softening, staining, and mounting was performed following the methodology of [7]. For light microscopy observation, the wood was softened in a 50/50 water/glycerol mixture for 30 min. Microscope slides of 15–20 micrometers were prepared using a LEICA SM2400 microtome (Leica, Holly, MI, USA). Slides were stained in a mixture of 0.5 g safranine powder, 100 mL distilled water, and 100 mL 96% alcohol. Excess safranine was removed with 96% alcohol and slides were dehydrated with 96% alcohol and pure alcohol, respectively, before mounting with Eukitt. The samples used for observation in scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were also oriented in their three sections and dried for 24 h at 80 °C, then adhered to an aluminum metal disc 20 mm in diameter using conducting tape. After reaching a vacuum, all the material was coated by gold/palladium sputtering for 90 s at 60 mA. Observations were also made using a LEICA mod. DM2500 light microscope (Leica Microsystems Inc., Buffalo Grove, IL, USA) with a DFC420 camera (Leica Microsystems Inc., Buffalo Grove, IL, USA), image processing software IM50 v.5 release 220, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) mod. JEOL JSM-6380. The wood anatomy was described following [14]. The descriptions in [15] and [16] were used to identify the wood.
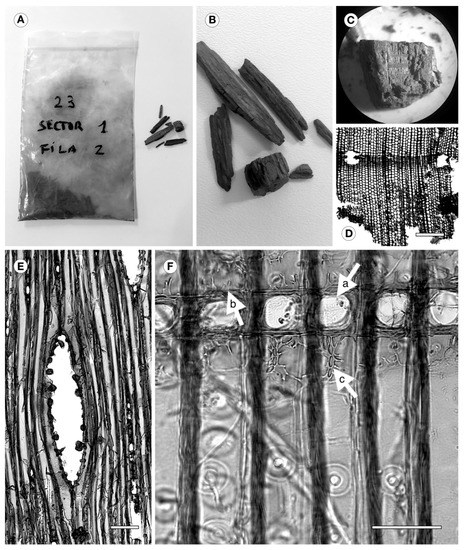

Figure 1.
(A–C) Samples from the coffin. (D) Transverse section—Distinct growth rings with abrupt transition and axial resin canals with thin-walled epithelial cells. (E) Tangential section—Multiseriate ray formerly containing a radial resin canal. (F) Heterogeneous ray—a, window-like cross-field pit, b, dentate ray tracheids, c, tracheid pits in end walls of ray tracheids. Scale bars—D, 400 μm; E, 150 μm; F, 50 μm.
The sample is a softwood with distinct growth rings, with abrupt transition, and axial (Figure 1D) and horizontal resin canals with thin-walled epithelial cells (Figure 1E). Rays heterogeneous, with window-like cross-field pits (Figure 1F-a) and prominent dentate ray tracheids that do not occupy the whole cell lumen (Figure 1F-b). These features correspond to P. sylvestris, which occurs in the northwest of the Madrid region, in Sierra de Guadarrama, and has been widely used for centuries in this area for construction, carpentry, furniture, and other applications.
The wood shows a high degree of decomposition due to soft-rot fungi, and hyphae are evident in all pieces examined (Figure 2A–C,G). Chains of cavities were observed inside the secondary wall of the axial tracheids, similar to those described by [3] due to soft-rot (Figure 2D) and containing numerous connected cavities at advanced stages of decomposition, as in this case (Figure 2D). Rows of trabeculae (Figure 2F) were also observed. According to [17], these are associated with attack by fungi, as described by [18] and [19].
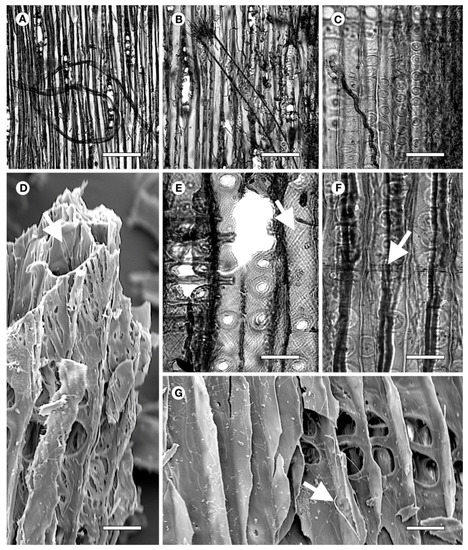
Figure 2.
