Effects of Understory Shrub Biomass on Variation of Soil Respiration in a Temperate-Subtropical Transitional Oak Forest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
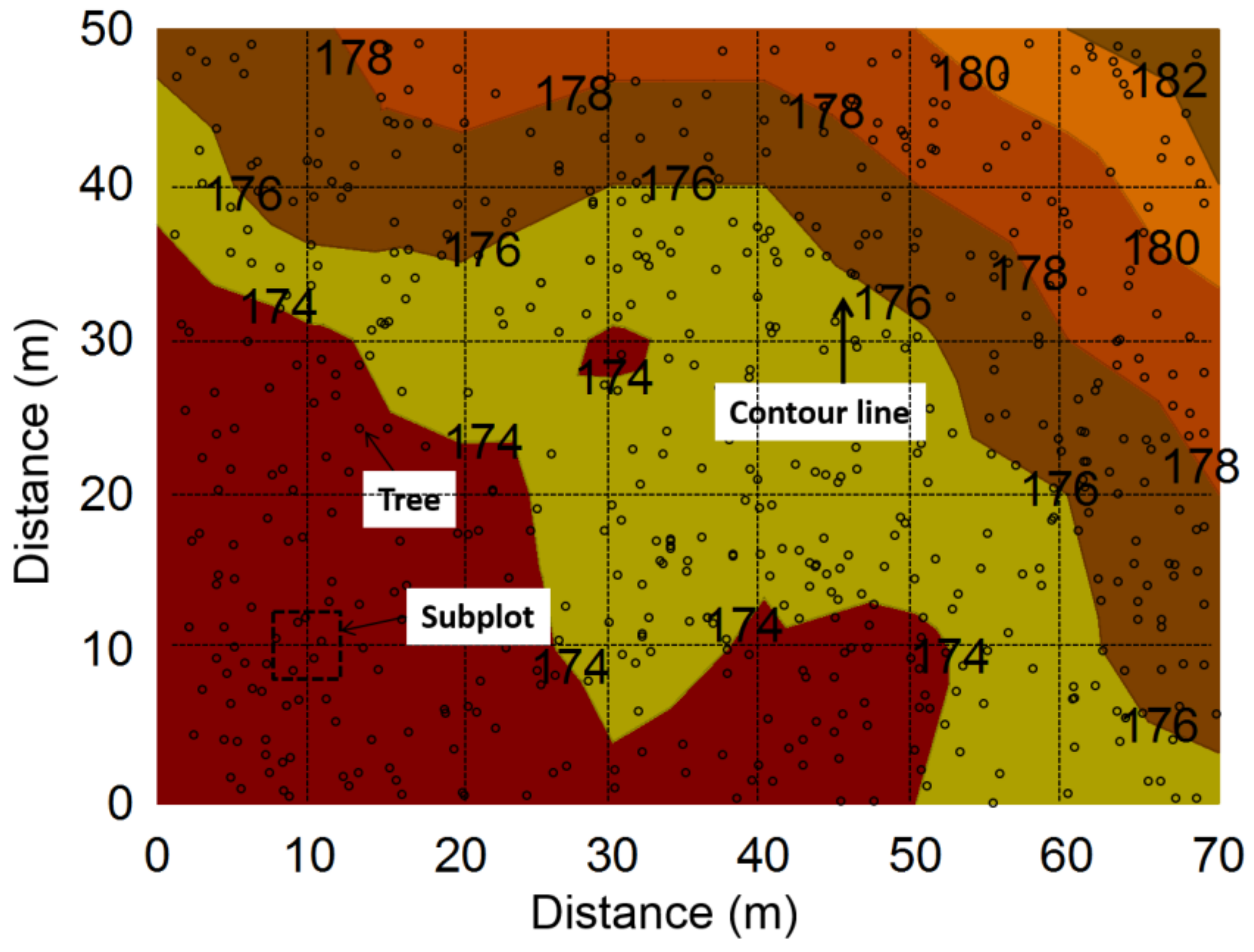
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Respiration, Temperature, and Moisture
2.4. Aboveground Biomass of Understory Plant and Fine Root Biomass
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
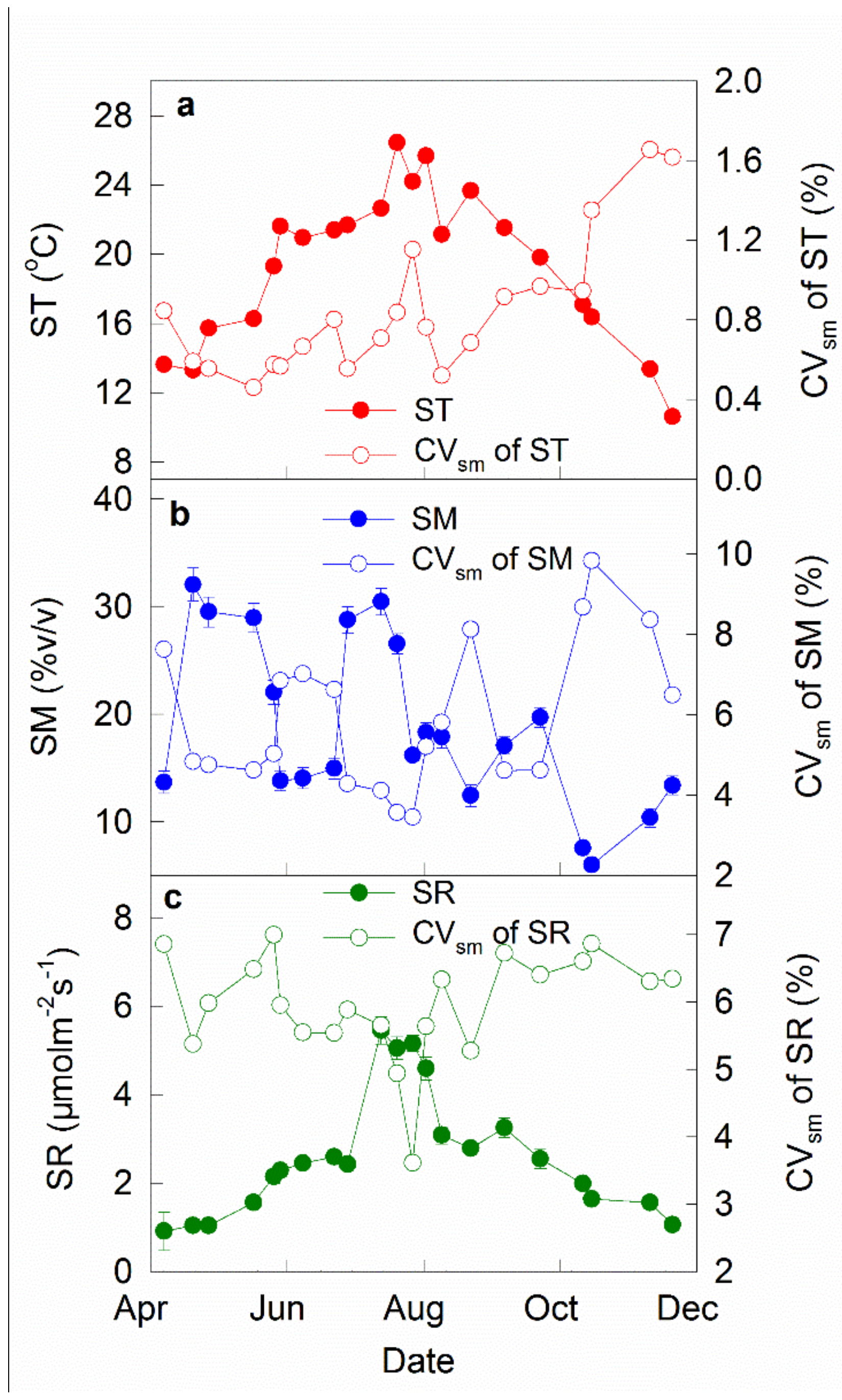
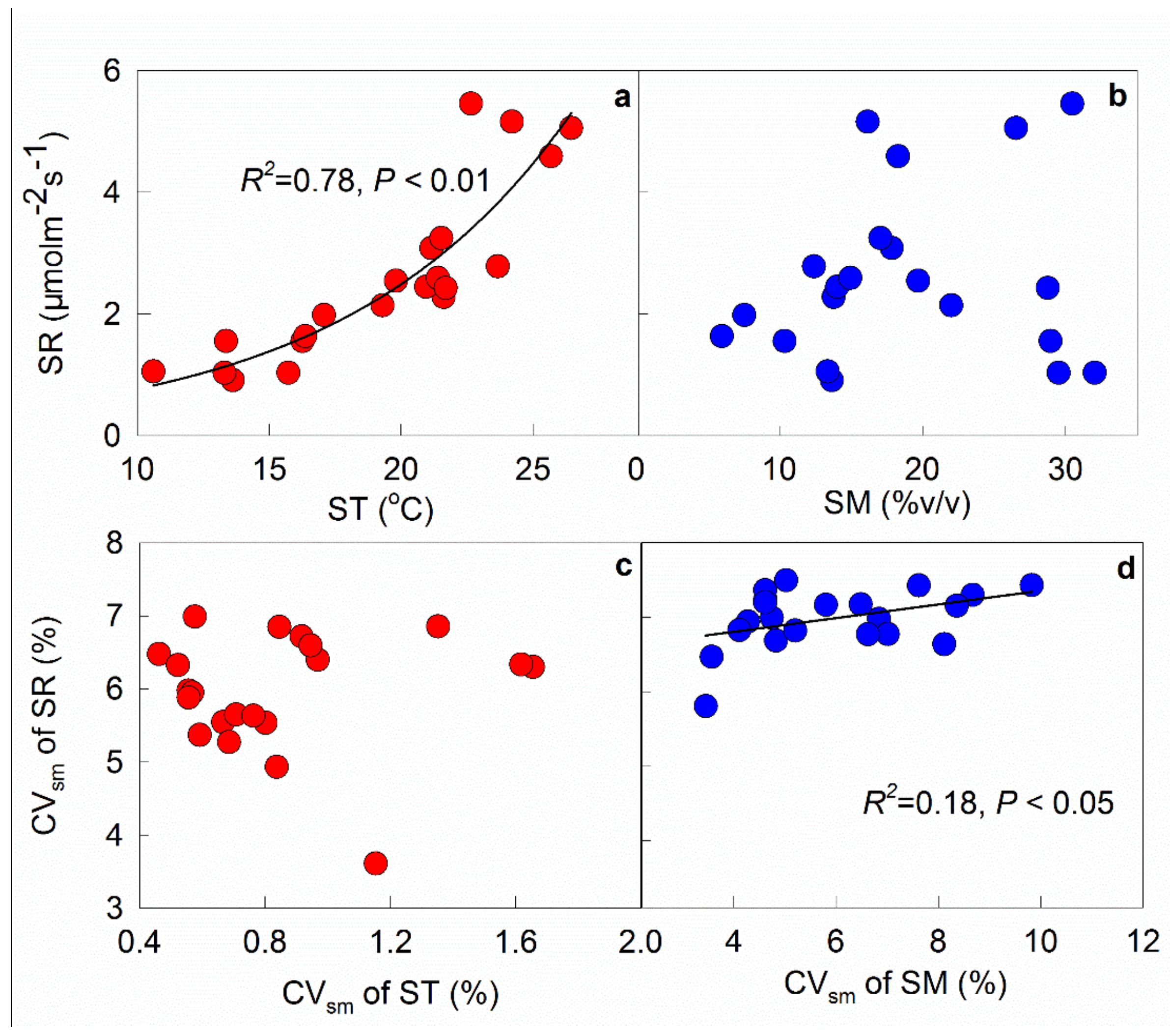
3.1. Temporal Variations of Soil Respiration, Temperature, and Moisture
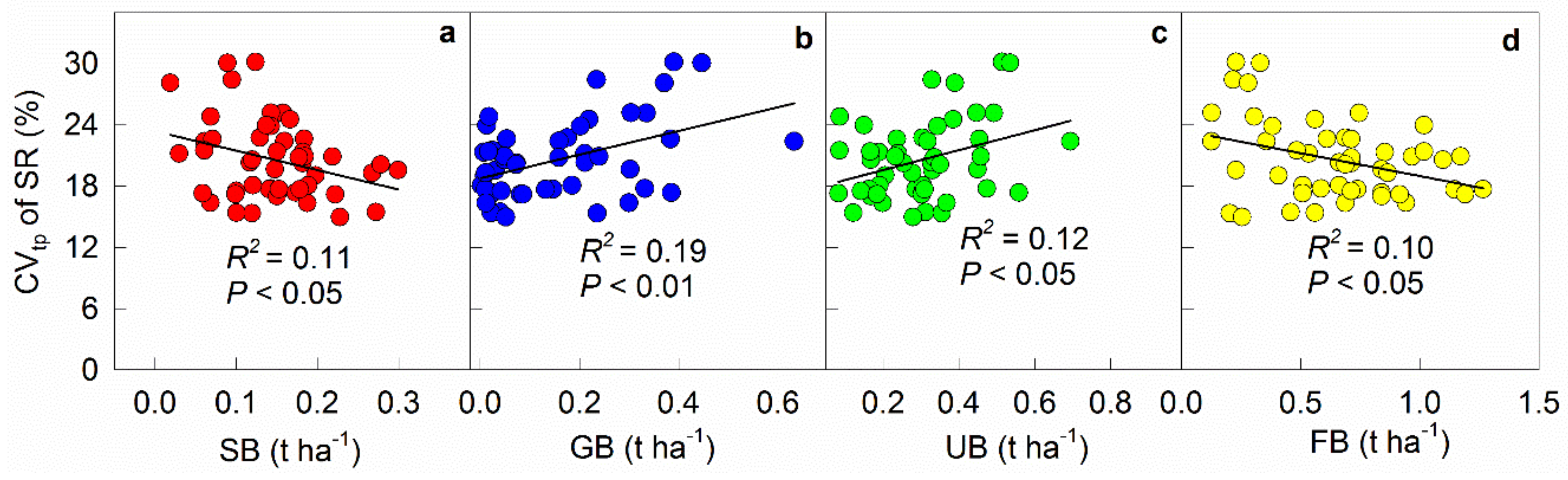
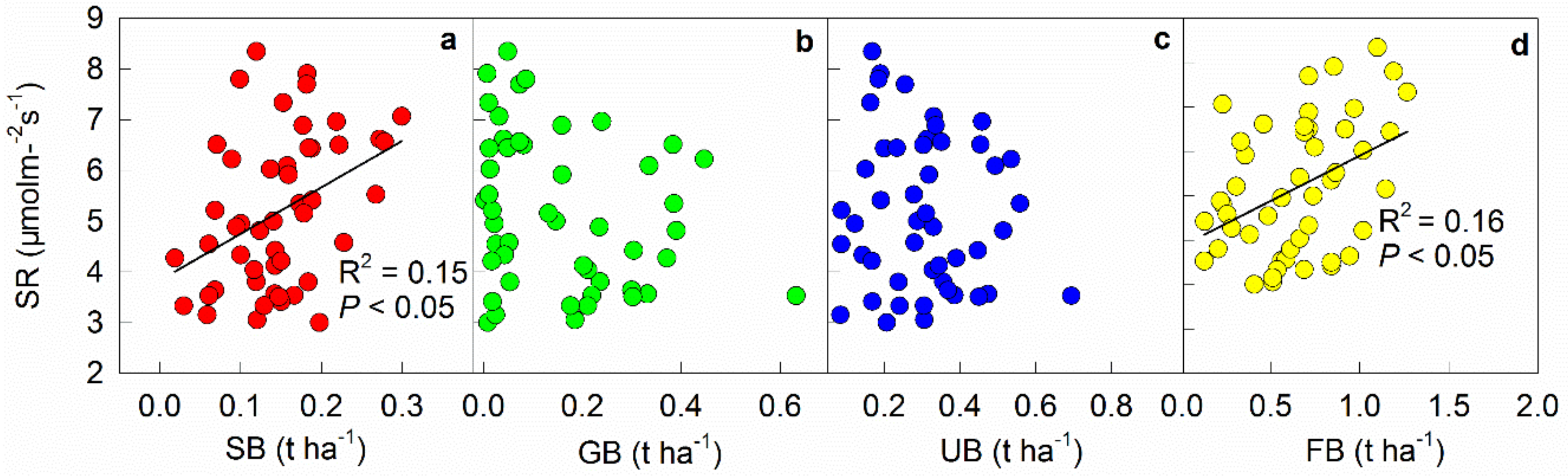
3.2. Effects of Understory Plant Biomass on the Temporal Variation of Soil Respiration
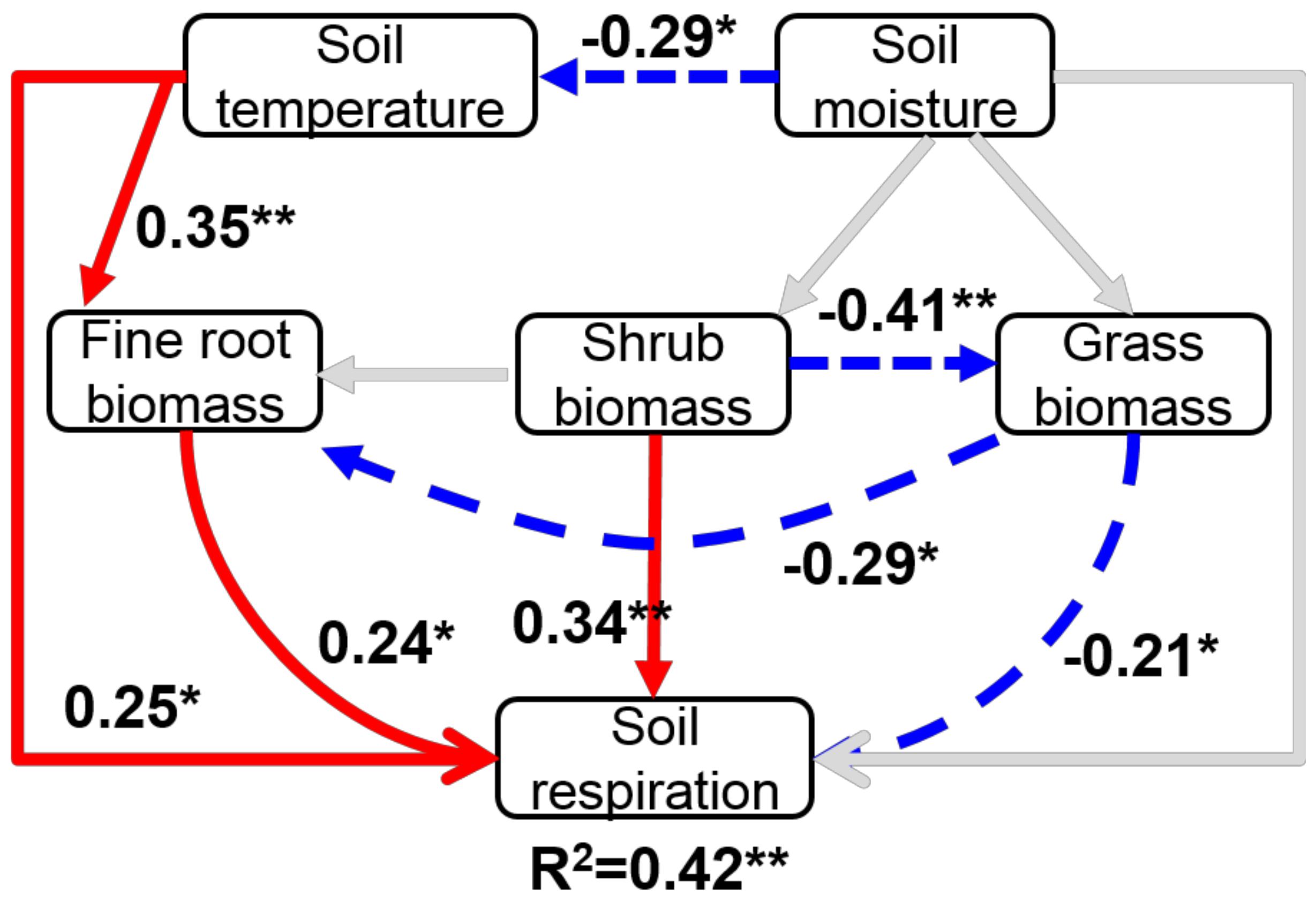
3.3. Structural Equation Modeling to Explain Temporal Variation in Soil Respiration
3.4. Seasonal Patterns of Soil Temperature, Moisture, and Respiration and Their Spatial Variability
3.5. Effects of Soil Temperature and Moisture on Spatial Variation of Soil Respiration
3.6. Mid-Growing Season Plant Biomass and its Effect on Spatial Variation of Soil Respiration
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal Variation of Soil Respiration
4.2. Spatial Variation of Soil Respiration Rate
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bond-Lamberty, B.; Thomson, A. Temperature-associated increases in the global soil respiration record. Nature 2010, 464, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, E.A.; Janssens, I.A. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change. Nature 2006, 440, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raich, J.; Schlesinger, W.H. The global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate. Tellus B 1992, 44, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, G.; Green, C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Kiese, R.; Avitabile, V.; Farrell, E.P. Seasonal