Complete Chloroplast Genome of Michelia shiluensis and a Comparative Analysis with Four Magnoliaceae Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and DNA Extraction
2.2. Genome Sequencing and Annotation
2.3. Sequence and Repeat Analysis
2.4. Genome Comparison and Sequence Divergence
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Structures and Features of M. shiluensis Chloroplast Genome
3.2. Codon Usage and RNA Analysis
3.3. Repeat Sequence Analysis
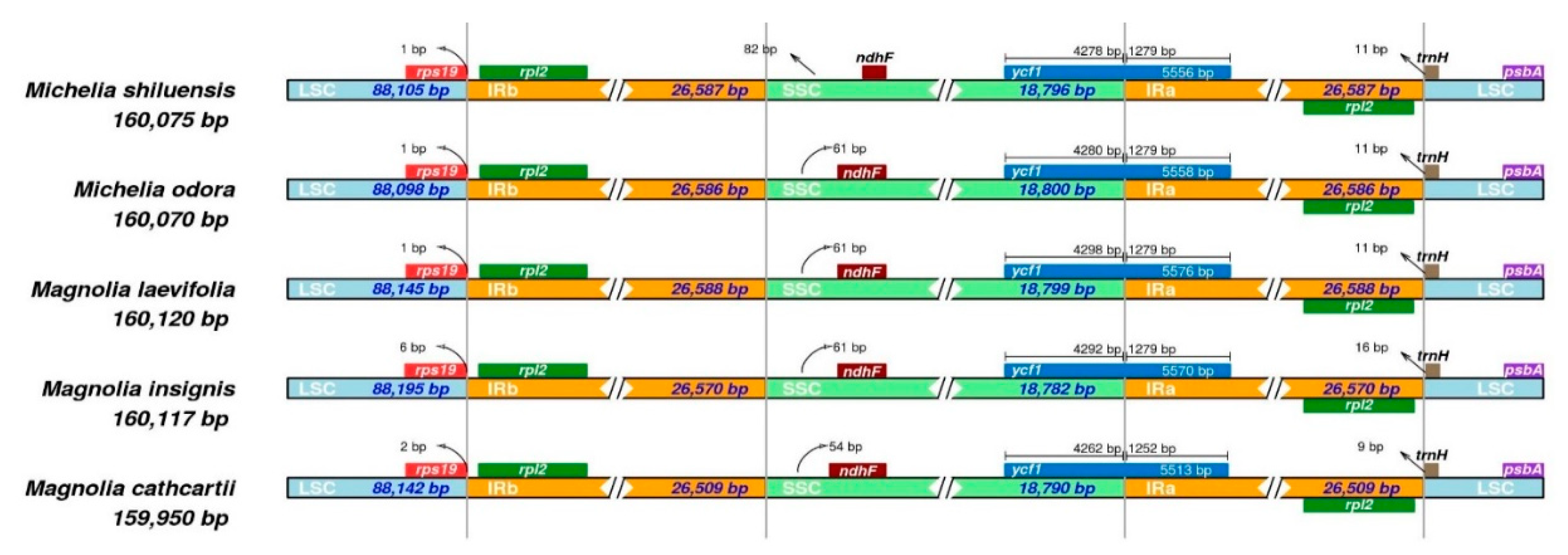
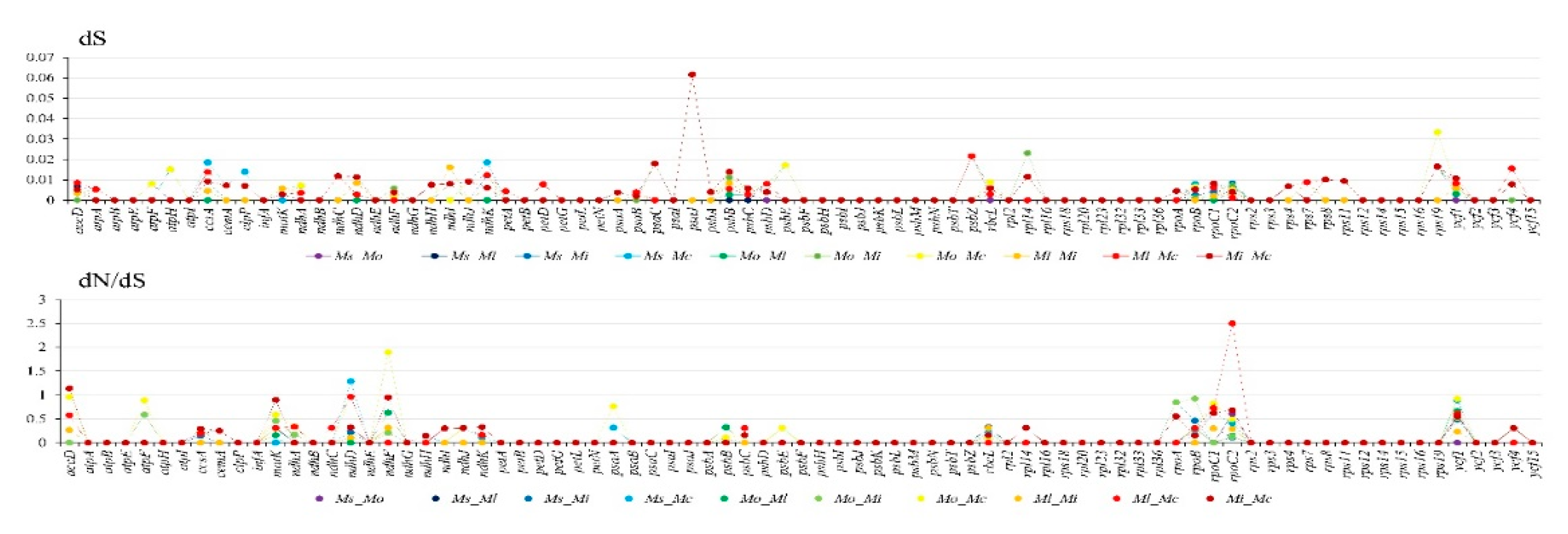
3.4. Genome Comparison and Sequence Divergence
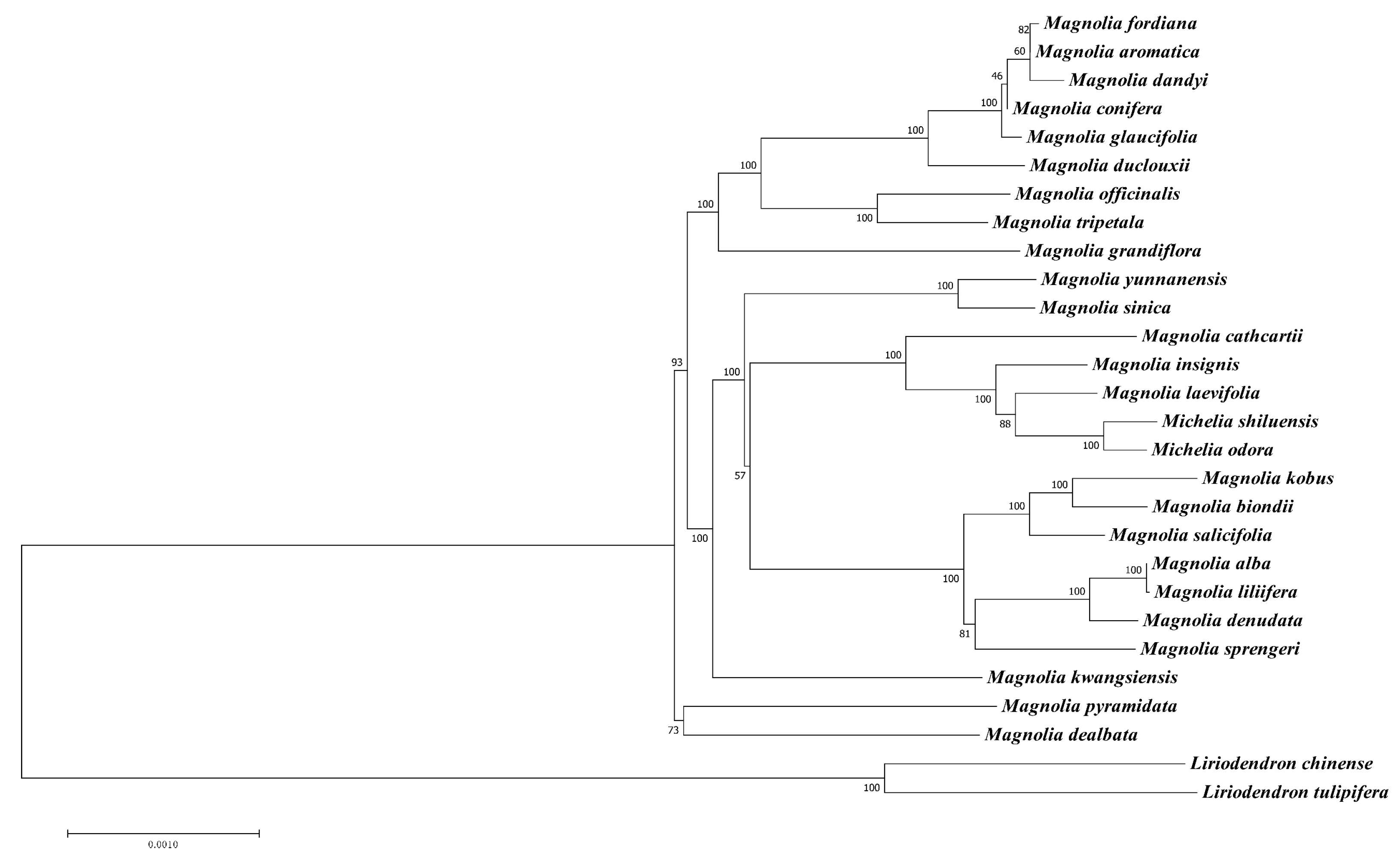
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francisco-Ortega, J.; Wang, F.-G.; Wang, Z.-S.; Xing, F.-W.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Xu, W.-X.; Luo, Y.-B.; Song, X.-Q.; Gale, S. Endemic seed plant species from Hainan Island: A checklist. Bot. Rev. 2010, 76, 295–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Zhou, S.; Yu, Y. Comparative anatomy of the leaves in Michelia. Guangxi Zhi Wu 2002, 22, 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, L.-J.; Qian, J.; Wang, P.-P.; Wang, X.-J.; Ma, G.-L.; Zeng, H.; Li, J.; Hu, J.-F. Structurally diverse sesquiterpenoids from the endangered ornamental plant Michelia shiluensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B. Forest wild biospecies diversity and its preservation in China. Chin. J. Ecol. 1993, 12, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Hong, F.; Yuan, L.; Kong, Y.; Shi, Y. Population distribution and age structure characteristics of Michelia shiluensis, an endangered and endemic species in Hainan Island. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2017, 38, 2280–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Forestry Administration of China. List of national key protected wild plants (first batch). State Counc. Bull. 1999, 13, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, M. International Union for Conservation of Nature. In The Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia of Globalization; Ritzer, G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Müller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, N.; Wu, H. Analyzing and characterizing the chloroplast genome of Salix wilsonii. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5190425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangphatsornruang, S.; Uthaipaisanwong, P.; Sangsrakru, D.; Chanprasert, J.; Yoocha, T.; Jomchai, N.; Tragoonrung, S. