Abstract
This study aims to quantify the potential contribution of nutrients derived from leaf litter in a short rotation coppice plantation which includes monocultures of the species Populus alba (PA) and Robina pseudoacacia (RP) as well as a mixture of 50PA:50RP, in the middle of the rotation. The P. alba monoculture was that which provided the most leaf litter (3.37 mg ha−1 yr−1), followed by the 50PA:50RP mixture (2.82 mg ha−1 yr−1) and finally the R. pseudoacacia monoculture (2.55 mg ha−1 yr−1). In addition to producing more litterfall, leaves were shed later in the P. alba monoculture later (December) than in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture (October) or the mix (throughout the fall). In terms of macronutrient supply per hectare, the contributions derived from leaf litter were higher for K, P and Mg in the case of P. alba and for N in R. pseudoacacia, the mix presenting the highest Ca content and intermediate concentrations for the rest of the nutrients. In addition, other factors such as C:N or N:MO ratios, as well as the specific characteristics of the soil, can have an important impact on the final contribution of these inputs. The carbon contribution derived from leaf fall was higher in the P. alba monoculture (1.5 mg ha−1 yr−1), intermediate in the mixed plot (1.3 mg ha−1 yr−1) and slightly lower for the R. pseudoacacia monoculture (1.3 mg ha−1 yr−1). Given these different strategies of monocultures with regard to the dynamism of the main nutrients, species mixing would appear to be suitable option to achieve a potential reduction in mineral fertilization in these plantations.
1. Introduction
Forest plantations of fast-growing species under a short rotation coppice system (SRC) can contribute to the supply of biomass for use in bioenergy and bioproducts within the context of the bioeconomy []. Salicaceae (poplars and willows) are suitable species for this purpose due to their high productivity, ease of vegetative multiplication and ample availability of genetic material [], resulting in crops of this family of genotypes being common in many areas of the world []. To a lesser extent, other species have been considered for SRC [,]. Among the latter, Robinia pseudoacacia L., of de Fabaceae family, is also a fast-growing species, with a certain degree of drought tolerance, capable of sprouting from the stumps and with a high nitrogen fixing capacity []. For these reasons, Robinia is considered suitable for cultivation in SRC in some areas of Europe [,], although it is also considered an invasive species introduced into Europe in the 17th century [].
Most SRC plantations are established as monocultures with a single species, although the possibility of mixed stands has also been explored [,,]. Mixed plantations, in addition to increasing genetic variability and favoring tolerance to certain stresses, can also provide productive benefits based on complementary or facilitation strategies [].
One of the main internal flows of the continuous vegetation–soil–fauna dynamic in forestry or agroforestry ecosystems is leaf litter, the subsequent decomposition process, and the consequent incorporation of organic matter and nutrients, needed for growth, into the soil [,,]. Leaf litter is therefore part of a key mechanism of recycling and redistribution of nutrients. Litterfall quantification allows the potentiality as regards the degree of annual return of nutrients to the soil to be assessed. The quantity of litterfall will depend on different factors such as the genotype, the climatic factors such as temperature and light, fertility and degree of soil moisture, type of management or age of the plot, among others [,,,].
In plantations with fast-growing species, the leaf litter plays an important role within the nutrient cycle, allowing the replacement of a high percentage of mineral nutrients to the soil [,,,]. Soil fertility and nutrient recycling is one of the main concerns in relation to sustainability [] and the assessment of forest plantations on agricultural soils is therefore pertinent. In the specific case of deciduous Populus spp., it is estimated that around 88% of N, 83% P and 78% K are returned through leaf litter in mature plantations []. Other authors, however, report lower return rates of between 20 and 40% and suggest that the rate depends highly on the genotype []. In general, nutrient cycling in poplar stands is considered efficient, with no significant loss of nutrients according to Meiresonne et al. [] and returns via leaf litter are also often rich in basic cations [,]. Data on these nutrient returns in the specific case of poplar growing in short rotation coppice point to between 60–80% of the nutrients absorbed being returned annually through litterfall []. However, in SRC plantations with another fast-growing species such as eucalyptus, Guo et al. [] reported rates of return of around 24% for N, although in this case it is an evergreen species.
Leaf litter decomposition rate is also important for determining how nutrients enter the soil and will also determine the amount of organic matter which accumulates. This rate is controlled by both biotic and abiotic factors, with the chemical composition of the leaf litter (especially N and P concentration and C:N ratio) being one of the main influencing factors [,,]. The variability of the chemical composition of the leaf litter will be determined, among other factors, by the efficiency of the reabsorption and relocation of nutrients at species level and by their interspecific variation [].
Additionally, to quantify the contribution of SRC to carbon content it is necessary to determine the sources of variation in C concentration and to address potential sequestration in these farming systems []. In recent years, studies have pointed to the high potential contribution of plantations with fast-growing species to the global carbon budget [,]. Moreover, such plantations have been proposed as part of a strategy to mitigate global warming in the short term [,].
In forest plantations with fast-growing species, and specifically in the case of high density, short rotation plantations for biomass production, this evaluation is necessary not only to promote more sustainable management, but also in order to value the ecosystem services associated with them. Furthermore, it is necessary to evaluate the potential adverse effects on forest soils associated with the implementation of intensive plantations [,,] on highly managed agricultural land, since these plantations are established on this type of land in many countries. Hence, the aims of this work are (i) to quantify the annual production of leaf litter and its composition in pure and mixed plots of high density, short rotation coppice (SRC) under Mediterranean conditions; and (ii) to determine the nutrient dynamics in this type of plantation and the potential impact on the soil. We hypothesized that mixed plantations improve the quality of the leaf litter with respect to monocultures, and consequently increase soil fertility.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The experimental plantation is located in the center of the Iberian Peninsula (40°28′ N, 3°22′ W) at an elevation of 595 m, average mean temperature 15.3 °C (mean absolute maximum 28.8 °C and mean absolute minimum of 3.1 °C), with annual precipitation of 281 mm. The main edaphic features are detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Average values ± standard deviation of physical-chemical parameters and concentrations of assimilable Phosphorus and interchangeable elements (Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium and Sodium) on the surface horizon of the soil (0–30 cm).
The plantation was established in 2012 with the aim of evaluating biomass yield under different species compositions. Different mixing ratios of two fast-growing species were tested under a high-density (10,000 trees ha−1, spacing 2.5 m × 0.40 m) short rotation coppice system. The two species were Populus alba L., genotype ‘111PK’, and Robinia pseudoacacia L., genotype ‘Nyirsegy’, and the trial included P. alba monoculture (PA), R. pseudoacacia monoculture (RP) and a mixture of both at a ratio of 50PA:50RP. The 50PA:50RP mix of both species was done tree by tree within the row and between rows. The figure design and the results of this research are described in Oliveira et al. []. The plantation was established using stem cuttings (unrooted in the case of P. alba and rooted for R. pseudoacacia) having followed the standard soil preparation procedure described for SRC plantations []. Since the Mediterranean climate is characterized by severe summer drought, the plantation was irrigated from June to September using a drip application system. No fertilization treatment was applied.
The experimental design included three blocks, each containing the P. alba and R. pseudoacacia monocultures as well as the 50PA:50RP mix of both species. Each block and plot contained 64 trees in total. Further details on the experimental design are given in Oliveira et al. [].
2.2. Litterfall Collection
Litterfall samples were collected from September to December in the 1st vegetative period of the 2nd rotation (R4S1, where R is the root age and S is the stool age), being the value of basal area of basal diameters (BA) and the height (H) of the species the following: the P. alba monoculture (BA = 23.94 cm2 and H = 5.46 m); the R. pseudoacacia monoculture (BA = 11.73 cm2 and H = 3.92 m) and the mix (BA = 20.75 cm2 and H = 4.89 m for PA and BA = 14.80 cm2 and H = 4.50 m for RP). Twelve litterfall traps (perforated plastic boxes with a surface area of 0.17 m2 and a height of 23 cm) were randomly placed in the rows of each block and plot and within the row, equidistant between two trees. The final number of traps was thirty-six.