and spatial variability of soil respiration in four Sitka spruce stands. Plant Soil 2006, 287, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, K. Roles of biotic and abiotic variables in determining spatial variation of soil respiration in secondary oak and planted pine forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, G.; Chu, H.; Noormets, A.; Ouyang, Z.; John, R.; Wan, S.; Guan, W. Long-term variability and environmental control of the carbon cycle in an oak-dominated temperate forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 313, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; You, Q.G.; Xu, M.H.; Zhou, X.H.; Wang, T.; Guo, J.; Xue, X. Effects of experimental warming on soil respiration and its components in an alpine meadow in the permafrost region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J. Temporal variability of soil respiration in experimental tree plantations in Lowland Costa Rica. Forests 2017, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnoli, A.; Di Iorio, A.; Terzaghi, M.; Trupiano, D.; Scippa, G.; Chiatante, D. Influence of soil temperature and water content on fine-root seasonal growth of European beech natural forest in Southern Alps, Italy. Eur. J. For. Res. 2014, 133, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Luo, Y.; Bradford, J.B.; Poorter, H.; Perry, C.H.; Oleksyn, J. Temperature drives global patterns in forest biomass distribution in leaves, stems, and roots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13721–13726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracho, R.; Natali, S.; Pegoraro, E.; Crummer, K.G.; Schädel, C.; Celis, G.; Hale, L.; Wu, L.; Yin, H.; Tiedje, J.M. Temperature sensitivity of organic matter decomposition of permafrost-region soils during laboratory incubations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, P.A.; Fahey, T.J.; Dawson, T.E. Seasonal air and soil temperature effects on photosynthesis in red spruce (Picea rubens) saplings. Tree Physiol. 