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Hevea brasiliensis reveals genome rearrangement, RNA editing sites and phylogenetic relationships. Gene 2011, 475, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.F.; Jansen, R.K.; Zanis, M.J.; Emery, N.C. Sources of inversion variation in the small single copy (SSC) region of chloroplast genomes. Am. J. Bot. 2015, 102, 1751–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.T. There large inversions in the chloroplast genomes and one loss of the chloroplast generps16 suggest an early evolutionary split in the genusAdonis (Ranunculaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 1999, 218, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-L.; Jansen, R.K.; Chumley, T.W.; Kim, K.-J. Gene relocations within chloroplast genomes of Jasminum and Menodora (Oleaceae) are due to multiple, overlapping inversions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1161–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.K.; Wojciechowski, M.F.; Sanniyasi, E.; Lee, S.-B.; Daniell, H. Complete plastid genome sequence of the chickpea (Cicer arietinum) and the phylogenetic distribution of rps12 and clpP intron losses among legumes (Leguminosae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 1204–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.; Lickey, E.B.; Schilling, E.E.; Small, R.L. Comparison of whole chloroplast genome sequences to choose noncoding regions for phylogenetic studies in angiosperms: The tortoise and the hare III. Am. J. Bot. 2007, 94, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V.; Kuznetsov, B.B.; Samigullin, T.H.; Antonov, A.S.; Kolganova, T.V.; Skyabin, K.G. Complete sequence of the duckweed (Lemna minor) chloroplast genome: Structural organization and phylogenetic relationships to other angiosperms. J. Mol. Evol. 2008, 66, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Kim, W.-J.; Yang, S.; Yeo, S.-M.; Li, H.; Moon, B.C. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Aconitum coreanum and Aconitum carmichaelii and comparative analysis with other Aconitum species. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Conran, J. Phylogenetic relationships in Magnoliaceae subfam. Magnolioideae: A morphological cladistic analysis. Plant Syst. Evol. 2003, 242, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Z. SOAPnuke: A MapReduce acceleration-supported software for integrated quality control and preprocessing of high-throughput sequencing data. Gigascience 2017, 7, gix120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq-versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Kahlau, S.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW—A suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W575–W581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. In Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols; Misener, S., Krawetz, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mower, J.P. The PREP suite: Predictive RNA editors for plant mitochondrial genes, chloroplast genes and user-defined alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W253–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D. Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1985, 19, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, K.; Gu, C.; Zheng, S.; Ma, L. Comparative and phylogenetic analyses of 26 Magnoliaceae species based on complete chloroplast genome sequences. Can. J. For. Res. 2018, 48, 1456–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaf, S.; Khan, A.L.; Khan, A.R.; Waqas, M.; Kang, S.-M.; Khan, M.A.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, I.-J. Complete chloroplast genome of Nicotiana otophora and its comparison with related species. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Duan, B.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Yao, H. Complete chloroplast genomes of Papaver rhoeas and Papaver orientale: Molecular structures, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; He, J. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of four Aconitum Medicinal Species. Molecules 2018, 23, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Yang, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. The complete chloroplast genome of the Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) and an adaptive evolutionary analysis of the ycf2 gene. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Qian, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Xu, X.; Chen, S. Complete chloroplast genome of medicinal plant Lonicera japonica: Genome rearrangement, intron gain and loss, and implications for phylogenetic studies. Molecules 2017, 22, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, A.; Brisson, N. Recombination and the maintenance of plant organelle genome stability. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saina, J.; Li, Z.-Z.; Gichira, A.; Liao, Y.-Y. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of tree of heaven (Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) (Sapindales: Simaroubaceae), an important pantropical tree. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaradua, S.S.; Alzahrani, D.A.; Albokhary, E.J.; Abba, A.; Bello, A. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Justicia flava: Genome comparative analysis and phylogenetic relationships among Acanthaceae. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4370258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, L.; Biradar, S.S.; Tan, X.; Wan, F.; Weining, S. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a major invasive species, crofton weed (Ageratina adenophora). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xue, Q. Comparative studies on codon usage pattern of chloroplasts and their host nuclear genes in four plant species. J. Genet. 2005, 84, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Lei, W.; Gao, J.; Qiu, X.; Wang, J. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of the medicinal plant Forsythia suspensa (Oleaceae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Park, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, B.-h.; Lee, J. The complete plastome sequence of an Antarctic bryophyte Sanionia uncinata (Hedw.) Loeske. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Duan, D.; Yang, J.; Feng, L.; Zhao, G. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of five Quercus species. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Chen, C.; Wei, Y.; Chang, Y.; Bai, G.; Li, Z.; Kanwal, N.; Zhao, G. Comparative transcriptome and chloroplast genome analyses of two related Dipteronia species. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provan, J.; Powell, W.; Hollingsworth, P.M. Chloroplast microsatellites: New tools for studies in plant ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.; Peakall, R. Chloroplast simple sequence repeats (cpSSRs): Technical resources and recommendations for expanding cpSSR discovery and applications to a wide array of plant species. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2009, 9, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Panah, N.; Shabanian, N.; Khadivi, A.; Rahmani, M.-S.; Emami, A. Genetic structure of gall oak (Quercus infectoria) characterized by nuclear and chloroplast SSR markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2017, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.F.; Jiao, F.C.; Xiao, B.G.; Li, Y.P.; Tong, Z.J. Genetic diversity analysis of genus Nicotiana based on SSR markers in chloroplast genome and mitochondria genome. Acta Tabacaria Sin. 2016, 22, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Xu, C.; Li, W.; Xie, X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Suo, Z. Phylogenetic resolution in Juglans based on complete chloroplast genomes and nuclear DNA sequences. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.-X.; Li, R.; Worth, J.R.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Cameron, K.M.; Fu, C.-X. The complete chloroplast genome of Chinese bayberry (Morella rubra, Myricaceae): Implications for understanding the evolution of Fagales. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.-S.; Li, P.; Qiu, Y.-X. The complete chloroplast genomes of three Cardiocrinum (Liliaceae) species: Comparative genomic and phylogenetic analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raubeson, L.A.; Peery, R.; Chumley, T.W.; Dziubek, C.; Fourcade, H.M.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. Comparative chloroplast genomics: Analyses including new sequences from the angiosperms Nuphar advena and Ranunculus macranthus. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Lee, H.-L. Complete chloroplast genome sequences from Korean ginseng (Panax schinseng Nees) and comparative analysis of sequence evolution among 17 vascular plants. DNA Res. 2004, 11, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, Y.; Mao, S.