Genetically Determined Differences in Annual Shoot Elongation of Young Norway Spruce
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
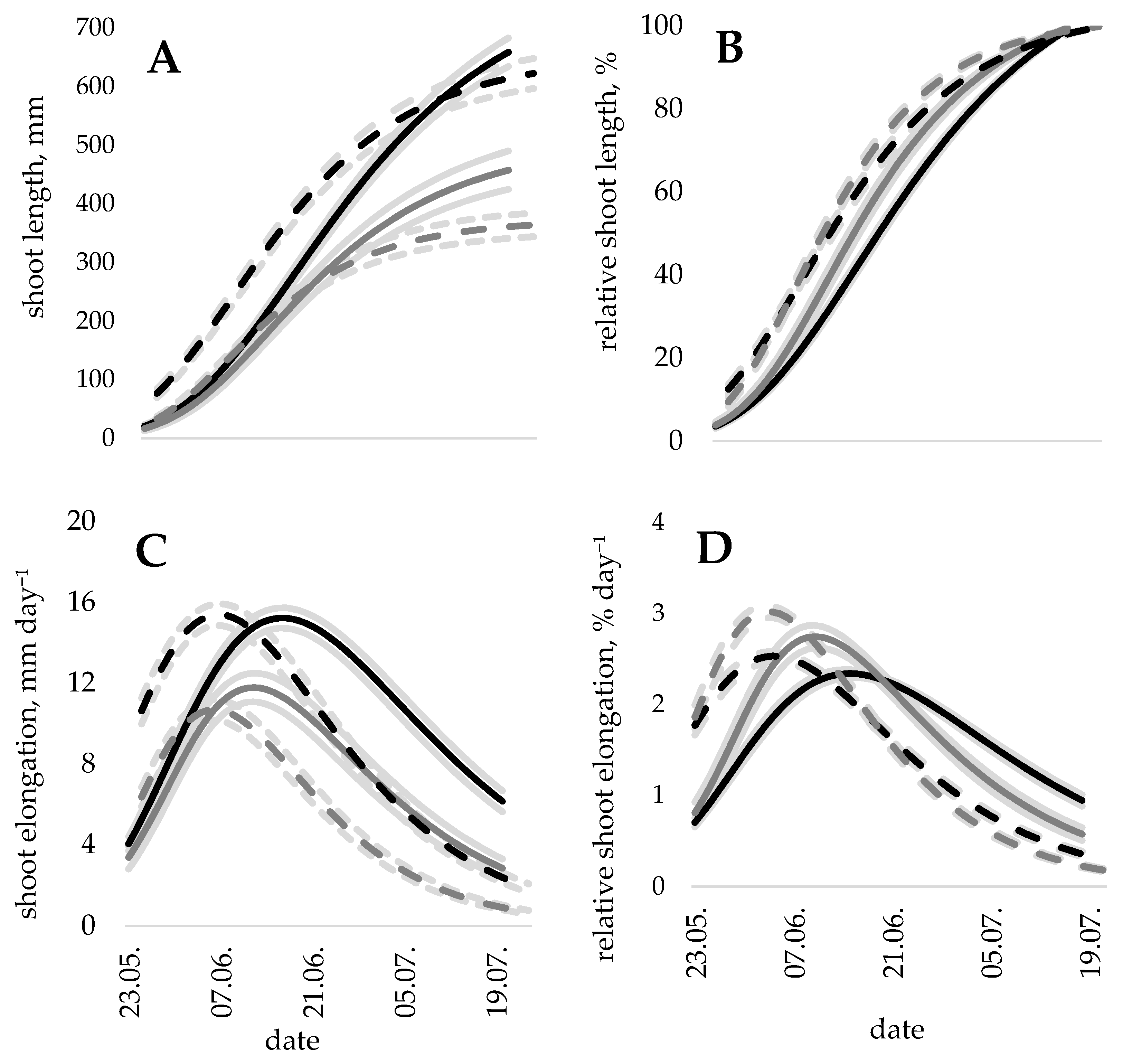
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rytter, L.; Johansson, K.; Karlsson, B.; Lars-Göran, S. Tree Species, Genetics and Regeneration for Bioenergy Feedstock in Northern Europe. In Forest BioEnergy Production: Management, Carbon Sequestration and Adaptation; Kellomäki, S., Kilpeläinen, A., Alam, A., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, G.; Hansen, J.K.; Haapanen, M.; Kvaalen, H.; Steffenrem, A. The genetic and economic gains from forest tree breeding programmes in Scandinavia and Finland. Scand. J. For. Res. 2017, 32, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liziniewicz, M.; Karlsson, B.; Helmersson, A. Improved varieties perform well in realized genetic gain trials with Norway spruce seed sources in southern Sweden. Scand. J. For. Res. 2019, 34, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, R.; Rosvall, O.; Gong, P.; Wibe, S. Profitability of measures to increase forest growth. For. Policy Econ. 2010, 12, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Ganguly, S.; Tømmervik, H.; Euskirchen, E.S.; Høgda, K.A.; Karlsen, S.R.; Brovkin, V.; Nemani, R.R.; Myneni, R.B. Changes in growing season duration and productivity of northern vegetation inferred from long-term remote sensing data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänninen, H. Climate warming and the risk of frost damage to boreal forest trees: Identification of critical ecophysiological traits. Tree Physiol. 2006, 26, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Piao, S.; Janssens, I.A.; Fu, Y.; Peng, S.; Lian, X.; Ciais, P.; Myneni, R.B.; Peñuelas, J.; Wang, T. Extension of the growing season increases vegetation exposure to frost. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannerz, M.; Sonesson, J.; Ekberg, I. Genetic correlations between growth and growth rhythm observed in a short-term test and performance in long-term field trials of Norway spruce. Can. J. For. Res. 1999, 29, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannerz, M. Evaluation of temperature models for predicting bud burst in Norway spruce. Can. J. For. Res. 1999, 29, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, G.; Curtu, A.L.; Garbacea, P.; Alexandru, A.M.; Mirancea, I.; Teodosiu, M. Genetic variation and inheritance of bud flushing in a Norway spruce seed orchard established in Romania. In Proceedings of the Biennial International Symposium “Forest and sustainable development”, Brașov, Romania, 25–27 October 2018; Borz, S.A., Curtu, A.L., Mușat, E.C., Eds.; Transilvania University Press: Brașov, Romania, 2019; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Skrøppa, T.; Hylen, G.; Dietrichson, J. Relationships between wood density components and juvenile height growth and growth rhythm traits for Norway spruce provenances and families. Silvae Genet. 1999, 48, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Skrøppa, T.; Steffenrem, A. Genetic variation in phenology and growth among and within Norway spruce populations from two altitudinal transects in mid-Norway. Silva Fenn. 2019, 53, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, M. Developing adaptive forest management strategies to cope with climate. Tree Physiol. 