Comparative Assessment of Vegetation Dynamics under the Influence of Climate Change and Human Activities in Five Ecologically Vulnerable Regions of China from 2000 to 2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
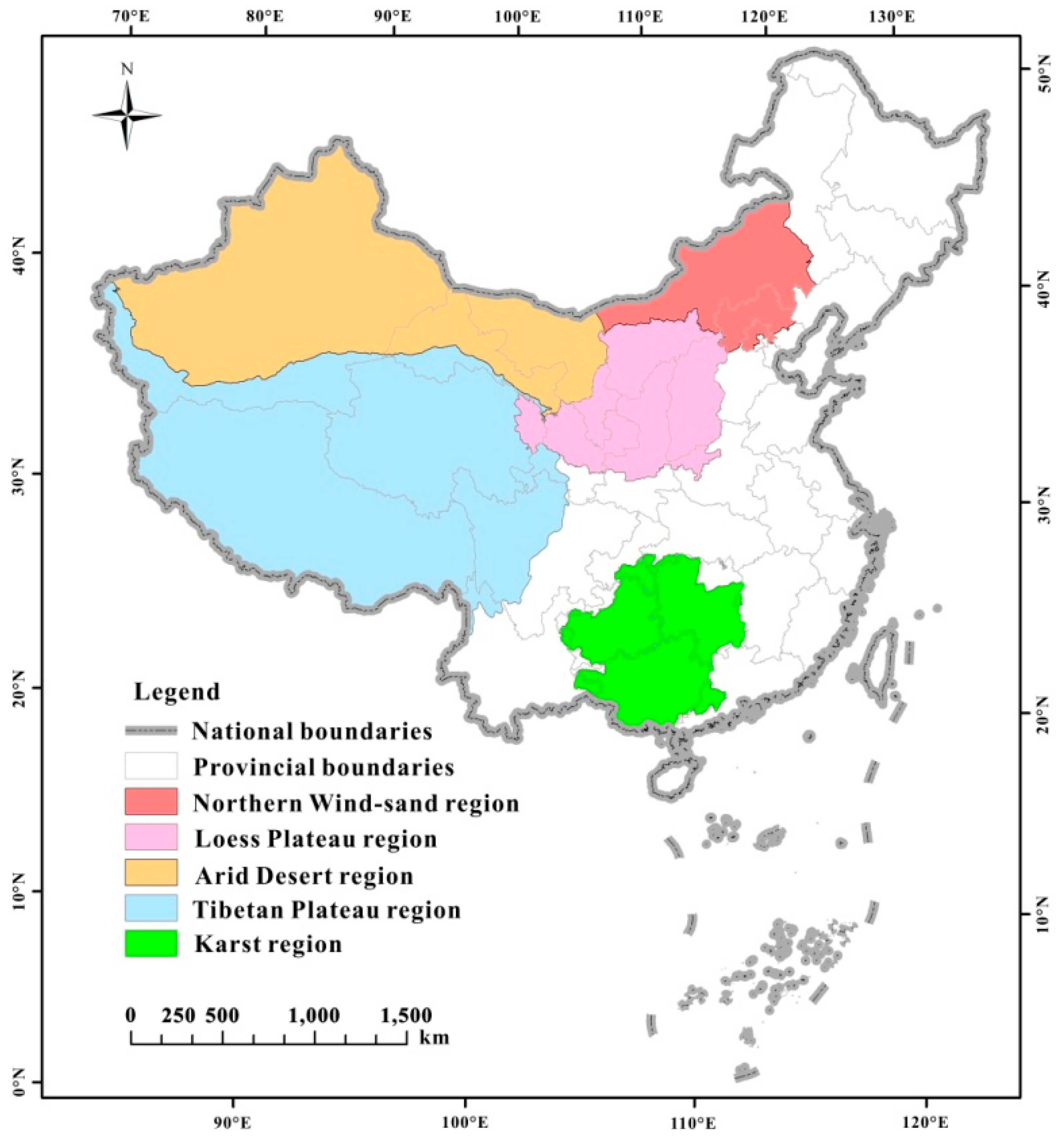
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
2.3. Estimate of Predicted NPP
2.4. Estimate of Actual NPP
2.5. Estimate of the Driving Scenarios
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Dynamic Analysis of NPPa
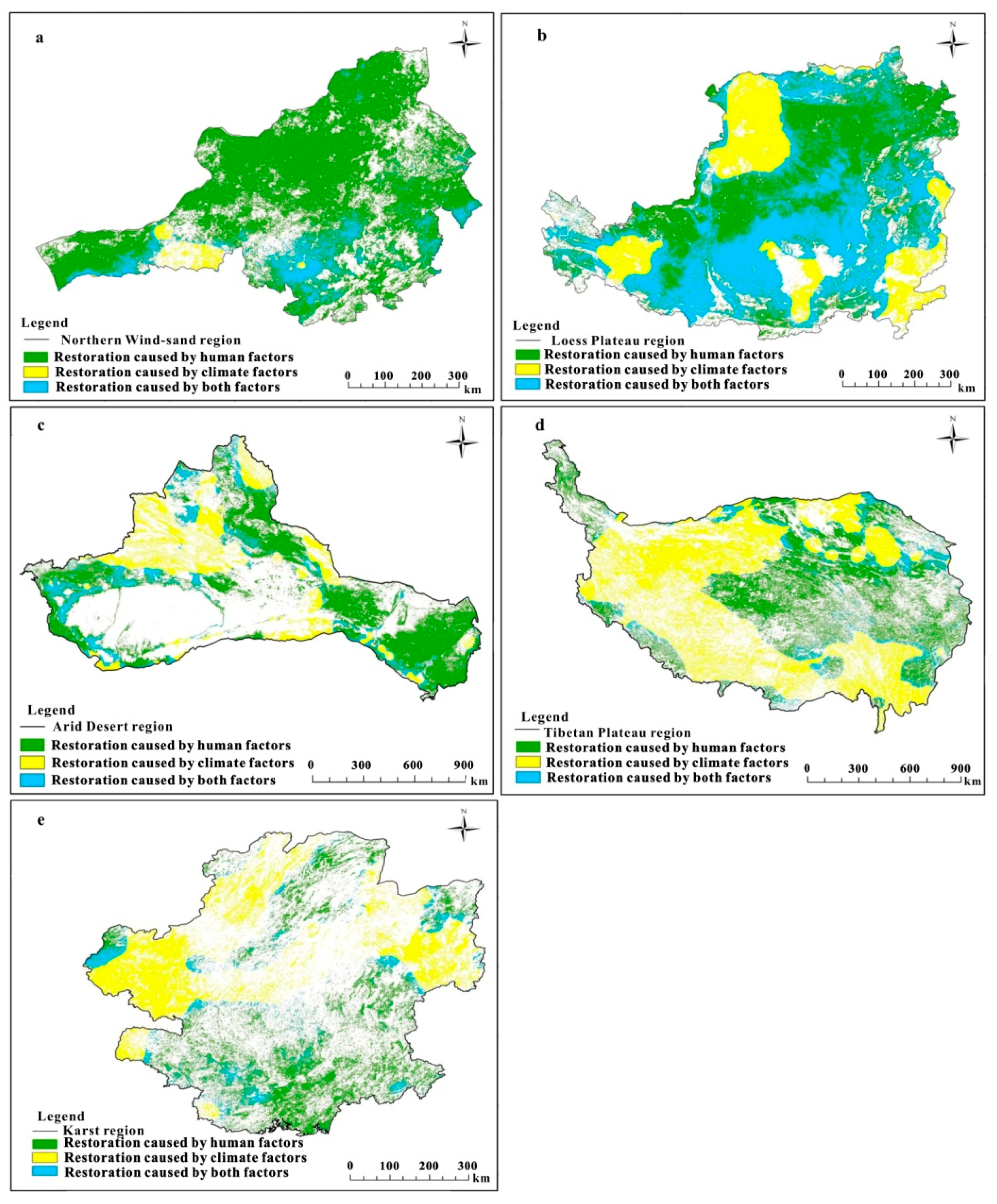
3.2. Vegetation Restoration under the Influence of Different Driving Factors
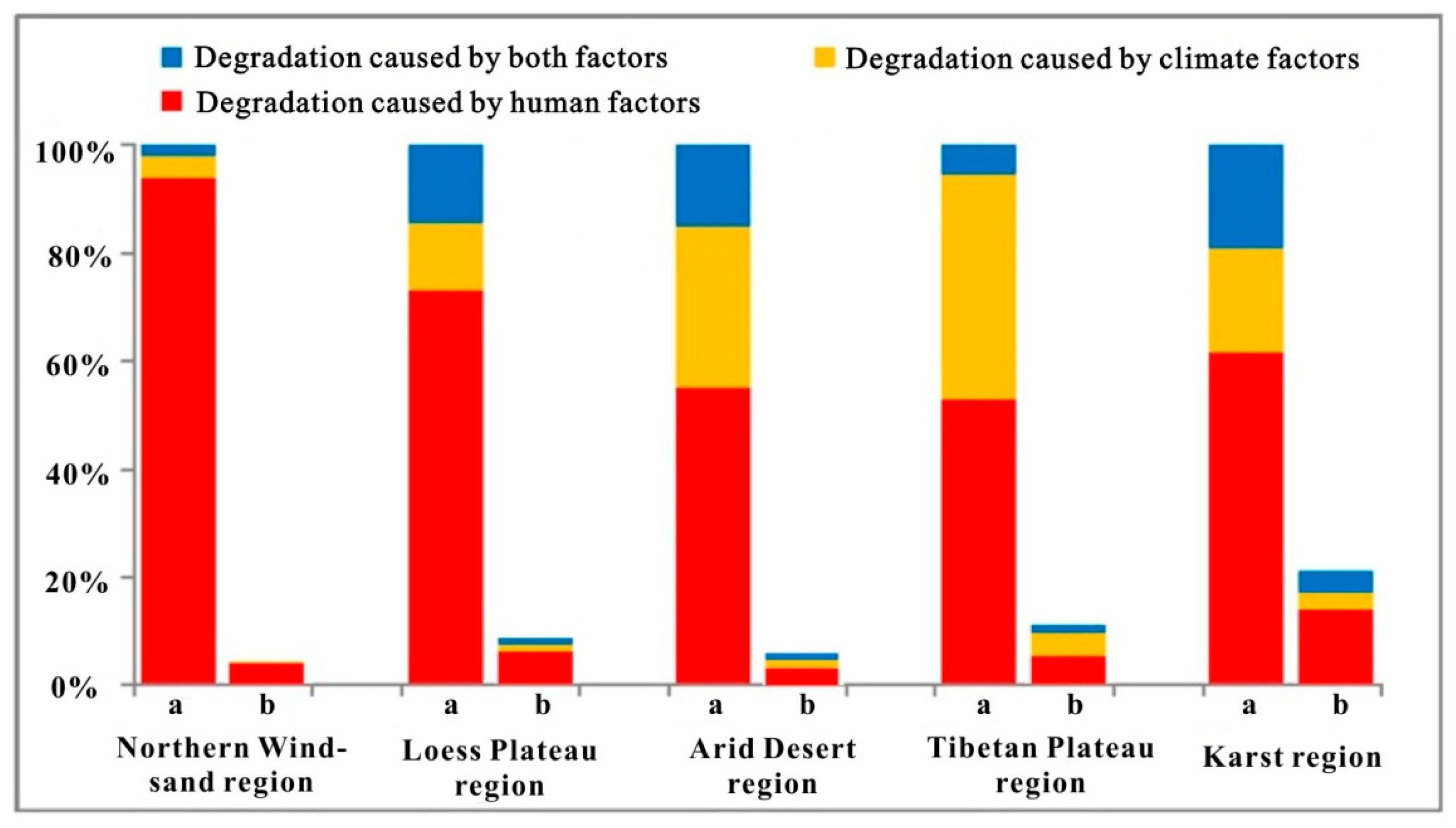
3.3. Vegetation Degradation under the Influence of Different Driving Factors
4. Discussion
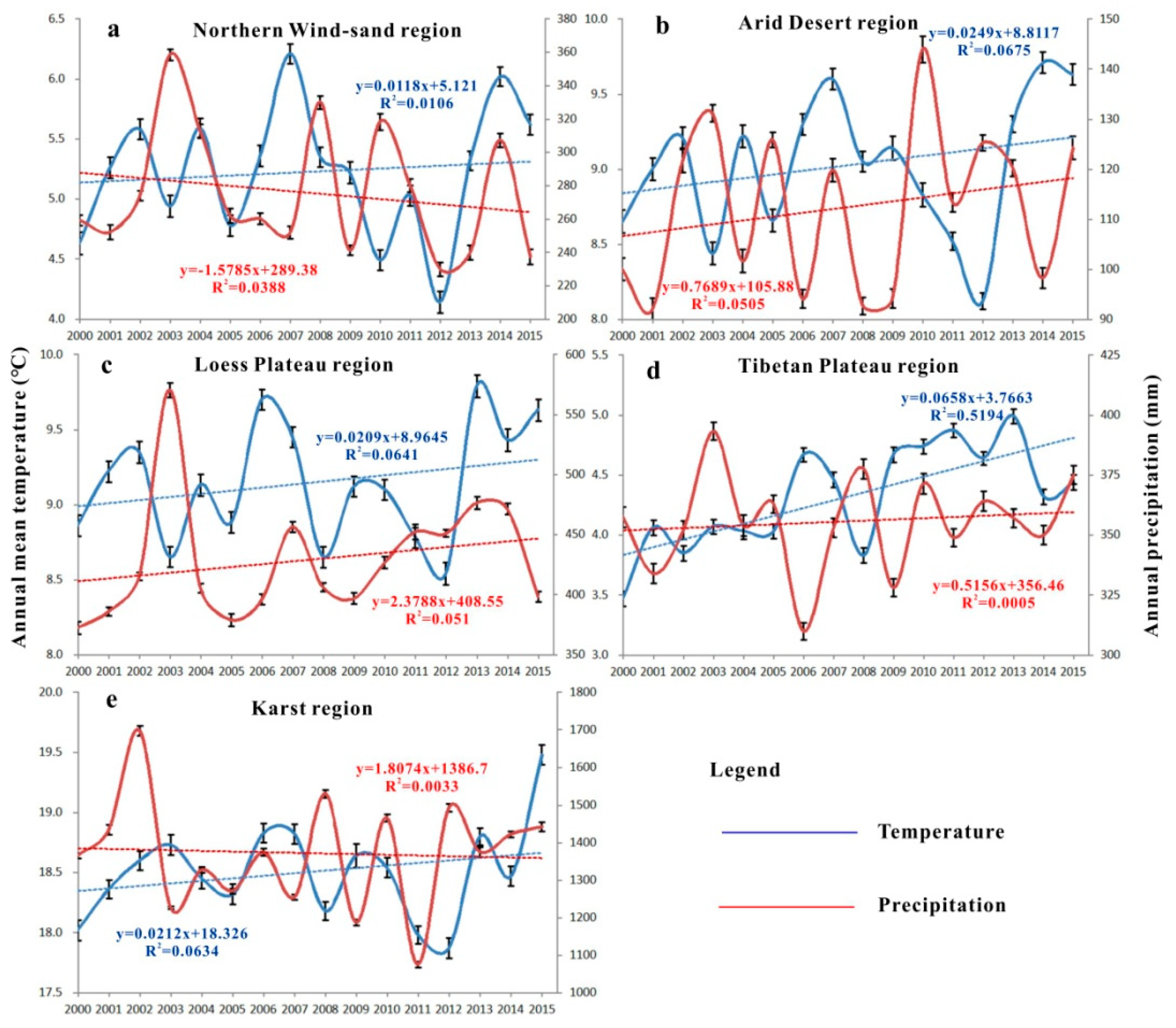
4.1. Vegetation Restoration
4.2. Vegetation Degradation
4.3. Limitations of Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, S.; Chen, L.; Shankman, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Excessive reliance on afforestation in China’s arid and semi-arid regions: Lessons in ecological restoration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 104, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, B.; Yao, X.; Li, J.; Wu, B. Recent ecological transitions in China: Greening, browning, and influential factors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8732. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.J.; Liu, G.H.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Degraded Ecosystem Restoration Techniques and Models in Typical Ecologically Vulnerable Regions; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.H.; Zhou, C.X.; Gao, J.X.; Ma, S.; Wang, W.J.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y. Location determination of ecologically vulnerable regions in China. Biodivers. Sci. 2015, 23, 725–732. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.H.; Fu, B.J.; Feng, X.M.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, R.Y.; Sun, G.; Wu, B.F. A policy-driven large scale ecological restoration: Quantifying ecosystem services changes in the Loess Plateau of China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31782. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, A. Regional differences in the relationship between climatic factors, vegetation, land surface conditions, and dust weather in China’s Beijing-Tianjin Sand Source Region. Nat. Hazards 2011, 62, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.M.; Fu, B.J.; Lv, N.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B.F. How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services: An analysis of carbon sequestration in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2846. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C. Impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation cover in hilly southern China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.M.; Fu, B.J.; Piao, S.L.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Lv, Y.H.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.H.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S. Why Large-Scale Afforestation Efforts in China Have Failed to Solve the Desertification Problem. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, C.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Qi, J.; Odeh, I. Quantitative assessment of the contributions of climate change and human activities on global grassland degradation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4273–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.H.; Fan, S.Y.; Zhou, L.H.; Dong, Z.H.; Zhang, K.C.; Feng, J.M. The temporal change of driving factors during the course of land desertification in arid region of North China: The case of Minqin County. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.L.; Lu, C.X.; Gao, Y.B. Impacts of human economic activities on wind and sand environment in Kerqin sandy land. Resour. Sci. 2003, 25, 78–83. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z. Assessing the Driving Forces in Vegetation Dynamics Using Net Primary Productivity as the Indicator: A Case Study in Jinghe River Basin in the Loess Plateau. Forests 2018, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.R.; Xie, Z.X.; Robert, C.; Jiang, L.H.; Shimizu, H. Did climate drive ecosystem change and induce desertification in Otindag sandy land, China over the past 40 years? J. Arid Environ. 2006, 64, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh, H.; Khajedein, S.J.; Amiri, F.; Shariff, A.R.B.M. Monitoring rangeland ground cover vegetation using multitemporal MODIS data. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, K.J.; Prince, S.D.; Reshef, I. Mapping land degradation by comparisonof vegetation production to spatially derived estimates of potential production. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberl, H.E.K.; Krausmann, F.; Gaube, V.; Bondeau, A.; Plutzar, C.; Gingrich, S.; Lucht, W.; Fischer-Kowalski, M. Quantifying and Mapping the Human Appropriation of Net Primary Production in Earth’s Terrestrial Ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12942–12947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Gang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Odeh, I.; Qi, J. Comparative assessment of grassland degradation dynamics in response to climate variation and human activities in China, Mongolia, Pakistan and Uzbekistan from 2000 to 2013. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 135, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.J.; Zhou, S.X.; Chen, Y.Z.; Li, J.L.; Ju, W.M.; Odeh, I.O.A. Assessing the impact of restoration-induced land conversion and management alternatives on net primary productivity in Inner Mongolian grassland, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 108, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Zhou, S.L.; Chen, D.X.; Wei, Z.Q.; Dai, L.; Li, X.G. Determining the contributions of urbanisation and climate change to NPP variations over the last decade in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, N.; Shi, Z.; Yang, X.; Gao, J.; Cai, D. Spatiotemporal trends of reference evapotranspiration and its driving factors in the Beijing–Tianjin Sand Source Control Project Region, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 200, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.W.; Wu, J.; He, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Drought offset ecological restoration program-induced increase in vegetation activity in the Beijing-Tianjin Sand Source Region, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12108–12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, G.H.; Li, Z.S.; Ye, X.; Wang, M.; Gong, L. Driving force and changing trends of vegetation phenology in the Loess Plateau of China from 2000 to 2010. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liang, W.; Fu, B.; Lv, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, S.; Su, H. Vegetation changes in recent large-scale ecological restoration projects and subsequent impact on water resources in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Mu, S.; Li, J. Effects of ecological restoration projects on land use and land cover change and its influences on territorial NPP in Xinjiang, China. CATENA 2014, 115, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.Z.; Wang, T.; Han, Z.W.; Qie, Y.F. Surveying sandy deserts and desertified lands in north western China by remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 3603–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Li, M.D.; Dong, S.K.; Shi, J.B. Temporal-spatial changes in ecosystem services and implications for the conservation of alpine rangelands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Rangel. J. 2015, 37, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Shang, Z.; Long, R.; Hou, Y.; Deng, B. The