-Y.; Gao, L.-Z. Thirteen Camellia chloroplast genome sequences determined by high-throughput sequencing: Genome structure and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fan, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, H.; Fu, L. Species-specific identification from incomplete sampling: Applying DNA barcodes to monitoring invasive Solanum plants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, C.W.; Webb, C.O. Plant DNA barcodes, taxonomic management, and species discovery in tropical forests. In DNA Barcodes. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols); Kress, W., Webb, C.O., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 858, pp. 379–393. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Wu, K.; Song, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, H.; Luo, K.; Dai, Y.; Xu, S.; Lin, Y. Expedient identification of Magnoliaceae species by DNA barcoding. Plant Omics 2014, 7, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Huan, H.V.; Trang, H.M.; Toan, N.V. Identification of DNA barcode sequence and genetic relationship among some species of Magnolia Family. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2018, 17, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, H.V.; Nguyen, L.T.T.; Quang, N.M. To create DNA barcode data of Magnolia chevalieri (Dandy) V.S. Kumar for identification species and researching genetic diversity. J. For. Sci. Technol. 2019, 18, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Azuma, H.; Thien, L.B.; Kawano, S. Molecular phylogeny of Magnolia (Magnoliaceae) inferred from cpDNA sequences and evolutionary divergence of the floral scents. J. Plant Res. 1999, 112, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R.A. Manual of Botany: Including the Structure, Classification, Properties, Uses, and Functions of Plants; J. & A. Churchill: London, UK, 1882. [Google Scholar]
- Azuma, H.; García-Franco, J.G.; Rico-Gray, V.; Thien, L.B. Molecular phylogeny of the Magnoliaceae: The biogeography of tropical and temperate disjunctions. Am. J. Bot. 2001, 88, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandy, J.E. A revised survey of the genus Magnolia together with Manglietia and Michelia. In Magnolias; Treseder, N.G., Ed.; Faber & Faber: London, UK, 1978; pp. 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.B.; Nooteboom, H.P. Notes on Magnoliaceae III: The Magnoliaceae of China. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1993, 80, 999–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figlar, R.B.; Nooteboom, H.P. Notes on Magnoliaceae IV. Blumea 2004, 49, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, C.W.; Kim, Y.D.; Suh, Y. Phylogenetic relationships in family Magnoliaceae inferred from ndhF sequences. Am. J. Bot. 2001, 88, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Nooteboom, H.P.; Park, C.-W.; Suh, Y. Taxonomic revision of Magnolia section Maingola (Magnoliaceae). Blumea 2002, 47, 319–339. [Google Scholar]