The monthly accumulated litterfall was taken to the laboratory where leaves were separated from the rest, which included twigs, bark, seeds, shoots, and other released components. The leaves were then dried at 65 °C to constant weight and finally weighed. The leaf litter contribution in each subplot was calculated by adding the results for the different traps. The calculation per unit area was performed by dividing the sum of the total dry weight of the different fractions by the area of the trap, extrapolating the result obtained to one hectare. The unit to express the contribution of leaf litter is therefore mg ha−1 yr−1 in dry matter.
Prior to the abscission of the leaf (end of August), when it was probable that the translocation of nutrients from the leaves to the reserve organs had not yet begun [,], fresh green leaves were collected from the trees in the same blocks and plots where the traps had been placed for further analysis.
2.3. Foliar Nutrient Analysis
The following analyses were performed on both the green leaves and senescent leaves collected over 3 months: Total C and N by dry combustion using an elemental analyzer (CNS-2000, LECO, St Joseph, MI, USA); and P, K, Ca and Mg were determined by optical emission spectroscopy using ICP-OES (Optima 5300 DV, Perkin-Elmer, Massachusetts, MA, USA) after wet digestion of the sample with nitric acid in a closed microwave system (Ethos plus, Milestone, Sorisole, Italy).
The percentage of nutrient resorption efficiency (NRE; hereafter retranslocation) between the two types of leaves (green and senescent) was calculated according to the following Equation []:
where Nugreen is the nutrient concentration in the green leaf and Nusenescent is the concentration in senescent leaf.
NRE = (Nugreen − Nusenescent)/Nugreen × 100
The nutrient use efficiency index was determined according to Vitousek [], through the relationship between dry mass and nutrient concentration ratio of leaf litter.
2.4. Data Analysis
A multivariate analysis of variance was performed to assess the effect of the treatments (plot type and sampling time) on leaf litter production and the chemical composition. A one-way ANOVA was performed when evaluating the effect of a single factor. Fisher’s Least Significant Difference (LSD) test was used to establish those means that are significantly different.
A non-parametric analysis was performed when the assumptions of the one-way ANOVA test were not met, using the Kruskal–Wallis test in these cases.
We worked with weighted annual averages according to weight fraction at subplot level when analyzing data related to leaf nutrients due to the variability in both concentration and input over the sampling period. The software package used was the R statistical program.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Leaf Litter Supply
The most representative fraction of litterfall in all plots of the plantation (both monocultures and 50PA:50RP mixture) corresponded to leaves (around 98%); therefore, we will refer to this component from now on, with leaf litter being understood as all the leaves falling into the litterfall traps. However, according to Medina-Villar et al. [], the leaf percentages for both species growing in the riparian ecosystem were lower (69%), probably because the litterfall trap contents comprised the entire annuity.
Leaf detachment in deciduous species mainly takes place throughout the fall. Abscission can occur at any time during this period, depending on various factors such as weather and edaphic conditions (water stress and soil fertility) but also on the species []. In our study, under the same soil and climate conditions, the maximum leaf litter values for the P. alba monoculture were reached in December, while leaf shedding in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture occurred earlier, reaching maximum values in October (Figure 1). This fact is in accordance with observed differences in phenology, as winter buds are formed earlier in R. pseudoacacia (early September) and later in P. alba (late October). This finding has previously been reported by Medina-Villar et al. [] for natural stands in a study area proximate to that of the present study and supports previous findings by González-Muñoz et al. [] and Castro-Díez et al. []. Furthermore, it may be attributable to differences in the strategies for minimizing the energy expenditure required to keep tissues alive when the temperatures fall [].
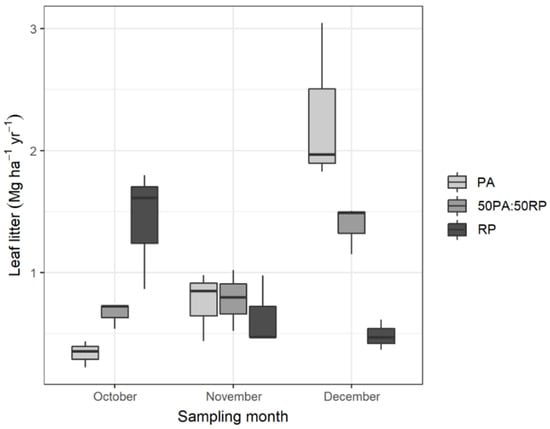
Figure 1.
Monthly contribution (mg ha−1 yr−1) of the leaf litter in the P. alba (PA) and R. pseudoacacia (RP) monocultures, and the 50PA:50RP mixture.
Since a greater amount of the leaves in the total leaf litter of the mixture corresponded to P. alba (60 % PA to 40% RP) (Figure 2), and as this species sheds most of its leaves in December (82%), this was the month in which leaf litter in the mixture reached a maximum.
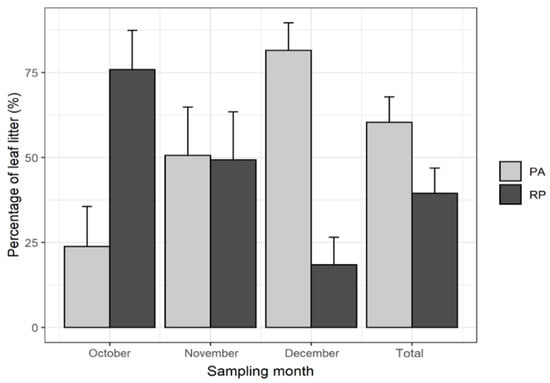
Figure 2.
Percentage contribution of P. alba (PA) and R. pseudoacacia (RP) to the total leaf litter of the 50PA:50RP mixture.
The total leaf litter expressed in Mg per hectare in the different plots is shown in Table 2. Although the amounts of leaf litter among plots were not significantly different (p-value = 0.2160), the annual inflow of leaves was more than 20% higher in the P. alba monoculture compared to R. pseudoacacia and the 50PA:50RP mixture. This trend contrasts with that described by Medina-Villar et al. [], who reported greater leaf litter for R. pseudoacacia and pointed to generally higher growth rates due to the invasive character of this species compared to native species [,]. These conflicting findings may be due to the rapid growth rate of the P. alba genotype in our case compared to R. pseudoacacia over two rotations of 3 years [,,].

Table 2.
Leaf litter total annual weight in P. alba or R. pseudoacacia monocultures and 50PA:50RP mixture plantations.
In contrast, the leaf litter production recorded in the P. alba monoculture (3.37 mg ha−1 yr−1) was similar to that obtained by Guenon et al. [], who reported 3.1 mg ha−1 yr−1 in SRC plantations of Populus deltoides × P. nigra, although in that case the planting density was lower (7200 tree ha−1). However, other authors have reported higher values for the same species growing in SRC plantations (5.3 mg ha−1 yr−1) []. The amount of leaf litter was much lower for both species (0.77 mg ha−1 yr−1 in P. alba and 1.02 mg ha−1 yr−1 in R. pseudoacacia) in the riparian ecosystems described by Medina-Villar et al. [], which is probably because of the lower tree density and the lower growth rate. The leaf litter in R. pseudoacacia plantations found by Tateno et al. [] was around 3.8 mg ha−1 yr−1, which is higher than the amounts obtained in the present study (2.55 mg ha−1 yr−1), despite having a lower planting density. In the mixed plantation, leaf litter accounted for 2.82 mg ha−1 yr−1, with this value being between that of the two monocultures although closer to that for the R. pseudoacacia monoculture, despite the greater contribution P. alba leaves.
3.2. Foliar Nutrient Concentration and Retranslocation Rate in Green Leaves and Senescent Leaves
3.2.1. Macronutrients and C
Leaf N concentration was significantly higher in green leaves compared to senescent leaves in all test plots (p-value = 0.0002 for PA; p-value = 0.0001 for 50PA:50RP and p-value = 0.0004 for RP) (Figure 3). This result was expected, since nitrogen resorption from senescent leaves at the end of the growing season is a key function in plants [].