2000, 20, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolte, A.; Ammer, C.; Löf, M.; Madsen, P.; Nabuurs, G.J.; Schall, P.; Spathelf, P.; Rock, J. Adaptive forest management in central Europe: Climate change impacts, strategies and integrative concept. Scand. J. For. Res. 2009, 24, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeltinš, P.; Katrevičs, J.; Gailis, A.; Maaten, T.; Desaine, I.; Jansons, A. Adaptation capacity of norway spruce provenances in Western Latvia. Forests 2019, 10, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabel, N.; Holliday, J.A.; Aitken, S.N. Forest genomics: Advancing climate adaptation, forest health, productivity, and conservation. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rweyongeza, D.M.; Yeh, F.C.; Dhir, N.K. Genetic parameters for seasonal height and height growth curves of white spruce seedlings and their implications to early selection. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 187, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liziniewicz, M.; Berlin, M.; Karlsson, B. Early assessments are reliable indicators for future volume production in Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst) genetic field trials. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 411, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liziniewicz, M.; Berlin, M. Differences in growth and areal production between Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst) regeneration material representing different levels of genetic improvement. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 435, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, G.; Danusevičius, D.; Grotehusman, H.; Kowalczyk, J.; Krajmerova, D.; Skrøppa, T.; Wolf, H. Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) H.Karst.). In Forest Tree Breeding in Europe: Current State-of-the-Art and Perspectives; Pâques, L.E., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 123–176. [Google Scholar]
- Hannrup, B.; Cahalan, C.; Chantre, G.; Grabner, M.; Karlsson, B.; Le Bayon, I.; Jones, G.L.; Müller, U.; Pereira, H.; Rodrigues, J.C.; et al. Genetic parameters of growth and wood quality traits in Picea abies. Scand. J. For. Res. 2004, 19, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, J. Comparison of phenotypic and genetic selections in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) single tree plot half-sib progeny tests. Dendrobiology 2005, 53, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kroon, J.; Ericsson, T.; Jansson, G.; Andersson, B. Patterns of genetic parameters for height in field genetic tests of Picea abies and Pinus sylvestris in Sweden. Tree Genet. Genomes 2011, 7, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovsgaard, J.P.; Vanclay, J.K. Forest site productivity: A review of the evolution of dendrometric concepts for even-aged stands. Forestry 2008, 81, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, T. Site index curves for Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) karst.) planted on abandoned farm land. New For. 1996, 11, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, J.Ô.; Hébert, J.; Brostaux, Y.; Lejeune, P.; Claessens, H. Modelling the top-height growth and site index of Norway spruce in Southern Belgium. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 298, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanič, T.; Gričar, J.; Gagen, M.; Jalkanen, R.; Loader, N.J.; McCarroll, D.; Oven, P.; Robertson, I. The climate sensitivity of Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) in the southeastern European Alps. Trees Struct. Funct. 2009, 23, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konôpka, B.; Pajtík, J.; Bošela, M.; Hlásny, T.; Sitková, Z. Inter-and intra-annual dynamics of height increment in young beech and spruce stands in relation to tree size and weather conditions. For. J. 2014, 60, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carles, S.; Boyer Groulx, D.; Lamhamedi, M.S.; Rainville, A.; Beaulieu, J.; Bernier, P.; Bousquet, J.; Deblois, J.; Margolis, H.A. Family variation in the morphology and physiology of white spruce (Picea glauca) seedlings in response to elevated CO2 and temperature. J. Sustain. For. 2015, 34, 169–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrøppa, T.; Magnussen, S. Provenance variation in shoot growth components of Norway spruce. Silvae Genet. 