1997, 17, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wan, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, K. Effects of experimental throughfall reduction and soil warming on fine root biomass and its decomposition in a warm temperate oak forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Zeng, D.-H. Heterogeneity in decomposition rates and annual litter inputs within fine-root architecture of tree species: Implications for forest soil carbon accumulation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 389, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wan, S.; Wang, J.; Luan, J.; Wang, H. Differential responses of soil respiration to soil warming and experimental throughfall reduction in a transitional oak forest in central China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 226–227, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, Z.; Táncsics, A.; Kriszt, B.; Kröel-Dulay, G.; Ónodi, G.; Hornung, E. Extreme effects of drought on composition of the soil bacterial community and decomposition of plant tissue. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmroth, S.; Maier, C.A.; McCarthy, H.R.; Oishi, A.C.; Kim, H.S.; Johnsen, K.H.; Katul, G.G.; Oren, R. Contrasting responses to drought of forest floor CO2 efflux in a Loblolly pine plantation and a nearby Oak-Hickory forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha, J.M.; Campos, M.C.C.; Gaio, D.C.; de Souza, Z.M.; Soares, M.D.R.; da Silva, D.M.P.; Simoes, E.L. Spatial variability of soil respiration in Archaeological Dark Earth areas in the Amazon. Catena 2018, 162, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Weile, C.; Shaopeng, W. Forest soil respiration and its heterotrophic and autotrophic components: Global patterns and responses to temperature