(A–C,G) Fungi hyphae. (D) Chains of cavities inside secondary wall due to soft-rot, (E) Advanced state of deterioration of cell wall, F, Trabecula inside axial tracheids, (G) Hyphae. Scale bars—A, 350 μm; B, 200 μm; C, 100 μm; D, E, F, G, 50 μm.
2.3. Reference Material
Recently felled P. sylvestris wood (the same species as the coffin wood) from the Rascafría forest, in the north of the province of Madrid, was used as reference material to compare the isotherms and the crystallinity of the coffin wood and the recently felled wood. The reference material was collected in the same region of provenance (region 10) [20], to avoid the influence of different regions of provenance on the wood anatomy [21,22].
Three trees more than 90 years old representative of the forest were felled. The juvenile and mature wood samples were obtained from a disc at breast height in each tree. The two types of recent wood were compared with the coffin wood because it has been shown that juvenile and mature wood have different hygroscopic behavior [23].
2.4. Sorption Isotherms
The isotherms were plotted in a Dynamic Vapor Sorption (DVS) instrument, model Q5000SA Sorption Analyzer (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA), weight range 0.1 g, weighing accuracy ± 0.1%, temperature range 5–85 °C, isothermal stability ± 0.1 °C, relative humidity range 0–98%, relative humidity accuracy ± 1%. The particles analyzed measured 0.2 mm and weighed 10 mg. To avoid hysteresis peaks that could cause misinterpretation of the results, as described by [24], the isotherms were plotted starting from saturation. The archaeological wood was submerged in deionized water until the samples dropped to the bottom of the container. The wood was considered to be saturated at this point. After the excess water had been removed, the samples were placed in the DVS instrument. This step was not necessary for the reference wood because the desorption isotherm was plotted as soon as the trees were felled. The isotherms were plotted using seven equilibrium points, from 15% to 95% at intervals of 15% and a final interval of 5%. It was considered that samples had reached equilibrium when the change in mass (dm/dt) was less than 0.001% min−1 for 10 min, recording the change in mass every minute. Moisture content was calculated using (1).
Ww: wet weight (g),
W0: anhydrous weight (g).
The sorption isotherms were fitted using the GAB (Guggenheim–Anderson–de Boer) model, which is widely used for wood [25,26] (2),
where X is equilibrium moisture content EMC (%), Xm is monolayer saturation moisture content (%), Cg is Guggenheim constant (dimensionless), K is constant (dimensionless), and aw is water activity (dimensionless). The isotherms were considered valid at R > 0.990 and RMSE < 4% [9,10,27].
2.5. Functional Groups. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
Functional groups were determined by ATR-FTIR following the procedure described by [28]. Samples were measured using a Spectra-Tech Performer FTIR spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Spectra were collected at 4 cm−1 resolution and 64 scans.
2.6. Two-Dimensional (2D) X-Ray Diffraction
All wood samples (1 × 1 × 0.1 cm) were analyzed under the same room temperature conditions using an X-ray diffractometer equipped with a PHOTON area detector (D8 Venture, Bruker, Germany)—using Cu Kα radiation. Each sample was measured in three different locations (transmission mode; incident X-ray beam perpendicular to fiber orientation; 50 mm sample-detector distance; X-ray beam diameter 0.2 mm; 120 s integration time). For each measurement a 1024 × 1024 image (100 µm pixel size) was collected. Cellulose crystal alignment, or angular spread (AS), and oriented fraction were determined from 2D-XRD patterns following the methodology described in greater detail elsewhere [28]. From 2D-XRD patterns, 2Theta scans were calculated by radially integrating all pixels. From 2Theta scans, wood crystallinity (crystallite size) and the proportion of crystalline cellulose Iβ and amorphous cellulose were determined by Rietveld refinement using TOPAS 5.0 (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany). Crystallite size was calculated from the cellulose Iβ phase peaks, considering an isotropous model. In addition, the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the main reflections was measured separately to study the anisotropic peak broadening.