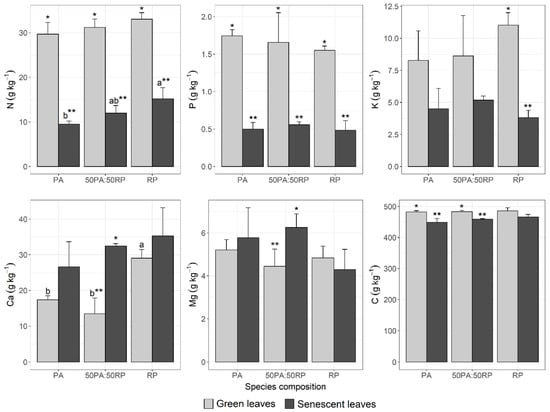
Figure 3.
Weighted annual averages according to weight fraction and their standard deviation for macronutrients and C in green and senescent leaves of P. alba (PA) and R. pseudoacacia (RP) monocultures and 50PA:50RP mixture. The significance between plot types for green leaves, and also for senescent leaves, is shown by letters; and the significance between green and senescent leaves within the same plot (PA, 50PA:50RP and RP respectively) is shown with asterisks. Both letters and asterisks are only shown when significant differences were found.
In green leaves, the concentration of N did not differ significantly between the different plots (p-value = 0.217). However, in absolute terms, the N concentration was higher in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture, the values for the mixed plantation being intermediate and the lowest values being those for P. alba, although still greater than 25 g kg−1, which is considered the threshold for nutrient-demanding broadleaves []. A higher concentration of N in the green leaves of a P. deltoides L.—Alnus glutinosa (L). Gaertn mixture in comparison to the monoculture of P. deltoides was also observed by Koupar et al. [].
The N efficiency index showed non-significant differences (p-value = 0.0582), although a higher mean efficiency value was observed for P. alba (357.36) in relation to that of R. pseudoacacia (171.38). The 50PA:50RP mixture showed an intermediate ratio (240.27) that did not differ significantly from monocultures. The low efficiency of R. pseudoacacia, which may be attributable to its N2-fixing character, has been previously reported by González -Muñoz et al. [].
The average concentration of N in senescent leaves was also significantly higher in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture and the 50PA:50RP mixture in comparison to the P. alba monoculture (p-value = 0.0258), with the 50PA:50RP mixture presenting intermediate concentrations (Figure 3). The concentrations detected in senescent leaves are in line with those described by Lee et al. [] for R. pseudoacacia leaf litter (19.9 g kg−1), Cotrufo et al. [] in relation to P. alba (9.6 g kg−1) or Das and Chaturvedi [] for P. deltoides (11.4 g kg−1). Similar trends, although with notably higher concentrations, are mentioned by Medina-Villar et al. []. However, Koupar et al. [] found higher concentrations of N in senescent leaves in mixed Populus and Alnus plantations than in their respective monocultures.
Similarly, in relation to P, the concentration in green leaves was significantly higher than in senescent leaves in all plots (p-value < 0.0001 for PA; p-value = 0.0091 for 50PA:50RP; and p-value = 0.0002 for RP) (Figure 3). In the case of green leaves (50PA:50RP mixture and monocultures) no significant differences among species were observed for P concentration (p-value = 0.6340), although absolute values were higher in P. alba. In senescent leaves, no significant differences were detected (p-value = 0.613), the highest concentrations corresponding to the 50PA:50RP mixture and the lowest to the R. pseudoacacia monoculture (Figure 3).
There were no significant differences in P use efficiency (p-value = 0.2881), with P. alba presenting the highest absolute value (6801), followed by R. pseudoacacia (5585) and finally the mixed plantation (5078).
In this study, the P concentrations in senescent leaves were lower than those detected in other studies. Lee et al. [] obtained mean values of 0.63 g kg−1 in R. pseudoacacia or ranges from 1.14 g kg−1 to 1.37 g kg−1 in Populus spp. [,].
The stoichiometric N:P ratio in green leaves, widely used as an indicator of probable N:P deficiency, showed values above 16 in our study, which is the upper threshold identified by Aerts and Chapin [] to indicate P deficiency, meaning that both species are far from displaying N deficiency. The leaves in our plots showed ratios close to normality in the P. alba monoculture (17.02). However, this proportion was 19.67 in the 50PA:50RP mixture and 21.34 in the case of the R. pseudoacacia monoculture, which could imply a progressive loss of fertility as regards P in these soils, since the leaf decomposition provides the main supply of this nutrient [,].
N2-fixing species such as R. pseudoacacia may have more demand for P than non-fixing species and this element may be the most limiting for its growth []. Cao and Chen [] also reported that P was more limiting than N for mature R. pseudoacacia plantations.
Regarding K concentration, even though the concentration in green leaves is always higher than that of senescent leaves in absolute terms, significant differences were only found in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture (p-value = 0.0004) (Figure 3), whereas no significant differences were found in the P. alba monoculture (p-value = 0.08) or the 50PA:50RP mixture (p-value = 0.132). No significant differences were detected among the plots (monocultures and 50PA:50RP mixture) (green leaves: p-value = 0.352; and senescent leaves: p-value = 0.311). This may be because K is a highly mobile element, both in plants and in the soil [], which is reflected in a high variability of the concentration detected in the leaves in all plots.
K concentration in senescent leaves reported in the literature for Populus spp. ranges widely from 1.2 to 10.8 g kg−1 [,,,,], the K concentration found in this study presenting intermediate values. Less information appears to be available for K concentration in senescent R. pseudoacacia leaves, although Lee et al. [] report levels of around 10.97 g kg−1, which is more than twice our values.
The greater difference in K detected between senescent and green leaves of R. pseudoacacia (7.22 mg g−1) in comparison to P. alba (3.77 mg g−1) could indicate greater importance of retranslocation as compared to recirculation via leaf litter.
According to the literature, the optimal range of NPK in green leaves for Populus species is 17–30 g kg−1 for N, 1.0–4.4 g kg−1 for P and 7–20 g kg−1 for K [,,,,,]. Narrower optimal ranges are established for site-demanding broadleaved [] and more specifically for Populus [] species, with 18–25 g kg−1 for N, 1.8–3.0 g kg−1 for P and 12–20 g kg−1 for K. The concentrations of N obtained in the green leaves of all our plots were above the optimal range, while in the case of P, they were very close to the lower limit. In the case of K, the levels indicate deficiency. Sardans et al. [] found green-leaf NPK ranges for P. alba at 41 different study points of 26.8–31.2, 1.96–2.08 and 4.8–26.5 g kg−1 respectively. The values for the P. alba monoculture plots were within this range for N and K in our study, although in the case of P, the concentrations were lower.
The green-leaf NPK concentration reported by Ozbucak et al. [] for R. pseudoacacia ranged from 20.0–44.2, 0.60–2.47 and 2.1–12 g kg−1, the concentrations detected in our plots being within these ranges. For the same species, Sardans et al. [] reported N and P ranges within those defined by Ozbucak et al. [] (35.2–44.2 and 1.94–2.48 g kg−1, respectively), although much higher for K (14.3–20.1 g kg−1), the values obtained in this study being below those ranges for P and K, and very close to the lower limit in the case of N. However, if we take into account the ranges for optimum nutrition of demanding broadleaves [,], the concentrations obtained in this study for R. pseudoacacia are below the critical levels for P and K. In contrast, in the case of N, the concentrations obtained were above the optimal range, as expected, since R. pseudoacacia is an N2-fixing species.
The low concentrations of K obtained in green leaves in this study could be due to the antagonistic relationship between Ca and K, given the high concentrations of interchangeable Ca in the soil (38.71 cmol kg−1) (Table 1). This could cause less absorption of K by the plant due to a lower presence of this element in the soil solution as both elements compete for plasma membrane absorption sites [,].
As regards Ca, the absolute values of the mean concentrations were higher in senescent leaves than in green leaves in the monocultures. However, the differences between the two types of leaves were only significant in the 50PA:50RP mixture (p-value = 0.0877 for PA; p-value = 0.0018 for 50PA:50RP and p-value = 0.263 for RP) (Figure 3), which would indicate that a greater amount of Ca is returned to the soil in the mixed plot in comparison to the monocultures plots. This finding is consistent with that of Sayyad et al. [] in pure and mixed stands of Populus deltoides and Alnus subcordata. The increase in the concentration in the senescent leaf is due to the low mobility of Ca, which is not an element retranslocated by plants. This low mobility causes Ca to be immobilized once assimilated, accumulating in structural components of the leaf such as membranes, cell walls and vacuoles []. Tzvetkova and Petkova [] also found that Ca concentrations for R. pseudoacacia increased in the leaves that fall later.