and precipitation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, A.C.; Palmroth, S.; Butnor, J.R.; Johnsen, K.H.; Oren, R. Spatial and temporal variability of soil CO2 efflux in three proximate temperate forest ecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wu, X.; Xiang, W.; Fang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Lei, P.; Deng, X.; Peng, C. Spatial variations in soil organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations related to stand characteristics in subtropical areas. Plant Soil 2017, 413, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Variation in soil respiration under the tree canopy in a temperate mixed forest, central China, under different soil water conditions. Ecol. Res. 2014, 29, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imer, D.; Merbold, L.; Eugster, W.; Buchmann, N. Temporal and spatial variations of soil CO2, CH4 and N2O fluxes at three differently managed grasslands. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 5931–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; Desjardins, R.; Pattey, E. Spatial and temporal variability of soil respiration in agricultural fields. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1991, 71, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bai, Z.; Jin, C.; Zhang, X.; Guan, D.; Wang, A.; Yuan, F.; Wu, J. The influence of tree species on small scale spatial heterogeneity of soil respiration in a temperate mixed forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhou, L.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fu, S. Interactive effects of understory removal and fertilization on soil respiration in subtropical Eucalyptus plantations. J. Plant Ecol. 2015, 8, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, X.A.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, X.; Fu, S. Dynamics of Understory Shrub Biomass in Six Young Plantations of Southern Subtropical China. Forests 2017, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.; Fu, S. Reforestation makes a minor contribution to soil carbon accumulation in the short term: Evidence from four subtropical plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 384, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Qiu, X.; Guo, M.; Musa, A.; Jiang, D. Accuracy of space-for-time substitution for vegetation state prediction following shrub restoration. J. Plant Ecol. 2018, 11, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlstein, I.; Daniel, J.S.; Solomon, S. Pace of shifts in climate regions increases with global temperature. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, W.; Zhu, S.; Wan, S.; Luo, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, L.; Dai, H.; Li, P.; et al. CAN Canopy Addition of Nitrogen Better Illustrate the Effect of Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition on Forest Ecosystem? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipollini, M.L.; Drake, B.G.; Whigham, D. Effects of elevated CO2 on growth and carbon/nutrient balance in the deciduous woody shrub Lindera benzoin (L.) Blume (Lauraceae). Oecologia 1993, 96, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epron, D.; Nouvellon, Y.; Roupsard, O.; Mouvondy, W.; Mabiala, A.; Saint-André, L.; Joffre, R.; Jourdan, C.; Bonnefond, J.-M.; Berbigier, P. Spatial and temporal variations of soil respiration in a Eucalyptus plantation in Congo. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 202, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, M.; Kumagai, T.O.; Kume, T.; Gyokusen, K.; Saitoh, T.M.; Suzuki, M. Characteristics of soil CO2 efflux variability in an aseasonal tropical rainforest in Borneo Island. Biogeochemistry 2008, 90, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Pol-van Dasselaar, A.; Corré, W.J.; Priemé, A.; Klemedtsson, Å.K.; Weslien, P.; Klemedtsson, L.; Stein, A.; Oenema, O. Spatial variability of methane, nitrous oxide, and carbon dioxide emissions from drained Grasslands. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wang, M. Environmental controls and the influence of tree species on temporal variation in soil respiration in subtropical China. Plant Soil 2014, 382, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacaldo, R.S.; Volk, T.A.; Briggs, R.D.; Abrahamson, L.P.; Bevilacqua, E.; Fabio, E.S. Soil CO2 effluxes, temporal and spatial variations, and root respiration in shrub willow biomass crops fields along a 19-year chronosequence as affected by regrowth and removal treatments. GCB Bioenergy 2014, 6, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Katahata, S.; Naramoto, M.; Mizunaga, H.; Wang, Q. Controlling factors of temporal variation of soil respiration in a natural beech forest as revealed by natural incubation experiments. Ecol. Res. 2014, 29, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Xu, M. Separating the effects of moisture and temperature on soil CO2 efflux in a coniferous forest in the Sierra Nevada mountains. Plant Soil 2001, 237, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Long, J.R.; Dorrepaal, E.; Kardol, P.; Nilsson, M.-C.; Teuber, L.M.; Wardle, D.A. Understory plant functional groups and litter species identity are stronger drivers of litter decomposition than warming along a boreal forest post-fire successional gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Ye, J.-S.; Gong, Y.; Pei, J.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y. Seasonal responses of soil respiration to warming and nitrogen addition in a semi-arid alfalfa-pasture of the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, Y.; Mitani, T.; Itoh, M.; Noguchi, S.; Tani, M.; Matsuo, N.; Takanashi, S.; Ohkubo, S.; Rahim Nik, A. Spatial and temporal variation in soil