- Nooteboom, H. Different looks at the classification of the Magnoliaceae. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Family Magnoliaceae, Guangzhou, China, 18–22 May 1998; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.-L.; Song, Y.; Ni, J.; Yao, X.; Tan, Y.-H.; Xu, Z.-F. Comparative chloroplast genomics and phylogenetics of nine Lindera species (Lauraceae). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noteboom, H. Notes on Magnoliaceae with a revision of Pachylarnax and Elmerrillia and the Malasian species of Manglietia and Michelia. Blumea 1985, 31, 65–121. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Z.-L.; Wen, J.; Azuma, H.; Qiu, Y.-L.; Sun, H.; Meng, Y.; Sun, W.-B.; Zimmer, E.A. Phylogenetic and biogeographic complexity of Magnoliaceae in the Northern Hemisphere inferred from three nuclear data sets. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhsam, M.; Rai, H.S.; Mathews, S.; Ross, T.G.; Graham, S.W.; Raubeson, L.A.; Mei, W.; Thomas, P.I.; Gardner, M.F.; Ennos, R.A. Does complete plastid genome sequencing improve species discrimination and phylogenetic resolution in Araucaria? Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
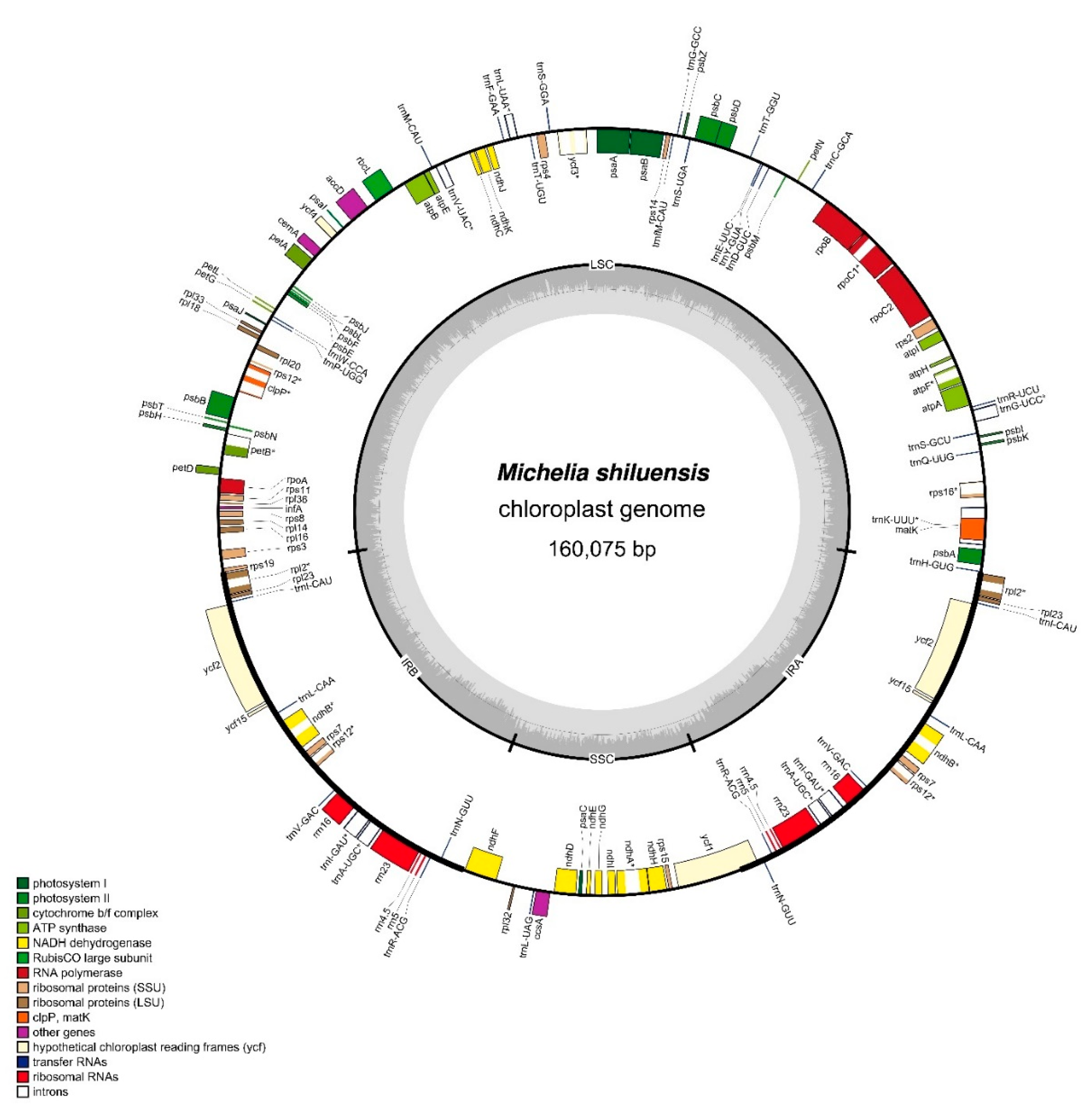
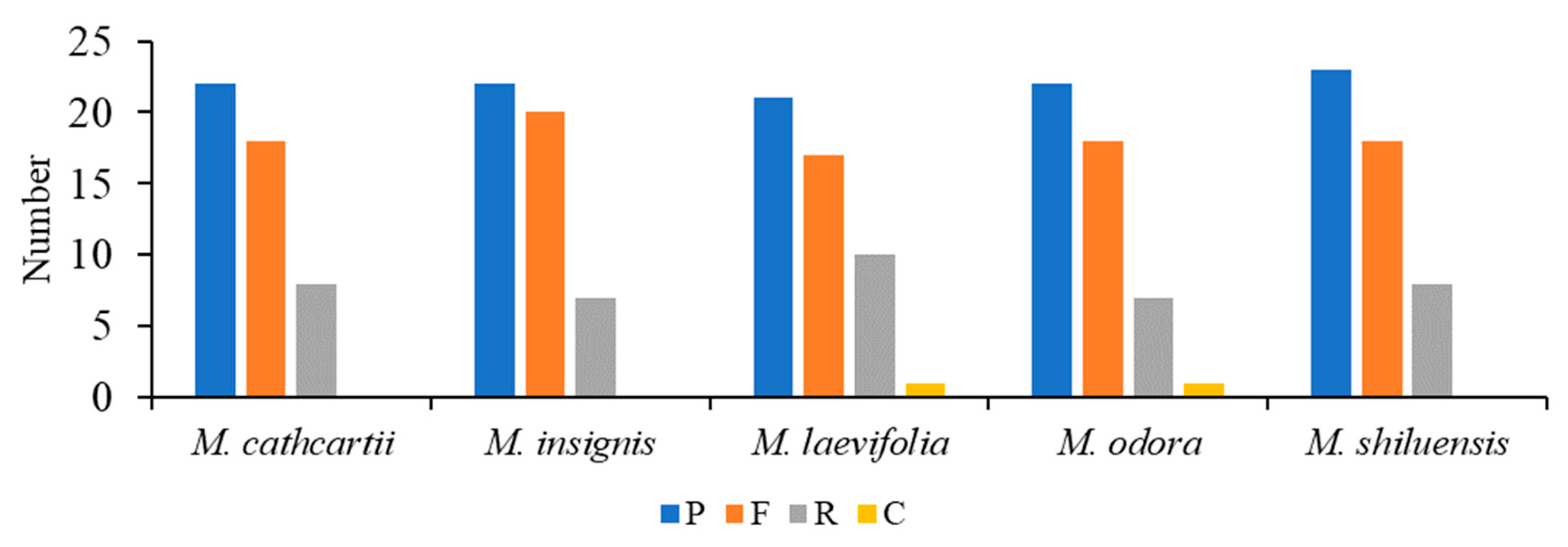
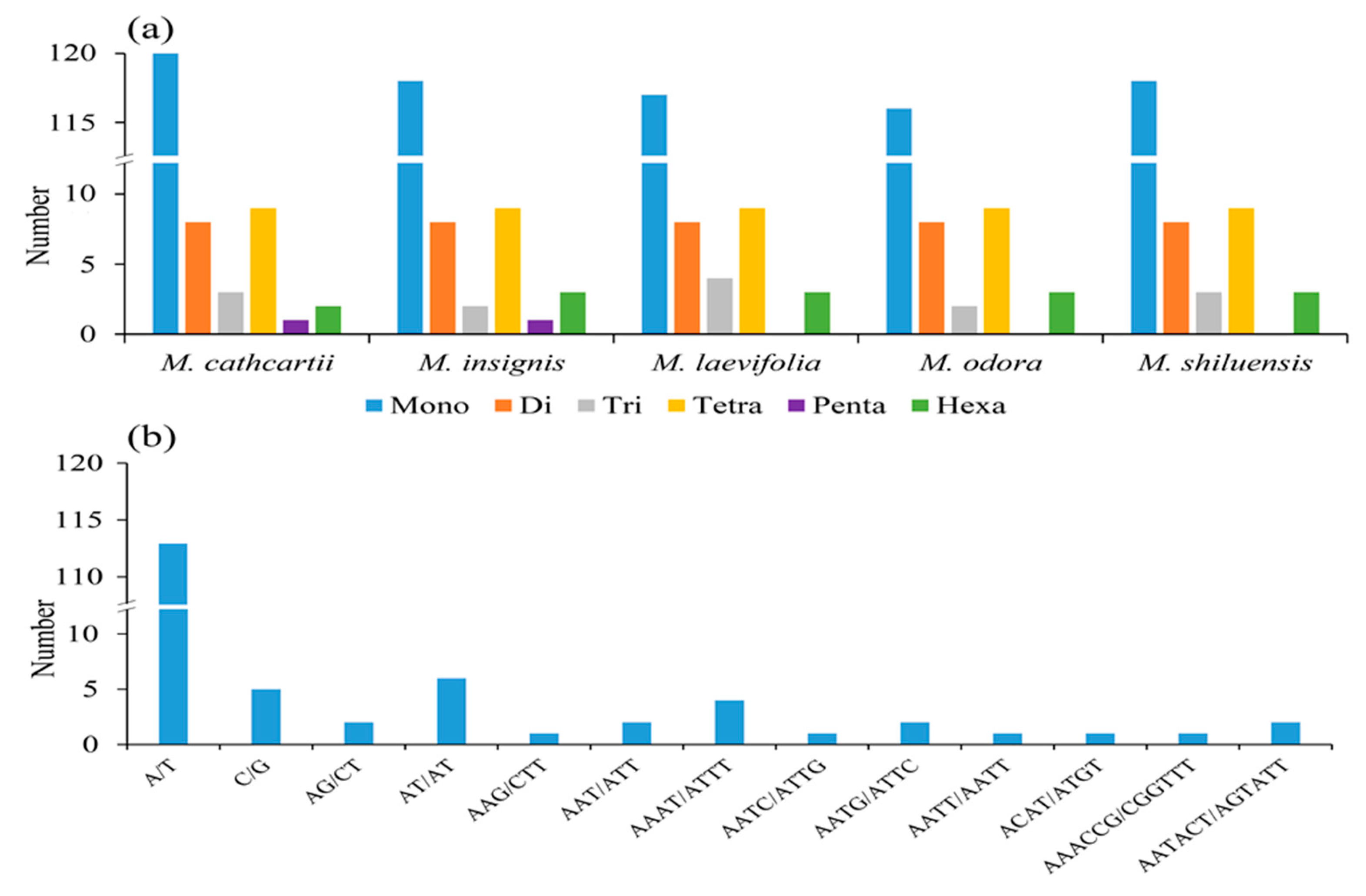
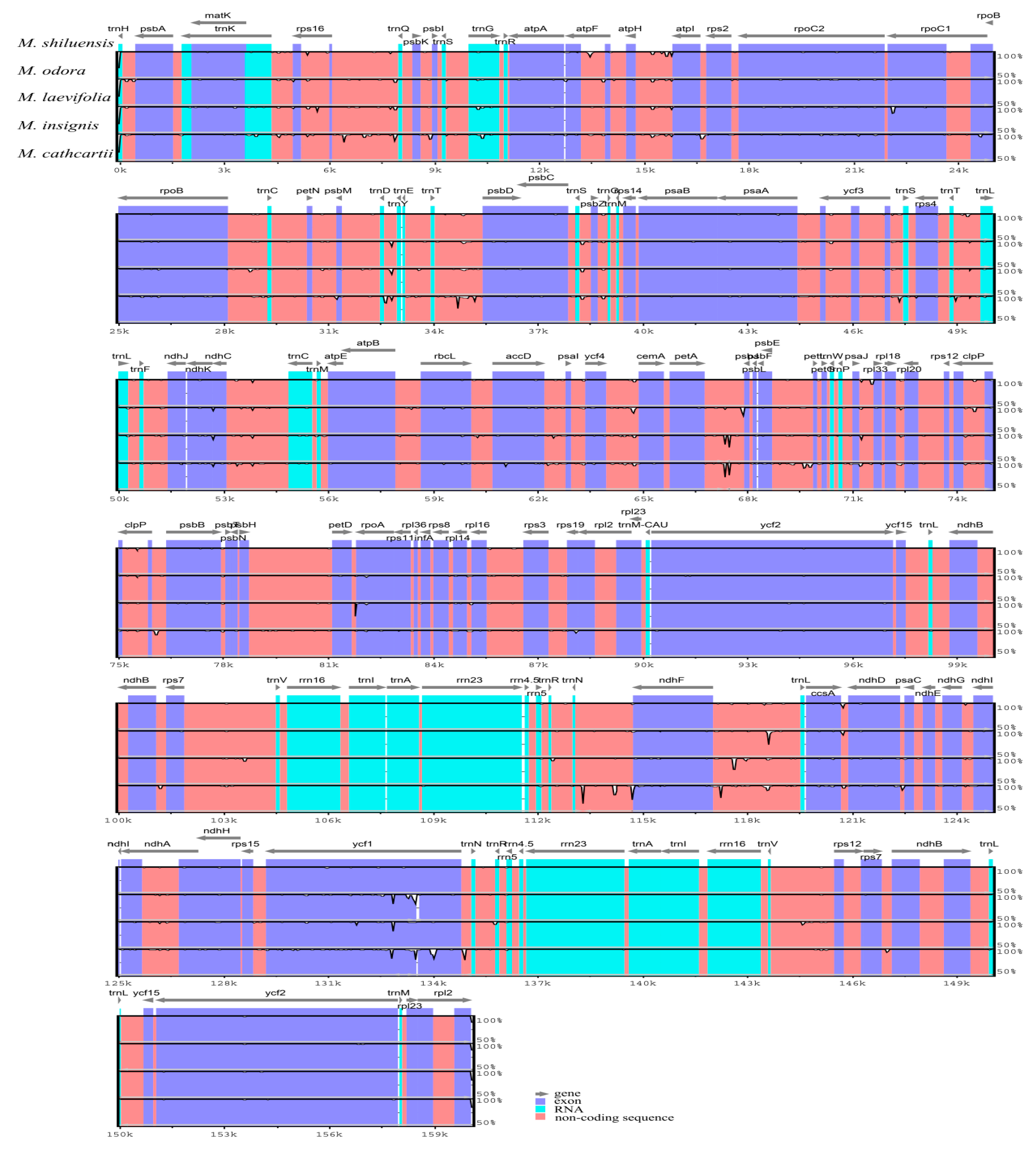

| M. shiluensis | M. odora | M. laevifolia | M. insignis | M. cathcartii | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession | MN418056 | NC023239 | NC035956 | NC035657 | NC023234 |
| Genome | |||||
| Length (bp) | 160,075 | 160,070 | 160,120 | 160,117 | 159,950 |
| GC (%) | 39.26 | 39.26 | 39.24 | 39.24 | 39.22 |
| LSC | |||||
| length (bp) | 88,105 | 88,098 | 88,145 | 88,195 | 88,142 |
| GC (%) | 37.95 | 37.95 | 37.9 | 37.92 | 37.91 |
| Length (%) | 55.04 | 55.04 | 55.05 | 55.08 | 55.11 |
| SSC | |||||
| length (bp) | 18,796 | 18,800 | 18,799 | 18,782 | 18,790 |
| GC (%) | 34.28 | 34.28 | 34.32 | 34.25 | 34.13 |
| Length (%) | 11.74 | 11.74 | 11.74 | 11.73 | 11.75 |
| IR | |||||
| length (bp) | 26,587 | 26,586 | 26,588 | 26,570 | 26,509 |
| GC (%) | 43.2 | 43.2 | 43.2 | 43.19 | 43.2 |
| Length (%) | 16.61 | 16.61 | 16.61 | 16.59 | 16.57 |
| No. of Genes (duplicated in IR) | |||||
| Genes | 131(18) | 131(18) | 131(18) | 131(18) | 131(18) |
| PCGs | 86(7) | 86(7) | 86(7) | 86(7) | 86(7) |
| tRNA | 37(7) | 37(7) | 37(7) | 37(7) | 37(7) |
| rRNA | 8(4) | 8(4) | 8(4) | 8(4) | 8(4) |
| With introns | 16(5) | 16(5) | 16(5) | 16(5) | 16(5) |
| Category of Genes | Subcategory of Genes | Gene Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-replication | rRNA genes | rrn 4.5 * | rrn5 * | rrn16 * | rrn23 * |