In senescent leaves, no significant differences were observed between the different plots (both monocultures and the mixture) (p-value = 0.287), while significant differences were found in green leaves between the R. pseudoacacia monoculture and both the P. alba monoculture and the mixture (p-value = 0.0017).
Although no significant differences were detected in the Ca use-efficiency index (p-value = 0.1479), higher values were observed in the P. alba monoculture (132.87) than in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture (71.06), with mixed plots presenting an intermediate value (87.18).
In the case of Mg, as for Ca, the concentrations in absolute values were higher in senescent leaves than in green leaves for the P. alba monoculture and 50PA:50RP plots, these differences being significant for the mixture (p-value = 0.538 for PA and p-value = 0.0378 for 50PA:50PR) (Figure 3). However, in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture, despite no significant differences being detected (p-value = 0.437), the mean concentration of Mg was slightly higher in green leaves than in senescent leaves. This may be because Mg is an element with partial mobility, which, in addition to its involvement in photosynthesis, is a cofactor of numerous enzymatic activities, among which is the nitrogenase activity involved in the fixation of N2 [], and therefore this N2-fixing species, with a higher photosynthetic activity [], may have a greater requirement for this element. Sayyad et al. [] found no significant differences in Mg concentrations between green and senescent leaves for the monoculture and Populus and Alnus mixture plantations. However, in R. pseudoacacia plantations, Tzvetkova and Petkova [] observed a slight decrease in Mg concentrations in leaves that fall later, in agreement with our findings (from 5.15 g kg−1 in October to 2.37 g kg−1 in December).
No significant differences were found in the concentration of Mg between the different plots either for green leaves (p-value = 0.390) or senescent leaves (p-value = 0.132), although in terms of absolute values, the mean concentration of Mg was lower in the senescent leaves in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture. As in this study, Sayyad et al. [] found lower Mg concentrations, both in green and senescent leaves in the N2-fixing species.
Harvey and Van den Driessche [] also reported higher concentrations of Ca and Mg in senescent leaves than in green leaves for Populus (15.80 and 4.78 g kg−1 vs. 9.65 and 3.14 g kg−1), these concentrations being lower than those obtained in this study.
Laganière et al. [] and Yanai et al. [] found ranges of between 10.8 and 18.9 g kg−1 for Ca and between 1.8 and 2.7 g kg−1 for Mg in senescent leaves of Populus, both of which are lower than the amounts found in this study.
In the case of green leaves, Sardans et al. [] reported a range of between 21.3–48.5 g kg−1 for Ca and between 1.9–7.2 g kg−1 for Mg in P. alba and Martín-García et al. [] reported values for the ‘I-214’ genotype of more than 26.4 g kg−1 for Ca and lower than 3.6 g kg−1 for Mg. However, Elferjani [] reported values for hybrid poplar genotypes of between 7.9–12 g kg−1 for Ca and 2.0–2.8 g kg−1 for Mg, these values again being lower than those obtained in this study.
According to the literature, the optimal Ca and Mg in green leaves of Populus species ranges from 3–17 g kg−1 for Ca and 1.4–4.0 g kg−1 for Mg [,,,,,]. However, Bergmann [] established narrower optimal ranges for Populus of 3–15 g kg−1 for Ca and of 2.0–3.0 g kg−1 for Mg. Hence, our Ca values for Populus are at the upper limit of the optimal range and above the optimal range in the case of Mg.
As regards R. pseudoacacia, Sardans et al. [] reported concentration ranges in green leaves of 12.3–22.7 g kg−1 for Ca and 2.09–2.69 g kg−1 for Mg, the mean concentrations found in this study being above those ranges for both Ca and Mg. With respect to other demanding broadleaved species such as Fraxinus excelsior, Bergmann [] established optimal ranges of 3.0–15.0 g kg−1 for Ca and 2.0–4.0 g kg−1 for Mg. As for less demanding broadleaved species such as beech, Stefan et al. [] established ranges of 4–8 g kg−1 for Ca and 1–1.5 g kg−1 for Mg. In our study, the R. pseudoacacia monoculture presents concentrations above the optimal nutritional range.
The high levels of Ca and Mg measured in this study may be due to the high concentrations of these elements in the exchange complex, which, together with the basic pH, would facilitate the absorption of these nutrients by the plant (Table 1). To this fact, it should be added that high concentrations of Mg can be caused by low levels of K according to Kirkby and Mengel [], a circumstance that would occur in the studied plantations.
The mean C values in green and senescent leaves were not significantly different between plots (p-value = 0.863 and p-value = 0.136, respectively) (Figure 3), nor were there significant differences between green and senescent leaves in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture (p-value = 0.0122 for PA; p-value = 0.0007 for 50PA:50RP and p-value = 0.0659 for RP). These values were very similar to those described for senescent poplar leaves by Cotrufo et al. [] of around 435 g kg−1 or to the C values in green leaves of R. pseudoacacia reported by Cao and Chen [] of around 480 g kg−1. Leaves account for an important fraction soil C contribution [].
3.2.2. Retranslocation
Regarding retranslocation, as expected, there was a significant reduction in NPK concentrations in senescent leaves compared to green leaves in all plots, which indicates significant internal recycling of nutrients. Figure 4 shows the percentage of retranslocation using the weighted annual averages according to weight fraction value for senescent leaves as there are three harvesting dates.
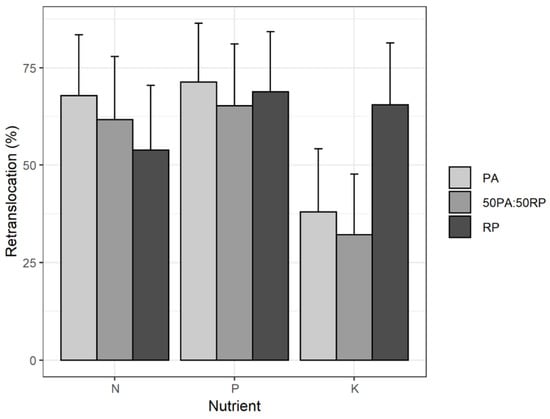
Figure 4.
Average values and standard deviation of the percentage of efficient retranslocation of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in P. alba (PA) and R. pseudoacacia (RP) monocultures and 50PA:50RP mixture.
The rate of N retranslocation (N-re) was significantly lower in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture compared to the P. alba monoculture (p-value = 0.05). Higher green leaf nutrient content is normally assumed to be associated with lower retranslocation efficiency [,]. No significant differences were detected for P and K in the different plots (p-value = 0.5866 and p-value = 0.2521, respectively). However, in absolute values, the rate of P retranslocation (P-re) was higher in P. alba and higher for K-re in R. pseudoacacia. Ozbucak et al. [] reported similar trends in the retranslocation of P and K in R. pseudoacacia, but found the opposite for N. The higher rate of P-re (71.36%) with respect to the rate of N-re (67.87%) in all plots could indicate, as suggested by Ozbucak et al. [], that P is a limiting nutrient in the study area. In fact, the values detected in the soil at the time of plantation were below 4 mg kg−1, which would indicate deficiency according to Andrades and Martínez [].
Aerts [] states that for deciduous species in general, efficient retranslocation ranges from 40 to 75% in the case of N and from 30 to 70% for P. Hence, the rates of N-re and P-re in the three studied plots (monocultures and 50PA:50RP mixture) would be within those ranges or proximate to them. However, in the case of R. pseudoacacia, lower NPK retranslocation values (45, 45 and 60% respectively) were reported by Ozbucak et al. []. According to Salehi et al. [], NPK in poplar hybrids ranges were 12–19%, 32–40% and 21–24%, respectively, while Das and Chaturvedi [] detected higher limits for P. deltoides of around 52–54%, 40–46% and 46–47% for NPK, respectively. In the present study, the retranslocation percentage in P. alba was higher than 50% for all nutrients except for K.