2.7. Thermodynamic Properties
Despite the limitations of using the sorption isotherms to obtain the thermodynamic properties [29,30], this method was applied because it permits relatively accurate assessment of the complex water–wood energy relation, and the values calculated are similar to those obtained by calorimetric methods. The methodology described by [11] was used.
The reference used to calculate total isosteric heat of sorption (IHS) was (3) [31].
where,
Qs is the total IHS (J mol-1),
ΔHvap is the latent vaporization heat (constant) (J mol-1),
qs is the net IHS (J mol-1).
Net HIS was calculated using the Clausius–Clapeyron method (4) [32].
where,
qs is the net IHS (J mol−1),
aw is the water activity (dimensionless),
T is the absolute temperature (K),
R is the universal gas constant (J (mol K) −1).
Total heat of wetting, known as the heat of the sorption process from fiber saturation point (FSP) to anhydrous state [33], was calculated by integrating the net isosteric heat curve (5) [31].
where,
W0 is the total heat of wetting (J mol−1 dry wood),
qs is the net IHS (J mol−1),
mf is the FSP moisture content (%).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistics Toolbox ver. 6.1 (MATLAB ver. 7.5.0. Release 2007, Natick, MA, USA) was used to fit the isotherms using the GAB model. To calculate the parameters of the GAB curves and their confidence intervals, a specific script in MATLAB language was developed.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sorption Isotherms
The isotherms obtained both in the reference wood (juvenile and mature) and the archaeological wood fitted to a type II sigmoid typical of cellulose-containing materials [31]. The fit to the GAB model was considered valid given that all the sigmoids met the condition of R > 0.990 and RMSE < 4%.
The isotherms of the juvenile wood (Figure 3, supplementary material: Table S1) are below the isotherms of the mature wood, as previously reported by [23] in Abies pinsapo (Boiss.) wood, and the isotherms of both these woods are in turn below those of the archaeological wood, in both adsorption and desorption, at 15 °C and 35 °C.
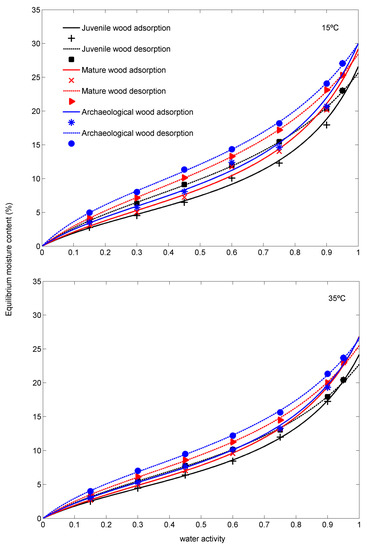
Figure 3.
The 15 °C and 35 °C adsorption-desorption isotherms of juvenile, mature, and archaeological wood.
The values of Xm, corresponding to the point of the isotherm where physisorption (or multilayer sorption) starts to prevail over chemisorption (or monolayer sorption), are significantly different between the three woods, except in the 15 °C isotherm in adsorption between the mature and the archaeological wood (Table 1). The higher Xm values in adsorption and desorption at both 15 °C and 35 °C in the archaeological wood indicate that the contribution of the monolayer is greater; i.e., the archaeological wood has a higher number of active sites available. This increase in –OH groups in buried wood agrees with the findings for P. sylvestris in place in a covered structure for 205 years [8], P. sylvestris wood that had spent 103 years under water [9], buried juvenile P. sylvestris wood [10], wood of Quercus spp. aged 5910 ± 250 BP [11], and poplar wood aged 690–790 BP [1].

Table 1.
Xm: monolayer saturation moisture content (%); K: constant; Cg: Guggenheim constant; R: correlation coefficient; RMSE: root medium square error; RH: relative humidity; EMCa: moisture content contributed by the monolayer in adsorption before the point of inflexion; EMCd: moisture content contributed by the monolayer in desorption before the point of inflexion; EMCf: water taken up via monolayer sorption after the point of inflexion. Different superscripts indicate significant differences.