relationship of vegetation and soil differentiation during the formation of black-soil-type degraded meadows in the headwater of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, K.; Brandt, M.S.; Yue, Y.; Liao, C.; Fensholt, R. Assessing Future Vegetation Trends and Restoration Prospects in the Karst Regions of Southwest China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, K.; Yue, Y.; Brandt, M.; Liu, B.; Zhang, C.; Liao, C.; Fensholt, R. Quantifying the effectiveness of ecological restoration projects on long-term vegetation dynamics in the karst regions of Southwest China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.H.; He, C.S.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B.F. Assessing the soil erosion control service of ecosystems change in the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.W.; Fu, B.J.; Lv, Y.H.; Zeng, Y. Balancing multiple ecosystem services in conservation priority setting. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gang, C.; Zhou, F.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, C. Quantitative assessment of the individual contribution of climate and human factors to desertification in northwest China using net primary productivity as an indicator. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.; White, A.; Lenton, T.M. An analysis of some diverse approaches to modelling terrestrial net primary productivity. Ecol. Model. 2004, 177, 353–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Feng, Q.; Liang, T.; Ren, J. Modelling global-scale potential grassland changes in spatio-temporal patterns to global climate change. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2012, 20, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, G. Nonuniform Time-Lag Effects of Asymmetric Warming on Net Primary Productivity across Global Terrestrial Biomes. Earth Interact. 2018, 22, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.H.; Fu, B.J. Evolution of ecosystem services in the Chinese Loess Plateau under climatic and land use changes. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 101, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Kang, E.; Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, R. Recent and Future Climate Change in Northwest China. Clim. Chang. 2006, 80, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slayback, D.A.; Pinzon, J.E.; Los, S.O.; Tucker, C.J. Northern hemisphere photosynthetic trends 1982–1999. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.; Wang, X.M.; Li, J.C.; Hua, T. Roles of climate changes and human interventions in land degradation: A case study by net primary productivity analysis in China’s Shiyanghe Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, L.J.; Mu, S.J.; Gang, C.C.; Sun, Z.G. Effects of ecological restoration-induced land-use change and improved management on grassland net primary productivity in the Shiyanghe River Basin, north-west China. Grass Forage Sci 2013, 10, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Ye, X.; Fu, B.; Lv, Y. Analysis of the Driving Forces in Vegetation Variation in the Grain for Green Program Region, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; He, B.; Lei, T.; Wang, Q. Increasing terrestrial vegetation activity of ecological restoration program in the Beijing–Tianjin Sand Source Region of China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, W.; Fan, J. Soil organic carbon dynamics in Xilingol grassland of northern China induced by the Beijing-Tianjin Sand Source Control Program. Front. Earth Sci. 2016, 11, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, W.; Tian, L.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, G.; Mu, X.; et al. Multiple afforestation programs accelerate the greenness in the ‘Three North’ region of China from 1982 to 2013. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.P.; Shan, L.; Zhang, H.; Turner, N.C. Improving agricultural water use efficiency in arid and semiarid areas of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Kuniyoshi, T.; Xu, C.C.; Chen, Y.P.; Xu, Z.X. Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the tarim basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Song, X.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G. Spatiotemporal vegetation cover variations associated with climate change and ecological restoration in the Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 209–210, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.B.; Xu, J.X.; Zheng, W. Spatiotemporal variations of vegetation cover on the Chinese Loess Plateau (1981–2006): Impacts of climate changes and human activities. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gang, C.; An, R.; Li, J. Vegetation dynamics and its driving forces from climate change and human activities in the Three-River Source Region, China from 1982 to 2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Tao, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. The impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on alpine grassland over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189–190, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wu, T. Responses of permafrost to climate change and their environmental significance, Qinghai-Tibet plateau. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F02S03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H. Influences of alpine ecosystem responses to climatic change on soil properties on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. CATENA 2007, 70, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.X.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X.Q.; Xiao, J.S.; Tang, Y.H.; Fang, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, S. High positive correlation between soil temperature and NDVI from 1982 to 2006 in alpine meadow of the Three-River Source Region on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.P. Managing the Three-Rivers Headwater Region, China: From Ecological Engineering to Social Engineering. Ambio 2013, 42, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.W.; Shao, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, J.B.; Harris, W.; Chen, Z.Q.; Zhong, H.P.; Xu, X.L.; Liu, R.G. Assessment of effects of climate change and grazing activity on grassland yield in the Three Rivers Headwaters Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Meng, J.J.; Cai, Y.L. Assessing vegetation dynamics impacted by climate change in the southwestern karst region of China with AVHRR NDVI and AVHRR NPP time-series. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Xiao, L. Is Forest Restoration in the Southwest China Karst Promoted Mainly by Climate Change or Human-Induced Factors? Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9895–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, X. Impact of China’s Grain for Green Project on the landscape of vulnerable arid and semi-arid agricultural regions: A case study in northern Shaanxi Province. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Chen, G.; Tang, Z.; Lu, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C. Assessing the Three-North Shelter Forest Program in China by a novel framework for characterizing vegetation changes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.X.; Cheng, G.D. Eco-environmental changes and causative analysis in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Environmentalist 2000, 20, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, L.; Yan, J.; Qu, R. Vegetation net primary productivity and its response to climate change during 2001–2008 in the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Lian, Y.; Qin, X. Rocky desertification in southwest China: Impacts, causes, and restoration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 132, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, P.; Qin, C. Spatial and temporal changes of meteorological disasters in China during 1950–2013. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2607–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Zhang, X.; Wan, H.; Pan, X. Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sp | Sh | Driving Forces of Vegetation Dynamics | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sa > 0 | |||
| Condition1 | <0 | >0 | Vegetation restoration primarily caused by human factors |
| Condition 2 | >0 | <0 | Vegetation restoration primarily caused by climate factors |
| Condition 3 | >0 | >0 | Vegetation restoration primarily caused by both climate and human factors |
| Sa < 0 | |||
| Condition 4 | >0 | <0 | Vegetation degradation primarily caused by human factors |
| Condition 5 | <0 | >0 | Vegetation degradation primarily caused by climate factors |
| Condition 6 | <0 | <0 | Vegetation degradation primarily caused by both climate and human factors |
| Variables | Northern Wind-Sand Region | Loess Plateau Region | Arid Desert Region | Tibetan Plateau Region | Karst Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Significant increase | 16 | 46 | 21 | 14 | 7 |
| Slight increase | 55 | 32 | 47 | 40 | 24 |
| Slight decrease | 26 | 15 | 27 | 37 | 48 |
| Significant decrease | 3 | 7 | 5 | 9 | 21 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z. Comparative Assessment of Vegetation Dynamics under the Influence of Climate Change and Human Activities in Five Ecologically Vulnerable Regions of China from 2000 to 2015. Forests 2019, 10, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10040317
Wang H, Liu G, Li Z, Wang P, Wang Z. Comparative Assessment of Vegetation Dynamics under the Influence of Climate Change and Human Activities in Five Ecologically Vulnerable Regions of China from 2000 to 2015. Forests. 2019; 10(4):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10040317
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Guohua Liu, Zongshan Li, Pengtao Wang, and Zhuangzhuang Wang. 2019. "Comparative Assessment of Vegetation Dynamics under the Influence of Climate Change and Human Activities in Five Ecologically Vulnerable Regions of China from 2000 to 2015" Forests 10, no. 4: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10040317
APA StyleWang, H., Liu, G., Li, Z., Wang, P., & Wang, Z. (2019). Comparative Assessment of Vegetation Dynamics under the Influence of Climate Change and Human Activities in Five Ecologically Vulnerable Regions of China from 2000 to 2015. Forests, 10(4), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10040317