This variability in the retranslocation rates could be due to the influence of the physical-chemical properties of the soil, as well as to the specific nutritional requirements of the plant in the retranslocation process, as suggested by Fife et al. []. Low percentages of retranslocation suggest a less conservative strategy, which implies a greater dependence on the circulation of nutrients from the soil []. In this study, where the soil has high levels of N, Ca and Mg fertility (Table 1), the retranslocation values obtained would therefore indicate a more conservative strategy as regards P in both species, as well as for K in the case of R. pseudoacacia, the plants being less dependent on the nutrient dynamics of the soil. Moreover, with the soil pH levels found in this study (around 8.65), formation of insoluble CaHPO4 and P fixation could be expected.
3.3. Temporal Variability of Nutrients in Senescent Leaves
Table 3 shows the evolution over time of the NPK, Ca and Mg concentrations over the months in which leaf shedding occurred. The N concentration of P. alba senescent leaves was greater in October than in November or December (p-value = 0.0134). However, in R. pseudoacacia, the opposite trend was observed, with no significant differences being detected (p-value = 0.103). In the case of the 50PA:50RP mixture, although there were no significant differences (p-value = 0.0792), the N concentration decreased as the sampling period progressed. This may be due to the lower percentage of R. pseudoacacia leaves as the sampling period progressed, caused by differences in the time of abscission of each leaf. With regard to P, no significant variation was observed over the months (p-value = 0.302 for PA, p-value = 0.966 for 50PA:50RP and p-value = 0.304 for RP). K concentration did not vary significantly in any of the plots as the sampling period progressed (p-value = 0.6 for PA, p-value = 0.21 for the 50PA:50RP mixture and p-value = 0.0514 for RP).

Table 3.
Monthly averages ± standard deviation of NPK concentrations in senescent leaves collected in October, November and December in P. alba and R. pseudoacacia monoculture plots and mixed (50PA:50RP) plots.
As for Ca and Mg, which are less mobile nutrients that tend to accumulate in the leaves, the variation in the concentrations in senescent leaves in all plots in the case of Mg and in R. pseudoacacia for Ca, followed the opposite pattern to that of more mobile nutrients which are retranslocated, with concentrations being higher in the months of greatest leaf fall. In the P. alba monoculture, Ca concentrations were very similar between the fall months of leaf shedding, while in the case of the mixture, the concentrations were significantly lower in the month with the highest litterfall production (p-value = 0.0007).
The different phenology of leaf fall can influence the loss of nutrients in senescent leaves and therefore modify the chemical composition. Thus, species with earlier leaf fall tend to retranslocate nutrients more quickly to compensate for the greater amount of initial leaf loss, especially in the case of N []. These authors found lower nutrient contents coinciding with the period of greatest leaf fall. This finding is in agreement with our observations in the case of N, which showed lower concentrations in the period of greatest leaf-fall (October in the case of the R. pseudoacacia monoculture, November and December for the P. alba monoculture and December for the 50PA:50RP mixture). However, in the subsequent months, we observed a decrease in retranslocation in R. pseudoacacia, coinciding with an increase in leaf concentration (Figure 4). This may be due to the higher rates of N-fixation in autumn and spring reported for this species []. The increase in N concentration with leaf age has also been reported by López et al. [] for another N2-fixing species, Alnus glutinosa.
In relation to P and K, the lowest concentrations also coincided with the period of greatest leaf fall in the P. alba monoculture. However, in the R. pseudoacacia monoculture, the lowest concentrations of P and K do not coincide with the time of greatest leaf fall. Specifically, the low concentrations of K obtained in the month of December could also be the result of leachate of this extremely mobile nutrient in leaves that have remained longer on the tree.
The decrease in NPK rates with leaf age has also been reported by other authors in deciduous species [].
3.4. Stoichiometric C:N Ratio in Senescent Leaves
The average C:N ratio values (Table 4) were significantly higher in the P. alba monoculture compared to the R. pseudoacacia monoculture (p-value = 0.0390). The increase in the ratio was greater in November and December compared to October, both in the P. alba monoculture (p-value = 0.0665) as well as in the 50PA:50RP mixture (p-value = 0.0665), although it was not significantly different among months. The opposite was observed for R. pseudoacacia, although again there were no significant differences (p-value = 0.3012), probably due to the different monthly contribution of leaf fall and therefore of the organic matter, which was higher in October for this species, unlike P. alba and the 50PA:50RP mixture, both of which present the highest leaf fall in December.

Table 4.
Average values ± standard deviation of C:N ratio in the three months of leaf litter harvesting for the plots studied.
N and P are important elements of the litter and have a strong influence on the decomposition rate due to the high demand for them by decomposer microorganisms [,,], with the initial stoichiometric C:N being a good predictor of the initial decomposition rate [,].
Leaf litter with a high C:N ratio normally displays a slower decomposition rate and immobilizes more N [,,]. The lower average total values of C:N in the leaf litter of the R. pseudoacacia monoculture and in the 50PA:50RP mixed plots reflects a greater amount of N mobilized in the leaf litter, which may be evidenced by a higher initial decomposition rate than that of the leaf litter of the P. alba monoculture. Hirschfeld et al. [] reported significantly lower C:N ratios in R. pseudoacacia (24.2) than in other North American broadleaves, such as white ash and sugar maple (43.8 and 83.2 respectively). In a P. alba short rotation plantation, Cotrufo et al. [] reported an average C:N value of 43, similar to that found in this study.
The leaf litter of mixed plantations decomposes more rapidly than that of monocultures as the leaf litter mixture leads to massive decomposition by increasing the loss of mass as well as by promoting the abundance and quality of soil decomposers []. This statement is partially supported by the results obtained in this study, in which the 50PA:50RP mixture showed a higher initial decomposition rate than that of the P. alba monoculture, but not of the R. pseudoacacia monoculture, suggesting that species could be an influential factor. Lee et al. [] found a higher rate of leaf litter decomposition in a mixed plot of Quercus mongolica and R. pseudoacacia than in a monoculture of Q. mongolica.
3.5. Nutrient Supply to the Soil Derived from Leaf Litter
The return to the soil of C, P and K derived from the leaf litter, expressed in kg per ha, was greater in the P. alba monoculture and in the 50PA:50RP mixture (Table 5), mainly because of the greater production of foliar biomass in these plots. The R. pseudoacacia monoculture, however, despite lower leaf litter production, presented the highest N contributions as a result of the higher N concentrations in senescent leaves.

Table 5.
Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium and Magnesium total annual weighted average contributions in leaf litter for P. alba and R. pseudoacacia monocultures, and 50PA:50RP mixture plantations.
Das and Chaturvedi [] found N contributions of 30.8–41.9 kg ha−1 yr−1, P of 4.3–5 kg ha−1 yr−1 and K of 19.4–20.1 kg ha−1 yr−1 in two 3-year-old poplar plantations. These values are similar to those obtained in our study for N, but higher than those for P and K.
In a P. deltoides × P. nigra plantation of the same age, Guénon et al. [] found NPK contributions of 48.0, 6.2 and 10.8 kg ha−1 yr−1, respectively, which are greater than our values for N and P but lower for K. The higher P contributions might be explained by the higher P content of the soil and greater availability due to a strongly alkaline pH. The low P contributions in all the plots in our study will probably be reflected in a low availability of this nutrient in the soil.
In a study conducted in a riparian stand with the same species composition, P. alba and R. pseudoacacia, Medina-Villar et al. [] reported lower N (8.8 and 15.3 kg ha−1 yr−1) and P (1.06 and 0.49 kg ha−1 yr−1) inputs, which is probably due to a much lower level of litter production compared to the levels found in our study.
Although the contribution of leaf litter was greater in P. alba monocultures, the 50PA:50RP mixture contributed the most in terms of Ca, which reflects the higher mean concentration of Ca in senescent leaves. In the case of Mg, the R. pseudoacacia monoculture presented the lowest returns because of the lower amount of leaf litter coupled with the lower concentration of Mg in senescent leaves.
In poplar SRC plantations, Guénon et al. [] measured Ca and Mg contributions of 80 and 22 kg ha−1, respectively, consistent with the findings of this study, although with slightly lower Ca. However, Perala and Alban [] reported lower contributions of Ca and Mg for P. tremuloides (60 and 8 kg ha−1, respectively).