In addition, the point of inflexion of the isotherms (Table 1, supplementary material: Figure S1), where the multilayer starts to predominate over the monolayer, tends to be slightly higher in the archaeological wood (36.4%), due to this greater availability of –OH groups.
The behavior pattern of the hysteresis coefficients is clear (Figure 4, supplementary material: Table S2). The archaeological wood has higher hysteresis coefficients than the mature wood, which in turn has higher hysteresis coefficients than the juvenile wood. Thus, the ageing conditions caused a greater difference between the desorption EMC and the adsorption EMC and, as a consequence, a larger hysteresis loop area in the archaeological wood (Figure 5, supplementary material: Table S3). The free energy in the process has therefore increased or, in other words, the archaeological wood is less hygroscopically stable [33]. These results differ from those reported by [8], also for P. sylvestris, but the two woods were exposed to different conditions during ageing. Humidity while the coffin was buried or in the crypt, compared to the dry conditions of the structure from the Aranjuez palace in the study by [8], may have resulted in selective degradation by fungi and bacteria in the first instance and by fungi only in the second. For example, whereas white-rot degrades all cell wall components [3] and some species preferentially attack lignin, brown- and soft-rot fungi preferentially attack carbohydrates and some lignin [3]. In contrast, wood located in aquatic media and buried in saturated soil is usually attacked by bacteria [34,35]. This indicates that the hygroscopic response in archaeological wood differs depending on the conditions of exposure and the mechanisms of selective degradation of cell wall components by different types of xylophagous agents.
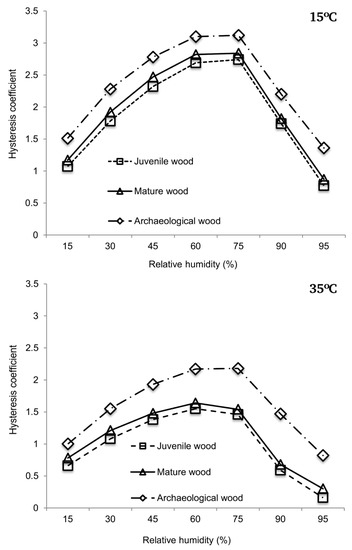
Figure 4.
Hysteresis coefficients for the 15 °C and 35 °C isotherms determined by the difference between desorption equilibrium moisture content (EMC) and adsorption EMC.
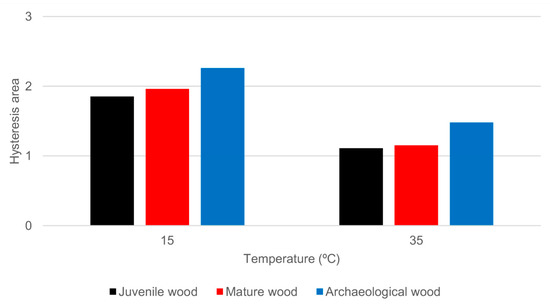
Figure 5.
Hysteresis area of reference wood (juvenile and mature) and archaeological wood.
3.2. Functional Groups
FTIR revealed the presence of the main functional groups typical of wood, except the 1740 cm−1 band, corresponding to the vibration of the acetyl and carbonyl bond in the xylan ring [8], which is absent in the archaeological wood (Table 2). This indicates hemicellulose deacetylation and degradation [9,36]. Hemicellulose is selectively degraded by bacteria [37], especially during initial stages in humid environments [38], although in wood submerged for more than 1000 years, both cellulose and hemicellulose were affected by degradation, especially the latter [39,40], probably cellulose is made more resistant due to its crystal structure [36]. Figure 6 shows that the intensity of the absorbance peaks of the archaeological wood is typically lower than those of the juvenile and mature reference wood. This means that the amount of material that interacts with the infrared beam is less, as a result of the loss of density due to degradation of the sample.

Table 2.
Main functional groups present in wood and their absorption band.