1993, 42, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ekberg, I.; Eriksson, G.; Namkoong, G.; Nilsson, C.; Norell, L. Genetic correlations for growth rhythm and growth capacity at ages 3–8 years in provenance hybrids of Picea abies. Scand. J. For. Res. 1994, 9, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matisons, R.; Zeltiņš, P.; Danusevičius, D.; Džeriņa, B.; Desaine, I.; Jansons, Ā. Genetic control of intra-annual height growth in 6-year-old norway spruce progenies in Latvia. iForest 2019, 12, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjørve, K.M.C.; Tjørve, E. The use of Gompertz models in growth analyses, and new Gompertz-model approach: An addition to the Unified-Richards family. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bušs, K. Forest ecosystem classification in Latvia. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. Sect. B Nat. Exact Appl. Sci. 1997, 51, 204–218. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team, R. The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R.; Buerkner, P.; Herve, M.; LOve, J.; Riebl, H.; Singmann, H. CRAN—Package Emmeans. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/emmeans/index.html (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Seo, J.W.; Salminen, H.; Jalkanen, R.; Eckstein, D. Chronological coherence between intra-annual height and radial growth of scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) in the northern boreal zone of Finland. Balt. For. 2010, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Partanen, J.; Koski, V.; Hänninen, H. Effects of photoperiod and temperature on the timing of bud burst in Norway spruce (Picea abies). Tree Physiol. 1998, 18, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutinen, S.; Partanen, J.; Viherä-Aarnio, A.; Häkkinen, R. Development and growth of primordial shoots in Norway spruce buds before visible bud burst in relation to time and temperature in the field. Tree Physiol. 2012, 32, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fløistad, I.S.; Granhus, A. Timing and duration of short-day treatment influence morphology and second bud flush in Picea abies seedlings. Silva Fenn. 2013, 47, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floistad, I.S.; Granhus, A. Morphology and phenology in picea abies seedlings in response to split short-day treatments. Balt. For. 2019, 25, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksa, T.; Heiskanen, J.; Miina, J.; Tuomola, J.; Kolström, T. Multilevel modelling of height growth in young Norway spruce plantations in southern Finland. Silva Fenn. 2005, 39, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Worrall, J. Seasonal, daily, and hourly growth of height and radius in Norway spruce. Can. J. For. Res. 1973, 3, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langvall, O.; Nilsson, U.; Örlander, G. Frost damage to planted Norway spruce seedlings—Influence of site preparation and seedling type. For. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 141, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, I.; Hänninen, H. Adaptation of the timing of bud burst of Norway spruce to temperate and boreal climates. Silva Fenn. 2002, 36, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hoch, G.; Richter, A.; Körner, C. Non-structural carbon compounds in temperate forest trees. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Salvador, P.; Uscola, M.; Jacobs, D.F. The role of stored carbohydrates and nitrogen in the growth and stress tolerance of planted forest trees. New For. 2015, 46, 813–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrevics, J.; Neimane, U.; Dzerina, B.; Kitenberga, M.; Jansons, J.; Jansons, A. Environmental factors affecting formation of lammas shoots in young stands of Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst.) in Latvia. iForest 2018, 11, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danjon, F. Heritabilities and genetic correlations for estimated growth curve parameters in maritime pine. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1994, 89, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haapanen, M.; Veiling, P.; Annala, M.-L. Progeny trial estimates of genetic parameters for growth and quality traits in Scots pine. Silva Fenn. 1997, 31, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, B.; Högberg, K. Genotypic parameters and clone x site interaction in clone tests of Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.). For. Genet. 1998, 5, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rweyongeza, D.M.; Yeh, F.C.; Dhir, N.K. Genetic parameters for bud flushing and growth characteristics of white spruce seedlings. Silvae Genet. 2010, 59, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ununger, J.; Ekberg, I.; Kang, H. Genetic control and age-related changes of juvenile growth characters in Picea abies. Scand. J. For. Res. 1988, 3, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial | Group of Families | Gompertz Model Coefficients | SL, mm | GI, mm day−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | β | k | ||||
| R | superior10% | 652 ± 29 a | 2.54 ± 0.12 a | 0.071 ± 0.002 a | 624 ± 26 a | 10.2 ± 0.4 a |
| rest | 518 ± 10 b | 2.83 ± 0.05 a | 0.079 ± 0.001 b | 499 ± 9 b | 8.1 ± 0.1 b | |
| inferior10% | 373 ± 21 c | 2.93 ± 0.14 a | 0.087 ± 0.002 c | 362 ± 21 c | 5.9 ± 0.3 c | |
| J | superior10% | 754 ± 36 a | 4.15 ± 0.14 a | 0.057 ± 0.002 a | 662 ± 26 a | 11.3 ± 0.4 a |
| rest | 636 ± 13 b | 4.21 ± 0.08 a | 0.065 ± 0.001 b | 558 ± 10 b | 9.4 ± 0.2 b | |
| inferior10% | 520 ± 41 b | 4.59 ± 0.31 a | 0.073 ± 0.004 c | 468 ± 33 c | 7.8 ± 0.6 c | |
| Trial | Parameters | h2 ± SE | CVa, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rembate | α | 0.21 ± 0.011 | 8 |
| β | 0.97 ± 0.08 | 17 | |
| k | 0.30 ± 0.10 | 5 | |
| Tree height | 0.24 ± 0.10 | 7 | |
| Shoot length | 0.23 ± 0.11 | 8 | |
| Jelgava | α | 0.03 ± 0.05 | 6 |
| β | 0.16 ± 0.06 | 17 | |
| k | 0.19 ± 0.08 | 7 | |
| Tree height | 0.31 ± 0.09 | 7 | |
| Shoot length | 0.08 ± 0.10 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jansone, B.; Neimane, U.; Šēnhofa, S.; Matisons, R.; Jansons, Ā. Genetically Determined Differences in Annual Shoot Elongation of Young Norway Spruce. Forests 2020, 11, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11121260
Jansone B, Neimane U, Šēnhofa S, Matisons R, Jansons Ā. Genetically Determined Differences in Annual Shoot Elongation of Young Norway Spruce. Forests. 2020; 11(12):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11121260
Chicago/Turabian StyleJansone, Baiba, Una Neimane, Silva Šēnhofa, Roberts Matisons, and Āris Jansons. 2020. "Genetically Determined Differences in Annual Shoot Elongation of Young Norway Spruce" Forests 11, no. 12: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11121260
APA StyleJansone, B., Neimane, U., Šēnhofa, S., Matisons, R., & Jansons, Ā. (2020). Genetically Determined Differences in Annual Shoot Elongation of Young Norway Spruce. Forests, 11(12), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11121260