| tRNA genes | trnA-UGC * | trnC-ACA | trnD-GUC | trnE-UUC | |
| trnF-GAA | trnfM-CAU | trnG-GCC | trnG-UCC | ||
| trnH-GUG | trnI-CAU | trnI-GAU * | trnK-UUU | ||
| trnL-CAA * | trnL-UAA | trnL-UAG | trnM-CAU * | ||
| trnN-GUU * | trnP-UGG | trnQ-UUG | trnR-ACG * | ||
| trnR-UCU | trnS-GCU | trnS-GGA | trnS-UGA | ||
| trnT-GGU | trnT-UGU | trnV-GAC * | trnV-UAC | ||
| trnW-CCA | trnY-GUA | ||||
| Small subunit of ribosome | rps2 | rps3 | rps4 | rps7 * | |
| rps8 | rps11 | rps12 * | rps14 | ||
| rps15 | rps16 | rps18 | rps19 | ||
| Large subunit of ribosome | rpl2 * | rpl14 | rpl16 | rpl20 | |
| rpl23 * | rpl32 | rpl33 | rpl36 | ||
| RNA polymerase subunits | rpoA | rpoB | rpoC1 | rpoC2 | |
| Photosynthesis | ATP synthase gene | atpA | atpB | atpE | atpF |
| atpH | atpI | ||||
| NADH dehydrogenase | ndhA | ndhB * | ndhC | ndhD | |
| ndhE | ndhF | ndhG | ndhH | ||
| ndhI | ndhJ | ndhK | |||
| Cytochrome b/f complex | petA | petB | petD | petG | |
| petL | petN | ||||
| Photosystem I | psaA | psaB | psaC | psaI | |
| psaJ | |||||
| Photosystem II | psbA | psbB | psbC | psbD | |
| psbE | psbF | psbH | psbI | ||
| psbJ | psbK | psbL | psbM | ||
| psbN | psbT | psbZ | |||
| Large chain of Rubisco | rbcL | ||||
| Other genes | ATP-dependent protease | clpP | |||
| Cytochrome c biogenesis | ccsA | ||||
| Acetyl-CoA carboxylase | accD | ||||
| Translation initiation factor IF-1 | infA | ||||
| Membrane protein | cemA | ||||
| Maturase | matK | ||||
| Unknown function | Hypothetical chloroplast reading frame | ycf1 | ycf2 * | ycf3 | ycf4 |
| ycf15 * | |||||
| Gene | Location | Exon I (bp) | Intron I (bp) | Exon II (bp) | Intron II (bp) | Extron III (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trnK-UUU | LSC | 35 | 2490 | 37 | ||
| rps16 | LSC | 217 | 825 | 44 | ||
| trnG-UCC | LSC | 24 | 768 | 48 | ||
| atpF | LSC | 411 | 706 | 144 | ||
| rpoC1 | LSC | 1624 | 722 | 434 | ||
| ycf3 | LSC | 154 | 729 | 227 | 739 | 126 |
| trnL-UAA | LSC | 35 | 491 | 50 | ||
| trnV-UAC | LSC | 37 | 584 | 56 | 565 | 39 |
| clpP | LSC | 246 | 630 | 291 | 781 | 69 |
| petB | LSC | 5 | 786 | 641 | ||
| rpl2 | IR | 432 | 658 | 387 | ||
| rps12 | IR/LSC | 114 | - | 25 | 536 | 232 |
| ndhB | IR | 756 | 700 | 777 | ||
| trnI-GAU | IR | 42 | 936 | 35 | ||
| trnA-UGC | IR | 38 | 799 | 35 | ||
| ndhA | SSC | 541 | 1078 | 551 |
| Codon | Amino Acid | Count | RSCU | Codon | Amino Acid | Count | RSCU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UUU | Phe | 714 | 1.1 | UAU | Tyr | 600 | 1.47 |
| UUC | Phe | 586 | 0.9 | UAC | Tyr | 214 | 0.53 |
| UUA | Leu | 671 | 1.66 | UAA | * | 147 | 0.98 |
| UUG | Leu | 510 | 1.26 | UAG | * | 137 | 0.91 |
| CUU | Leu | 439 | 1.09 | CAU | His | 429 | 1.41 |
| CUC | Leu | 206 | 0.51 | CAC | His | 178 | 0.59 |