respiration in a Southeast Asian tropical rainforest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 147, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Jenerette, G.D.; Hui, D.; Phillips, R.P.; Ren, H. Effects of changing precipitation regimes on dryland soil respiration and C pool dynamics at rainfall event, seasonal and interannual scales. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Mackay, D.S.; Pendall, E.; Ewers, B.E.; Cleary, M.B. Does vegetation structure regulate the spatial structure of soil respiration within a sagebrush steppe ecosystem? J. Arid. Environ. 2014, 103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, B.; Kelliher, F.; Baldocchi, D.; Anthoni, P.; Irvine, J.; Moore, D.V.; Van Tuyl, S. Spatial and temporal variation in respiration in a young ponderosa pine forest during a summer drought. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 110, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Allometric equation | Model R2 | p value | Number of Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. glauca | B = 73.190 × D2.5889 | 0.9424 | <0.001 | 15 |
| V. negundo | B = 16.413 × D1.8824 | 0.8136 | <0.001 | 14 |
| S. chinensis | B = 50.139 × D2.7133 | 0.8513 | <0.001 | 13 |
| Others | B = 62.680 × D2.5858 | 0.8994 | <0.001 | 42 |
| Variables | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | CVtp (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Maximum | Minimum | ||||
| SR (μmol m−2 s−1) | 2.52 ± 0.11 | 4.13 | 1.57 | 20.64 ± 0.55 | 30.21 | 15.01 |
| ST (oC) | 18.99 ± 0.13 | 20.97 | 17.78 | 8.30 ± 0.07 | 9.31 | 7.21 |
| SM (%v/v) | 17.93 ± 0.70 | 34.25 | 8.71 | 15.61 ± 0.48 | 22.30 | 7.92 |
| Understory vegetation variables | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | CVs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SB (t ha−1) | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.02 | 6.13 |