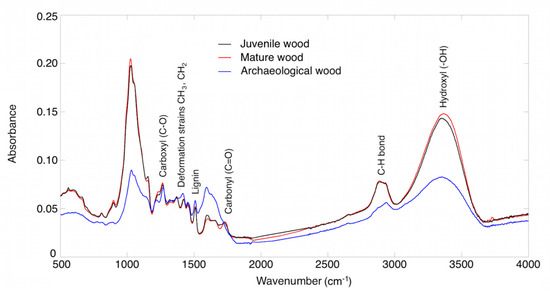
Figure 6.
ATR-FTIR spectrum of juvenile, mature, and archaeological wood.
As expected, the same functional groups were observed in the juvenile and mature wood, as reported by [23] in A. pinsapo.
3.3. Two-Dimensional (2D) X-ray Diffraction
Wood crystallinity and structural organization were studied using 2D X-ray diffraction (2D-XRD). The 2D-XRD patterns of the juvenile and mature wood show a characteristic fiber texture produced by cellulose Iβ crystals preferentially oriented with their c-axis aligned parallel to the wood fibers (Figure 7A,B). The pattern of the mature wood is very similar to that of the juvenile wood, although the former has a slightly greater degree of preferential orientation (smaller AS values; Table 3). These patterns are very similar to other untreated wood or cotton fibers made of aligned cellulose crystals [28,41]. In contrast, the archaeological wood diffracts more weakly and produces rings with nearly homogeneous intensity, indicating that they are formed by randomly oriented cellulose crystals (Figure 7C). The decreased scattering intensity of X-rays of this sample can be attributed to a wood density loss due to degradation. Nevertheless, there is some weak arcing superimposed on the rings, indicating that a small fraction of cellulose crystals remains preferentially oriented parallel to the fibers. The angular scattering of cellulose crystals remains very high (AS up to 74.6°) compared to what occurs with the juvenile and mature wood (AS 29.9°–35.8°), indicating that cellulose crystals in the archaeological wood have an almost random orientation (Table 3). In addition, the 2Theta scans calculated show considerable differences between the three samples. The juvenile and mature wood have well defined 004 and 200 diffraction peaks, whereas the archaeological wood shows much broader (FWHM_200 10.31° in the archaeological wood compared to 3.96° in the mature wood) and weaker diffraction peaks, indicating that the archaeological wood has a much lower degree of crystallinity and is nearly amorphous. Additionally, juvenile and mature wood has a notable anisotropic peak broadening (FWHM of 200 and 004 reflections is 4.18°–3.96° and 2.19°–2.25°, respectively) due to the elongated shape of cellulose crystallites (20 × 37 Å) as estimated from peak broadening using the Scherrer equation [28].
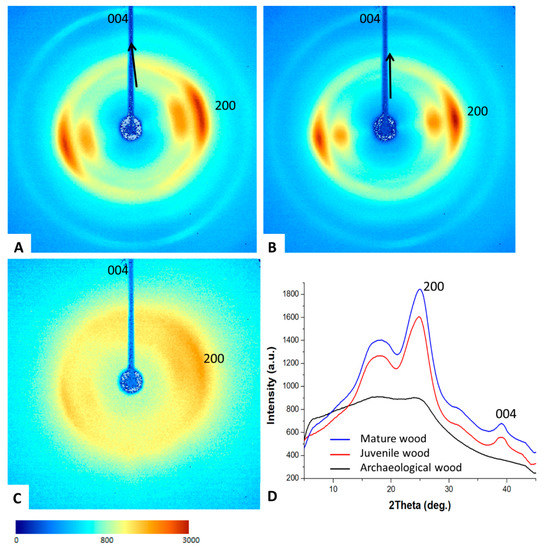
Figure 7.
X-ray diffraction analysis. 2D-XRD patterns of juvenile (A), mature (B), and archaeological (C) wood samples. (D) 2Theta scans calculated by radially integrating the intensity of 2D-XRD patterns (A–C). Color intensity scale.

Table 3.
Crystallinity, crystal orientation, and % cellulose Iβ determined using Rietveld refinement of X-ray diffraction data.