The total C content was higher in the P. alba monoculture due to the greater content of leaf litter. Therefore, the greatest contribution of C returned to the soil through leaf litter was measured in this plot (1507 kg C ha−1 yr−1), followed by the 50PA:50RP mixture (1297 kg C ha−1 yr−1), and finally the R. pseudoacacia monoculture contributed the least amount (1187 kg C ha−1 yr−1). In a P. deltoides × P. nigra plantation of the same age as that of this study, Guénon et al. [] measured C contributions of 1400 kg ha−1 yr−1, similar to those found in this study.
4. Conclusions
Different patterns in the amount and time of leaf fall were observed among the P. alba and the R. pseudoacacia monocultures and the mixed plantation. The soil conditions at the study site are representative of areas with high Ca and Mg availability, relatively poor in organic matter and total N, and strongly alkaline pH. As the P. alba monoculture provides the highest amount of litter and obtained the highest K, P and Mg from the litter, a mixed design is advantageous for the species R. pseudoacacia in relation to these nutrients. Even so, P. alba could also benefit from a mixed design derived from the higher concentration of N that R. pseudoacacia provides. Therefore, the mixed planting seems advantageous as a result of the different strategies shown by the two species in terms of the amount of litter and the dynamics of the main nutrients. The contribution of N derived from leaf fall in the P. alba monoculture is dependent on a high rate of N mineralization, which could be affected in the medium term by the higher C:N rates. The lower rates of total N and soil OM, lower N concentrations in green leaves and higher N resorption in poplar may indicate less stability in N nutrition. However, as a N2-fixing species, R. pseudoacacia shows less N resorption, more N returned to the soil in the form of litterfall, and a lower C:N rate. The most limiting nutrients were P and K. Both species showed high retranslocation ratios for P, but poplar relied more on internal cycling for P and N, whereas R. pseudoacacia had higher rates of K resorption and therefore more internal cycling is required.
Although mixing the species does not increase biomass yield or net contribution of nutrients, it may be a good strategy to reduce future needs for mineral fertilization, that it is a common practice in SRC plantations, given the differences between the two monocultures in terms of processing the main nutrients. Determining the potential foliar contribution to the pool of nutrients in the soil as well as the dynamics would appear to be of importance for the sustainable management of plantations in short rotation. However, more conclusive results would require the study of leaf litter decomposition dynamics and the final incorporation of nutrients into the soil.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.O. and H.S.; Data curation, I.G. and H.S.; Formal analysis. I.G. and N.O.; Funding acquisition, H.S; Investigation, N.O. and H.S.; Methodology, H.S., I.G. and R.R.-S.; Project administration, H.S. and R.R.-S.; Resources, N.O., H.S., and I.G.; Supervision, H.S. and R.R.-S.; Validation, H.S.; Writing—original draft, I.G., N.O. and H.S.; Writing—review and editing, I.G., H.S., R.R.-S, and N.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by MINECO (Spain) through the framework of the project’s RTA 2008-00025-C02-01 and RTA2017-00015-CO2 co-financed with funds from FEDER.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank José Pablo de la Iglesia and Ana Parras for their careful monitoring of the plantation. We also thank Biopolar and Alasia Clones for providing the plant material. We are also grateful to Adam Collins for his English language review of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- European Commision. Review of the 2012 European Bioeconomy Strategy; European Commision: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, R.J. The genecology of Populus. In Biology of Populus and Its Implications for Management and Conservation; Stettler, R.F., Bradshaw, H.D., Jr., Heilman, P.H., Hinckley, T.M., Eds.; NRC Research Press, National Research Council of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1996; pp. 33–55. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The International Commission on Poplars and Other Fast-Growing Trees Sustaining People and the Environment (IPC): International register of cultivars of Populus L. 2016. Available online: http://www.fao.org/forestry/ipc/69637@204274/en/ (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Aravanopoulos, F.A. Breeding of fast growing forest tree species for biomass production in Greece. Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, N.; Sixto, H.; Cañellas, I.; Rodríguez-Soalleiro, R.; Pérez-Cruzado, C. Productivity model and reference diagram for short rotation biomass crops of poplar grown in Mediterranean environments. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 72, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straker, K.C.; Quinn, L.D.; Voigt, T.B.; Lee, D.K.; Kling, G.J. Black Locust as a bioenergy feedstock: A review. Bioenergy Res. 2015, 8, 1117–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinkenstein, A.; Wöllecke, J.; Böhm, C.; Grünewald, H.; Freese, D.; Schneider, B.U.; Hüttl, R.F. Ecological benefits of the alley cropping agroforestry system in sensitive regions of Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2009, 12, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slazak, A.; Freese, D. Phosphorus sorption kinetics in reclaimed lignite mine soils under different age stands of Robinia pseudoacacia L. in northeast Germany. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2015, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítková, M.; Müllerová, J.; Sádlo, J.; Pergl, J.; Pyšek, P. Black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) beloved and despised: A story of an invasive tree in Central Europe. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 384, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergante, S.; Facciotto, G.; Minotta, G. Identification of the main site factors and management intensity affecting the establishment of Short-Rotation-Coppices (SRC) in Northern Italy through stepwise regression analysis. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2010, 5, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marron, N.; Priault, P.; Gana, C.; Gérant, D.; Epron, D. Prevalence of interspecific competition in a mixed poplar/black locust plantation under adverse climate conditions. Ann. For. Sci. 2018, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, N.; del Río, M.; Forrester, D.I.; Rodríguez-Soalleiro, R.; Pérez-Cruzado, C.; Cañellas, I.; Sixto, H. Mixed short rotation plantations of Populus alba and Robinia pseudoacacia for biomass yield. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 410, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, D.I.; Bauhus, J. A Review of Processes Behind Diversity—Productivity Relationships in Forests. Curr. For. Rep. 2016, 2, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facelli, J.M.; Pickett, S.T.A. Plant litter: Its dynamics and effects on plant community structure. Bot. Rev. 1991, 57, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, D.A. Branch mortality and potential litterfall from Douglas-fir trees in stands of varying density. For. Ecol. Manag. 1994, 70, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, F.S.; Matson, P.A.; Mooney, H.A. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Malhi, Y.; Metcalfe, D.B.; Silva-Espejo, J.E.; Jiménez, E.; Navarrete, D.; Almeida, S.; Costa, A.C.L.; Salinas, N.; Phillips, O.L.; et al. Above—and below-ground net primary productivity across ten Amazonian forests on contrasting soils. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 2759–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ramedy, H.R.; Alshaal, T.A.; Amer, M.; Domokos-Szabolcsy, E.; Elhawat, N.; Prokisch, J.; Fari, M. Soil Quality and Plant Nutrition. In Sustainable Agricultural Reviews 14; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 345–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M.P.; Mohan, M. Litter decomposition in forest ecosystems: A review. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2017, 2, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giweta, M. Role of litter production and its decomposition, and factors affecting the processes in a tropical forest ecosystem: A review. J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Tripathi, S.K. Litterfall, litter decomposition and nutrient release patterns in four native tree species raised on coal mine spoil at Singrauli, India. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1999, 29, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.M. Litter dynamics in plantation and agroforestry systems of the tropics-a review of observations and methods. In Ecological Basis of Agroforestry; Batish, D.R., Kohli, R.K., Jose, S., Singh, H.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 181–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamdoust, J.; Sohrabi, H. Carbon storage in biomass, litter, and soil of different native and introduced fast-growing tree plantations in the South Caspian Sea. J. For. Res. 2018, 29, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz, A.C. Dinámica de Nutrientes en Parcelas Experimentales de Populus x Euramericana (Dode) Guinier ‘I-214’. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2005. Available online: http://oa.upm.es/328/ (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Gruhn, P.; Goletti, F.; Yudelman, M. Integrated Nutrient Management, Soil Fertility, and Sustainable Agriculture: Current Issues and Future Challenges; Food Agriculture and Environment Discussion Paper IFRPI 2020 Vision Brief; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.K.; Chaturvedi, O.P. Structure and function of Populus deltoides agroforestry systems in eastern India: 2. Nutrient dynamics. Agrofor. Syst. 2005, 65, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, A.; Ghorbanzadeh, N.; Salehi, M. Soil nutrient status, nutrient return and retranslocation in poplar species and clones in northern Iran. IForest 2013, 6, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiresonne, L.; De Schrijver, A.; De Vos, B. Nutrient cycling in a poplar plantation (Populus trichocarpa x Populus deltoides ‘Beaupré’) on former agricultural land in northern Belgium. Can. J. For. Res. 2007, 37, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, W.; Vel, E.; Reinds, G.J.; Deelstra, H.; Klap, J.M.; Leeters, E.E.J.M.; Hendriks, C.M.A.; Kerkvoorden, M.; Landmann, G.; Herkendell, J.; et al. Intensive monitoring of forest ecosystems in Europe 1. Objectives, set-up and evaluation strategy. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 174, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, H.; Nothdurft, A.; Block, J.; Bauhus, J. Forest restoration with Betula ssp. and Populus ssp. nurse crops increases productivity and soil fertility. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 339, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, A.; Ranger, J.; Gelhaye, D. Nutrient uptake and immobilization in a short-rotation coppice stand of hybrid poplars in north-west France. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 128, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.B.; Sims, R.E.H.; Horne, D.J. Biomass production and nutrient cycling in Eucalyptus short rotation energy forests in New Zealand: II. Litter fall and nutrient return. Biomass Bioenerg 2006, 30, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, C.E.; Vesterdal, L.; Pratt, J.; Venner, K.H.; De Montigny, L.M.; Trofymow, J.A. Nutrient concentrations and nitrogen mineralization in forest floors of single species conifer plantations in coastal British Columbia. Can. J. For. Res. 2000, 30, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahajoe, J.S. The Role of Litter Production and Decomposition of Dominant Tree Species on the Nutrient Cycle in Natural Forest with Various Substrate Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Teklay, T. Decomposition and nutrient release from pruning residues of two indigenous agroforestry species during the wet and dry seasons. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2007, 77, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbucak, T.B.; Kutbay, H.G.; Kilic, D.; Korkmaz, H.; Bilgin, A.; Yalçin, E.; Apaydin, Z. Foliar resorption of nutrients in selected sympatric tree species in gallery forest (black sea region). Pol. J. Ecol. 2008, 56, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo, C.B.M.; Bhatti, J.S.; Chang, S.X.; Sidders, D. Land use change effects on ecosystem carbon balance: From agricultural to hybrid poplar plantation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 141, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Lugo, A.E.; Chapman, J. Biomass of tropical tree plantations and its implications for the global carbon budget. Can. J. For. Res. 1986, 16, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytter, R.M. The potential of willow and poplar plantations as carbon sinks in Sweden. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 36, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfapietra, C.; Gielen, B.; Galema, A.N.J.; Lukac, M.; De Angelis, P.; Moscatelli, M.C.; Ceulemans, R.; Scarascia-Mugnozza, G. Free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) enhances biomass production in a short-rotation poplar plantation. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Cruzado, C.; Mohren, G.M.J.; Merino, A.; Rodríguez-Soalleiro, R. Carbon balance for different management practices for fast growing tree species planted on former pastureland in southern Europe: A case study using the CO2 Fix model. Eur. J. For. Res. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrette, M.; Leblanc, M.; Thiffault, N.; Paquette, A.; Lavoie, L.; Bélanger, L.; Bujold, F.; Côté, L.; Lamoureux, J.; Schneider, R.; et al. Issues and solutions for intensive plantation silviculture in a context of ecosystem management. For. Chron. 2014, 90, 732–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thiffault, E.; Barrette, J.; Paré, D.; Titus, B.D.; Keys, K.; Morris, D.M.; Hope, G. Developing and validating indicators of site suitability for forest harvesting residue removal. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiffault, N.; Elferjani, R.; Hébert, F.; Paré, D.; Gagné, P. Intensive mechanical site preparation to establish short rotation hybrid poplar plantations-A case-study in Quebec, Canada. Forests 2020, 11, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixto, H.; Hernández-Garasa, M.J.; Ciria, P.; Carrasco, J.E.; Cañellas, I. Manual de Cultivo de Populus spp. para la Producción deBiomasa con Fines Energéticos; Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Instituto Nacional de Investigación y Tecnología Agraria y Alimentaria (INIA): Madrid, Spain, 2010.
- Stettler, R.F.; Bradshaw, H.D., Jr.; Heilman, P.E.; Hinckley, T.M. Biology of Populus and Its Implications for Management and Conservation; Stettler, R.F., Bradshaw, H.D., Jr., Heilman, P.E., Hinckley, T.M., Eds.; NRC Research Press, National Research Council of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1996.
- Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, E. Leaf nutrient concentration, nutrient resorption and litter decomposition in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in eastern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 239, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M. Litterfall, nutrient cycling, and nutrient limitation in tropical forests. Ecology 1984, 65, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Villar, S.; Castro-Díez, P.; Alonso, A.; Cabra-Rivas, I.; Parker, I.M.; Pérez-Corona, E. Do the invasive trees, Ailanthus altissima and Robinia pseudoacacia, alter litterfall dynamics and soil properties of riparian ecosystems in Central Spain? Plant Soil 2015, 396, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, S.E. Plant species effects on nutrient cycling: Revisiting litter feedbacks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Muñoz, N.; Castro-Díez, P.; Parker, I.M. Differences in nitrogen use strategies between native and exotic tree species: Predicting impacts on invaded ecosystems. Plant Soil 2013, 363, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Díez, P.; Valle, G.; González-Muñoz, N.; Alonso, Á. Can the life-history strategy explain the success of the exotic trees Ailanthus altissima and Robinia pseudoacacia in Iberian floodplain forests? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, C.M.; Pérez-Ramos, I.M.; Marañón, T.; Mediterráneo, U.B. Aporte de hojarasca al suelo en un bosque mediterraneo. Almoraima 2004, 31, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, N.; Rodríguez-Soalleiro, R.; Pérez-Cruzado, C.; Cañellas, I.; Sixto, H.; Ceulemans, R. Above- and below-ground carbon accumulation and biomass allocation in poplar short rotation plantations under Mediterranean conditions. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 410, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixto, H.; Gil, P.; Ciria, P.; Camps, F.; Sánchez, M.; Cañellas, I.; Voltas, J. Performance of hybrid poplar clones in short rotation coppice in Mediterranean environments: Analysis of genotypic stability. GCB Bioenergy 2014, 6, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guénon, R.; Bastien, J.C.; Thiébeau, P.; Bodineau, G.; Bertrand, I. Carbon and nutrient dynamics in short-rotation coppice of poplar and willow in a converted marginal land, a case study in central France. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2016, 106, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; De Angelis, P.; Polle, A. Leaf litter production and decomposition in a poplar short-rotation coppice exposed to free air CO2 enrichment (POPFACE). Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateno, R.; Tokuchi, N.; Yamanaka, N.; Du, S.; Otsuki, K.; Shimamura, T.; Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Hou, Q. Comparison of litterfall production and leaf litter decomposition between an exotic black locust plantation and an indigenous oak forest near Yan’an on the Loess Plateau, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 241, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R. Nitrogen Partitioning between Resorption and Decomposition Pathways: A Trade-Off between Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Litter Decomposibility? Oikos 1997, 80, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneau, M. Le diagnostic foliaire. Rev. For. Fr. 1988, 40, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koupar, S.A.M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Modirrahmati, A.; Tabari, M.; Golchin, A.; Rad, F.H. Effect of pure and mixed plantations of Populus deltoides with Alnus subcordata on growth, nutrition and soil properties: A case study of Foman Region, Iran. Asian J. Chem. 2011, 23, 5261–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Nam, J.M.; Kim, J.G. The influence of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) flower and leaf fall on soil phosphate. Plant Soil 2011, 341, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, H.P.; Van Den Driessche, R. Poplar nutrient resorption in fall or drought: Influence of nutrient status and clone. Can. J. For. Res. 1999, 29, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R.; Chapin, F.S. The Mineral Nutrition of Wild Plants Revisited: A Re-evaluation of Processes and Patterns. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1999, 30, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, J.; López-Acevedo, M.; Roquero, C. Edafología para la Agricultura y el Medio Ambiente; Prensa, M., Ed.; Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, Spain, 2006; ISBN 84-7114-468-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett, W.L.; Fisher, R.F. Properties and Management of Forest Soils, 2nd ed.; John and Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Coupling of plant and soil C:N:P stoichiometry in black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) plantations on the Loess Plateau, China. Trees 2017, 31, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, A. Deposition on forest soils—Effect of tree canopy on throughfall. In Acidification in Finland; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Yanai, R.D.; Arthur, M.A.; Acker, M.; Levine, C.R.; Park, B.B. Variation in mass and nutrient concentration of leaf litter across years and sites in a northern hardwood forest. Can. J. For. Res. 2012, 42, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganière, J.; Paré, D.; Bradley, R.L. How does a tree species influence litter decomposition? Separating the relative contribution of litter quality, litter mixing, and forest floor conditions. Can. J. For. Res. 2010, 40, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, B.; Camiré, C. Tree growth and nutrient cycling in dense plantings of hybrid poplar and black alder. Can. J. For. Res. 1987, 17, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, D.S. Spatial variation in black cottonwood (Populus trichocarpa) foliar nutrient concentrations at seven alluvial sites in coastal British Columbia. Can. J. For. Res. 1990, 20, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makeshin, F.; Rehfuess, K.F.; Ruesch, I. Short-rotation plantations of poplars and willows on formerly arable land-sites, nutritional-status, biomass production, and ecological effects. Forstwiss. Cent. 1989, 108, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytter, L.; Ericsson, T. Leaf nutrient analysis in Salix viminalis (L.) energy forest stands growing on agricultural land. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenkd. 1993, 156, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jug, A.; Hofmann-Schielle, C.; Makeschin, F.; Rehfuess, K.E. Short-rotation plantations of balsam poplars, aspen and willows on former arable land in the Federal Republic of Germany. II. Nutritional status and bioelement export by harvested shoot axes. For. Ecol. Manag. 1999, 121, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinsdorf, D. Ergebnisse von Minersldungungsveruchen zu Androscoggin-Papplen auf Kippsanden ausgekohlter Braunkohlentagebaue im Bezirk Cottbus. Beitr. Forstwirtsch. 1985, 19, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, W. Nutritional Disorders of Plants: Developments, Visual and Analytical Diagnosis; Gustav Fischer Verlag Jena: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sardans, J.; Janssens, I.A.; Alonso, R.; Veresoglou, S.D.; Rillig, M.C.; Sanders, T.G.M.; Carnicer, J.; Filella, I.; Farré-Armengol, G.; Peñuelas, J. Foliar elemental composition of European forest tree species associated with evolutionary traits and present environmental and competitive conditions. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavolta, E. Avaliação do Estado Nutricional das Plantas: Princípios e Aplicações, 2nd ed.; Potafos: Piracicaba, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sayyad, E.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mokhtari, J.; Mahdavi, R.; Jalali, S.G.; Akbarinia, M.; Tabari, M. Comparison of growth, nutrition and soil properties of pure and mixed stands of Populus deltoides and Alnus subcordata. Silva Fenn. 2006, 40, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvetkova, N.; Petkova, K. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by the leaves of Robinia pseudoacacia as a bioindicator tree in industrial zones. J. Environ. Biol. 2015, 36, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Pascual, M.; María, N.; Felipe, M. Fijación biológica del nitrógeno: Factores limitantes. In Proceedings of the Ciencia y Medio Ambiente—Segundas Jornadas Científicas sobre Medio Ambiente del CCMA-CSIC, Madrid, Spain, 16–17 April 2002; pp. 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, J.O.; Gordon, J.C. Nitrogen Fixation in Relation to Photosynthesis in Alnus glutinosa. Bot. Gaz. 1979, 140, 70–75. Available online: www.jstor.org/stable/2474206 (accessed on 5 August 2020). [CrossRef]
- Martín-García, J.; Merino, A.; Diez, J.J. Relating visual crown conditions to nutritional status and site quality in monoclonal poplar plantations (Populus × euramericana). Eur. J. For. Res. 2012, 131, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elferjani, R.; DesRochers, A.; Tremblay, F. Effects of mixing clones on hybrid poplar productivity, photosynthesis and root development in northeastern Canadian plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 327, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, K.; Fürst, A.; Hacker, R.; Bartels, U. Forest Foliar Condition in Europe. Results of Large-Scale Foliar Chemistry Surveys (Survey 1995 and Data from Previous Years); European Commission—United Nations/Economic Commission for Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkby, E.A.; Mengel, K. The role of magnesium in plant nutrition. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenkd. 1976, 139, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, W.S.; Jackson, R.B. Nutrient concentrations in fine roots. Ecology 2000, 81, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Li, L.H.; Han, X.G.; Huang, J.H.; Jiang, G.M.; Wan, S.Q.; Zhang, W.H.; Chen, Q.S. Nitrogen resorption from senescing leaves in 28 plant species in a semi-arid region of northern China. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 63, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobe, R.K.; Lepczyk, C.A.; Iyer, M. Resorption efficiency decreases with increasing green leaf nutrients in a global data set. Ecology 2005, 86, 2780–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrades, M.; Martinez, E. Fertilidad del Suelo y Parámetros que la Definen, 3rd ed.; Universidad la Rioja-Servicio Publicaciones: La Rioja, Spain, 2014; ISBN 978-84-695-9286-1. [Google Scholar]
- Fife, D.N.; Nambiar, E.K.S.; Saur, E. Retranslocation of foliar nutrients in evergreen tree species planted in a Mediterranean environment. Tree Physiol. 2008, 28, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, A.R.; Cleveland, C.C.; Asner, G.P.; Bustamante, M.M.C. Controls over foliar N:P ratios in tropical rain forests. Ecology 2007, 88, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinemets, Ü.; Tamm, Ü. Species differences in timing of leaf fall and foliage chemistry modify nutrient resorption efficiency in deciduous temperate forest stands. Tree Physiol. 2005, 25, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.C.P. Entradas Biológicas de Nitrógeno en un Bosque Ripario; Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Servicio de Publicaciones: Madrid, Spain, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- López, E.S.; Pardo, I.; Felpeto, N. Seasonal differences in green leaf breakdown and nutrient content of deciduous and evergreen tree species and grass in a granitic headwater stream. Hydrobiologia 2001, 464, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.D.R.; de Oliveira, L.E.M.; do Nascimento, M.N.; Reis, K.L.; Bonome, L.T.D.S. Concentração e redistribuição de nutrientes minerais nos diferentes estádios foliares de seringueira. Acta Amaz. 2012, 42, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Guo, J.F.; Chen, G.S.; Xie, J.S.; Cai, L.P.; Lin, P. Litterfall, nutrient return, and leaf-litter decomposition in four plantations compared with a natural forest in subtropical China. Ann. For. Sci. 2004, 61, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Li, H.; Xie, B. Decomposition and nutrient release of four potential mulching materials for poplar plantations on upland sites. Agrofor. Syst. 2008, 74, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Zeng, D.H.; Yu, Z.Y.; Fan, Z.P.; Yang, D.; Liu, Y.X. Impact of litter quality and soil nutrient availability on leaf decomposition rate in a semi-arid grassland of Northeast China. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, M.J.; Domingo, F. Litter decomposition in four woody species in a Mediterranean climate: Weight loss, N and P dynamics. Ann. Bot. 2000, 86, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of Soils; Prentice Hall: Upper Sadle River, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, B.; Staaf, H. Leaching, accumulation and release of nitrogen in decomposing forest litter. Ecol. Bull. 1981, 33, 163–178. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni, S.; Jackson, R.B.; Trofymow, J.A.; Porporato, A. The global stoichiometry of litter nitrogen mineralization. Science 2008, 231, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschfeld, J.R.; Finn, J.T.; Patterson, W.A. Effects of Robinia pseudoacacia on leaf litter decomposition and nitrogen mineralization in a northern hardwood stand. Can. J. For. Res. 1984, 14, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, T.B.; Cardon, Z.G. Decomposition dynamics in mixed-species leaf litter. Oikos 2004, 104, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perala, D.A.; Alban, D.H. Rates of Forest Floor Decomposition and Nutrient Turnover in Aspen, Pine, and Spruce Stands on Two Soils; Research Paper NC-227; North Central Forest Experiment Station, USDA Forest Service: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 1982.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).