| GB (t ha−1) | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 14.07 |
| UB (t ha−1) | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 0.69 | 0.08 | 6.09 |
| FB (t ha−1) | 0.65 ± 0.04 | 1.27 | 0.13 | 7.16 |
| Parameter | Equation | C0 | C0 + C | A | C0/(C0 + C) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST (oC) | Gaussian | 0.103 | 1.171 | 74.357 | 0.912 | 0.998*** |
| SM (%v/v) | Linear | 29.081 | 29.081 | 32.746 | 1.000 | 0.996*** |
| SR (μmol m−2 s−1) | Exponential | 0.040 | 0.694 | 20.110 | 0.057 | 0.497** |
| SB (t ha−1) | Linear | 0.023 | 0.023 | 32.746 | 1.000 | 0.693** |
| GB (t ha−1) | Spherical | 0.032 | 0.267 | 11.210 | 0.120 | 0.535* |
| UB (t ha−1) | Linear | 0.023 | 0.323 | 11.945 | 0.070 | 0.720** |
| FB (t ha−1) | Spherical | 33.000 | 837.900 | 17.100 | 0.961 | 0.796*** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Shang, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, S. Effects of Understory Shrub Biomass on Variation of Soil Respiration in a Temperate-Subtropical Transitional Oak Forest. Forests 2019, 10, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10020088
Liu Y, Shang Q, Wang L, Liu S. Effects of Understory Shrub Biomass on Variation of Soil Respiration in a Temperate-Subtropical Transitional Oak Forest. Forests. 2019; 10(2):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10020088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanchun, Qing Shang, Lei Wang, and Shirong Liu. 2019. "Effects of Understory Shrub Biomass on Variation of Soil Respiration in a Temperate-Subtropical Transitional Oak Forest" Forests 10, no. 2: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10020088
APA StyleLiu, Y., Shang, Q., Wang, L., & Liu, S. (2019). Effects of Understory Shrub Biomass on Variation of Soil Respiration in a Temperate-Subtropical Transitional Oak Forest. Forests, 10(2), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10020088