Rietveld refinement analysis of 2Theta scans shows that the calculated percentage of cellulose Iβ differs considerably among the wood samples. The juvenile and mature wood samples have a larger amount of cellulose Iβ (17.5% and 14.6%, respectively) than the archaeological wood (9.6%). The calculated crystallite size is much smaller in the archaeological wood (7 Å) than in the juvenile and mature wood (15.7 and 14.2 Å, respectively). Moreover, there is increasing disorganization of the remaining cellulose crystallites, which are almost randomly oriented (AS increased to 74.6°). The data therefore provide a good definition of the changes in the crystallinity and structural organization of the juvenile and mature wood compared to the archaeological wood, indicating that the degradation process during burial caused a significant decrease in the degree of cellulose crystallinity (decreased crystallite size and % of cellulose Iβ), and the cellulose also became highly disorganized (very low oriented fraction). These changes in the XRD patterns are very similar to that described during the transformation of nanocrystalline cotton cellulose into amorphous cellulose due to ball milling [42]. The cellulose in the archaeological wood is therefore amorphized.
3.4. Thermodynamic Properties
With regard to the thermodynamic properties, the isosteric heats are higher in desorption than in adsorption, as expected (Table 4). This is because the bond energy is greater in desorption than in adsorption. Some authors [32] explained this by the higher number of bonds available in desorption as a result of the hysteresis in the process. The greater availability of –OH groups in the archaeological wood gives rise to greater net isosteric heats than in the other two woods, in adsorption and desorption. Such high net isosteric heats for low EMC (supplementary material: Figure S2) are due to the greater availability of free polar groups. In contrast, low values for net isosteric heat at high EMC indicate that the bond energy decreases considerably as the fiber saturation point is reached.

Table 4.
Thermodynamic parameters of juvenile, mature, and archaeological wood. FSP (%) is the fiber saturation point; qs is the net isosteric heat of sorption; W0 is the total heat of wetting.
In agreement with the results of other studies [23], the mature wood has higher maximum net isosteric heat values than the juvenile wood, indicating greater bond energy in the mature wood.
The higher total heat of wetting in the archaeological wood than in the reference wood (juvenile and mature) indicates a greater amount of heat is involved in the sorption process in the archaeological wood.
4. Conclusions
The most notable changes experienced after initial burial of Pinus sylvestris wood followed by storage in a damp location were hemicellulose degradation, a considerable decrease in cellulose crystallinity (becoming nearly amorphous), and a disorganization of the cellulose crystallites, which have an almost random orientation in the cell wall. These changes in the archaeological wood due to degradation led to a higher number of polar sites (–OH), causing greater hygroscopicity in this wood than in the recently felled wood, and therefore a greater amount of heat was involved in the sorption process in the archaeological wood.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4907/11/7/712/s1, Figure S1. Derivatives of the isotherms of juvenile, mature, and archaeological wood at 15 °C and 35 °C, Figure S2. Comparison of net isosteric heat of adsorption and desorption of juvenile, mature, and archaeological wood, Table S1. Equilibrium moisture content of juvenile, mature, and archaeological wood for plotting the 15 °C and 35 °C isotherms in adsorption (EMCa) and desorption (EMCd), Table S2. Hysteresis coefficients for the 15 °C and 35 °C determined by the difference between desorption EMC adsorption EMC, Table S3. Hysteresis area of reference wood (juvenile and mature) and archaeological wood.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G.-I., F.G.F., L.G.E., P.d.P., and A.B.R.-N.; formal analysis, A.G.-I., F.G.F. and A.B.R.-N.; methodology, L.G.E., F.G.F., R.H. and A.B.R.-N.; software, F.G.F. and A.B.R.-N.; investigation, A.G.-I., F.G.F., L.G.E., L.G.S, P.d.P. and A.B.R.-N.; resources, F.G.F., L.G.E., L.G.S., R.H. and A.B.R.-N.; data curation, F.G.F. and A.B.R.-N.; writing—original draft preparation, A.G.-I., L.G.E. and A.B.R.-N.; writing—review and editing, A.G.-I., F.G.F., L.G.E., L.G.S., R.H., P.d.P. and A.B.R.-N.; validation, A.G.-I., F.G.F. and L.G.E.; visualization, A.G.-I., F.G.F., L.G.E., and A.B.R.-N.; supervision, L.G.E.; project administration, A.G.-I., L.G.E. and P.d.