| CUA | Leu | 400 | 0.99 | CAA | Gln | 560 | 1.41 |
| CUG | Leu | 197 | 0.49 | CAG | Gln | 237 | 0.59 |
| AUU | Ile | 893 | 1.28 | AAU | Asn | 712 | 1.44 |
| AUC | Ile | 545 | 0.78 | AAC | Asn | 278 | 0.56 |
| AUA | Ile | 647 | 0.93 | AAA | Lys | 777 | 1.37 |
| AUG | Met | 602 | 1 | AAG | Lys | 359 | 0.63 |
| GUU | Val | 474 | 1.37 | GAU | Asp | 631 | 1.54 |
| GUC | Val | 202 | 0.58 | GAC | Asp | 189 | 0.46 |
| GUA | Val | 487 | 1.41 | GAA | Glu | 780 | 1.42 |
| GUG | Val | 223 | 0.64 | GAG | Glu | 318 | 0.58 |
| UCU | Ser | 457 | 1.6 | UGU | Cys | 214 | 1.36 |
| UCC | Ser | 266 | 0.93 | UGC | Cys | 100 | 0.64 |
| UCA | Ser | 373 | 1.3 | UGA | * | 166 | 1.11 |
| UCG | Ser | 192 | 0.67 | UGG | Trp | 427 | 1 |
| CCU | Pro | 345 | 1.41 | CGU | Arg | 256 | 1.15 |
| CCC | Pro | 213 | 0.87 | CGC | Arg | 72 | 0.32 |
| CCA | Pro | 307 | 1.25 | CGA | Arg | 289 | 1.3 |
| CCG | Pro | 117 | 0.48 | CGG | Arg | 129 | 0.58 |
| ACU | Thr | 426 | 1.49 | AGU | Ser | 324 | 1.13 |
| ACC | Thr | 237 | 0.83 | AGC | Ser | 107 | 0.37 |
| ACA | Thr | 358 | 1.26 | AGA | Arg | 410 | 1.84 |
| ACG | Thr | 120 | 0.42 | AGG | Arg | 179 | 0.8 |
| GCU | Ala | 537 | 1.82 | GGU | Gly | 542 | 1.33 |
| GCC | Ala | 185 | 0.63 | GGC | Gly | 171 | 0.42 |
| GCA | Ala | 335 | 1.13 | GGA | Gly | 628 | 1.54 |
| GCG | Ala | 126 | 0.43 | GGG | Gly | 291 | 0.71 |
| Species | Number | Location | Regions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSC | IR | SSC | CDS | Intron | IGS | ||
| M. cathcartii | 143 | 103 | 7 | 26 | 25 | 18 | 100 |
| M. insignis | 141 | 102 | 7 | 25 | 26 | 15 | 100 |
| M. laevifolia | 141 | 101 | 7 | 26 | 27 | 18 | 96 |
| M. odora | 138 | 99 | 7 | 25 | 24 | 19 | 95 |
| M. shiluensis | 141 | 102 | 7 | 25 | 25 | 19 | 97 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Y.; Luo, Y.; He, Y.; Qin, X.; Li, C.; Deng, X. Complete Chloroplast Genome of Michelia shiluensis and a Comparative Analysis with Four Magnoliaceae Species. Forests 2020, 11, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11030267
Deng Y, Luo Y, He Y, Qin X, Li C, Deng X. Complete Chloroplast Genome of Michelia shiluensis and a Comparative Analysis with Four Magnoliaceae Species. Forests. 2020; 11(3):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11030267
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Yanwen, Yiyang Luo, Yu He, Xinsheng Qin, Chonggao Li, and Xiaomei Deng. 2020. "Complete Chloroplast Genome of Michelia shiluensis and a Comparative Analysis with Four Magnoliaceae Species" Forests 11, no. 3: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11030267
APA StyleDeng, Y., Luo, Y., He, Y., Qin, X., Li, C., & Deng, X. (2020). Complete Chloroplast Genome of Michelia shiluensis and a Comparative Analysis with Four Magnoliaceae Species. Forests, 11(3), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11030267