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guo, J.; Zhou, H.; Stevanic, J.S.; Dong, M.; Yu, M.; Salmén, L.; Yin, Y. Effects of ageing on the cell wall and its hygroscopicity of wood in ancient timber construction. Wood Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebotnik, E.; Messner, K. Immunoelectron microscopical study of the porosity of brown-rot degraded pine wood. Holzforschung 1991, 45, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, R.A. A review of microbial deterioration found in archaeological wood. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2000, 46, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.B.; Schmitt, U.; Koch, G.; Felby, C.; Thygesen, L.G. Lignin distribution in waterlogged archaeological Picea abies (L.) Karst degraded by erosion bacteria. Holzforschung 2014, 68, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.B.; Gierlinger, N.; Thygesen, L.G. Bacterial and abiotic decay in waterlogged archaeological Picea abies (L.) Karst studied by Confocal Raman imaging and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintner, J.; Smidt, E.; Tieben, J.; Reschreiter, H.; Kowarik, K.; Grabner, M. Aging of wood under long-term storage in a salt environment. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- García-Iruela, A.; Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; Garcia Fernandez, F.; Martin-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M. Changes in Cell Wall Components of Pinus sylvestris L. Wood after 300 Years in Contact with Salt (NaCl). BioResources 2019, 14, 3069–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; Fernandez, F.G.; Guindeo, A.; de Palacios, P.; Gril, J. Comparison of the hygroscopic behaviour of 205-year-old and recently cut juvenile wood from Pinus sylvestris L. Ann. For. Sci. 2006, 63, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; Fernandez, F.G.; Guindeo, A.; Conde, M.; Baonza, V. Sorption and thermodynamic properties of juvenile Pinus sylvestris L. wood after 103 years of submersion. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; García Fernandez, F.; Martin, J.A.; Genova, M.; Fernandez-Golfin, J.I. Sorption and thermodynamic properties of buried juvenile Pinus sylvestris L. wood aged 1,170 ± 40 BP. Wood Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; García Fernandez, F.; García-Amorena, I. Effects of burial of Quercus spp. wood aged 5910 ± 250 BP on sorption and thermodynamic properties. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2010, 64, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, C.; Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; Fernandez, F.G.; García-Iruela, A.; Martín-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M.E. Sorption and thermodynamic properties of wood of Pinus canariensis C. Sm. ex DC. buried in volcanic ash during eruption. Wood Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blanchette, R.A.; Cease, K.R.; Abad, A.R.; Koestler, R.J.; Simpson, E.; Sams, G.K. An Evaluation of Different Forms of Deterioration Found in Archaeological Wood. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 1991, 28, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAWA Committee. IAWA list of microscopic features for softwood identification. IAWA J. 2004, 25, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; Guindeo, A. Anatomía e Identificación de Maderas de Coníferas Españolas; AiTiM: Madrid, Spain, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; Guindeo, A.; García, L.; Lázaro, I.; González, L.; Rodríguez, Y.; García, F.; Bobadilla, I.; Camacho, A. Anatomía e Identificación de Maderas de Coníferas a Nivel de Especie/Anatomy and Identification of Conifers Wood as a Species; Fundación Conde del Valle de Salazar-Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Troncoso, O.; Greslebin, A. Trabeculae in Patagonian mountain cypress (Austrocedrus chilensis) associated with Phytophthora austrocedri infection. IAWA J. 2018, 39, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, E.C. The Anatomy of Woody Plants; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1917. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, J.D. The structure of wood. In Canadian Woods: Their Properties and Uses; Forest Service Department of Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Catalán, G.; Gil, P.; Galera, R.M.; Martín, S.; Agúndez, D.; Alía, R. Las Regiones de Procedencia de Pinus Sylvestris L. y Pinus Nigra Arn. subsp. Salzmannii (Dunal) Franco en España; Instituto Nacional para la Conservación de la Naturaleza: Madrid, Spain, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, J.A.; Esteban, L.G.; de Palacios, P.; García Fernández, F. Variation in wood anatomical traits of Pinus sylvestris L. between Spanish regions of provenance. Trees 2010, 24, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; Martín, J.A.; de Palacios, P.; García-Fernández, F. Influence of region of provenance and climate factors on wood anatomical traits of Pinus nigra Arn. subsp. salzmannii. Eur. J. Forest Res. 2012, 131, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; Simón, C.; Fernández, F.G.; de Palacios, P.; Martín-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M.E.; Hosseinpourpia, R. Juvenile and mature wood of Abies pinsapo Boissier: Sorption and thermodynamic properties. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, M.; Thybring, E.E. Scanning or desorption isotherms? Characterising sorption hysteresis of wood. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4477–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Pinedo, A.; Giraldo-Zuñiga, A.D.; Dos Santos, F.L.; Arevalo, R.P. Sorption isotherms experimental data and mathematical models for murici pulp (Byrsonima sericea). In Proceedings of the 14th International Drying Symposium, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 22–25 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jannot, Y.; Kanmogne, A.; Talla, A.; Monkam, L. Experimental determination and modelling of water desorption isotherms of tropical woods: Afzelia, Ebony, Iroko, Moabi and Obeche. Holz. Roh. Werkst. 2006, 64, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollaz, P.E.; Rovedo, C.O. Equilibrium sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of starch and gluten. J. Food Eng. 1999, 40, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Iruela, A.; Esteban, L.G.; García Fernández, F.; de Palacios, P.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A.B.; Martí-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M.E. Effect of vacuum/pressure cycles on cell wall composition and structure of poplar wood. Cellulose 2019, 26, 8543–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, W. Sorption theories applied to wood. Wood Fiber Sci. 1980, 12, 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zelinka, S.L.; Glass, S.V.; Thybring, E.E. Myth versus reality: Do parabolic sorption isotherm models reflect actual wood–water thermodynamics? Wood Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramidis, S. The basics of sorption. In Proceedings of the International Conference of COST Action E8: Mechanical Performance of Wood and Wood Products, Copenhagen, Denmark, 16–17 June 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, P.N.; Bangi, A.P.; Lee, A.W.C. Thermodynamics of moisture sorption by the giant-timber bamboo. Holzforschung 1997, 51, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siau, J.F. Wood: Influence of Moisture on Physical Properties; Department of Wood Science and Forest Products, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette, R.A. Biodeterioration of archaeological wood. CAB Biodeterior. Abstr. 1995, 9, 113–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bjordal, C.G.; Nilsson, T.; Daniel, G. Microbial decay of waterlogged wood found in Sweden applicable to archaeology and conservation. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 1999, 43, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilgör, N.; Köse, C.; Kartal, S.N. Effect of 300 year water-logging on chemical properties and natural decay and termite resistance of wood Abies bornmuleriana M. Wood Res. Slovak. 2005, 50, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gelbrich, J.; Mai, C.; Militz, H. Chemical changes in wood degraded by bacteria. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2008, 61, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S. Chemical characteristics of waterlogged archaeological wood. Holzforschung 1990, 44, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fengel, D. Aging and fossilization of wood and its components. Wood Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 153–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardet, M.; Foray, M.F.; Maron, S.; Goncalves, P.; Trân, Q.K. Characterization of wood components of Portuguese medieval dugout canoes with high-resolution solid-state-NMR. Carbohyd. Polym. 2004, 57, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.D.; Kim, H.J. Cotton fiber structure. In Cotton Fiber, Physics and Biology; Fang, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 13–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Z.; Wang, T.; Makarem, M.; Santiago-Cintrón, M.; Cheng, H.N.; Kang, X.; Bacher, M.; Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T.; King, H.; et al. Effects of ball milling on the structure of cotton cellulose. Cellulose 2019, 26, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).